results are usually interpreted on the basis of forward type curvematching or high gas content liquids.
|
|
|
- Roberta Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAPACITIVE PERTURBATIONS IN WELL INTERFERENCE TESTING by Gunnar Bodvarsson, School of Oceanography, Oregon State University. Corvall is, Oregon Introduction Conventional well interference testing is applied to obtain observational data on reservoir parameters such as fluid conductivity, fluid diffusivity and structural inhomogeneities or boundaries. Test results are usually interpreted on the basis of forward type curvematching methods (Ramey, 1970)., t 3 id Field procedures are generally based on the use of standard size. wells for both injection and response monitoring. The pressure sensors are placed into the wells that serye as observational ports. Obviously, the monitoring wells consititute capacitive inhomogenei ties that can perturb the reservoir flow field and thereby distort the pressure readings. In particular, the capacitance of wellbores with two-phase fluids, gas caps or even a free fluid surface is relatively large and the perturbation can then be substantial. Quite erroneous test results may be obtained in such situations. Moreover, analog perturbations can result from the presence of inactive high-capacitance wells and other reservoir "soft spots" in the neighborhood of the test wells. For example, geothermal systems that appear 1 iquid-dominated may actually include local spots with two-phase pore fluids that have a higher compressibility than the pure 1 iquid. In particular, such soft-spots are likely to develop in regions wit temperatures close to boiling and/ or high gas content liquids. As a matter of course, the capacitive effects are well known and are in the petroleum industry usually referred to as wellbore storage effects. A considerable literature exists, mainly relating to such effects in sing1 e-well pressure-buildup or drawdown testing (see, for example, Ramey, 1970; Earlougher and Ramey, 1973; Raghavan, 1976: Chen and Brigham, 1978; Miller, 1979). For further references, we refer to the monograph by Earlougher (1977). A number of aspects relating specifically to interference testing have been discussed by Prats and Scott (1975), Jargon (1976) and Sandal et a1. (1979). sing, it is of interest to remark thzt sensor capacitance is a matter of extremely general relevance. For example, capacitive effects interfere withthe measurement of tine-varying temperatures. Just as we refer to temperature gauges as thermcneters, v!e wii1 here apply the term pressometers for the pressure mocitoring devices. In interference testing, the pressoineter consists of the entire noni toying well setup. The purpose of the present shgrt note is to discuss the capacitive effects from a rather qeneral point of view and, in partiular, to derive some basic expression; to enable us to correct for pressometer and soft-spot capacitance. The approach will be based on the assumption of a formrd tj/pe interpretational procedure. In other words, -85-
2 -86- the development is based on definite field models that lead to a wellposed problem setting. By varying the model parameters, the solutions yield the type-curves that are used to interpret field data. Data. interpretation on the basis of so-called inverse procedures is usually not feasible and would lead to a practically impossible problem setting. Notation and basic equations are as given in the paper by.bodvarsson (1978). t, An ul trasimpl e model In the case of slowly varying fields, well pressometers can quite often be lumped into an equivalent admittance (conductance) A and an equivalent capacitance C. That is to say, that given the ambient timevarying pressure field to be measured p(t) and the pressometer reading pm(t), the mass flow into the meter system satisfies the folloiding equations q = '(P-Pm) I 9 E PCDpm (1 1 where D = d/dt and p is the density of the fluid. Let to = pc/a be the pressometer relaxation or response time and the above equations can then be combined into one equation t including only the parameter to. It is convenient to introduce the correction pressure p1 that has to be added to Pm to obtain the ambient field p such that p = (p, + PI). We have then the relation 1 7 Depending on a number of circumstances such as the flow and phase situation in the well, the parametersa; C and t can be taken to be constant over a limited range of pressure. Equation 92) is then a simple differential equation in Pm 2nd the relation (3) involves only a single differentiation. In interference testing, :ve can usua7ly take that pressure monitoring proceeds from an equilibrium situation where pr = p and because of linearity, we can then put p,,(o) = p(0) = 0, that is, the system is causal. In + operational form,.the solution of (1) is then -1 = (1 + t,d) p Pm (4) f which yields a Taylor series in the operator t,d. c
3 -87- An injection/monitoring well pair in a distributed reservoir model Consider now a more general situation involving a porous and permeable fluid-saturated reservoir model with a given fixed boundary C where prescribed conditions are to be applied. Let c = f?/u be the fluid conductivity operator where 8 is the formation permeability operator and u the kinematic vi.scosity of the fluid. The density of the fluid is p, the wet formation capacitivity or storage coefficient is s and hence' the fluid diffusivity a -- c/ps. Let P = (x,y,r) be the general field point. Two wells have been drilled Snto the reservoir, one for injection purposes and the other is to be applied as a pressometer that is assumed to have a known capacitance C taken to be constant within the pressure range of interest. Moreover, the distance between the two wells is taken to be very large compared with the dimensions of the formation/well contact openings such that for mathematical convenience the injection zone, as seen from the monitoring well, can be lumped into a point Q. This situation is easily generalized to the case of a distributed source. The problem setting Is now the following. The system is initially in equilibrium and starting at t = 0 the mass flow f(t) is being injected into the reservoir at Q. In the case of fluid withdrawal the sign of f(t) is negative. The fluid injection raises the reservoir pressure leading to the reading p,(t) at t.he'pressometer well. We are interested in the pressure p(p,t) at the nionitoring well as unperturbed by the pressometer capacitance and will therefore derive the correction pressure pi such that at the pressometer p = Pm + p1. As compared with the simple situation in the preceding section, the present case is more complex in that the correction pressure is a field function p (P,t) that has to be derived by the integration of a diffusion type P B E. To derive the pressure field equations, we simplify the topology of the reservoir by neglecting the conductivity perturbance of the pressometer and replace it by an equivalent capacity function su(p) such that the space integral over this function is equal to C. Obviously, the function u(p) is localized in that it is zero everywhere except at the pressometer we1 1 Moreover, let n(c) be the generalized Laplacian that in the case of a homogeneous and isotropic medium simplifies to n(c) = -c+. In this setting with the pressometer well included, the total pressure field (p-p1) satisfies the equation. Q L t d+u)at(p-p, 1 + (c) 1 fs(p-q) 9 (5) where 3(P-Q) is the spstial delta-function centered at Q. The pressure field p unperturbed by the pressometer capacitance satisfies wtp + n(c) P = fw-q),. (6)
4 -88- and hence the correction field pl satisfies To cope with this equation, we observe that the pressure within the pressometer is constant and equal to the observed pressure pm. Since Pm represents the total field there, we take that pm = (p-pl)over the support of u(p) and equation (7) can thus be expressed f PSatPl + X(C)P~ = PSUDPm, (8) where D = d/dt and the expression on the right is now a known function in space and time. Moreover, it is quite obvious that (p-p1) and p should satisfy the same boundary conditions on z and p1, therefore satisfies homogeneous conditions there. It follows that equation (8) can be integrated to obtain the perturbation pressure pi. Let the diffusion operator on the left of (7) be expressed and H-l be its inverse a t the conditions specified. (8) is thus formally The solution of 1, This equation takes now the place of equation (3) which holds only in the much simplifed lumped case of constant A. In fact, in the case of fields varying so slowly that the time-derivative on the right of (7) can be neglected, equation (8) reduces to a potential equation that can be integrated to yield an expression for pi. For the field pressure at the pressometer, this integral then reduces to the same form as (3). It is of importance to remark that to correct the pressometer reading Pm(t), the pressure p1 (t) has to be evaluated at the source of this field. The result is therefore strongly dependent on the selection of a correct local model for the pressometer sys%eii?. We will refrain from entering into a detailed discussion of the integral (lo), and limit our remarks to perhaps the simplest case relevznt in the present context. We assume a homogeneous and isotropic reservoir of such an extent that as viewed from the pressometer, it can be aken to be infinite. Moreover, the pressometer system consists of, or s equivalent to, a spherical cavity of radius R. To investigate the response of a system of this type, we turn to a spectral type of ana ysis and investigate the integral 0 c
5 -89- (10) when pm = p exp(iwt) and w is the circular frequency. These assumptions simp 4 ify. the procedure very considerably. Omitting details, we obtain for the amplitude of the correction pressure p1 at the cavity p1 = iwpcpo/as[(l+i)(r/d) + 13, (11 1 where C is the capacitance f the pressometer, A = 4~cR admittance and d = (2c/ps~) F is the skin depth of-the pressure its static field at the frequency W. This expression is useful in that it gives the amplitude, of the spectral components of p1. The dominant physical factor is the ratio R/d. Expression (11) is analog to (3) above.. a Soft spots As already stated, even small reservoir t spots, that are sufficiently close to the pressometer, can perturb the pressure readings, For example, there may be an inactive well with a free liquid surface in the close vicinity of the monitoring well. Considering such a case that has a known capacitance K, we are interested in some estiniates of the resulting perturbation of pm(t). Here, it is appropriate to make the simp1 ifying assumption that multiple pressure field scattering can be neglected. In other words the secondary fjelds due to the pressometer and the soft spot do not scatter and their perturbation of the primary field is therefore additive. Hence, to obtain the perturbation due to the soft spot at the pressometer we can neglect the capactanre of the pressometer. Under these circumstances, it is possible to proceed in much the same way as above. Let p2(p,t) be the perturbation pressure field due to the soft-spot. The field has then to satisfy an equation of the same type as (7) above. There is, however, the important difference in that there is no monitoring device in the soft spot and the pressure there is now unknown. The integration expressed by (10) can therefore not be performed. There are nevertheless a the anel iorating circumstances that we are only interested in the value of p2 at the pressometer. As viewed from this-distance, details of the model at the softspot are less important and we can in many przcticslly relevant cases resort to a perturbation approach where th2 pressure field at the softspot is taken to be equal to the primary field at this position. On this basis the integration prescribed by (10) can be performed by equating Pm with the primary field and we have thw BR estimate of p2 that can be evaluated at the pressometer well. A variety of situations are of practical interest, but we will refrain from a detailed ~~SCUSS~O~I. A sim?le investigation on standard size wells shows that in interference tests, the action radius of inactive wells is relatively small. Beyond distances of the order of a very few hundred meter.s,open inactive weils can for the most practical purposes be neglected.
6 References -._ Bodvarsson, G., 1978, Mechanism 0-f reservoir testing, 4th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, December 1978, Stanford University Stanford, California. Chen, H.K., W.E. Brigham, 1978, Pressure buildup for a well with storage and skin in a closed square, J. of Petr. Tech., January, 1978, Earlougher, R.C., Jr., 1977, Advances in well test analysis, SOC. of Petr. Eng. of AIME, New York, N.Y., and Dallas, Texas. Earlougher, R.C., Jr., and H.J. Ramey, Jr., 1973, Interference analysis in bounded systems, J. Can. Pet. Tech., 0ct.-Dec., 1973, Jargon, J.R., 1976, Effect of wellbore storage and wellbore damage at the active well on interference test analysis, J. Petr. Tech., August, 1976, Miller, C.W., 1979, Wellbore storage effects in geothermal wells, SOC. of Petro. Eng. of AIME, SPE Prats, M. and J.B. Scott, 1975, Effect of wellbore storage on pulse-test pressure response, JPT Forum, J. of Petro. Tech Raghavan, R., 1976, Some practical considerations in the analysis of pressure data, J. of Petro. Tech., October, 1976, Ramey, H.J., Jr., 1970, Short-time well test data interpretation in the presence of skin effect and wellbore storage, J. of Petro. Tech., January 1970, Sandal, H.M., Horne, R.N., Ramey, H.J., Jr., and J. Wight, 1979, Interference testing with wellbore storage and skin effect at the produced well, SOC. of Petro. Eng. of AIME, SPE c
ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VARIATION OF FLUID IN BOUNDED CIRCULAR RESERVOIRS UNDER THE CONSTANT PRESSURE OUTER BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
SPE Uncertainty in rock and fluid properties.
 SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well
 UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Factors that affect pressure distribution of horizontal wells in a layered reservoir with simultaneous gas cap and bottom water drive
 Vol. 6(1), pp. 1-9, January, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JPGE 2013.0180 Article Number: 3C2A1DC50083 ISSN 2I41-2677 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jpge
Vol. 6(1), pp. 1-9, January, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JPGE 2013.0180 Article Number: 3C2A1DC50083 ISSN 2I41-2677 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jpge
THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT
 THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT L. S. Mannon Atlantic Richfield Co. 1860 Lincoln Suite 501 Denver, Colorado 80295 and P. G. Atkinson Union Oil Co. P. 0. Box 6854 2099
THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT L. S. Mannon Atlantic Richfield Co. 1860 Lincoln Suite 501 Denver, Colorado 80295 and P. G. Atkinson Union Oil Co. P. 0. Box 6854 2099
Effect of Sorption/Curved Interface Thermodynamics on Pressure transient
 PROCEEDINGS, Twentieth Workshop on Geothermal Rey~volr Englneerlng Stanford Unhrenlty, Stanfoni, Callfornla, January 2426 1995 SGP-m-150 Effect of Sorption/Curved Interface Thermodynamics on Pressure transient
PROCEEDINGS, Twentieth Workshop on Geothermal Rey~volr Englneerlng Stanford Unhrenlty, Stanfoni, Callfornla, January 2426 1995 SGP-m-150 Effect of Sorption/Curved Interface Thermodynamics on Pressure transient
Inflow Performance 1
 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot
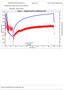 BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
The Effects of Adsorption and Desorption on Production and Reinjection in Vapor- Dominated Geothermal Fields
 Home et al The Effects of Adsorption and Desorption on Production and Reinjection in Vapor- Dominated Geothermal Fields Roland N Horne, Henry J Ramey, Jr, Shubo Shang, Antonio Correa, John Hornbrook Stanford
Home et al The Effects of Adsorption and Desorption on Production and Reinjection in Vapor- Dominated Geothermal Fields Roland N Horne, Henry J Ramey, Jr, Shubo Shang, Antonio Correa, John Hornbrook Stanford
Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE
 Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE 143613 Outline P-T diagram of Gas reservoirs Diffusion equation linearization using gas
Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE 143613 Outline P-T diagram of Gas reservoirs Diffusion equation linearization using gas
INFERRING RELATIVE PERMEABILITY FROM RESISTIVITY WELL LOGGING
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 3-February 2, 25 SGP-TR-76 INFERRING RELATIVE PERMEABILITY FROM RESISTIVITY WELL LOGGING
PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 3-February 2, 25 SGP-TR-76 INFERRING RELATIVE PERMEABILITY FROM RESISTIVITY WELL LOGGING
-338- RESERVOIR EXPLORATION/TESTING BY ELASTOMECHANICAL METHODS. Gunnar Bodvarsson, School of Oceanography, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR
 -338- RESERVOIR EXPLORATION/TESTING BY ELASTOMECHANICAL METHODS Gunnar Bodvarsson, School of Oceanography, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR Introduction The recovery of geothermal energy for power
-338- RESERVOIR EXPLORATION/TESTING BY ELASTOMECHANICAL METHODS Gunnar Bodvarsson, School of Oceanography, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR Introduction The recovery of geothermal energy for power
Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering. Texas A&M University. Lecture 07: Wellbore Phenomena
 Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS USING RESISTIVITY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
J. A. Acuna, I. Ershaghi and Y. C. Yortsos
 PROCEEDINGS, Seventeenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 1992 SGY-7l-141 FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE TRANSIENTS IN THE GEYSERS GEOTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Seventeenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 1992 SGY-7l-141 FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE TRANSIENTS IN THE GEYSERS GEOTHERMAL
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS
 NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials. These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials. These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used
PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING. December 14-15,1977
 SGPTR258 PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING December 1415,1977 *Conducted under Subcontract No. 16735 with Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Universityof California, sponsored by the
SGPTR258 PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING December 1415,1977 *Conducted under Subcontract No. 16735 with Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Universityof California, sponsored by the
Vapour Generation in Hot Permeable Rock Through Injection of Water
 .............................. -.._.._ -...~~- - PROCEEDINGS, Seventeenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 1992 SGP-m-14 1 Vapour Generation
.............................. -.._.._ -...~~- - PROCEEDINGS, Seventeenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 1992 SGP-m-14 1 Vapour Generation
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion.
 Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
ENEL. ENEL - Gruppo Minerario Larderello, Italy. At present our model considers a non-penetrating wellbore as it will
 PROGRESS REPORT ON A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A PARALLELEPIPED RESERVOIR WITH NO PENETRATING WELLBORE AND MIXED BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ENEL A. Barelli and G. Manetti Centro Ricerca Geotermica, Pisa, Italy R.
PROGRESS REPORT ON A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A PARALLELEPIPED RESERVOIR WITH NO PENETRATING WELLBORE AND MIXED BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ENEL A. Barelli and G. Manetti Centro Ricerca Geotermica, Pisa, Italy R.
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY
 GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
Trevor M. Hunta and Warwick M. %slingb
 PROCEEDINGS, Nineteenth Workshop on Geothennal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 16-2, 1994 SGP-TR-147 Estimation of reservoir permeability using gravity change measurements
PROCEEDINGS, Nineteenth Workshop on Geothennal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 16-2, 1994 SGP-TR-147 Estimation of reservoir permeability using gravity change measurements
Pressure Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL
 HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL Marcel Rosca University of Oradea, Armata Romana 5, RO-37 Oradea, Romania Key Words: low enthalpy, numerical modeling, wellbore heat transfer, Oradea reservoir,
HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL Marcel Rosca University of Oradea, Armata Romana 5, RO-37 Oradea, Romania Key Words: low enthalpy, numerical modeling, wellbore heat transfer, Oradea reservoir,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESERVOIR PRODUCTIVITY AND PORE PRESSURE DROP
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESERVOIR PRODUCTIVITY AND PORE PRESSURE DROP Musaed N. J. Al-Awad Petroleum Eng. Dept, College of Eng., King Saud University, ABSTRACT The significance of permeability sensitivity
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESERVOIR PRODUCTIVITY AND PORE PRESSURE DROP Musaed N. J. Al-Awad Petroleum Eng. Dept, College of Eng., King Saud University, ABSTRACT The significance of permeability sensitivity
A HYBRID SEMI-ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL METHOD FOR MODELING WELLBORE HEAT TRANSMISSION
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 5 SGP-TR-176 A HYBRID SEMI-ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL METHOD FOR MODELING
PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 5 SGP-TR-176 A HYBRID SEMI-ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL METHOD FOR MODELING
kt r klim 9 = - KVT (3) Karsten Pruess Earth Sciences Division Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California 94720
 Proceedings Seventh Workshop Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford, December 1981. SGP-TR-55. HEAT TRANSFER N FRACTURED GEOTHERMAL RESERVORS WTH BOLNG Karsten Pruess Earth Sciences Division Lawrence
Proceedings Seventh Workshop Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford, December 1981. SGP-TR-55. HEAT TRANSFER N FRACTURED GEOTHERMAL RESERVORS WTH BOLNG Karsten Pruess Earth Sciences Division Lawrence
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi
 A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions
 . Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
. Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
Presentation of MSc s Thesis
 Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
WITH THE FIRST ANALYSIS of a junction transistor
 Transistor Switching Analysis Dr. C. A. MEAD* With the widespread application of junction transistors in switching applications, the need for a general method of analysis useful in the region of collector
Transistor Switching Analysis Dr. C. A. MEAD* With the widespread application of junction transistors in switching applications, the need for a general method of analysis useful in the region of collector
SPE Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow
 SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
Explorative Study of NMR Drilling Fluids Measurement
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 15, 2007 Explorative Study of NMR Drilling Fluids Measurement Rizal Rismanto, Claas van der Zwaag University of Stavanger, Dep. of Petroleum Technology,
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 15, 2007 Explorative Study of NMR Drilling Fluids Measurement Rizal Rismanto, Claas van der Zwaag University of Stavanger, Dep. of Petroleum Technology,
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions
 SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
Oil and Gas Well Performance
 Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Chapter Seven. For ideal gases, the ideal gas law provides a precise relationship between density and pressure:
 Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Introduction to Well Stimulation
 Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
CONF SLUG TESTING IN WELLS WITH FINITE-THICKNESS SKIN A.F. Moench and P.A. Hsieh. U.S. Geological Survey Menlo Park, CA 94025
 .'PROCEEDINGS, Tenth Workahop on Ceothernal Rescrvuir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24. 1985 SGP-TR-84 CONF-850107-29 SLUG TESTING IN WELLS WITH FINITE-THICKNESS SKIN
.'PROCEEDINGS, Tenth Workahop on Ceothernal Rescrvuir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24. 1985 SGP-TR-84 CONF-850107-29 SLUG TESTING IN WELLS WITH FINITE-THICKNESS SKIN
WELL TEST INTERPRETATION AND PRODUCTION PREDICTION FOR WELL SD-01 IN THE SKARDDALUR LOW-TEMPERATURE FIELD, SIGLUFJÖRDUR, N-ICELAND
 GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME Reports 2011 Orkustofnun, Grensasvegur 9, Number 19 IS-108 Reykjavik, Iceland WELL TEST INTERPRETATION AND PRODUCTION PREDICTION FOR WELL SD-01 IN THE SKARDDALUR LOW-TEMPERATURE
GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME Reports 2011 Orkustofnun, Grensasvegur 9, Number 19 IS-108 Reykjavik, Iceland WELL TEST INTERPRETATION AND PRODUCTION PREDICTION FOR WELL SD-01 IN THE SKARDDALUR LOW-TEMPERATURE
A PSEUDO FUNCTION APPROACH IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 58 67 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information A PSEUDO FUNCTION APPROACH IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION ZHANGXIN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 58 67 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information A PSEUDO FUNCTION APPROACH IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION ZHANGXIN
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics
 Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks
 SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
SPE Copyright 1997, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Inc.
 SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
A Model for Parametric Analysis of Pulse Tube Losses in Pulse Tube Refrigerators
 A Model for Parametric Analysis of Pulse Tube Losses in Pulse Tube Refrigerators C. Dodson 1, 2, A. Razani 1, 2 and T. Roberts 1 1 Air Force Research Laboratory Kirtland AFB, NM 87117 2 The University
A Model for Parametric Analysis of Pulse Tube Losses in Pulse Tube Refrigerators C. Dodson 1, 2, A. Razani 1, 2 and T. Roberts 1 1 Air Force Research Laboratory Kirtland AFB, NM 87117 2 The University
Coalbed Methane Properties
 Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
The effect of heterogeneity on unsteady-state displacements
 The effect of heterogeneity on unsteady-state displacements Abstract Darryl Fenwick, Nicole Doerler, and Roland Lenormand, Institut Français du Pétrole In this paper, we discuss the effect of heterogeneity
The effect of heterogeneity on unsteady-state displacements Abstract Darryl Fenwick, Nicole Doerler, and Roland Lenormand, Institut Français du Pétrole In this paper, we discuss the effect of heterogeneity
An approximate analytical solution for non-darcy flow toward a well in fractured media
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 3, 1023, 10.1029/2001WR000713, 2002 An approximate analytical solution for non-arcy flow toward a well in fractured media Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences ivision, Lawrence
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 3, 1023, 10.1029/2001WR000713, 2002 An approximate analytical solution for non-arcy flow toward a well in fractured media Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences ivision, Lawrence
SPE Copyright 2003, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc.
 SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS
 THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
PRELIMINARY EFFORTS TO COUPLE TETRAD WITH GEOPHYSICS MODELS
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 28-30, 2002 SGP-TR-171 PRELIMINARY EFFORTS TO COUPLE TETRAD WITH GEOPHYSICS MODELS
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 28-30, 2002 SGP-TR-171 PRELIMINARY EFFORTS TO COUPLE TETRAD WITH GEOPHYSICS MODELS
A BENCHMARK CALCULATION OF 3D HORIZONTAL WELL SIMULATIONS
 INTERNATINAL JURNAL F NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MDELING Volume 1, Number 2, Pages 189 201 c 2004 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information A BENCHMARK CALCULATIN F 3D HRIZNTAL WELL SIMULATINS ZHANGIN
INTERNATINAL JURNAL F NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MDELING Volume 1, Number 2, Pages 189 201 c 2004 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information A BENCHMARK CALCULATIN F 3D HRIZNTAL WELL SIMULATINS ZHANGIN
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT
 MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT Osamah A. Al-Omair and Richard L. Christiansen Petroleum Engineering Department, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT A
MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT Osamah A. Al-Omair and Richard L. Christiansen Petroleum Engineering Department, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT A
CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION
 CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION Jericho L. P. Reyes, Chih-Ying Chen, Keen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program,
CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION Jericho L. P. Reyes, Chih-Ying Chen, Keen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program,
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION WITH RADIAL FLOW IN A FRACTURE
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION
Apparent Permeability Effective Stress Laws: Misleading Predictions Resulting from Gas Slippage, Northeastern British Columbia
 Apparent Permeability Effective Stress Laws: Misleading Predictions Resulting from Gas Slippage, Northeastern British Columbia E.A. Letham, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, ealetham@gmail.com
Apparent Permeability Effective Stress Laws: Misleading Predictions Resulting from Gas Slippage, Northeastern British Columbia E.A. Letham, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, ealetham@gmail.com
Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques
 1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
Fractional flow in radial flow systems: a study for peripheral waterflood
 J Petrol Expl Prod Technol (2016) 6:441 450 DOI 10.1007/s13202-015-0197-3 ORIGINAL PAPER - PRODUCTION ENGINEERING Fractional flow in radial flow systems: a study f peripheral waterflood Kegang Ling 1 Received:
J Petrol Expl Prod Technol (2016) 6:441 450 DOI 10.1007/s13202-015-0197-3 ORIGINAL PAPER - PRODUCTION ENGINEERING Fractional flow in radial flow systems: a study f peripheral waterflood Kegang Ling 1 Received:
Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA)
 PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. S.P. Sukhatme Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. S.P. Sukhatme Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. 18 Forced Convection-1 Welcome. We now begin our study of forced convection
Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. S.P. Sukhatme Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. 18 Forced Convection-1 Welcome. We now begin our study of forced convection
OVERVIEW OF THE WAIRAKEI-TAUHARA SUBSIDENCE INVESTIGATION PROGRAM
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31 - February 2, 2011 SGP-TR-191 OVERVIEW OF THE WAIRAKEI-TAUHARA SUBSIDENCE INVESTIGATION
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31 - February 2, 2011 SGP-TR-191 OVERVIEW OF THE WAIRAKEI-TAUHARA SUBSIDENCE INVESTIGATION
CONSIDER a simply connected magnetic body of permeability
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 50, NO. 1, JANUARY 2014 7000306 Scalar Potential Formulations for Magnetic Fields Produced by Arbitrary Electric Current Distributions in the Presence of Ferromagnetic
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 50, NO. 1, JANUARY 2014 7000306 Scalar Potential Formulations for Magnetic Fields Produced by Arbitrary Electric Current Distributions in the Presence of Ferromagnetic
Applications of Partial Differential Equations in Reservoir Simulation
 P-32 Applications of Partial Differential Equations in Reservoir Simulation Deepak Singh Summary The solution to stochastic partial differential equations may be viewed in several manners. One can view
P-32 Applications of Partial Differential Equations in Reservoir Simulation Deepak Singh Summary The solution to stochastic partial differential equations may be viewed in several manners. One can view
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Log
 Objective The development of the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) log was fueled by the desire to obtain an estimate of permeability from a continuous measurement. Previous work had relied on empirical
Objective The development of the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) log was fueled by the desire to obtain an estimate of permeability from a continuous measurement. Previous work had relied on empirical
Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques
 1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
Lab-scale Investigation of a Multi Well Enhanced Geothermal Reservoir
 PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 2018 SGP-TR-213 Lab-scale Investigation of a Multi Well Enhanced Geothermal Reservoir
PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 2018 SGP-TR-213 Lab-scale Investigation of a Multi Well Enhanced Geothermal Reservoir
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
where x represents the mass fraction of steam and % and hf the enthalpy of steam vapor and liquid water, respecively. The equation can also be
 PROCEEDINGS, Thhkmth Workshop on Gcothcrmal R-oir Stanford University. Stanford, California, Jmuq 19-21, 1988 SOP-TR-113 EnginariDg CONPRE88IBILITY ARID 8089IC VELOCITY IN BTEAn/WATER NIXTVRES Sigurgeir
PROCEEDINGS, Thhkmth Workshop on Gcothcrmal R-oir Stanford University. Stanford, California, Jmuq 19-21, 1988 SOP-TR-113 EnginariDg CONPRE88IBILITY ARID 8089IC VELOCITY IN BTEAn/WATER NIXTVRES Sigurgeir
Carbon Sequestration in Basalts: Laboratory Studies and Field Demonstration
 Carbon Sequestration in Basalts: Laboratory Studies and Field Demonstration H. T. Schaef B.P. McGrail Workshop on Geologic Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Stanford University November 28, 2017 Needles
Carbon Sequestration in Basalts: Laboratory Studies and Field Demonstration H. T. Schaef B.P. McGrail Workshop on Geologic Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Stanford University November 28, 2017 Needles
Thermal diffusion effect on MHD free convection flow of stratified viscous fluid with heat and mass transfer
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 03, 4():-9 ISSN: 0976-860 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Thermal diffusion effect on MHD free convection flow of stratified
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 03, 4():-9 ISSN: 0976-860 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Thermal diffusion effect on MHD free convection flow of stratified
PRELIMINARY REPORT. Evaluations of to what extent CO 2 accumulations in the Utsira formations are possible to quantify by seismic by August 1999.
 SINTEF Petroleumsforskning AS SINTEF Petroleum Research N-7465 Trondheim, Norway Telephone: +47 73 59 11 Fax: +477359112(aut.) Enterprise no.: NO 936 882 331 MVA TITLE PRELIMINARY REPORT Evaluations of
SINTEF Petroleumsforskning AS SINTEF Petroleum Research N-7465 Trondheim, Norway Telephone: +47 73 59 11 Fax: +477359112(aut.) Enterprise no.: NO 936 882 331 MVA TITLE PRELIMINARY REPORT Evaluations of
18 Single vertical fractures
 18 Single vertical fractures 18.1 Introduction If a well intersects a single vertical fracture, the aquifer s unsteady drawdown response to pumping differs significantly from that predicted by the Theis
18 Single vertical fractures 18.1 Introduction If a well intersects a single vertical fracture, the aquifer s unsteady drawdown response to pumping differs significantly from that predicted by the Theis
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL. A Thesis ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL
 TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
THE EFFECT OF THERMOELASTIC STRESS CHANGE IN THE NEAR WELLBORE REGION ON HYDRAULIC FRACTURE GROWTH
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, 30 Jan 2011-1 Feb 2012 THE EFFECT OF THERMOELASTIC STRESS CHANGE IN THE NEAR WELLBORE
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, 30 Jan 2011-1 Feb 2012 THE EFFECT OF THERMOELASTIC STRESS CHANGE IN THE NEAR WELLBORE
GeothermEx, Inc. GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION HOLE PROGRAM, KILAUEA EAST RIFT ZONE, HAWAII TASK 1 REPORT
 (415) 527 9876 CABLE ADDRESS- GEOTHERMEX TELEX 709152 STEAM UD FAX (415) 527-8164 Geotherm Ex, Inc. RICHMOND. CALIFORNIA 94804-5829 GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION
(415) 527 9876 CABLE ADDRESS- GEOTHERMEX TELEX 709152 STEAM UD FAX (415) 527-8164 Geotherm Ex, Inc. RICHMOND. CALIFORNIA 94804-5829 GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION
Phenomenological Modeling of Critical Condensate Saturation and Relative Permeabilities in Gas/ Condensate Systems
 Phenomenological Modeling of Critical Condensate Saturation and Relative Permeabilities in Gas/ Condensate Systems Kewen Li, SPE, and Abbas Firoozabadi, SPE, Reservoir Engineering Research Inst. Summary
Phenomenological Modeling of Critical Condensate Saturation and Relative Permeabilities in Gas/ Condensate Systems Kewen Li, SPE, and Abbas Firoozabadi, SPE, Reservoir Engineering Research Inst. Summary
Non-Darcy Skin Effect with a New Boundary Condition
 International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
Correlation Between Resistivity Index, Capillary Pressure and Relative Permeability
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 Correlation Between Resistivity Index, Capillary Pressure and Kewen Li Stanford Geothermal Program, Stanford University, Stanford,
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 Correlation Between Resistivity Index, Capillary Pressure and Kewen Li Stanford Geothermal Program, Stanford University, Stanford,
Dimensionless Wellbore Storage Coefficient: Skin Factor: Notes:
 This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
Introduction to Formation Evaluation Abiodun Matthew Amao
 Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC FRACTURE NETWORK MODEL FOR GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR STIMULATION
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31 - February 2, 2011 SGP-TR-191 A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC FRACTURE NETWORK
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31 - February 2, 2011 SGP-TR-191 A THREE-DIMENSIONAL STOCHASTIC FRACTURE NETWORK
Numerical Simulation of Devolution and Evolution of Steam-Water Two-Phase Zone in a Fractured Geothermal Reservoir at Ogiri, Japan
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Numerical Simulation of Devolution and Evolution of Steam-Water Two-Phase Zone in a Fractured Geothermal Reservoir at Ogiri, Japan Yohei Tateishi 1, Ryuichi Itoi 1, Toshiaki
GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Numerical Simulation of Devolution and Evolution of Steam-Water Two-Phase Zone in a Fractured Geothermal Reservoir at Ogiri, Japan Yohei Tateishi 1, Ryuichi Itoi 1, Toshiaki
MOMENTUM TRANSPORT Velocity Distributions in Turbulent Flow
 TRANSPORT PHENOMENA MOMENTUM TRANSPORT Velocity Distributions in Turbulent Flow Introduction to Turbulent Flow 1. Comparisons of laminar and turbulent flows 2. Time-smoothed equations of change for incompressible
TRANSPORT PHENOMENA MOMENTUM TRANSPORT Velocity Distributions in Turbulent Flow Introduction to Turbulent Flow 1. Comparisons of laminar and turbulent flows 2. Time-smoothed equations of change for incompressible
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks
 Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
WETTABILITY CHANGE TO GAS-WETNESS IN POROUS MEDIA
 WETTABILITY CHANGE TO GAS-WETNESS IN POROUS MEDIA Kewen Li and Abbas Firoozabadi Reservoir Engineering Research Institute (RERI) Abstract In the petroleum literature, gas is assumed to be the non-wetting
WETTABILITY CHANGE TO GAS-WETNESS IN POROUS MEDIA Kewen Li and Abbas Firoozabadi Reservoir Engineering Research Institute (RERI) Abstract In the petroleum literature, gas is assumed to be the non-wetting
Theory - SBRC fundamentals
 Chapter 2 Theory - SBRC fundamentals The approach proposed to estimate hydraulic properties of rocks using microseismicity is called Seismicity Based Reservoir Characterization (SBRC). It uses a spatio-temporal
Chapter 2 Theory - SBRC fundamentals The approach proposed to estimate hydraulic properties of rocks using microseismicity is called Seismicity Based Reservoir Characterization (SBRC). It uses a spatio-temporal
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DEEPENED WELLS 420DA AND 517DA IN THE LEYTE GEOTHERMAL PRODUCTION FIELD, PHILIPPINES
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 213 SGP-TR-198 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DEEPENED WELLS 42DA AND 517DA
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 213 SGP-TR-198 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DEEPENED WELLS 42DA AND 517DA
TEMPERATURE LOGGING IN PERFORATED WELLS
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-First Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30-February 1, 2006 SGP-TR-179 TEMPERATURE LOGGING IN PERFORATED WELLS Per-Gunnar
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-First Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30-February 1, 2006 SGP-TR-179 TEMPERATURE LOGGING IN PERFORATED WELLS Per-Gunnar
Comparison of Using Combination of Acetic Acid and Hydrochloric Acid with Only Hydrochloric Acid as Matrix Pre Flush
 International Journal of Petroleum and Geoscience Engineering (IJPGE), 1 ISSN xxxx-xxxx Academic Research Online Publisher Research Article Comparison of Using Combination of Acetic Acid and Hydrochloric
International Journal of Petroleum and Geoscience Engineering (IJPGE), 1 ISSN xxxx-xxxx Academic Research Online Publisher Research Article Comparison of Using Combination of Acetic Acid and Hydrochloric
Waterflooding Performance of Communicating Stratified Reservoirs With Log-Normal Permeability Distribution
 Waterflooding Performance of Communicating Stratified Reservoirs With Log-Normal Permeability Distribution Noaman El-Khatib, SPE, King Saud U. Summary An analytical solution is developed for waterflooding
Waterflooding Performance of Communicating Stratified Reservoirs With Log-Normal Permeability Distribution Noaman El-Khatib, SPE, King Saud U. Summary An analytical solution is developed for waterflooding
INJECTION, CONDUCTION AND PRODUCTION
 Chapter III Injection, Conduction and Production Chapter III From a physical point of view strictly steady-state conditions of heterogeneous-fluid flow in oil-producing systems are virtually never encountered.
Chapter III Injection, Conduction and Production Chapter III From a physical point of view strictly steady-state conditions of heterogeneous-fluid flow in oil-producing systems are virtually never encountered.
CONSOLIDATION OF SOIL
 Lecture-6 Soil consolidation Dr. Attaullah Shah 1 CONSOLIDATION OF SOIL When a soil mass is subjected to a compressive force there is a decrease in volume of soil mass. The reduction in volume of a saturated
Lecture-6 Soil consolidation Dr. Attaullah Shah 1 CONSOLIDATION OF SOIL When a soil mass is subjected to a compressive force there is a decrease in volume of soil mass. The reduction in volume of a saturated
The failure of the sounding assumption in electroseismic investigations
 The failure of the sounding assumption in electroseismic investigations F.D. Fourie, J.F. Botha Institute for Groundwater Studies, University of the Free State, PO Box 339, Bloemfontein, 9300, South Africa
The failure of the sounding assumption in electroseismic investigations F.D. Fourie, J.F. Botha Institute for Groundwater Studies, University of the Free State, PO Box 339, Bloemfontein, 9300, South Africa
C. R. McKee and M. E. Hanson Lawrence Livermore Laboratory University of California Livermore, California 94550
 PREDICTING EXPLOSION-GENERATED PERMEABILITY AROUND GEOTHERMAL WELLS C. R. McKee and M. E. Hanson Lawrence Livermore Laboratory University of California Livermore, California 94550 The problem of stimulating
PREDICTING EXPLOSION-GENERATED PERMEABILITY AROUND GEOTHERMAL WELLS C. R. McKee and M. E. Hanson Lawrence Livermore Laboratory University of California Livermore, California 94550 The problem of stimulating
PROBING THE CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN PORES IN ROCK CORE SAMPLES
 SCA2007-42 1/6 PROBING THE CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN PORES IN ROCK CORE SAMPLES Geir Humborstad Sørland 1,3, Ketil Djurhuus 3, Hege Christin Widerøe 2, Jan R. Lien 3, Arne Skauge 3, 1 Anvendt Teknologi AS,
SCA2007-42 1/6 PROBING THE CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN PORES IN ROCK CORE SAMPLES Geir Humborstad Sørland 1,3, Ketil Djurhuus 3, Hege Christin Widerøe 2, Jan R. Lien 3, Arne Skauge 3, 1 Anvendt Teknologi AS,
