1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium
|
|
|
- Andra Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium The preceding section involved only single phase systems. For it to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, a homogeneous system must be in thermal equilibrium (infinitesimal difference in temperature between system and environment) and in mechanical equilibrium (infinitesimal difference in pressure). A heterogeneous system can involve more than one phase and, for it, thermodynamic equilibrium requires an additional criterion, the system must also be in chemical equilibrium (no conversion of mass between one phase and the other). Thermodynamic equilibrium between phases introduces additional constraints that actually reduce the degrees of freedom of a heterogeneous sytem below those of a homogeneous system. 1a. Chemical Equilibrium Let s consider a two-component mixture of dry air and water with the latter existing in vapor and possibly one condensed phase. For the two phases to be in equilibrium, in addition to thermal and mechanical equilibrium, the phases must also be in chemical equilibrium. The GIbbs function is used because here T and P are independent variables and the process of condensation is an isobaric and isothermal process. The change in Gibbs function is: (We will now move away from the use of specific quantities and multiply by mass) The total Gibbs function is G tot = G g + G c where g, c, and tot denote the gaseous phase, condensed phase and total system. Now the mass can change so: For the gas phase, the change in the Gibbs function is: dg g = dt + T p,n For the condensed phase ( ) Gc dg c = T dp + p T,n dt + p,n n d ( ) Gc dp + p T,n dn d + T,p,n n c n v dn v T,p,n (1) dn c (2) T,p,n ( G The quantity µ i = n i is defined as the chemical potential of component i. Adding the two )T,p,n n i components: 1
2 ( Gg dg tot = T + G ) ( c Gg dt + T p,n p + G ) c dp+µ d dn d +µ v dn v +µ c dn c p T,n (3) Let s consider a virtual displacement at constant T and p of the closed system (n d + n v + n c = constant) assuming n d = constant. Then dn d = dt = dp = 0 and dn c = dn v. dg tot = (µ v µ c )dn v (4) The condition for stale equilibrium is dg tot 0 for an arbitrary dn v, since dn v can be positive or negative, chemical equilibrium requires that: µ v = µ c (5) 2. Thermodynamic Degrees of Freedom A system comprised of c components and σ phases. Each phase of each component we have temperature T i and pressure p i - how Consider a single-compnent system involving two phases (water and water vapor) we have respectively p, T and p, T. For mechanical, thermal and chemical equilibrium between the two phases we must have: p = p (6) T = T µ = µ Since there are four potential independent variables and three relations among them, there is only one independent variable in general A one-component system involving two phases at equilibrium with one another possesses only one thermodynamic degree of freedom. Such a system must possess an equation of state of the form: p = p(t ) (7) If three phases (solid, lilquid and gas) are present simultaneously in equilib- 2
3 rium, then we have: p = p = p (8) T = T = T (9) µ = µ = µ (10) Since there are six unknowns and six relations among them, there are no independent variables. All values are fixed and define a triple point where all three phases are in equilibrium. In general, the number of thermodynamic degrees of freedom possessed by a heterogeneous system is described by the following principle i. Gibbs Phase Rule The number of state variables for a heterogeneous system involving c dynamically distinct by nonreactive components and σ phases is given by: n = c + 2 σ (11) 3. Thermodynamic Characteristics of Water Water is a pure substance so its equation of state is: 1. If only vapor Eq. 12 is the equation of state. p = p(α, T ) (12) 2. If two phases are present Eq. 12 reduces to p = p(t ) In heterogeneous state, when different phases coexist at equilibrium, the individual phases are said to be saturated. The net flux of mass from one state to another vanishes. If one of the phases is vapor, the pressure of the heterogeneous system represents the equilibrium vapor pressure with respect to water of ice p w or p i respectively. According to the Gibbs phase ruel, there exists a single state at which all three phases coexist at equilibrium, the triple point is defined by: 3
4 p T = 6.1mb (13) T T = 273K (14) α T v = m 3 kg 1 (15) α T w = m 3 kg 1 (16) α T i = m 3 kg 1 (17) 4. Equilibrium Phase Transformations The specific latent heat of a transformation is defined as the heat absorbed by the system (per unit mass) during an isobaric phase transformation: l = dq = dh αdp (18) = dh (19) l v l f l s latent heat of vaporization (liquid-gas) = Jkg 1 at 0 C latent heat of fusion (solid-liquid) = Jkg 1 at 0 C latent heat of sublimation (solid-vapor) = Jkg 1 at 0 C l s = l f + l v However, the latent heat is a property of the system and depends on the thermodynamic state (generally expressed as a function of temperature) 4a. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation In states involving two phases, the system of pure water possesses only one thermodynamic degree of freedom (specifying temperature determines its pressure). We can derive the equation of state using fundamental relations subject to conditions of chemical equilibrium. Consider two phases a and b, and a transformation between them that occurs reversibly. The heat transfer during such a process equals the latent heat of transformation...for specific quantities: ds = l T (20) 4
5 For a system of dry air and water inwhich the latter appears only in trace abundance, the Chemical Potential (which is the partial molar Gibbs function) is approximately equal to the specific Gibbs function: ( ) G µ k = = g k (21) n k pt n Consequently, for chemical equilibrium to occur: applying the fundamental relation: g a = g b (22) dg q = dg b (23) or (s b s a )dt + (α b α a )dp = 0 (24) dp dt = s α Incorporating Equation 20 yields: (25) dp dt = l T α (26) Where l is the latent heat appropriate to the phases present. This is the Clausius- Clapeyron equation and related the equilibrium vapor pressure to the temperature of the heterogeneous system. It constitutes an equation of state for the heterogeneous system when two phases are present. i. Water-Ice l is the latent heat of fusion. It is more convenient to express the equation as: dt dp = T α l (27) Because the change in volume during fusion is negligible, the equation of state becomes: 5
6 dt dp 0 (28) So the surface of water and ice in a T-p diagram is vertical. ii. Water-Vapor or Ice-Vapor The change of volume is approximately equal to that of the vapor produced: α R vt p (29) which can also be expressed as: ( ) dlnp for l constant dt dp dt = vaporization or sublimation ln p 2 p 1 = l R v lp T 2 R v (30) ( 1 T 1 1 T 2 = l R v T 2 (31) ) (32) Using the respective l v for vaporization and l s for sublimation yields (p w, p i in mb) log 10 p w = T log 10 p i = T (33) (34) (35) For a better approximation we can use an equation to express the change in latent heat with temperature. (HW) These equations describe the surfaces that correspond to vapor being in chemical equilibrium with a condensed phase and to the system pressure equaling the equilibrium vapor pressure. I 6
Evaluating properties of pure substances
 Evaluating properties of pure substances Pure substance A pure substance has the same chemical composition throughout. Are the following confined in a fixed volume pure substances: Ice (single component,
Evaluating properties of pure substances Pure substance A pure substance has the same chemical composition throughout. Are the following confined in a fixed volume pure substances: Ice (single component,
Chapter 8 Phase Diagram, Relative Stability of Solid, Liquid, and Gas
 Chapter 8 Phase Diagram, Relative Stability of Solid, Liquid, and Gas Three states of matter: solid, liquid, gas (plasma) At low T: Solid is most stable. At high T: liquid or gas is most stable. Ex: Most
Chapter 8 Phase Diagram, Relative Stability of Solid, Liquid, and Gas Three states of matter: solid, liquid, gas (plasma) At low T: Solid is most stable. At high T: liquid or gas is most stable. Ex: Most
Chapter 5. On-line resource
 Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
NENG 301 Week 8 Unary Heterogeneous Systems (DeHoff, Chap. 7, Chap )
 NENG 301 Week 8 Unary Heterogeneous Systems (DeHoff, Chap. 7, Chap. 5.3-5.4) Learning objectives for Chapter 7 At the end of this chapter you will be able to: Understand the general features of a unary
NENG 301 Week 8 Unary Heterogeneous Systems (DeHoff, Chap. 7, Chap. 5.3-5.4) Learning objectives for Chapter 7 At the end of this chapter you will be able to: Understand the general features of a unary
4) It is a state function because enthalpy(h), entropy(s) and temperature (T) are state functions.
 Chemical Thermodynamics S.Y.BSc. Concept of Gibb s free energy and Helmholtz free energy a) Gibb s free energy: 1) It was introduced by J.Willard Gibb s to account for the work of expansion due to volume
Chemical Thermodynamics S.Y.BSc. Concept of Gibb s free energy and Helmholtz free energy a) Gibb s free energy: 1) It was introduced by J.Willard Gibb s to account for the work of expansion due to volume
The Gibbs Phase Rule F = 2 + C - P
 The Gibbs Phase Rule The phase rule allows one to determine the number of degrees of freedom (F) or variance of a chemical system. This is useful for interpreting phase diagrams. F = 2 + C - P Where F
The Gibbs Phase Rule The phase rule allows one to determine the number of degrees of freedom (F) or variance of a chemical system. This is useful for interpreting phase diagrams. F = 2 + C - P Where F
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4)
 The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
Phase Diagrams. NC State University
 Chemistry 433 Lecture 18 Phase Diagrams NC State University Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function of temperature
Chemistry 433 Lecture 18 Phase Diagrams NC State University Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function of temperature
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems. Kwangheon Park Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering
 Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
WEEK 6. Multiphase systems
 WEEK 6 Multiphase systems Multiphase systems P 237. Processes usually deal with material being transferred from one phase (gas, liquid, or solid) to another. 6.1a Phase diagrams F = force on piston Water
WEEK 6 Multiphase systems Multiphase systems P 237. Processes usually deal with material being transferred from one phase (gas, liquid, or solid) to another. 6.1a Phase diagrams F = force on piston Water
Thermodynamic condition for equilibrium between two phases a and b is G a = G b, so that during an equilibrium phase change, G ab = G a G b = 0.
 CHAPTER 5 LECTURE NOTES Phases and Solutions Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between
CHAPTER 5 LECTURE NOTES Phases and Solutions Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between
MS212 Thermodynamics of Materials ( 소재열역학의이해 ) Lecture Note: Chapter 7
 2017 Spring Semester MS212 Thermodynamics of Materials ( 소재열역학의이해 ) Lecture Note: Chapter 7 Byungha Shin ( 신병하 ) Dept. of MSE, KAIST Largely based on lecture notes of Prof. Hyuck-Mo Lee and Prof. WooChul
2017 Spring Semester MS212 Thermodynamics of Materials ( 소재열역학의이해 ) Lecture Note: Chapter 7 Byungha Shin ( 신병하 ) Dept. of MSE, KAIST Largely based on lecture notes of Prof. Hyuck-Mo Lee and Prof. WooChul
The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations
 PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics September 11, 2013 The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy applied to thermal systems. Here, we develop the principles of thermodynamics for a discrete
First Law of Thermodynamics September 11, 2013 The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy applied to thermal systems. Here, we develop the principles of thermodynamics for a discrete
Application of Thermodynamics in Phase Diagrams. Today s Topics
 Lecture 23 Application of Thermodynamics in Phase Diagrams The Clausius Clapeyron Equation A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics The Clapeyron equation Integration
Lecture 23 Application of Thermodynamics in Phase Diagrams The Clausius Clapeyron Equation A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics The Clapeyron equation Integration
Chemical Potential. Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties)
 Chemical Potential Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties) du = TdS pdv Hence For an open system, that is, one that can gain or lose mass, U will also
Chemical Potential Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties) du = TdS pdv Hence For an open system, that is, one that can gain or lose mass, U will also
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics
 Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
12. Heat of melting and evaporation of water
 VS 12. Heat of melting and evaporation of water 12.1 Introduction The change of the physical state of a substance in general requires the absorption or release of heat. In this case, one speaks of a first
VS 12. Heat of melting and evaporation of water 12.1 Introduction The change of the physical state of a substance in general requires the absorption or release of heat. In this case, one speaks of a first
Pure Substance. Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State. Vapour-Liquid-Solid Phase Equilibrium
 Pure Substance Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of echanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
Pure Substance Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of echanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Quasi-equilibrium transitions
 Quasi-equilibrium transitions We have defined a two important equilibrium conditions. he first is one in which there is no heating, or the system is adiabatic, and dh/ =0, where h is the total enthalpy
Quasi-equilibrium transitions We have defined a two important equilibrium conditions. he first is one in which there is no heating, or the system is adiabatic, and dh/ =0, where h is the total enthalpy
More on phase diagram, chemical potential, and mixing
 More on phase diagram, chemical potential, and mixing Narayanan Kurur Department of Chemistry IIT Delhi 13 July 2013 Melting point changes with P ( ) Gα P T = V α V > 0 = G α when P Intersection point
More on phase diagram, chemical potential, and mixing Narayanan Kurur Department of Chemistry IIT Delhi 13 July 2013 Melting point changes with P ( ) Gα P T = V α V > 0 = G α when P Intersection point
Pure Substance. Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State. Vapour-Liquid-Solid Phase Equilibrium
 Pure Substance Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of echanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
Pure Substance Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of echanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances.
 I. Generalities. CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances. A. Definitions: 1. A phase of a substance is a form of matter that is uniform throughout in chemical composition and physical state.
I. Generalities. CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances. A. Definitions: 1. A phase of a substance is a form of matter that is uniform throughout in chemical composition and physical state.
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
At this point, we've developed the tools and basic concepts necessary to apply
 18 Lecture 0 At this point, we've developed the tools and basic concepts necessary to apply thermodynamics to a number of different systems, with the ultimate goal of describing chemically reacting systems.
18 Lecture 0 At this point, we've developed the tools and basic concepts necessary to apply thermodynamics to a number of different systems, with the ultimate goal of describing chemically reacting systems.
Chapter 7 PHASE EQUILIBRIUM IN A ONE-COMPONENT SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 PHASE EQUILIBRIUM IN A ONE-COMPONENT SYSTEM 7.1 INTRODUCTION The intensive thermodynamic properties of a system are temperature, pressure, and the chemical potentials of the various species occurring
Chapter 7 PHASE EQUILIBRIUM IN A ONE-COMPONENT SYSTEM 7.1 INTRODUCTION The intensive thermodynamic properties of a system are temperature, pressure, and the chemical potentials of the various species occurring
Chapter 3. The Second Law Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201)
 Chapter 3. The Second Law 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 The entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific
Chapter 3. The Second Law 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 The entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific
6 Physical transformations of pure substances
 6 Physical transformations of pure substances E6.b E6.2b E6.3b E6.4b Solutions to exercises Discussion questions Refer to Fig. 6.8. The white lines represent the regions of superheating and supercooling.
6 Physical transformations of pure substances E6.b E6.2b E6.3b E6.4b Solutions to exercises Discussion questions Refer to Fig. 6.8. The white lines represent the regions of superheating and supercooling.
ln( P vap(s) / torr) = T / K ln( P vap(l) / torr) = T / K
 Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Number 9 Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 9-4. Paraphrase: Given expressions
Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Number 9 Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 9-4. Paraphrase: Given expressions
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
water Plays dominant role in radiation All three phases emit and absorb in longwave radiation
 4.,4. water Plays dominant role in radiation All three phases emit and absorb in longwave radiation Some shortwave (solar) radiation is absorbed by all phases of water Principal role in the shortwave radiation
4.,4. water Plays dominant role in radiation All three phases emit and absorb in longwave radiation Some shortwave (solar) radiation is absorbed by all phases of water Principal role in the shortwave radiation
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Liquids and Solids. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Liquids and Solids Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gases, Liquids and Solids Gases are compressible fluids. They have no proper volume and proper
Liquids and Solids Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gases, Liquids and Solids Gases are compressible fluids. They have no proper volume and proper
Kelvin Effect. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
For an incompressible β and k = 0, Equations (6.28) and (6.29) become:
 Internal Energy and Entropy as Functions of T and V These are general equations relating the internal energy and entropy of homogeneous fluids of constant composition to temperature and volume. Equation
Internal Energy and Entropy as Functions of T and V These are general equations relating the internal energy and entropy of homogeneous fluids of constant composition to temperature and volume. Equation
Chapter 4. The Physical transformations of pure substances Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201)
 Chapter 4. The Physical transformations of pure substances 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents Phase Diagrams 4.1 The stabilities of phases 4.2 Phase boundaries 4.3 Three representative
Chapter 4. The Physical transformations of pure substances 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents Phase Diagrams 4.1 The stabilities of phases 4.2 Phase boundaries 4.3 Three representative
General Physical Chemistry I
 General Physical Chemistry I Lecture 11 Aleksey Kocherzhenko March 12, 2015" Last time " W Entropy" Let be the number of microscopic configurations that correspond to the same macroscopic state" Ø Entropy
General Physical Chemistry I Lecture 11 Aleksey Kocherzhenko March 12, 2015" Last time " W Entropy" Let be the number of microscopic configurations that correspond to the same macroscopic state" Ø Entropy
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II. Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition
 MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
1. Water Vapor in Air
 1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]
![Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]](/thumbs/81/83694823.jpg) Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
 DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY LECTURE NOTES 6151- ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY-II UNIT II CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS Unit syllabus: Terminology of thermodynamics - Second law: Entropy - entropy change for an ideal
DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY LECTURE NOTES 6151- ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY-II UNIT II CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS Unit syllabus: Terminology of thermodynamics - Second law: Entropy - entropy change for an ideal
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure
P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.
![P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C. P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.](/thumbs/79/79184286.jpg) Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Lecture 4 Clausius Inequality
 Lecture 4 Clausius Inequality Entropy distinguishes between irreversible and reversible processes. irrev S > 0 rev In a spontaneous process, there should be a net increase in the entropy of the system
Lecture 4 Clausius Inequality Entropy distinguishes between irreversible and reversible processes. irrev S > 0 rev In a spontaneous process, there should be a net increase in the entropy of the system
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES. Chapter 3. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Chapter 3. Property Relations The essence of macroscopic thermodynamics Dependence of U, H, S, G, and F on T, P, V, etc.
 Chapter 3 Property Relations The essence of macroscopic thermodynamics Dependence of U, H, S, G, and F on T, P, V, etc. Concepts Energy functions F and G Chemical potential, µ Partial Molar properties
Chapter 3 Property Relations The essence of macroscopic thermodynamics Dependence of U, H, S, G, and F on T, P, V, etc. Concepts Energy functions F and G Chemical potential, µ Partial Molar properties
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Physical transformations of pure substances Boiling, freezing, and the conversion of graphite to diamond examples of phase transitions changes of
 Physical transformations of pure substances Boiling, freezing, and the conversion of graphite to diamond examples of phase transitions changes of phase without change of chemical composition. In this chapter
Physical transformations of pure substances Boiling, freezing, and the conversion of graphite to diamond examples of phase transitions changes of phase without change of chemical composition. In this chapter
Chemistry 163B. One-Component. Phase Diagram Basics
 Chemistry 163B One-Component Phase Diagram Basics 1 qualitative factors in phase changes solid melting liquid freezing/fusion vaporization ENDOTHERMIC liquid gas condensation EXOTHERMIC sublimation solid
Chemistry 163B One-Component Phase Diagram Basics 1 qualitative factors in phase changes solid melting liquid freezing/fusion vaporization ENDOTHERMIC liquid gas condensation EXOTHERMIC sublimation solid
OCN 623: Thermodynamic Laws & Gibbs Free Energy. or how to predict chemical reactions without doing experiments
 OCN 623: Thermodynamic Laws & Gibbs Free Energy or how to predict chemical reactions without doing experiments Definitions Extensive properties Depend on the amount of material e.g. # of moles, mass or
OCN 623: Thermodynamic Laws & Gibbs Free Energy or how to predict chemical reactions without doing experiments Definitions Extensive properties Depend on the amount of material e.g. # of moles, mass or
Business. Business. Multiphase Systems Ch. 6. P vs T Diagram: Water (pure component) P vs T Diagram: CO 2 LYNN ORR
 Business LYNN ORR Izatt-Christensen Lecturer Former Assistant Secretary of Energy Public lecture Thursday 11 am, JSB Auditorium Technical lecture, Friday, 11 am, Varsity Theater Courtesy Corbin Critchfield
Business LYNN ORR Izatt-Christensen Lecturer Former Assistant Secretary of Energy Public lecture Thursday 11 am, JSB Auditorium Technical lecture, Friday, 11 am, Varsity Theater Courtesy Corbin Critchfield
Classical Thermodynamics. Dr. Massimo Mella School of Chemistry Cardiff University
 Classical Thermodynamics Dr. Massimo Mella School of Chemistry Cardiff University E-mail:MellaM@cardiff.ac.uk The background The field of Thermodynamics emerged as a consequence of the necessity to understand
Classical Thermodynamics Dr. Massimo Mella School of Chemistry Cardiff University E-mail:MellaM@cardiff.ac.uk The background The field of Thermodynamics emerged as a consequence of the necessity to understand
3.012 PS 7 Thermo solutions Issued: Fall 2003 Graded problems due:
 3.012 PS 7 Thermo solutions 3.012 Issued: 11.17.03 Fall 2003 Graded problems due: 11.26.03 Graded problems: 1. Analysis of equilibrium phases with a binary phase diagram. Shown below is the phase diagram
3.012 PS 7 Thermo solutions 3.012 Issued: 11.17.03 Fall 2003 Graded problems due: 11.26.03 Graded problems: 1. Analysis of equilibrium phases with a binary phase diagram. Shown below is the phase diagram
Free energy dependence along the coexistence curve
 Free energy dependence along the coexistence curve In a system where two phases (e.g. liquid and gas) are in equilibrium the Gibbs energy is G = GG l + GG gg, where GG l and GG gg are the Gibbs energies
Free energy dependence along the coexistence curve In a system where two phases (e.g. liquid and gas) are in equilibrium the Gibbs energy is G = GG l + GG gg, where GG l and GG gg are the Gibbs energies
Thermodynamics of phase transitions
 Thermodynamics of phase transitions Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron Department of Theoretical of Physics Wroc law University of Science and Technology, Poland March 12, 2017 Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron (WUST) Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics of phase transitions Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron Department of Theoretical of Physics Wroc law University of Science and Technology, Poland March 12, 2017 Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron (WUST) Thermodynamics
Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries
 Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between two phases.
Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between two phases.
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II. Partial Properties of Solutions
 MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Partial Properties of Solutions A total property of a system consisting of multiple substances is represented as nm = n i M i If the system consists of a liquid
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Partial Properties of Solutions A total property of a system consisting of multiple substances is represented as nm = n i M i If the system consists of a liquid
PART ONE TWO-PHASE FLOW
 PART ONE TWO-PHASE FLOW 1 Thermodynamic and Single-Phase Flow Fundamentals 1.1 States of Matter and Phase Diagrams f Pure Substances 1.1.1 Equilibrium States Recall from thermodynamics that f a system
PART ONE TWO-PHASE FLOW 1 Thermodynamic and Single-Phase Flow Fundamentals 1.1 States of Matter and Phase Diagrams f Pure Substances 1.1.1 Equilibrium States Recall from thermodynamics that f a system
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles
 An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
Lecture 4 Clausius Inequality
 Lecture 4 Clausius Inequality We know: Heat flows from higher temperature to lower temperature. T A V A U A + U B = constant V A, V B constant S = S A + S B T B V B Diathermic The wall insulating, impermeable
Lecture 4 Clausius Inequality We know: Heat flows from higher temperature to lower temperature. T A V A U A + U B = constant V A, V B constant S = S A + S B T B V B Diathermic The wall insulating, impermeable
CHEM-UA 652: Thermodynamics and Kinetics
 1 CHEM-UA 652: Thermodynamics and Kinetics Notes for Lecture 13 I. PHASE DIAGRAMS The different phases of substances are characterized by different ranges of thermodynamic variables in which these phasesarethestablephases.
1 CHEM-UA 652: Thermodynamics and Kinetics Notes for Lecture 13 I. PHASE DIAGRAMS The different phases of substances are characterized by different ranges of thermodynamic variables in which these phasesarethestablephases.
Lecture Phase transformations. Fys2160,
 Lecture 12 01.10.2018 Phase transformations Fys2160, 2018 1 A phase transformation Discontinuous change in the properties of substance when the environent is changed infinitesimaly. Change between phases
Lecture 12 01.10.2018 Phase transformations Fys2160, 2018 1 A phase transformation Discontinuous change in the properties of substance when the environent is changed infinitesimaly. Change between phases
Gibb s free energy change with temperature in a single component system
 Gibb s free energy change with temperature in a single component system An isolated system always tries to maximize the entropy. That means the system is stable when it has maximum possible entropy. Instead
Gibb s free energy change with temperature in a single component system An isolated system always tries to maximize the entropy. That means the system is stable when it has maximum possible entropy. Instead
Introduction: Introduction. material is transferred from one phase (gas, liquid, or solid) into another.
 Introduction: Virtually all commercial chemical processes involve operations in which material is transferred from one phase (gas, liquid, or solid) into another. rewing a cup of Coffee (Leaching) Removal
Introduction: Virtually all commercial chemical processes involve operations in which material is transferred from one phase (gas, liquid, or solid) into another. rewing a cup of Coffee (Leaching) Removal
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS. Andrew S. Rosen
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Andrew S. Rosen SYMBOL DICTIONARY 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Symbol Dictionary... 3 1. Measured Thermodynamic Properties and Other Basic Concepts... 5 1.1 Preliminary Concepts
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Andrew S. Rosen SYMBOL DICTIONARY 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Symbol Dictionary... 3 1. Measured Thermodynamic Properties and Other Basic Concepts... 5 1.1 Preliminary Concepts
UNIT 15: THERMODYNAMICS
 UNIT 15: THERMODYNAMICS ENTHALPY, DH ENTROPY, DS GIBBS FREE ENERGY, DG ENTHALPY, DH Energy Changes in Reactions Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies that are at different temperatures.
UNIT 15: THERMODYNAMICS ENTHALPY, DH ENTROPY, DS GIBBS FREE ENERGY, DG ENTHALPY, DH Energy Changes in Reactions Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies that are at different temperatures.
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Paper-II Chapter- TS-equation, Maxwell s equation. z = z(x, y) dz = dx + dz = Mdx + Ndy. dy Now. = 2 z
 aper-ii Chapter- S-equation, Maxwell s equation Let heorem: Condition o exact dierential: Where M Hence, z x dz dx and N Q. Derive Maxwell s equations z x z zx, z dx + dz Mdx + Nd z d Now 2 z x M N x x
aper-ii Chapter- S-equation, Maxwell s equation Let heorem: Condition o exact dierential: Where M Hence, z x dz dx and N Q. Derive Maxwell s equations z x z zx, z dx + dz Mdx + Nd z d Now 2 z x M N x x
HOMOGENEOUS CLOSED SYSTEM
 CHAE II A closed system is one that does not exchange matter with its surroundings, although it may exchange energy. W n in = 0 HOMOGENEOUS CLOSED SYSEM System n out = 0 Q dn i = 0 (2.1) i = 1, 2, 3,...
CHAE II A closed system is one that does not exchange matter with its surroundings, although it may exchange energy. W n in = 0 HOMOGENEOUS CLOSED SYSEM System n out = 0 Q dn i = 0 (2.1) i = 1, 2, 3,...
Solutions to Problem Set 5
 Cornell University, Physics Department Fall 204 PHYS-334 Statistical Physics Prof. Itai Cohen Solutions to Problem Set 5 David C. sang, Woosong Choi 5. Refrigeration Reif 5.22: Refrigeration cycles have
Cornell University, Physics Department Fall 204 PHYS-334 Statistical Physics Prof. Itai Cohen Solutions to Problem Set 5 David C. sang, Woosong Choi 5. Refrigeration Reif 5.22: Refrigeration cycles have
Phase Equilibria I. Introduction. Heat and Phase Changes
 Phase Equilibria I 2 Introduction In the previous chapter, it was discussed the thermodynamics principles that are the basis of thermochemistry. It was shown how to calculate the energy involved in any
Phase Equilibria I 2 Introduction In the previous chapter, it was discussed the thermodynamics principles that are the basis of thermochemistry. It was shown how to calculate the energy involved in any
The Chemical Potential
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2017 The Chemical Potential Here we complete our pivot towards chemical thermodynamics with the introduction of the Chemical Potential ( ). This concept was first introduced
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2017 The Chemical Potential Here we complete our pivot towards chemical thermodynamics with the introduction of the Chemical Potential ( ). This concept was first introduced
Homework - Lecture 11.
 Homework - Lecture 11. Name: Topic: Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Type: Numerical 1. Two liquids, A and B, are mixed together, and the resulting temperature is 22 C. If liquid A has mass m and was initially
Homework - Lecture 11. Name: Topic: Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Type: Numerical 1. Two liquids, A and B, are mixed together, and the resulting temperature is 22 C. If liquid A has mass m and was initially
 Physical Chemistry Physical chemistry is the branch of chemistry that establishes and develops the principles of Chemistry in terms of the underlying concepts of Physics Physical Chemistry Main book: Atkins
Physical Chemistry Physical chemistry is the branch of chemistry that establishes and develops the principles of Chemistry in terms of the underlying concepts of Physics Physical Chemistry Main book: Atkins
 3.012 PS 7 3.012 Issued: 11.05.04 Fall 2004 Due: 11.12.04 THERMODYNAMICS 1. single-component phase diagrams. Shown below is a hypothetical phase diagram for a single-component closed system. Answer the
3.012 PS 7 3.012 Issued: 11.05.04 Fall 2004 Due: 11.12.04 THERMODYNAMICS 1. single-component phase diagrams. Shown below is a hypothetical phase diagram for a single-component closed system. Answer the
df dz = dp dt Essentially, this is just a statement of the first law in one of the forms we derived earlier (expressed here in W m 3 ) dq p dt dp
 A problem with using entropy as a variable is that it is not a particularly intuitive concept. The mechanics of using entropy for evaluating system evolution is well developed, but it sometimes feels a
A problem with using entropy as a variable is that it is not a particularly intuitive concept. The mechanics of using entropy for evaluating system evolution is well developed, but it sometimes feels a
Phase Diagrams. Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Kanpur India
 Phase Diagrams 1 Increasing the temperature isobarically T-v diagram of constant-pressure phase-change processes of a pure substance at various pressures numerical values are for water. 2 Temperature -
Phase Diagrams 1 Increasing the temperature isobarically T-v diagram of constant-pressure phase-change processes of a pure substance at various pressures numerical values are for water. 2 Temperature -
CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES 3.1. The Carnot Cycle Consider the following reversible cyclic process involving one mole of an ideal gas:
 CHATER 3 LECTURE NOTES 3.1. The Carnot Cycle Consider the following reversible cyclic process involving one mole of an ideal gas: Fig. 3. (a) Isothermal expansion from ( 1, 1,T h ) to (,,T h ), (b) Adiabatic
CHATER 3 LECTURE NOTES 3.1. The Carnot Cycle Consider the following reversible cyclic process involving one mole of an ideal gas: Fig. 3. (a) Isothermal expansion from ( 1, 1,T h ) to (,,T h ), (b) Adiabatic
Chapter 16. In Chapter 15 we analyzed combustion processes under CHEMICAL AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM. Objectives
 Chapter 16 CHEMICAL AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM In Chapter 15 we analyzed combustion processes under the assumption that combustion is complete when there is sufficient time and oxygen. Often this is not the
Chapter 16 CHEMICAL AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM In Chapter 15 we analyzed combustion processes under the assumption that combustion is complete when there is sufficient time and oxygen. Often this is not the
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 4. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 4 1 Sensible heat effects are characterized by temperature changes Experimental measurements provide heat effects of chemical reactions, phase
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 4 1 Sensible heat effects are characterized by temperature changes Experimental measurements provide heat effects of chemical reactions, phase
Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes)
 10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture No 16
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No 16 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good afternoon. In the last class, we were
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No 16 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good afternoon. In the last class, we were
Lecture 20. The Chemical Potential
 MIT 3.00 Fall 2002 c W.C Carter 135 Last Time Internal Degrees of Freedom Lecture 20 The Chemical Potential At constant P, T : G, which represents the internal degrees of freedom, is minimized. The Chemical
MIT 3.00 Fall 2002 c W.C Carter 135 Last Time Internal Degrees of Freedom Lecture 20 The Chemical Potential At constant P, T : G, which represents the internal degrees of freedom, is minimized. The Chemical
Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. A.W. Date Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. A.W. Date Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 32 Stefan Flow Model We are now familiar with
Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. A.W. Date Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 32 Stefan Flow Model We are now familiar with
Phase Equilibria in a One-Component System I
 5.60 spring 2005 Lecture #17 page 1 Phase Equilibria in a One-Component System I Goal: Understand the general phenomenology of phase transitions and phase coexistence conditions for a single component
5.60 spring 2005 Lecture #17 page 1 Phase Equilibria in a One-Component System I Goal: Understand the general phenomenology of phase transitions and phase coexistence conditions for a single component
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere
![Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere](/thumbs/72/66535634.jpg) Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Chemistry Review Unit 5 Physical Behavior of Matter
 Chemistry Review Phases of Matter, Changes of Phase, Substances, Mixtures, Solutions, Effect of Solute on Solution, Energy, Kinetics of Solids, Liquids and Gases Matter, Phases and Gas Laws 1. Matter is
Chemistry Review Phases of Matter, Changes of Phase, Substances, Mixtures, Solutions, Effect of Solute on Solution, Energy, Kinetics of Solids, Liquids and Gases Matter, Phases and Gas Laws 1. Matter is
Exam 3, Chemistry 481, 8 December 2017
 1 Exam 3, Chemistry 481, 8 December 2017 Show all work for full credit Useful constants: k B = 1.3807 10 23 J K 1 ; R (molar gas constant) = 8.314 J K 1 mol 1 Helmholz free energy: A = U S, so that da
1 Exam 3, Chemistry 481, 8 December 2017 Show all work for full credit Useful constants: k B = 1.3807 10 23 J K 1 ; R (molar gas constant) = 8.314 J K 1 mol 1 Helmholz free energy: A = U S, so that da
1 mol ideal gas, PV=RT, show the entropy can be written as! S = C v. lnt + RlnV + cons tant
 1 mol ideal gas, PV=RT, show the entropy can be written as! S = C v lnt + RlnV + cons tant (1) p, V, T change Reversible isothermal process (const. T) TdS=du-!W"!S = # "Q r = Q r T T Q r = $W = # pdv =
1 mol ideal gas, PV=RT, show the entropy can be written as! S = C v lnt + RlnV + cons tant (1) p, V, T change Reversible isothermal process (const. T) TdS=du-!W"!S = # "Q r = Q r T T Q r = $W = # pdv =
Chemical reactors. H has thermal contribution, pressure contribution (often negligible) and reaction contribution ( source - like)
 Chemical reactors - chemical transformation of reactants into products Classification: a) according to the type of equipment o batch stirred tanks small-scale production, mostly liquids o continuous stirred
Chemical reactors - chemical transformation of reactants into products Classification: a) according to the type of equipment o batch stirred tanks small-scale production, mostly liquids o continuous stirred
Thermodynamics Free E and Phase D. J.D. Price
 Thermodynamics Free E and Phase D J.D. Price Force - the acceleration of matter (N, kg m/s 2 ) Pressure (P)( ) - a force applied over an area (N/m 2 ) Work (W) - force multiplied by distance (kg( m 2 /s
Thermodynamics Free E and Phase D J.D. Price Force - the acceleration of matter (N, kg m/s 2 ) Pressure (P)( ) - a force applied over an area (N/m 2 ) Work (W) - force multiplied by distance (kg( m 2 /s
2σ e s (r,t) = e s (T)exp( rr v ρ l T ) = exp( ) 2σ R v ρ l Tln(e/e s (T)) e s (f H2 O,r,T) = f H2 O
 Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics. Monday, January 6, 14
 Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Molecular Simulations Molecular dynamics: solve equations of motion Monte Carlo: importance sampling r 1 r 2 r n MD MC r 1 r 2 2 r n 2 3 3 4 4 Questions How can
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Molecular Simulations Molecular dynamics: solve equations of motion Monte Carlo: importance sampling r 1 r 2 r n MD MC r 1 r 2 2 r n 2 3 3 4 4 Questions How can
Properties of Entropy
 Properties of Entropy Due to its additivity, entropy is a homogeneous function of the extensive coordinates of the system: S(λU, λv, λn 1,, λn m ) = λ S (U, V, N 1,, N m ) This means we can write the entropy
Properties of Entropy Due to its additivity, entropy is a homogeneous function of the extensive coordinates of the system: S(λU, λv, λn 1,, λn m ) = λ S (U, V, N 1,, N m ) This means we can write the entropy
Phase Transitions. µ a (P c (T ), T ) µ b (P c (T ), T ), (3) µ a (P, T c (P )) µ b (P, T c (P )). (4)
 Phase Transitions A homogeneous equilibrium state of matter is the most natural one, given the fact that the interparticle interactions are translationally invariant. Nevertheless there is no contradiction
Phase Transitions A homogeneous equilibrium state of matter is the most natural one, given the fact that the interparticle interactions are translationally invariant. Nevertheless there is no contradiction
Hence. The second law describes the direction of energy transfer in spontaneous processes
 * Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
* Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
Lecture 4-6 Equilibrium
 Lecture 4-6 Equilibrium Discontinuity in the free energy, G verses T graph is an indication of phase transition. For one-component system, existing in two phases, the chemical potentials of each of these
Lecture 4-6 Equilibrium Discontinuity in the free energy, G verses T graph is an indication of phase transition. For one-component system, existing in two phases, the chemical potentials of each of these
Simplified Microphysics. condensation evaporation. evaporation
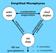 Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
