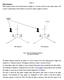
Figure 1-44: 4-Wire Wye PT Configurations
|
|
|
- Gabriel Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Principles and Practice ii) PT onnection There are two most common PT combinations on three-phase, three-wire systems as shown in Figure The vector diagrams are identical between PT configurations and the Open Delta is more common because it only requires two PTs, thereby dropping the cost by one-third. PTab PTbc PTca PTab PTbc 3 WIRE DELT WITH 3 PTs 3 WIRE DELT WITH 2 PTs (Open Delta) Figure 1-43: 3-Wire Delta PT onfigurations The two most common PT configurations for four-wire, Wye systems are shown in Figure The line-to-line voltage magnitudes and angles between the two configurations are identical and Open-Delta configurations commonly used if line-toneutral voltages are not required by the relay or application PTab PTbc PTca 59an 59bn 59cn 4 WIRE WYE WITH 3 PTs PTab PTbc 4 WIRE WYE WITH 2 PTs (Open Delta) Figure 1-44: 4-Wire Wye PT onfigurations 38
3 hapter 1: Electrical Fundamentals onfusing line-to-ground and line-to-line setting values is the most common mistake related to voltages and relays. Review the manufacturer s specifications to make sure the correct voltage levels are expected and set. Use the chart in Figure 1-45 for the most common PT secondary voltages. alculate nominal PT secondary voltages by dividing the rated primary voltage by the PT ratio. Never mix Line-to-Line and Line-to- Ground voltages when performing PT ratio calculations. For example, medium voltage PT ratios are typically rated using line voltages (eg. 4200V / 120V = PT ratio 35:1) but substation PTs are typically rated using phase-to-neutral voltage ratios and secondary nominal voltages (E.g. 1200:1 PT 67V = 80,400V / 67V Line-to-Neutral or 138,000V / 115V Line-to-Line) 3-Wire Delta 2 PTs 4-Wire Wye 3 PTs 4-Wire Wye 2 PTs o nnectio ns Line -Grou nd No minal Line -Line No minal V, V, V V, V N/ 120V or 115V V, V, V V N, V N, V N 69.28V or 66.40V or 67.0V 120V or 115V or V V, V, V N/ 120V or 115V Figure 1-45: Nominal PT Voltages 39
4 Principles and Practice 4. Fault Types The electrical system can be affected by many problems, but protective relays are primarily designed to protect the electrical system and/or equipment from fault situations. The threephase electrical system typically has three phases that are connected together by highimpedance loads. low impedance connection between phases and/or ground can cause extremely high fault currents, arc flashes, heat, and explosive forces, and catastrophic damage to equipment and personnel. low impedance connection between phases and/or ground could be caused by a tree falling onto a transmission line, foreign material falling across a live bus, very humid conditions with insufficient clearance between phases, or failing insulation. There are an unlimited number of scenarios that can cause an electrical fault which are typically categorized into four fault types. It is very common for an electrical fault to start in one category and cascade into another if the problem is not cleared in time. The most common fault types are: ) Three-Phase Faults Three-phase (3Ø or 3P) Faults occur when all three phases are connected together with low impedance. We typically create balanced 3Ø Faults when creating simulations which are the equivalent of leaving safety grounds on a system and then energizing that system. Figure 1-46: Three-Phase Fault 3-Line Drawing three-phase fault causes all three currents to increase simultaneously with equal magnitudes. The magnitude of fault current will depend on the impedance and location of the fault, as well as the strength of the electrical system. The safety grounds connected to the grid in our example will cause much higher fault currents than the same safety grounds connected to an isolated generator. Similarly, a fault closer to the source (Figure 1-46 Left Side) will produce more fault current than a fault at the end of the line (Figure 1-46 Right Side) because there will be more impedance between the source and the fault in the second situation. The current will lag the voltage by some value usually determined by the voltage class of the system. ll three voltages will decrease simultaneously with equal magnitudes. The magnitude of fault voltage will depend on the impedance and location of the fault, as well as the strength 40
5 hapter 1: Electrical Fundamentals of the electrical system. The voltage drop will not be as significant if the safety grounds are connected to the grid compared to the huge voltage drop that will be observed in an isolated system which could cause the voltage to drop to zero. Similarly, a fault closer to the source will create a larger voltage drop than a fault at the end of the line because there will be more impedance between the source and the fault. The following phasor diagrams demonstrate the difference between a normal system and the same system with a three-phase fault. Notice that all phasors are still 120 apart, the voltages stayed at the same at the same phase angles, and the current magnitudes increased with a greater lag from the voltages. - - Prefault or Normal Three-Phase Fault Figure 1-47: Three-Phase Fault Phasor Diagram It is always a good idea to simulate conditions as close to a true fault when performing tests and a 3Ø fault simulation should have the following characteristics: Prefault: nominal: 3Ø voltage magnitudes with 120 between phases in the normal phase rotation. Fault Voltage: Reduced, but identical, voltage magnitudes on all three phases with no change in phase angles from the prefault condition. Fault urrent: Larger than nominal current on all three phases with identical magnitudes and 120 between phases with the normal phase rotation. The current should lag the voltage by to. 41
6 Principles and Practice ) Phase-to-Phase Faults Phase-to-phase (P-P or Ø-Ø) faults occur when two phases are connected together with low impedance. Ø-Ø fault can occur when a bird flies between two transmission conductors and its wing-tips touch both conductors simultaneously. Phase-to-phase faults are described by the phases that are affected by the low-impedance connection. The - fault in Figure 1-48 is a Ø-Ø fault that connects -phase and -phase. Figure 1-48: Phase-Phase Fault 3-Line Drawing The magnitude of fault current will depend on the impedance and location of the fault, as well as the strength of the electrical system. fault closer to the source will produce more fault current than a fault at the end of the line because there will be more impedance between the source and the fault in the second situation. The fault current will lag the fault voltage by some value usually determined by the voltage class of the system. If you follow the flow of current in Figure 1-48, you should notice that the current flows from the -phase source into the fault, and then returns to the source via -phase. asic electrical theory states that the current flowing in a circuit must be equal, so the -phase and -phase currents must have the same magnitudes. However, relays monitor current leaving the source so the relay will see this fault as two equal currents with opposite polarity. Therefore, when we simulate a P-P fault, the currents injected into a relay must have the same magnitudes and be 180 apart from each other. The current flowing through the actual fault will be equal to 2x the injected currents. Injectected urrent = = Ifault Fault urrent = + - Fault urrent 150 Fault urrent = 150 Figure 1-49: Fault urrent vs. Injected urrent 42
7 hapter 1: Electrical Fundamentals The effect of a P-P fault on the faulted voltages is even more complex. The faulted voltages will have equal magnitudes because the impedance between the source and the fault on each faulted phase should be equal. fault closer to the source will create a larger voltage drop than a fault at the end of the line because there will be more impedance between the source and the fault. The faulted voltage angles are also affected because the ratio of reactance and resistance in the circuit changes when the fault is introduced. There is a lot of information to consider when creating the correct voltage magnitudes and angles and we discuss the calculations in detail in hapter 15: Line Distance (21) Element Testing. For our purposes in this chapter, it is important that you be able to recognize a Ø-Ø fault as the following phasor diagrams demonstrate. Notice that the faulted voltages have collapsed and come together to change the voltage triangle from an equiangular/equilateral triangle (three equal magnitudes and angles) in prefault to an acute, isosceles triangle (two equal magnitudes, two equal angles, and all angles are less than ). - - Prefault or Normal Phase-Phase Fault Figure 1-50: Phase-Phase Fault It is always a good idea to simulate conditions as close to a true fault when performing tests and a Ø-Ø fault simulation should have the following characteristics: 1. Prefault: nominal, 3Ø voltage magnitudes with 120 between phases in the normal phase rotation. 2. Fault Voltage: Reduced, but identical, voltage magnitudes on both phases affected by the fault. The phase angle between the faulted phases should be less than The unaffected phase voltage should be identical to the prefault condition. 4. Fault urrent: Increased, but identical, current magnitudes on both phases affected by the fault. The phase angle between the faulted phases should be The unaffected phase current does not change between prefault and fault. 43
8 Principles and Practice ) Phase-to-Ground Faults Phase-to-ground (P-G, P-N, Ø-G or Ø-N), or single-phase faults occur when any one phase is connected to the ground or neutral conductor with low impedance. Ø-N fault can occur when a tree falls on a transmission line. Phase-to-ground faults are described by the phase that is affected by the low-impedance connection. The -N fault in Figure 1-51 is a Ø-N fault that connects -phase to the neutral. Figure 1-51: Phase-Ground Fault 3-Line Drawing The magnitude of fault current will depend on the impedance and location of the fault, as well as the strength of the electrical system. fault closer to the source will produce more fault current than a fault at the end of the line because there will be more impedance between the source and the fault in the second situation. The fault current will lag the fault voltage by some value usually determined by the voltage class of the system. The fault only affects -phase voltages and currents, so the -phase and -phase currents are nearly identical to the prefault values. The -phase current will increase and lag the voltage at some value between and. The -phase and -phase voltages will also be unaffected by the fault and they will have the same magnitude and phase angle during the fault as existed in prefault. The -phase voltage magnitude will decrease, but the phase angle will not change between prefault and fault. Ø-N fault example is demonstrated in Figure Notice that the faulted voltage has collapsed to change the voltage triangle from an equiangular/equilateral triangle (three equal magnitudes and angles) in prefault to an isosceles triangle. 44
9 hapter 1: Electrical Fundamentals - - Prefault or Normal Phase-Ground Fault Figure 1-52: Phase-Ground Fault It is always a good idea to simulate conditions as close to a true fault when performing tests and a Ø-N fault simulation should have the following characteristics: 1. Prefault: nominal, 3Ø voltage magnitudes with 120 between phases in the normal phase rotation. 2. Fault Voltage: Reduced voltage the phase affected by the fault. The voltage angle is identical to prefault. 3. The unaffected phase voltages should be identical to the prefault condition. 4. Fault urrent: Increased magnitude on the affected phase. The phase angle should lag the phase voltage by a value between and. 5. The unaffected phase currents do not change between prefault and fault. 45
10 Principles and Practice D) Phase-to-Phase-to-Ground Faults Phase-to-phase-to-ground (P-P-G, P-P-N, Ø-Ø-G or Ø-Ø-N), or two-phase-to-ground faults occur when any two phases are connected to the ground or neutral conductor with low impedance. Ø-N fault can occur when a tree falls on two phases of a transmission line. Two phase-to-ground faults are described by the phases that are affected by the lowimpedance connection. The --G fault in Figure 1-53 is a Ø-Ø-N fault that connects and -phases to Ground. Figure 1-53: Phase-Phase-Ground Fault 3-Line Drawing P-P-G ground are very complex faults that are very difficult to reproduce without modeling software to calculate all of the fault quantities involved which is beyond the scope of this book. However, you should be able to see the characteristics of a P-P-G fault as shown in Figure Prefault or Normal Phase-Phase-Ground Fault Figure 1-54: Phase-Phase-Ground Fault 46
THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS
 THR-HAS CIRCUITS 4.1 Introduction Generation, Transmission and distribution of electricity via the National Grid system is accomplished by three-phase alternating currents. The voltage induced by a single
THR-HAS CIRCUITS 4.1 Introduction Generation, Transmission and distribution of electricity via the National Grid system is accomplished by three-phase alternating currents. The voltage induced by a single
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Ch 8. Three-phase systems
 Ch 8. Three-ase systems Lecture outcomes (what you are supposed to learn): Generation of three-ase voltages Connection of three-ase circuits Wye-Delta transformation Power of three-ase connected loads
Ch 8. Three-ase systems Lecture outcomes (what you are supposed to learn): Generation of three-ase voltages Connection of three-ase circuits Wye-Delta transformation Power of three-ase connected loads
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults
 Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
Chapter 8: Unsymmetrical Faults Introduction The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used for finding out fault current during unsymmetrical faults.
1. Explain the various methods of methods of grounding. In power system, grounding or earthing means connecting frame of electrical equipment (non-cur
 1. Explain the various methods of methods of grounding. In power system, grounding or earthing means connecting frame of electrical equipment (non-current carrying part) or some electrical part of the
1. Explain the various methods of methods of grounding. In power system, grounding or earthing means connecting frame of electrical equipment (non-current carrying part) or some electrical part of the
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME: EE 2303 - TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION YEAR / SEM: III/V UNIT-I TRANSMISSION SYSTEM INTRODUCTION PART-A 1. What is
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME: EE 2303 - TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION YEAR / SEM: III/V UNIT-I TRANSMISSION SYSTEM INTRODUCTION PART-A 1. What is
Consider Figure What is the horizontal axis grid increment?
 Chapter Outline CHAPER 14 hree-phase Circuits and Power 14.1 What Is hree-phase? Why Is hree-phase Used? 14.2 hree-phase Circuits: Configurations, Conversions, Analysis 14.2.1 Delta Configuration Analysis
Chapter Outline CHAPER 14 hree-phase Circuits and Power 14.1 What Is hree-phase? Why Is hree-phase Used? 14.2 hree-phase Circuits: Configurations, Conversions, Analysis 14.2.1 Delta Configuration Analysis
ECE 476. Exam #2. Tuesday, November 15, Minutes
 Name: Answers ECE 476 Exam #2 Tuesday, November 15, 2016 75 Minutes Closed book, closed notes One new note sheet allowed, one old note sheet allowed 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 20 4. / 20 5. / 20 Total / 100
Name: Answers ECE 476 Exam #2 Tuesday, November 15, 2016 75 Minutes Closed book, closed notes One new note sheet allowed, one old note sheet allowed 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 20 4. / 20 5. / 20 Total / 100
Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Potential and Current Transformers (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So far we
Electrical Machines-I Prof. D. Kastha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Potential and Current Transformers (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So far we
ECE 420. Review of Three Phase Circuits. Copyright by Chanan Singh, Panida Jirutitijaroen, and Hangtian Lei, For educational use only-not for sale.
 ECE 40 Review of Three Phase Circuits Outline Phasor Complex power Power factor Balanced 3Ф circuit Read Appendix A Phasors and in steady state are sinusoidal functions with constant frequency 5 0 15 10
ECE 40 Review of Three Phase Circuits Outline Phasor Complex power Power factor Balanced 3Ф circuit Read Appendix A Phasors and in steady state are sinusoidal functions with constant frequency 5 0 15 10
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES. School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION. Session
 Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
Name: Student ID: Signature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications FINALEXAMINATION Session 00 ELEC46 Power System Analysis TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours TOTAL
THREE PHASE SYSTEMS Part 1
 ERT105: ELECTRCAL TECHNOLOGY CHAPTER 3 THREE PHASE SYSTEMS Part 1 1 Objectives Become familiar with the operation of a three phase generator and the magnitude and phase relationship. Be able to calculate
ERT105: ELECTRCAL TECHNOLOGY CHAPTER 3 THREE PHASE SYSTEMS Part 1 1 Objectives Become familiar with the operation of a three phase generator and the magnitude and phase relationship. Be able to calculate
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
Faults on Electrical System. A Research
 Faults on Electrical System A Research Presented to Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Architecture Mindanao University of Science and Technology Cagayan de Oro City In partial fulfilment
Faults on Electrical System A Research Presented to Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Architecture Mindanao University of Science and Technology Cagayan de Oro City In partial fulfilment
Fault Calculation Methods
 ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Fault Calculation Methods There are two major problems that can occur in electrical systems: these are open circuits and short circuits. Of the two, the
ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Fault Calculation Methods There are two major problems that can occur in electrical systems: these are open circuits and short circuits. Of the two, the
Symmetrical Components. References
 Symmetrical Components Review of basics Sequence Equivalents Fault Analysis Symmetrical Components Fall 28 References Your power systems analysis class text book NPAG: Chapter 4 (analysis) Chapter 5 (equipment
Symmetrical Components Review of basics Sequence Equivalents Fault Analysis Symmetrical Components Fall 28 References Your power systems analysis class text book NPAG: Chapter 4 (analysis) Chapter 5 (equipment
Three Phase Circuits
 Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
NEW DESIGN OF GROUND FAULT PROTECTION
 NEW DESIGN OF GROUND FAULT PROTECTION The 71st Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers Siemens AG 2018 All rights reserved. siemens.com/energy-management Why do we need ground fault protection?
NEW DESIGN OF GROUND FAULT PROTECTION The 71st Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers Siemens AG 2018 All rights reserved. siemens.com/energy-management Why do we need ground fault protection?
UNIT- I Phase Sequence:
 UNIT- I Phase Sequence: Phase sequence refers to the relation between voltages (or currents, as well) in a three-phase system. The common representation of this relation is in terms of a phasor diagram,
UNIT- I Phase Sequence: Phase sequence refers to the relation between voltages (or currents, as well) in a three-phase system. The common representation of this relation is in terms of a phasor diagram,
SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Year/ Semester/ Class : III/ V/ EEE Academic Year: Subject Code/ Name: EE6501/ Power System Analysis
 Srividya colllege of Engg & Tech,Virudhunagar Sri Vidya College of Engineering And Technology Virudhunagar 626 005 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering QUESTION BANK SHORT QUESTIONS AND
Srividya colllege of Engg & Tech,Virudhunagar Sri Vidya College of Engineering And Technology Virudhunagar 626 005 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering QUESTION BANK SHORT QUESTIONS AND
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION
 EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
4.10 Unbalanced fault analysis using Z BUS matrix:
 4.10 Unbalanced fault analysis using Z BUS matrix: In the previous section, it is observed that, for fault calculations the Thevenin s equivalent networs, at the fault point, are needed for the three sequence
4.10 Unbalanced fault analysis using Z BUS matrix: In the previous section, it is observed that, for fault calculations the Thevenin s equivalent networs, at the fault point, are needed for the three sequence
EE 451 Power System Stability
 EE 451 Power System Stability Power system operates in synchronous mode Power system is subjected to a wide range of disturbances (small and large) - Loads and generation changes - Network changes - Faults
EE 451 Power System Stability Power system operates in synchronous mode Power system is subjected to a wide range of disturbances (small and large) - Loads and generation changes - Network changes - Faults
Generation, transmission and distribution, as well as power supplied to industrial and commercial customers uses a 3 phase system.
 Three-phase Circuits Generation, transmission and distribution, as well as power supplied to industrial and commercial customers uses a 3 phase system. Where 3 voltages are supplied of equal magnitude,
Three-phase Circuits Generation, transmission and distribution, as well as power supplied to industrial and commercial customers uses a 3 phase system. Where 3 voltages are supplied of equal magnitude,
Electrical Circuits Lab Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram
 Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
STUDY ON THE INFLUENCE OF THE STAR CONNECTION NEUTRAL ON THE ELECTRICAL TRANSFORMERS WINDINGS ON ELECTRIC- SECURITY AND ON THE ELECTRICAL NETWORK
 STUDY ON THE INFLUENE OF THE STA ONNETION NEUTAL ON THE ELETIAL TANSFOMES WINDINGS ON ELETI- SEUITY AND ON THE ELETIAL NETWOK ISTINEL POPESU, University of onstantin Brâncuşi of Tg-Jiu OZMA VASILE, University
STUDY ON THE INFLUENE OF THE STA ONNETION NEUTAL ON THE ELETIAL TANSFOMES WINDINGS ON ELETI- SEUITY AND ON THE ELETIAL NETWOK ISTINEL POPESU, University of onstantin Brâncuşi of Tg-Jiu OZMA VASILE, University
Power System Engineering Prof. Debapriya Das Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Power System Engineering Prof. Debapriya Das Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 41 Application of capacitors in distribution system (Contd.) (Refer Slide
Power System Engineering Prof. Debapriya Das Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 41 Application of capacitors in distribution system (Contd.) (Refer Slide
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA.
 PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
CHAPTER 2 OVERVOLTAGE DUE TO SELF-EXCITATION AND INRUSH CURRENT DUE TO CAPACITOR SWITCHING
 20 CHAPTER 2 OVERVOLTAGE DUE TO SELF-EXCITATION AND INRUSH CURRENT DUE TO CAPACITOR SWITCHING 2.1 INTRODUCTION It is becoming more common to find use of shunt capacitors for the application of powerfactor
20 CHAPTER 2 OVERVOLTAGE DUE TO SELF-EXCITATION AND INRUSH CURRENT DUE TO CAPACITOR SWITCHING 2.1 INTRODUCTION It is becoming more common to find use of shunt capacitors for the application of powerfactor
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 13 : Sequence Modeling (Tutorial) Objectives In this lecture we will solve tutorial problems on fault analysis in sequence domain Per unit values
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 13 : Sequence Modeling (Tutorial) Objectives In this lecture we will solve tutorial problems on fault analysis in sequence domain Per unit values
SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS. ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems
 SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Power System Faults 3 Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow
SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Power System Faults 3 Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow
VKES. Contents. Page 2 No 213, 13th Main RBI Layout JP Nagar 7th Phase, Bangalore Vidyuth Kanti Engineering Services
 Contents What is earthing... 4 Why do we do earthing... 4 What is the Scope of this guideline... 4 How to protect a person in a substation against electrical shock... 4 What happens during a fault... 4
Contents What is earthing... 4 Why do we do earthing... 4 What is the Scope of this guideline... 4 How to protect a person in a substation against electrical shock... 4 What happens during a fault... 4
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
Determination of Fault Location in Shunt Capacitor Bank through Compensated Neutral Current
 International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering (ijasre) E-ISSN : 2454-8006 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/ijasre.2018.32630 Volume 4, Issue 3 March - 2018 Determination of Fault
International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering (ijasre) E-ISSN : 2454-8006 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/ijasre.2018.32630 Volume 4, Issue 3 March - 2018 Determination of Fault
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA
 PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA I m VECTOR. Cause I m committing crimes with magnitude and direction at the same time!" What are phasors??? In normal practice,
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA I m VECTOR. Cause I m committing crimes with magnitude and direction at the same time!" What are phasors??? In normal practice,
Electric Circuits II Power Measurement. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits II Power Measurement Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Single-Phase Power Measurement 2 Three-Phase Power Measurement 2 Single-Phase Power Measurement The wattmeter is the instrument
Electric Circuits II Power Measurement Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Single-Phase Power Measurement 2 Three-Phase Power Measurement 2 Single-Phase Power Measurement The wattmeter is the instrument
Secured Busbar Differential Protection Using A Computationally Efficient Dot Product Technique
 Secured Busbar Differential Protection Using A Computationally Efficient Dot Product Technique Krish Narendra, ERLPhase Power Technologies Dave Fedirchuk, ERLPhase Power Technologies Abstract The use of
Secured Busbar Differential Protection Using A Computationally Efficient Dot Product Technique Krish Narendra, ERLPhase Power Technologies Dave Fedirchuk, ERLPhase Power Technologies Abstract The use of
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A 1. What are the advantages of an inter connected system? The advantages of an inter-connected system are
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A 1. What are the advantages of an inter connected system? The advantages of an inter-connected system are
Capacitors. Dominik Pieniazek, P.E. VI Engineering, LLC Nicholas A. Losito Jr. Castle Power Solutions, LLC
 Capacitors Dominik Pieniazek, P.E. VI Engineering, LLC Nicholas A. Losito Jr. Castle Power Solutions, LLC Outline Day 1 Basic Power Calculations Capacitor Fundamentals Capacitor Ratings Capacitor Application
Capacitors Dominik Pieniazek, P.E. VI Engineering, LLC Nicholas A. Losito Jr. Castle Power Solutions, LLC Outline Day 1 Basic Power Calculations Capacitor Fundamentals Capacitor Ratings Capacitor Application
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
EE301 Three Phase Power
 Learning Objectives a. Compute the real, reactive and apparent power in three phase systems b. Calculate currents and voltages in more challenging three phase circuit arrangements c. Apply the principles
Learning Objectives a. Compute the real, reactive and apparent power in three phase systems b. Calculate currents and voltages in more challenging three phase circuit arrangements c. Apply the principles
CHAPTER 16,18,19 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: Points: 58 Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: Points: 58 Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response
Considerations in Choosing Directional Polarizing Methods for Ground Overcurrent Elements in Line Protection Applications
 Considerations in Choosing Directional Polarizing Methods for Ground Overcurrent Elements in Line Protection Applications Technical Report to the Line Protection Subcommittee of the PES, Power Systems
Considerations in Choosing Directional Polarizing Methods for Ground Overcurrent Elements in Line Protection Applications Technical Report to the Line Protection Subcommittee of the PES, Power Systems
Chapter 15 Power And Harmonics in Nonsinusoidal Systems
 Chapter 15 Power And Harmonics in Nonsinusoidal Systems 15.1. Average power in terms of Fourier series 15.2. RMS value of a waveform 15.3. Power factor THD Distortion and Displacement factors 15.4. Power
Chapter 15 Power And Harmonics in Nonsinusoidal Systems 15.1. Average power in terms of Fourier series 15.2. RMS value of a waveform 15.3. Power factor THD Distortion and Displacement factors 15.4. Power
Exercise Dr.-Ing. Abdalkarim Awad. Informatik 7 Rechnernetze und Kommunikationssysteme
 Exercise1 1.10.015 Informatik 7 Rechnernetze und Kommunikationssysteme Review of Phasors Goal of phasor analysis is to simplify the analysis of constant frequency ac systems v(t) = max cos(wt + q v ) i(t)
Exercise1 1.10.015 Informatik 7 Rechnernetze und Kommunikationssysteme Review of Phasors Goal of phasor analysis is to simplify the analysis of constant frequency ac systems v(t) = max cos(wt + q v ) i(t)
An Introduction to Insulation Resistance Testing
 An Introduction to Insulation Resistance Testing In a perfect world, electrical insulation would allow no current to flow through it. Unfortunately, a number of factors can over time result in the deterioration
An Introduction to Insulation Resistance Testing In a perfect world, electrical insulation would allow no current to flow through it. Unfortunately, a number of factors can over time result in the deterioration
Selecting the current rating for equipment
 Selecting the current rating for equipment 1. Rated current: the maximum continuous load current. Short-time withstand current: thermal withstand current term term is given for 1s or 3s short circuit current
Selecting the current rating for equipment 1. Rated current: the maximum continuous load current. Short-time withstand current: thermal withstand current term term is given for 1s or 3s short circuit current
Power system conductor volume calculation
 Power system conductor volume calculation Dr Audih alfaoury T&D power systems 2017-1018 Electrical Energy Engineering Department Dr Audih alfaoury 1 The transmission of electric power is carried at high
Power system conductor volume calculation Dr Audih alfaoury T&D power systems 2017-1018 Electrical Energy Engineering Department Dr Audih alfaoury 1 The transmission of electric power is carried at high
CHAPTER 8 UNSYMMETRICAL FAULTS
 CHAPTER 8 UNSYMMETRCAL FAULTS The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used or inding out ult current during unsymmetrical ults. Speciically we are
CHAPTER 8 UNSYMMETRCAL FAULTS The sequence circuits and the sequence networks developed in the previous chapter will now be used or inding out ult current during unsymmetrical ults. Speciically we are
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Reactive Power Solutions
 GE Digital Energy Reactive Power Solutions Effects of Series Capacitors on Line Protection Relaying Design and Settings Presented by: Paul Datka, GE Energy Consulting Luis Polanco, GE Energy Consulting
GE Digital Energy Reactive Power Solutions Effects of Series Capacitors on Line Protection Relaying Design and Settings Presented by: Paul Datka, GE Energy Consulting Luis Polanco, GE Energy Consulting
ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018
 ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018 Name: KEY UIN: Section: Score: Part 1 / 40 Part 2 / 0 Part / 0 Total / 100 This exam is 75 minutes, closed-book, closed-notes. A standard calculator and one 8.5 x11 note sheet
ECEN 460 Exam 1 Fall 2018 Name: KEY UIN: Section: Score: Part 1 / 40 Part 2 / 0 Part / 0 Total / 100 This exam is 75 minutes, closed-book, closed-notes. A standard calculator and one 8.5 x11 note sheet
mywbut.com Lesson 16 Solution of Current in AC Parallel and Seriesparallel
 esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
Three Phase Systems 295
 Three Phase Systems 95 9. MEASUEMENT OF POE Star-Connected Balanced Load with Neutral Point Power can be measured in this case by connecting a single wattmeter with its current coil in one line and the
Three Phase Systems 95 9. MEASUEMENT OF POE Star-Connected Balanced Load with Neutral Point Power can be measured in this case by connecting a single wattmeter with its current coil in one line and the
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
Notes on Electric Circuits (Dr. Ramakant Srivastava)
 Notes on Electric ircuits (Dr. Ramakant Srivastava) Passive Sign onvention (PS) Passive sign convention deals with the designation of the polarity of the voltage and the direction of the current arrow
Notes on Electric ircuits (Dr. Ramakant Srivastava) Passive Sign onvention (PS) Passive sign convention deals with the designation of the polarity of the voltage and the direction of the current arrow
Chapter 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts
 Chapter 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W.1 Examples and Problems on Electric Circuits 1W.2 Examples on Magnetic Concepts This chapter includes additional examples
Chapter 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W.1 Examples and Problems on Electric Circuits 1W.2 Examples on Magnetic Concepts This chapter includes additional examples
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
Relay Protection Condition Assessment Based on Variable Weight Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation
 Relay Protection Condition Assessment Based on Variable Weight Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation Speaker: Liang Weichen School : North China Electric Power University Email : liangweichenheng@163.com Introduction
Relay Protection Condition Assessment Based on Variable Weight Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation Speaker: Liang Weichen School : North China Electric Power University Email : liangweichenheng@163.com Introduction
2/7/2013. Topics. 15-System Model Text: One-Line Diagram. One-Line Diagram
 /7/013 Topics 15-ystem Model Text: 5.8 5.11 One-line Diagram ystem Modeling Regulating Transformers ECEGR 451 Power ystems Dr. Henry Louie 1 Dr. Henry Louie Generator us Transformer Transmission line Circuit
/7/013 Topics 15-ystem Model Text: 5.8 5.11 One-line Diagram ystem Modeling Regulating Transformers ECEGR 451 Power ystems Dr. Henry Louie 1 Dr. Henry Louie Generator us Transformer Transmission line Circuit
Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations
 Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations 5-1 Repeating the Example on Power Factor Correction (Given last Class) P? Q? S? Light Motor From source 1000 volts @ 60 Htz 10kW
Lecture (5) Power Factor,threephase circuits, and Per Unit Calculations 5-1 Repeating the Example on Power Factor Correction (Given last Class) P? Q? S? Light Motor From source 1000 volts @ 60 Htz 10kW
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of:
 Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Potential Energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Circuit Current Voltage Resistance Coulomb Notes 7.1: Electrostatic Force This lesson
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Potential Energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Circuit Current Voltage Resistance Coulomb Notes 7.1: Electrostatic Force This lesson
6. Three-Phase Systems. Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Information Engineering (DEI) - University of Bologna
 6. Three-Phase Systems J B G Three-Phase Systems v v v i i i The generation and the distribution of electrical energy is usually done by three- phase systems. There are three wire system connected to a
6. Three-Phase Systems J B G Three-Phase Systems v v v i i i The generation and the distribution of electrical energy is usually done by three- phase systems. There are three wire system connected to a
SSC-JE EE POWER SYSTEMS: GENERATION, TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
Familiarization, and Ohm's Law
 1 1 Familiarization, and Ohm's Law Objectives To be familiar with the laboratory equipment and components. Verification of Ohm s law. Series and parallel circuits. Theory Part I : Lab equipment and components:
1 1 Familiarization, and Ohm's Law Objectives To be familiar with the laboratory equipment and components. Verification of Ohm s law. Series and parallel circuits. Theory Part I : Lab equipment and components:
NZQA registered unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 6
 Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate and apply knowledge of capacitance, inductance, power factor, and power factor correction Level 3 Credits 7 Purpose This unit standard covers an introduction to alternating
Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate and apply knowledge of capacitance, inductance, power factor, and power factor correction Level 3 Credits 7 Purpose This unit standard covers an introduction to alternating
TRANSMISSION LINES. All aluminum alloy conductor (AAAC) Aluminum conductor alloy reinforced (ACAR)
 TRANSMISSION LINES. Transmission Structures An overhead transmission line consists of conductor, insulators, support structures and in most cases shield wires. Overhead power transmission lines are classified
TRANSMISSION LINES. Transmission Structures An overhead transmission line consists of conductor, insulators, support structures and in most cases shield wires. Overhead power transmission lines are classified
ELECTRIC POWER CIRCUITS BASIC CONCEPTS AND ANALYSIS
 Contents ELEC46 Power ystem Analysis Lecture ELECTRC POWER CRCUT BAC CONCEPT AND ANALY. Circuit analysis. Phasors. Power in single phase circuits 4. Three phase () circuits 5. Power in circuits 6. ingle
Contents ELEC46 Power ystem Analysis Lecture ELECTRC POWER CRCUT BAC CONCEPT AND ANALY. Circuit analysis. Phasors. Power in single phase circuits 4. Three phase () circuits 5. Power in circuits 6. ingle
Fault Analysis Power System Representation
 .1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
.1. Power System Representation Single Line Diagram: Almost all modern power systems are three phase systems with the phases of equal magnitude and equal phase difference (i.e., 10 o ). These three phase
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis
 Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
Three-phase AC Circuits. Measurement of Power in a Three-phase Circuit
 Three-phase AC Circuits Lesson Measurement of Power in a Three-phase Circuit In the previous lesson, the phase and line currents for balanced delta-connected load fed from a three-phase supply, along with
Three-phase AC Circuits Lesson Measurement of Power in a Three-phase Circuit In the previous lesson, the phase and line currents for balanced delta-connected load fed from a three-phase supply, along with
THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS. Historical Profiles
 C H A P T E R THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS 1 2 Society is never prepared to receive any invention. Every new thing is resisted, and it takes years for the inventor to get people to listen to him and years more
C H A P T E R THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS 1 2 Society is never prepared to receive any invention. Every new thing is resisted, and it takes years for the inventor to get people to listen to him and years more
A. P. Sakis Meliopoulos and George J. Cokkinides Power System Relaying, Theory and Applications. Chapter 8 2 Generator Protection 2
 DRAFT and INCOMPLETE Table of Contents from A. P. Sakis Meliopoulos and George J. Cokkinides Power System Relaying, Theory and Applications Chapter 8 Generator Protection 8. Introduction 8. Generator Protection
DRAFT and INCOMPLETE Table of Contents from A. P. Sakis Meliopoulos and George J. Cokkinides Power System Relaying, Theory and Applications Chapter 8 Generator Protection 8. Introduction 8. Generator Protection
Fatima Michael College of Engineering & Technology
 ANNA UNIVERSITY AFFILIATED COLLEGES BE EEE SEMESTER VI EE2353 - HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING UNIT IOVER VOLTAGES IN ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS 1. What is surge arrester? 2. Name the sources of switching surges.
ANNA UNIVERSITY AFFILIATED COLLEGES BE EEE SEMESTER VI EE2353 - HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING UNIT IOVER VOLTAGES IN ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS 1. What is surge arrester? 2. Name the sources of switching surges.
High Voltage DC Transmission Prof. Dr. S.N. Singh Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 High Voltage DC Transmission Prof. Dr. S.N. Singh Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 02 Lecture No. # 09 Analysis of Converter Circuit So, let us,
High Voltage DC Transmission Prof. Dr. S.N. Singh Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 02 Lecture No. # 09 Analysis of Converter Circuit So, let us,
E8EB-N0C2B E8EB-N0B2B
 Slim Sensor CSM DS_E 1 Ideal for Workpiece Position and Original Checking The to 1 kpa model can be used for workpiece position checking. The to 1MPa model is ideal for original pressure checking. Degree
Slim Sensor CSM DS_E 1 Ideal for Workpiece Position and Original Checking The to 1 kpa model can be used for workpiece position checking. The to 1MPa model is ideal for original pressure checking. Degree
Brief Steady of Power Factor Improvement
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 531-539 International Research PublicationHouse http://www.irphouse.com Brief Steady of Power Factor Improvement
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 531-539 International Research PublicationHouse http://www.irphouse.com Brief Steady of Power Factor Improvement
Module 4. Single-phase AC circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Single-phase circuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How
Module 4 Single-phase circuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How
ANALYSIS OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEM FAULTS IN THE PHASE DOMAIN. A Thesis JUN ZHU
 ANALSS OF TRANSMSSON SSTEM FAULTS N THE PHASE DOMAN A Thesis by JUN ZHU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
ANALSS OF TRANSMSSON SSTEM FAULTS N THE PHASE DOMAN A Thesis by JUN ZHU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
The per unit system is based on the formula shown in Equation (1).
 TECHNCAL ULLETN 007 Overview The per unit system is based on the formula shown in Equation (1). (1) per unit actual quantity base quantity Using this method, all quantities are expressed as ratios of some
TECHNCAL ULLETN 007 Overview The per unit system is based on the formula shown in Equation (1). (1) per unit actual quantity base quantity Using this method, all quantities are expressed as ratios of some
Experiment 2 Electric Field Mapping
 Experiment 2 Electric Field Mapping I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand Anonymous OBJECTIVE To visualize some electrostatic potentials and fields. THEORY Our goal is to explore
Experiment 2 Electric Field Mapping I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand Anonymous OBJECTIVE To visualize some electrostatic potentials and fields. THEORY Our goal is to explore
TECHNICAL BULLETIN 006 Symmetrical Components Overview. Introduction. I a g I b g I c
 Introduction The method of symmetrical components is a mathematical technique that allows the engineer to solve unbalanced systems using balanced techniques. Developed by C. Fortescue and presented in
Introduction The method of symmetrical components is a mathematical technique that allows the engineer to solve unbalanced systems using balanced techniques. Developed by C. Fortescue and presented in
Influence of Grounding Material s Property on the Impulse Grounding Resistance of Grounding Grids
 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Mechatronics (ICEEM 2015) Influence of Grounding Material s Property on the Impulse Grounding Resistance of Grounding Grids Leishi Xiao1, Qian Li1
International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Mechatronics (ICEEM 2015) Influence of Grounding Material s Property on the Impulse Grounding Resistance of Grounding Grids Leishi Xiao1, Qian Li1
A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SHORT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS
 NIJOTECH VOL. 5 NO. 1 MARCH 1981 EJEBE 46 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SHORT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS BY G.C. EJEBE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA, NSUKKA.
NIJOTECH VOL. 5 NO. 1 MARCH 1981 EJEBE 46 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SHORT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS BY G.C. EJEBE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA, NSUKKA.
Section 5. TADS Data Reporting Instruction Manual DRAFT Section 5 and Associated Appendices With Proposed Event Type Numbers
 Section 5 TADS Data Reporting Instruction Manual DRAFT Section 5 and Associated Appendices With Proposed Event Type Numbers Rev. 5/10/2010 1 Section 5 Form for Event ID and Event Type Number Data TO s
Section 5 TADS Data Reporting Instruction Manual DRAFT Section 5 and Associated Appendices With Proposed Event Type Numbers Rev. 5/10/2010 1 Section 5 Form for Event ID and Event Type Number Data TO s
THF / 1SCC330001M THF 1S1 C
 THF 2247 0191/ 1SCC330001M5803 34 THF 1S1 C Installation and Operation Instruction for THF Filter and Protective Unit THF 1_ THF 1S_ THF 1BS_ General guidelines Due to the fact that most UK building earth
THF 2247 0191/ 1SCC330001M5803 34 THF 1S1 C Installation and Operation Instruction for THF Filter and Protective Unit THF 1_ THF 1S_ THF 1BS_ General guidelines Due to the fact that most UK building earth
SECTION 1: SHADE IN THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON THE BUBBLE SHEET. (60%)
 PHYSICS 3204 Unit 2 Test #1 NAME: SECTION 1: SHADE IN THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON THE BUBBLE SHEET. (60%) 1 The elementary charge is the amount of charge on -?-. A) an atom B) a proton C) an electron
PHYSICS 3204 Unit 2 Test #1 NAME: SECTION 1: SHADE IN THE LETTER OF THE BEST ANSWER ON THE BUBBLE SHEET. (60%) 1 The elementary charge is the amount of charge on -?-. A) an atom B) a proton C) an electron
Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits
 Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits 1 Single Phase Parallel A.C. Circuits (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) n parallel a.c. circuits similar
Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits 1 Single Phase Parallel A.C. Circuits (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) n parallel a.c. circuits similar
Request Ensure that this Instruction Manual is delivered to the end users and the maintenance manager.
 Request Ensure that this Instruction Manual is delivered to the end users and the maintenance manager. 1 -C - Safety section - This Safety section should be read before starting any work on the relay.
Request Ensure that this Instruction Manual is delivered to the end users and the maintenance manager. 1 -C - Safety section - This Safety section should be read before starting any work on the relay.
5) Ohm s Law gives the relationship between potential difference and current for a.
 ) During any process, the net charge of a closed system. a) increases b) decreases c) stays constant ) In equilibrium, the electric field in a conductor is. a) always changing b) a constant non-zero value
) During any process, the net charge of a closed system. a) increases b) decreases c) stays constant ) In equilibrium, the electric field in a conductor is. a) always changing b) a constant non-zero value
4 Fault Calculations. Introduction 4.1. Three phase fault calculations 4.2. Symmetrical component analysis 4.3 of a three-phase network
 ault Calculations ntroduction 4. Three phase fault calculations 4. Symmetrical component analysis 4.3 of a three-phase network Equations and network connections 4.4 for various types of faults Current
ault Calculations ntroduction 4. Three phase fault calculations 4. Symmetrical component analysis 4.3 of a three-phase network Equations and network connections 4.4 for various types of faults Current
ALTERNATING CURRENT
 ATENATING UENT Important oints:. The alternating current (A) is generally expressed as ( ) I I sin ω t + φ Where i peak value of alternating current.. emf of an alternating current source is generally
ATENATING UENT Important oints:. The alternating current (A) is generally expressed as ( ) I I sin ω t + φ Where i peak value of alternating current.. emf of an alternating current source is generally
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET
 FCLTY F ENGNEERNG LB SHEET EEL1196 nstrumentation & Measurement Techniques TRMESTER 2 2017-2018 M2: Power Measurement sing Two Wattmeter Method *Note: Students will have to tabulate the theoretical values
FCLTY F ENGNEERNG LB SHEET EEL1196 nstrumentation & Measurement Techniques TRMESTER 2 2017-2018 M2: Power Measurement sing Two Wattmeter Method *Note: Students will have to tabulate the theoretical values
Electricity Review completed.notebook. June 13, 2013
 Which particle in an atom has no electric charge associated with it? a. proton c. neutron b. electron d. nucleus Jun 12 9:28 PM The electrons in a metal sphere can be made to move by touching it with a
Which particle in an atom has no electric charge associated with it? a. proton c. neutron b. electron d. nucleus Jun 12 9:28 PM The electrons in a metal sphere can be made to move by touching it with a
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Pre-Lab. Introduction
 Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
In the previous chapter, attention was confined
 4 4 Principles of Power System CHAPTE CHAPTE 8 Unsymmetrical Fault Calculations 8. Usymmetrical Faults on -Phase System 8. Symmetrical Components Method 8. Operator a 8.4 Symmetrical Components in Terms
4 4 Principles of Power System CHAPTE CHAPTE 8 Unsymmetrical Fault Calculations 8. Usymmetrical Faults on -Phase System 8. Symmetrical Components Method 8. Operator a 8.4 Symmetrical Components in Terms
