Ragnar Norberg University of Oslo
|
|
|
- Hortense Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIERARCHICAL CREDIBILITY: ANALYSIS OF A RANDOH EFFEC'i' LINEAR ~10DEL WITH NESTED CLASSIFICATION by Ragna Nobeg Univeity of Olo Abtact A andom coefficient egeion model with multi -tage neted claification i conideed. Linea Baye etimato ae obtained fo andom effect at all tage, and etimato of the tuctual paamete ae popoed. Key od: Random effect; Regeion; Neted claification; Hieachical cedibility.
2 Intoduction In tandad cedibility analyi the unobevable chaacteitic of the individual ik ae epeented by i.i.d. (independent and identically ditibuted) andom element. Thi::o way of atto.ck i appopiate when the potfolio can be egaded a a andom ample fom a population of ik. In many ituation, hov;eve, the potfolio i compoed of ik clae that peumably diffe fom one anothe with epect to baic ik condition. In uch cae moe geneal model ae called fo that allow fo tochatic dependence between ik belonging to one and the ame cla. A an example, conide wokmen' compenation inuance witten by fim to cove employee accident: the entie potfolio can be divided into indutie (heavy induty, tanpotation, agicultue,... ), each induty can be futhe divul2d in-to banche (heavy induty into melting wok, mining, engine wok,... ), and o on until we end up with the individual fim. In thi example the ik ae claified in a neted o hieachical manne. Simila patten aie in a numbe of line ot inuance, and they have become a epaate iue of tudy unde the heading "hieachical cedibility". The topic wa launched by Jewell (1975), who- inpied by Taylo (1974) -conideed a hieachy with two tage. Taylo (1979) extended the analyi to hieachie ~vith a geneal numbe of tage. Hieachical extenion of Hachemeite' (1974) egeion model wee teated by Sundt (1979, ), fit in the cae of two tage and then in the geneal multin -tage cae.- The two-tage ege ion cae wa analyed in a Baye ia etting in an ealy wok by Lindley and Smith (1972). ' To thi mall aembly of wok on hieachical cedibility one could add an immene lit of elevant efeence fom geneal ::otatitic; jut like tandad cedibility eentially deal with andom effect model with one-way claification, hieachical cedibility fit into the famewok of andom effect model with neted
3 - 2 - claification. What i peculia to cedibility, i ::"':ldi: <-~mlf-,_.:-u~ :i.:3.i laid on etimation of andom effect and on epeenting the etimato a cedibility weighted mean. t1oeove, cedibility pimaily ha in view ituation ',vith unbalanced deign and nonpaametic familie of ditibution and, theefoe, cente on ditibution-fee method depending only on the fit and econd ode moment of the obevation. In geneal tatitic andom effect ae by tadition tudied unde nomality aumption, which incidentally - alo lead to method baed on moment up to econd ode. Bayeian liteatue, boadly epeented by Box and Tiao (1973), i concened with etimation of hidden andom effect; ampling theoetic liteatue, notably Scheffe (1959) and Swamy (1971), concentate on infeence about expected value and vaiance component (called tuctual paamete in the cedibility teminology). Thoe who hould ty to apply the exiting theoy on hieachical cedibility in pactice, may face poblem of two kind. In the fit place, thee exit no explicit algoithm fo calculation of cedibility etimato fom factual data in the geneal multi-tage egeion cae. 'In the econd place, the poblem of paamete etimation ha eceived little attention. It i the intent of thi pape to upplement the theoy at thee point. It i alo hoped that the peent teatment will open an eay way to faily geneal eult; the poof ae elementay and computationally oiented, the tating point being a model fo the obevation a they peent themelve in pactical application. The content of the pape ae oganized in ection a follow. The hieachical model i intoduced in ection 2. In ection 3 well known eult on linea Baye etimation in the nonhieachical egeion model ae eviewed and then extended to the hieachical cae. In ection 4 etimato ae popoed fo the 1t and 2nd ode moment appeaing in the linea Baye etimato, wheeby empiical linea Baye etimato ae obtained.
4 - 3 - l~e end thi intoduction by laying down a few notational convention. ~ne dimenion of a vecto o matix may be indicated by a topcipt; thu Lqxn denote a matix L with q ow and n column. n. xn. By diag(a. 1 1 )._ 1 1-1,,m i meant the (E.n. )x(l:.n.) matix with A1,...,~m placed in conecutive ode downwod the pincipal diagonal and zeo elewhee. The ymbol Cov and Va deignate covaiance and vaiance matice, epectively. Thu, if x and y ae andom column vecto 1 \ve have Cov( X 1 y 1 ) = E ( xy 1 ) - ExEy 1 1 and Va x = Cov(x,x 1 ). The conditional covaiance of x and y, given a andom element e 1 i denoted by Cov( x, y 1 I e). We emind of the elation 'Cov (X I y I ) = Cov { E (X I e) IE ( y I I e) } + E Cov (X I y I I e) ( 1 1 )
5 A hieachical egeion model Conide a ytem of quantitie anked in a hieachical ode a follow. Stage l : i 1 =l,.,m; Stage 2: i 1 =l,.,m Stage : i =1,...,m i 1 =1,...,m; Stage : e i1 i =1,, m. J.l i 1 =1,...,m; Obevable x. J.l i =1 1 o 1 ffi J.l... i i 1=1,...,m. The hieachical tuctue i viualized by Figue 1. (To be in pefect keeping with the notion of hieachy, the figue ought to be tuned upide down, the idea being that all quantitie labeled by ome elevant index e.,..., e i 1 p, with p >, ae govened by The peent olution i choen fo teminological eaon: it i convenient to peak of a~l quantitie labeled by an -tuple, e.g. i 1, a being at tage. Accodingly, we hall athe think of e.,..., e.. a "unqe lying" all "' 1 quantitie labeled i 1 i.) One intepetation of the quanti P tie i the following: x.. and e.. ae, epectively, 1 1 " " 1 the obeved claim expeience and the hidden ik chaacte~tic of a unit ik cla C.. ; thi cla i the m.. clae contituting a hype-cla l i -th of
6 - 5 - Obevable X i1 i 1 i - X m - 1 1""" 1 Stage e m " Stage ~.. I.. ~ e e m., ::J Stage 2 ~ e. 1.1f;l. 1.1 Stage 1 e 1 Figue 1. A hieachy of clae at tage
7 - 6 - hidden ik chaacteitic -cla i the i -th 1 - in it tun thi hype- hype-clae contituting a "hype-hype-cla" C.. with hidden ik chaacteitic ~, ~-2 ; and o on.... i 2 - Fomally, a cla C.. ~1 ~ i identified with the quantitie that ae pecifically belonging to it, viz. all quantitie at tage p) labeled i 1 i. In Figue 1 they ae found in the p local hieachy above and including e.. ~,... ~ ide denote by e the aembly of all latent quanti tie p intoduce eo= 0. at tage p' ; =1,..,. It i convenient alo to All quantitie intoduced o fa ae enviaged a andom element. \\Te make the following model aumption, the lat thee of which add futhe content to the notion of hiea~hy. ( i) Each i a vecto of dimenion n.. ~,... ~ exit a vecto-valued function and, fo each n.. xq ~,... ~ a nonandom, knmm matix Y. ~1 i E(x. le ) = ~,... ~ with ay. Thee uch that ). ( 2. 1 )... i.1. All the andom vecto econd ode moment.... i and b. -~ 1 have finite (ii) The tage 1 clae chaacteitic e. ~1 C. ae independent, and thei ik ~, ae identically ditibuted; i 1 =1,..,m.
8 - 7 - (iii) vh thin each cla C. 1.1 i at tage ~ aumption (ii) ha the following analogue: conditionally, given 0 the tage +1 clae C... l1... Ll+1 ik chaacteitic e ll+1 ae identically ditibuted; i + 1 =1,...,m ( i v) All the vecto (e.,e..,...,e ae independent, and thei ae identically ditibuted (implying that all hidden vaiable e l. a given tage aume thei value in the ame pace, which may be quite geneal). at He now oganize the data cla-wie a follow. Fo each cla let x.. and. '!:' vecto of.:~,ll Y.. denote, epectively, the cegeand and the matix of all egeo belonging to that cla. Moe pecifically, we tat fom the aleady intoduced elementay data and Y elated to clae at tage, and define the coeponding aggegate quantitie at lowe tage by the ecuive elation X~ = (X~ I X' I 1.1 m. 1.1 y~ = (Y~ I '. y ' i m. 1.1 ( 2. 2) ( 2. 3 ) validfoallelevant (i 1,...,i) and all =1,...,. (Inthe following we hall feel fee to dop uch lengthy and elf-evident pecification of domain of ubcipt.) Clealy, and Y. ae of ode 1.1 whee the n. ' i n.. x1 and n.. xq, epectively, ae defined ecuively a
9 - 8 - n. = I n. ~, ~, i i +l -+l Fo each (i 1,...,i) intoduce b. = E:(b. I e ) ~, ll = 1,,. ( 2. 4) Now it i een that each cla C poee~ ~.eg.eil ion tuctue imila to that of the tage by aumption (i), namely clae a pecified E(x.. le ) = ~,... ~ Y.. b '~ ~, '~ ( 2. 5 ) with element defined by (2.2)-(2.4). Thu, in a hieachy of ode thee ae embedded hieachie of all ode (. The following moment ae well defined unde the aumption ( i)-( iv): (2. 6) E Va(b.. 1e 1 ) ~,... ~ - ( 2. 7) 1 = E Va(x.. le ) ~,... ~ ( 2. 8) 'd { i 1,, i ) ; = 1,,. Thee quantitie have a taightfowad intepetation: ~ i the mean ik level in the potfolio, A meaue the ik diffeen tial between tage clae in one and the ame tage cla, and - in a ene - <I>.. meaue the vaiability in ~,... ~ claim expeience that i not explained by between cla vaiation at tage 1,...,. The baic paamete ae ~, the A, and the at tage. In ection 3 it will be hown that each at tage < i a function of and the
10 Linea Baye etimation by known paamete Fomulation of the poblem. Fo each cla C.. we eek l.,... J. an etimato ~.. of b.. given by (2.4), the pupoe being 1 1""" 1 1 1""" 1 to minimize the expected weighted quaed eo o (oveall) ik, whee qxq w = E{b.. - b.. } 'W{b b.. }, l.1"""l. i a nonandom p.d.. (poitive definite ymmetic) matix. In view of the independence aumption (ii), only X. l.1 elevant fo the pupoe. We confine ouelve to inhomogeneou linea etimato of the fom ( 3. 1 ) i v b.. = g 0 + Gx., 1 1""" (3. 2) whee qx1 go and qxn G ae allowed to depend on y and the paamete of the ditibution. The optimal etimato will be called the LB (linea Baye) etimato, and the minimum value of the ik will be called the LB ik. The cae = 1 The imple non-hieachical andom coefficient egeion model wa fit tudied in the context of cedibility theoy by Hachemeite (1975). It hall be teated in ome detail ince thee exit no ingle efeence that pell out the eult in the fom equied hee. Thu, conide the model (i)-(iv) in the pecial cae = 1, wheeby item (iii) and (iv) become void. The poblem i to etimate b. = b( 9. ) (ay) by mean of x., the paamete (2. 6)- ( 2. 8) )_1 being aumed to be known. To ave notation, dop all indice and conide the imple model ~elation nxl nxq qx1 E(x 19) = Y b (9) ( 3. 3) and the paamete
11 b( e ), A qxq = Va b( e) I nxn ~ = E Va(xle). ( 3 4) Lemma 3.1 (tandad). Aume ~ to be p.d.. The LB etimato of b(e) i - b = Ac + (I -AM)~, ( 3 5) whee qx1 c and Hqxq ae defined a c = Y' (YAY' + ~) X (I MA)Y'~ = - X M = Y' (YAY'+ ~) y Y(AY'~ = Y'~ y + I ). (3.6a) (3.6b) (3.7a) (3.7b) Lemma 3.1 i a claical eult in cedibility and Bayeian egeion. It i tated hee in a fom that i paticulaly well uited fo ou pupoe. Notice that neithe A no Y need to be of full ank. In fact, fomula (3.5) emain valid if A= 0 and even if n = 0 (no obevation) if c and.ivi ae then intepeted a 0. In both cae b educe to ~, of coue. The o-called cedibility matix i defined a Z = AM (3.8.a) = AY' (YAY' + ~) Y (3.8.b) = I - (AY'~ Y + I). (3.8.c) In cae n ) q and Y ha full ank q, b can be cat in the fom of a cedibility weighted mean, b = z~ + ( I-z ) ~, ( 3. 9) with /\ b = (Y'~ Y) Y'~ x. (3.1 0)
12 The identitie in (3.6) and (3.7) tun out to be intumental in the analyi of the geneal hieachical model. They ae alo computationally convenient; if n ( q, ue fomula (3.6a) and (3.7a), which involve inveion of an nxn matix; othewie povided that ~ i eaily inveted- ue (3.6b) and (3.7b), which equie inveion of a qxq matix. The meit of fomula (3.9) i on the intepetative athe than the computational ide, ee e.g. Nobeg (1980). Fo the ake of completene, and in the abence of a uitable efeence, we pove the lemma. Then the poof of (3.9) will be an eay execie. Poof of Lemma 3.1. The LB etimato i (ee e.g. Nobeg, 1980) b = E b(9) + Cov{b(e),x' }(Va x)- 1 (x-ex). (3.11) In the peence of aumption (3.3) the moment appeaing on the ight of (3.11) can be expeed by the paamete in (3.4) a E b( e) = ~, co v { b ( e ), x ' } = tty ', Va x = YAY' + ~. Ex= Y~. (3.12) (3. 1 3) (3.14) (3. 15) The expeion (3.13) and (3.14) ae eay conequence of (1.1). On ineting (3.12)-(3.15) in (3.11), we obtain b = ~ + AQ(x-Y~), (3.16) whee Q = Y'(YAY' + ~). (3.17) The elation (3.16) and (3.17) ae equivalent to (3.5), (3.6a), and (3.7a). It emain to demontate the identitie aeted in (3.6) and (3. 7).
13 Potmultiplication by YAY' + ~ in (3.17) yield the equivalent elation QYA y I + Q~ = y I (3.18) Futhe, potmultiplying by ~ y in (3.18) give QYAY'~ Y + QY = Y'~ Y, fom which we olve QY = Y'~ Y(AY'~ Y + I). (3.19) A M = QY (compae (3.7a) and (3.17)), (3.19) i jut the identity aeted in (3.7). Finally, ubtitute (3.19) back into (3.18) to obtain Q = (I - MA)Y'~, which implie that (3.6a) and (3.6b) ae identical. To complete the poof, it mut be etablihed that i alway invetible when ~ i. Thi follow by ue of the identity x and B one get AY I~ y + I I I x lab+ II = BA +I, valid fo any pai of matice A (Zellne, 1971, p. 231 ). Putting A= AY' and B = ~ Y, IAY'~y + II = ~~- 1 YAY' + II = I~. IIYAY' + ~I. ( 3. 20) Since ~ i p.d.., o i both ~ and YAY' + ~. hence both deteminant in (3.20) ae tictly poitive. It can be concluded that AY'~ Y + I ha a non-zeo deteminant and, theefoe, i invetible. D The hieachical cae, > 1. We now tun to the genuine hieachical model and et out by demontating ome ueful ecuive elation. On ineting (2.2) in the definition of the dipeion
14 matice in (2.8) and ecalling the independence aumption (iii), it i een that = diag{e Va(x. le }. _ 1 1 i ,...,m (3.21) Applying (1.1) to the conditional vaiance in (3.21 ), noticing that e C8 1 andthenuing (2.5), (2.7),and (2.8), yield +1 E Va(x.. le ) ~1 ~+1 = E[Va{E(x.. le +1 ) le } 1 1 ~+ 1 + E { va ( x. I e ) I e } ] ~ = E Va (Y.. b.. I e ) ~1 ~+1 ~, ~+1 + E Va(x.. 1e+1 ) ~, ~+1 (3.22) Combination of (3.21) and (3.22) give the ecuive fomula = diag(y.. A + 1 Y~ ~1 " 1 +1 ~1 i+1 (3.23) Fo each i 1 define, by vitue of (3.6) and (3.7), ( 3 24 a) (3.24b) M.. ~,... ~ (3.25a). +I). ' l. t" (3.25b) (The poitive definitene of each eli.., which i neceay fo ~1 ~ the identitie in (3.24) and (3.25) to hold tue, i a tivi~l conequence of (3.23) and the poitive definitene of each eli. ~1 at
15 at tage.) By ue of (2.2), (2.3), (3.23), and (3.24a), it follow that Y'.. q;.. X ' ' 1 ~1.L = I c.... l1... l l ( ) whence, by ubtitution in (3.24b), = (I-M.. A )I c... l1... l ll+1 l+1 ( 3. 27) Similaly, (3.25) give y~. <li.. Y.. l1oool l,... l l,... l = I M ].]. +1 J.+1 (3.28) and = I M... (A I 1 1 ' M... +I) 1 1 ' ( 3 29 ) We ae now in a poition to contuct LB etimato of all andom effect b.. given by (2.4). Cqnide fit the poblem 1 1 ' 1 of etimating effect at tage 1. Application of Lemma 3.1 to the egeion (2.5) with = 1, give: Lemma 3.2. The LB etimato of b. i ].1 (3.30) whee c. l1 and M. ].1 ae defined by (3.24) and (3.25).
16 To contuct the LB etimato b.. of a geneal b.., 1.1 ".l. 1.1.l. we call on a beautiful eult poved in the univaiate cae by Jewell (1975) and genealized to the egeion cae by Sundt (1980). Lemma 3.3(Jewell/Sundt). LB ~timato at neighbouing tage ae elated by the fomula (3.31) By compaion of fomula (3.30) and (3.31 ), it i een that i obtained by fomally teating b.. l.1... l. - a a tage effect in the local hieachy of with b l. the place of ~. Sundt pove (3.31) by veifying that the expeion on the ight hand ide atifie the nomal equation detemining b. -. l.1... l. He hall give an altenative, diect agument, which may peent an inteet of it own. in Poof of Lemma 3.3. Since LB etimato depend only on the 1t and 2nd ode moment of the ditibution, it uffice to pove the -eult fo one paticula choice of ditibution with the equied moment tuctue. 'Ide pick the following. Suppoe that all the latent quantitie ae mutually independent, each having a q-vaiate nomal ditibution with mean and vaiance A, and that, conditional on e, each... ~. -vaiate nomal dit.ibqti.on '"ith mean Y.. b ]_1 and vaiance ~.., whee b. = ~ + e. + +e..ll. ' i (and, conequently, b i = ~ + e. + + e.. ) the In thi model the joint ditibution of the... i ' i multivaiate nomal, hence the conditional mean ' and
17 of b.., given the x. ', i a linea function (Andeon, ~, ~ ~, ~ 1958, p.29). Now it i well known that thi conditional mean i the uneticted Baye etimato of b.., and- being of the fom ~,... l (3.2) - it i alo LB. Theefoe, in the peent cae l,... ~ = E(b.. lx. ) ~, = E{E(b.. le 1,x. ) lx. } ll... ~ - ~, ~, = E{E(b.. le 1,x.. ) lx. }, ~,.. ~ - l,... ~ ll (3.32a) (3.32b) the lat equation being a conequence of aumption (iii). Unde the peent aumption the inne expectation in (3.32b) aume the fom E(b.. 1e 1,x. ll... ~ - ~,... i ( 3. 33) Thi aetion follow by noting that, conditional on e-l, the local hieachy within C.. ha the ame ditibutional tuc- 1i ~ tue a the global hieachy, with b.. I A,,A I ~,... ~ ~- playing the ole of ~, A1,...,A, ~- ~, l. It follow ~, that the conditional mean on the left of (3.33) i - fomally - the LB etimato of b il in the conditional model, which, accoding to Lemma 3.2, i the expeion on the ight of (3.33). Now, upon ubtituting (3.33) in (3.32b) and then uing (3.32a), thi time at tage, we aive at (3.31). 0 The eult above ae now ummaized a a complete algoithm fo computation of LB etimato. Theoem 3.4. LB etimato ae found fo all andom effect by fit calculating all the quantitie c ~ and M. by the ecuive elation (3.27) and (3.29), ll... l tating fom tage, and then calculating all the b.' ~,...]_ by the ecuive elation (3.31 ), tating fom (3.30) at tage 1.
18 It i notewothy that the LB etimato do not depend on the weighting w. Comment. Sundt' (1980) etting i diffeent fom the peent one; in tem of ou definition, he focue attention at one tage cla C.. and wok with tatitic x 1,..., x, whee ~1 ~ x = x.. and each x ; =1,..., ; conit of the tage ~ 1 ~ tatitic x.. h ; h +l * i +1. The tating point of ou ~1 ~ +1 model i the aembly of all obevable x. in unit ik ~1... i clae, and Theoem 3.4 explain how to actually calculate LB etimato fom thee data. The poof given hee of Lemma 3.3 i elementay and contuctive. The technique can be caied ove to a numbe of complex etimation poblem that othewie would equie eithe heavy algeba o efined Hilbet pace method (de Vylde, 1976) fo thei olution. It eve, inte alia, to jutify the witch fom conditional to unconditional moment in Taylo' poof of Lemma 3.3 fo the univaiate cae (Taylo, 1979, Theoem 4, item 1). If Y.. i of ank q, then ( ) can be ewitten in ~1 ~ the fom of a cedibility weighted mean, b.. ~1 ~ whee and = z.. is.. ~1 ~ ~1 ~ + (I-Z.. )b.. ~ 1 ~ ~ 1 ~ = (Y ~. ~.. Y.. ) Y~. ~.. X.. ~1. ~ ~1 ~ ~1 ~ ~1 ~ ~1. ~ ~1 ~ = o: M. ) ~1 i i I c.... ~,.. ~ ~ +1 ~+l LB +l ( 3. 34) (3.35) z. = A M. ~, ~, (3.36) The demontation of thee fomula i taightfowad by vitue of (3.8)-(3.10). Fom a computational point of view (3.31) i moe convenient than (3.34). Beide, the cae whee Y.. i not of ~1 ~ full ank q i of geat pactical elevance: inuance companie ae contantly facing the poblem of fixing pemium fo new witten
19 buine. If a new ik o cla of ik can be claified with othe ik, poibly in a hieachical ytem a viualized in Figue 1, then it pemium can be detemined in a ational manne within the famewok of a andom effect model, the point being that the model pecifie a elationhip between the ik. An inuance company woking with a fixed effect model, a advocated by Gebe (1982), would be at a lo when confonted with the poblem of aeing a ik with no claim expeience of it own. Fo a futhe dicuion of thee matte, ee Nobeg (1985). Linea Baye ik. The LB ik fo the poblem of etimating i eaily hown to be (Nobeg, 1980) (3.37) whee 6.. i the LB ik matix given by 11 ol = V a b.. - Cov ( b ol i, X~ ) (Va X. ) Cov (X., b ~. ). 11 ll ll ll. 0 ol (3.38) Notice that the LB ik depend on the weighting matix H, ~vheea the LB ik matice - jut like the LB etimato - do not. The following theoem tate that the LB ik.in (3.37) can be calculated by a ecuive pocedue once the matice have been found by ue of the ecuion (3.29). Theoem 3.5. The by the ecuive elation LB ik matice in (3.38) can be calculated... ~ t:' ) +A}, t:' ( ) tating fom tage with ( ) the matice ae given by (3.29) and (3.36) 0
20 Poof: To demontate (3.40), ubtitute (3.13) and (3.14) with b.,x.,y.,a 1,~ =1. Thi give in the ole of b(e),x,y,a,~ into (3.38) fo which, by (3.25a) and (3.36), i jut fomula (3.40). To pove (3.39), apply the ame tick a in the poof of Lemma 3.3. In the nomal model pecified thee the LB ik matix coincide with the uneticted Baye ik ~tix, that i, t:... = E Va(b.. lx. ) (3.41) Applying pinciple (1.1) to the conditional vaiance and aguing a in the poof of Lemma 3.3, ewite (3.41) a t:... = E [Va { E (b.. I e 1 'X. ) I X. } E { Va (b.. I e 1 'X. ) I X. } J = E v a { E ( b.. I e 1, x.. ) I x. } (3.42) + EE { va ( b.. I e 1, x.. ) I e 1 } Now ubtitute (3.33) in the fit tem in (3.42) and ob~eve that the inne expectation in the econd tem i - fomally - the Baye ik fo the poblem of etimating b.. a a tage the local hieachy of C.., conditional on pinciple (3.40) applie. It follow that effect in e 1 SO that in = E V a { ( I-A ~.. ) b.. I x. } + ( I-Z.. ) A, 11.. olli ~ which by (3.36) and (3.41) i the ame a (3.39). 0
21 Etimation of paamete; empiical linea Baye etimato Fo the pupoe of paamete etimation only clae with obevation ae elevant, and o all n. 1.,... i be geate than 0. ' ae now taken to Etimation of the econd ode moment in (2.7) and (2.8) i in geneal not feaible unle futhe tuctue i impoed on the matice ~... Theefoe, in the peent ection it will be 1., ; 1. aumed - a i tandad in egeion theoy - that thee exit a poitive function v and nonandom, kno\'m p.d.. matice P.. uch that l. Va(x. 1.1 Then I e ) = < e e. ) P-:-. 1 v.,..., l. '1.1.. ol. whee... ]. ~ = Ev ( e.,..., e i and the elevant et of paamete become ~I A,,,A I~. ( 4. 1 ) The tating point fo contucting etimato ae th~ expeion... ~ ' ~ I ( 4. 2) (~~ +I&.... A )Y~. = ' J1 J J1 J... ~p. (4.3).. ol.,jl.. J l..l whee equal if and 0 othewie. Relation (4.3) i obtained by epeated ue of pinciple ( 1. 1 )
22 A cla of unbiaed etimato of the paamete in (4.1) i contucted a follow. Fo each i 1,...,i, denote by the ank of the egeo matix Y.., and let L (Y.. ) be the. -dimenional linea pace panned by the column of i Y.. Let A. and B.. be matice of ode t 1.1 i n.. x q and n.. 11 "1 11 "1 uch that the column of A. column of L(Y. - l.l... i ). x ( n ), epectively, i pan L(Y.. ) and the - l., l. i a bai of the othocomplement of By (4.2), a taightfowad etimato of ~ i (4. 4) Fo each i 1,...,i 8, intoduce the tatitic 1 ( 4. 5 ) = t ( B.. B ~. X. X ~ 1 1"" ' 1 1 1"' ' 1 1.1,,_ 1.1 ). By (4.3) and fact that the column of y ]. thoe of ae othogonal to = <!> t ( B... i 1.. B ~. P.. ) 1... ] ,_ ]. Theefoe, an unbiaed etimato of <1> i * <!> = {I t (B.. B ~. P.. ) },...,i 1 1 ' ' ' ' 1 i 1 with defined by (4.5). ~. 1 1,, ]. (4.6)
23 Etimato of A 1,...,A ae baed on the quantitie I j + 1 ' 'j : :i_ } 5 j +1 * i+1 (I ( ) =O,..., (4.7) i 1,...,i whee the um E ( ) extend ove all i 1,..., i fo,,,hich the indicated inveion ae.valid. It i obviou how to intepet the ummation in the cae =O and =: fo = the um ove j+1,...,j include only i 1,...,i. It i. een that involve all poduct of obevation in diffeent tage clae within the ame tage G +l cla. Thu, all poduct x.. x'.. ae utilized in the etimation. Uing (4.3), it J1 J i eaily checked that EG = ~~ with ~~ + A + + A 1 ~~ + Al + + A + <PH =O: =1,..., : =: H = cp{l() (A'.. Y ,...,15 )... i A~. P.. A } <I < > i1 '...,i (4. 8) It follow that a et of y~metic i given by unbiaed etimato of the A (4. 9) whee the G and H ae defined by (4.7) and (4.8), epectively. Note that the matice in (4.9) need not be poitive definite. Thu the old poblem of negative etimate of vaiance component may aie.
24 The etimato in (4.4) i well defined if and only if the egeo matix of all the obevation unit, Y = (Y~,...,Y~)', i of full ank q. The etimato in (4.6) i well defined if at leat one n.. -. i geate than 0. Both thee ~,.. 1 1, i ~equiement ae vey weak. The etimato A * in (4.9) i well defined if G in ( 4. 7) i, which equie that thee exit at leat one tage cla C. with a tage +1 ubcla uch that the matix obtained by deleting the block fom Y i of ank q. If any one of thee equiement i not fulfilled, the coeponding paamete i not identifiable fom the obevation. The quetion of how to chooe the matice A.. and hall not be dicued in any detail hee. If the deign i balanced, it i, of coue, optimal to,take all (A..,B.. ) equal (Nobeg, 1977), but thi cae i of 11 " 1 11 ' 1 little inteet in inuance and othe non-expeimental field. In geneal no unifomly optimal choice can be made. A "natual" choice, paying egad to the amount of infomation contained in the individual ik clae, i A.. = Y'. P. 11 ' ' if. = q.., B.. B~. = P Y.. (Y~ P.. Y.. ) Y!. P. ",_,_1.. ' ' 1 11 ' ' ' i and, Then the expeion in (4.4) become y~. p,. y, 1 1 ' ' I ' ' ' I ~... ~. ) I i1,..,i which would be the bet linea unbiaed etimato if A= =A=O, 1 and (4.5) educe to the odinay ample etimate of
25 v ( 9. ].1 9 I I 11 multiplied by the degee of feedom, n.. - q.. If the econd ode moment wee known, J.1.. J. J.1 J. the bet linea unbiaed etimato of { Y 1 ( V a x ) Y} Y 1 ( V a x ) x, would be then (4.10) whee x = ( xl,..., x~) 1 and Y = (Y l,..., Y~) 1 By independence between clae at tage 1, the expeion in (4.10) i equal to m L Y! cf?. x. i =1 ].1 ] o, by ineting (3.26) and (3.28), (4.11) which can be calculated ecuively by (3.27) and (3.29). A genuine etimato (4.11) by thei etimato. i obtained by eplacing ail econd ode moment in The etimato defined by (4.4), (4.6), and (4.9) ae conitent a m - the numbe of tage clae - inceae, povided that the ank.. and the peciion P.. do not tend J.1 J. J.1 1 to too mall value, oughly peaking. Thi eult i, howeve, mainly of theoetical inteet to inuance people becaue in thei application thee vlill uually be a limited numbe of clae at tage 1. Finally, empiical LB etimato of andom effect ae obtained upon eplacing the paamete occuing in the fomula in ection 3 by thei etimato in (4.4), (4.6), and (4.9).
26 Refeence Andeon, T.W. (1958). An Intoduction to Multivaiate Statitical Analyi. Wiley, New Yok. Box, G.E. and Tiao. G.C. (1973). Baveian Infeence in Statitical Analyi. Addion-Weley. De Vylde (1976). Geometical cedibility. Scand. Actuaial J., 1979, Gebe, H.U. (1982). An unbayeed appoach to cedibility. Inuance Math. Econ., 1, Hachemeite, C.A. (1975). Cedibility fo egeion model with application to tend. In Cedibility: Theoy and application (ed. P.M. Kahn), pp , Hiley, New Yok. Jewell, w.. (1975). The ue of collateal data in cedibility: a hieachical model. Reeach Memoandum of the Intenational Intitute fo Applied Sytem Analyi, Laxenbug, Autia. Lindley, D.V. and Smith, A.F.M. (1972). Baye etimate fo the linea model. (Hith dicuion.) J.R. Statit. Soc. B, 34, Nobeg, R. (1977). Infeence in andom coefficient egeion model with one-way and neted claification. Scand. J. Statit. 4, Nobeg, R. (1980). Empiical Baye cedibility. Scand. Actuial J. 1980, Nobeg, R. (1985). Unbayeed cedibility eviited. ASTIN Bulletin 15, Scheffe, H. (1959). The Analvi of Vaiance. Wiley, New Yok. Sundt, B. (1979). A hieachical cedibility egeion model. Scand. Actuaial J., 1979, Sundt, B. (1980). A multi-level hieachical cedibility egeion model. Scand. Actuaial J., 1980, Swamy, P.A.V.B. (1971). Statitical infeence in andom coefficient egeion model. Lectue Note in Oneation Reeach and Mathematical Sytem, 55, Spinge-Velag, Belin. Taylo, G.C. (1974). Expeience ating vdth cedibility adjutment of the manual pemium. ASTIN Bulletin, 7, Taylo, G.C. (1979). Cedibility analyi of a geneal hieachical model. Scand. Actuaial J., 1979, 12. Zellne, A. (1971). An Intoduction to Bayeian Infeence in Econometic. Hiley, New Yok.
Inference for A One Way Factorial Experiment. By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo
 Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Determining the Best Linear Unbiased Predictor of PSU Means with the Data. included with the Random Variables. Ed Stanek
 Detemining te Bet Linea Unbiaed Pedicto of PSU ean wit te Data included wit te andom Vaiable Ed Stanek Intoduction We develop te equation fo te bet linea unbiaed pedicto of PSU mean in a two tage andom
Detemining te Bet Linea Unbiaed Pedicto of PSU ean wit te Data included wit te andom Vaiable Ed Stanek Intoduction We develop te equation fo te bet linea unbiaed pedicto of PSU mean in a two tage andom
Estimation and Confidence Intervals: Additional Topics
 Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
Precision Spectrophotometry
 Peciion Spectophotomety Pupoe The pinciple of peciion pectophotomety ae illutated in thi expeiment by the detemination of chomium (III). ppaatu Spectophotomete (B&L Spec 20 D) Cuvette (minimum 2) Pipet:
Peciion Spectophotomety Pupoe The pinciple of peciion pectophotomety ae illutated in thi expeiment by the detemination of chomium (III). ppaatu Spectophotomete (B&L Spec 20 D) Cuvette (minimum 2) Pipet:
Several new identities involving Euler and Bernoulli polynomials
 Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 9107 No. 1, 016, 101 108 Seveal new identitie involving Eule and Benoulli polynomial by Wang Xiaoying and Zhang Wenpeng Abtact The main pupoe of thi pape i uing
Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 9107 No. 1, 016, 101 108 Seveal new identitie involving Eule and Benoulli polynomial by Wang Xiaoying and Zhang Wenpeng Abtact The main pupoe of thi pape i uing
Chapter 19 Webassign Help Problems
 Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
Gravity. David Barwacz 7778 Thornapple Bayou SE, Grand Rapids, MI David Barwacz 12/03/2003
 avity David Bawacz 7778 Thonapple Bayou, and Rapid, MI 495 David Bawacz /3/3 http://membe.titon.net/daveb Uing the concept dicued in the peceding pape ( http://membe.titon.net/daveb ), I will now deive
avity David Bawacz 7778 Thonapple Bayou, and Rapid, MI 495 David Bawacz /3/3 http://membe.titon.net/daveb Uing the concept dicued in the peceding pape ( http://membe.titon.net/daveb ), I will now deive
Theorem 2: Proof: Note 1: Proof: Note 2:
 A New 3-Dimenional Polynomial Intepolation Method: An Algoithmic Appoach Amitava Chattejee* and Rupak Bhattachayya** A new 3-dimenional intepolation method i intoduced in thi pape. Coeponding to the method
A New 3-Dimenional Polynomial Intepolation Method: An Algoithmic Appoach Amitava Chattejee* and Rupak Bhattachayya** A new 3-dimenional intepolation method i intoduced in thi pape. Coeponding to the method
Maximum Likelihood Logistic Regression With Auxiliary Information
 niveity of Wollongong Reeach Online Cente fo Statitical Suvey Methodology Woking Pape Seie Faculty of Engineeing and Infomation Science 2008 Maximum Likelihood Logitic Regeion With Auxiliay Infomation
niveity of Wollongong Reeach Online Cente fo Statitical Suvey Methodology Woking Pape Seie Faculty of Engineeing and Infomation Science 2008 Maximum Likelihood Logitic Regeion With Auxiliay Infomation
SIMPLE LOW-ORDER AND INTEGRAL-ACTION CONTROLLER SYNTHESIS FOR MIMO SYSTEMS WITH TIME DELAYS
 Appl. Comput. Math., V.10, N.2, 2011, pp.242-249 SIMPLE LOW-ORDER AND INTEGRAL-ACTION CONTROLLER SYNTHESIS FOR MIMO SYSTEMS WITH TIME DELAYS A.N. GÜNDEŞ1, A.N. METE 2 Abtact. A imple finite-dimenional
Appl. Comput. Math., V.10, N.2, 2011, pp.242-249 SIMPLE LOW-ORDER AND INTEGRAL-ACTION CONTROLLER SYNTHESIS FOR MIMO SYSTEMS WITH TIME DELAYS A.N. GÜNDEŞ1, A.N. METE 2 Abtact. A imple finite-dimenional
A note on rescalings of the skew-normal distribution
 Poyeccione Jounal of Mathematic Vol. 31, N o 3, pp. 197-07, Septembe 01. Univeidad Católica del Note Antofagata - Chile A note on ecaling of the kew-nomal ditibution OSVALDO VENEGAS Univeidad Católica
Poyeccione Jounal of Mathematic Vol. 31, N o 3, pp. 197-07, Septembe 01. Univeidad Católica del Note Antofagata - Chile A note on ecaling of the kew-nomal ditibution OSVALDO VENEGAS Univeidad Católica
Shrinkage Estimation of Reliability Function for Some Lifetime Distributions
 Ameican Jounal of Computational and Applied Mathematic 4, 4(3): 9-96 DOI:.593/j.ajcam.443.4 Shinkage Etimation of eliability Function fo Some Lifetime Ditibution anjita Pandey Depatment of Statitic, niveity
Ameican Jounal of Computational and Applied Mathematic 4, 4(3): 9-96 DOI:.593/j.ajcam.443.4 Shinkage Etimation of eliability Function fo Some Lifetime Ditibution anjita Pandey Depatment of Statitic, niveity
Solutions Practice Test PHYS 211 Exam 2
 Solution Pactice Tet PHYS 11 Exam 1A We can plit thi poblem up into two pat, each one dealing with a epaate axi. Fo both the x- and y- axe, we have two foce (one given, one unknown) and we get the following
Solution Pactice Tet PHYS 11 Exam 1A We can plit thi poblem up into two pat, each one dealing with a epaate axi. Fo both the x- and y- axe, we have two foce (one given, one unknown) and we get the following
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/101586781.jpg) INTERMEDIATE HANKEL OPERATORS ON THE FOCK SPACE OLIVIA CONSTANTIN axiv:181103137v1 [mathcv] 7 Nov 2018 Abtact We contuct a natual equence of middle Hankel opeato on the Fock pace, ie opeato which ae intemediate
INTERMEDIATE HANKEL OPERATORS ON THE FOCK SPACE OLIVIA CONSTANTIN axiv:181103137v1 [mathcv] 7 Nov 2018 Abtact We contuct a natual equence of middle Hankel opeato on the Fock pace, ie opeato which ae intemediate
Then the number of elements of S of weight n is exactly the number of compositions of n into k parts.
 Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Section 25 Describing Rotational Motion
 Section 25 Decibing Rotational Motion What do object do and wh do the do it? We have a ve thoough eplanation in tem of kinematic, foce, eneg and momentum. Thi include Newton thee law of motion and two
Section 25 Decibing Rotational Motion What do object do and wh do the do it? We have a ve thoough eplanation in tem of kinematic, foce, eneg and momentum. Thi include Newton thee law of motion and two
Simulation of Spatially Correlated Large-Scale Parameters and Obtaining Model Parameters from Measurements
 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model Paamete fom PER ZETTERBERG Stockholm Septembe 8 TRITA EE 8:49 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model
Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model Paamete fom PER ZETTERBERG Stockholm Septembe 8 TRITA EE 8:49 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model
QUADRATIC DEPENDENCE MEASURE FOR NONLINEAR BLIND SOURCES SEPARATION
 QUADRATI DPNDN MASUR FR NNLINAR BLIND SURS SPARATIN Sophie Achad Dinh Tuan Pham Univ. of Genoble Laboatoy of Modeling and omputation IMAG.N.R.S. B.P. 5X 84 Genoble edex Fance Sophie.Achad@imag.f Dinh-Tuan.Pham@imag.f
QUADRATI DPNDN MASUR FR NNLINAR BLIND SURS SPARATIN Sophie Achad Dinh Tuan Pham Univ. of Genoble Laboatoy of Modeling and omputation IMAG.N.R.S. B.P. 5X 84 Genoble edex Fance Sophie.Achad@imag.f Dinh-Tuan.Pham@imag.f
On the quadratic support of strongly convex functions
 Int. J. Nonlinea Anal. Appl. 7 2016 No. 1, 15-20 ISSN: 2008-6822 electonic http://dx.doi.og/10.22075/ijnaa.2015.273 On the quadatic uppot of tongly convex function S. Abbazadeh a,b,, M. Ehaghi Godji a
Int. J. Nonlinea Anal. Appl. 7 2016 No. 1, 15-20 ISSN: 2008-6822 electonic http://dx.doi.og/10.22075/ijnaa.2015.273 On the quadatic uppot of tongly convex function S. Abbazadeh a,b,, M. Ehaghi Godji a
Second Order Fuzzy S-Hausdorff Spaces
 Inten J Fuzzy Mathematical Achive Vol 1, 013, 41-48 ISSN: 30-34 (P), 30-350 (online) Publihed on 9 Febuay 013 wwweeachmathciog Intenational Jounal o Second Ode Fuzzy S-Haudo Space AKalaichelvi Depatment
Inten J Fuzzy Mathematical Achive Vol 1, 013, 41-48 ISSN: 30-34 (P), 30-350 (online) Publihed on 9 Febuay 013 wwweeachmathciog Intenational Jounal o Second Ode Fuzzy S-Haudo Space AKalaichelvi Depatment
Basic propositional and. The fundamentals of deduction
 Baic ooitional and edicate logic The fundamental of deduction 1 Logic and it alication Logic i the tudy of the atten of deduction Logic lay two main ole in comutation: Modeling : logical entence ae the
Baic ooitional and edicate logic The fundamental of deduction 1 Logic and it alication Logic i the tudy of the atten of deduction Logic lay two main ole in comutation: Modeling : logical entence ae the
A Neural Network for the Travelling Salesman Problem with a Well Behaved Energy Function
 A Neual Netwok fo the Tavelling Saleman Poblem with a Well Behaved Enegy Function Maco Budinich and Babaa Roaio Dipatimento di Fiica & INFN, Via Valeio, 347 Tiete, Italy E-mail: mbh@tiete.infn.it (Contibuted
A Neual Netwok fo the Tavelling Saleman Poblem with a Well Behaved Enegy Function Maco Budinich and Babaa Roaio Dipatimento di Fiica & INFN, Via Valeio, 347 Tiete, Italy E-mail: mbh@tiete.infn.it (Contibuted
On Locally Convex Topological Vector Space Valued Null Function Space c 0 (S,T, Φ, ξ, u) Defined by Semi Norm and Orlicz Function
 Jounal of Intitute of Science and Technology, 204, 9(): 62-68, Intitute of Science and Technology, T.U. On Locally Convex Topological Vecto Space Valued Null Function Space c 0 (S,T, Φ, ξ, u) Defined by
Jounal of Intitute of Science and Technology, 204, 9(): 62-68, Intitute of Science and Technology, T.U. On Locally Convex Topological Vecto Space Valued Null Function Space c 0 (S,T, Φ, ξ, u) Defined by
ASTR 3740 Relativity & Cosmology Spring Answers to Problem Set 4.
 ASTR 3740 Relativity & Comology Sping 019. Anwe to Poblem Set 4. 1. Tajectoie of paticle in the Schwazchild geomety The equation of motion fo a maive paticle feely falling in the Schwazchild geomety ae
ASTR 3740 Relativity & Comology Sping 019. Anwe to Poblem Set 4. 1. Tajectoie of paticle in the Schwazchild geomety The equation of motion fo a maive paticle feely falling in the Schwazchild geomety ae
Let {X n, n 1} be a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables with a common cdf F (x) and pdf f(x).
 Kangweon-Kyungki Math Jou 2 24, No, pp 5 22 RCURRNC RLATION FOR QUOTINTS OF TH POWR DISTRIBUTION BY RCORD VALUS Min-Young Lee and Se-Kyung Chang Abtact In thi pape we etablih ome ecuence elation atified
Kangweon-Kyungki Math Jou 2 24, No, pp 5 22 RCURRNC RLATION FOR QUOTINTS OF TH POWR DISTRIBUTION BY RCORD VALUS Min-Young Lee and Se-Kyung Chang Abtact In thi pape we etablih ome ecuence elation atified
Considerations Regarding the Flux Estimation in Induction Generator with Application at the Control of Unconventional Energetic Conversion Systems
 Conideation Regading the Flux Etimation in Induction Geneato with Application at the Contol of Unconventional Enegetic Conveion Sytem Ioif Szeidet, Octavian Potean, Ioan Filip, Vaa Citian Depatment of
Conideation Regading the Flux Etimation in Induction Geneato with Application at the Contol of Unconventional Enegetic Conveion Sytem Ioif Szeidet, Octavian Potean, Ioan Filip, Vaa Citian Depatment of
Interest-Bearing Surplus Model with Liquid Reserves
 Inteet-Beaing Suplu Model with Liquid Reeve Kitina P Sendova 1 and Yanyan Zang 2 Abtact: We conide a uin model whee the uplu poce of an inuance company i contucted o that pat of the cuent uplu i kept available
Inteet-Beaing Suplu Model with Liquid Reeve Kitina P Sendova 1 and Yanyan Zang 2 Abtact: We conide a uin model whee the uplu poce of an inuance company i contucted o that pat of the cuent uplu i kept available
Multivariable Control Systems
 Multivaiable Contol Sytem Ali Kaimpou Aociate ofeo Fedowi Univeity of Mahhad Refeence ae appeaed in the lat lide. Stability of Multivaiable Feedback Contol Sytem Topic to be coveed include: Well - oedne
Multivaiable Contol Sytem Ali Kaimpou Aociate ofeo Fedowi Univeity of Mahhad Refeence ae appeaed in the lat lide. Stability of Multivaiable Feedback Contol Sytem Topic to be coveed include: Well - oedne
A Fundamental Tradeoff between Computation and Communication in Distributed Computing
 1 A Fundamental Tadeoff between Computation and Communication in Ditibuted Computing Songze Li, Student embe, IEEE, ohammad Ali addah-ali, embe, IEEE, Qian Yu, Student embe, IEEE, and A. Salman Avetimeh,
1 A Fundamental Tadeoff between Computation and Communication in Ditibuted Computing Songze Li, Student embe, IEEE, ohammad Ali addah-ali, embe, IEEE, Qian Yu, Student embe, IEEE, and A. Salman Avetimeh,
Matrix regularization techniques for online multitask learning
 Matix egulaization technique fo online multitak leaning Alekh Agawal Compute Science Diviion UC Bekeley alekh@c.bekeley.edu Pete L. Batlett Compute Science Diviion Depatment of Statitic UC Bekeley batlett@c.bekeley.edu
Matix egulaization technique fo online multitak leaning Alekh Agawal Compute Science Diviion UC Bekeley alekh@c.bekeley.edu Pete L. Batlett Compute Science Diviion Depatment of Statitic UC Bekeley batlett@c.bekeley.edu
ψ - exponential type orbitals, Frictional
 ew develoment in theoy of Laguee olynomial I. I. Gueinov Deatment of Phyic, Faculty of At and Science, Onekiz Mat Univeity, Çanakkale, Tukey Abtact The new comlete othonomal et of L -Laguee tye olynomial
ew develoment in theoy of Laguee olynomial I. I. Gueinov Deatment of Phyic, Faculty of At and Science, Onekiz Mat Univeity, Çanakkale, Tukey Abtact The new comlete othonomal et of L -Laguee tye olynomial
Histogram Processing
 Hitogam Poceing Lectue 4 (Chapte 3) Hitogam Poceing The hitogam of a digital image with gay level fom to L- i a dicete function h( )=n, whee: i the th gay level n i the numbe of pixel in the image with
Hitogam Poceing Lectue 4 (Chapte 3) Hitogam Poceing The hitogam of a digital image with gay level fom to L- i a dicete function h( )=n, whee: i the th gay level n i the numbe of pixel in the image with
Passive Pressure on Retaining Wall supporting c-φ Backfill using Horizontal Slices Method
 Cloud Publication Intenational Jounal of Advanced Civil Engineeing and Achitectue Reeach 2013, Volume 2, Iue 1, pp. 42-52, Aticle ID Tech-106 Reeach Aticle Open Acce Paive Peue on Retaining Wall uppoting
Cloud Publication Intenational Jounal of Advanced Civil Engineeing and Achitectue Reeach 2013, Volume 2, Iue 1, pp. 42-52, Aticle ID Tech-106 Reeach Aticle Open Acce Paive Peue on Retaining Wall uppoting
On the Quasi-inverse of a Non-square Matrix: An Infinite Solution
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
On the undulatory theory of positive and negative electrons
 Su la théoie ondulatoie de électon poitif and negatif J. Phy. et le Rad. 7 (1936) 347-353. On the undulatoy theoy of poitive and negative electon By AL. PROCA Intitut Heni Poincaé Pai Tanlated by D. H.
Su la théoie ondulatoie de électon poitif and negatif J. Phy. et le Rad. 7 (1936) 347-353. On the undulatoy theoy of poitive and negative electon By AL. PROCA Intitut Heni Poincaé Pai Tanlated by D. H.
New problems in universal algebraic geometry illustrated by boolean equations
 New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
New On-Line Algorithms for the Page Replication Problem. Susanne Albers y Hisashi Koga z. Abstract
 New On-Line Algoithm fo the Page Replication Poblem Suanne Albe y Hiahi Koga z Abtact We peent impoved competitive on-line algoithm fo the page eplication poblem and concentate on impotant netwok topologie
New On-Line Algoithm fo the Page Replication Poblem Suanne Albe y Hiahi Koga z Abtact We peent impoved competitive on-line algoithm fo the page eplication poblem and concentate on impotant netwok topologie
The Analysis of the Influence of the Independent Suspension on the Comfort for a Mine Truck
 16 3 d Intenational Confeence on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electical Engineeing (ICVMEE 16 ISBN: 978-1-6595-37- The Analyi of the Influence of the Independent Supenion on the Comfot fo a Mine Tuck JINGMING
16 3 d Intenational Confeence on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electical Engineeing (ICVMEE 16 ISBN: 978-1-6595-37- The Analyi of the Influence of the Independent Supenion on the Comfot fo a Mine Tuck JINGMING
Mathematical Modeling of Metabolic Processes in a Living Organism in Relation to Nutrition
 Mathematical Modeling of Metabolic Pocee in a Living Oganim in Relation to Nutition Dimitova N., Makov S. Depatment Biomathematic Intitute of Mathematic and Infomatic Bulgaian Academy of Science 8 Acad.
Mathematical Modeling of Metabolic Pocee in a Living Oganim in Relation to Nutition Dimitova N., Makov S. Depatment Biomathematic Intitute of Mathematic and Infomatic Bulgaian Academy of Science 8 Acad.
KR- 21 FOR FORMULA SCORED TESTS WITH. Robert L. Linn, Robert F. Boldt, Ronald L. Flaugher, and Donald A. Rock
 RB-66-4D ~ E S [ B A U R L C L Ii E TI KR- 21 FOR FORMULA SCORED TESTS WITH OMITS SCORED AS WRONG Robet L. Linn, Robet F. Boldt, Ronald L. Flaughe, and Donald A. Rock N This Bulletin is a daft fo inteoffice
RB-66-4D ~ E S [ B A U R L C L Ii E TI KR- 21 FOR FORMULA SCORED TESTS WITH OMITS SCORED AS WRONG Robet L. Linn, Robet F. Boldt, Ronald L. Flaughe, and Donald A. Rock N This Bulletin is a daft fo inteoffice
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Auchmuty High School Mathematics Department Advanced Higher Notes Teacher Version
 The Binomial Theoem Factoials Auchmuty High School Mathematics Depatment The calculations,, 6 etc. often appea in mathematics. They ae called factoials and have been given the notation n!. e.g. 6! 6!!!!!
The Binomial Theoem Factoials Auchmuty High School Mathematics Depatment The calculations,, 6 etc. often appea in mathematics. They ae called factoials and have been given the notation n!. e.g. 6! 6!!!!!
Determination of storage lengths of right-turn lanes at signalized. intersections
 Detemination of toage length of ight-tun lane at ignalized inteection By Jinghui Wang Lei Yu Hui Xu ABSTRACT Thi pape develop an analytical method of detemining toage length of ight-tun lane at ignalized
Detemination of toage length of ight-tun lane at ignalized inteection By Jinghui Wang Lei Yu Hui Xu ABSTRACT Thi pape develop an analytical method of detemining toage length of ight-tun lane at ignalized
Pearson s Chi-Square Test Modifications for Comparison of Unweighted and Weighted Histograms and Two Weighted Histograms
 Peason s Chi-Squae Test Modifications fo Compaison of Unweighted and Weighted Histogams and Two Weighted Histogams Univesity of Akueyi, Bogi, v/noduslód, IS-6 Akueyi, Iceland E-mail: nikolai@unak.is Two
Peason s Chi-Squae Test Modifications fo Compaison of Unweighted and Weighted Histogams and Two Weighted Histogams Univesity of Akueyi, Bogi, v/noduslód, IS-6 Akueyi, Iceland E-mail: nikolai@unak.is Two
Direct Torque Control of Double Feed Induction Machine (DTC-DFIM)
 Jounal of Advanced Reeach in Science and echnology ISSN: 232-9989 Diect oque Contol of Double Feed Induction Machine (DC-DFIM) Zemmit Abdeahim, Sadouni Radhwane 2 and Meoufel Abdelkade 2 Electical Engineeing
Jounal of Advanced Reeach in Science and echnology ISSN: 232-9989 Diect oque Contol of Double Feed Induction Machine (DC-DFIM) Zemmit Abdeahim, Sadouni Radhwane 2 and Meoufel Abdelkade 2 Electical Engineeing
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Add Impotant Rotational Kinetic Enegy Page: 353 NGSS Standad: N/A Rotational Kinetic Enegy MA Cuiculum Famewok (006):.1,.,.3 AP Phyic 1 Leaning Objective: N/A, but olling poblem have appeaed on peviou
Add Impotant Rotational Kinetic Enegy Page: 353 NGSS Standad: N/A Rotational Kinetic Enegy MA Cuiculum Famewok (006):.1,.,.3 AP Phyic 1 Leaning Objective: N/A, but olling poblem have appeaed on peviou
The Substring Search Problem
 The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS
 6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
Two-Body Problem with Varying Mass in Case. of Isotropic Mass Loss
 Adv Theo Appl Mech Vol no 69-8 Two-Body Poblem with Vaying Ma in Cae of Iotopic Ma o W A Rahoma M K Ahmed and I A El-Tohamy Caio Univeity Faculty of Science Dept of Atonomy Caio 6 Egypt FA Abd El-Salam
Adv Theo Appl Mech Vol no 69-8 Two-Body Poblem with Vaying Ma in Cae of Iotopic Ma o W A Rahoma M K Ahmed and I A El-Tohamy Caio Univeity Faculty of Science Dept of Atonomy Caio 6 Egypt FA Abd El-Salam
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017](/thumbs/88/114976486.jpg) On The Numbe Of Unlabeled Bipatite Gaphs Abdullah Atmaca and A Yavuz Ouç axiv:7050800v [mathco] 4 May 207 Abstact This pape solves a poblem that was stated by M A Haison in 973 [] This poblem, that has
On The Numbe Of Unlabeled Bipatite Gaphs Abdullah Atmaca and A Yavuz Ouç axiv:7050800v [mathco] 4 May 207 Abstact This pape solves a poblem that was stated by M A Haison in 973 [] This poblem, that has
Approximation Techniques for Spatial Data
 Appoximation Technique fo Spatial Data Abhinandan Da Conell Univeity ada@c.conell.edu Johanne Gehke Conell Univeity johanne@c.conell.edu Miek Riedewald Conell Univeity miek@c.conell.edu ABSTRACT Spatial
Appoximation Technique fo Spatial Data Abhinandan Da Conell Univeity ada@c.conell.edu Johanne Gehke Conell Univeity johanne@c.conell.edu Miek Riedewald Conell Univeity miek@c.conell.edu ABSTRACT Spatial
556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I
 556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I CHAPTER 5: STOCHASTIC CONVERGENCE The following efinitions ae state in tems of scala anom vaiables, but exten natually to vecto anom vaiables efine on the same obability
556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I CHAPTER 5: STOCHASTIC CONVERGENCE The following efinitions ae state in tems of scala anom vaiables, but exten natually to vecto anom vaiables efine on the same obability
Above Flux Estimation Issues in Induction Generators with Application at Energy Conversion Systems
 Acta Polytechnica Hungaica Vol. 3, No. 3, 2006 Above Flux Etimation Iue in Induction Geneato with Application at Enegy Conveion Sytem Ioif Szeidet, Octavian Potean, Ioan Filip, Vaa Citian Depatment of
Acta Polytechnica Hungaica Vol. 3, No. 3, 2006 Above Flux Etimation Iue in Induction Geneato with Application at Enegy Conveion Sytem Ioif Szeidet, Octavian Potean, Ioan Filip, Vaa Citian Depatment of
New Analysis for The FGM Thick Cylinders Under Combined Pressure and Temperature Loading
 Ameican Jounal of Applied Science 5 (7): 85-859, 008 ISSN 546-939 008 Science Publication New Analyi fo The FGM Thick Cylinde Unde Combined Peue and Tempeatue Loading K. Abinia, H. Naee, F. Sadeghi and
Ameican Jounal of Applied Science 5 (7): 85-859, 008 ISSN 546-939 008 Science Publication New Analyi fo The FGM Thick Cylinde Unde Combined Peue and Tempeatue Loading K. Abinia, H. Naee, F. Sadeghi and
Bounds for Codimensions of Fitting Ideals
 Ž. JOUNAL OF ALGEBA 194, 378 382 1997 ATICLE NO. JA966999 Bounds fo Coensions of Fitting Ideals Michał Kwiecinski* Uniwesytet Jagiellonski, Instytut Matematyki, ul. eymonta 4, 30-059, Kakow, Poland Communicated
Ž. JOUNAL OF ALGEBA 194, 378 382 1997 ATICLE NO. JA966999 Bounds fo Coensions of Fitting Ideals Michał Kwiecinski* Uniwesytet Jagiellonski, Instytut Matematyki, ul. eymonta 4, 30-059, Kakow, Poland Communicated
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE
 ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
V V The circumflex (^) tells us this is a unit vector
 Vecto Vecto have Diection and Magnitude Mike ailey mjb@c.oegontate.edu Magnitude: V V V V x y z vecto.pptx Vecto Can lo e Defined a the oitional Diffeence etween Two oint 3 Unit Vecto have a Magnitude
Vecto Vecto have Diection and Magnitude Mike ailey mjb@c.oegontate.edu Magnitude: V V V V x y z vecto.pptx Vecto Can lo e Defined a the oitional Diffeence etween Two oint 3 Unit Vecto have a Magnitude
Development of Model Reduction using Stability Equation and Cauer Continued Fraction Method
 Intenational Jounal of Electical and Compute Engineeing. ISSN 0974-90 Volume 5, Numbe (03), pp. -7 Intenational Reeach Publication Houe http://www.iphoue.com Development of Model Reduction uing Stability
Intenational Jounal of Electical and Compute Engineeing. ISSN 0974-90 Volume 5, Numbe (03), pp. -7 Intenational Reeach Publication Houe http://www.iphoue.com Development of Model Reduction uing Stability
Surveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces
 Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Multiple Experts with Binary Features
 Multiple Expets with Binay Featues Ye Jin & Lingen Zhang Decembe 9, 2010 1 Intoduction Ou intuition fo the poect comes fom the pape Supevised Leaning fom Multiple Expets: Whom to tust when eveyone lies
Multiple Expets with Binay Featues Ye Jin & Lingen Zhang Decembe 9, 2010 1 Intoduction Ou intuition fo the poect comes fom the pape Supevised Leaning fom Multiple Expets: Whom to tust when eveyone lies
FRACTIONAL ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION BASED ON GENETIC ALGORITHMS
 Jounal of Engineeing Science and Technology Vol. 8, No. 6 (2013) 713-722 School of Engineeing, Taylo niveity FRACTIONAL ORDER SSTEM IDENTIFICATION BASED ON GENETIC ALGORITHMS MAZIN Z. OTHMAN*, EMAD A.
Jounal of Engineeing Science and Technology Vol. 8, No. 6 (2013) 713-722 School of Engineeing, Taylo niveity FRACTIONAL ORDER SSTEM IDENTIFICATION BASED ON GENETIC ALGORITHMS MAZIN Z. OTHMAN*, EMAD A.
Symmetry of Lagrangians of holonomic systems in terms of quasi-coordinates
 Vol 18 No 8, Augut 009 c 009 Chin. Phy. Soc. 1674-1056/009/1808/3145-05 Chinee Phyic B an IOP Publihing Lt Symmety of Lagangian of holonomic ytem in tem of quai-cooinate Wu Hui-Bin an Mei Feng-Xiang School
Vol 18 No 8, Augut 009 c 009 Chin. Phy. Soc. 1674-1056/009/1808/3145-05 Chinee Phyic B an IOP Publihing Lt Symmety of Lagangian of holonomic ytem in tem of quai-cooinate Wu Hui-Bin an Mei Feng-Xiang School
Information Retrieval Advanced IR models. Luca Bondi
 Advanced IR models Luca Bondi Advanced IR models 2 (LSI) Pobabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (plsa) Vecto Space Model 3 Stating point: Vecto Space Model Documents and queies epesented as vectos in the
Advanced IR models Luca Bondi Advanced IR models 2 (LSI) Pobabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (plsa) Vecto Space Model 3 Stating point: Vecto Space Model Documents and queies epesented as vectos in the
Chapter 5 Linear Equations: Basic Theory and Practice
 Chapte 5 inea Equations: Basic Theoy and actice In this chapte and the next, we ae inteested in the linea algebaic equation AX = b, (5-1) whee A is an m n matix, X is an n 1 vecto to be solved fo, and
Chapte 5 inea Equations: Basic Theoy and actice In this chapte and the next, we ae inteested in the linea algebaic equation AX = b, (5-1) whee A is an m n matix, X is an n 1 vecto to be solved fo, and
Bogoliubov Transformation in Classical Mechanics
 Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
Simulink Model of Direct Torque Control of Induction Machine
 Ameican Jounal of Applied Science 5 (8): 1083-1090, 2008 ISSN 1546-9239 2008 Science Publication Simulink Model of Diect Toque Contol of Induction Machine H.F. Abdul Wahab and H. Sanui Faculty of Engineeing,
Ameican Jounal of Applied Science 5 (8): 1083-1090, 2008 ISSN 1546-9239 2008 Science Publication Simulink Model of Diect Toque Contol of Induction Machine H.F. Abdul Wahab and H. Sanui Faculty of Engineeing,
Compactly Supported Radial Basis Functions
 Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
10/04/18. P [P(x)] 1 negl(n).
![10/04/18. P [P(x)] 1 negl(n). 10/04/18. P [P(x)] 1 negl(n).](/thumbs/92/110495316.jpg) Mastemath, Sping 208 Into to Lattice lgs & Cypto Lectue 0 0/04/8 Lectues: D. Dadush, L. Ducas Scibe: K. de Boe Intoduction In this lectue, we will teat two main pats. Duing the fist pat we continue the
Mastemath, Sping 208 Into to Lattice lgs & Cypto Lectue 0 0/04/8 Lectues: D. Dadush, L. Ducas Scibe: K. de Boe Intoduction In this lectue, we will teat two main pats. Duing the fist pat we continue the
Using DEA and AHP for Multiplicative Aggregation of Hierarchical Indicators
 Ameican Jounal of Opeation Reeach, 205, 5, 327-336 Publihed Online Septembe 205 in SciRe. http://www.cip.og/jounal/ajo http://dx.doi.og/0.4236/ajo.205.55026 Uing DEA and AHP fo Multiplicative Aggegation
Ameican Jounal of Opeation Reeach, 205, 5, 327-336 Publihed Online Septembe 205 in SciRe. http://www.cip.og/jounal/ajo http://dx.doi.og/0.4236/ajo.205.55026 Uing DEA and AHP fo Multiplicative Aggegation
COMPLEX MODE SUPERPOSITION METHOD CONSIDERING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE FOLD EIGENVALUE IN SEISMIC DESIGN
 The 4 th Wold Confeence on Eathquae Engineeing Octobe -7, 008, Being, China COMPLEX MODE SUPERPOSITION METHOD CONSIDERING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE FOLD EIGENVALUE IN SEISMIC DESIGN Ruifang Yu,, Xiyuan Zhou
The 4 th Wold Confeence on Eathquae Engineeing Octobe -7, 008, Being, China COMPLEX MODE SUPERPOSITION METHOD CONSIDERING THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE FOLD EIGENVALUE IN SEISMIC DESIGN Ruifang Yu,, Xiyuan Zhou
18.06 Problem Set 4 Solution
 8.6 Poblem Set 4 Solution Total: points Section 3.5. Poblem 2: (Recommended) Find the lagest possible numbe of independent vectos among ) ) ) v = v 4 = v 5 = v 6 = v 2 = v 3 =. Solution (4 points): Since
8.6 Poblem Set 4 Solution Total: points Section 3.5. Poblem 2: (Recommended) Find the lagest possible numbe of independent vectos among ) ) ) v = v 4 = v 5 = v 6 = v 2 = v 3 =. Solution (4 points): Since
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
An Efficient Algorithm for the Exact Analysis of Multiclass Queueing Networks with Large Population Sizes
 An Efficient Algoithm fo the Exact Analyi of Multicla Queueing Netwok with Lage Population Size iuliano Caale Neptuny R&D via Duando 0-, I-08 Milan, Italy and Politecnico di Milano - DEI Via Ponzio /,
An Efficient Algoithm fo the Exact Analyi of Multicla Queueing Netwok with Lage Population Size iuliano Caale Neptuny R&D via Duando 0-, I-08 Milan, Italy and Politecnico di Milano - DEI Via Ponzio /,
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Noether Theorem, Noether Charge and All That
 Noethe Theoem, Noethe Chage and All That Ceated fo PF by Samalkhaiat 10 Tanfomation Let G be a Lie goup whoe action on Minkowki pace-time fomally ealized by coodinate tanfomation ( ) ( 1,3,η) M i Infiniteimally,
Noethe Theoem, Noethe Chage and All That Ceated fo PF by Samalkhaiat 10 Tanfomation Let G be a Lie goup whoe action on Minkowki pace-time fomally ealized by coodinate tanfomation ( ) ( 1,3,η) M i Infiniteimally,
6 Matrix Concentration Bounds
 6 Matix Concentation Bounds Concentation bounds ae inequalities that bound pobabilities of deviations by a andom vaiable fom some value, often its mean. Infomally, they show the pobability that a andom
6 Matix Concentation Bounds Concentation bounds ae inequalities that bound pobabilities of deviations by a andom vaiable fom some value, often its mean. Infomally, they show the pobability that a andom
University of East London Institutional Repository:
 Univeity of Eat London Intitutional Repoitoy: http://oa.uel.ac.uk hi pape i made available online in accodance with publihe policie. Pleae coll down to view the document itelf. Pleae efe to the epoitoy
Univeity of Eat London Intitutional Repoitoy: http://oa.uel.ac.uk hi pape i made available online in accodance with publihe policie. Pleae coll down to view the document itelf. Pleae efe to the epoitoy
Fall 2004/05 Solutions to Assignment 5: The Stationary Phase Method Provided by Mustafa Sabri Kilic. I(x) = e ixt e it5 /5 dt (1) Z J(λ) =
 8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
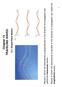 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Encapsulation theory: radial encapsulation. Edmund Kirwan *
 Encapsulation theoy: adial encapsulation. Edmund Kiwan * www.edmundkiwan.com Abstact This pape intoduces the concept of adial encapsulation, wheeby dependencies ae constained to act fom subsets towads
Encapsulation theoy: adial encapsulation. Edmund Kiwan * www.edmundkiwan.com Abstact This pape intoduces the concept of adial encapsulation, wheeby dependencies ae constained to act fom subsets towads
Σr2=0. Σ Br. Σ br. Σ r=0. br = Σ. Σa r-s b s (1.2) s=0. Σa r-s b s-t c t (1.3) t=0. cr = Σ. dr = Σ. Σa r-s b s-t c t-u d u (1.4) u =0.
 0 Powe of Infinite Seie. Multiple Cauchy Poduct The multinomial theoem i uele fo the powe calculation of infinite eie. Thi i becaue the polynomial theoem depend on the numbe of tem, o it can not be applied
0 Powe of Infinite Seie. Multiple Cauchy Poduct The multinomial theoem i uele fo the powe calculation of infinite eie. Thi i becaue the polynomial theoem depend on the numbe of tem, o it can not be applied
A hint of renormalization
 A hint of enomalization Betand Delamotte a) Laboatoie de Phyique Théoique et Haute Enegie, Univeité Pai VI, Piee et Maie Cuie, Pai VII, Deni Dideot, 2 Place Juieu, 75251 Pai Cedex 05, Fance Received 28
A hint of enomalization Betand Delamotte a) Laboatoie de Phyique Théoique et Haute Enegie, Univeité Pai VI, Piee et Maie Cuie, Pai VII, Deni Dideot, 2 Place Juieu, 75251 Pai Cedex 05, Fance Received 28
Estimates on Invariant Tori near an Elliptic Equilibrium Point of a Hamiltonian System
 jounal of diffeential equation 131, 277303 (1996) aticle no. 0165 Etimate on Invaiant Toi nea an Elliptic Equilibium Point of a Hamiltonian Sytem Amadeu Delham* Depatament de Matema tica Aplicada I, Univeitat
jounal of diffeential equation 131, 277303 (1996) aticle no. 0165 Etimate on Invaiant Toi nea an Elliptic Equilibium Point of a Hamiltonian Sytem Amadeu Delham* Depatament de Matema tica Aplicada I, Univeitat
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
Goodness-of-fit for composite hypotheses.
 Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
A Crash Course in (2 2) Matrices
 A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
HOW TO TEACH THE FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION SCIENCE, CODING, DECODING AND NUMBER SYSTEMS?
 6th INTERNATIONAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY CONFERENCE HOW TO TEACH THE FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION SCIENCE, CODING, DECODING AND NUMBER SYSTEMS? Cecília Sitkuné Göömbei College of Nyíegyháza Hungay Abstact: The
6th INTERNATIONAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY CONFERENCE HOW TO TEACH THE FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION SCIENCE, CODING, DECODING AND NUMBER SYSTEMS? Cecília Sitkuné Göömbei College of Nyíegyháza Hungay Abstact: The
Optimization of Prediction Intervals for Order Statistics Based on Censored Data
 Poceeding of the Wold Conge on Engineeing ol I WCE, July 6-8,, London, UK Optimization of Pediction Inteval fo Ode Statitic Baed on Cenoed Data Nichola A Nechval, Membe, IAENG, Mai Pugaili, Kontantin N
Poceeding of the Wold Conge on Engineeing ol I WCE, July 6-8,, London, UK Optimization of Pediction Inteval fo Ode Statitic Baed on Cenoed Data Nichola A Nechval, Membe, IAENG, Mai Pugaili, Kontantin N
Fractional Zero Forcing via Three-color Forcing Games
 Factional Zeo Focing via Thee-colo Focing Games Leslie Hogben Kevin F. Palmowski David E. Robeson Michael Young May 13, 2015 Abstact An -fold analogue of the positive semidefinite zeo focing pocess that
Factional Zeo Focing via Thee-colo Focing Games Leslie Hogben Kevin F. Palmowski David E. Robeson Michael Young May 13, 2015 Abstact An -fold analogue of the positive semidefinite zeo focing pocess that
CALCULUS II Vectors. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS II Vectos Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Peface... ii Vectos... 3 Intoduction... 3 Vectos The Basics... 4 Vecto Aithmetic... 8 Dot Poduct... 13 Coss Poduct... 21 2007 Paul Dawkins i http://tutoial.math.lama.edu/tems.aspx
CALCULUS II Vectos Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Peface... ii Vectos... 3 Intoduction... 3 Vectos The Basics... 4 Vecto Aithmetic... 8 Dot Poduct... 13 Coss Poduct... 21 2007 Paul Dawkins i http://tutoial.math.lama.edu/tems.aspx
3.1 Random variables
 3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
Concomitants of Dual Generalized Order Statistics from Farlie Gumbel Morgenstern Type Bivariate Inverse Rayleigh Distribution
 J Stat Appl Po 4, No, 53-65 5 53 Jounal of Statitic Application & Pobability An Intenational Jounal http://dxdoiog/785/jap/46 Concomitant of Dual Genealized Ode Statitic fom Falie Gumbel ogenten Type Bivaiate
J Stat Appl Po 4, No, 53-65 5 53 Jounal of Statitic Application & Pobability An Intenational Jounal http://dxdoiog/785/jap/46 Concomitant of Dual Genealized Ode Statitic fom Falie Gumbel ogenten Type Bivaiate
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 1 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 1 Apr 2011 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 1 Apr 2011](/thumbs/93/113446429.jpg) Weight enumeation of codes fom finite spaces Relinde Juius Octobe 23, 2018 axiv:1104.0172v1 [math.co] 1 Ap 2011 Abstact We study the genealized and extended weight enumeato of the - ay Simplex code and
Weight enumeation of codes fom finite spaces Relinde Juius Octobe 23, 2018 axiv:1104.0172v1 [math.co] 1 Ap 2011 Abstact We study the genealized and extended weight enumeato of the - ay Simplex code and
16 Modeling a Language by a Markov Process
 K. Pommeening, Language Statistics 80 16 Modeling a Language by a Makov Pocess Fo deiving theoetical esults a common model of language is the intepetation of texts as esults of Makov pocesses. This model
K. Pommeening, Language Statistics 80 16 Modeling a Language by a Makov Pocess Fo deiving theoetical esults a common model of language is the intepetation of texts as esults of Makov pocesses. This model
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE. We consider second order constant coefficient scalar linear PDEs on R n. These have the form
 MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
Chapter 8 Sampling. Contents. Dr. Norrarat Wattanamongkhol. Lecturer. Department of Electrical Engineering, Engineering Faculty, sampling
 Content Chate 8 Samling Lectue D Noaat Wattanamongkhol Samling Theoem Samling of Continuou-Time Signal 3 Poceing Continuou-Time Signal 4 Samling of Dicete-Time Signal 5 Multi-ate Samling Deatment of Electical
Content Chate 8 Samling Lectue D Noaat Wattanamongkhol Samling Theoem Samling of Continuou-Time Signal 3 Poceing Continuou-Time Signal 4 Samling of Dicete-Time Signal 5 Multi-ate Samling Deatment of Electical
An invariance principle for maintaining the operating point of a neuron
 Netwok: Computation in Neual Sytem Septembe 2008; 19(3): 213 235 An invaiance pinciple fo maintaining the opeating point of a neuon TERRY ELLIOTT, XUTAO KUANG, NIGEL R. SHADBOLT, & KLAUS-PETER ZAUNER Depatment
Netwok: Computation in Neual Sytem Septembe 2008; 19(3): 213 235 An invaiance pinciple fo maintaining the opeating point of a neuon TERRY ELLIOTT, XUTAO KUANG, NIGEL R. SHADBOLT, & KLAUS-PETER ZAUNER Depatment
SENSORLESS SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMS BASED ON ADAPTIVE OBSERVERS LUENBERGER AND GOPINATH
 Annal of the Univeity of Caiova, Electical Engineeing eie, No. 32, 2008; ISSN 1842-4805 SENSORLESS SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMS BASED ON ADAPTIVE OBSERVERS LUENBERGER AND GOPINATH Maiu-Auelian PICIU, Lauenţiu
Annal of the Univeity of Caiova, Electical Engineeing eie, No. 32, 2008; ISSN 1842-4805 SENSORLESS SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMS BASED ON ADAPTIVE OBSERVERS LUENBERGER AND GOPINATH Maiu-Auelian PICIU, Lauenţiu
