Security of Nyberg-Rueppel digital signatures without message recovery
|
|
|
- Annice Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 62, No. 4, 2014 DOI: /bpsts Security of Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigtures without messge recovery T. ADAMSKI 1 W. NOWAKOWSKI 2 1 Istitute of Electroic Systems, Wrsw Uiversity of Techology, 15/19 Nowowiejsk St., Wrsw, Pol 2 Istitute of Mthemticl Mchies, 34 Krzywickiego St., Wrsw, Pol Abstrct. The pper els with Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigtures without messge recovery. Probbility of sigture forgery is lyze ssesse. Some simple methos to miimize probbility of sigture forgery re propose. Key wors: cryptogrphy, igitl sigtures, Nyberg-Rueppel sigtures, probbility of sigture forgery. List of Symbols N set of turl umbers, Z set of itegers, Z rig of itegers moulo, Z multiplictive group of the rig Z, <, m > set of iteger greter eve to less eve to m, R + set of oegtive rel umbers, ϕ Euler s fuctio, CDm, ) gretest commo ivisor of two itegers m, #A umber of elemets i the fiite set A, # orer of the fiite group, EX) verge of the rom vrible X, D 2 X) vrice of the rom vrible X, itio moulo, multiplictio moulo, subtrctio moulo, BX, Y ) set of ll bijectios f : X Y, BX) σ-fiel of ll Borel sets of topologicl spce X, 2 X set of ll subsets of the set X, ceilig fuctio. 1. Itrouctio I cotemporry electroics, t like softwre, mesuremet t, trsmitte t lso structure of electroic circuits) c be chge i mlicious, frequetly gerous wy. Digitl sigtures re methos prevetig these mlicious ttcks. Every igitl sigture scheme like commo h writte sigture uer ocumet hs three mi properties: 1. the sigture of perso A c be crete oly by the perso A, 2. the sigture shoul be uforgeble, 3. the sigture shoul be verifible. Every sigture scheme is compose of two lgorithms: lgorithm of sigig use by ocumet Siger) lgorithm of verifictio use by sigture Verifier). There re my ifferet sigture schemes. I geerl sigture schemes re ivie ito two ctegories: oe-time sigture schemes [1, 2] multi-use sigture schemes [1, 2]. There re lso two kis of sigture schemes: sigture with messge recovery sigture schemes with ppeix i.e. without messge recovery). There re lso specil sigtures with itiol fuctiolity like bli sigtures clle lso i blco sigtures), ueible sigture schemes fil-stop sigtures. For exmple, oe-time sigture schemes re the followig lgorithms: oe-time Rbi sigtures, oe-time Lmport sigtures oe time Mtys-Meyer sigtures. Wiely pplie i prctice multi use schemes re the followig: RSA, Elml, DSA Digitl Sigture Algorithm), ECDSA Elliptic Curve DSA), Rbi, Shore sigtures, filly Nyberg-Rueppel clss of sigtures. Some of them re itrouce to the public key cryptogrphy str IEEE P1363. Nyberg-Rueppel sigture schemes re wie clss of igitl sigtures with very iterestig properties. All Nyberg- Rueppel sigtures re probbilistic i the sese tht the sigture epes o sige ocumet rom vrible. Security of ll Nyberg-Rueppel sigtures is bse o DLP Discrete Logrithm Problem). We cosier i the pper simple prticulr cse of Nyberg- Rueppel scheme: so clle Nyberg-Rueppel scheme without messge recovery i.e. sigture scheme with ppeix). I the sequel we lyze ssess probbility of forgery i this sigture scheme propose simple methos to cotrol probbility of forgery. e-mil: t.mski@ise.pw.eu.pl 817
2 T. Amski W. Nowkowski 2. Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigture scheme without messge recovery Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigture i the cosiere i the pper versio) is the sigture scheme with ppeix i.e. without pli text messge recovery. eerl ssumptios re the followig. Assume is fiite group of the orer i.e. f #. Aitiolly we ssume 3 to voi trivility. The plitext messge m the messge which is sige) is ietifie with elemet of the group the m. Assume itiolly tht f : Z is rbitrry but fixe bijectio of the group o the rig Z of itegers moulo. Assume lso tht g, g 1 is geertor of the group or elemet of the sufficietly lrge orer. We ssume for security resos tht the group the elemet g re chose i this wy tht the iscrete logrithm problem DLP) with the bsis g is prcticlly usolvble i the group. Siger chooses t rom umber x Z so, tht CDx, ) 1 x 1. The umber x is privte key is secret. Now, Siger computes g x publishes y f g x s public key. Siger publishes lso the orer of the group i.e., bijectio f : Z elemet g. If # 2 the Z 2 {1} oly possible choice of x Z 2 is x 1. Becuse y g1 g everyoe kows immeitely the Siger s privte key. Hece the orer of the group is ssume i the sequel 3. I prctice the orer of the group is lrge umber becuse DLP hve to be usolvble. Algorithm of sigig ocumet plitext messge m) i.e. sigture geertio is show i Fig. 1. The sige ocumet m is rbitrry elemet of the group. The sigture is orere pir, b) Z. The ocumet is sige i similr wy like i Elml sigture scheme. The sige ocumet is orere pir m,, b)). Nyberg-Rueppel sigture verifictio lgorithm is show i Fig. 2. Fig. 1. Nyberg-Rueppel sigture geertio lgorithm Fig. 2. Nyberg-Rueppel sigture verifictio lgorithm 818 Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624) 2014
3 Security of Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigtures without messge recovery 3. Solutio of lier cogruecies Theorem 3.1. Assume, x, y Z, m N, m 2. If CD, m) 1 the x ymom) if oly if x ymom). If f CD, m) > 1 the x ymom) if oly if x ymom/). Proof. 1. If CD, m) 1 the iverse 1 of umber mo m) i the rig Z m exists. Hece, multiplyig both sies of the cogruece x ymom) by 1, we hve 1 x 1 ymom). Becuse 1 mom) 1 the x ymom). If x ymom) the multiplyig both sies of the cogruece by we obti x ymom). 2. Directly from cogruece efiitio we hve, tht x ymo m) if oly if x y mo m ). But itegers m re reltively prime becuse NWD, m). Applyig the the first prt of the theorem we obti x y mo m ) if oly if x ymom/) filly we hve x ymom) if oly if x ymom/). Corollry. Cogruecies c be ivie sie by sie if ivisio i Z is possible) by iteger which is reltively prime with the moulus m N, m 2. More precisely, if, x, y Z, m N, m 2, CD, m) 1 x ymom) the x ymom). Exmple. Becuse ) mo 6) CD5, 6) 1, the we hve lso 2 4)mo6). Theorem 3.2. o solutios of the lier cogruece x bmom) for CD, m) 1). Assume, b Z, m N, m 2. If CD, m) 1 the the cogruece x bmom) hs solutio x Z give by the formul x b 1 mom), where 1 is iverse of the umber mom) i the rig Z m. Aitiolly every umber x Z is the cogruece solutio if oly if x xmom). Proof. 1. We c esily verify tht the iteger x b 1 mo m) where 1 is iverse of the iteger mom) i the rig Z m ) is solutio of the cogruece x bmom). Iee b 1 mom))mom) 1 )mom)b)mom) bmom) i.e. x bmom) for x b 1 mom). If x is such iteger, tht x bmom) the x bmom) if oly if x xmom). From the prove bove Theorem 3.1 o ivisio sie by sie we obti ow, tht x xmom). O the other h if x xmom) the of course x is solutio of the cogruece x bmom). Theorem 3.3. Assume, b Z, m N, m 2 eote by CD, f m). 1. If b the the cogruece x bmom) hs solutio give by the formul ) ) 1 b x mo m ), ) 1 where is iverse of the iteger mo ) m ) i the rig of itegers moulo m iteger x is solutio of the cogruece x bmom) if oly if x xmom/). Aitiolly i the set Z m we hve exctly solutios of the cogruece x bmom). 2. If b is ot ivisible by the the cogruece x bmom) hs o solutio. Proof. A 1. Assume b CD, m)). If x bmom) the there is k Z tht x b + k m we hve x b + k m. It mes tht x b mo m ). If we hve x b mo m ) the of course x bmom) filly we obti x bmom) if oly if, x b mo m ). Becuse the itegers m re reltively prime the we hve from the previous Theorem 3.2 o lier cogruece solutio), tht the cogruece x b mo m ) hs the solutio, x mo m ) ) ) 1 b ) 1, where is iverse of the umber mo ) m ) i the rig of itegers moulo m ) iteger x is solutio of the cogruece x b mo m ) if oly if, x x mo m ). The the cogruece x bmom) hs the solutio ) ) 1 b x mo m ) the iteger x is solutio of the cogruece x bmom) if oly if, x x mo m ). The lst cogruece is fulfille for exctly umbers x from the set Z x x+k m for k 0, 1,..., 1). The i the set Z m we hve exctly solutios of the cogruece x bmom). A. 2. Assume iversely, tht there is solutio x of the cogruece x bmom). The there is k Z tht x b + k m x k m b. The left sie of the lst equlity is ivisible by where CD, m)) but the right sie is ot, which is impossible. Hece the ssumptio tht the cogruece x bmom) hs solutio les to cotrictio. Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624)
4 T. Amski W. Nowkowski 4. Some bsic theorems The followig simple fct from commuttive rig theory is very useful i the sequel. Fct 4.1 Assume Z is rig of itegers moulo Z. A elemet Z is ivertible i the rig Z if oly if CD, ) 1. Proof. see [3 5]. Theorem 4.2. Assume is fiite group of the orer 3, m is sige pli text messge, x Z is privte key, g, g 1 is rbitrry fixe elemet of the group, y f g x is public key f : Z is bijectio. If the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture is correctly compute i.e. g k m, 1) b k 1 1 f) x), 2) where k Z is rbitrry elemet chose from Z the verifictio formul y f) b m b g 1 is fulfille. Proof. From properties of risig to power i groups we hve: y f) b g xf) g k m) b g xf) g k b m b g xf) k b m b. It follows from the Lgrge theorem tht for every elemet we hve # 1 i.e. 1. The for rbitrry r Z we hve r r mo ). 3) From 2) we obti tht the followig equlity is fulfille 1 f) x k b. The from 3) we hve: g xf) k b g xf) k b) mo ) g 1 filly we obti: y f) b g xf) k b m b g 1 m b. Theorem 4.3. If f : Z is bijectio x Z is fixe elemet of the multiplictive group Z the for every c Z the fuctio β : g) c f) x) Z is bijectio, i prticulr the fuctio h : h) 1 p f) x) Z is bijectio. Proof. If x Z the from the Theorem 3.2 we obti irectly tht the fuctio γ 1 : γ 1 ) f) x Z is bijectio. The fuctio γ 2 : Z z γ 2 ) c z Z is lso bijectio the β γ 2 γ 1 ) s superpositio of two bijectios is bijectio. Corollry 4.4. Uer ssumptios of the theorem 4.3 the umber of elemets for which CD1 f) x, ) 1 is exctly eve to ϕ), where ϕ : N N is the Euler s fuctio. Proof. A umber of ivertible elemets i the rig Z is equl to ϕ). The fuctio h: g)1 p f) x) Z from the Theorem 4.3 is bijectio the the umber of elemets for which CD1 f) x, ) 1 is exctly eve to ϕ). Theorem 4.5. Assume is fiite group of the orer 3, m is sige pli text messge, x Z is Siger s privte key, g, g 1 rbitrry fixe elemet of the group, y f g x f : Z is bijectio the: 1. If b is the seco coorite of the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture, b) of the pli text messge m more strictly b is compute s b k 1 1 p f) x) for chose t rom k Z, the fixe privte key x Z g k m) the b Z if oly if CD1 f) x, ) For every, b) Z, if CD1 f) x, )1 or equivletly b Z ) the we c fi oly oe orere pir m, k) Z tht g k m, 4) b k 1 1 f) x). 5) I other wors there is oly oe pli text messge m oe rom vlue k Z tht the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture compute for m k Z for the fixe Siger s privte key x Z) gives, b) Z. The there is o pli text messge m, m m, for which the Siger s sigture is equl to, b). As result the sigture forgery is impossible. 3. If g is geertor of the group the for every, b) Z : if CD1 f) x, ) > 1 the there re t lest two ifferet pli text messges m, m, m m hvig the sme sigture, b). Proof. A. 1. If we hve k Z 1 f) x Z the from 5) we obti b Z. If we hve b Z, k Z the from 5) we obti tht 1 p f) x is ivertible. Hece CD1 f) x, )1. A. 2. If CD1 f) x, ) 1 the we c solve i uique wy i Z Eq. 5) with ukow k. see the Theorem 3.2). Hvig k Z, we compute from Eq. 4) the uique vlue m. A. 3. From the Theorem 3.3 we obti tht Eq. 5) with ukow k) hs ifferet solutios i Z from Eq. 4) we obti ifferet pli text messges which fulfill the Eq. 4). Two possible situtios forgery impossible, forgery possible) s metioe i the Theorem 4.5 re show i Fig Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624) 2014
5 Security of Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigtures without messge recovery Fig. 3. Two possible situtios ) b) for ) forgery is impossible for b) forgery is possible, ifferet messges c hve the sme sigture, the fuctio h : Z is give for with the formul h) 1 pf) x Z Theorem 4.6. Assume is group of the orer 3, g, g 1, m, k Z, f : Z is bijectio, y is public key y g f x, for privte key x Z ), b Z b Z or equivletly CD1 f) x, ) 1). Assume itiolly tht m is uique pli text messge which gives the sigture, b) Z for the privte key x Z, existece uiqueess of m for every, b) Z see the Theorem 4.5). If m eotes the messge obtie by Verifier for verifictio i.e m,, b))) the the verifictio formul c be i equivlet wy writte s m m 6) y f) b m b g 1. 7) I other wors: the problem if, b) Z is sigture writte by perso with privte key x) uer the pli text messge m is equivlet to fulfillmet of the formul 7). Proof. 1. From the Theorem 4.5 we obti tht for the give orere pir, b) Z there is uique orere pir m, k) Z for which we hve g k m, 8) b k 1 1 f) x). 9) We ssume tht CD1 f) x, ) 1 the 1 f) x Z. A prouct of two ivertible umbers from Z is ivertible the b is ivertible i.e. b Z. From 9) we hve k b 1 1 f) x). 10) O the other h we hve from 8) usig 10) we obti m g k m g b 1 1 f) x). 11) 2. Verifictio of the sigture m,, b)) is simply verifictio if m m. Usig 11) we c write ow equivletly equtio m m s g b 1 1 f) x) m. If we rise both sies of this equtio to the power b Z the we equivletly hve It c be writte s b g b b 1 1 f) x) m b. b g 1 f) x m b. Becuse g 1 the equivletly we hve b g g f)x m b. The bove equtio c be equivletly writte s g x ) f) b g 1 m b. But the public key y g x the filly we hve y f) b g 1 m b. I short, verifictio if m m is equivlet to verifictio if y f) b g 1 m b. It is importt tht i the verifictio formul 7) we hve o secret privte key x. 5. Probbility of forgery From the Theorem 4.5 we obti irectly the followig corollry. Corollry 5.1. If is fiite cyclic group of the orer 3, g 1, g is geertor of the group, x Z is fixe privte key of Siger f : Z fixe rbitrry bijectio the for every : Nyberg-Rueppel sigture, b) is uforgeble if oly if CD1 f) x, ) 1. I other wors if elemet 1 f) x is ivertible or equivletly CD1 f) x, ) 1) the the sigture, b) is uforgeble. The elemet 1 f) x Z is ivertible if oly if b Z the seco coorite of sigture) is ivertible. The rom elemet k Z hs o ifluece o ivertibility of the elemet 1 f) x. We hve oly ϕ) elemets of the group for which the elemet 1 f) x Z is ivertible. Deote A{ f ; CD1 f) x, ) 1}, of course #A ϕ). For every A forgery is ot possible. Assume tht ssumptios o the Corollry 5.1 re fulfille we hve efie two rom vribles X 1 X 2 see Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624)
6 T. Amski W. Nowkowski the Appeix A). The rom vrible X 1 escribes choosig t rom vlue k Z the rom vrible X 2 escribes choosig pli text messge m. From the Theorem A4 from the Appeix A) it follows tht if oe of these rom vribles hs uiform probbility istributio X 1, X 2 re iepeet the the rom vrible g X1 X 2 which escribes computtio of the first coorite of the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture) hs uiform probbility istributio o. Hece probbility, tht the first coorite g X1 X 2 of the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture belogs to \A, is eve to 1 ϕ)/ i.e. Pg X1 X 2 \A) 1 ϕ), I other wors, probbility of forgery is exctly eve to 1 ϕ)/. Becuse the vlue 1 ϕ)/ escribes probbility of forgery it is importt to choose the pproprite so tht 1 ϕ)/ woul be smll. Theorem 5.2. If r N is fixe turl umber p k1 1 p k p kr r, where p 1, p 2,..., p r re primes p 1 < p 2 <... < p r k 1, k 2,..., k r N the ϕ) lim p 1,p 2,...,p r + 1. Proof. It is irect coclusio from bsic properties of the Euler s fuctio ϕ. ϕ) ϕpk1 1 pk pkr p k1 1 pk pkr r r ) ϕpk1 1 ) ϕpk2 2 )... ϕpkr p k1 1 pk pkr r r ) p 1 1)p k1 1 1 p 2 1)p k p r 1)pr kr 1 p k1 p k2... pkr r 1 1p1 ) 1 1p2 )... 2 r 1 1pr ). The ϕ) lim p 1,p 2,...,p r + ) ) lim 1 )1 1p1 1p pr 1. p 1,p 2,...,p r + But i geerl the followig well kow property hols. Theorem 5.3. If ϕ is the Euler fuctio the lim if ϕ) Proof. see [3, 4, 6]. 0 limsup ϕ) 1. Theorem 5.4. Assume B, Z ) is the set of ll bijectios f : Z from the group of the orer 3, to the rig Z B, Z ), 2 B,Z), P) is probbilistic spce. If the probbility istributio P is uiform o B, Z ) the for every fixe every fixe x Z we hve: P{f B, Z ); CD1 f) x, ) 1}) ϕ), where ϕ is the Euler fuctio. Proof. 1. The fuctio h : Z Z efie with the formul hz) 1 z x is bijectio. Deote B h 1 Z ), of course #B ϕ). 2. Assume we hve fixe x Z the: bijectio f : Z fulfills the coitio CD1 f) x, ) 1 if oly if f) B. 3. It follows from the p. 2 tht the umber of ll bijectios f B, Z ) fulfillig the coitio CD1 f) x, ) 1 is equl to ϕ) 1)! o the other h #B, Z )! the: P{f B, Z ); CD1 f) x, ) 1}) ϕ) 1)!! ϕ). 6. Simple methos to improve the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture scheme cotrol probbility of forgery We propose i the sequel two methos to cotrol probbility of forgery i the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture schemes. The first is bse o the Theorem 5.4 Beroulli process, the seco is bse o the Theorem 6.1 formulte below. The first metho which llows to cotrol probbility of forgery. Assume B, Z ), 2 B,Z), P) probbilistic spce with the uiform probbility istributio P o B, Z ). If is fixe elemet of the group x Z is fixe elemet of Z the usig the Theorem 5.4 we c efie sequece of iepeet rom vribles: X 1, X 2,..., X s,... with vlues i the set {0, 1} i the followig wy. Assume we o series of iepeet experimets. I every experimet we choose t rom bijectio f from the set B, Z )with the uiform istributio). For every i N: X i 1 if oly if i the i-th experimet we hve chose bijectio f : Z so tht CD1 f) x, ) 1. From the Theorem 5.4 it follows tht the sequece of iepeet rom vribles X i ) is Beroulli stochstic process efie o the probbilistic spce B, Z ), 2 B,Z), P) with probbility of success equl to ϕ) it mes tht for every i N we hve PX i 1) ϕ) PX i 0) 1 ϕ). Itrouce ow, the rom vrible Y efie o the probbilistic spce B, Z ), 2 B,Z), P),with vlues i the set N {+ } i the followig wy. We hve efie bove Beroulli process X i ) of iepeet experimets. For every s N {+ }, Y s if oly if the coitio CD1 f) x, ) 1 is true the first time i the s-th experimet, Y + if oly if the coitio CD1 f) x, ) > 1 is true i every experimet. 822 Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624) 2014
7 Security of Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigtures without messge recovery Equivletly Y s if oly if X 1 0, X 2 0,..., X s 1 0, X s 1 Y + if oly if for every i N, X i 0. The rom vrible Y is time till the first success i the Beroulli process the it hs geometricl istributio we hve see [3]): for every s N PY s) D 2 Y ) 1 ϕ) EY ) ϕ) 1 ϕ) ) s 1 ϕ), 12) ) 2 13) ϕ)) 2. Propose metho is bse o rom choosig bijectio f : Z from the set B, Z ) with the uiform probbility istributio o B, Z )) ext verifyig if CD1 f) x, ) 1. If CD1 f) x, ) 1 the we hve fou the pproprite bijectio. If CD1 f) x, ) > 1 the we repet the rom choosig. I short, we try t rom some ifferet iepeet bijectios sequece of bijectios) till the first success. From the formuls 13) we hve tht the verge time till the first success i.e. the first bijectio f i : Z tht CD1 f i ) x, ) 1) is equl to ϕ). The seco metho which llows to cotrol probbility of forgery The seco etermiistic) metho which llows to cotrol probbility of forgery is bse o the followig theorem. Theorem 6.1. Assume is fiite group of the orer, 3 x Z is fixe elemet of the multiplictive group Z. For every N there is fiite sequece of r bijectios f 1, f 2,..., f r, where for every i < 1, r >, f i : Z with the followig property: for every there is i < 1, r > tht CD1 f i ) x, ) 1. The smllest r from the bove theorem is equl to 2. ϕ) Proof. 1. It is possible to write ow the set s sum of r subsets A 1, A 2,..., A r r A i, where r for every i < 1, r > we hve ϕ) #A i ϕ) itiolly for every i, j < 1, r 1 >, i j we hve A i A j. It mes tht A 1, A 2,..., A r 1 re isjoit i pirs. As the the lst subset A r we c tke every set which fulfils two coitios: #A i ϕ) \ r 1 A i A r. 2. Now, we c efie r bijectios h 1, h 2,..., h r, where for every i < 1, r >, h i : Z h i A i ) Z. 3. For every bijectio h i : Z we c choose bijectio f i : Z i this wy tht for every, we hve h i ) 1 f i ) x. It is possible becuse we c tke for every, f i ) h f i ) 1) x 1, where x 1 is iverse i the multiplictive group Z. The fuctio f i : Z is bijectio s superpositio of 3 bijectios. 4. From the poit 1, we obti ow tht for every there is i < 1, r > tht h i ) Z or equivletly 1 f i ) x Z. The filly we hve fou fiite sequece of r bijectios f 1, f 2,..., f r, tht for every there is i < 1, r > tht CD1 f i ) x, ) It is obvious tht if h 1, h 2,..., h s is rbitrry fiite sequece of s bijectios h i : Z the the smllest umber s for which the followig coitio 14) s h 1 i Z ) 14) is fulfille is equl to of course 2). ϕ) ϕ) Equivletly the coitio 14) c be writte i the followig wy i <1,s> hi ) Z. 15) If we ssume tht for every we hve h i ) h) 1 f i ) x the the coitio 15) we c write i the form i.e. i <1,s> i <1,s> 1 f i ) x Z 16) CD1 f i ) x) 1. 17) The i short: for the give fiite sequece f 1, f 2,..., f s of s bijectios f i : Z the smllest umber s for which the coitio 16) is fulfille is equl to. ϕ) Tht is esy to verify tht for the group of the orer 2 the thesis of the bove theorem is lso fulfille, but i the pper we ssume for uiformity reso tht 3. Of course we hve i <1,r> CD1 f i ) x, ) 1, A i where A 1, A 2,..., A r re subsets of efie i the proof of the Theorem 6.2 or equivletly i <1,r> 1 f i ) x Z. A i The lgorithm of the propose metho repets the ie of the Theorem 6.1 proof. Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624)
8 T. Amski W. Nowkowski 1. Like i poit 1 of the proof, we choose i rbitrry wy sequece of r subsets A 1, A 2,..., A r r A i, where r for every i < 1, r > we hve ϕ) #A i ϕ) itiolly for every i, j < 1, r 1 >, i j we hve A i A j. It mes tht A 1, A 2,..., A r 1 re isjoit i pirs. As the the lst subset A r we c tke every set which fulfils two coitios: #A i ϕ) \ r 1 A i A r. 2. Usig A 1, A 2,..., A r we fi fiite sequece of r bijectios f 1, f 2,..., f r, with the property, tht for every there is i < 1, r > tht CD1 f i ) x, ) The we pply sequetilly bijectios f 1, f 2,..., f r verifyig for i 1, 2,..., r if CD1 f i ) x, ) 1. The first i < 1, r > for which CD1 f i ) x, ) 1 gives bijectio f i use to sig ocumet m. 7. Coclusios 1. We c esily ssess probbility of possible forgery i Nyberg-Rueppel sigture schemes. 2. Security of the Nyberg-Rueppel sigture scheme epes o the orer of the group. The the orer of the group hve to be crefully chose. 3. I the pper two simple methos of fully relible Nyberg- Rueppel like sigture schemes were propose. The first, probbilistic is bse o the Beroulli stochstic process is relible from probbilistic poit of view. The seco metho is etermiistic works lwys correctly. The essece of the presete two methos is tht we re chgig the bijectio f so tht forgery woul be impossible. As result the bijectio f is ot uiversl prmeter for the sigture scheme like i clssicl Nyberg-Rueppel methos the the chose bijectio f hve to be e s thir coorite to the sigture. The sige pli text messge hs the shpe m,, b, f)). Appeix Rom vribles with vlues i groups Defiitio A.1 topologicl group) Assume, ) is group, T) is topologicl spce, where T 2 is topology. The group is clle topologicl group iff the followig two coitios re fulfille: 1. the prouct : is cotiuous mppig of oto, 2. the iversio x x 1 is cotiuous mppig of oto. A topologicl group is lso i turl wy mesurble spce, B)), where B) is σ fiel of Borel subsets of. Hece we c efie rom vribles with vlues i. I the pper we re itereste i fiite groups for which we mit tht T 2 B) 2. The every fiite group c be trete s topologicl group mesurble spce. Defiitio A.2 covolutio of two fiite mesures) Assume is Abeli topologicl group µ 1 µ 2 re two fiite mesures o the mesurble spce, B)), B) B), µ 1 µ 2 ) is prouct of two spces with mesure:, B), µ 1 ), B), µ 2 ). Assume itiolly tht µ is iuce mesure by the cotiuous mppig f : x, y) x y i.e. for every A B) we hve µa) µ 1 µ 2 f 1 A)). The mesure µ is clle covolutio of two mesures: µ 1 µ 2 is eote by µ 1 µ 2 i.e. µ µ 1 µ 2. Theorem A1. Assume is Abeli topologicl group µ 1 µ 2 re two fiite mesures o the mesurble spce, B)). If µ µ 1 µ 2 the 1. The fuctio f : x µ 1 A x 1 ) R + is µ 2 itegrble the fuctio g : x µ 2 A x 1 ) R + is µ 1 itegrble 2. for every A B) we hve µa) µ 1 µ 2 A) µ 1 A x 1 )µ 2 x) Proof. See [7]. µ 2 A x 1 )µ 1 x). Theorem A2. Assume X 1 X 2 re iepeet rom vribles efie o probbilistic spce Ω, M, P) with vlues i Abeli topologicl group. If P Xi eotes probbility istributio of the rom vrible X i for i 1, 2 the 1. Y f X 1 X 2 is rom vrible 2. the probbility istributio P Y of the rom vrible Y is give by the followig formul Proof. See [8]. P Y P X1 P X2. Defiitio A.3 uiform probbility istributio o group ). Assume X is rom vribles efie o probbilistic spce Ω, M, P) with vlues i Abeli topologicl group. We sy tht the rom vrible X hs uiform probbility istributio iff for every A B) every x we hve P X A) P X A x), where P X eotes probbility istributio of the rom vrible X. Theorem A3. Assume X 1 X 2 re iepeet rom vribles efie o probbilistic spce Ω, M, P) with vlues 824 Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624) 2014
9 Security of Nyberg-Rueppel igitl sigtures without messge recovery i Abeli topologicl group. If P Xi eotes probbility istributio of the rom vrible X i for i 1, 2 oe of the probbility istributios P X1,P X2 is uiform the rom vrible Y f X 1 X 2 hs the uiform istributio. Proof. Assume P X1 is the uiform probbility istributio the from theorems A1 A2 we obti for every A B) P Y A) P X1 P X2 A) P X1 A x 1 )P X2 x) P X1 A)P X2 x) P X1 A) 1P X2 x) P X1 A). The the rom vrible Y f X 1 X 2 hs the uiform istributio. The bove theorem is frequetly use i cryptogrphy i the cse whe the Abeli group is fiite. For the fiite cyclic group, the followig simple fct is true. If g is geertor of the fiite cyclic group, the orer of is equl to X is rom vrible with uiform probbility istributio o the rig Z the rom vrible g X hs uiform probbility istributio o. Theorem A4. Assume we hve two iepeet rom vribles X 1 X 2 efie o probbilistic spce Ω, M, P). Assume itiolly tht g is geertor of the fiite cyclic group, orer of is equl to 2, X 1 is rom vrible ito the rig Z X 2 is rom vrible with vlues i the group. If oe of the rom vribles X 1, X 2 hs uiform probbility istributio X 1 o Z or X 2 o ) the rom vrible g X1 X 2 hs uiform probbility istributio o. Proof. A fiite cyclic group is Abeli s i the Theorem A3. Hece if the rom vrible X 2 hs uiform probbility istributio o the from theorem A3 we obti tht the probbility istributio of the rom vrible g X1 X 2 is uiform. If the rom vrible X 1 hs the uiform probbility istributio o Z the the rom vrible g X1 hs the uiform istributio o from Theorem A3 we hve tht the probbility istributio of the rom vrible g X1 X 2 hs uiform probbility istributio o. REFERENCES [1] A. Meezes, P. Oorschot, S. Vstoe, Hbook of Applie Cryptogrphy, CRC Press Ic., 1997, [2] J. Pieprzyk, T. Hrjoo, J. Seberry, Fumetls of Computer Security, Spriger, Berli, [3] V. Shoup, A Computtiol Itrouctio to Number Theory Algebr, Cmbrige Uiversity Press, Cmbrige, [4] S. Y, Number Theory for Computig, Spriger, Berli- Heielberg, [5] N. Koblitz, A Course i Number Theory Cryptogrphy, Spriger, New York, [6] W. Nrkiewicz, Number Theory, PWN, Wrszw, 1990, i Polish). [7] K. Muri, Alysis, PWN, Wrszw, 1991, i Polish). [8] J. Jkubowski R. Sztecel, Itrouctio to Probbility Theory, Script, Wrszw, 2004, i Polish). [9] C.C. Li C.S. Lih, Cryptlysis of Nyberg-Ruppel s messge recovery scheme, IEEE Commuictios Letters 4 7), ), DOI: / [10]. Ateiese B. Meeiros, A provbly secure Nyberg- Rueppel sigture vrit with pplictios, Cryptology eprit Archive, Report 2004/93, ). [11] IEEE Str Specifictios for Public-Key Cryptogrphy DOI: /IEEESTD [12] I. Blke,. Seroussi, N. Smrt, Elliptic Curves i Cryptogrphy, Uiversity of Cmbrige, Cmbrige, Bull. Pol. Ac.: Tech. 624)
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS
 M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
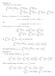 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions (4.1, 4.2, 4.4, 4.6)
 WQ017 MAT16B Lecture : Mrch 8, 017 Aoucemets W -4p Wellm 115-4p Wellm 115 Q4 ue F T 3/1 10:30-1:30 FINAL Expoetil Logrithmic Fuctios (4.1, 4., 4.4, 4.6) Properties of Expoets Let b be positive rel umbers.
WQ017 MAT16B Lecture : Mrch 8, 017 Aoucemets W -4p Wellm 115-4p Wellm 115 Q4 ue F T 3/1 10:30-1:30 FINAL Expoetil Logrithmic Fuctios (4.1, 4., 4.4, 4.6) Properties of Expoets Let b be positive rel umbers.
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Schrödinger Equation Via Laplace-Beltrami Operator
 IOSR Jourl of Mthemtics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov. - Dec. 7), PP 9-95 www.iosrjourls.org Schrödiger Equtio Vi Lplce-Beltrmi Opertor Esi İ Eskitşçioğlu,
IOSR Jourl of Mthemtics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov. - Dec. 7), PP 9-95 www.iosrjourls.org Schrödiger Equtio Vi Lplce-Beltrmi Opertor Esi İ Eskitşçioğlu,
Power Series Solutions to Generalized Abel Integral Equations
 Itertiol Jourl of Mthemtics d Computtiol Sciece Vol., No. 5, 5, pp. 5-54 http://www.isciece.org/jourl/ijmcs Power Series Solutios to Geerlized Abel Itegrl Equtios Rufi Abdulli * Deprtmet of Physics d Mthemtics,
Itertiol Jourl of Mthemtics d Computtiol Sciece Vol., No. 5, 5, pp. 5-54 http://www.isciece.org/jourl/ijmcs Power Series Solutios to Geerlized Abel Itegrl Equtios Rufi Abdulli * Deprtmet of Physics d Mthemtics,
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
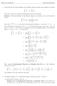 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
lecture 24: Gaussian quadrature rules: fundamentals
 133 lecture 24: Gussi qudrture rules: fudmetls 3.4 Gussi qudrture It is cler tht the trpezoid rule, b 2 f ()+ f (b), exctly itegrtes lier polyomils, but ot ll qudrtics. I fct, oe c show tht o qudrture
133 lecture 24: Gussi qudrture rules: fudmetls 3.4 Gussi qudrture It is cler tht the trpezoid rule, b 2 f ()+ f (b), exctly itegrtes lier polyomils, but ot ll qudrtics. I fct, oe c show tht o qudrture
Prior distributions. July 29, 2002
 Prior distributios Aledre Tchourbov PKI 357, UNOmh, South 67th St. Omh, NE 688-694, USA Phoe: 4554-64 E-mil: tchourb@cse.ul.edu July 9, Abstrct This documet itroduces prior distributios for the purposes
Prior distributios Aledre Tchourbov PKI 357, UNOmh, South 67th St. Omh, NE 688-694, USA Phoe: 4554-64 E-mil: tchourb@cse.ul.edu July 9, Abstrct This documet itroduces prior distributios for the purposes
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
Double Sums of Binomial Coefficients
 Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
Lecture 14. Encryption
 Lecture 4. Ecryptio T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso d R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukw Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-207 Networkig Lbortory
Lecture 4. Ecryptio T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso d R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukw Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-207 Networkig Lbortory
Numbers (Part I) -- Solutions
 Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Reversing the Arithmetic mean Geometric mean inequality
 Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Asymptotic Theory Greene Ch. 4, App. D, Kennedy App. C, R scripts: module3s1a, module3s1b, module3s1c, module3s1d
 Asymptotic Theory Greee Ch. 4, App. D, Keey App. C, R scripts: moule3s, moule3sb, moule3sc, moule3s Overview of key cocepts Cosier rom vrible x tht itself is fuctio of other rom vribles smple size (e.g
Asymptotic Theory Greee Ch. 4, App. D, Keey App. C, R scripts: moule3s, moule3sb, moule3sc, moule3s Overview of key cocepts Cosier rom vrible x tht itself is fuctio of other rom vribles smple size (e.g
Geometric Sequences. Geometric Sequence. Geometric sequences have a common ratio.
 s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
Unit 1. Extending the Number System. 2 Jordan School District
 Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
A general theory of minimal increments for Hirsch-type indices and applications to the mathematical characterization of Kosmulski-indices
 Mlysi Jourl of Librry & Iformtio Sciece, Vol. 9, o. 3, 04: 4-49 A geerl theory of miiml icremets for Hirsch-type idices d pplictios to the mthemticl chrcteriztio of Kosmulski-idices L. Egghe Uiversiteit
Mlysi Jourl of Librry & Iformtio Sciece, Vol. 9, o. 3, 04: 4-49 A geerl theory of miiml icremets for Hirsch-type idices d pplictios to the mthemticl chrcteriztio of Kosmulski-idices L. Egghe Uiversiteit
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Vectors. Vectors in Plane ( 2
 Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
3.7 The Lebesgue integral
 3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
The Elementary Arithmetic Operators of Continued Fraction
 Americ-Eursi Jourl of Scietific Reserch 0 (5: 5-63, 05 ISSN 88-6785 IDOSI Pulictios, 05 DOI: 0.589/idosi.ejsr.05.0.5.697 The Elemetry Arithmetic Opertors of Cotiued Frctio S. Mugssi d F. Mistiri Deprtmet
Americ-Eursi Jourl of Scietific Reserch 0 (5: 5-63, 05 ISSN 88-6785 IDOSI Pulictios, 05 DOI: 0.589/idosi.ejsr.05.0.5.697 The Elemetry Arithmetic Opertors of Cotiued Frctio S. Mugssi d F. Mistiri Deprtmet
Completion of a Dislocated Metric Space
 69 Chpter-3 Completio o Dislocte Metric Spce 3 Itrouctio: metric o X [] i We recll tht istce uctio o set X is si to be islocte i) y ) ii) 0 implies y iii) z) z or ll y z i X I is islocte metric o X the
69 Chpter-3 Completio o Dislocte Metric Spce 3 Itrouctio: metric o X [] i We recll tht istce uctio o set X is si to be islocte i) y ) ii) 0 implies y iii) z) z or ll y z i X I is islocte metric o X the
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systems Linear Equations
 MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Basic Limit Theorems
 Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Analytic Number Theory Solutions
 Aalytic Number Theory Solutios Sea Li Corell Uiversity sl6@corell.eu Ja. 03 Itrouctio This ocumet is a work-i-progress solutio maual for Tom Apostol s Itrouctio to Aalytic Number Theory. The solutios were
Aalytic Number Theory Solutios Sea Li Corell Uiversity sl6@corell.eu Ja. 03 Itrouctio This ocumet is a work-i-progress solutio maual for Tom Apostol s Itrouctio to Aalytic Number Theory. The solutios were
A GENERALIZATION OF GAUSS THEOREM ON QUADRATIC FORMS
 A GENERALIZATION OF GAU THEOREM ON QUADRATIC FORM Nicole I Brtu d Adi N Cret Deprtmet of Mth - Criov Uiversity, Romi ABTRACT A origil result cocerig the extesio of Guss s theorem from the theory of biry
A GENERALIZATION OF GAU THEOREM ON QUADRATIC FORM Nicole I Brtu d Adi N Cret Deprtmet of Mth - Criov Uiversity, Romi ABTRACT A origil result cocerig the extesio of Guss s theorem from the theory of biry
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-5(1), 2014, Available online through ISSN
 Itertiol Jourl of Mthemticl Archive-5( 4 93-99 Avilble olie through www.ijm.ifo ISSN 9 546 GENERALIZED FOURIER TRANSFORM FOR THE GENERATION OF COMPLE FRACTIONAL MOMENTS M. Gji F. Ghrri* Deprtmet of Sttistics
Itertiol Jourl of Mthemticl Archive-5( 4 93-99 Avilble olie through www.ijm.ifo ISSN 9 546 GENERALIZED FOURIER TRANSFORM FOR THE GENERATION OF COMPLE FRACTIONAL MOMENTS M. Gji F. Ghrri* Deprtmet of Sttistics
General properties of definite integrals
 Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Certain sufficient conditions on N, p n, q n k summability of orthogonal series
 Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Particle in a Box. and the state function is. In this case, the Hermitian operator. The b.c. restrict us to 0 x a. x A sin for 0 x a, and 0 otherwise
 Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Stalnaker s Argument
 Stlker s Argumet (This is supplemet to Coutble Additiviy, Dutch Books d the Sleepig Beuty roblem ) Stlker (008) suggests rgumet tht c be stted thus: Let t be the time t which Beuty wkes o Mody morig. Upo
Stlker s Argumet (This is supplemet to Coutble Additiviy, Dutch Books d the Sleepig Beuty roblem ) Stlker (008) suggests rgumet tht c be stted thus: Let t be the time t which Beuty wkes o Mody morig. Upo
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
=> PARALLEL INTERCONNECTION. Basic Properties LTI Systems. The Commutative Property. Convolution. The Commutative Property. The Distributive Property
 Lier Time-Ivrit Bsic Properties LTI The Commuttive Property The Distributive Property The Associtive Property Ti -6.4 / Chpter Covolutio y ] x ] ] x ]* ] x ] ] y] y ( t ) + x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ x( t) * h(
Lier Time-Ivrit Bsic Properties LTI The Commuttive Property The Distributive Property The Associtive Property Ti -6.4 / Chpter Covolutio y ] x ] ] x ]* ] x ] ] y] y ( t ) + x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ x( t) * h(
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
18.01 Calculus Jason Starr Fall 2005
 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
ALGEBRA HW 7 CLAY SHONKWILER
 ALGEBRA HW 7 CLAY SHONKWILER Prove, or isprove a salvage: If K is a fiel, a f(x) K[x] has o roots, the K[x]/(f(x)) is a fiel. Couter-example: Cosier the fiel K = Q a the polyomial f(x) = x 4 + 3x 2 + 2.
ALGEBRA HW 7 CLAY SHONKWILER Prove, or isprove a salvage: If K is a fiel, a f(x) K[x] has o roots, the K[x]/(f(x)) is a fiel. Couter-example: Cosier the fiel K = Q a the polyomial f(x) = x 4 + 3x 2 + 2.
Some Results on the Variation of Composite Function of Functions of Bounded d Variation
 AMRICAN JOURNAL OF UNDRGRADUAT RSARCH OL. 6 NO. 4 Some Results o the ritio o Composite Fuctio o Fuctios o Boue ritio Mohse Soltir Deprtmet o Mthemtics Fculty o Sciece K.N. Toosi Uiversity o Techology P.O.
AMRICAN JOURNAL OF UNDRGRADUAT RSARCH OL. 6 NO. 4 Some Results o the ritio o Composite Fuctio o Fuctios o Boue ritio Mohse Soltir Deprtmet o Mthemtics Fculty o Sciece K.N. Toosi Uiversity o Techology P.O.
Lesson 4 Linear Algebra
 Lesso Lier Algebr A fmily of vectors is lierly idepedet if oe of them c be writte s lier combitio of fiitely my other vectors i the collectio. Cosider m lierly idepedet equtios i ukows:, +, +... +, +,
Lesso Lier Algebr A fmily of vectors is lierly idepedet if oe of them c be writte s lier combitio of fiitely my other vectors i the collectio. Cosider m lierly idepedet equtios i ukows:, +, +... +, +,
is infinite. The converse is proved similarly, and the last statement of the theorem is clear too.
 12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
DETERMINANT. = 0. The expression a 1. is called a determinant of the second order, and is denoted by : y + c 1
 NOD6 (\Dt\04\Kot\J-Advced\SMP\Mths\Uit#0\NG\Prt-\0.Determits\0.Theory.p65. INTRODUCTION : If the equtios x + b 0, x + b 0 re stisfied by the sme vlue of x, the b b 0. The expressio b b is clled determit
NOD6 (\Dt\04\Kot\J-Advced\SMP\Mths\Uit#0\NG\Prt-\0.Determits\0.Theory.p65. INTRODUCTION : If the equtios x + b 0, x + b 0 re stisfied by the sme vlue of x, the b b 0. The expressio b b is clled determit
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2008/09 PROBLEM SET 10 SOLUTIONS. f m. and. f m = 0. and x i = a + i. a + i. a + n 2. n(n + 1) = a(b a) +
 MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
The limit comparison test
 Roerto s Notes o Ifiite Series Chpter : Covergece tests Sectio 4 The limit compriso test Wht you eed to kow lredy: Bsics of series d direct compriso test. Wht you c ler here: Aother compriso test tht does
Roerto s Notes o Ifiite Series Chpter : Covergece tests Sectio 4 The limit compriso test Wht you eed to kow lredy: Bsics of series d direct compriso test. Wht you c ler here: Aother compriso test tht does
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Surds, Indices, and Logarithms Radical
 MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
Section 2.2. Matrix Multiplication
 Mtri Alger Mtri Multiplitio Setio.. Mtri Multiplitio Mtri multiplitio is little more omplite th mtri itio or slr multiplitio. If A is the prout A of A is the ompute s follow: m mtri, the is k mtri, 9 m
Mtri Alger Mtri Multiplitio Setio.. Mtri Multiplitio Mtri multiplitio is little more omplite th mtri itio or slr multiplitio. If A is the prout A of A is the ompute s follow: m mtri, the is k mtri, 9 m
(II.G) PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES
 II.G PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES I II.C, we used the Chiese Remider Theorem to reduce cogrueces modulo m r i i to cogrueces modulo r i i. For exmles d roblems, we stuck with r i 1 becuse we hd
II.G PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES I II.C, we used the Chiese Remider Theorem to reduce cogrueces modulo m r i i to cogrueces modulo r i i. For exmles d roblems, we stuck with r i 1 becuse we hd
AN INEQUALITY OF GRÜSS TYPE FOR RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL AND APPLICATIONS FOR SPECIAL MEANS
 RGMIA Reserch Report Collectio, Vol., No., 998 http://sci.vut.edu.u/ rgmi/reports.html AN INEQUALITY OF GRÜSS TYPE FOR RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL AND APPLICATIONS FOR SPECIAL MEANS S.S. DRAGOMIR AND I.
RGMIA Reserch Report Collectio, Vol., No., 998 http://sci.vut.edu.u/ rgmi/reports.html AN INEQUALITY OF GRÜSS TYPE FOR RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL AND APPLICATIONS FOR SPECIAL MEANS S.S. DRAGOMIR AND I.
Chapter 2 Transformations and Expectations
 Chapter Trasformatios a Epectatios Chapter Distributios of Fuctios of a Raom Variable Problem: Let be a raom variable with cf F ( ) If we efie ay fuctio of, say g( ) g( ) is also a raom variable whose
Chapter Trasformatios a Epectatios Chapter Distributios of Fuctios of a Raom Variable Problem: Let be a raom variable with cf F ( ) If we efie ay fuctio of, say g( ) g( ) is also a raom variable whose
arxiv: v4 [math.co] 5 May 2011
![arxiv: v4 [math.co] 5 May 2011 arxiv: v4 [math.co] 5 May 2011](/thumbs/90/102209301.jpg) A PROBLEM OF ENUMERATION OF TWO-COLOR BRACELETS WITH SEVERAL VARIATIONS arxiv:07101370v4 [mathco] 5 May 011 VLADIMIR SHEVELEV Abstract We cosier the problem of eumeratio of icogruet two-color bracelets
A PROBLEM OF ENUMERATION OF TWO-COLOR BRACELETS WITH SEVERAL VARIATIONS arxiv:07101370v4 [mathco] 5 May 011 VLADIMIR SHEVELEV Abstract We cosier the problem of eumeratio of icogruet two-color bracelets
LEVEL I. ,... if it is known that a 1
 LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
Error-free compression
 Error-free compressio Useful i pplictio where o loss of iformtio is tolerble. This mybe due to ccurcy requiremets, legl requiremets, or less th perfect qulity of origil imge. Compressio c be chieved by
Error-free compressio Useful i pplictio where o loss of iformtio is tolerble. This mybe due to ccurcy requiremets, legl requiremets, or less th perfect qulity of origil imge. Compressio c be chieved by
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
The Definite Integral
 The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
On triangular billiards
 O triagular billiars Abstract We prove a cojecture of Keyo a Smillie cocerig the oexistece of acute ratioal-agle triagles with the lattice property. MSC-iex: 58F99, 11N25 Keywors: Polygoal billiars, Veech
O triagular billiars Abstract We prove a cojecture of Keyo a Smillie cocerig the oexistece of acute ratioal-agle triagles with the lattice property. MSC-iex: 58F99, 11N25 Keywors: Polygoal billiars, Veech
Chapter Real Numbers
 Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
Similar idea to multiplication in N, C. Divide and conquer approach provides unexpected improvements. Naïve matrix multiplication
 Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
6.451 Principles of Digital Communication II Wednesday, March 9, 2005 MIT, Spring 2005 Handout #12. Problem Set 5 Solutions
 6.51 Priciples of Digital Commuicatio II Weesay, March 9, 2005 MIT, Sprig 2005 Haout #12 Problem Set 5 Solutios Problem 5.1 (Eucliea ivisio algorithm). (a) For the set F[x] of polyomials over ay fiel F,
6.51 Priciples of Digital Commuicatio II Weesay, March 9, 2005 MIT, Sprig 2005 Haout #12 Problem Set 5 Solutios Problem 5.1 (Eucliea ivisio algorithm). (a) For the set F[x] of polyomials over ay fiel F,
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
1 = 2 d x. n x n (mod d) d n
 HW2, Problem 3*: Use Dirichlet hyperbola metho to show that τ 2 + = 3 log + O. This ote presets the ifferet ieas suggeste by the stuets Daiel Klocker, Jürge Steiiger, Stefaia Ebli a Valerie Roiter for
HW2, Problem 3*: Use Dirichlet hyperbola metho to show that τ 2 + = 3 log + O. This ote presets the ifferet ieas suggeste by the stuets Daiel Klocker, Jürge Steiiger, Stefaia Ebli a Valerie Roiter for
Topic 4 Fourier Series. Today
 Topic 4 Fourier Series Toy Wves with repetig uctios Sigl geertor Clssicl guitr Pio Ech istrumet is plyig sigle ote mile C 6Hz) st hrmoic hrmoic 3 r hrmoic 4 th hrmoic 6Hz 5Hz 783Hz 44Hz A sigle ote will
Topic 4 Fourier Series Toy Wves with repetig uctios Sigl geertor Clssicl guitr Pio Ech istrumet is plyig sigle ote mile C 6Hz) st hrmoic hrmoic 3 r hrmoic 4 th hrmoic 6Hz 5Hz 783Hz 44Hz A sigle ote will
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES
 Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
Chapter 2 Infinite Series Page 1 of 9
 Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Lecture 17
 CS 70 Discrete Mthemtics d Proility Theory Sprig 206 Ro d Wlrd Lecture 7 Vrice We hve see i the previous ote tht if we toss coi times with is p, the the expected umer of heds is p. Wht this mes is tht
CS 70 Discrete Mthemtics d Proility Theory Sprig 206 Ro d Wlrd Lecture 7 Vrice We hve see i the previous ote tht if we toss coi times with is p, the the expected umer of heds is p. Wht this mes is tht
Test Info. Test may change slightly.
 9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE
 MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
Students must always use correct mathematical notation, not calculator notation. the set of positive integers and zero, {0,1, 2, 3,...
 Appedices Of the vrious ottios i use, the IB hs chose to dopt system of ottio bsed o the recommedtios of the Itertiol Orgiztio for Stdrdiztio (ISO). This ottio is used i the emitio ppers for this course
Appedices Of the vrious ottios i use, the IB hs chose to dopt system of ottio bsed o the recommedtios of the Itertiol Orgiztio for Stdrdiztio (ISO). This ottio is used i the emitio ppers for this course
Chapter System of Equations
 hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
Section IV.6: The Master Method and Applications
 Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
SM2H. Unit 2 Polynomials, Exponents, Radicals & Complex Numbers Notes. 3.1 Number Theory
 SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
Inference on One Population Mean Hypothesis Testing
 Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
Iferece o Oe Popultio Me ypothesis Testig Scerio 1. Whe the popultio is orml, d the popultio vrice is kow i. i. d. Dt : X 1, X,, X ~ N(, ypothesis test, for istce: Exmple: : : : : : 5'7" (ull hypothesis:
Principles of Mathematical Analysis
 Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Algebra II, Chapter 7. Homework 12/5/2016. Harding Charter Prep Dr. Michael T. Lewchuk. Section 7.1 nth roots and Rational Exponents
 Algebr II, Chpter 7 Hrdig Chrter Prep 06-07 Dr. Michel T. Lewchuk Test scores re vilble olie. I will ot discuss the test. st retke opportuit Sturd Dec. If ou hve ot tke the test, it is our resposibilit
Algebr II, Chpter 7 Hrdig Chrter Prep 06-07 Dr. Michel T. Lewchuk Test scores re vilble olie. I will ot discuss the test. st retke opportuit Sturd Dec. If ou hve ot tke the test, it is our resposibilit
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 1: Linear Algebra Review March 18 th, 2006
 Sttistics for Ficil Egieerig Sessio : Lier Algebr Review rch 8 th, 6 Topics Itroductio to trices trix opertios Determits d Crmer s rule Eigevlues d Eigevectors Quiz The cotet of Sessio my be fmilir to
Sttistics for Ficil Egieerig Sessio : Lier Algebr Review rch 8 th, 6 Topics Itroductio to trices trix opertios Determits d Crmer s rule Eigevlues d Eigevectors Quiz The cotet of Sessio my be fmilir to
