Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration. Unit 1: Kinematics
|
|
|
- Allen Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics
2 Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure speed, you need to know two things: 1) Distance 2) Time Velocity is speed with a specific direction it is a vector quantity. To measure velocity you need to know three things: 1) Distance 2) Time 3) Direction
3 The skier has traveled 400 meters in 6 seconds. What is his speed? Distance traveled is 400 meters The time it took was 6 seconds. The speed is the distance traveled divided by the time taken. speed = 400 meters 6 seconds speed = m s
4 Formula In this formula; x is the symbol for displacement Usually measured in meters t is the symbol for time The formula for velocity is v = x t Usually measured in seconds v is the symbol for velocity Usually measured in m/s. It must agree with whatever the distance and time is measured in! Velocity is actually speed with a direction (known as a VECTOR quantity). EX: 60 mph on I-80 going east.
5 Formula In this formula; d total is the symbol for total distance Usually measured in meters t total is the symbol for total time The formula for average speed is s avg = d total t total Usually measured in seconds s avg is the symbol for average speed Usually measured in m/s. It must agree with whatever the distance and time is measured in!
6 Problems When Evelyn Ashford was in the Olympics she broke the record for the 200 m run by completing it in 11s. What was her speed? Remember: We have a specific 5-step method for solving problems the GUESS method.
7 G: givens d = 200 m t = 11 s U: unknowns v =? E: equation v = x t S: substitution v = S: solution v = 18 m/s G: write down the givens you can do any necessary conversions at this point. U: write down the unknowns E: write down the equation(s) you may want to re-arrange the equation at this point S: write down the substitution Plug everything in S: write down the solution remember to include the units! When Evelyn Ashford was in the Olympics she broke the record for the 200 m run by completing it in 11s. What was her speed?
8 Problems On average, a cheetah can reach speeds of up to 95 km/hr. If the cheetah can maintain that speed for about 30 seconds, how far will it travel in that time? G: givens v = 95 km/hr t = 30 seconds U: unknowns x =? E: equation 1 hour = 3600 seconds v = x t Rearrange for x, x = vt S: substitution x = ( m/s)(30 sec) S: solution v = m
9 Problems In 1931, "'Big Bill' Tilden delivered the fastest serve ever officially measured. The speed was m/s. If the serve covered 30.5 m, how much time did Bill s opponent have to react before the ball reached him? G: givens x = 30.5 m v = m/s U: unknowns t =? E: equation t = x v S: substitution t = 30.5m 73.14m/s S: solution t = 0.42 sec
10 ACCELERATION What is acceleration? The rate at which velocity changes compared to the time it takes to change. This is also a vector quantity because it includes a direction. a = v t = v f v i t = final velocity initial velocity change in time UNITS: m/s s = m/s/s or m/s 2
11 EX: If your old Chevy can go from 20 m/s to 60 m/s in 4 seconds, What is your car s acceleration? 1. Given: Initial Velocity = 20 m/s Final Velocity = 60 m/s Δ v = = 40 m/s Time = 4 seconds 2. Unknown: 3. Equation: Acceleration =? a = v t 4 sec 4 sec 4. Substitute: 5. Solve: a = 40 4 a = 10 m/s 2 This means your car accelerates 10 m/s each second
12 More about acceleration. Lets say the stop light turns red and you put the brakes on. Are you accelerating? *Any change in speed, is acceleration. *Any change in direction is acceleration.
13 When is there zero acceleration? If you are traveling at a constant speed of 50 mph for 1 hour, are you accelerating? Remember: a = v t Is your speed changing? No? Then acceleration = 50 mph 50 mph = 0 mph = ZERO! 1 hr 1 hr *Acceleration is ZERO if you travel at a constant speed!* Zero acceleration = cruise control
14 All of the Kinematics Equations Based on what information you have, pick the correct equation!
15 Acceleration Practice You try the following problems 1. A car must come to an emergency stop. What is its acceleration if it took 8 seconds for it to stop when it was traveling at 30 m/s? 2. It was once recorded that a Jaguar left skid marks that were 290 m in length. Assuming that the Jaguar skidded to a stop with a constant acceleration of m/s 2, determine the speed of the Jaguar before it began to skid.
16 Gravity pulls all things down toward the center of Earth with the same acceleration If you drop an object straight down and no other forces are acting on it, it accelerates in free fall. GRAVITY Free Fall Acceleration on Earth = m/s 2 (also known as the acceleration of gravity)
17 Gravity Problem A stone is dropped into a deep well and is heard to hit the water 3.41 s after being dropped. Determine the depth of the well.
18 Visualizing Motion: Position and Time
19 Position vs. Time Graphs Distance/position runs vertically (the y-axis). The higher up the graph we go the further we are from the starting point Time always runs horizontally (the x- axis). The further to the right, the longer time that has passed since leaving the starting position The slope of a position time graph = change in position change in time Which is the equation for.??? VELOCITY!!!
20 P-T Graphs If something is not moving, a horizontal line is drawn on a distance-time graph. Time is increasing to the right, but its distance does not change. This graph shows an object that is stationary. Slope = 0 = velocity
21 P-T Graphs If something is moving at a steady speed, it means we expect the same increase in distance in a given time. Time is increasing to the right, and distance is increasing steadily with time. This graph shows an object that moves at a steady, constant speed.
22 P-T Graphs Both the lines below show that each object moved the same distance, but the steeper yellow line got there before the other one. What does this indicate? A steeper slope indicates a larger distance moved in a given time. In other words, higher speed. This is shown in yellow.
23 P-T Graphs For the first part of the journey shown by the graph below, the object moved at a constant (slow) speed. Then the object suddenly increased its speed, covering a much larger distance in the same time. The speed increased in the second part of the journey.
24 P-T Graphs There are three parts to the journey shown here Where is the graph showing motion that is: Stopped? B! C Moving at a quick constant speed? C! A B Traveling at a slow constant speed? A!
25 P-T Graphs: Negative Slopes What do these graphs, with a NEGATIVE SLOPE mean? They show an object that is moving leftward or backwards. C Negative in physics means left, down, West, or South Positive means right, up, North, or East
26 You Try It: Graphing Position Vs. Time Suppose you are helping a friend who is training for a track meet. She wants to know if she is running at constant speed. You mark the track in 50-meter increments and measure her time at each position during a practice run. Calculate her average speed based on the data. Time (s) Position (m) s avg = d total = 150 t total 30 = 50 m/s
27 Graphing Position Vs. Time What is different about the data shown here? It s not changing at a constant rate. What does that mean? It means that she s accelerating and getting faster and faster in the same amount of time. Time (s) Position (m)
28 Position Vs. Time - Changing Velocity Now consider a car that has a changing velocity. It is not moving at a constant rate, but getting faster by the second (i.e. it s accelerating) What would this graph look like? You try it in your notes first
29 P-T Graphs: Acceleration The line below is curving upwards. This shows an increase in speed, since the slope is getting steeper over time. It is accelerating
30 Acceleration in a P-T Graph + acceleration - acceleration
31
32 Visualizing Motion: Velocity and Time
33 VELOCITY vs TIME GRAPH You just finished designing your own Hot Wheels car and you are ready to race it down the driveway. You take out your stopwatch and record the time from start (zero) to the end of the driveway. You then calculated the speed and created a chart. Let s take a look at how your car did. What would a velocity vs. time graph look like with this data? Do it in your notes!
34 What does the slope of a velocity vs. time graph tell you? Remember: Slope = y change in speed = x change in time What else have we talked about that s formula is change in speed change in time? Acceleration = change in speed change in time So the slope of a speed vs time graph gives us acceleration!
35 -The graph shows a slope with a straight line. According to the graph, what does this tell you about the acceleration? Straight line, so same slope Your car accelerates the same amount every second (constant acceleration) -How much is your car accelerating every second?
36 What to know about the speed vs. time graph. *If you see a slope, you are seeing acceleration* A = upward slope = positive acceleration, speeding up B = downward slope = negative acceleration, slowing down C= No slope (completely horizontal) = zero acceleration, but constant speed, so object is still moving unless the line is at zero
37 Learning Check
38 Comparisons
39 Speeding Up While Falling What could cause this? Object being dropped!
40 Free Fall/Gravity on a P-T Graph Trajectory of a ball being thrown upward
41 Free Fall/Gravity on a P-T Graph What is happening at each point?
42 Free Fall/Gravity on a P-T Graph What is happening at: J: Slowing Down K: Slowing Down L: Slowing Down M: Stopped N: Speeding Up O: Speeding Up P: Speeding Up Gravity is fighting the upward motion of the object on the way up, so the acceleration is -9.8 m/s/s (negative) Gravity is making the object move faster on the way down so the acceleration is 9.8 m/s/s
Four Types of Motion We ll Study
 Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Physics. Chapter 3 Linear Motion
 Physics Chapter 3 Linear Motion Motion is Relative How fast are you moving? We can only speak of how fast in relation to some other thing. Unless otherwise specified, we will assume motion relative to
Physics Chapter 3 Linear Motion Motion is Relative How fast are you moving? We can only speak of how fast in relation to some other thing. Unless otherwise specified, we will assume motion relative to
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
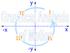 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
4.1 Motion Is Relative. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. You can describe the motion of an object by its
 4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
3.3 Acceleration An example of acceleration Definition of acceleration Acceleration Figure 3.16: Steeper hills
 3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Converting Base Units The Step Stair Method is a simple trick to converting these units. Kilo (k) Hecta (h) Deka (D) Larger unit as you go up the steps! Divide
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Converting Base Units The Step Stair Method is a simple trick to converting these units. Kilo (k) Hecta (h) Deka (D) Larger unit as you go up the steps! Divide
Lecture 2. 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion.
 Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Section Distance and displacment
 Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Using Units in Science
 Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D
 AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
Unit 1 Parent Guide: Kinematics
 Unit 1 Parent Guide: Kinematics Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects. Scientists can represent this information in the following ways: written and verbal descriptions, mathematically (with
Unit 1 Parent Guide: Kinematics Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects. Scientists can represent this information in the following ways: written and verbal descriptions, mathematically (with
RECAP!! Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on a straight road. Time (s)
 RECAP!! What is uniform motion? > Motion in a straight line > Moving at a constant speed Yes or No? Yes or No? Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on
RECAP!! What is uniform motion? > Motion in a straight line > Moving at a constant speed Yes or No? Yes or No? Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on
Problem Set : Kinematics in 1 Dimension
 Problem Set : Kinematics in 1 Dimension Assignment One-Dimensional Motion Page 1 of 6 Name: Date: Solve the following problems and answer the questions on separate paper. Be neat and complete. Include
Problem Set : Kinematics in 1 Dimension Assignment One-Dimensional Motion Page 1 of 6 Name: Date: Solve the following problems and answer the questions on separate paper. Be neat and complete. Include
Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 8 & Physics
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 8 & 9 2016 Physics Physics is the study of how the universe behaves. This
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 8 & 9 2016 Physics Physics is the study of how the universe behaves. This
Physics 101 Discussion Week 3 Explanation (2011)
 Physics 101 Discussion Week 3 Explanation (2011) D3-1. Velocity and Acceleration A. 1: average velocity. Q1. What is the definition of the average velocity v? Let r(t) be the total displacement vector
Physics 101 Discussion Week 3 Explanation (2011) D3-1. Velocity and Acceleration A. 1: average velocity. Q1. What is the definition of the average velocity v? Let r(t) be the total displacement vector
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down?
 5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
Comment: Unlike distance, displacement takes into consideration the direction of motion from the point of origin (where the object starts to move).
 Chapter 3 Kinematics (A) Distance Vs Displacement 1. Compare distance and displacement in terms of: (a) definition Distance is the total length of travel, irrespective of direction. Displacement is the
Chapter 3 Kinematics (A) Distance Vs Displacement 1. Compare distance and displacement in terms of: (a) definition Distance is the total length of travel, irrespective of direction. Displacement is the
Chapter 2 Section 2: Acceleration
 Chapter 2 Section 2: Acceleration Motion Review Speed is the rate that an object s distance changes Distance is how far an object has travelled Speed = distance/time Velocity is rate that an object s displacement
Chapter 2 Section 2: Acceleration Motion Review Speed is the rate that an object s distance changes Distance is how far an object has travelled Speed = distance/time Velocity is rate that an object s displacement
Lecture 2. 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion.
 Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
QuickCheck. A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65
 QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Section 1: Units, Measurements and Error What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Qualitative and Quantitative Descriptions
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Section 1: Units, Measurements and Error What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Qualitative and Quantitative Descriptions
Physics Review. Do: Page # Which of the following is an appropriate unit for velocity? A. s B. m C. m/s 2 D. km/h
 Physics Review Do: Page 413 417 #1 51 1. Which of the following is an appropriate unit for velocity? A. s B. m C. m/s 2 D. km/h Use the following information to answer Question 2. The following distance
Physics Review Do: Page 413 417 #1 51 1. Which of the following is an appropriate unit for velocity? A. s B. m C. m/s 2 D. km/h Use the following information to answer Question 2. The following distance
Lesson 1.2 Position Time Graphs
 Lesson 1.2 Position Time Graphs Be able to explain the motion represented in a position time graph Be able to calculate the avg. vel, x, and t for portions of a position time graph. Be able to draw a position
Lesson 1.2 Position Time Graphs Be able to explain the motion represented in a position time graph Be able to calculate the avg. vel, x, and t for portions of a position time graph. Be able to draw a position
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) v = 0 a = 0
 Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
AP Physics C: Mechanics Ch. 2 Motion. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics C: Mechanics Ch. Motion SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) Car A is traveling at twice the speed of car
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics C: Mechanics Ch. Motion SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) Car A is traveling at twice the speed of car
Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS
 Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS 31. On the position-time graph below, sketch a plot representing the motion of an object which is.... Label each line with the corresponding letter (e.g., "a", "b",
Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS 31. On the position-time graph below, sketch a plot representing the motion of an object which is.... Label each line with the corresponding letter (e.g., "a", "b",
acceleration versus time. LO Determine a particle s change in position by graphical integration on a graph of velocity versus time.
 Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY
 THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating
THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating
Motion along a straight line. Physics 11a. 4 Basic Quantities in Kinematics. Motion
 Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Acceleration review. Regular
 Acceleration review Regular Book pg 82 #91 A car is traveling 20m/s when the driver sees a child standing on the road. She takes 0.80s to react, then steps on the brakes and slows at 7.0m/s 2. How far
Acceleration review Regular Book pg 82 #91 A car is traveling 20m/s when the driver sees a child standing on the road. She takes 0.80s to react, then steps on the brakes and slows at 7.0m/s 2. How far
Chapter 2. Kinematic Equations. Problem 1. Kinematic Equations, specific. Motion in One Dimension
 Kinematic Equations Chapter Motion in One Dimension The kinematic equations may be used to solve any problem involving one-dimensional motion with a constant You may need to use two of the equations to
Kinematic Equations Chapter Motion in One Dimension The kinematic equations may be used to solve any problem involving one-dimensional motion with a constant You may need to use two of the equations to
Unit 1 Our Dynamic Universe
 North Berwick High School Higher Physics Department of Physics Unit 1 Our Dynamic Universe Section 1 Equations of Motion Section 1 Equations of Motion Note Making Make a dictionary with the meanings of
North Berwick High School Higher Physics Department of Physics Unit 1 Our Dynamic Universe Section 1 Equations of Motion Section 1 Equations of Motion Note Making Make a dictionary with the meanings of
Some Motion Terms. Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector
 Motion Some Motion Terms Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector Scalar versus Vector Scalar - magnitude only (e.g. volume, mass, time) Vector - magnitude
Motion Some Motion Terms Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector Scalar versus Vector Scalar - magnitude only (e.g. volume, mass, time) Vector - magnitude
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers
 Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line This chapter uses the definitions of length and time to study the motions of particles in space. This task is at the core of physics and applies to all objects irregardless
Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line This chapter uses the definitions of length and time to study the motions of particles in space. This task is at the core of physics and applies to all objects irregardless
Part I: Review Data Tables & Graphing Part II: Speed Acceleration
 Part I: Review Data Tables & Graphing Part II: Speed Acceleration A Standard Data table consist of two columns. The left-hand column contains the values for the Independent Variable in numerical order.
Part I: Review Data Tables & Graphing Part II: Speed Acceleration A Standard Data table consist of two columns. The left-hand column contains the values for the Independent Variable in numerical order.
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16
 PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
Lecture Notes Kinematics Recap 2.4 Acceleration
 Lecture Notes 2.5-2.9 Kinematics Recap 2.4 Acceleration Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The SI unit for acceleration is m/s 2 Acceleration is a vector, and thus has both a magnitude
Lecture Notes 2.5-2.9 Kinematics Recap 2.4 Acceleration Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The SI unit for acceleration is m/s 2 Acceleration is a vector, and thus has both a magnitude
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 2-3
 A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers
 Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension
 Register Clickers Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics
Register Clickers Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics
Chapter 4 Linear Motion
 Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 2: Kinematics
 Section 1 Chapter 2: Kinematics To simplify the concept of motion, we will first consider motion that takes place in one direction. To measure motion, you must choose a frame of reference. Frame of reference
Section 1 Chapter 2: Kinematics To simplify the concept of motion, we will first consider motion that takes place in one direction. To measure motion, you must choose a frame of reference. Frame of reference
Motion along a straight line
 1 Motion along a straight line Relativeness of motion Activity: Observations from inside and outside of a moving bus. When you look outside a moving bus, do the trees and houses appear to move backwards?
1 Motion along a straight line Relativeness of motion Activity: Observations from inside and outside of a moving bus. When you look outside a moving bus, do the trees and houses appear to move backwards?
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension. Slide 2-1
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Slide 2-1 MasteringPhysics, PackBack Answers You should be on both by now. MasteringPhysics first reading quiz Wednesday PackBack should have email & be signed up 2014
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Slide 2-1 MasteringPhysics, PackBack Answers You should be on both by now. MasteringPhysics first reading quiz Wednesday PackBack should have email & be signed up 2014
EDEXCEL INTERNATIONAL A LEVEL MATHEMATICS. MECHANICS 1 Student Book SAMPLE COPY
 SPECIFICATIN 1.1.1 UNIT 1 THE MARKET i EDEXCEL INTERNATINAL A LEVEL MATHEMATICS MECHANICS 1 Student Book CNTENTS ii ABUT THIS BK VI 1 MATHEMATICAL MDELS IN MECHANICS 2 2 VECTRS IN MECHANICS 12 3 CNSTANT
SPECIFICATIN 1.1.1 UNIT 1 THE MARKET i EDEXCEL INTERNATINAL A LEVEL MATHEMATICS MECHANICS 1 Student Book CNTENTS ii ABUT THIS BK VI 1 MATHEMATICAL MDELS IN MECHANICS 2 2 VECTRS IN MECHANICS 12 3 CNSTANT
Not every object is going to travel at the same VELOCITY all the time.
 ACCELERATION Not every object is going to travel at the same VELOCITY all the time. ACCELERATION is the rate of change in velocity. Mathematically A = velocity time Remember means change in There are 3
ACCELERATION Not every object is going to travel at the same VELOCITY all the time. ACCELERATION is the rate of change in velocity. Mathematically A = velocity time Remember means change in There are 3
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 5 Newton s Laws of Motion
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 5 Newton s Laws of Motion First Law We saw that the type of motion which was most difficult for Aristotle to explain was horizontal motion of nonliving objects, particularly after they've
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 5 Newton s Laws of Motion First Law We saw that the type of motion which was most difficult for Aristotle to explain was horizontal motion of nonliving objects, particularly after they've
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs. Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute
 Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement
 Name: Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1b.html
Name: Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1b.html
Chapter 2. Preview. Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically
 Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
Describing Mo tion. Speed and Velocity. What is speed?
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics and dynamics
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics and dynamics
Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion
 Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion Motion... Particle Models Vectors vs. Scalars Position, Displacement and Distance Velocity vs. Speed Instantaneous vs. Average Acceleration start time Particle motion
Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion Motion... Particle Models Vectors vs. Scalars Position, Displacement and Distance Velocity vs. Speed Instantaneous vs. Average Acceleration start time Particle motion
Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics
 Chapter : 1-D Kinematics Types of Motion Translational Motion Circular Motion Projectile Motion Rotational Motion Natural Motion Objects have a proper place Objects seek their natural place External forces
Chapter : 1-D Kinematics Types of Motion Translational Motion Circular Motion Projectile Motion Rotational Motion Natural Motion Objects have a proper place Objects seek their natural place External forces
During the second part of the trip then we travelled at 50 km/hr for hour so x = v avg t =
 PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 19, Troublesome questions for HW4 (5 or more people got 0 or 1 points on them): 1, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19. Yikes!
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Troublesome questions for HW4 (5 or more people got 0 or 1 points on them): 1, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19. Yikes! Troublesome HW4 questions 1. Two objects of inertias
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Troublesome questions for HW4 (5 or more people got 0 or 1 points on them): 1, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19. Yikes! Troublesome HW4 questions 1. Two objects of inertias
Kinematics 2. What equation relates the known quantities to what is being asked?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Chapter 2: Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter : Motion in One Dimension Review: velocity can either be constant or changing. What is the mathematical meaning of v avg? The equation of a straight line is y = mx + b. From the definition of average
Chapter : Motion in One Dimension Review: velocity can either be constant or changing. What is the mathematical meaning of v avg? The equation of a straight line is y = mx + b. From the definition of average
4.1 - Acceleration. What is acceleration?
 4.1 - Acceleration How do we describe speeding up or slowing down? What is the difference between slowing down gradually and hitting a brick wall? Both these questions have answers that involve acceleration.
4.1 - Acceleration How do we describe speeding up or slowing down? What is the difference between slowing down gradually and hitting a brick wall? Both these questions have answers that involve acceleration.
Physics Essentials Homework Packet
 Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics. Free Response Problems
 PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PHYS1100 Practice problem set, Chapter 2: 6, 10, 13, 17, 22, 24, 25, 34, 42, 50, 55, 65, 71, 82
 PHYS00 Practice problem set, Chapter : 6, 0, 3, 7,, 4, 5, 34, 4, 50, 55, 65, 7, 8.6. Model: We will consider Larry to be a particle. Solve: Since Larry s speed is constant, we can use the following equation
PHYS00 Practice problem set, Chapter : 6, 0, 3, 7,, 4, 5, 34, 4, 50, 55, 65, 7, 8.6. Model: We will consider Larry to be a particle. Solve: Since Larry s speed is constant, we can use the following equation
Motion, Forces, and Newton s Laws
 Motion, Forces, and Newton s Laws Describing Motion What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Motion, Forces, and Newton s Laws Describing Motion What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST **
 Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]
![Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]](/thumbs/77/76428187.jpg) Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
KINEMATICS. File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation. Monday, June 17, 13
 KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
Physics! Unit 2 Review Constant Acceleration Particle Model
 Physics! Unit 2 Review Constant Acceleration Particle Model Name 1. Use the graph to answer the following questions. a. Describe the motion of the object. b. Determine the of the object from the graph.
Physics! Unit 2 Review Constant Acceleration Particle Model Name 1. Use the graph to answer the following questions. a. Describe the motion of the object. b. Determine the of the object from the graph.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres. Chapter 2 Motion Cengage Learning
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
Analyzing Motion: Enrichment
 Chapter 2 Analyzing Motion: Enrichment Note to Teachers: The concepts involved in motion position, velocity, acceleration, and time should be developed using the four modes of representation: visual, numeric,
Chapter 2 Analyzing Motion: Enrichment Note to Teachers: The concepts involved in motion position, velocity, acceleration, and time should be developed using the four modes of representation: visual, numeric,
VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home.
 VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home. a. What distance did you travel? b. What was the displacement
VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home. a. What distance did you travel? b. What was the displacement
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
One dimensional Motion test 8/24
 8/16/017 One dimensional Motion test 8/4 The Nature of Science Observation: important first step toward scientific theory; requires imagination to tell what is important. Theories: created to explain observations;
8/16/017 One dimensional Motion test 8/4 The Nature of Science Observation: important first step toward scientific theory; requires imagination to tell what is important. Theories: created to explain observations;
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph.
 Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration
 Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time
 Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Recall the initial position and clock reading data from the previous lab. When considering
Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Recall the initial position and clock reading data from the previous lab. When considering
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
Speed. Change of Distance (in meters) Change of Time (in seconds) Step 2: Formula. 100m in 10sec. 200m in 10sec T. 200m in 20sec.
 Speed Unit 6:1 Speed Speed is how fast something is moving. Precisely, it is how far an object travels in a certain amount of time. The standard metric units are meters per second (m/s), but any units
Speed Unit 6:1 Speed Speed is how fast something is moving. Precisely, it is how far an object travels in a certain amount of time. The standard metric units are meters per second (m/s), but any units
Items to pick-up: Admit Ticket/Exit Ticket (3) Cornell Note Sheets
 Items to pick-up: Admit Ticket/Exit Ticket (3) Cornell Note Sheets DUE TODAY!!! COMPOSITION NOTEBOOK CHECK (Journal Entries will begin next week) MONDAY AUGUST 8, 2016 All Periods will meet in Lab 2 Admit
Items to pick-up: Admit Ticket/Exit Ticket (3) Cornell Note Sheets DUE TODAY!!! COMPOSITION NOTEBOOK CHECK (Journal Entries will begin next week) MONDAY AUGUST 8, 2016 All Periods will meet in Lab 2 Admit
(UNIT I) Measuring Activity Name
 (UNIT I) Measuring Activity Name Purpose: To become more familiar with the metric system (SI) of measurement. Make estimates first and then measure it. Pre Lab reading: http://www.cnn.com/tech/space/9909/30/mars.metric.02/#1
(UNIT I) Measuring Activity Name Purpose: To become more familiar with the metric system (SI) of measurement. Make estimates first and then measure it. Pre Lab reading: http://www.cnn.com/tech/space/9909/30/mars.metric.02/#1
PH Fall - Section 04 - Version A DRAFT
 1. A truck (traveling in a straight line), starts from rest and accelerates to 30 m/s in 20 seconds. It cruises along at that constant speed for one minute, then brakes, coming to a stop in 25 m. Determine
1. A truck (traveling in a straight line), starts from rest and accelerates to 30 m/s in 20 seconds. It cruises along at that constant speed for one minute, then brakes, coming to a stop in 25 m. Determine
CHAPTER 4 -- KINEMATICS
 Solutions--Ch. 4 (Kinematics CHAPTER 4 -- KINEMATICS 4.1 a. The total distance traversed (versus the net displacement divided by the elapsed time. That scalar is: s = dist/time = (440 m/(49 sec = 8.98
Solutions--Ch. 4 (Kinematics CHAPTER 4 -- KINEMATICS 4.1 a. The total distance traversed (versus the net displacement divided by the elapsed time. That scalar is: s = dist/time = (440 m/(49 sec = 8.98
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
The graphs above are based on the average data from our marble trials. What are the differences between these two graphs? Why do you suppose they are
 The graphs above are based on the average data from our marble trials. What are the differences between these two graphs? Why do you suppose they are different? What does each graph tell us about our experiment?
The graphs above are based on the average data from our marble trials. What are the differences between these two graphs? Why do you suppose they are different? What does each graph tell us about our experiment?
2008 FXA. DISPLACEMENT (s) / metre (m) 1. Candidates should be able to : The distance moved by a body in a specified direction.
 DISPLACEMENT (s) / metre (m) 1 Candidates should be able to : Define displacement, instantaneous speed, average speed, velocity and acceleration. Select and use the relationships : average speed = distance
DISPLACEMENT (s) / metre (m) 1 Candidates should be able to : Define displacement, instantaneous speed, average speed, velocity and acceleration. Select and use the relationships : average speed = distance
12/06/2010. Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension
 Register Clickers Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics
Register Clickers Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics
Physics Motion Math. (Read objectives on screen.)
 Physics 302 - Motion Math (Read objectives on screen.) Welcome back. When we ended the last program, your teacher gave you some motion graphs to interpret. For each section, you were to describe the motion
Physics 302 - Motion Math (Read objectives on screen.) Welcome back. When we ended the last program, your teacher gave you some motion graphs to interpret. For each section, you were to describe the motion
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
