OA = 6, 5, 4 2, 7, 1 = 4, 12, 3 AB, AC, and = 5, 3, 3 3, 4, 12 = = 39 = 39. AC, AD) = = 3 AC) AC) AD
|
|
|
- Antonia Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math Fall First Eam Solutions October, Problem. ( pts.) Consider the points A(, 7, ), B(6,, 4), C(6,, 3), and D(7, 4, 4). (a pts.) Find the area of the parallelogram defined b AB and AC. First we calculate the vectors: AB = OB OA = 6,, 4, 7, = 4,, 3 AC = OC OA = 6,, 3, 7, = 4, 9, Then we use the propert of the cross-product: Area( AB, AC) = AB AC = = 4 7, 8, = 3, 4, = = 69 = 3 (b pts.) Find the volume of the parallelipiped defined b AB, AC, and The vector AD =, 3, 3, so Volume( AB, AC, 3 3 AD) = = AD ( AB AC) =, 3, 3 3, 4, = + 36 = 39 = 39. AD. (c pts.) Find the distance from the point D to the plane defined b AB and AC. Since Volume(parallelipiped) = Area(base) height, d(d, Π) = height = Volume( AB, AC, AD) Area( AB, AC) = 39 3 = 3 Alternativel, d(d, Π) = comp AB AC AD = ( AB AC) AD AB AC = 3, 4,, 3, 3 3, 4, = 39 3 = 3 Problem. ( pts.) Consider the vectors a =,, 3 and b = 3, 3, 4. (a pts.) Find the vector projection of b onto a. proj a b = (comp a b) a a = ( ) b a a a a = b a a a a =,, 3 = ,, 3 = 9 7, 9 4, 7 4. (b pts.) Find the scalar projection of a onto b. comp b a = a b b = a b 9 = = 9. b
2 Problem 3. ( pts.) (a pts.) Find the parametric equation for the line of intersection of the planes 3 6 = 3 and + =. To write down a parametric equation of a line, we need a point on a line and a direction vector. Since our line is the line of intersection of two planes, its direction vector should be perpendicular to normal vectors of both planes. We use the cross-product again: v = 3 6 = 4,,. To find a point on the line, we set one of the coordinates to ero and solve for the other two. For eample, setting =, we get 3 = 3, =, and we see that the point P (,, ) is on both planes. So we get: (t) = + 4t (t) = (t) = (b pts.) Find an equation of the plane containing the lines l : r(t) =,, +, 3, t t t l : r(s) =,, +,, 3 s. Since both of the direction vectors v =, 3, and v =,, 3 must lie in the plane, we can obtain the normal vector for the plane b taking their cross-product: n = v v = 3 = 9, 6, + 3 = 8, 7,. 3 Since the point P (,, ) is obviousl on both lines (and therefore on the plane), we get the following equation: (c pts.) Find the point where the line 8, 7,, +, = (t) = t (t) = 3t (t) = + t = 8 7 ( ) + = intersects the plane + 3 = 6. Plugging in (t), (t), and (t) in the equation of the plane, we get ( t) (3t) + 3( + t) = 6 t 3t t = t = 6 t =, so the line intersects the plane when value of the parameter t is. Plugging in, we get the point of intersection ( ( P ) (, ) (, )) ( 3 = P, 3, ). Problem 4. ( pts.) An unevenl heated plate has temperature T (, ) in C at the point (, ). If T (, ) = 3 and T (, ) = and T (, ) =, estimate the temperature at the point (.4,.97). Given the above information, the best we can do to estimate the change in temperature from the point (, ) to (.4,.97) is b using the lineariation; that is, instead of the actual change T we use the approimate change T +T. Since =.4 =.4 and =.97 =.3, we get T (.4,.97) T (.) + T + T = (.3) = = 36..
3 3 Problem. ( pts.) A to plane model was fling according to the rule r(t) = t, t 3 t, + 7t t + t 3 when at t = seconds its engine broke. Ignoring gravit, find when and where it hit the ground. In this problem it is convenient to introduce a new parameter s that is equal to the time after the engine broke, i.e., s = t. Then at the time t = (or s = ) seconds the plane is at the point r(t = ) =, 4, 3 and its instanteneous velocit at this point is r (t = ) =, 3t t, 7 t + 3t =, 8,. If we assume that no forces act on the model, t= the plane will continue to fl along the tangent line to the trajector at t = with the constant velocit r (t = ). The equation of this line is l(s) = r() + sr () =, 4, 3 +, 8, s = + s, 4 + 8s, 3 s, so the plane hits the ground = when s = 3 at the point l(3) =, 8, seconds after it started fling. Remark. To get a more realistic picture we need to take gravit into account. From F = ma = mg we see that the trajector of the plane after the engine broke should satisf the equations Then r (s) =,, g, r (s = ) = v(s = ) =, 8,, r(s = ) =, 4, 3 r (s) =, 8, gs, r(s) = + s, 4 + 8s, gs s + 3, and the plane hits the ground when gs + s 3 =. So s = ± + 6g and taking the positive root we get s = g 6g +.9 seconds (or.9 seconds after the plane started fling), and at this moment the plane will be at g r(.9).9,.37,
4 4 Problem 6. ( pts.) Consider the function f(, ) = and the point P (3, ). (a pts.) Find the gradient vector f(3, ). f = f, f =,, f(3, ) =,. (b pts.) Write down an equation of the tangent line to the level curve of f(, ) at the point P (3, ). Since the gradient vector f(p ) is perpendicular to the level curve (since the rate of change of f along the level curve is ero), the equation of the tangent line will be f(, 3) 3, = + = 3 + = 3 or + 6 =. (c pts.) Find the rate of change of f(, ) at P (3, ) in the direction of v =, 3. First, we need to find the unit vector u in the direction of v. Since v =, u = 3,. Then Problem 7. ( pts) (No partial credit) True or False? () For an two vectors a and b, proj a b = proj b a. D u f(3, ) = f(3, ) u =, 3, = 34. False. There are man reasons wh it is false, for eample, proj a b is a vector in the direction of a, and proj b a is a vector in the direction of b. () If comp a b =, then proj b a =. True. Since comp a b = a b a, comp a b = means that a and b are perpendicular, so proj b a =. (3) If comp a b =, then comp b a =. True for the same reasons as the previous question. (4) a (b c) = (a b) c. False. The epression on the left is a number, the epression on the right is meaningless, since a b is a number, and ou can t take a cross-product of a number and a vector. () a (b c) = (a b) c. True. Both are equal to det(a, b, c) = vol(a, b, c) (up to a ± sign). (6) Two lines perpendicular to a given plane must be parallel. True. The direction vectors for both lines are (up to a multiple) equal to the normal vector of the plane, v = λn, v = µn, so v = λ µ v. (7) Two lines parallel to a given plane must be parallel. False. The direction vectors must be both perpendicular to the normal vector of the plane, n v = n v =, but this does not mean that v v = (take two intersecting lines in the -plane, for eample). (8) Two planes parallel to a given line must be parallel. False. The normal vectors for the planes must be both perpendicular to the direction vector of the line, n v = n v =, but this does not mean that n n = (for eample, both and planes are paralell to the line l(t) =,, t ). (9) Two planes perpendicular to a given line must be parallel. True. The direction vector of the line can be taken as a normal vector for both planes.
5 () An object moving with constant speed has ero acceleration. False. Acceleration corresponds to change in velocit. For motion in three-dimensional (or even two-dimensional) space, velocit is a vector, and so it has both magnitude (called speed) and direction. So if we keep the speed constant, we can still change the direction of motion producing acceleration. For eample, and object moving with constant speed on a circular trajector will have acceleration pointing towards the center of the circle. Problem 8. ( pts.) (No partial credit) (a 8 pts.) Match the graphs of parametric curves with their parametric equations. (I).... We see that this curve lies above the circle in the -plane, and the motion is periodic in as well, so it must be r 3 (t) = cos t, sin t, sin 6t. Note that si peaks correspond to the fact that the curve oscillates in the -direction si times faster than in the and directions. (II) 3 3 We see that this curve lies above the circle in the -plane, so it must be r (t) = cos t, t, sin t. The t term makes this curve look different from the heli though. (III).3.3 This curve stas near the -ais most of the time, and this is due to the eponential deca in the and components of the corresponding equation r 4 (t) = t, 3te t, t e t (IV) This curve lies above the line = in the plane, so it must be r (t) = ( + sin t)t, ( + sin t)t, ( + cos t)t (b pts.) What is the maimum value of achieved on curve (I)? Either from the plot or from the equation we can see that the maimum value of achieved on this curve is.
Math 323 Exam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions. 2. Given the vectors a = 1,2,0, b = 1,0,2, and c = 0,1,1, compute the following:
 Math 323 Eam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions 1. Given the vectors a = 2,, 1, b = 3, 2,4, and c = 1, 4,, compute the following: (a) A unit vector in the direction of c. u = c c = 1, 4, 1 4 =,, 1+16+ 17 17
Math 323 Eam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions 1. Given the vectors a = 2,, 1, b = 3, 2,4, and c = 1, 4,, compute the following: (a) A unit vector in the direction of c. u = c c = 1, 4, 1 4 =,, 1+16+ 17 17
13.1. For further details concerning the physics involved and animations of the trajectories of the particles, see the following websites:
 8 CHAPTER VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provide us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes in
8 CHAPTER VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provide us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes in
Multiple Choice. 1.(6 pts) Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (2, 5, 1) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9.
 Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Cumulative Review of Vectors
 Cumulative Review of Vectors 1. For the vectors a! 1, 1, and b! 1, 4, 1, determine the following: a. the angle between the two vectors! the scalar and vector projections of a! on the scalar and vector
Cumulative Review of Vectors 1. For the vectors a! 1, 1, and b! 1, 4, 1, determine the following: a. the angle between the two vectors! the scalar and vector projections of a! on the scalar and vector
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS. MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
Overview. Distances in R 3. Distance from a point to a plane. Question
 Overview Yesterda we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrar points r in terms of a specific point and the direction vector v.
Overview Yesterda we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrar points r in terms of a specific point and the direction vector v.
Vector Fields. Field (II) Field (V)
 Math 1a Vector Fields 1. Match the following vector fields to the pictures, below. Eplain our reasoning. (Notice that in some of the pictures all of the vectors have been uniforml scaled so that the picture
Math 1a Vector Fields 1. Match the following vector fields to the pictures, below. Eplain our reasoning. (Notice that in some of the pictures all of the vectors have been uniforml scaled so that the picture
Review of Prerequisite Skills, p. 350 C( 2, 0, 1) B( 3, 2, 0) y A(0, 1, 0) D(0, 2, 3) j! k! 2k! Section 7.1, pp
 . 5. a. a a b a a b. Case If and are collinear, then b is also collinear with both and. But is perpendicular to and c c c b 9 b c, so a a b b is perpendicular to. Case If b and c b c are not collinear,
. 5. a. a a b a a b. Case If and are collinear, then b is also collinear with both and. But is perpendicular to and c c c b 9 b c, so a a b b is perpendicular to. Case If b and c b c are not collinear,
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
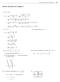 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
13.1. For further details concerning the physics involved and animations of the trajectories of the particles, see the following websites:
 8 CHAPTER 3 VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provie us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes
8 CHAPTER 3 VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provie us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes
Scalar functions of several variables (Sect. 14.1)
 Scalar functions of several variables (Sect. 14.1) Functions of several variables. On open, closed sets. Functions of two variables: Graph of the function. Level curves, contour curves. Functions of three
Scalar functions of several variables (Sect. 14.1) Functions of several variables. On open, closed sets. Functions of two variables: Graph of the function. Level curves, contour curves. Functions of three
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential functions are those with variable powers, e.g. = a. Their graphs take two forms: (0, 1) (0, 1) When a > 1, the graph: is alwas increasing is alwas positive
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential functions are those with variable powers, e.g. = a. Their graphs take two forms: (0, 1) (0, 1) When a > 1, the graph: is alwas increasing is alwas positive
3, 1, 3 3, 1, 1 3, 1, 1. x(t) = t cos(πt) y(t) = t sin(πt), z(t) = t 2 t 0
 Math 5 Final Eam olutions ecember 5, Problem. ( pts.) (a 5 pts.) Find the distance from the point P (,, 7) to the plane z +. olution. We can easil find a point P on the plane b choosing some values for
Math 5 Final Eam olutions ecember 5, Problem. ( pts.) (a 5 pts.) Find the distance from the point P (,, 7) to the plane z +. olution. We can easil find a point P on the plane b choosing some values for
CHAPTER 11 Vector-Valued Functions
 CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
3 = arccos. A a and b are parallel, B a and b are perpendicular, C a and b are normalized, or D this is always true.
 Math 210-101 Test #1 Sept. 16 th, 2016 Name: Answer Key Be sure to show your work! 1. (20 points) Vector Basics: Let v = 1, 2,, w = 1, 2, 2, and u = 2, 1, 1. (a) Find the area of a parallelogram spanned
Math 210-101 Test #1 Sept. 16 th, 2016 Name: Answer Key Be sure to show your work! 1. (20 points) Vector Basics: Let v = 1, 2,, w = 1, 2, 2, and u = 2, 1, 1. (a) Find the area of a parallelogram spanned
(6, 4, 0) = (3, 2, 0). Find the equation of the sphere that has the line segment from P to Q as a diameter.
 Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Math 21a: Multivariable calculus. List of Worksheets. Harvard University, Spring 2009
 Math 2a: Multivariable calculus Harvard Universit, Spring 2009 List of Worksheets Vectors and the Dot Product Cross Product and Triple Product Lines and Planes Functions and Graphs Quadric Surfaces Vector-Valued
Math 2a: Multivariable calculus Harvard Universit, Spring 2009 List of Worksheets Vectors and the Dot Product Cross Product and Triple Product Lines and Planes Functions and Graphs Quadric Surfaces Vector-Valued
Math 2400, Midterm 1
 Math 4, Midterm 1 February 1, 18 PRINT your name: PRINT instructor s name: Mark your section/instructor: Section 1 Kevin Berg 8: 8:5 Section Xingzhou Yang 8: 8:5 Section 3 Albert Bronstein 9: 9:5 Section
Math 4, Midterm 1 February 1, 18 PRINT your name: PRINT instructor s name: Mark your section/instructor: Section 1 Kevin Berg 8: 8:5 Section Xingzhou Yang 8: 8:5 Section 3 Albert Bronstein 9: 9:5 Section
MATH 223 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE ( )
 MATH 3 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE (017-018) The following questions can be used as a review for Math 3 These questions are not actual samples of questions that will appear on the final eam, but the will provide
MATH 3 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE (017-018) The following questions can be used as a review for Math 3 These questions are not actual samples of questions that will appear on the final eam, but the will provide
Lecture 5. Equations of Lines and Planes. Dan Nichols MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts.
 Lecture 5 Equations of Lines and Planes Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 Universit of Massachusetts Februar 6, 2018 (2) Upcoming midterm eam First midterm: Wednesda Feb. 21, 7:00-9:00
Lecture 5 Equations of Lines and Planes Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 Universit of Massachusetts Februar 6, 2018 (2) Upcoming midterm eam First midterm: Wednesda Feb. 21, 7:00-9:00
Math 101 chapter six practice exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
4.3 Worksheet - Derivatives of Inverse Functions
 AP Calculus 3.8 Worksheet 4.3 Worksheet - Derivatives of Inverse Functions All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit.. What are the following derivatives
AP Calculus 3.8 Worksheet 4.3 Worksheet - Derivatives of Inverse Functions All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit.. What are the following derivatives
Derivatives 2: The Derivative at a Point
 Derivatives 2: The Derivative at a Point 69 Derivatives 2: The Derivative at a Point Model 1: Review of Velocit In the previous activit we eplored position functions (distance versus time) and learned
Derivatives 2: The Derivative at a Point 69 Derivatives 2: The Derivative at a Point Model 1: Review of Velocit In the previous activit we eplored position functions (distance versus time) and learned
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Review: critical point or equivalently f a,
 Review: a b f f a b f a b critical point or equivalentl f a, b A point, is called a of if,, 0 A local ma or local min must be a critical point (but not conversel) 0 D iscriminant (or Hessian) f f D f f
Review: a b f f a b f a b critical point or equivalentl f a, b A point, is called a of if,, 0 A local ma or local min must be a critical point (but not conversel) 0 D iscriminant (or Hessian) f f D f f
Calculus 4 Final Exam Review / Winter 2009
 Calculus 4 Final Eam Review / Winter 9 (.) Set-up an iterate triple integral for the volume of the soli enclose between the surfaces: 4 an 4. DO NOT EVALUATE THE INTEGRAL! [Hint: The graphs of both surfaces
Calculus 4 Final Eam Review / Winter 9 (.) Set-up an iterate triple integral for the volume of the soli enclose between the surfaces: 4 an 4. DO NOT EVALUATE THE INTEGRAL! [Hint: The graphs of both surfaces
Section Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 13.1 Section 13.1 Goals: Graph certain plane curves. Compute limits and verify the continuity of vector functions. Multivariable Calculus 1 / 32 Section 13.1 Equation of a Line The equation of
Section 13.1 Section 13.1 Goals: Graph certain plane curves. Compute limits and verify the continuity of vector functions. Multivariable Calculus 1 / 32 Section 13.1 Equation of a Line The equation of
MATH 2300 review problems for Exam 3 ANSWERS
 MATH 300 review problems for Eam 3 ANSWERS. Check whether the following series converge or diverge. In each case, justif our answer b either computing the sum or b b showing which convergence test ou are
MATH 300 review problems for Eam 3 ANSWERS. Check whether the following series converge or diverge. In each case, justif our answer b either computing the sum or b b showing which convergence test ou are
Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 1 Functions of Several Variables 1.1 Introduction A real valued function of n variables is a function f : R, where the domain is a subset of R n. So: for each ( 1,,..., n ) in, the value of f is
Chapter 1 Functions of Several Variables 1.1 Introduction A real valued function of n variables is a function f : R, where the domain is a subset of R n. So: for each ( 1,,..., n ) in, the value of f is
(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)
![(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2) (a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)](/thumbs/85/92620692.jpg) . f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
. f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math 21a, Spring 2003
 SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math a, Spring 3 Problem ) ( points) Circle for each of the questions the correct letter. No justifications are needed. Your score will be C W where C is the number of
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math a, Spring 3 Problem ) ( points) Circle for each of the questions the correct letter. No justifications are needed. Your score will be C W where C is the number of
1-D and 2-D Motion Test Friday 9/8
 1-D and -D Motion Test Frida 9/8 3-1 Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocit, force, momentum A scalar has onl a magnitude. Some scalar
1-D and -D Motion Test Frida 9/8 3-1 Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocit, force, momentum A scalar has onl a magnitude. Some scalar
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions
 Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
MAC 1105 Review for Exam 4. Name
 MAC 1105 Review for Eam Name For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f() = +, g() = 8-7; Find (f g)(). 1) Find the domain of the composite function f g. 9 ) f() = + 9;
MAC 1105 Review for Eam Name For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f() = +, g() = 8-7; Find (f g)(). 1) Find the domain of the composite function f g. 9 ) f() = + 9;
Triple Integrals in Cartesian Coordinates. Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates. Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates
 Chapter 3 Multiple Integral 3. Double Integrals 3. Iterated Integrals 3.3 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates 3.4 Triple Integrals Triple Integrals in Cartesian Coordinates Triple Integrals in Clindrical
Chapter 3 Multiple Integral 3. Double Integrals 3. Iterated Integrals 3.3 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates 3.4 Triple Integrals Triple Integrals in Cartesian Coordinates Triple Integrals in Clindrical
SOLUTIONS 1 (27) 2 (18) 3 (18) 4 (15) 5 (22) TOTAL (100) PROBLEM NUMBER SCORE MIDTERM 2. Form A. Recitation Instructor : Recitation Time :
 Math 5 March 8, 206 Form A Page of 8 Name : OSU Name.# : Lecturer:: Recitation Instructor : SOLUTIONS Recitation Time : SHOW ALL WORK in problems, 2, and 3. Incorrect answers with work shown may receive
Math 5 March 8, 206 Form A Page of 8 Name : OSU Name.# : Lecturer:: Recitation Instructor : SOLUTIONS Recitation Time : SHOW ALL WORK in problems, 2, and 3. Incorrect answers with work shown may receive
MATHEMATICS 200 December 2013 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATICS 2 December 21 Final Eam Solutions 1. Short Answer Problems. Show our work. Not all questions are of equal difficult. Simplif our answers as much as possible in this question. (a) The line L
MATHEMATICS 2 December 21 Final Eam Solutions 1. Short Answer Problems. Show our work. Not all questions are of equal difficult. Simplif our answers as much as possible in this question. (a) The line L
Mechanics Departmental Exam Last updated November 2013
 Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Exact Differential Equations. The general solution of the equation is f x, y C. If f has continuous second partials, then M y 2 f
 APPENDIX C Additional Topics in Differential Equations APPENDIX C. Eact First-Order Equations Eact Differential Equations Integrating Factors Eact Differential Equations In Chapter 6, ou studied applications
APPENDIX C Additional Topics in Differential Equations APPENDIX C. Eact First-Order Equations Eact Differential Equations Integrating Factors Eact Differential Equations In Chapter 6, ou studied applications
Solution. The relationship between cartesian coordinates (x, y) and polar coordinates (r, θ) is given by. (x, y) = (r cos θ, r sin θ).
 Problem 1. Let p 1 be the point having polar coordinates r = 1 and θ = π. Let p 2 be the point having polar coordinates r = 1 and θ = π/2. Find the Euclidean distance between p 1 and p 2. The relationship
Problem 1. Let p 1 be the point having polar coordinates r = 1 and θ = π. Let p 2 be the point having polar coordinates r = 1 and θ = π/2. Find the Euclidean distance between p 1 and p 2. The relationship
Math Vector Calculus II
 Math 255 - Vector Calculus II Review Notes Vectors We assume the reader is familiar with all the basic concepts regarding vectors and vector arithmetic, such as addition/subtraction of vectors in R n,
Math 255 - Vector Calculus II Review Notes Vectors We assume the reader is familiar with all the basic concepts regarding vectors and vector arithmetic, such as addition/subtraction of vectors in R n,
Solutions to O Level Add Math paper
 Solutions to O Level Add Math paper 4. Bab food is heated in a microwave to a temperature of C. It subsequentl cools in such a wa that its temperature, T C, t minutes after removal from the microwave,
Solutions to O Level Add Math paper 4. Bab food is heated in a microwave to a temperature of C. It subsequentl cools in such a wa that its temperature, T C, t minutes after removal from the microwave,
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
MATHEMATICS 200 December 2011 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATICS December 11 Final Eam Solutions 1. Consider the function f(, ) e +4. (a) Draw a contour map of f, showing all tpes of level curves that occur. (b) Find the equation of the tangent plane to
MATHEMATICS December 11 Final Eam Solutions 1. Consider the function f(, ) e +4. (a) Draw a contour map of f, showing all tpes of level curves that occur. (b) Find the equation of the tangent plane to
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards
 Lesson 5 CALCULUS (8) Rate of change Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome : Functions and Algebra Assessment standard 1..7(e) Solve practical problems involving optimisation and
Lesson 5 CALCULUS (8) Rate of change Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome : Functions and Algebra Assessment standard 1..7(e) Solve practical problems involving optimisation and
Mathematics Extension 2
 Student Number ABBOTSLEIGH AUGUST 007 YEAR ASSESSMENT 4 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE TRIAL EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes. Working time 3 hours. Write using blue
Student Number ABBOTSLEIGH AUGUST 007 YEAR ASSESSMENT 4 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE TRIAL EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes. Working time 3 hours. Write using blue
AP Calculus BC Final Exam Preparatory Materials December 2016
 AP Calculus BC Final Eam Preparatory Materials December 06 Your first semester final eam will consist of both multiple choice and free response questions, similar to the AP Eam The following practice problems
AP Calculus BC Final Eam Preparatory Materials December 06 Your first semester final eam will consist of both multiple choice and free response questions, similar to the AP Eam The following practice problems
a. Graph each scenario. How many days will it take to infect our whole class in each scenario?
 Math 111 Section.3 Notes Zombie Tag! A Zombie is loose in our classroom! How long until we are all infected? Eample 1. Fill in the table for each scenario. Scenario 1: The initial zombie infects one new
Math 111 Section.3 Notes Zombie Tag! A Zombie is loose in our classroom! How long until we are all infected? Eample 1. Fill in the table for each scenario. Scenario 1: The initial zombie infects one new
Edexcel GCE A Level Maths. Further Maths 3 Coordinate Systems
 Edecel GCE A Level Maths Further Maths 3 Coordinate Sstems Edited b: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebl.com 1 kumarmaths.weebl.com kumarmaths.weebl.com 3 kumarmaths.weebl.com 4 kumarmaths.weebl.com 5 1. An ellipse
Edecel GCE A Level Maths Further Maths 3 Coordinate Sstems Edited b: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebl.com 1 kumarmaths.weebl.com kumarmaths.weebl.com 3 kumarmaths.weebl.com 4 kumarmaths.weebl.com 5 1. An ellipse
Math 2300 Calculus II University of Colorado
 Math 3 Calculus II University of Colorado Spring Final eam review problems: ANSWER KEY. Find f (, ) for f(, y) = esin( y) ( + y ) 3/.. Consider the solid region W situated above the region apple apple,
Math 3 Calculus II University of Colorado Spring Final eam review problems: ANSWER KEY. Find f (, ) for f(, y) = esin( y) ( + y ) 3/.. Consider the solid region W situated above the region apple apple,
Answer Key 1973 BC 1969 BC 24. A 14. A 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. C 28. D 29. C 30. D 31. C 13. C 12. D 12. E 3. A 32. B 27. E 34. C 14. D 25. B 26.
 Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Limits and the derivative function. Limits and the derivative function
 The Velocity Problem A particle is moving in a straight line. t is the time that has passed from the start of motion (which corresponds to t = 0) s(t) is the distance from the particle to the initial position
The Velocity Problem A particle is moving in a straight line. t is the time that has passed from the start of motion (which corresponds to t = 0) s(t) is the distance from the particle to the initial position
Lines and Planes 1. x(t) = at + b y(t) = ct + d
 1 Lines in the Plane Lines and Planes 1 Ever line of points L in R 2 can be epressed as the solution set for an equation of the form A + B = C. Will we call this the ABC form. Recall that the slope-intercept
1 Lines in the Plane Lines and Planes 1 Ever line of points L in R 2 can be epressed as the solution set for an equation of the form A + B = C. Will we call this the ABC form. Recall that the slope-intercept
Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the shaded region about the given axis. Use the disc/washer method 1) About the x-axis
 Final eam practice for Math 6 Disclaimer: The actual eam is different Find the volume of the solid generated b revolving the shaded region about the given ais. Use the disc/washer method ) About the -ais
Final eam practice for Math 6 Disclaimer: The actual eam is different Find the volume of the solid generated b revolving the shaded region about the given ais. Use the disc/washer method ) About the -ais
Math Exam 1a. c) lim tan( 3x. 2) Calculate the derivatives of the following. DON'T SIMPLIFY! d) s = t t 3t
 Math 111 - Eam 1a 1) Evaluate the following limits: 7 3 1 4 36 a) lim b) lim 5 1 3 6 + 4 c) lim tan( 3 ) + d) lim ( ) 100 1+ h 1 h 0 h ) Calculate the derivatives of the following. DON'T SIMPLIFY! a) y
Math 111 - Eam 1a 1) Evaluate the following limits: 7 3 1 4 36 a) lim b) lim 5 1 3 6 + 4 c) lim tan( 3 ) + d) lim ( ) 100 1+ h 1 h 0 h ) Calculate the derivatives of the following. DON'T SIMPLIFY! a) y
is the curve of intersection of the plane y z 2 and the cylinder x oriented counterclockwise when viewed from above.
 The questions below are representative or actual questions that have appeared on final eams in Math from pring 009 to present. The questions below are in no particular order. There are tpicall 10 questions
The questions below are representative or actual questions that have appeared on final eams in Math from pring 009 to present. The questions below are in no particular order. There are tpicall 10 questions
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2009 Exam 4 December 15, 2009
 MA 3 Calculus I Fall 009 Eam December 5, 009 Answer all of the questions - 7 and two of the questions 8-0. Please indicate which problem is not to be graded b crossing through its number in the table below.
MA 3 Calculus I Fall 009 Eam December 5, 009 Answer all of the questions - 7 and two of the questions 8-0. Please indicate which problem is not to be graded b crossing through its number in the table below.
Solutions to Math 41 First Exam October 12, 2010
 Solutions to Math 41 First Eam October 12, 2010 1. 13 points) Find each of the following its, with justification. If the it does not eist, eplain why. If there is an infinite it, then eplain whether it
Solutions to Math 41 First Eam October 12, 2010 1. 13 points) Find each of the following its, with justification. If the it does not eist, eplain why. If there is an infinite it, then eplain whether it
DIFFERENTIATION. 3.1 Approximate Value and Error (page 151)
 CHAPTER APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION.1 Approimate Value and Error (page 151) f '( lim 0 f ( f ( f ( f ( f '( or f ( f ( f '( f ( f ( f '( (.) f ( f '( (.) where f ( f ( f ( Eample.1 (page 15): Find
CHAPTER APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION.1 Approimate Value and Error (page 151) f '( lim 0 f ( f ( f ( f ( f '( or f ( f ( f '( f ( f ( f '( (.) f ( f '( (.) where f ( f ( f ( Eample.1 (page 15): Find
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON
 BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
MATH 122A FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE (Spring 2014)
 MATH A FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE (Spring 0) The final eam for spring 0 will have a multiple choice format. This will allow us to offer the final eam as late in the course as possible, giving more in-class
MATH A FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE (Spring 0) The final eam for spring 0 will have a multiple choice format. This will allow us to offer the final eam as late in the course as possible, giving more in-class
Chapter One. Chapter One
 Chapter One Chapter One CHAPTER ONE Hughes Hallett et al c 005, John Wile & Sons ConcepTests and Answers and Comments for Section.. Which of the following functions has its domain identical with its range?
Chapter One Chapter One CHAPTER ONE Hughes Hallett et al c 005, John Wile & Sons ConcepTests and Answers and Comments for Section.. Which of the following functions has its domain identical with its range?
MAT 127: Calculus C, Fall 2010 Solutions to Midterm I
 MAT 7: Calculus C, Fall 00 Solutions to Midterm I Problem (0pts) Consider the four differential equations for = (): (a) = ( + ) (b) = ( + ) (c) = e + (d) = e. Each of the four diagrams below shows a solution
MAT 7: Calculus C, Fall 00 Solutions to Midterm I Problem (0pts) Consider the four differential equations for = (): (a) = ( + ) (b) = ( + ) (c) = e + (d) = e. Each of the four diagrams below shows a solution
Sample Questions to the Final Exam in Math 1111 Chapter 2 Section 2.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs
 Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS /3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL
N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS /3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL
Student s Printed Name:
 MATH 1060 Test Answer Ke Spring 016 Calculus of One Variable I Version A Sections..9 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: CUID: Section: Instructions: You are not permitted to use a calculator on an portion
MATH 1060 Test Answer Ke Spring 016 Calculus of One Variable I Version A Sections..9 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: CUID: Section: Instructions: You are not permitted to use a calculator on an portion
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Midterm 1 Review Solutions
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
y = (x2 +1) cos(x) 2x sin(x) d) y = ln(sin(x 2 )) y = 2x cos(x2 ) by the chain rule applied twice. Once to ln(u) and once to
 M408N Final Eam Solutions, December 13, 2011 1) (32 points, 2 pages) Compute dy/d in each of these situations. You do not need to simplify: a) y = 3 + 2 2 14 + 32 y = 3 2 + 4 14, by the n n 1 formula.
M408N Final Eam Solutions, December 13, 2011 1) (32 points, 2 pages) Compute dy/d in each of these situations. You do not need to simplify: a) y = 3 + 2 2 14 + 32 y = 3 2 + 4 14, by the n n 1 formula.
CHAPTER 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
11 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS, POLAR COORDINATES, AND CONIC SECTIONS
 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS, POLAR COORDINATES, AND CONIC SECTIONS. Parametric Equations Preliminar Questions. Describe the shape of the curve = cos t, = sin t. For all t, + = cos t + sin t = 9cos t + sin t =
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS, POLAR COORDINATES, AND CONIC SECTIONS. Parametric Equations Preliminar Questions. Describe the shape of the curve = cos t, = sin t. For all t, + = cos t + sin t = 9cos t + sin t =
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Algebra 1 Unit 9 Quadratic Equations
 Algebra 1 Unit 9 Quadratic Equations Part 1 Name: Period: Date Name of Lesson Notes Tuesda 4/4 Wednesda 4/5 Thursda 4/6 Frida 4/7 Monda 4/10 Tuesda 4/11 Wednesda 4/12 Thursda 4/13 Frida 4/14 Da 1- Quadratic
Algebra 1 Unit 9 Quadratic Equations Part 1 Name: Period: Date Name of Lesson Notes Tuesda 4/4 Wednesda 4/5 Thursda 4/6 Frida 4/7 Monda 4/10 Tuesda 4/11 Wednesda 4/12 Thursda 4/13 Frida 4/14 Da 1- Quadratic
Math Lagrange Multipliers
 Math 213 - Lagrange Multipliers Peter A. Perr Universit of Kentuck October 12, 2018 Homework Re-read section 14.8 Begin practice homework on section 14.8, problems 3-11 (odd), 15, 21, 23 Begin (or continue!)
Math 213 - Lagrange Multipliers Peter A. Perr Universit of Kentuck October 12, 2018 Homework Re-read section 14.8 Begin practice homework on section 14.8, problems 3-11 (odd), 15, 21, 23 Begin (or continue!)
Physics 207, Lecture 4, Sept. 15
 Phsics 07, Lecture 4, Sept. 15 Goals for hapts.. 3 & 4 Perform vector algebra (addition & subtraction) graphicall or b, & z components Interconvert between artesian and Polar coordinates Distinguish position-time
Phsics 07, Lecture 4, Sept. 15 Goals for hapts.. 3 & 4 Perform vector algebra (addition & subtraction) graphicall or b, & z components Interconvert between artesian and Polar coordinates Distinguish position-time
+ 4 Ex: y = v = (1, 4) x = 1 Focus: (h, k + ) = (1, 6) L.R. = 8 units We can have parabolas that open sideways too (inverses) x = a (y k) 2 + h
 Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 1 CHAPTER 2. BASIC TRIGONOMETRY 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONS 1 Vectors in Two Dimensions A vector is an object which has magnitude
1 CHAPTER 2. BASIC TRIGONOMETRY 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONS 1 Vectors in Two Dimensions A vector is an object which has magnitude
5.6. Differential equations
 5.6. Differential equations The relationship between cause and effect in phsical phenomena can often be formulated using differential equations which describe how a phsical measure () and its derivative
5.6. Differential equations The relationship between cause and effect in phsical phenomena can often be formulated using differential equations which describe how a phsical measure () and its derivative
APPM 1360 Final Exam Spring 2016
 APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
3.5 Continuity of a Function One Sided Continuity Intermediate Value Theorem... 23
 Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 MATH 214 (R1) Winter 2008 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #8 Completion Date: Friday March 14, 2008 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question 1.
MATH 214 (R1) Winter 2008 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #8 Completion Date: Friday March 14, 2008 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question 1.
SUPPLEMENT I. Example. Graph the vector 4, 3. Definition. Given two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), the vector represented by # AB is # AB =,
 SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
6.5 Trigonometric Equations
 6. Trigonometric Equations In this section, we discuss conditional trigonometric equations, that is, equations involving trigonometric functions that are satisfied only by some values of the variable (or
6. Trigonometric Equations In this section, we discuss conditional trigonometric equations, that is, equations involving trigonometric functions that are satisfied only by some values of the variable (or
Sample Final Exam Problems Solutions Math 107
 Sample Final Eam Problems Solutions Math 107 1 (a) We first factor the numerator and the denominator of the function to obtain f() = (3 + 1)( 4) 4( 1) i To locate vertical asymptotes, we eamine all locations
Sample Final Eam Problems Solutions Math 107 1 (a) We first factor the numerator and the denominator of the function to obtain f() = (3 + 1)( 4) 4( 1) i To locate vertical asymptotes, we eamine all locations
15.4 Equation of a Circle
 Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
1 k. cos tan? Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. 1. A sequence is defined by the recurrence relation u 2u 1, u 3.
 Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions.
N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions.
Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods
 Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods Foundational Knowledge Created b Triumph Tutoring Copright info Copright Triumph Tutoring 07 Triumph Tutoring Pt Ltd ABN 60 607 0 507 First published in 07 All rights
Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods Foundational Knowledge Created b Triumph Tutoring Copright info Copright Triumph Tutoring 07 Triumph Tutoring Pt Ltd ABN 60 607 0 507 First published in 07 All rights
MATH Line integrals III Fall The fundamental theorem of line integrals. In general C
 MATH 255 Line integrals III Fall 216 In general 1. The fundamental theorem of line integrals v T ds depends on the curve between the starting point and the ending point. onsider two was to get from (1,
MATH 255 Line integrals III Fall 216 In general 1. The fundamental theorem of line integrals v T ds depends on the curve between the starting point and the ending point. onsider two was to get from (1,
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
MATHEMATICS 317 December 2010 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATI 317 December 1 Final Eam olutions 1. Let r(t) = ( 3 cos t, 3 sin t, 4t ) be the position vector of a particle as a function of time t. (a) Find the velocity of the particle as a function of time
MATHEMATI 317 December 1 Final Eam olutions 1. Let r(t) = ( 3 cos t, 3 sin t, 4t ) be the position vector of a particle as a function of time t. (a) Find the velocity of the particle as a function of time
Homework Assignments Math /02 Spring 2015
 Homework Assignments Math 1-01/0 Spring 015 Assignment 1 Due date : Frida, Januar Section 5.1, Page 159: #1-, 10, 11, 1; Section 5., Page 16: Find the slope and -intercept, and then plot the line in problems:
Homework Assignments Math 1-01/0 Spring 015 Assignment 1 Due date : Frida, Januar Section 5.1, Page 159: #1-, 10, 11, 1; Section 5., Page 16: Find the slope and -intercept, and then plot the line in problems:
Math 122 Fall Solutions to Homework #5. ( ) 2 " ln x. y = x 2
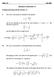 Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Circle. Paper 1 Section A. Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks. 5. A circle has equation. 4. The point P( 2, 4) lies on the circle
 PSf Circle Paper 1 Section A Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks. 1. A circle has equation ( 3) 2 + ( + 4) 2 = 20. Find the gradient of the tangent to the circle at the point (1, 0).
PSf Circle Paper 1 Section A Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks. 1. A circle has equation ( 3) 2 + ( + 4) 2 = 20. Find the gradient of the tangent to the circle at the point (1, 0).
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
 H Mathematics Higher Paper Practice Paper E Time allowed hour minutes NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Read carefull Calculators ma NOT be used in this paper. Section A Questions ( marks) Instructions for completion
H Mathematics Higher Paper Practice Paper E Time allowed hour minutes NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Read carefull Calculators ma NOT be used in this paper. Section A Questions ( marks) Instructions for completion
Math 20 Spring 2005 Final Exam Practice Problems (Set 2)
 Math 2 Spring 2 Final Eam Practice Problems (Set 2) 1. Find the etreme values of f(, ) = 2 2 + 3 2 4 on the region {(, ) 2 + 2 16}. 2. Allocation of Funds: A new editor has been allotted $6, to spend on
Math 2 Spring 2 Final Eam Practice Problems (Set 2) 1. Find the etreme values of f(, ) = 2 2 + 3 2 4 on the region {(, ) 2 + 2 16}. 2. Allocation of Funds: A new editor has been allotted $6, to spend on
You are required to show your work on each problem on this exam. The following rules apply:
 Math 5335 Fall 2017 Eam 2 12/5/18 Time Limit: 80 Minutes Name (Print): KEY This eam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 13 problems heck to see if an pages are missing Enter all requested
Math 5335 Fall 2017 Eam 2 12/5/18 Time Limit: 80 Minutes Name (Print): KEY This eam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 13 problems heck to see if an pages are missing Enter all requested
Answer Explanations. The SAT Subject Tests. Mathematics Level 1 & 2 TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE
 The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
