( ) ( ) SALCs as basis functions. LCAO-MO Theory. Rewriting the Schrödinger Eqn. Matrix form of Schrödinger Eqn. Hφ j. φ 1. φ 3. φ 2. φ j. φ i.
|
|
|
- Brice Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LCAO-MO Theory In molecular orbital theory the MOs, { }, are usually expanded as combinations of atomic orbitals, {φ i }. For the µ th MO, we write this expansion as = c iµ φ i = c 1µ φ 1 + c µ φ + c 3µ φ 3 +! i The MOs are solutions to an effective Schrödinger equation: H = E µ Read: Harris & Bertolucci, Symmetry and Spectroscopy..., Chapter 4, pp SALCs as basis functions Instead of AO basis functions, we can use precombined SALCs as basis functions. So, when we write the expansion = c iµ φ i = c 1µ φ 1 + c µ φ + c 3µ φ 3 +! i the basis, {φ 1, φ, }, may be AOs or they may be SALCs. The ultimate form of the MOs won t change, but the coefficients in this expansion will depend on the basis. Example: Express π MOs for allyl in AO and SALC bases. Rewriting the Schrödinger Eqn. H = E µ H = (H ) Now, we introduce the LCAO expansion, = c µ φ = c 1µ φ 1 + c µ φ + c 3µ φ 3 +! So we obtain a different form of the eqn.: = c µ (H )φ (H ) c µ φ Matrix form of Schrödinger Eqn. c µ (H )φ Mult. on the left by φ i and integrate: ( ) c µ φ i Hφ dτ φ i φ dτ H i Hφ dτ S i φ dτ ( ) c µ H i S i For a proper treatment using variational method, see for example Levine s Quantum Chemistry text.
2 Matrix Schrödinger Eqn., cont. (H) i = H i ( H i S i ) c µ in matrix form, this can be written as [H S]c µ or Hc µ = E µ Sc µ where the matrix elements are φ i Hφ dτ (S) i = S i φ i φ dτ A 3 basis function example ( )c 1µ + ( H 1 S 1 )c µ + ( H 13 S 13 )c 3µ ( H 1 S 1 )c 1µ + ( )c µ + ( H 3 S 3 )c 3µ ( H 31 S 31 )c 1µ + ( H 3 S 3 )c µ + ( H 33 )c 3µ H 1 S 1 H 13 S 13 H 1 S 1 H 3 S 3 H 31 S 31 H 3 S 3 H 33 This is called the Secular Equation. c 1µ c µ c 3µ = SALCs as the Expansion Basis Previously, we introduced the LCAO expansion, = c µ φ = c 1µφ 1 + c µ φ + c 3µ φ 3 +! If the functions {φ } are "precombined" SALCs, then the basis functions belong to irred. reps. We can use what we know about zero - value integrals H i Hφ dτ and S i φ dτ if Γ i Γ contains the totally symmetric representation. φ i and φ must belong to the same IR. The Matrix Equation when the basis is the set of MOs If we choose the MOs as basis functions to begin with, the equation simplifies drastically: H i = E i δ i for all i and S i = δ i E 1! c 1µ E! c µ = " " # " " "! E m E µ c mµ When E µ = one of the E i, the matrix is singular
3 What s the use of Group Theory? Using SALCs as a basis simplifies the Secular Eqn. For example, when SALCs are used as the basis functions, the secular equation for H O becomes: H 1 S 1 H 13 S 13 H 1 S 1 H 3 S 3 H 31 S 31 H 65 S 65 H 33 H 44 H 55 H 56 S 56 H 65 S 65 H 66 c 1µ c µ c 3µ c 4µ c 5µ c 6µ = Example, Usefulness of SALCs In the pictorial construction of the MOs of water given earlier, how many H i s would have been zero if we had used AOs (on the O atom and both H atoms) for the basis functions? How many are nonzero with the SALCs that were used? (Note: H i s involving two AOs centered on the same atom are automatically zero) Another Example Naphthalene π-orbital SALCs In problem 6.1, we constructed SALCs for the π orbitals of naphthalene. The IRs spanned by the pπ orbitals were ( 3), B 3g ( 3), B g ( ), A u ( ) If we used the pπ orbitals as our AO basis in the secular eqn., we would have had one 1 1 matrix eqn. Using SALCs, we have two 3 3 s (for and B 3g ) and two s (for B g and A u ). B 3g B g A u B 3g B3g B g A u
4 H 1 B1u H 13 H 1 H 3 H 31 H 3 H 33 Form of the Naphthalene π Orbital Secular Equation H 44 B3g H 45 H 46 H 54 H 55 H 56 H 64 H 65 H 66 Au H 77 H 78 H 87 H 88 Bg H 99 H 9,1 H 1,9 H 1,1 The Content and Solutions of the Secular Equation We need to calculate or estimate the matrix elements (the H i s and S i s) Once the matrix elements are known, we need to find solutions of the secular equation energies are found by finding the roots of the secular determinant eigenfunctions (the MO coefficients) are found by plugging the energies back into the secular eqn. The Crudest Approximation: In the Hückel approximation (applied to π systems where all the atoms are of the same type) the following substitutions are made (in this case the basis functions are understood to be AOs, not SALCs): a. H ii = α (can choose, if all atoms carbon) b. H i = β if i and are neighbors c. H i otherwise d. S ii = 1 (normalization) and S i Neglect of Overlap: Consequences A general secular determinant is E H 1 ES 1 H 1 ES 1 E expanding the determinant gives E H + H H S S 1 E + H H H S 1 solutions are of the form: E ± = b ± D (1 S 1 ) ; b = + H 1 S 1 ; D = b 4(1 S 1 )( H 1 )
5 Neglect of Overlap: Consequences A secular determinant w/o overlap is E H 1 H 1 E expanding the determinant gives Neglect of Overlap: Consequences E+ destabilization E+ E + E + H 1 solutions are of the form: E ± = b ± D ; b = + ; D = ( ) + 4H 1 E- Neglect of Overlap Overlap Included stabilization destabilization = E- stabilization destabilization > stabilization Examples Trivial example: ethylene π orbitals Cyclopropenium ion benzene Hückel π bond-order resonance other C N symmetry systems T N symmetry systems D 6h E C 6 C 3 C 3C 3C i S 3 S 6 σ h 3σ d 3σ v A 1g x + y, z A g R z B 1g B g E 1g (R x, R y ) (xz, yz) E g (x y,xy) A 1u A u z B u E 1u (x, y) E u
6 Fixing Accidental Degeneracies Spin Density for Benzyl Radical Use Change button, then click the atoms shown, then type in.1 for the alpha value, then click Ok! Turn on Verbose option, then read coefficients!
$ +! j. % i PERTURBATION THEORY AND SUBGROUPS (REVISED 11/15/08)
 PERTURBATION THEORY AND SUBGROUPS REVISED 11/15/08) The use of groups and their subgroups is of much importance when perturbation theory is employed in understanding molecular orbital theory and spectroscopy
PERTURBATION THEORY AND SUBGROUPS REVISED 11/15/08) The use of groups and their subgroups is of much importance when perturbation theory is employed in understanding molecular orbital theory and spectroscopy
PAPER:2, PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY-I QUANTUM CHEMISTRY. Module No. 34. Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Application PART IV
 Subject PHYSICAL Paper No and Title TOPIC Sub-Topic (if any), PHYSICAL -II QUANTUM Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Module No. 34 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes. Hückel Molecular Orbital (HMO) Theory
Subject PHYSICAL Paper No and Title TOPIC Sub-Topic (if any), PHYSICAL -II QUANTUM Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Module No. 34 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes. Hückel Molecular Orbital (HMO) Theory
Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Application PART III
 Subject PHYSICAL Paper No and Title TOPIC Sub-Topic (if any) 2, PHYSICAL -I QUANTUM Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Module No. 33 PAPER: 2, PHYSICAL -I TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Hückel
Subject PHYSICAL Paper No and Title TOPIC Sub-Topic (if any) 2, PHYSICAL -I QUANTUM Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Module No. 33 PAPER: 2, PHYSICAL -I TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Hückel
Module:32,Huckel Molecular Orbital theory- Application Part-II PAPER: 2, PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY-I QUANTUM CHEMISTRY
 Subject PHYSICAL Paper No and Title TOPIC Sub-Topic (if any) 2, PHYSICAL -I QUANTUM Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Application PART II Module No. 32 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Hückel Molecular
Subject PHYSICAL Paper No and Title TOPIC Sub-Topic (if any) 2, PHYSICAL -I QUANTUM Hückel Molecular orbital Theory Application PART II Module No. 32 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Hückel Molecular
Chemistry 431. Lecture 14. Wave functions as a basis Diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules Huckel theory. NC State University
 Chemistry 431 Lecture 14 Wave functions as a basis Diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules Huckel theory NC State University Wave functions as the basis for irreducible representations The energy of the
Chemistry 431 Lecture 14 Wave functions as a basis Diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules Huckel theory NC State University Wave functions as the basis for irreducible representations The energy of the
Molecular Orbital Theory
 Molecular Orbital Theory While FMO theory allows prediction of reactions (by thermodynamics, regio or stereochemistry), all predictions seen so far have been qualitative We have predicted that HOMO or
Molecular Orbital Theory While FMO theory allows prediction of reactions (by thermodynamics, regio or stereochemistry), all predictions seen so far have been qualitative We have predicted that HOMO or
Chapter 3. Orbitals and Bonding
 Chapter 3. Orbitals and Bonding What to master Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals Constructing Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals with Simple MO Theory Understanding Sigma and Pi Bonds Identifying
Chapter 3. Orbitals and Bonding What to master Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals Constructing Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals with Simple MO Theory Understanding Sigma and Pi Bonds Identifying
Lecture 12. Symmetry Operations. NC State University
 Chemistry 431 Lecture 12 Group Theory Symmetry Operations NC State University Wave functions as the basis for irreducible representations The energy of the system will not change when symmetry Operations
Chemistry 431 Lecture 12 Group Theory Symmetry Operations NC State University Wave functions as the basis for irreducible representations The energy of the system will not change when symmetry Operations
Quantum Mechanical Operators and Wavefunctions. Orthogonality of Wavefunctions. Commuting Operators have Common Eigenfunctions
 Quantum Mechanical perators and Wavefunctions "well behaved" functions (φ), have the following properties must be continuous (no "breaks") must have continuous derivatives (no "kinks") must be normalizable.
Quantum Mechanical perators and Wavefunctions "well behaved" functions (φ), have the following properties must be continuous (no "breaks") must have continuous derivatives (no "kinks") must be normalizable.
3: Many electrons. Orbital symmetries. l =2 1. m l
 3: Many electrons Orbital symmetries Atomic orbitals are labelled according to the principal quantum number, n, and the orbital angular momentum quantum number, l. Electrons in a diatomic molecule experience
3: Many electrons Orbital symmetries Atomic orbitals are labelled according to the principal quantum number, n, and the orbital angular momentum quantum number, l. Electrons in a diatomic molecule experience
Electronic Structure Models
 Electronic Structure Models Hückel Model (1933) Basic Assumptions: (a) One orbital per atom contributes to the basis set; all orbitals "equal" (b) The relevant integrals involving the Hamiltonian are α
Electronic Structure Models Hückel Model (1933) Basic Assumptions: (a) One orbital per atom contributes to the basis set; all orbitals "equal" (b) The relevant integrals involving the Hamiltonian are α
σ u * 1s g - gerade u - ungerade * - antibonding σ g 1s
 One of these two states is a repulsive (dissociative) state. Other excited states can be constructed using linear combinations of other orbitals. Some will be binding and others will be repulsive. Thus
One of these two states is a repulsive (dissociative) state. Other excited states can be constructed using linear combinations of other orbitals. Some will be binding and others will be repulsive. Thus
Same idea for polyatomics, keep track of identical atom e.g. NH 3 consider only valence electrons F(2s,2p) H(1s)
 XIII 63 Polyatomic bonding -09 -mod, Notes (13) Engel 16-17 Balance: nuclear repulsion, positive e-n attraction, neg. united atom AO ε i applies to all bonding, just more nuclei repulsion biggest at low
XIII 63 Polyatomic bonding -09 -mod, Notes (13) Engel 16-17 Balance: nuclear repulsion, positive e-n attraction, neg. united atom AO ε i applies to all bonding, just more nuclei repulsion biggest at low
5.4. Electronic structure of water
 5.4. Electronic structure of water Water belongs to C 2v point group, we have discussed the corresponding character table. Here it is again: C 2v E C 2 σ v (yz) σ v (xz) A 1 1 1 1 1 A 2 1 1-1 -1 B 1 1-1
5.4. Electronic structure of water Water belongs to C 2v point group, we have discussed the corresponding character table. Here it is again: C 2v E C 2 σ v (yz) σ v (xz) A 1 1 1 1 1 A 2 1 1-1 -1 B 1 1-1
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, November 29, 2007
 Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, November 29, 2007 (1) Trigonal prismatic coordination is fairly common in solid-state inorganic chemistry. In most cases the geometry of the trigonal prism is such
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, November 29, 2007 (1) Trigonal prismatic coordination is fairly common in solid-state inorganic chemistry. In most cases the geometry of the trigonal prism is such
PRACTICE PROBLEMS Give the electronic configurations and term symbols of the first excited electronic states of the atoms up to Z = 10.
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 2 1. Based on your knowledge of the first few hydrogenic eigenfunctions, deduce general formulas, in terms of n and l, for (i) the number of radial nodes in an atomic orbital (ii) the
PRACTICE PROBLEMS 2 1. Based on your knowledge of the first few hydrogenic eigenfunctions, deduce general formulas, in terms of n and l, for (i) the number of radial nodes in an atomic orbital (ii) the
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
1 r A. r B. 2m e. The potential energy of the electron is. r A and r B are the electron s distances from the nuclei A and B. This expression can be
 Introduction to Molecular Structure The Born-Oppenheimer approximation The Born-Oppenheimer approximation supposes that the nuclei, being so much heavier than the electron, move relatively slow and may
Introduction to Molecular Structure The Born-Oppenheimer approximation The Born-Oppenheimer approximation supposes that the nuclei, being so much heavier than the electron, move relatively slow and may
On the Uniqueness of Molecular Orbitals and limitations of the MO-model.
 On the Uniqueness of Molecular Orbitals and limitations of the MO-model. The purpose of these notes is to make clear that molecular orbitals are a particular way to represent many-electron wave functions.
On the Uniqueness of Molecular Orbitals and limitations of the MO-model. The purpose of these notes is to make clear that molecular orbitals are a particular way to represent many-electron wave functions.
AN INTRODUCTION TO MOLECULAR ORBITALS
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MOLECULAR ORBITALS by YVES JEAN and FRANCOIS VOLATRON translated and edited by Jeremy Burdett New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents Introduction, xiii I INTRODUCTION
AN INTRODUCTION TO MOLECULAR ORBITALS by YVES JEAN and FRANCOIS VOLATRON translated and edited by Jeremy Burdett New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 Contents Introduction, xiii I INTRODUCTION
Electronic structure of solids
 Electronic structure of solids Eigenvalue equation: Áf(x) = af(x) KNOWN: Á is an operator. UNKNOWNS: f(x) is a function (and a vector), an eigenfunction of Á; a is a number (scalar), the eigenvalue. Ackowledgement:
Electronic structure of solids Eigenvalue equation: Áf(x) = af(x) KNOWN: Á is an operator. UNKNOWNS: f(x) is a function (and a vector), an eigenfunction of Á; a is a number (scalar), the eigenvalue. Ackowledgement:
Chem120a : Exam 3 (Chem Bio) Solutions
 Chem10a : Exam 3 (Chem Bio) Solutions November 7, 006 Problem 1 This problem will basically involve us doing two Hückel calculations: one for the linear geometry, and one for the triangular geometry. We
Chem10a : Exam 3 (Chem Bio) Solutions November 7, 006 Problem 1 This problem will basically involve us doing two Hückel calculations: one for the linear geometry, and one for the triangular geometry. We
CHAPTER 11 MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY
 CHAPTER 11 MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Molecular orbital theory is a conceptual extension of the orbital model, which was so successfully applied to atomic structure. As was once playfuly remarked, a molecue
CHAPTER 11 MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Molecular orbital theory is a conceptual extension of the orbital model, which was so successfully applied to atomic structure. As was once playfuly remarked, a molecue
Chemistry 3502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2003 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 25, November 5, 2003
 Chemistry 3502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2003 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 25, November 5, 2003 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Chemistry 3502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2003 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 25, November 5, 2003 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Molecular Orbital Theory
 Junior Sophister Quantum Chemistry Course 333 (Part) Molecular Orbital Theory D.A.Morton-Blake Molecular orbital theory We have seen how the atomic orbital wave function provides a complete description
Junior Sophister Quantum Chemistry Course 333 (Part) Molecular Orbital Theory D.A.Morton-Blake Molecular orbital theory We have seen how the atomic orbital wave function provides a complete description
Symmetry III: Molecular Orbital Theory. Reading: Shriver and Atkins and , 6.10
 Lecture 9 Symmetry III: Molecular Orbital Theory Reading: Shriver and Atkins 2.7-2.9 and g 6.6-6.7, 6.10 The orbitals of molecules H H The electron energy in each H atom is -13.6 ev below vacuum. What
Lecture 9 Symmetry III: Molecular Orbital Theory Reading: Shriver and Atkins 2.7-2.9 and g 6.6-6.7, 6.10 The orbitals of molecules H H The electron energy in each H atom is -13.6 ev below vacuum. What
Molecular orbitals for σbonding in T d complexes
 Molecular orbitals for σbonding in T d complexes The set of n A B σ bonds in AB n (T d n = 4) molecules are often thought of as independent entities. The concept of MO s allows us to begin with a very
Molecular orbitals for σbonding in T d complexes The set of n A B σ bonds in AB n (T d n = 4) molecules are often thought of as independent entities. The concept of MO s allows us to begin with a very
Lecture 26: Qualitative Molecular Orbital Theory: Hückel Theory
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 5.6 Physical Chemistry I Fall, 07 Professor Robert W. Field Lecture 6: Qualitative Molecular Orbital Theory: Hückel Theory Models in Physical Chemistry Our job is
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 5.6 Physical Chemistry I Fall, 07 Professor Robert W. Field Lecture 6: Qualitative Molecular Orbital Theory: Hückel Theory Models in Physical Chemistry Our job is
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Group Theory: Matrix Representation & Consequences of Symmetry
 Group Theory: Matrix Representation & Consequences of Symmetry Matrix Representation of Group Theory Reducible and Irreducible Representations The Great Orthogonality Theorem The ive Rules The Standard
Group Theory: Matrix Representation & Consequences of Symmetry Matrix Representation of Group Theory Reducible and Irreducible Representations The Great Orthogonality Theorem The ive Rules The Standard
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, December 2, 2008
 Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, December 2, 2008 (1) (a) Trigonal bipyramidal (tbp) coordination is fairly common. Calculate the group overlaps of the appropriate SALCs for a tbp with the 5 d-orbitals
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, December 2, 2008 (1) (a) Trigonal bipyramidal (tbp) coordination is fairly common. Calculate the group overlaps of the appropriate SALCs for a tbp with the 5 d-orbitals
Symmetry. Chemistry 481(01) Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Upali Siriwardane Office: CTH 311 Phone Office Hours:
 Chemistry 481(01) Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Upali Siriwardane e-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: CT 311 Phone 257-4941 Office ours: M,W 8:00-9:00 & 11:00-12:00 am; Tu,Th, F 9:30-11:30 a.m. April 4, 2017:
Chemistry 481(01) Spring 2017 Instructor: Dr. Upali Siriwardane e-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: CT 311 Phone 257-4941 Office ours: M,W 8:00-9:00 & 11:00-12:00 am; Tu,Th, F 9:30-11:30 a.m. April 4, 2017:
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, December 1, 2005
 otton, Problem 9.3 (assume D 4h symmetry) Additional Problems: hem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, December 1, 2005 (1) Infrared and Raman spectra of Benzene (a) Determine the symmetries (irreducible
otton, Problem 9.3 (assume D 4h symmetry) Additional Problems: hem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, December 1, 2005 (1) Infrared and Raman spectra of Benzene (a) Determine the symmetries (irreducible
On semiempirical treatment of hydrocarbons
 On semiempirical treatment of hydrocarbons Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics, IInd Year Chennai Mathematical Institute 27..2009 Abstract As, we do in case of small systems like H + 2 or He atom, we write
On semiempirical treatment of hydrocarbons Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics, IInd Year Chennai Mathematical Institute 27..2009 Abstract As, we do in case of small systems like H + 2 or He atom, we write
7: Hückel theory for polyatomic molecules
 7: ückel theory for polyatomic molecules Introduction Approximate treatment of π electron systems in organic molecules: 1 Approximations 3 4 5 6 1. π and σ frameworks completely separated. Trial wavefunctions
7: ückel theory for polyatomic molecules Introduction Approximate treatment of π electron systems in organic molecules: 1 Approximations 3 4 5 6 1. π and σ frameworks completely separated. Trial wavefunctions
The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then
 1 The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then filled with the available electrons according to
1 The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then filled with the available electrons according to
Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy
 Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy Molecular Orbital Theory: A Review - LCAO approximaton & AO overlap - Variation Principle & Secular Determinant - Homonuclear Diatomic MOs - Energy Levels, Bond Order
Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy Molecular Orbital Theory: A Review - LCAO approximaton & AO overlap - Variation Principle & Secular Determinant - Homonuclear Diatomic MOs - Energy Levels, Bond Order
This is called a singlet or spin singlet, because the so called multiplicity, or number of possible orientations of the total spin, which is
 9. Open shell systems The derivation of Hartree-Fock equations (Chapter 7) was done for a special case of a closed shell systems. Closed shell means that each MO is occupied by two electrons with the opposite
9. Open shell systems The derivation of Hartree-Fock equations (Chapter 7) was done for a special case of a closed shell systems. Closed shell means that each MO is occupied by two electrons with the opposite
Calculation of band structure using group theory. Sudeep Kumar Ghosh, Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore.
 Calculation of band structure using group theory Sudeep Kumar Ghosh, Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Plan of the talk Brief overview of the representation theory and the
Calculation of band structure using group theory Sudeep Kumar Ghosh, Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Plan of the talk Brief overview of the representation theory and the
VALENCE Hilary Term 2018
 VALENCE Hilary Term 2018 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
VALENCE Hilary Term 2018 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
Ψ g = N g (1s a + 1s b ) Themes. Take Home Message. Energy Decomposition. Multiple model wave fns possible. Begin describing brain-friendly MO
 Themes Multiple model wave fns possible Different explanations of bonding Some you have seen before Errors vary (not consistently better or worse) Convenience varies Brain v. algebra v. computer Where
Themes Multiple model wave fns possible Different explanations of bonding Some you have seen before Errors vary (not consistently better or worse) Convenience varies Brain v. algebra v. computer Where
The Hückel Approximation Consider a conjugated molecule i.e. a molecule with alternating double and single bonds, as shown in Figure 1.
 The Hückel Approximation In this exercise you will use a program called Hückel to look at the p molecular orbitals in conjugated molecules. The program calculates the energies and shapes of p (pi) molecular
The Hückel Approximation In this exercise you will use a program called Hückel to look at the p molecular orbitals in conjugated molecules. The program calculates the energies and shapes of p (pi) molecular
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Chapter 10.8, Morrison and Boyd
 MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Chapter 10.8, Morrison and Boyd more understanding: why oxygen is paramagnetic, why H2 + exists; explanation of excited electronic states (e.g., visible spectra) eliminates need
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Chapter 10.8, Morrison and Boyd more understanding: why oxygen is paramagnetic, why H2 + exists; explanation of excited electronic states (e.g., visible spectra) eliminates need
Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory
 Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory In this section, the conceptual framework of molecular orbital theory is developed. Applications are presented and problems are given and solved within qualitative
Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory In this section, the conceptual framework of molecular orbital theory is developed. Applications are presented and problems are given and solved within qualitative
26 Group Theory Basics
 26 Group Theory Basics 1. Reference: Group Theory and Quantum Mechanics by Michael Tinkham. 2. We said earlier that we will go looking for the set of operators that commute with the molecular Hamiltonian.
26 Group Theory Basics 1. Reference: Group Theory and Quantum Mechanics by Michael Tinkham. 2. We said earlier that we will go looking for the set of operators that commute with the molecular Hamiltonian.
Orbital Alignments. March 25, 2003
 Orbital Alignments March 25, 2003 1 Introduction In discussions of twisted ethylene derivatives, Figure 1, and similar discussions concerning Woodward Hoffman rules 1 the cos χ (χ is the twist angle dependence
Orbital Alignments March 25, 2003 1 Introduction In discussions of twisted ethylene derivatives, Figure 1, and similar discussions concerning Woodward Hoffman rules 1 the cos χ (χ is the twist angle dependence
NH 3 H 2 O N 2. Why do they make chemical bonds? Molecular Orbitals
 N 2 NH 3 H 2 O Why do they make chemical bonds? 5 Molecular Orbitals Why do they make chemical bonds? Stabilization Bond energy Types of Chemical Bonds Metallic Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Covalent Bond
N 2 NH 3 H 2 O Why do they make chemical bonds? 5 Molecular Orbitals Why do they make chemical bonds? Stabilization Bond energy Types of Chemical Bonds Metallic Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Covalent Bond
Chem Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions
 Page 1 of 10 Chem 370 - Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions 5.1 Additional combinations are p z ± d z 2, p x ±d xz, and p y ±d yz. p z ± d z 2 p x ±d xz or p y ±d yz 5.2 a. Li 2 has the configuration
Page 1 of 10 Chem 370 - Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions 5.1 Additional combinations are p z ± d z 2, p x ±d xz, and p y ±d yz. p z ± d z 2 p x ±d xz or p y ±d yz 5.2 a. Li 2 has the configuration
CHEMISTRY Topic #1: Bonding What Holds Atoms Together? Spring 2012 Dr. Susan Lait
 CHEMISTRY 2000 Topic #1: Bonding What Holds Atoms Together? Spring 2012 Dr. Susan Lait Why Do Bonds Form? An energy diagram shows that a bond forms between two atoms if the overall energy of the system
CHEMISTRY 2000 Topic #1: Bonding What Holds Atoms Together? Spring 2012 Dr. Susan Lait Why Do Bonds Form? An energy diagram shows that a bond forms between two atoms if the overall energy of the system
Experiment 15: Atomic Orbitals, Bond Length, and Molecular Orbitals
 Experiment 15: Atomic Orbitals, Bond Length, and Molecular Orbitals Introduction Molecular orbitals result from the mixing of atomic orbitals that overlap during the bonding process allowing the delocalization
Experiment 15: Atomic Orbitals, Bond Length, and Molecular Orbitals Introduction Molecular orbitals result from the mixing of atomic orbitals that overlap during the bonding process allowing the delocalization
The Hydrogen Molecule-Ion
 Sign In Forgot Password Register ashwenchan username password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki BioWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register ashwenchan username password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki BioWiki
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 9. Molecular Orbitals, Part 4. Beyond Diatomics, continued
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 9. Molecular Orbitals, Part 4. Beyond Diatomics, continued Topics: Name(s): Element: 1. Using p-orbitals for σ-bonding: molecular orbital diagram
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2012 Day 9. Molecular Orbitals, Part 4. Beyond Diatomics, continued Topics: Name(s): Element: 1. Using p-orbitals for σ-bonding: molecular orbital diagram
General Physical Chemistry II
 General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 13 Aleksey Kocherzhenko October 16, 2014" Last time " The Hückel method" Ø Used to study π systems of conjugated molecules" Ø π orbitals are treated separately from
General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 13 Aleksey Kocherzhenko October 16, 2014" Last time " The Hückel method" Ø Used to study π systems of conjugated molecules" Ø π orbitals are treated separately from
A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics
 A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics Fundamental Postulate: O! = a! What is!?! is an oracle! operator wave function (scalar) observable Where does! come from?! is refined Variational Process H! = E!
A One-Slide Summary of Quantum Mechanics Fundamental Postulate: O! = a! What is!?! is an oracle! operator wave function (scalar) observable Where does! come from?! is refined Variational Process H! = E!
A Rigorous Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory and its Applications in Chemistry
 A Rigorous Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory and its Applications in Chemistry Zachary Chin, Alex Li, Alex Liu November 2018 1 Contents 1 Preface 4 2 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics 5 2.1 Fundamentals.....................................................
A Rigorous Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory and its Applications in Chemistry Zachary Chin, Alex Li, Alex Liu November 2018 1 Contents 1 Preface 4 2 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics 5 2.1 Fundamentals.....................................................
Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model Covalent Bonding: Orbitals A. Hybridization 1. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal
Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model Covalent Bonding: Orbitals A. Hybridization 1. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal
My additional comments, questions are colored in blue in the following slides.
 My additional comments, questions are colored in blue in the following slides. Do not forget to work the assigned HW from the text that is also posted on the boardlist. I will post my answers to these
My additional comments, questions are colored in blue in the following slides. Do not forget to work the assigned HW from the text that is also posted on the boardlist. I will post my answers to these
CHAPTER 10 Tight-Binding Model
 CHAPTER 0 Tight-Binding Model Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) Application to Bands from s-levels General Features of Tight-Binding Levels Wannier Functions 6 a : S S P 3S Core FE Semicore
CHAPTER 0 Tight-Binding Model Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) Application to Bands from s-levels General Features of Tight-Binding Levels Wannier Functions 6 a : S S P 3S Core FE Semicore
Lecture 6. Tight-binding model
 Lecture 6 Tight-binding model In Lecture 3 we discussed the Krönig-Penny model and we have seen that, depending on the strength of the potential barrier inside the unit cell, the electrons can behave like
Lecture 6 Tight-binding model In Lecture 3 we discussed the Krönig-Penny model and we have seen that, depending on the strength of the potential barrier inside the unit cell, the electrons can behave like
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 2: LCAO-MO theory for homonuclear diatomic molecules
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 2: LCAO-MO theory for homonuclear diatomic molecules Marc R. Roussel January 5, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Homonuclear diatomics January 5, 2018 1 / 17 MO theory for homonuclear diatomic
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 2: LCAO-MO theory for homonuclear diatomic molecules Marc R. Roussel January 5, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Homonuclear diatomics January 5, 2018 1 / 17 MO theory for homonuclear diatomic
Constructing a MO of NH 3. Nitrogen AO symmetries are
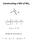 Constructing a MO of NH 3 Nitrogen AO symmetries are To develop a MO scheme for NH 3 assume that only the 2s and2p orbitals of nitrogen interact with the hydrogen 1s orbitals (i.e., the nitrogen 1s orbital
Constructing a MO of NH 3 Nitrogen AO symmetries are To develop a MO scheme for NH 3 assume that only the 2s and2p orbitals of nitrogen interact with the hydrogen 1s orbitals (i.e., the nitrogen 1s orbital
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2011 Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 011 Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy Name(s): lement: Topics: 1. The visible spectrum and the d-orbitals 3. Octahedral fields. Term symbols
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 011 Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy Name(s): lement: Topics: 1. The visible spectrum and the d-orbitals 3. Octahedral fields. Term symbols
I. CSFs Are Used to Express the Full N-Electron Wavefunction
 Chapter 11 One Must be Able to Evaluate the Matrix Elements Among Properly Symmetry Adapted N- Electron Configuration Functions for Any Operator, the Electronic Hamiltonian in Particular. The Slater-Condon
Chapter 11 One Must be Able to Evaluate the Matrix Elements Among Properly Symmetry Adapted N- Electron Configuration Functions for Any Operator, the Electronic Hamiltonian in Particular. The Slater-Condon
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 18. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Ligand Field Theory continued
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 18. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Ligand Field Theory continued Topics: 1. The three scenarios 2. Scenario 3: π-back bonding 1. The three scenarios for the MO energy
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 18. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Ligand Field Theory continued Topics: 1. The three scenarios 2. Scenario 3: π-back bonding 1. The three scenarios for the MO energy
VALENCE Hilary Term 2019
 VALENCE Hilary Term 2019 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
VALENCE Hilary Term 2019 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
General Physical Chemistry II
 General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 10 Aleksey Kocherzhenko October 7, 2014" Last time " promotion" Promotion and hybridization" [He] 2s 2 2p x 1 2p y 1 2p z0 " 2 unpaired electrons" [He] 2s 1 2p x 1
General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 10 Aleksey Kocherzhenko October 7, 2014" Last time " promotion" Promotion and hybridization" [He] 2s 2 2p x 1 2p y 1 2p z0 " 2 unpaired electrons" [He] 2s 1 2p x 1
Chapter 5 Equations for Wave Function
 Chapter 5 Equations for Wave Function In very simple cases, the explicit expressions for the SALCs could be deduced by inspection, but not for complicated system. It would be useful for cases like these
Chapter 5 Equations for Wave Function In very simple cases, the explicit expressions for the SALCs could be deduced by inspection, but not for complicated system. It would be useful for cases like these
Concept of a basis. Based on this treatment we can assign the basis to one of the irreducible representations of the point group.
 Concept of a basis A basis refers to a type of function that is transformed by the symmetry operations of a point group. Examples include the spherical harmonics, vectors, internal coordinates (e..g bonds,
Concept of a basis A basis refers to a type of function that is transformed by the symmetry operations of a point group. Examples include the spherical harmonics, vectors, internal coordinates (e..g bonds,
Chapter 12: Chemical Bonding II: Additional Aspects
 General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci Harwood Herring 8 th Edition Chapter 12: Chemical Bonding II: Additional Aspects Philip Dutton University of Windsor, Canada N9B 3P4 Prentice-Hall
General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci Harwood Herring 8 th Edition Chapter 12: Chemical Bonding II: Additional Aspects Philip Dutton University of Windsor, Canada N9B 3P4 Prentice-Hall
General Chemistry. Contents. Chapter 12: Chemical Bonding II: Additional Aspects What a Bonding Theory Should Do. Potential Energy Diagram
 General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci Harwood Herring 8 th Edition Chapter 12: Chemical Bonding II: Additional Aspects Philip Dutton University of Windsor, Canada N9B 3P4 Contents
General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci Harwood Herring 8 th Edition Chapter 12: Chemical Bonding II: Additional Aspects Philip Dutton University of Windsor, Canada N9B 3P4 Contents
MO theory is better for spectroscopy (Exited State Properties; Ionization)
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 25: MO Theory L25-1 Molecular Orbital Theory (MO theory) VB theory treats bonds as electron pairs. o There is a real emphasis on this point (over-emphasis actually). VB theory is very
CHEM 2060 Lecture 25: MO Theory L25-1 Molecular Orbital Theory (MO theory) VB theory treats bonds as electron pairs. o There is a real emphasis on this point (over-emphasis actually). VB theory is very
Molecular Orbital Theory This means that the coefficients in the MO will not be the same!
 Diatomic molecules: Heteronuclear molecules In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, the relative contribution of atomic orbitals to each MO is not equal. Some MO s will have more contribution from AO s on
Diatomic molecules: Heteronuclear molecules In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, the relative contribution of atomic orbitals to each MO is not equal. Some MO s will have more contribution from AO s on
Chapter 2. Model Problems That Form Important Starting Points
 Chapter 2. Model Problems That Form Important Starting Points The model problems discussed in this Chapter form the basis for chemists understanding of the electronic states of atoms, molecules, nano-clusters,
Chapter 2. Model Problems That Form Important Starting Points The model problems discussed in this Chapter form the basis for chemists understanding of the electronic states of atoms, molecules, nano-clusters,
Chapter 3 Answers to Problems
 Chapter 3 Answers to Problems 3.1 (a) a = A 1 + B 2 + E (b) b = 3A 1 + A 2 + 4E (c) c = 2A 1' + E' + A 2" (d) d = 4A 1 + A 2 + 2B 1 + B 2 + 5E (e) e = A 1g + A 2g + B 2g + E 1g + 2E 2g + A 2u + B 1u +
Chapter 3 Answers to Problems 3.1 (a) a = A 1 + B 2 + E (b) b = 3A 1 + A 2 + 4E (c) c = 2A 1' + E' + A 2" (d) d = 4A 1 + A 2 + 2B 1 + B 2 + 5E (e) e = A 1g + A 2g + B 2g + E 1g + 2E 2g + A 2u + B 1u +
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012 Lectures 15-16
 Chemistry 1B Fall 2012 Quantum Mechanics of the Covalent Bond for chapter 14 animations and links see: http://switkes.chemistry.ucsc.edu/teaching/chem1b/www_other_links/ch14_links.htm 1 LISTEN UP!!! WE
Chemistry 1B Fall 2012 Quantum Mechanics of the Covalent Bond for chapter 14 animations and links see: http://switkes.chemistry.ucsc.edu/teaching/chem1b/www_other_links/ch14_links.htm 1 LISTEN UP!!! WE
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 1: Introduction to the molecular orbital theory
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 1: Introduction to the molecular orbital theory Marc R. Roussel January 5, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Introduction to molecular orbitals January 5, 2018 1 / 24 Review: quantum mechanics
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 1: Introduction to the molecular orbital theory Marc R. Roussel January 5, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Introduction to molecular orbitals January 5, 2018 1 / 24 Review: quantum mechanics
Lecture 33: Intermolecular Interactions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 5.61 Physical Chemistry I Fall, 2017 Professors Robert W. Field Lecture 33: Intermolecular Interactions Recent Lectures Non-degenerate Perturbation Theory vs. Variational
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 5.61 Physical Chemistry I Fall, 2017 Professors Robert W. Field Lecture 33: Intermolecular Interactions Recent Lectures Non-degenerate Perturbation Theory vs. Variational
Benzene: E. det E E 4 E 6 0.
 Benzene: 2 5 3 4 We will solve Schodinger equation for this molecule by considering only porbitals of six carbons under the Huckel approximation. Huckel approximation, though quite crude, provides very
Benzene: 2 5 3 4 We will solve Schodinger equation for this molecule by considering only porbitals of six carbons under the Huckel approximation. Huckel approximation, though quite crude, provides very
Chem 442 Review for Exam 2. Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative (3D) components.
 Chem 44 Review for Exam Hydrogenic atoms: The Coulomb energy between two point charges Ze and e: V r Ze r Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative
Chem 44 Review for Exam Hydrogenic atoms: The Coulomb energy between two point charges Ze and e: V r Ze r Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative
Applications of Quantum Theory to Some Simple Systems
 Applications of Quantum Theory to Some Simple Systems Arbitrariness in the value of total energy. We will use classical mechanics, and for simplicity of the discussion, consider a particle of mass m moving
Applications of Quantum Theory to Some Simple Systems Arbitrariness in the value of total energy. We will use classical mechanics, and for simplicity of the discussion, consider a particle of mass m moving
Chemistry 1B, Fall 2013 Lectures 15-16
 Chemistry 1, Fall 2013 Lectures 1516 Chemistry 1 Fall 2013 Lectures 1516 Quantum Mechanics of the Covalent ond LISTEN UP!!! WE WILL E COVERING SECOND PRT OF CHPTER 14 (pp 676688) FIRST You will go CRZY
Chemistry 1, Fall 2013 Lectures 1516 Chemistry 1 Fall 2013 Lectures 1516 Quantum Mechanics of the Covalent ond LISTEN UP!!! WE WILL E COVERING SECOND PRT OF CHPTER 14 (pp 676688) FIRST You will go CRZY
Electronic Spectroscopy of Polyatomics
 Electronic Spectroscopy of Polyatomics We shall discuss the electronic spectroscopy of the following types of polyatomic molecules: 1. general AH 2 molecules, A = first-row element 2. formaldehyde 3. benzene
Electronic Spectroscopy of Polyatomics We shall discuss the electronic spectroscopy of the following types of polyatomic molecules: 1. general AH 2 molecules, A = first-row element 2. formaldehyde 3. benzene
Chemistry 483 Lecture Topics Fall 2009
 Chemistry 483 Lecture Topics Fall 2009 Text PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY A Molecular Approach McQuarrie and Simon A. Background (M&S,Chapter 1) Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric effect DeBroglie Wavelength Atomic
Chemistry 483 Lecture Topics Fall 2009 Text PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY A Molecular Approach McQuarrie and Simon A. Background (M&S,Chapter 1) Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric effect DeBroglie Wavelength Atomic
5/2/12. Hückel MO theory: Is it s3ll useful? Brno, May Molecular orbitals cannot (adequately) describe many- electron systems:
 Hückel MO theory: Is it s3ll useful? Brno, May 2012 Erich Hückel (09.08.1896 Berlin - 16.02.1980 Marburg) Postdoc with Max Born in GöNngen and Peter Debye in Zürich (Debye Hückel theory, Habilita3on 1925)
Hückel MO theory: Is it s3ll useful? Brno, May 2012 Erich Hückel (09.08.1896 Berlin - 16.02.1980 Marburg) Postdoc with Max Born in GöNngen and Peter Debye in Zürich (Debye Hückel theory, Habilita3on 1925)
NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis
 Lab 5: NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis A brief theoretical background 1 Some of the available chemical quantum methods for calculating NMR chemical shifts are based on the Hartree-Fock self-consistent
Lab 5: NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis A brief theoretical background 1 Some of the available chemical quantum methods for calculating NMR chemical shifts are based on the Hartree-Fock self-consistent
Electrocyclic Reactions
 Farzana Latif Ansari, Rumana Qureshi, Masood Latif Qureshi Electrocyclic Reactions From Fundamentals to Research WILEY-VCH Weinheim New York Chichester Brisbane Singapore Toronto Preface Acknowledgements
Farzana Latif Ansari, Rumana Qureshi, Masood Latif Qureshi Electrocyclic Reactions From Fundamentals to Research WILEY-VCH Weinheim New York Chichester Brisbane Singapore Toronto Preface Acknowledgements
Theoretical Concepts of Spin-Orbit Splitting
 Chapter 9 Theoretical Concepts of Spin-Orbit Splitting 9.1 Free-electron model In order to understand the basic origin of spin-orbit coupling at the surface of a crystal, it is a natural starting point
Chapter 9 Theoretical Concepts of Spin-Orbit Splitting 9.1 Free-electron model In order to understand the basic origin of spin-orbit coupling at the surface of a crystal, it is a natural starting point
Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity. Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity. Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity
 Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity When there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms, then the bond between them is polar. It is possible for a molecule to contain polar bonds, but
Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity When there is a difference in electronegativity between two atoms, then the bond between them is polar. It is possible for a molecule to contain polar bonds, but
Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory Electronic Structure of Six and Four-Coordinate Complexes Using Crystal Field Theory, we can generate energy level
Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory Electronic Structure of Six and Four-Coordinate Complexes Using Crystal Field Theory, we can generate energy level
Spectroscopic Selection Rules
 E 0 v = 0 v = 1 v = 2 v = 4 v = 3 For a vibrational fundamental (Δv = ±1), the transition will have nonzero intensity in either the infrared or Raman spectrum if the appropriate transition moment is nonzero.
E 0 v = 0 v = 1 v = 2 v = 4 v = 3 For a vibrational fundamental (Δv = ±1), the transition will have nonzero intensity in either the infrared or Raman spectrum if the appropriate transition moment is nonzero.
Morrison and Boyd, Organic Chemistry, Interference of waves 1) constructive (in-phase) 2) destructive (out-of-phase)
 Morrison and Boyd, Organic Chemistry, 1973 Interference of waves 1) constructive (in-phase) 2) destructive (out-of-phase) Electron wave function with n, l, m l => orbitals Molecular orbital theory 1) molecule
Morrison and Boyd, Organic Chemistry, 1973 Interference of waves 1) constructive (in-phase) 2) destructive (out-of-phase) Electron wave function with n, l, m l => orbitals Molecular orbital theory 1) molecule
Hückel Molecular Orbital (HMO) Theory
 Hückel Molecular Orbital (HMO) Theory A simple quantum mechanical concept that gives important insight into the properties of large molecules Why HMO theory The first MO theory that could be applied to
Hückel Molecular Orbital (HMO) Theory A simple quantum mechanical concept that gives important insight into the properties of large molecules Why HMO theory The first MO theory that could be applied to
Wave Equations of Polyatomic Molecules
 Wave Equations of Polyatomic Molecules! Approximate wave functions are sought by combining atomic wave functions for the bonded atoms.! Several different approaches have been taken to constructing trial
Wave Equations of Polyatomic Molecules! Approximate wave functions are sought by combining atomic wave functions for the bonded atoms.! Several different approaches have been taken to constructing trial
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5, pm SES
 Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi. Lecture 28, December 08, 2014
 Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi Lecture 28, December 08, 2014 Solved Homework Water, H 2 O, involves 2 hydrogen atoms and an oxygen
Chem 4502 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics and Spectroscopy 3 Credits Fall Semester 2014 Laura Gagliardi Lecture 28, December 08, 2014 Solved Homework Water, H 2 O, involves 2 hydrogen atoms and an oxygen
Quantum Number. i. Degeneracy is when orbitals have the same value of n.
 Quantum Number 1. Principal Quantum Number a. Is represented by n b. Has values from ranging from 1 c. Indicates the size and energy level in which the electron is housed. The bigger the n value, the further
Quantum Number 1. Principal Quantum Number a. Is represented by n b. Has values from ranging from 1 c. Indicates the size and energy level in which the electron is housed. The bigger the n value, the further
Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found.
 Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found. In applying quantum mechanics to 'real' chemical problems, one is usually faced with a Schrödinger
Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found. In applying quantum mechanics to 'real' chemical problems, one is usually faced with a Schrödinger
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.04, Principles
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.04, Principles
