(L-4) Free fall, review
|
|
|
- Kathryn Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (L-4) Free fall, review If we neglect air resistance, all objects, regardless of their mass, fall to earth with the same acceleration g 10 m/s 2 This means that if they start at the same height, they will both hit the ground at the same time.
2 Free fall velocity and distance If you drop a ball from the top of a building it gains speed as it falls. Every second, its speed increases by 10 m/s. Also it does not fall equal distances in equal time intervals time (s) speed (m/s) distance (m)
3 Motion with constant acceleration A ball falling under the influence of gravity is an example of what we call motion with constant acceleration. The nice thing about this is that if we know where the ball starts and how fast it is moving at the beginning we can figure out where the ball will be and how fast it is going at any later time!
4 Simplest case is acceleration = 0 If the acceleration = 0 then the velocity is constant. [remember that acceleration is the rate of change of velocity] In this case the distance an object will travel in a certain amount of time is given by distance = velocity x time For example, if you drive at 60 mph for one hour you go 60 mph x 1 hr = 60 mi.
5 Example running the 100 m dash Justin Gatlin won the 100 m dash in just under 10 s. Did he run with constant velocity, or was his motion accelerated? He started from rests and accelerated, so his velocity was not constant. Although his average speed was about 100 m/10 s = 10 m/s, he did not maintain this speed all through the race.
6 The velocity of a falling ball Suppose that at the moment you start watching the ball it has an initial velocity equal to v 0 Then its present velocity is related to the initial velocity and acceleration by present velocity = initial velocity + acceleration time Or in symbols : v = v 0 + a t
7 Ball dropped from rest If the ball is dropped from rest then that means that its initial velocity is zero, v 0 = 0 Then its present velocity = a t, where a is the acceleration of gravity g 10 m/s 2 or 32 ft/s 2, for example: What is the velocity of a ball 5 seconds after it is dropped from rest from the Sears Tower? v = 32 ft/s 2 5 s = 160 ft/s
8 The position of a falling ball Suppose we would like to know where a ball would be at a certain time after it was dropped Or, for example, how long would it take a ball to fall to the ground from the top of the Sears Tower (1450 ft). Since the acceleration is constant (g) we can figure this out!
9 Falling distance Suppose the ball falls from rest so its initial velocity is zero After a time t the ball will have fallen a distance distance = ½ acceleration time 2 Or d = ½ g t 2
10 Falling from the Sears Tower After 5 seconds, the ball falling from the Sears Tower will have fallen distance = ½ 32 ft/s 2 (5 s) 2 = = 400 feet. We can turn the formula around to figure out how long it would take the ball to fall all the way to the ground (1450 ft) time = square root of (2 x distance/g)
11 Look at below! Or time = 2 distance g time ft 2900 = = = 90.6 = 9.5s ft s 2 32 / 32 when it hit the ground it would be moving at v = g t =32 ft/s sec = 305 ft/s or about 208 mph (watch out!)
12 How high will it go? Let s consider the problem of throwing a ball straight up with a speed v. How high will it go? As it goes up, it slows down because gravity is pulling on it. At the very top its speed is zero. It takes the same amount of time to come down as go it v = 0 for an instant
13 An amazing thing! When the ball comes back down to ground level it has exactly the same speed as when it was thrown up, but its velocity is reversed. This is an example of the law of conservation of energy. We give the ball some kinetic energy when we toss it up, but it gets it all back on the way down.
14 So how high will it go? If the ball is tossed up with a speed v, it will reach a maximum height h given by 2 v h= v= 2gh 2g Notice that if h = 1m, v = 2101 i i = 20 = 4.5 m/s this is the same velocity that a ball will have after falling 1 meter.
15 Example Randy Johnson can throw a baseball at 100 mph. If he could throw one straight up, how high would it go? 1 mph = 0.45 m/s 100 mph = 45 m/s h = v 2 2 g = (45) 2 2 x 10 = = 101 meters About 100 yards or the length of a football field!
16 Example comparing masses If you have 2 cubes of the same material, one with side 1 cubic centimeter and the other with side 2 cubic centimeters, how do the masses compare? The mass is proportional to the volume which is given by s 3 where s is the length of the side. Thus the 2 cm cube has 8 times the volume and 8 times the mass.
17 Escape from planet earth To escape from the gravitational pull of the earth an object must be given a velocity at least as great as the so called escape velocity For earth the escape velocity is 7 mi/sec or 11,000 m/s, 11 kilometers/sec or about 25,000 mph. An object given this velocity on the earth s surface will not return.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres. Chapter 2 Motion Cengage Learning
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
Galileo. t = 0 t = 1 second t = 2 seconds t = 3 seconds
 Physics 5.2 Galilei Galileo 1600 s Studied how things fell Didn t have a good clock Rolled balls down an inclined plane Found that the speed increased as it rolled down the ramp 1st person to explain acceleration
Physics 5.2 Galilei Galileo 1600 s Studied how things fell Didn t have a good clock Rolled balls down an inclined plane Found that the speed increased as it rolled down the ramp 1st person to explain acceleration
Kinematics 2. What equation relates the known quantities to what is being asked?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Linear Motion III Free Falling Bodies
 Linear Motion III Free Falling Bodies Level : Physics I Teacher : Kim Objectives i) Describe the motion of an object in free fall ii) Distinguish between speed and velocity iii) Describe the motion of
Linear Motion III Free Falling Bodies Level : Physics I Teacher : Kim Objectives i) Describe the motion of an object in free fall ii) Distinguish between speed and velocity iii) Describe the motion of
Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion. Physics 3 rd /4th 6wks Updated as of 12/17/15
 Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion Physics 3 rd /4th 6wks Updated as of 12/17/15 Newton s 2 nd Law: Football Correlation Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion What is the difference between tossing a ball and throwing
Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion Physics 3 rd /4th 6wks Updated as of 12/17/15 Newton s 2 nd Law: Football Correlation Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion What is the difference between tossing a ball and throwing
MOTION (Chapter 2) Student Learning Objectives 2/11/2016. Compare and contrast terms used to describe motion Analyze circular and parabolic motion
 MOTION (Chapter 2) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxc-hhqldbe Student Learning Objectives Compare and contrast terms used to describe motion Analyze circular and parabolic motion PHYSICS:THE MOST FUNDAMENTAL
MOTION (Chapter 2) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxc-hhqldbe Student Learning Objectives Compare and contrast terms used to describe motion Analyze circular and parabolic motion PHYSICS:THE MOST FUNDAMENTAL
Free Fall. Last new topic that will be on the Midterm
 Homework Questions? Free Fall Last new topic that will be on the Midterm Do now: Calculate acceleration due to gravity on earth Announcements 3.03 is due Friday Free Fall Introduction: Doc Shuster (AP
Homework Questions? Free Fall Last new topic that will be on the Midterm Do now: Calculate acceleration due to gravity on earth Announcements 3.03 is due Friday Free Fall Introduction: Doc Shuster (AP
Logarithmic Differentiation (Sec. 3.6)
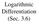 Logarithmic Differentiation (Sec. 3.6) Logarithmic Differentiation Use logarithmic differentiation if you are taking the derivative of a function whose formula has a lot of MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION, and/or
Logarithmic Differentiation (Sec. 3.6) Logarithmic Differentiation Use logarithmic differentiation if you are taking the derivative of a function whose formula has a lot of MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION, and/or
Some Motion Terms. Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector
 Motion Some Motion Terms Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector Scalar versus Vector Scalar - magnitude only (e.g. volume, mass, time) Vector - magnitude
Motion Some Motion Terms Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector Scalar versus Vector Scalar - magnitude only (e.g. volume, mass, time) Vector - magnitude
p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change
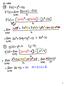 1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
QuickCheck. A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65
 QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
Unit Assessment: Relationship Between Force, Motion, and Energy
 Assessment Unit Assessment: Relationship Between Force, Motion, and Energy Instructions Check your understanding with this assessment. 1) Lifting a 20,000 N anvil one meter requires 20,000 joules (newtons/meter).
Assessment Unit Assessment: Relationship Between Force, Motion, and Energy Instructions Check your understanding with this assessment. 1) Lifting a 20,000 N anvil one meter requires 20,000 joules (newtons/meter).
Physics 201 Homework 1
 Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS
 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
12/06/2010. Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2 Motion Speed Speed. Definitions: Speed The rate at which something moves a given distance. Faster speeds = greater distances
 Chapter 2 Motion 2-1. Speed 2-2. Vectors 2-3. Acceleration 2-4. Distance, Time, and Acceleration 2-5. Free Fall System 2-6. Air Resistance 2-7. First Law of Motion 2-8. Mass 2-9. Second Law of Motion 2-10.
Chapter 2 Motion 2-1. Speed 2-2. Vectors 2-3. Acceleration 2-4. Distance, Time, and Acceleration 2-5. Free Fall System 2-6. Air Resistance 2-7. First Law of Motion 2-8. Mass 2-9. Second Law of Motion 2-10.
Phys 2425: University Physics I Summer 2016 Practice Exam 1
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
5 Projectile Motion. Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion.
 Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion. In the previous chapter we studied simple straight-line motion linear motion. Now we extend these ideas to nonlinear
Projectile motion can be described by the horizontal and vertical components of motion. In the previous chapter we studied simple straight-line motion linear motion. Now we extend these ideas to nonlinear
Calculating Acceleration
 Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Using Derivatives To Measure Rates of Change
 Using Derivatives To Measure Rates of Change A rate of change is associated with a variable f(x) that changes by the same amount when the independent variable x increases by one unit. Here are two examples:
Using Derivatives To Measure Rates of Change A rate of change is associated with a variable f(x) that changes by the same amount when the independent variable x increases by one unit. Here are two examples:
Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics
 Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics Description of motion involves the relationship between position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A fundamental goal of 1D kinematics is to determine x(t) if given initial
Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics Description of motion involves the relationship between position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A fundamental goal of 1D kinematics is to determine x(t) if given initial
Motion Graphs Practice
 Name Motion Graphs Practice d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs 1. The graph below represents the relationship between velocity and time of travel for a toy car moving in a straight line. 3. The
Name Motion Graphs Practice d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs 1. The graph below represents the relationship between velocity and time of travel for a toy car moving in a straight line. 3. The
Accl g Motion graph prac
 Accl g Motion graph prac 1. An object starts from rest and falls freely. What is the velocity of the object at the end of 3.00 seconds? A) 9.81 m/s B) 19.6 m/s C) 29.4 m/s D) 88.2 m/s 2. An object is dropped
Accl g Motion graph prac 1. An object starts from rest and falls freely. What is the velocity of the object at the end of 3.00 seconds? A) 9.81 m/s B) 19.6 m/s C) 29.4 m/s D) 88.2 m/s 2. An object is dropped
3.2 Projectile Motion
 Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion.
 Applications of Calculus: Projectile Motion ID: XXXX Name Class In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion. Open the file CalcActXX_Projectile_Motion_EN.tns
Applications of Calculus: Projectile Motion ID: XXXX Name Class In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion. Open the file CalcActXX_Projectile_Motion_EN.tns
Motion, Forces, and Energy
 Motion, Forces, and Energy What is motion? Motion - when an object changes position Types of Motion There are 2 ways of describing motion: Distance Displacement Distance Distance is the total path traveled.
Motion, Forces, and Energy What is motion? Motion - when an object changes position Types of Motion There are 2 ways of describing motion: Distance Displacement Distance Distance is the total path traveled.
Classical mechanics: Newton s laws of motion
 Classical mechanics: Newton s laws of motion Homework next week will be due on Thursday next week You will soon be receiving student evaluations Occam s razor Given two competing and equally successful
Classical mechanics: Newton s laws of motion Homework next week will be due on Thursday next week You will soon be receiving student evaluations Occam s razor Given two competing and equally successful
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Web Resources for Physics 1 Physics Classroom http://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/ Quantities in Motion Any motion involves three
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Web Resources for Physics 1 Physics Classroom http://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/ Quantities in Motion Any motion involves three
Falling Objects and Projectile Motion
 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Gravity influences motion in a particular way. How does a dropped object behave? accelerate, or speed constant? What if they have: different masses? different shapes?
Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Gravity influences motion in a particular way. How does a dropped object behave? accelerate, or speed constant? What if they have: different masses? different shapes?
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
Look over: Chapter 2 Sections 1-9 Sample Problems 1, 2, 5, 7. Look over: Chapter 2 Sections 1-7 Examples 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 PHYS 2211
 PHYS 2211 Look over: Chapter 2 Sections 1-9 Sample Problems 1, 2, 5, 7 PHYS 1111 Look over: Chapter 2 Sections 1-7 Examples 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 Topics Covered 1) Average Speed 2) Average Velocity
PHYS 2211 Look over: Chapter 2 Sections 1-9 Sample Problems 1, 2, 5, 7 PHYS 1111 Look over: Chapter 2 Sections 1-7 Examples 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 Topics Covered 1) Average Speed 2) Average Velocity
9.2 Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY
 9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
Kinematics A train accelerates from rest at a rate of 2 m/(s*s), for a time of 20 seconds. How much distance does the train cover?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: 1.
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: 1.
Graphing Motion Part 2
 Kinematics 2: Motion Graphs & Free Fall Sep 5 10:34 AM Sep 5 1:25 PM Graphing Motion Part 2 How do you calculate the slope of a line? What would the slope of a distance vs time graph represent? What would
Kinematics 2: Motion Graphs & Free Fall Sep 5 10:34 AM Sep 5 1:25 PM Graphing Motion Part 2 How do you calculate the slope of a line? What would the slope of a distance vs time graph represent? What would
MLK Day!!! Solving Equations with Radicals Day 1. Practice. Solving Equations with Radicals Day 2. Practice. Applications of Radicals.
 Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Chapter 2. Preview. Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically
 Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
Do Now 10 Minutes Topic Free Fall
 Do Now 10 Minutes Topic Free Fall I will be passing out a pop quiz right now. You have ten minutes to complete the pop quiz. Homework Complete the Motion Graph Lab Turn in the Kinematic Equations Worksheet
Do Now 10 Minutes Topic Free Fall I will be passing out a pop quiz right now. You have ten minutes to complete the pop quiz. Homework Complete the Motion Graph Lab Turn in the Kinematic Equations Worksheet
5.1 Area and Estimating with Finite Sums
 5.1 Area and Estimating with Finite Sums Ideas for this section The ideas for this section are Left-Hand Sums Ideas for this section The ideas for this section are Left-Hand Sums Right-Hand Sums Ideas
5.1 Area and Estimating with Finite Sums Ideas for this section The ideas for this section are Left-Hand Sums Ideas for this section The ideas for this section are Left-Hand Sums Right-Hand Sums Ideas
Name Period. Algebra 2 Agenda. Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade
 Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Department of Natural Sciences Clayton State University. Physics 1111 Quiz 2
 Department of Natural Sciences Physics 1111 Quiz September 11, 006 Name SOLUTION A ball is thrown straight up and reaches its maximum height after.00 s. a. What is the acceleration of the ball after it
Department of Natural Sciences Physics 1111 Quiz September 11, 006 Name SOLUTION A ball is thrown straight up and reaches its maximum height after.00 s. a. What is the acceleration of the ball after it
9/7/11. Which of the following is not a vector? Physics 101 Tuesday 9/6/11 Class 4
 Reading Quiz Which of the following is not a vector? Physics 101 Tuesday 9/6/11 Class 4 Chapter 3 Sections 3.1 3.4 Free fall Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors A: speed
Reading Quiz Which of the following is not a vector? Physics 101 Tuesday 9/6/11 Class 4 Chapter 3 Sections 3.1 3.4 Free fall Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors A: speed
Acceleration Worksheet Definitions: velocity: speed in a given direction acceleration: the rate at which the velocity is changing
 Name: Period: Date: / / Acceleration Worksheet Definitions: velocity: speed in a given direction acceleration: the rate at which the velocity is changing Acceleration Notes: 1. What are the three things
Name: Period: Date: / / Acceleration Worksheet Definitions: velocity: speed in a given direction acceleration: the rate at which the velocity is changing Acceleration Notes: 1. What are the three things
Chapter 2 Review Answer Key
 Chapter Review Answer Key Select the correct term to complete the sentences. Section.. force. Newton s first law. inertia. net force. newton Section. 6. acceleration 7. Newton s second law Section. 8.
Chapter Review Answer Key Select the correct term to complete the sentences. Section.. force. Newton s first law. inertia. net force. newton Section. 6. acceleration 7. Newton s second law Section. 8.
Calculus AB a Solutions Thomas Handout Student Questions
 Give the positions s = f(t) of a body moving on a coordinate line, with s in meters and t in seconds. (a) Find the body's displacement and average velocity for the given time interval. (b) Fine the body's
Give the positions s = f(t) of a body moving on a coordinate line, with s in meters and t in seconds. (a) Find the body's displacement and average velocity for the given time interval. (b) Fine the body's
Midterm α, Physics 1P21/1P91
 Midterm α, Physics 1P21/1P91 Prof. D. Crandles March 1, 2013 Last Name First Name Student ID Circle your course number above No examination aids other than those specified on this examination script are
Midterm α, Physics 1P21/1P91 Prof. D. Crandles March 1, 2013 Last Name First Name Student ID Circle your course number above No examination aids other than those specified on this examination script are
Projectile Motion. Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition. Projectile Motion. Projectile Motion. Projectile Motion. This lecture will help you understand:
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Projectile motion is a combination of a horizontal component, and Chapter 10: PROJECTILE AND SATELLITE MOTION a vertical component. This lecture will help you understand:
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Projectile motion is a combination of a horizontal component, and Chapter 10: PROJECTILE AND SATELLITE MOTION a vertical component. This lecture will help you understand:
Practice Test What two units of measurement are necessary for describing speed?
 Practice Test 1 1. What two units of measurement are necessary for describing speed? 2. What kind of speed is registered by an automobile? 3. What is the average speed in kilometers per hour for a horse
Practice Test 1 1. What two units of measurement are necessary for describing speed? 2. What kind of speed is registered by an automobile? 3. What is the average speed in kilometers per hour for a horse
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: Q5. Q7.
 Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Kinematics 2. Kinematics Equations. How to solve a Physics problem:
 Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: What is the question asking for? List the given quantities with units Equation Substitution with units Solution with units Does the answer
Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: What is the question asking for? List the given quantities with units Equation Substitution with units Solution with units Does the answer
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 10: PROJECTILE AND SATELLITE MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Projectile Motion Fast-Moving Projectiles Satellites Circular Satellite Orbits Elliptical
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 10: PROJECTILE AND SATELLITE MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Projectile Motion Fast-Moving Projectiles Satellites Circular Satellite Orbits Elliptical
Conceptual Integrated Science, 2e (Hewitt et al.) Chapter 2 Describing Motion. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Conceptual Integrated Science, 2e (Hewitt et al.) Chapter 2 Describing Motion Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Whereas Aristotle relied on logic in explaining nature, Galileo relied on A) observation. B) patterns.
Conceptual Integrated Science, 2e (Hewitt et al.) Chapter 2 Describing Motion Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Whereas Aristotle relied on logic in explaining nature, Galileo relied on A) observation. B) patterns.
Kinematic Equations. t! +! 1 2 at 2!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!v f 2 =!v i 2 +!2ad. !!!!!!!!!!!!!!d! =!v i. !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
 Kinematic Equations Objectives: Students will use kinematic equations to describe and represent the motion of objects by determining: the distance traveled by an object with constant acceleration. the
Kinematic Equations Objectives: Students will use kinematic equations to describe and represent the motion of objects by determining: the distance traveled by an object with constant acceleration. the
FIRST MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 10 Spring 009 George Williams FIRST MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS A data sheet is provided at the end. Problems labeled [Ch. 4] are relevant to the second midterm. 1. Convert 747 m to feet. Convert
Physics 10 Spring 009 George Williams FIRST MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS A data sheet is provided at the end. Problems labeled [Ch. 4] are relevant to the second midterm. 1. Convert 747 m to feet. Convert
6. Find the centripetal acceleration of the car in m/s 2 a b c d e. 32.0
 PHYSICS 5 TEST 2 REVIEW 1. A car slows down as it travels from point A to B as it approaches an S curve shown to the right. It then travels at constant speed through the turn from point B to C. Select
PHYSICS 5 TEST 2 REVIEW 1. A car slows down as it travels from point A to B as it approaches an S curve shown to the right. It then travels at constant speed through the turn from point B to C. Select
3) Which of the following quantities has units of a displacement? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
 FLEX Physical Sciences AP Physics 1 (Honors Physics) Final Homework Exam 1) A toy rocket is launched vertically from ground level at time t = 0 s. The rocket engine provides constant upward acceleration
FLEX Physical Sciences AP Physics 1 (Honors Physics) Final Homework Exam 1) A toy rocket is launched vertically from ground level at time t = 0 s. The rocket engine provides constant upward acceleration
Exam 2--PHYS 101--Fall 2014
 Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101--Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider these vectors. What is A-B? a. a c. c b. b d. d 2. Consider
Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101--Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider these vectors. What is A-B? a. a c. c b. b d. d 2. Consider
This chapter covers all kinds of problems having to do with work in physics terms. Work
 Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
9/5/17. Aristotle on Motion. Galileo's Concept of Inertia. Galileo's Concept of Inertia
 Aristotle on Motion Aristotle classified motion into two kinds: Natural motion motion that is straight up or straight down Violent motion imposed motion resulting from an external push or pull Galileo's
Aristotle on Motion Aristotle classified motion into two kinds: Natural motion motion that is straight up or straight down Violent motion imposed motion resulting from an external push or pull Galileo's
10.2
 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 d = ½ g t 2 d = 5 m g = 10 m/s 2 t = sqrt (2d/g) t = sqrt (1) t = 1 second Time to hit ground = 1 second In that 1 second, horizontal distance travelled = 20m Horizontal speed
10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 d = ½ g t 2 d = 5 m g = 10 m/s 2 t = sqrt (2d/g) t = sqrt (1) t = 1 second Time to hit ground = 1 second In that 1 second, horizontal distance travelled = 20m Horizontal speed
General Physics (PHY 170) Chap 2. Acceleration motion with constant acceleration. Tuesday, January 15, 13
 General Physics (PHY 170) Chap 2 Acceleration motion with constant acceleration 1 Average Acceleration Changing velocity (non-uniform) means an acceleration is present Average acceleration is the rate
General Physics (PHY 170) Chap 2 Acceleration motion with constant acceleration 1 Average Acceleration Changing velocity (non-uniform) means an acceleration is present Average acceleration is the rate
Page 1. Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is A) 34 m B) 30.
 Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
1.5 Look Out Below! A Solidify Understanding Task
 22 1.5 Look Out Below A Solidify Understanding Task What happens when you drop a ball? It falls to the ground. That question sounds as silly as Why did the chicken cross the road? (To get to the other
22 1.5 Look Out Below A Solidify Understanding Task What happens when you drop a ball? It falls to the ground. That question sounds as silly as Why did the chicken cross the road? (To get to the other
1. The process of changing position
 1. The process of changing position 2. The starting point you choose to describe the location, or position of an object 3. The distance an object travels in a unit of time 4. Speed & direction of a moving
1. The process of changing position 2. The starting point you choose to describe the location, or position of an object 3. The distance an object travels in a unit of time 4. Speed & direction of a moving
Chapter 2: Motion a Straight Line
 Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
physics Chapter 4 Lecture a strategic approach randall d. knight FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS Chapter 4_Lecture1 THIRD EDITION
 Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
Gravity and Orbits. Objectives. Clarify a number of basic concepts. Gravity
 Gravity and Orbits Objectives Clarify a number of basic concepts Speed vs. velocity Acceleration, and its relation to force Momentum and angular momentum Gravity Understand its basic workings Understand
Gravity and Orbits Objectives Clarify a number of basic concepts Speed vs. velocity Acceleration, and its relation to force Momentum and angular momentum Gravity Understand its basic workings Understand
Vocabulary Preview. Oct 21 9:53 AM. Projectile Motion. An object shot through the air is called a projectile.
 Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Pre-Test for One-Dimensional Motion
 Pre-Test for One-Dimensional Motion 1.) Let's say that during a thunderstorm you measure the time lag between the flash and the thunderclap to be 3 seconds. If the speed of sound is about 340 m/s, which
Pre-Test for One-Dimensional Motion 1.) Let's say that during a thunderstorm you measure the time lag between the flash and the thunderclap to be 3 seconds. If the speed of sound is about 340 m/s, which
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Conceptual Physical Science
 Hewitt/Suchocki/Hewitt Conceptual Physical Science Fourth Edition Chapter 1: PATTERNS OF MOTION AND EQUILIBRIUM This lecture will help you understand: Aristotle on Motion Galileo s Concept of Inertia Mass
Hewitt/Suchocki/Hewitt Conceptual Physical Science Fourth Edition Chapter 1: PATTERNS OF MOTION AND EQUILIBRIUM This lecture will help you understand: Aristotle on Motion Galileo s Concept of Inertia Mass
Change in Time = Final speed -Beginning speed Acceleration
 Name: 1. Solving acceleratiol'1 problems Solve the following problems using the equation for acceleration. Remember the units for acceleration are meters per ond per ond or ml. The first problem is done
Name: 1. Solving acceleratiol'1 problems Solve the following problems using the equation for acceleration. Remember the units for acceleration are meters per ond per ond or ml. The first problem is done
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST
 STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Problem Set 1
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Car and Bicycle Rider Problem Set 1 A car is driving along a straight line with a speed v 0. At time t = 0 the car is at the
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Car and Bicycle Rider Problem Set 1 A car is driving along a straight line with a speed v 0. At time t = 0 the car is at the
Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions
 Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions Section 5.1 - Differentiating Functions Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change of a function. We have proven that if f is a variable dependent
Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions Section 5.1 - Differentiating Functions Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change of a function. We have proven that if f is a variable dependent
acceleration versus time. LO Determine a particle s change in position by graphical integration on a graph of velocity versus time.
 Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
C) D) 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart.
 1. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope
1. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope
Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration. Unit 1: Kinematics
 Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure
Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure
Phys 2425: University Physics I Spring 2016 Practice Exam 1
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 140 c. PHYS 45 d. PHYS 46 Survey Questions no points. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 140 c. PHYS 45 d. PHYS 46 Survey Questions no points. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of
PYP 001 FIRST MAJOR EXAM CODE: TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1
 TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1 *Read the following (20) questions and choose the right answer: 1 The figure below represents the speed-time graph for the motion of a vehicle during a 7.0-minute
TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1 *Read the following (20) questions and choose the right answer: 1 The figure below represents the speed-time graph for the motion of a vehicle during a 7.0-minute
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions. Problem Solving
 Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source unknown "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, therefore, is not an act,
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source unknown "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, therefore, is not an act,
Projectile Motion trajectory Projectile motion
 Projectile Motion The path that a moving object follows is called its trajectory. An object thrown horizontally is accelerated downward under the influence of gravity. Gravitational acceleration is only
Projectile Motion The path that a moving object follows is called its trajectory. An object thrown horizontally is accelerated downward under the influence of gravity. Gravitational acceleration is only
CH 56 APPLYING THE QUADRATIC FORMULA
 1 CH 56 APPLYING THE QUADRATIC FORMULA Rectangles Notice that our first example is a geometry word problem that is almost identical to a type that we had before, except that the word perimeter has been
1 CH 56 APPLYING THE QUADRATIC FORMULA Rectangles Notice that our first example is a geometry word problem that is almost identical to a type that we had before, except that the word perimeter has been
4.1 Motion Is Relative. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. You can describe the motion of an object by its
 4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
A scalar quantity has just magnitude A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction
 Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
From rest, a rock is dropped and falls for 3.0 seconds before hitting the ground. What is its velocity right before it hits the ground?
 Physics Lecture #6: Falling Objects A falling object accelerates as it falls. A bowling ball dropped on your foot will hurt more if it is dropped from a greater height since it has more time to increase
Physics Lecture #6: Falling Objects A falling object accelerates as it falls. A bowling ball dropped on your foot will hurt more if it is dropped from a greater height since it has more time to increase
Kinematics and Dynamics
 AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PHYS 101 Fall 2013 (Purcell), Fake Midterm #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a
PHYS 101 Fall 2013 (Purcell), Fake Midterm #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a
Types of Motion. Photo of ball falling
 Gravity an Projectiles Acceleration of Gravity Loses spee for each interval of time it rises on an upwar throw Gains at same rate on its ownwar path Upwar motion Acte upon by gravity, just like a falling
Gravity an Projectiles Acceleration of Gravity Loses spee for each interval of time it rises on an upwar throw Gains at same rate on its ownwar path Upwar motion Acte upon by gravity, just like a falling
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
Chapter 4 Linear Motion
 Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Physics General Physics. Lecture 3 Newtonian Mechanics. Fall 2016 Semester. Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 3 Newtonian Mechanics Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Review of Lectures 1 and 2 In the previous lectures we learned how to describe some special types of
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 3 Newtonian Mechanics Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Review of Lectures 1 and 2 In the previous lectures we learned how to describe some special types of
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction
 Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide
 Name: Date of Test: Vocabulary 5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide Motion- a change in position relative to a point of reference, a change in speed, or a change in distance. Point of Reference (Reference
Name: Date of Test: Vocabulary 5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide Motion- a change in position relative to a point of reference, a change in speed, or a change in distance. Point of Reference (Reference
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Calculus AB Unit 6 Packet Antiderivatives. Antiderivatives
 Antiderivatives Name In mathematics, we use the inverse operation to undo a process. Let s imagine undoing following everyday processes. Process Locking your car Going to sleep Taking out your calculator
Antiderivatives Name In mathematics, we use the inverse operation to undo a process. Let s imagine undoing following everyday processes. Process Locking your car Going to sleep Taking out your calculator
