COURSE CODE: GEE 212 COURSE TITLE: ENGINEERING MECHANICS NUMBER OF UNITS: 3 Units COURSE DURATION: Three hours per week
|
|
|
- Dwight Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COURSE CODE: GEE 212 COURSE TITLE: ENGINEERING MECHANICS NUMBER OF UNITS: 3 Units COURSE DURATION: Three hours per week COURSE LECTURER: DR. BALOGUNAIZEBEOJE INCENT INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES At the completion of this course, students are expected to: 1. State the concept and principles of mechanics 2. Understand the First and Second moment of area 3. Understand the application of vectors to resolution of forces at equilibrium by defining their free body diagrams. 4. Explain the kinematics of particles and rigid bodies by the applications of Newton s laws of motion. 5. Understand the elements of fluid statics as applicable to fluid dynamics. 6. Replicate the principles of statics and dynamics for a given engineering design problem. COURSE DETAILS: Week Module Description Number 1-2 Statics: Laws of statics, system of forces and their properties, Simple problems, Friction. 3 Particle dynamics: Kinematics of plane motion. Newton's laws- Kinetics of particles, momentum and energy methods. 4-5 Kinematics of rigid body- velocity and acceleration diagrams for simple problems. Kinetics of rigid bodies- Two dimensional motion of rigid bodies, energy and momentum, 6-7 Kinetic energy in general plane motion, power in general plane motion, Mass Moment of inertia, Simple problems, impulse, centre of pressure and percussion, frameworks, Simple harmonic motions. 8 Mid- Semester Test 9-10 Fluid Mechanics: Elements of fluid statics; density; pressure, surface tension, viscosity, compressibility etc
2 Hydrostatic forces on submerged surfaces due to incompressible fluid. 11 Introduction to fluid dynamics- conservation laws. Introduction to viscous flow. 12 Revision. RESOURCES Lecturer s Office Hours: Engr. Dr. Balogun A.. Mondays 2:00-4:00pm. Course lecture Notes: Books: Johnston, E. R., Beer, F., & Eisenberg, E. (2009). ector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics. McGraw-Hill. Khurmi R. S. (2012). Applied Mechanics and Strength of Materials. S. Chand & Company Ltd, India. Practical/ Project: Multiple parts (2 or 3). Homeworks + Project: ~ 40% of final grade. Examinations: Final, comprehensive (according to the University's schedule): ~ 60% of final grade Assignments & Grading Academic Honesty: All class work should be done independently, unless explicitly stated otherwise on the assignment handout. You may discuss general solution strategies, but must write up the solutions yourself. If you discuss any problem with anyone else, you must write their name at the top of your assignment, labeling them collaborators. NO LATE SUBMISSION OF HOMEWORKS ACCEPTED Turn in what you have at the time it s due. All homework are due at the start of class. If you will be away, turn in the homework early. ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 2
3 PREAMBLE: In this course on Engineering Mechanics, we shall be learning about mechanical interaction between bodies. That is where we will learn how different bodies apply forces on one another and how they then balance to keep each other in equilibrium. That will be done in the first part of the course. So in the first part we will be dealing with STATICS. In the second part we then go to the motion of particles and see the motion of particles get affected when a force is applied on them. We will be discussing the behavior of single particles in statics and latter move onto describe the motion of rigid bodies in dynamics. ENGINEERING MECHANICS by Balogun A. incent is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 3
4 Review of the laws of motion and vector algebra It is important to review the Newton's laws of motion and vectors since they formed the basis of all solutions to mechanics problems in one form or the other. Therefore the Newton's laws are defined thus: Newton First law of motion: A body does not change its state of motion unless a force acts upon it. Newton Second law of motion: FF = mmmm (1) where m is the inertial mass of the body. mm 1 aa 1 = mm 2 aa 2 mm 2 = aa 1 aa 2 mm 1 (2) Newton Third law of motion: Newton's third law states that if a body A applies a force F on body B, then B also applies an equal and opposite force on A as shown in Figure 1. A F B Figure 1: Force application on a static body ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 4
5 EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCES FORCE A force is simply push or pull. This can be related to a man that exert a push on a stationary object to create motion or to bring an already moving object to a stop. Therefore, a force can create or tends to create or destroys the motion of a body. For example if a horse applies force to pull a cart and to set it in motion (Khurmi 2012). EFFECTS OF A FORCE A force may produce the following effects in a body, on which it acts. 1. It may change the motion = body at rest = set in motion. 2. It may retard the motion of a body. 3. It may retard the forces, already aching on a body, thus bringing it to rest or in equilibrium. 4. It may give rise to the internal stresses in the body on which it acts. CHARACTERISTICS OF A FORCE 1. Magnitude of the force (i.e. 100N, 50N, 20KN etc.) 2. The direction of the line, along which the force acts (i.e. along OX, OY, 30O North etc. 3. Name of force (i.e. whether push or pull) 4. The point at which (or through which) the force acts on the body. PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL INDEPENDENCE OF FORCES It states if a number of forces are simultaneously acting on a particle, then each one of them will produce the same effects which it would have done while acting alone. PRINCIPLE OF TRANSMISSIBILITY OF FORCES It states if a force acts at any one point on a rigid body, the force may also be considered to act along its line of action at any other point, so far that this point is rigidly connected with the body. ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 5
6 A rigid body can be defined as a body that has the potential to retain its shape and size at every point in time if subjected to some external forces. It is only an assumption that a body is perfectly rigid. This might not be true in real life practice its only for simplicity. SYSTEM OF FORCES 1. Coplanar forces line of action on same plane 2. Collinear forces line of action on same line. 3. Concurrent forces forces meet at one point. 4. Coplanar concurrent 1 & 3 5. Coplanar non-concurrent do obey 1 and disobey 3 6. Non-planar concurrent disobey 1, obey Non planar non concurrent disobeys 1 & 3. RESULTANT FORCE A single force that could replace number of forces acting simultaneously on a particle. RESOLUTION OF A FORCE This is the process of splitting up the given force into a number of components without changing its effect on the body. PRINCIPLE OF RESOLUTION The principle of resolution of forces states that The algebraic sum of the individual components of forces resolved into a number of forces in a given direction is equal to the resolved part of their resultant in the same direction (Shames and Rao, 1967). METHOD OF RESOLUTION OF THE RESULTANT FORCE 1. Resolve all the forces horizontally and find the algebraic sum of all the horizontal components. (i.e. H). 2. Then, resolve vertical forces ( ) ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 6
7 3. Resultant R = ( HH) 2 + ( ) 2 4. The resultant force inclined at an angle Ө with the horizontal Tan Ө = HH EXAMPLE 1 A triangle ABC has its side AB = 40mm along positive x-axis and side BC=30mm along positive y-axis. Three forces of 40N, 50N and 30N act along sides AB, BC and CA respectively. Define the magnitude of the resultant of such a system of forces. SOLUTION Free body diagram of the described triangle is as shown below: 50N C 30 30N A Ѳ 40 B 40N AC = 50mm (how?) SinӨ = = 0.6 CosӨ = = 0.8 H = 40 (30 cosө) = 40 (30 x 0.8) = 16N = 50 (30 sinө) = 50 (30 x 0.6) = 32N R = ( HH) 2 + ( ) 2 = (16) 2 + (32) 2 N ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 7
8 R = 35.8N. EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCES If the resultant of a number of forces acting on a particle is zero, the particle will be in equilibrium. PRINCIPLE OF EQUILIBRIUM 1. Two force principle, 2. Three force principle3. Four force principle METHODS FOR THE EQUILIBRIUM OF COPLANAR FORCES TWO METHODS: 1. Analytical 2. Graphical. ANALYTICAL METHOD FOR THE EQUILIBRIUM OF COPLANAR FORCES By Lami s theorem: PP SSSSSS = QQ = RR SSSSSSSS γγ P Q γ β α Figure 2: Lami's theorem analogy P, Q, R are three forces, α, β, γ are angles. ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 8 R
9 EXAMPLE 2 A load weighing 15N hangs from a point C, by two strings AC and BC fixed at points A and B respectively. If the string AC is inclined at 60 o to the horizontal and BC inclined at 45 o to the vertical as shown below, determine the forces in the strings AC and BC by using the Lami's theorem. 60 o A B 45 o C SOLUTION Given weight at AC = 15N Let T 1 = Force in the string AC T 2 = Force in the string BC ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 9
10 B 45 o 60 o T 2 T 1 A C Angle between TT 1 and 15N = 150 o Angle btw TT 2 and 15n = 135 o Therefore, Angle ACB = 180 o (45 o + 60 o ) = 75 o Applying Lami s equation at C Hence, TT 1 = 15 SSSSSS 45 SSSSSS 75 TT 1 = 10.98N. And TT 2 = 7.76N Sin (180 Ө) = Sin Ө 15 SSSSSS 75 = TT1 SSSSSS 45 = TT2 SSSSSS 150 ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 10
11 GRAPHICAL METHOD FOR THE EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCES 1. Converse of the law of triangle of forces 2. Converse of the law of polygon of forces. CONERSE OF THE LAW OF TRIANGLE OF FORCES States that if three forces acting at a point be represented in magnitude and direction by the three sides of a triangle, taken in order, the forces shall be in equilibrium. CONERSE OF THE LAW OF POLYGON OF FORCES States that if any number of forces acting at a point be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a closed polygon, taken in order, the forces shall be in equilibrium. EXAMPLE 5 A load weighing 15N hangs from a point C, by two strings AC and BC fixed at points A and B respectively. If the string AC is inclined at 60 o to the horizontal and BC inclined at 45 o to the vertical as shown below, determine the forces in the strings AC and BC by using the graphical method. 60 o A B 45 o C SOLUTION Given, weight at C = 15N ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 11
12 Let TT 1= Force in the string AC TT 2 = Force in the string BC. Draw the space diagram for the joint C and name the forces according to Bow s notations as shown in (a) below: B A r T 2 R T 1 p T o P 75 o C 150 o Q 15 v T 1 (a) ForceTT 1 = RRRR, TT 2 = PPPP q (b) Draw the vector diagram for the given system of forces as shown in (b). 1. Draw a vertical line equal to 15N to a suitable scale from p to q. 2. Through p draw a line parallel to PR and terminate at r 3. Close the triangle 4. Measure AC (T1), BC (T2) TT 1 = 11.0NN, TT 2 = 7.8NN. CONDITIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM If we consider a body being acted upon by a number of coplanar non-concurrent forces, the body may have any of the following characteristics. 1. The body may move in any one direction. 2. The body may rotate about itself without moving. ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 12
13 3. The body may move in any one direction and at the same time it may also rotate about itself. 4. The body may be completely at rest no resultant force nor a couple acting on it. TYPES OF EQUILIBRIUM Practically, a body is said to be in equilibrium when it comes back to its original position, after it is slightly displaced from its position of rest. There are three types of equilibrium: 1. STABLE A smooth cylinder lying in a curved surface as shown in Figure 3. F Figure 3: Stable body 2. UNSTABLE A smooth cylinder lying on a convex surface. F Figure 4: Unstable body 3. NEUTRAL Occupies a new position and remains at rest in the new position. A smooth cylinder lying on a horizontal plane. ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 13
14 F Figure 5: Neutral body ENGINEERING MECHANICS by Balogun A. incent is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License ENGINEERING MECHANICS, EDO UNIERSITY IYAMHO Page 14
TEST-1 MEACHNICAL (MEACHNICS)
 1 TEST-1 MEACHNICAL (MEACHNICS) Objective Type Questions:- Q.1 The term force may be defined as an agent t which produces or tends to produce, destroys or tends to destroy motion. a) Agree b) disagree
1 TEST-1 MEACHNICAL (MEACHNICS) Objective Type Questions:- Q.1 The term force may be defined as an agent t which produces or tends to produce, destroys or tends to destroy motion. a) Agree b) disagree
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action
 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC 107 1. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action 1. Meet on the same plane 2. Meet at one point 3. Lie
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC 107 1. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action 1. Meet on the same plane 2. Meet at one point 3. Lie
Statics deal with the condition of equilibrium of bodies acted upon by forces.
 Mechanics It is defined as that branch of science, which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. Engineering mechanics applies the principle of mechanics
Mechanics It is defined as that branch of science, which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. Engineering mechanics applies the principle of mechanics
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
Physical Science and Engineering. Course Information. Course Number: ME 100
 Physical Science and Engineering Course Number: ME 100 Course Title: Course Information Basic Principles of Mechanics Academic Semester: Fall Academic Year: 2016-2017 Semester Start Date: 8/21/2016 Semester
Physical Science and Engineering Course Number: ME 100 Course Title: Course Information Basic Principles of Mechanics Academic Semester: Fall Academic Year: 2016-2017 Semester Start Date: 8/21/2016 Semester
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK UNIT I - PART-A
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
2. a) Explain the equilibrium of i) Concurrent force system, and ii) General force system.
 Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action
 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC 107 1. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action 1. Meet on the same plane 2. Meet at one point 3. Lie
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC 107 1. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action 1. Meet on the same plane 2. Meet at one point 3. Lie
PESIT-BSC Department of Science & Humanities
 Class No. 1. 2. 3. LESSON PLAN 15CIV13/23 ELEMENTS OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Course objectives: AND ENGINEERING MECHANICS The objectives of this course is to make students to learn basics of Civil Engineering
Class No. 1. 2. 3. LESSON PLAN 15CIV13/23 ELEMENTS OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Course objectives: AND ENGINEERING MECHANICS The objectives of this course is to make students to learn basics of Civil Engineering
K.GNANASEKARAN. M.E.,M.B.A.,(Ph.D)
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG. Engineering Mechanics I YEAR 2th SEMESTER) Two Marks Question Bank UNIT-I Basics and statics of particles 1. Define Engineering Mechanics Engineering Mechanics is defined
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG. Engineering Mechanics I YEAR 2th SEMESTER) Two Marks Question Bank UNIT-I Basics and statics of particles 1. Define Engineering Mechanics Engineering Mechanics is defined
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES SCI 1105 COURSE MATERIAL UNIT - I
 MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES SCI 1105 COURSE MATERIAL UNIT - I Engineering Mechanics Branch of science which deals with the behavior of a body with the state of rest or motion, subjected to the action of forces.
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES SCI 1105 COURSE MATERIAL UNIT - I Engineering Mechanics Branch of science which deals with the behavior of a body with the state of rest or motion, subjected to the action of forces.
GOPALAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT Department of Civil Engineering COURSE PLAN
 Appendix - C GOPALAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT Department of Civil Engineering Academic Year: 2017-18 Semester: EVEN COURSE PLAN Semester: II Subject Code& Name: 15CIV23& Elements of Civil
Appendix - C GOPALAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT Department of Civil Engineering Academic Year: 2017-18 Semester: EVEN COURSE PLAN Semester: II Subject Code& Name: 15CIV23& Elements of Civil
CHAPTER 5 ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES. Expected Outcome:
 CHAPTER ANALYSIS O STRUCTURES Expected Outcome: Able to analyze the equilibrium of structures made of several connected parts, using the concept of the equilibrium of a particle or of a rigid body, in
CHAPTER ANALYSIS O STRUCTURES Expected Outcome: Able to analyze the equilibrium of structures made of several connected parts, using the concept of the equilibrium of a particle or of a rigid body, in
where G is called the universal gravitational constant.
 UNIT-I BASICS & STATICS OF PARTICLES 1. What are the different laws of mechanics? First law: A body does not change its state of motion unless acted upon by a force or Every object in a state of uniform
UNIT-I BASICS & STATICS OF PARTICLES 1. What are the different laws of mechanics? First law: A body does not change its state of motion unless acted upon by a force or Every object in a state of uniform
Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics
![Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics](/thumbs/77/74871041.jpg) Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following
Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following
2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No - 1 I B.Tech I Semester Regular/Supple. Examinations Nov./Dec. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem. E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E, Textile Engg.) Time: 3 hours
Set No - 1 I B.Tech I Semester Regular/Supple. Examinations Nov./Dec. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem. E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E, Textile Engg.) Time: 3 hours
Chapter 4: Newton s Second Law F = m a. F = m a (4.2)
 Lecture 7: Newton s Laws and Their Applications 1 Chapter 4: Newton s Second Law F = m a First Law: The Law of Inertia An object at rest will remain at rest unless, until acted upon by an external force.
Lecture 7: Newton s Laws and Their Applications 1 Chapter 4: Newton s Second Law F = m a First Law: The Law of Inertia An object at rest will remain at rest unless, until acted upon by an external force.
APPLIED MATHEMATICS IM 02
 IM SYLLABUS (2013) APPLIED MATHEMATICS IM 02 SYLLABUS Applied Mathematics IM 02 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hours) Applied Mathematics (Mechanics) Aims A course based on this syllabus
IM SYLLABUS (2013) APPLIED MATHEMATICS IM 02 SYLLABUS Applied Mathematics IM 02 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hours) Applied Mathematics (Mechanics) Aims A course based on this syllabus
for any object. Note that we use letter, m g, meaning gravitational
 Lecture 4. orces, Newton's Second Law Last time we have started our discussion of Newtonian Mechanics and formulated Newton s laws. Today we shall closely look at the statement of the second law and consider
Lecture 4. orces, Newton's Second Law Last time we have started our discussion of Newtonian Mechanics and formulated Newton s laws. Today we shall closely look at the statement of the second law and consider
Upthrust and Archimedes Principle
 1 Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Objects immersed in fluids, experience a force which tends to push them towards the surface of the liquid. This force is called upthrust and it depends on the density
1 Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Objects immersed in fluids, experience a force which tends to push them towards the surface of the liquid. This force is called upthrust and it depends on the density
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: RECTANGULAR COORDINATES Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Apply Newton s second law to determine forces and accelerations for particles in rectilinear motion. In-Class
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: RECTANGULAR COORDINATES Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Apply Newton s second law to determine forces and accelerations for particles in rectilinear motion. In-Class
Equilibrium. Rigid Bodies VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS. Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies Contents Introduction
Eighth E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies Contents Introduction
Chapter 4: Newton's Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Lecture Chapter 4: Newton's Laws of Motion Goals for Chapter 4 To understand force either directly or as the net force of multiple components. To study and apply Newton's first law. To study
Chapter 4 Lecture Chapter 4: Newton's Laws of Motion Goals for Chapter 4 To understand force either directly or as the net force of multiple components. To study and apply Newton's first law. To study
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Force. Zero Net Force. Lectures 9 and 10 The Laws of Motion. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I Lectures 9 and 10 The Laws of Motion A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch off your handphone and pager Switch off your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I Lectures 9 and 10 The Laws of Motion A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch off your handphone and pager Switch off your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
SYLLABUS FORM WESTCHESTER COMMUNITY COLLEGE Valhalla, NY lo595. l. Course #: PHYSC NAME OF ORIGINATOR /REVISOR: ALENA O CONNOR
 SYLLABUS FORM WESTCHESTER COMMUNITY COLLEGE Valhalla, NY lo595 l. Course #: PHYSC 121 2. NAME OF ORIGINATOR /REVISOR: ALENA O CONNOR NAME OF COURSE ENGINEERING PHYSICS 1 WITH LAB 3. CURRENT DATE: SUMMER
SYLLABUS FORM WESTCHESTER COMMUNITY COLLEGE Valhalla, NY lo595 l. Course #: PHYSC 121 2. NAME OF ORIGINATOR /REVISOR: ALENA O CONNOR NAME OF COURSE ENGINEERING PHYSICS 1 WITH LAB 3. CURRENT DATE: SUMMER
Mathematics. Statistics
 Mathematics Statistics Table of Content. Introduction.. arallelogram law of forces. 3. Triangle law of forces. 4. olygon law of forces. 5. Lami's theorem. 6. arallel forces. 7. Moment. 8. Couples. 9. Triangle
Mathematics Statistics Table of Content. Introduction.. arallelogram law of forces. 3. Triangle law of forces. 4. olygon law of forces. 5. Lami's theorem. 6. arallel forces. 7. Moment. 8. Couples. 9. Triangle
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
Dr. ANIL PATIL Associate Professor M.E.D., D.I.T., Dehradun
 by Dr. ANIL PATIL Associate Professor M.E.D., D.I.T., Dehradun 1 2 Mechanics The study of forces and their effect upon body under consideration Statics Deals with the forces which are acting on a body
by Dr. ANIL PATIL Associate Professor M.E.D., D.I.T., Dehradun 1 2 Mechanics The study of forces and their effect upon body under consideration Statics Deals with the forces which are acting on a body
Chapter 3, Problem 28. Agenda. Forces. Contact and Field Forces. Fundamental Forces. External and Internal Forces 2/6/14
 Agenda Today: Homework Quiz, Chapter 4 (Newton s Laws) Thursday: Applying Newton s Laws Start reading Chapter 5 Chapter 3, Problem 28 A ball with a horizontal speed of 1.25 m/s rolls off a bench 1.00 m
Agenda Today: Homework Quiz, Chapter 4 (Newton s Laws) Thursday: Applying Newton s Laws Start reading Chapter 5 Chapter 3, Problem 28 A ball with a horizontal speed of 1.25 m/s rolls off a bench 1.00 m
ME101: Engineering Mechanics ( )
 ME101: Engineering Mechanics (3 1 0 8) 2016-2017 (II Semester); Division IV Budhaditya Hazra Room N-307 Department of Civil Engineering budhaditya.hazra@iitg.ernet.in Phone: 258 3334/5334 Web: www.iitg.ernet.in/budhaditya.hazra
ME101: Engineering Mechanics (3 1 0 8) 2016-2017 (II Semester); Division IV Budhaditya Hazra Room N-307 Department of Civil Engineering budhaditya.hazra@iitg.ernet.in Phone: 258 3334/5334 Web: www.iitg.ernet.in/budhaditya.hazra
ENGINEERING MECHANICS - Question Bank
 E Semester-_IST YEAR (CIVIL, MECH, AUTO, CHEM, RUER, PLASTIC, ENV,TT,AERO) ENGINEERING MECHANICS - Question ank All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 Define space,time matter and force, scalar
E Semester-_IST YEAR (CIVIL, MECH, AUTO, CHEM, RUER, PLASTIC, ENV,TT,AERO) ENGINEERING MECHANICS - Question ank All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 Define space,time matter and force, scalar
Unit-II ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 ECHNICS in motion. Unit-II ENGINEERING ECHNICS By Prof. V. adhava Rao, SJCE, ysore It s a branch of science, which deals with the action of forces on bodies at rest or ENGINEERING ECHNICS engineering.
ECHNICS in motion. Unit-II ENGINEERING ECHNICS By Prof. V. adhava Rao, SJCE, ysore It s a branch of science, which deals with the action of forces on bodies at rest or ENGINEERING ECHNICS engineering.
Physics C: Mechanics
 Physics C: Mechanics 2013 2014 PISCATAWAY TOWNSHIP SCHOOLS COURSE SYLLABUS Mr. Rohan Gokhale rgokhale@pway.org www.piscatawayschools.org/phs Brief Description of Course The AP Physics course is a full
Physics C: Mechanics 2013 2014 PISCATAWAY TOWNSHIP SCHOOLS COURSE SYLLABUS Mr. Rohan Gokhale rgokhale@pway.org www.piscatawayschools.org/phs Brief Description of Course The AP Physics course is a full
Dynamics of Machinery
 1 Preamble Dynamics of Machinery Relation between motion and forces causing is a fascinating subject. This study is a generally referred as dynamic. Modern Engineering aims at analysing and predicting
1 Preamble Dynamics of Machinery Relation between motion and forces causing is a fascinating subject. This study is a generally referred as dynamic. Modern Engineering aims at analysing and predicting
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE DESCRIPTION
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURE DECRIPTION Course Code Course Title : A10302 : ENGINEERING MECHANIC Course tructure : Lectures Tutorials Practical Credits 3 - - 6 Course Coordinator : Dr.D.Govardhan,
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURE DECRIPTION Course Code Course Title : A10302 : ENGINEERING MECHANIC Course tructure : Lectures Tutorials Practical Credits 3 - - 6 Course Coordinator : Dr.D.Govardhan,
STATICS. Bodies. Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Design of a support
 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Model Answers Attempt any TEN of the following :
 (ISO/IEC - 70-005 Certified) Model Answer: Winter 7 Sub. Code: 17 Important Instructions to Examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 70-005 Certified) Model Answer: Winter 7 Sub. Code: 17 Important Instructions to Examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Applied Mathematics B Study Guide
 Science, Engineering and Technology Portfolio School of Life and Physical Sciences Foundation Studies (Applied Science/Engineering) Applied Mathematics B Study Guide Topics Kinematics Dynamics Work, Energy
Science, Engineering and Technology Portfolio School of Life and Physical Sciences Foundation Studies (Applied Science/Engineering) Applied Mathematics B Study Guide Topics Kinematics Dynamics Work, Energy
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis. Lecture 19
 ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 19 SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: In-Class Activities: a) Define a simple
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 19 SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: In-Class Activities: a) Define a simple
ISBN :
 ISBN : 978-81-909042-4-7 - www.airwalkpublications.com ANNA UNIVERSITY - R2013 GE6253 ENGINEERING MECHANICS UNIT I: BASICS AND STATICS OF PARTICLES 12 Introduction Units and Dimensions Laws of Mechanics
ISBN : 978-81-909042-4-7 - www.airwalkpublications.com ANNA UNIVERSITY - R2013 GE6253 ENGINEERING MECHANICS UNIT I: BASICS AND STATICS OF PARTICLES 12 Introduction Units and Dimensions Laws of Mechanics
You may use g = 10 m/s 2, sin 60 = 0.87, and cos 60 = 0.50.
 1. A child pulls a 15kg sled containing a 5kg dog along a straight path on a horizontal surface. He exerts a force of a 55N on the sled at an angle of 20º above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction
1. A child pulls a 15kg sled containing a 5kg dog along a straight path on a horizontal surface. He exerts a force of a 55N on the sled at an angle of 20º above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction
F R. + F 3x. + F 2y. = (F 1x. j + F 3x. i + F 2y. i F 3y. i + F 1y. j F 2x. ) i + (F 1y. ) j. F 2x. F 3y. = (F ) i + (F ) j. ) j
 General comments: closed book and notes but optional one page crib sheet allowed. STUDY: old exams, homework and power point lectures! Key: make sure you can solve your homework problems and exam problems.
General comments: closed book and notes but optional one page crib sheet allowed. STUDY: old exams, homework and power point lectures! Key: make sure you can solve your homework problems and exam problems.
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section V
 PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section V Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 2.5 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section V Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 2.5 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
 Subject : Engineering Mechanics Subject Code : 1704 Page No: 1 / 6 ----------------------------- Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Subject : Engineering Mechanics Subject Code : 1704 Page No: 1 / 6 ----------------------------- Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE
 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE: CODE NO. : SEMESTER: Two PROGRAM: AUTHOR: Aviation Technology Flight Douglas McKinnon DATE: Jan 2013
SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE: CODE NO. : SEMESTER: Two PROGRAM: AUTHOR: Aviation Technology Flight Douglas McKinnon DATE: Jan 2013
Mechanics of Material 11/29/2017. General Information
 General Information Assistant Lecturer: Asmaa Ab. Mustafa Email : asmaa.abdulmajeed@ishik.edu.iq Department : Civil Engineering Course Title : Engineering Mechanics I Code : Credit : 2 Office Hour : Monday
General Information Assistant Lecturer: Asmaa Ab. Mustafa Email : asmaa.abdulmajeed@ishik.edu.iq Department : Civil Engineering Course Title : Engineering Mechanics I Code : Credit : 2 Office Hour : Monday
Fall 2014: PHYSICS 170 GENERAL PHYSICS I
 Fall 2014: PHYSICS 170 GENERAL PHYSICS I MTWF 9:30-10:20 am (Section 1) WAT 420 Instructor: Milincic Radovan (milincic@hawaii.edu) Office hours (tentative): MW 10:25 11:30 PSB 204 Course description: This
Fall 2014: PHYSICS 170 GENERAL PHYSICS I MTWF 9:30-10:20 am (Section 1) WAT 420 Instructor: Milincic Radovan (milincic@hawaii.edu) Office hours (tentative): MW 10:25 11:30 PSB 204 Course description: This
Physics Pre-comp diagnostic Answers
 Name Element Physics Pre-comp diagnostic Answers Grade 8 2017-2018 Instructions: THIS TEST IS NOT FOR A GRADE. It is to help you determine what you need to study for the precomps. Just do your best. Put
Name Element Physics Pre-comp diagnostic Answers Grade 8 2017-2018 Instructions: THIS TEST IS NOT FOR A GRADE. It is to help you determine what you need to study for the precomps. Just do your best. Put
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
MECHANICS. MRS KL FALING Grade 11 Physical Science
 MECHANICS MRS KL FALING Grade 11 Physical Science Revision from grade 10 Fill in the missing words A quantity can be either a scalar or a. Examples of scalars are,, and. A vector quantity is only fully
MECHANICS MRS KL FALING Grade 11 Physical Science Revision from grade 10 Fill in the missing words A quantity can be either a scalar or a. Examples of scalars are,, and. A vector quantity is only fully
Upon successful completion of this course, students should be competent to perform the following tasks:
 Course Information Course Prefix/Number: PHY 221 Course Title: University Physics Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0 VA Statement/Distance Learning Attendance Textbook
Course Information Course Prefix/Number: PHY 221 Course Title: University Physics Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0 VA Statement/Distance Learning Attendance Textbook
Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Jan./Feb ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 3 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Jan./Feb. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Question Paper Consists
3 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Jan./Feb. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Question Paper Consists
APPLIED MATHEMATICS AM 02
 AM SYLLABUS (2013) APPLIED MATHEMATICS AM 02 SYLLABUS Applied Mathematics AM 02 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs)+paper II (3 hrs) Applied Mathematics (Mechanics) Aims A course based on
AM SYLLABUS (2013) APPLIED MATHEMATICS AM 02 SYLLABUS Applied Mathematics AM 02 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs)+paper II (3 hrs) Applied Mathematics (Mechanics) Aims A course based on
GCE Advanced Level 2014
 GCE Advanced Level 2014 Combined Mathematics I Model Paper 04 PART A (Answer all questions) Time 3 hrs 1. A cyclist rides along a straight path with uniform velocity u and passes a motor car, which is
GCE Advanced Level 2014 Combined Mathematics I Model Paper 04 PART A (Answer all questions) Time 3 hrs 1. A cyclist rides along a straight path with uniform velocity u and passes a motor car, which is
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
STATICS. Bodies VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Ninth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 N E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
N E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Introduction to Engineering Analysis - ENGR1100 Course Description and Syllabus Tuesday / Friday Sections. Spring '13.
 Introduction to Engineering Analysis - ENGR1100 Course Description and Syllabus Tuesday / Friday Sections Spring 2013 Back exams, HW solutions, and other useful links can be found at the following website:
Introduction to Engineering Analysis - ENGR1100 Course Description and Syllabus Tuesday / Friday Sections Spring 2013 Back exams, HW solutions, and other useful links can be found at the following website:
Forces. 3. The graph given shows the weight of three objects on planet X as a function of their mass. A. 0 N. B. between 0 N and 12 N C.
 Name: Date: 1. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. The force of static friction acting on the box is 3. The graph given shows the weight
Name: Date: 1. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. The force of static friction acting on the box is 3. The graph given shows the weight
FORCE. Definition: Combining Forces (Resultant Force)
 1 FORCE Definition: A force is either push or pull. A Force is a vector quantity that means it has magnitude and direction. Force is measured in a unit called Newtons (N). Some examples of forces are:
1 FORCE Definition: A force is either push or pull. A Force is a vector quantity that means it has magnitude and direction. Force is measured in a unit called Newtons (N). Some examples of forces are:
2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec 2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com. to AE, AME, BOT, CHEM, CE, EEE, ME, MTE, MM, PCE, PE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part-A
Set No 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec 2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com. to AE, AME, BOT, CHEM, CE, EEE, ME, MTE, MM, PCE, PE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part-A
Chapter Four Holt Physics. Forces and the Laws of Motion
 Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Lesson Plan. Name of the Faculty : SANDEEP (VTF in CIVIL ENGG.) Lesson plan duration : 15 Weeks(July 2018 to Nov 2018)
 Lesson Plan Name of the Faculty : SANDEEP (VTF in CIVIL ENGG.) Discipline : CIVIL Engg. Semester : 3 rd Subject : Applied Mechanics Lesson plan duration : 15 s(july 2018 to Nov 2018) - 1 2 3 Theory Practical
Lesson Plan Name of the Faculty : SANDEEP (VTF in CIVIL ENGG.) Discipline : CIVIL Engg. Semester : 3 rd Subject : Applied Mechanics Lesson plan duration : 15 s(july 2018 to Nov 2018) - 1 2 3 Theory Practical
Two Hanging Masses. ) by considering just the forces that act on it. Use Newton's 2nd law while
 Student View Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Edit Assignment Settings per Student Exam 2 - Forces [ Print ] Due: 11:59pm on Tuesday, November 1, 2011 Note: To underst how points are
Student View Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Edit Assignment Settings per Student Exam 2 - Forces [ Print ] Due: 11:59pm on Tuesday, November 1, 2011 Note: To underst how points are
FENG CHIA UNIVERSITY
 FENG CHIA UNIVERSITY Fundamentals of Physics I (With Lab) PHYS114, Summer 2018 (May14-Jun15) Lecturer: TBA E-mail: TBA Time: Monday through Friday Contact hours: 60 (50 minutes each) Credits: 4 Office
FENG CHIA UNIVERSITY Fundamentals of Physics I (With Lab) PHYS114, Summer 2018 (May14-Jun15) Lecturer: TBA E-mail: TBA Time: Monday through Friday Contact hours: 60 (50 minutes each) Credits: 4 Office
CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
Q2. A book whose mass is 2 kg rests on a table. Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the table on the book.
 AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE CODE NO. : MCH110 SEMESTER: TWO
 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE: APPLIED MECHANICS CODE NO. : SEMESTER: TWO PROGRAM: AUTHOR: DATE: APPROVED: TOTAL CREDITS: PREREQUISITE(S):
SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE: APPLIED MECHANICS CODE NO. : SEMESTER: TWO PROGRAM: AUTHOR: DATE: APPROVED: TOTAL CREDITS: PREREQUISITE(S):
Where, m = slope of line = constant c = Intercept on y axis = effort required to start the machine
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
 PHYS 195 CIC Approval: 04/27/2006 BOT APPROVAL: 05/25/2006 STATE APPROVAL: EFFECTIVE TERM: Fall 2006 SECTION I SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE
PHYS 195 CIC Approval: 04/27/2006 BOT APPROVAL: 05/25/2006 STATE APPROVAL: EFFECTIVE TERM: Fall 2006 SECTION I SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE
Resolving Forces. This idea can be applied to forces:
 Page 1 Statics esolving Forces... 2 Example 1... 3 Example 2... 5 esolving Forces into Components... 6 esolving Several Forces into Components... 6 Example 3... 7 Equilibrium of Coplanar Forces...8 Example
Page 1 Statics esolving Forces... 2 Example 1... 3 Example 2... 5 esolving Forces into Components... 6 esolving Several Forces into Components... 6 Example 3... 7 Equilibrium of Coplanar Forces...8 Example
A. Objective of the Course: Objectives of introducing this subject at second year level in civil branches are: 1. Introduction 02
 Subject Code: 0CL030 Subject Name: Mechanics of Solids B.Tech. II Year (Sem-3) Mechanical & Automobile Engineering Teaching Credits Examination Marks Scheme Theory Marks Practical Marks Total L 4 T 0 P
Subject Code: 0CL030 Subject Name: Mechanics of Solids B.Tech. II Year (Sem-3) Mechanical & Automobile Engineering Teaching Credits Examination Marks Scheme Theory Marks Practical Marks Total L 4 T 0 P
ENGINEERING MECHANICS SOLUTIONS UNIT-I
 LONG QUESTIONS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SOLUTIONS UNIT-I 1. A roller shown in Figure 1 is mass 150 Kg. What force P is necessary to start the roller over the block A? =90+25 =115 = 90+25.377 = 115.377 = 360-(115+115.377)
LONG QUESTIONS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SOLUTIONS UNIT-I 1. A roller shown in Figure 1 is mass 150 Kg. What force P is necessary to start the roller over the block A? =90+25 =115 = 90+25.377 = 115.377 = 360-(115+115.377)
UNIT-07. Newton s Three Laws of Motion
 1. Learning Objectives: UNIT-07 Newton s Three Laws of Motion 1. Understand the three laws of motion, their proper areas of applicability and especially the difference between the statements of the first
1. Learning Objectives: UNIT-07 Newton s Three Laws of Motion 1. Understand the three laws of motion, their proper areas of applicability and especially the difference between the statements of the first
USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Feb. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Feb. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme - G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Civil, Chemical, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Group Course Code : AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS Semester : Second Subject Title :
Scheme - G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Civil, Chemical, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Group Course Code : AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS Semester : Second Subject Title :
Unit 1. (a) tan α = (b) tan α = (c) tan α = (d) tan α =
 Unit 1 1. The subjects Engineering Mechanics deals with (a) Static (b) kinematics (c) Kinetics (d) All of the above 2. If the resultant of two forces P and Q is acting at an angle α with P, then (a) tan
Unit 1 1. The subjects Engineering Mechanics deals with (a) Static (b) kinematics (c) Kinetics (d) All of the above 2. If the resultant of two forces P and Q is acting at an angle α with P, then (a) tan
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Units of Chapter 4 Force Newton s First Law of Motion Mass Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion Weight the Force of Gravity; and the Normal
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Units of Chapter 4 Force Newton s First Law of Motion Mass Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion Weight the Force of Gravity; and the Normal
Bachelor of Technology Civil Engineering. 01CI0301: Mechanics of Solids
 01CI0301: Mechanics of Solids Objective of the Course Objectives of introducing this subject at second year level in civil branches are: To study about identification of different types of forces, systematic
01CI0301: Mechanics of Solids Objective of the Course Objectives of introducing this subject at second year level in civil branches are: To study about identification of different types of forces, systematic
STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts
 Contents Preface to Adapted Edition... (v) Preface to Third Edition... (vii) List of Symbols and Abbreviations... (xi) PART - I STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts 1-1 Scope of Mechanics... 1 1-2 Preview
Contents Preface to Adapted Edition... (v) Preface to Third Edition... (vii) List of Symbols and Abbreviations... (xi) PART - I STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts 1-1 Scope of Mechanics... 1 1-2 Preview
Lecture 14 February 16, 2018
 Statics - TAM 210 & TAM 211 Lecture 14 February 16, 2018 SoonTrending.com Announcements Structured office hours of working through practice problems will be held during Sunday office hours, starting Sunday
Statics - TAM 210 & TAM 211 Lecture 14 February 16, 2018 SoonTrending.com Announcements Structured office hours of working through practice problems will be held during Sunday office hours, starting Sunday
Engineering Mechanics
 F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 00 Q. Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.(a) Difference
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 00 Q. Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.(a) Difference
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
 ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 6: Particle Kinetics Kinetics of a particle (Chapter 13) - 13.4-13.6 Chapter 13: Objectives
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 6: Particle Kinetics Kinetics of a particle (Chapter 13) - 13.4-13.6 Chapter 13: Objectives
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107. Lecture-5 : Newton s laws - Part Two
 Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Lecture-5 : Newton s laws - Part Two Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Lecture-5 : Newton s laws - Part Two Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is
Questions from all units
 Questions from all units S.NO 1. 1 UNT NO QUESTON Explain the concept of force and its characteristics. BLOOMS LEVEL LEVEL 2. 2 Explain different types of force systems with examples. Determine the magnitude
Questions from all units S.NO 1. 1 UNT NO QUESTON Explain the concept of force and its characteristics. BLOOMS LEVEL LEVEL 2. 2 Explain different types of force systems with examples. Determine the magnitude
Academic Course Description. BHARATH UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
 BME202 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course (catalog) description Academic Course Description BHARATH UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering BME202 - ENGINEERING
BME202 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course (catalog) description Academic Course Description BHARATH UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering BME202 - ENGINEERING
JNTU World. Subject Code: R13110/R13 '' '' '' ''' '
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Sept. - 2014 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Sept. - 2014 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1
 R Fr F W 24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1 Mass: So far, in our studies of mechanics, we have considered the motion of idealised particles moving geometrically through space. Why a particular particle
R Fr F W 24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1 Mass: So far, in our studies of mechanics, we have considered the motion of idealised particles moving geometrically through space. Why a particular particle
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF MECHANICS Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of force systems.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF MECHANICS Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of force systems.
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA COURSE OUTLINE
 INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA COURSE OUTLINE Kulliyyah / Institute Department / Centre Programme Name of Course / Mode Engineering Mechanical Engineering All Engineering programmes Statics
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA COURSE OUTLINE Kulliyyah / Institute Department / Centre Programme Name of Course / Mode Engineering Mechanical Engineering All Engineering programmes Statics
Vectors. Example: Example: 2 cm. Parts of a vector: 3 cm. Body / Line Segment. Tail / Toe. Tip / Head
 Vectors The study of motion involves the introduction of a variety of quantities which are used to describe the physical world. Examples of such quantities include distance, displacement, speed, velocity,
Vectors The study of motion involves the introduction of a variety of quantities which are used to describe the physical world. Examples of such quantities include distance, displacement, speed, velocity,
I B.TECH EXAMINATIONS, JUNE ENGINEERING MECHANICS (COMMON TO CE, ME, CHEM, MCT, MMT, AE, AME, MIE, MIM)
 Code.No: 09A1BS05 R09 SET-1 I B.TECH EXAMINATIONS, JUNE - 2011 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (COMMON TO CE, ME, CHEM, MCT, MMT, AE, AME, MIE, MIM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
Code.No: 09A1BS05 R09 SET-1 I B.TECH EXAMINATIONS, JUNE - 2011 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (COMMON TO CE, ME, CHEM, MCT, MMT, AE, AME, MIE, MIM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE questions All questions
Part A Atwood Machines Please try this link:
 LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE Assignment 2 Inclined Planes, Pulleys and Accelerating Fluids Problems 83, 108 & 109 (and some handouts) Part A Atwood Machines Please try this link: http://www.wiley.com/college/halliday/0470469080/simulations/sim20/sim20.html
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE Assignment 2 Inclined Planes, Pulleys and Accelerating Fluids Problems 83, 108 & 109 (and some handouts) Part A Atwood Machines Please try this link: http://www.wiley.com/college/halliday/0470469080/simulations/sim20/sim20.html
Process Fluid Mechanics
 Process Fluid Mechanics CENG 2220 Instructor: Francesco Ciucci, Room 2577A (Lift 27-29), Tel: 2358 7187, email: francesco.ciucci@ust.hk. Office Hours: Tuesday 17:00-18:00 or by email appointment Teaching
Process Fluid Mechanics CENG 2220 Instructor: Francesco Ciucci, Room 2577A (Lift 27-29), Tel: 2358 7187, email: francesco.ciucci@ust.hk. Office Hours: Tuesday 17:00-18:00 or by email appointment Teaching
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: b) c)
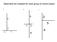 Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
