lecture 24: Gaussian quadrature rules: fundamentals
|
|
|
- Lynne Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 133 lecture 24: Gussi qudrture rules: fudmetls 3.4 Gussi qudrture It is cler tht the trpezoid rule, b 2 f ()+ f (b), exctly itegrtes lier polyomils, but ot ll qudrtics. I fct, oe c show tht o qudrture rule of the form w f ()+w b f (b) will exctly itegrte ll qudrtics over [, b], regrdless of the choice of costts w d w b. However, otice tht geerl qudrture rule with two poits, w 0 f (x 0 )+w 1 f (x 1 ), hs four prmeters (w 0, x 0, w 1, x 1 ). We might the hope tht we could pick these four prmeters i such fshio tht the qudrture rule is exct for four-dimesiol subspce of fuctios, P 3. This sectio explores geerliztios of this questio A specil 2-poit rule Suppose we cosider more geerl clss of 2-poit qudrture rules, where we do ot iitilly fix the poits t which the itegrd f is evluted: I( f )=w 0 f (x 0 )+w 1 f (x 1 ) for ukows odes x 0, x 1 2 [, b] d weights w 0 d w 1. We wish to pick x 0, x 1, w 0, d w 1 so tht the qudrture rule exctly itegrtes ll polyomils of the lrgest degree possible. Sice this qudrture rule is lier, it will suffice to check tht it is exct o moomils. There re four ukows; to get four equtios, we will require I( f ) to exctly itegrte 1, x, x 2, x 3. f (x) =1: f (x) =x : f (x) =x 2 : f (x) =x 3 : 1dx = I(1) =) b = w 0 + w 1 x dx = I(x) =) 1 2 (b2 2 )=w 0 x 0 + w 1 x 1 x 2 dx = I(x 2 ) =) 1 3 (b3 3 )=w 0 x w 1x 2 1 x 3 dx = I(x 3 ) =) 1 4 (b4 4 )=w 0 x w 1x 3 1
2 134 Three of these costrits re olier equtios of the ukows x 0, x 1, w 0, d w 1 : thus questios of existece d uiqueess of solutios becomes bit more subtle th for the lier equtios we so ofte ecouter. I this cse, solutio does exist: w 0 = w 1 = 1 2 (b ), x 0 = 1 p 2 (b + ) 3 6 (b ), x 1 = 1 p 2 (b + )+ 3 6 (b ). Notice tht x 0, x 1 2 [, b]: If this were ot the cse, we could ot use these poits s qudrture odes, sice f might ot be defied outside [, b]. Whe [, b] = [ 1, 1], the iterpoltio poits re ±1/ p 3, givig the qudrture rule I( f )= f ( 1/ p 3)+ f (1/ p 3) Geerliztio to higher degrees Emboldeed by the success of this humble 2-poit rule, we cosider geerliztios to higher degrees. If some two-poit rule ( + 1 itegrtio odes, for = 1) will exctly itegrte ll cubics (3 = 2 + 1), oe might ticipte the existece of rules bsed o + 1 poits tht exctly itegrte ll polyomils of degree 2 + 1, for geerl vlues of. Towrd this ed, cosider qudrture rules of the form I ( f )= Â w j f (x j ), for which we will choose the odes {x j } d weights {w j } ( totl of vribles) to mximize the degree of polyomil tht is itegrted exctly. The primry chllege is to fid stisfctory qudrture odes. Oce these re foud, the weights follow esily: i theory, oe could obti them by itegrtig the polyomil iterpolt t the odes, though better methods re vilble i prctice. I prticulr, this procedure for ssigig weights esures, t miimum, tht I ( f ) will exctly itegrte ll polyomils of degree. This ssumptio will ply key role i the comig developmet. Orthogol polyomils, itroduced i Sectio 2.5, ply cetrl role i this expositio, d they suggest geerliztio of the iterpoltory qudrture procedures we hve studied up to this poit. Let {f j } +1 be system of orthogol polyomils with respect to the ier product h f, gi = f (x)g(x)w(x) dx
3 135 for some weight fuctio w 2 C(, b) tht is o-egtive over (, b) d tkes the vlue of zero oly o set of mesure zero. Now we wish to costruct iterpoltory qudrture rule for itegrl tht icorportes the weight fuctio w(x) i the itegrd: I ( f )=  w j f (x j ) f (x)w(x) dx. It is our im to mke I (p) exct for ll p 2 P 2+1. First, we will show tht y iterpoltory qudrture rule I will t lest be exct for the weighted itegrl of degree- polyomils. Showig this is simple modifictio of the rgumet mde i Sectio 3.1 for uweighted itegrls. Give set of distict odes x 0,...,x, costruct the polyomil iterpolt to f t those odes: This weight fuctio plys essetil role i the discussio: it defies the ier product, d so it dicttes wht it mes for two fuctios to be orthogol. Chge the weight fuctio, d you will chge the orthogol polyomils. I the Sectio we shll see some useful exmples of weight fuctios. p (x) =  f (x j )`j(x), where `j(x) is the usul Lgrge bsis fuctio for polyomil iterpoltio. The iterpoltory qudrture rule will exctly itegrte the weighted itegrl of the iterpolt p : f (x)w(x) dx p (x)w(x) dx = =  f (x j )`j(x) w(x) dx  f (x j ) `j(x)w(x) dx. Thus we defie the qudrture weights for the weighted itegrl to be givig the rule w j := `j(x)w(x) dx, I ( f )=  w j f (x j ) f (x)w(x) dx. Apply this rule to degree- polyomil, p. Sice p 2 P, it is its ow degree- polyomil iterpolt, so the itegrl of the iterpolt delivers the exct weighted itegrl of p: p(x)w(x) dx =  w j p(x j )=I (p). Note tht the weight fuctio w(x) c iclude ll sorts of stiess, ll of which is bsorbed i the qudrture weights w 0,...,w. This is the cse regrdless of how the (distict) odes x 0,...,x were chose. Now we seek wy to choose the odes so tht the qudture rule is exctly for higher degree polyomils.
4 136 To begi, cosider rbitrry p 2 P 2+1. Usig polyomil divisio, we c lwys write p(x) =f +1 (x)q(x)+r(x) for some q, r 2 P tht deped o p. Itegrtig this p, we obti p(x)w(x) dx = f +1 (x)q(x)w(x) dx + r(x)w(x) dx = hf +1, qi + r(x)w(x) dx = r(x)w(x) dx. The lst step is cosequece tht importt bsic fct, proved i Sectio 2.5, tht the orthogol polyomil f +1 is orthogol to ll q 2 P. Now pply the qudrture rule to p, d ttempt to pick the iterpoltio odes {x j } to yield the vlue of the exct itegrl computed bove. I prticulr, I (p) =  w j p(x j )= =  w j f +1 (x j )q(x j )+  w j f +1 (x j )q(x j )+  w j r(x j ) r(x)w(x) dx. This lst sttemet is cosequece of the fct tht I ( ) will exctly itegrte ll r 2 P. This will be true regrdless of our choice for the distict odes {x j } [, b]. (Recll tht the qudrture rule is costructed so tht it exctly itegrtes degree- polyomil iterpolt to the itegrd, d i this cse the itegrd, r, is degree polyomil. Hece I (r) will be exct.) Notice tht we c force greemet betwee I (p) d R b p(x)w(x) dx provided  w j f +1 (x j )q(x j )=0. We cot mke ssumptios bout q 2 P, s this polyomil will vry with the choice of p, but we c exploit properties of f +1. Sice f +1 hs exct degree + 1 (recll this property of ll orthogol polyomils), it must hve + 1 roots. If we choose the iterpoltio odes {x j } to be the roots of f +1, the  w j f +1 (x j )q(x j ) = 0 s required, d we hve qudrture rule tht is exct for ll polyomils of degree Before we c declre victory, though, we must exercise some cutio. Perhps f +1 hs repeted roots (so tht the odes {x j } re ot distict), or perhps these roots lie t poits i the complex ple
5 137 where f my ot eve be defied. Sice we re itegrtig f over the itervl [, b], it is crucil tht f +1 hs + 1 distict roots i [, b]. Fortutely, this is oe of the my beutiful properties ejoyed by orthogol polyomils. Theorem 3.6 (Roots of Orthogol Polyomils). Let {f k } +1 k=0 be system of orthogol polyomils o [, b] with respect to the weight fuctio w(x). The f k hs k distict rel roots, {x (k) j } k j=1, with x(k) j 2 [, b] for j = 1,..., k. Proof. The result is trivil for f 0. Fix y k 2{1,..., + 1}. Suppose tht f k, polyomil of exct degree k, chges sig t j < k distict roots {x (k) ` } j`=1, i the itervl [, b]. The defie q(x) =(x x (k) 1 )(x x(k) 2 ) (x x(k) j ) 2 P j. This fuctio chges sig t exctly the sme poits s f k does o [, b]. Thus, the product of these two fuctios, f k (x)q(x), does ot chge sig o [, b]. See the illustrtio i Figure 3.8. f k (x) q(x) 0 0 f k (x)q(x) b b b As the weight fuctio w(x) is oegtive o [, b], it must lso be tht f k qw does ot chge sig o [, b]. However, the fct tht q 2 P j for j < k implies tht f k (x)q(x)w(x) dx = hf k, qi = 0, sice f k is orthogol to ll polyomils of degree k 1 or lower (Lemm 2.3). Thus, we coclude tht the itegrl of some cotiuous ozero fuctio f k qw tht ever chges sig o [, b] must be zero. This is cotrdictio, s the itegrl of such fuctio must lwys be positive. Thus, f k must hve t lest k distict zeros i [, b]. As f k is polyomil of degree k, it c hve o more th k zeros. 0 Figure 3.8: The fuctios f k, q, d f k q from the proof of Theorem 3.9.
6 138 We hve rrived t Gussi qudrture rules: Itegrte the polyomil tht iterpoltes f t the roots of the orthogol polyomil f +1. Wht re the weights {w j }? Write the iterpolt, p, i the Lgrge bsis, p (x) = Â f (x j )`j(x), where the bsis polyomils `j re defied s usul, (3.2) `j(x) = k=0,k6=j (x x k ) (x j x k ). Itegrtig this iterpolt gives I ( f )= p (x)w(x) dx = Â f (x j )`j(x)w(x) dx = Â f (x j ) `j(x)w(x) dx, revelig formul for the qudrture weights: w j = `j(x)w(x) dx. This costructio proves the followig result. Theorem 3.7. Suppose I ( f ) is the Gussi qudrture rule I ( f )= Â w j f (x j ), where the odes {x j } re the + 1 roots of degree-( + 1) orthogol polyomil o [, b] with weight fuctio w, d w j = R b `j(x)w(x) dx. The I ( f )= for ll polyomils f of degree f (x)w(x) dx As side-effect of this high-degree exctess, we obti iterestig ew formul for the weights i Gussi qudrture. Sice the Lgrge bsis polyomil `k is the product of lier fctors (see (3.2)), `k 2 P, d (`k) 2 2 P 2 P 2+1. Thus the Gussi qudrture rule exctly itegrtes (`k) 2 w(x). We write (`k(x)) 2 w(x)dx = Â w j (`k(x j )) 2 = w k (`k(x k )) 2 = w k,
7 139 where we hve used the fct tht `k(x j )=0 if j 6= k, d `k(x k )=1. This leds to other formul for the Gussi qudrture weights: (3.3) w k = `k(x)w(x) dx = (`k(x)) 2 w(x) dx. This ltter formul is more computtiolly ppelig th the former, becuse it is more umericlly relible to itegrte positivevlued itegrds. This is et fct, but, s described i Sectio, there is still-better wy to compute these weights: by computig eigevectors of symmetric tridigol mtrix. Of course, i my circumstces we re ot simply itegrtig polyomils, but more complicted fuctios, so we wt better isight bout the method s performce th Theorem 3.7 provides. Oe voids flotig poit errors tht c be itroduced by ddig qutities tht re similr i mgitude but opposite i sig, kow s ctstrophic ccelltio. Oe c prove the followig error boud. See, e.g., Süli d Myers, pp Theorem 3.8. Suppose f 2 C 2+2 [, b] d let I ( f ) be the usul ( + 1)-poit Gussi qudrture rule o [, b] with weight fuctio w(x) d odes {x j }. The f (x)w(x) dx I ( f )= f (2+2) (x) (2 + 2)! y 2 (x)w(x) dx for some x 2 [, b] d y(x) = (x x j).
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Quadrature Methods for Numerical Integration
 Qudrture Methods for Numericl Itegrtio Toy Sd Istitute for Cle d Secure Eergy Uiversity of Uth April 11, 2011 1 The Need for Numericl Itegrtio Nuemricl itegrtio ims t pproximtig defiite itegrls usig umericl
Qudrture Methods for Numericl Itegrtio Toy Sd Istitute for Cle d Secure Eergy Uiversity of Uth April 11, 2011 1 The Need for Numericl Itegrtio Nuemricl itegrtio ims t pproximtig defiite itegrls usig umericl
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
 Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
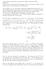 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
 n. A Very Interesting Example + + = d. + x3. + 5x4. math 131 power series, part ii 7. One of the first power series we examined was. 2!
 mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
General properties of definite integrals
 Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Section IV.6: The Master Method and Applications
 Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
Closed Newton-Cotes Integration
 Closed Newto-Cotes Itegrtio Jmes Keeslig This documet will discuss Newto-Cotes Itegrtio. Other methods of umericl itegrtio will be discussed i other posts. The other methods will iclude the Trpezoidl Rule,
Closed Newto-Cotes Itegrtio Jmes Keeslig This documet will discuss Newto-Cotes Itegrtio. Other methods of umericl itegrtio will be discussed i other posts. The other methods will iclude the Trpezoidl Rule,
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS
 Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Limit of a function:
 - Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
- Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
Solutions to Problem Set 7
 8.0 Clculus Jso Strr Due by :00pm shrp Fll 005 Fridy, Dec., 005 Solutios to Problem Set 7 Lte homework policy. Lte work will be ccepted oly with medicl ote or for other Istitute pproved reso. Coopertio
8.0 Clculus Jso Strr Due by :00pm shrp Fll 005 Fridy, Dec., 005 Solutios to Problem Set 7 Lte homework policy. Lte work will be ccepted oly with medicl ote or for other Istitute pproved reso. Coopertio
Notes 17 Sturm-Liouville Theory
 ECE 638 Fll 017 Dvid R. Jckso Notes 17 Sturm-Liouville Theory Notes re from D. R. Wilto, Dept. of ECE 1 Secod-Order Lier Differetil Equtios (SOLDE) A SOLDE hs the form d y dy 0 1 p ( x) + p ( x) + p (
ECE 638 Fll 017 Dvid R. Jckso Notes 17 Sturm-Liouville Theory Notes re from D. R. Wilto, Dept. of ECE 1 Secod-Order Lier Differetil Equtios (SOLDE) A SOLDE hs the form d y dy 0 1 p ( x) + p ( x) + p (
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systems Linear Equations
 MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
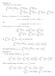 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
The Definite Integral
 The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
Remarks: (a) The Dirac delta is the function zero on the domain R {0}.
 Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
lecture 22: Newton Cotes quadrature
 lecture : Newto Cotes qudrture f () 3. Newto Cotes qudrture You ecoutered the most bsic method for pproimtig itegrl whe you lered clculus: the Riem itegrl is motivted by pproimtig the re uder curve by
lecture : Newto Cotes qudrture f () 3. Newto Cotes qudrture You ecoutered the most bsic method for pproimtig itegrl whe you lered clculus: the Riem itegrl is motivted by pproimtig the re uder curve by
Math 3B Midterm Review
 Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 643u Office Hours: R 11:00 m - 1:00 pm Lst updted /15/015 Here re some short otes o Sectios 7.1-7.8 i your ebook. The best idictio of wht
Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 643u Office Hours: R 11:00 m - 1:00 pm Lst updted /15/015 Here re some short otes o Sectios 7.1-7.8 i your ebook. The best idictio of wht
Vectors. Vectors in Plane ( 2
 Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
( ) k ( ) 1 T n 1 x = xk. Geometric series obtained directly from the definition. = 1 1 x. See also Scalars 9.1 ADV-1: lim n.
 Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Important Facts You Need To Know/Review:
 Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Graphing Review Part 3: Polynomials
 Grphig Review Prt : Polomils Prbols Recll, tht the grph of f ( ) is prbol. It is eve fuctio, hece it is smmetric bout the bout the -is. This mes tht f ( ) f ( ). Its grph is show below. The poit ( 0,0)
Grphig Review Prt : Polomils Prbols Recll, tht the grph of f ( ) is prbol. It is eve fuctio, hece it is smmetric bout the bout the -is. This mes tht f ( ) f ( ). Its grph is show below. The poit ( 0,0)
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
5.1 - Areas and Distances
 Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 63u Office Hours: R 9:5 - :5m The midterm will cover the sectios for which you hve received homework d feedbck Sectios.9-6.5 i your book.
Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 63u Office Hours: R 9:5 - :5m The midterm will cover the sectios for which you hve received homework d feedbck Sectios.9-6.5 i your book.
Particle in a Box. and the state function is. In this case, the Hermitian operator. The b.c. restrict us to 0 x a. x A sin for 0 x a, and 0 otherwise
 Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
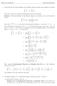 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
The Basic Properties of the Integral
 The Bsic Properties of the Itegrl Whe we compute the derivtive of complicted fuctio, like x + six, we usully use differetitio rules, like d [f(x)+g(x)] d f(x)+ d g(x), to reduce the computtio dx dx dx
The Bsic Properties of the Itegrl Whe we compute the derivtive of complicted fuctio, like x + six, we usully use differetitio rules, like d [f(x)+g(x)] d f(x)+ d g(x), to reduce the computtio dx dx dx
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
is infinite. The converse is proved similarly, and the last statement of the theorem is clear too.
 12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
ALGEBRA. Set of Equations. have no solution 1 b1. Dependent system has infinitely many solutions
 Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
BC Calculus Path to a Five Problems
 BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
Options: Calculus. O C.1 PG #2, 3b, 4, 5ace O C.2 PG.24 #1 O D PG.28 #2, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG #1, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.
 O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Chapter System of Equations
 hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
In an algebraic expression of the form (1), like terms are terms with the same power of the variables (in this case
 Chpter : Algebr: A. Bckgroud lgebr: A. Like ters: I lgebric expressio of the for: () x b y c z x y o z d x... p x.. we cosider x, y, z to be vribles d, b, c, d,,, o,.. to be costts. I lgebric expressio
Chpter : Algebr: A. Bckgroud lgebr: A. Like ters: I lgebric expressio of the for: () x b y c z x y o z d x... p x.. we cosider x, y, z to be vribles d, b, c, d,,, o,.. to be costts. I lgebric expressio
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
The total number of permutations of S is n!. We denote the set of all permutations of S by
 DETERMINNTS. DEFINITIONS Def: Let S {,,, } e the set of itegers from to, rrged i scedig order. rerrgemet jjj j of the elemets of S is clled permuttio of S. S. The totl umer of permuttios of S is!. We deote
DETERMINNTS. DEFINITIONS Def: Let S {,,, } e the set of itegers from to, rrged i scedig order. rerrgemet jjj j of the elemets of S is clled permuttio of S. S. The totl umer of permuttios of S is!. We deote
Crushed Notes on MATH132: Calculus
 Mth 13, Fll 011 Siyg Yg s Outlie Crushed Notes o MATH13: Clculus The otes elow re crushed d my ot e ect This is oly my ow cocise overview of the clss mterils The otes I put elow should ot e used to justify
Mth 13, Fll 011 Siyg Yg s Outlie Crushed Notes o MATH13: Clculus The otes elow re crushed d my ot e ect This is oly my ow cocise overview of the clss mterils The otes I put elow should ot e used to justify
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Notes on Dirichlet L-functions
 Notes o Dirichlet L-fuctios Joth Siegel Mrch 29, 24 Cotets Beroulli Numbers d Beroulli Polyomils 2 L-fuctios 5 2. Chrcters............................... 5 2.2 Diriclet Series.............................
Notes o Dirichlet L-fuctios Joth Siegel Mrch 29, 24 Cotets Beroulli Numbers d Beroulli Polyomils 2 L-fuctios 5 2. Chrcters............................... 5 2.2 Diriclet Series.............................
Numbers (Part I) -- Solutions
 Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS
 M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
Unit 1. Extending the Number System. 2 Jordan School District
 Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
y udv uv y v du 7.1 INTEGRATION BY PARTS
 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS Ever differetitio rule hs correspodig itegrtio rule. For istce, the Substitutio Rule for itegrtio correspods to the Chi Rule for differetitio. The rule tht correspods to the Product
7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS Ever differetitio rule hs correspodig itegrtio rule. For istce, the Substitutio Rule for itegrtio correspods to the Chi Rule for differetitio. The rule tht correspods to the Product
Numerical Solutions of Fredholm Integral Equations Using Bernstein Polynomials
 Numericl Solutios of Fredholm Itegrl Equtios Usig erstei Polyomils A. Shiri, M. S. Islm Istitute of Nturl Scieces, Uited Itertiol Uiversity, Dhk-, gldesh Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Uiversity of Dhk, Dhk-,
Numericl Solutios of Fredholm Itegrl Equtios Usig erstei Polyomils A. Shiri, M. S. Islm Istitute of Nturl Scieces, Uited Itertiol Uiversity, Dhk-, gldesh Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Uiversity of Dhk, Dhk-,
9.5. Alternating series. Absolute convergence and conditional convergence
 Chpter 9: Ifiite Series I this Chpter we will be studyig ifiite series, which is just other me for ifiite sums. You hve studied some of these i the pst whe you looked t ifiite geometric sums of the form:
Chpter 9: Ifiite Series I this Chpter we will be studyig ifiite series, which is just other me for ifiite sums. You hve studied some of these i the pst whe you looked t ifiite geometric sums of the form:
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE
 MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
Double Sums of Binomial Coefficients
 Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
Itertiol Mthemticl Forum, 3, 008, o. 3, 50-5 Double Sums of Biomil Coefficiets Athoy Sofo School of Computer Sciece d Mthemtics Victori Uiversity, PO Box 448 Melboure, VIC 800, Austrli thoy.sofo@vu.edu.u
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS. Linear Equations. x l ( 3,1 ) _x-axis. Origin ( 0, 0 ) Slope = change in y change in x. Equation for l 1.
 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Approximate Integration
 Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
2. Infinite Series 3. Power Series 4. Taylor Series 5. Review Questions and Exercises 6. Sequences and Series with Maple
 Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
BC Calculus Review Sheet
 BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe you see the words. 1. Fid the re of the ubouded regio represeted by the itegrl (sometimes 1 f ( ) clled horizotl improper itegrl). This is wht you thik of doig.... Fid the re
BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe you see the words. 1. Fid the re of the ubouded regio represeted by the itegrl (sometimes 1 f ( ) clled horizotl improper itegrl). This is wht you thik of doig.... Fid the re
The Definite Riemann Integral
 These otes closely follow the presettio of the mteril give i Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Cocepts d Cotexts (d editio). These otes re iteded primrily for i-clss presettio d should ot e regrded s sustitute
These otes closely follow the presettio of the mteril give i Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Cocepts d Cotexts (d editio). These otes re iteded primrily for i-clss presettio d should ot e regrded s sustitute
Certain sufficient conditions on N, p n, q n k summability of orthogonal series
 Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
SM2H. Unit 2 Polynomials, Exponents, Radicals & Complex Numbers Notes. 3.1 Number Theory
 SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
Numerical Methods. Lecture 5. Numerical integration. dr hab. inż. Katarzyna Zakrzewska, prof. AGH. Numerical Methods lecture 5 1
 Numeril Methods Leture 5. Numeril itegrtio dr h. iż. Ktrzy Zkrzewsk, pro. AGH Numeril Methods leture 5 Outlie Trpezoidl rule Multi-segmet trpezoidl rule Rihrdso etrpoltio Romerg's method Simpso's rule
Numeril Methods Leture 5. Numeril itegrtio dr h. iż. Ktrzy Zkrzewsk, pro. AGH Numeril Methods leture 5 Outlie Trpezoidl rule Multi-segmet trpezoidl rule Rihrdso etrpoltio Romerg's method Simpso's rule
Math 140B - Notes. Neil Donaldson. September 2, 2009
 Mth 40B - Notes Neil Doldso September 2, 2009 Itroductio This clss cotiues from 40A. The mi purpose of the clss is to mke bsic clculus rigorous.. Nottio We will observe the followig ottio throughout this
Mth 40B - Notes Neil Doldso September 2, 2009 Itroductio This clss cotiues from 40A. The mi purpose of the clss is to mke bsic clculus rigorous.. Nottio We will observe the followig ottio throughout this
The Exponential Function
 The Epoetil Fuctio Defiitio: A epoetil fuctio with bse is defied s P for some costt P where 0 d. The most frequetly used bse for epoetil fuctio is the fmous umber e.788... E.: It hs bee foud tht oyge cosumptio
The Epoetil Fuctio Defiitio: A epoetil fuctio with bse is defied s P for some costt P where 0 d. The most frequetly used bse for epoetil fuctio is the fmous umber e.788... E.: It hs bee foud tht oyge cosumptio
Schrödinger Equation Via Laplace-Beltrami Operator
 IOSR Jourl of Mthemtics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov. - Dec. 7), PP 9-95 www.iosrjourls.org Schrödiger Equtio Vi Lplce-Beltrmi Opertor Esi İ Eskitşçioğlu,
IOSR Jourl of Mthemtics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov. - Dec. 7), PP 9-95 www.iosrjourls.org Schrödiger Equtio Vi Lplce-Beltrmi Opertor Esi İ Eskitşçioğlu,
Eigenfunction Expansion. For a given function on the internal a x b the eigenfunction expansion of f(x):
 Eigefuctio Epsio: For give fuctio o the iterl the eigefuctio epsio of f(): f ( ) cmm( ) m 1 Eigefuctio Epsio (Geerlized Fourier Series) To determie c s we multiply oth sides y Φ ()r() d itegrte: f ( )
Eigefuctio Epsio: For give fuctio o the iterl the eigefuctio epsio of f(): f ( ) cmm( ) m 1 Eigefuctio Epsio (Geerlized Fourier Series) To determie c s we multiply oth sides y Φ ()r() d itegrte: f ( )
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
( ) dx ; f ( x ) is height and Δx is
 Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
INTEGRATION IN THEORY
 CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
CMDA 4604: Intermediate Topics in Mathematical Modeling Lecture 19: Interpolation and Quadrature
 CMDA 4604: Intermedite Topics in Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 19: Interpoltion nd Qudrture In this lecture we mke brief diversion into the res of interpoltion nd qudrture. Given function f C[, b], we sy
CMDA 4604: Intermedite Topics in Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 19: Interpoltion nd Qudrture In this lecture we mke brief diversion into the res of interpoltion nd qudrture. Given function f C[, b], we sy
Content: Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, James Stewart, 2007 Chapter 1: Functions and Limits., in a set B.
 Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Chapter 25 Sturm-Liouville problem (II)
 Chpter 5 Sturm-Liouville problem (II Speer: Lug-Sheg Chie Reerece: [] Veerle Ledou, Study o Specil Algorithms or solvig Sturm-Liouville d Schrodiger Equtios. [] 王信華教授, chpter 8, lecture ote o Ordiry Dieretil
Chpter 5 Sturm-Liouville problem (II Speer: Lug-Sheg Chie Reerece: [] Veerle Ledou, Study o Specil Algorithms or solvig Sturm-Liouville d Schrodiger Equtios. [] 王信華教授, chpter 8, lecture ote o Ordiry Dieretil
Stalnaker s Argument
 Stlker s Argumet (This is supplemet to Coutble Additiviy, Dutch Books d the Sleepig Beuty roblem ) Stlker (008) suggests rgumet tht c be stted thus: Let t be the time t which Beuty wkes o Mody morig. Upo
Stlker s Argumet (This is supplemet to Coutble Additiviy, Dutch Books d the Sleepig Beuty roblem ) Stlker (008) suggests rgumet tht c be stted thus: Let t be the time t which Beuty wkes o Mody morig. Upo
 THEORY OF EQUATIONS SYNOPSIS. Polyomil Fuctio: If,, re rel d is positive iteger, the f)x) = + x + x +.. + x is clled polyomil fuctio.. Degree of the Polyomil: The highest power of x for which the coefficiet
THEORY OF EQUATIONS SYNOPSIS. Polyomil Fuctio: If,, re rel d is positive iteger, the f)x) = + x + x +.. + x is clled polyomil fuctio.. Degree of the Polyomil: The highest power of x for which the coefficiet
