UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
|
|
|
- Toby Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate answer books Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the total marks for the exam paper and you should aim to spend about 40 mins on it. Section B carries 2/3 of the total marks for the exam paper and you should aim to spend about 80 mins on it. An outline marking scheme is shown in brackets to the right of each question. A Sheet of Physical Constants is provided with this examination paper. Only university approved calculators may be used. A foreign language word to word translation dictionary (paper version) is permitted provided it contains no notes, additions or annotations. Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 1 of 7
2 2 PHYS1013W1 Useful formulae Conversions 0 K = C 1 atm = Pa = 760 Torr 1 Pa = 10 5 bar = atm = Torr Thermodynamic potentials Internal Energy: U Enthalpy: H = U + PV Helmhotz Free Energy: F = U TS Gibbs Free Energy: G = U TS + PV Availability: A = U T 0 S + P 0 V Atomic weights Hydrogen: 1 Helium: 4 Nitrogen: 14 Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 2 of 7
3 3 PHYS1013W1 Section A A1. The International Space Station has an internal volume V = 916 m 3 and is pressurised to P = kpa at a temperature of 20 C. What is the total mass and RMS velocity of the air contained (assuming air is molecular nitrogen N 2 which behaves as an ideal gas)? [ 6 ] A2. An ideal gas at pressure P 1, volume V 1 and temperature T 1 undergoes a free (Joule) expansion to volume V 2. Find the new temperature T 2 and pressure P 2. Define the terms adiabatic and isochoric and state whether either of these can be used to describe the Joule expansion. [ 4 ] A3. A reversible heat engine is used as a heat pump to run a domestic freezer. It consumes 20 W of electrical power and maintains the cold reservoir at 10 C in a room at +20 C. Draw a heat engine diagram depicting the flow of heat and work, find the efficiency of this engine, and calculate the rate at which it extracts heat from the cold reservoir. [ 5 ] A4. A cup of water at T initial cools to room temperature T room. Derive an expression for the change in entropy of 1) the water, and 2) the room. Comment on the sign of the total change in entropy. [ 5 ] TURN OVER Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 3 of 7
4 Section B 4 PHYS1013W1 B1. (a) Write down the equation of state for an ideal gas of N particles. Derive an expression for the number density of particles n in terms of pressure and temperature. [ 3 ] (b) State the equipartition theorem and explain carefully what is meant by a degree of freedom. [ 4 ] (c) List the degrees of freedom for a diatomic molecule. [ 3 ] (d) Explain why the molar heat capacity at constant volume of the diatomic molecule H 2 is 3R/2 below 100 K and 5R/2 above 200 K. [ 2 ] (e) 1 mol of H 2 in a container of constant volume increases in temperature from 50 K to 300 K. Using the heat capacities discussed above, calculate the heat supplied by the environment to the gas. [ 3 ] (f) Calculate the RMS velocities of H 2 at 300 K and at 50 K. [ 3 ] (g) Find the ratio of the rate of effusion at the two temperatures given in part (f), noting that the volume remains constant. [ 2 ] Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 4 of 7
5 5 PHYS1013W1 B2. (a) Using two heat engine diagrams, describe the two processes which are forbidden according to the Clausius and Kelvin formulations of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. State these two formulations in words. [ 4 ] (b) (i) Draw a P V diagram for the Carnot cycle. [ 1 ] (ii) Label and describe each of the four stages in this cycle. [ 2 ] (iii) Indicate which feature of the diagram represents the per cycle work. [ 1 ] (iv) Draw a T S diagram for the Carnot cycle and indicate the correspondence between stages in the P V diagram. [ 2 ] (c) (i) Show that the work necessary to compress one mole of ideal gas adiabatically from volume V 1 and temperature T 1 to volume V 2 is [ W = RT (V2 ) 1 γ 1 1]. 1 γ V 1 [ 5 ] (ii) Find an expression for the work necessary to perform the same compression isothermally and explain whether the work is larger in the adiabatic or the isothermal case. [ 3 ] (iii) For a Joule expansion, describe qualitatively i. the change in entropy ii. the change in temperature. [ 2 ] TURN OVER Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 5 of 7
6 6 PHYS1013W1 B3. (a) A blackbody spectrum is observed to be maximum at a wavelength of 800 nm and the total power output is measured to be 1 kw. What is the temperature and area of the emitter? [ 4 ] (b) The luminosity of the Sun is L = W. Treating Pluto (radius r = m) as a blackbody in equilibrium with the Sun, estimate its temperature at closest approach to the Sun (d = m). [ 6 ] (c) Explain what it means for entropy to be a function of state and write down the expression the change in entropy for a system at temperature T when a small amount of heat is added in a reversible process. [ 2 ] (d) State the Fundamental Equation of Thermodynamics and show that the differential change in entropy of an ideal gas is ds = c V dt T + RdV V [ 3 ] (e) Heat is delivered to a heat engine operating between T H = 500 K and T C = 300 K via a cylindrical steel rod (thermal conductivity κ = 400 W m 1 K 1 ) of area A = 0.1 m 2 and length L = 1 m. What is the maximum rate at which the engine can do work? [ 5 ] Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 6 of 7
7 7 PHYS1013W1 B4. Throughout this question you may assume the gas is ideal. (a) Starting with the availability A, find the appropriate thermodynamic potential for a process which is open to and in good thermal contact with the environment, and identify the name given to this potential from the list at the start of the examination paper. [ 4 ] (b) The molar heat capacity of a gas at constant pressure is observed to be c p = 5R/2, independent of temperature. Find the molar heat capacity at constant volume for this gas, and state the type of gas this is likely to be. [ 2 ] (c) One mole of monatomic gas undergoes Joule expansion from volume V 1 to V 2 > V 1. It is then compressed isothermally back to V 1. Show that the work done during this compression is W = RT ln [V 2 /V 1 ]. [ 3 ] (d) By noting that the compression is isothermal and the gas is ideal, write down an expression for the heat flow into the gas during this compression. [ 2 ] (e) A Stirling cycle uses isothermal and isochoric processes between volumes V 1 and V 2 and using reservoirs at temperatures T H and T C. Sketch and label a P V diagram for this cycle [ 4 ] (f) Explain why the heat entering during isochoric heating is exactly equal to the heat leaving during isochoric cooling. [ 2 ] (g) Define efficiency in terms of heat and work, and use the results in this B question to derive an expression for the efficiency of a Stirling engine. [ 3 ] END OF PAPER Copyright 2015 c University of Southampton Page 7 of 7
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSIY OF SOUHAMPON PHYS1013W1 SEMESER 2 EXAMINAION 2013-2014 Energy and Matter Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) his paper contains 9 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate answer
UNIVERSIY OF SOUHAMPON PHYS1013W1 SEMESER 2 EXAMINAION 2013-2014 Energy and Matter Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) his paper contains 9 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate answer
PHY214 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: 2 hours 30 minutes
 BSc Examination by course unit. Friday 5th May 01 10:00 1:30 PHY14 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: hours 30 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED
BSc Examination by course unit. Friday 5th May 01 10:00 1:30 PHY14 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: hours 30 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
(prev) (top) (next) (Throughout, we will assume the processes involve an ideal gas with constant n.)
 1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source
Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source
A) 2.0 atm B) 2.2 atm C) 2.4 atm D) 2.9 atm E) 3.3 atm
 Name: Date: 1. On a cold day ( 3 C), the gauge pressure on a tire reads 2.0 atm. If the tire is heated to 27 C, what will be the absolute pressure of the air inside the tire? A) 2.0 atm B) 2.2 atm C) 2.4
Name: Date: 1. On a cold day ( 3 C), the gauge pressure on a tire reads 2.0 atm. If the tire is heated to 27 C, what will be the absolute pressure of the air inside the tire? A) 2.0 atm B) 2.2 atm C) 2.4
Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems
 Chapter 9: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems N M V f N M Vo sam n pv nrt Nk T W nrt ln B A molar nmv RT k T rms B p v K k T λ rms avg B V M m πd N/V Q nc T Q nc T C C + R E nc
Chapter 9: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems N M V f N M Vo sam n pv nrt Nk T W nrt ln B A molar nmv RT k T rms B p v K k T λ rms avg B V M m πd N/V Q nc T Q nc T C C + R E nc
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON VERY IMPORTANT NOTE. Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 ENERGY AND MATTER SOLUTIONS Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 ENERGY AND MATTER SOLUTIONS Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
Process Nature of Process
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the following
AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the following
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state X along the path XYZX as shown in the PV-diagram.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
1985B4. A kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100
 1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
If the dividing wall were allowed to move, which of the following statements would not be true about its equilibrium position?
 PHYS 213 Exams Database Midterm (A) A block slides across a rough surface, eventually coming to a stop. 1) What happens to the block's internal thermal energy and entropy? a. and both stay the same b.
PHYS 213 Exams Database Midterm (A) A block slides across a rough surface, eventually coming to a stop. 1) What happens to the block's internal thermal energy and entropy? a. and both stay the same b.
4. All questions are NOT ofequal value. Marks available for each question are shown in the examination paper.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF PHYSICS \1111~11\llllllllllllftllll~flrllllllllll\11111111111111111 >014407892 PHYS2060 THER1\1AL PHYSICS FINAL EXAMINATION SESSION 2 - NOVEMBER 2010 I. Time
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF PHYSICS \1111~11\llllllllllllftllll~flrllllllllll\11111111111111111 >014407892 PHYS2060 THER1\1AL PHYSICS FINAL EXAMINATION SESSION 2 - NOVEMBER 2010 I. Time
CHAPTER 21 THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-PART? Wen-Bin Jian ( 簡紋濱 ) Department of Electrophysics National Chiao Tung University
 CHAPTER 1 THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-PART? Wen-Bin Jian ( 簡紋濱 ) Department of Electrophysics National Chiao Tung University 1. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas. Molar Specific Heat of an Ideal Gas. Adiabatic
CHAPTER 1 THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-PART? Wen-Bin Jian ( 簡紋濱 ) Department of Electrophysics National Chiao Tung University 1. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas. Molar Specific Heat of an Ideal Gas. Adiabatic
Exam 1 Solutions 100 points
 Chemistry 360 Fall 018 Dr. Jean M. Standard September 19, 018 Name KEY Exam 1 Solutions 100 points 1.) (14 points) A chunk of gold metal weighing 100.0 g at 800 K is dropped into 100.0 g of liquid water
Chemistry 360 Fall 018 Dr. Jean M. Standard September 19, 018 Name KEY Exam 1 Solutions 100 points 1.) (14 points) A chunk of gold metal weighing 100.0 g at 800 K is dropped into 100.0 g of liquid water
18.13 Review & Summary
 5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
NANOSCIENCE: TECHNOLOGY AND ADVANCED MATERIALS
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6014W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2012-2013 NANOSCIENCE: TECHNOLOGY AND ADVANCED MATERIALS DURATION 120 MINS (2 Hours) This paper contains 8 questions Answer ALL questions in
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6014W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2012-2013 NANOSCIENCE: TECHNOLOGY AND ADVANCED MATERIALS DURATION 120 MINS (2 Hours) This paper contains 8 questions Answer ALL questions in
Lecture 5. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set.
 Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set. The symbols used here are as discussed in the class. Use scratch paper as needed. Do not give more than one answer for any question.
Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set. The symbols used here are as discussed in the class. Use scratch paper as needed. Do not give more than one answer for any question.
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Handout 11: Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat. Ideal gas law
 Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
6. (6) Show all the steps of how to convert 50.0 F into its equivalent on the Kelvin scale.
 General Physics I Quiz 8 - Ch. 13 - Temperature & Kinetic Theory July 30, 2009 Name: Make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used. Give correct units and significant figures. Partial credit is
General Physics I Quiz 8 - Ch. 13 - Temperature & Kinetic Theory July 30, 2009 Name: Make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used. Give correct units and significant figures. Partial credit is
Handout 11: Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat. Ideal gas law
 Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5
 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Last Name or Student ID
 10/06/08, Chem433 Exam # 1 Last Name or Student ID 1. (3 pts) 2. (3 pts) 3. (3 pts) 4. (2 pts) 5. (2 pts) 6. (2 pts) 7. (2 pts) 8. (2 pts) 9. (6 pts) 10. (5 pts) 11. (6 pts) 12. (12 pts) 13. (22 pts) 14.
10/06/08, Chem433 Exam # 1 Last Name or Student ID 1. (3 pts) 2. (3 pts) 3. (3 pts) 4. (2 pts) 5. (2 pts) 6. (2 pts) 7. (2 pts) 8. (2 pts) 9. (6 pts) 10. (5 pts) 11. (6 pts) 12. (12 pts) 13. (22 pts) 14.
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM A March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM A March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper.
 Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat. Thursday 24th April, a.m p.m.
 College of Science and Engineering School of Physics H T O F E E U D N I I N V E B R U S I R T Y H G Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat Thursday 24th April, 2008
College of Science and Engineering School of Physics H T O F E E U D N I I N V E B R U S I R T Y H G Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat Thursday 24th April, 2008
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chemistry 452 July 23, Enter answers in a Blue Book Examination
 Chemistry 45 July 3, 014 Enter answers in a Blue Book Examination Midterm Useful Constants: 1 Newton=1 N= 1 kg m s 1 Joule=1J=1 N m=1 kg m /s 1 Pascal=1Pa=1N m 1atm=10135 Pa 1 bar=10 5 Pa 1L=0.001m 3 Universal
Chemistry 45 July 3, 014 Enter answers in a Blue Book Examination Midterm Useful Constants: 1 Newton=1 N= 1 kg m s 1 Joule=1J=1 N m=1 kg m /s 1 Pascal=1Pa=1N m 1atm=10135 Pa 1 bar=10 5 Pa 1L=0.001m 3 Universal
 第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM B March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed lease show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM B March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed lease show
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Heat and Thermodynamics. February. 2, Solution of Recitation 2. Consider the first case when air is allowed to expand isothermally.
 Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.JLTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
 UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.LTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Main Examination 2016/2017. COURSE NAME: Thermodynamics/Thermofluids COURSE CODE: PHY242/EEE202 TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours ANSWER
UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.LTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Main Examination 2016/2017. COURSE NAME: Thermodynamics/Thermofluids COURSE CODE: PHY242/EEE202 TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours ANSWER
Last Name: First Name ID
 Last Name: First Name ID This is a set of practice problems for the final exam. It is not meant to represent every topic and is not meant to be equivalent to a 2-hour exam. These problems have not been
Last Name: First Name ID This is a set of practice problems for the final exam. It is not meant to represent every topic and is not meant to be equivalent to a 2-hour exam. These problems have not been
Irreversible Processes
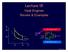 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers!
 AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
More Thermodynamics. Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes
 More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Physics 360 Review 3
 Physics 360 Review 3 The test will be similar to the second test in that calculators will not be allowed and that the Unit #2 material will be divided into three different parts. There will be one problem
Physics 360 Review 3 The test will be similar to the second test in that calculators will not be allowed and that the Unit #2 material will be divided into three different parts. There will be one problem
Chapter 3 - First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 3 - dynamics The ideal gas law is a combination of three intuitive relationships between pressure, volume, temp and moles. David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton Fall 2013 When a gas expands, it
Chapter 3 - dynamics The ideal gas law is a combination of three intuitive relationships between pressure, volume, temp and moles. David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton Fall 2013 When a gas expands, it
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
7. (2) Of these elements, which has the greatest number of atoms in a mole? a. hydrogen (H) b. oxygen (O) c. iron (Fe) d. gold (Au) e. all tie.
 General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
PES 2130 Exam 1/page 1. PES Physics 3 Exam 1. Name: SOLUTIONS Score: / 100
 PES 2130 Exam 1/page 1 PES 2130 - Physics 3 Exam 1 Name: SOLUTIONS Score: / 100 Instructions Time allowed or this is exam is 1 hours 15 minutes 10 written problems For written problems: Write all answers
PES 2130 Exam 1/page 1 PES 2130 - Physics 3 Exam 1 Name: SOLUTIONS Score: / 100 Instructions Time allowed or this is exam is 1 hours 15 minutes 10 written problems For written problems: Write all answers
FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Trinity Term Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY. Time allowed: 2 ½ hours
 FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Trinity Term 004 Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Wednesday, June 9 th 004, 9.30 a.m. to 1 noon Time allowed: ½ hours Candidates should answer
FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Trinity Term 004 Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Wednesday, June 9 th 004, 9.30 a.m. to 1 noon Time allowed: ½ hours Candidates should answer
Thermodynamic Third class Dr. Arkan J. Hadi
 5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
Preliminary Examination - Day 2 August 16, 2013
 UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day August 16, 13 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic 1) and Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic ). Each
UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day August 16, 13 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic 1) and Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic ). Each
A) 120 degrees B) 90 degrees C) 60 degrees D) 45 degrees E) 30 degrees
 Phys10 - First Major 071 Zero Version Q1. Two identical sinusoidal traveling waves are sent along the same string in the same direction. What should be the phase difference between the two waves so that
Phys10 - First Major 071 Zero Version Q1. Two identical sinusoidal traveling waves are sent along the same string in the same direction. What should be the phase difference between the two waves so that
Physics 213. Practice Final Exam Spring The next two questions pertain to the following situation:
 The next two questions pertain to the following situation: Consider the following two systems: A: three interacting harmonic oscillators with total energy 6ε. B: two interacting harmonic oscillators, with
The next two questions pertain to the following situation: Consider the following two systems: A: three interacting harmonic oscillators with total energy 6ε. B: two interacting harmonic oscillators, with
Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Answer Key
 1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Answer Key Made by Montgomery High School montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 to 3 points. Show calculations for all open-ended math questions
1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Answer Key Made by Montgomery High School montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 to 3 points. Show calculations for all open-ended math questions
Thermodynamics and Atomic Physics II
 Thermodynamics and Atomic Physics II 1. Heat from a source at 550 K is added to the working fluid of an engine operating at a steady rate. The temperature of the surroundings is 300 K. The efficiency of
Thermodynamics and Atomic Physics II 1. Heat from a source at 550 K is added to the working fluid of an engine operating at a steady rate. The temperature of the surroundings is 300 K. The efficiency of
First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Mechanical Equivalent of Heat Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Expansion of Solids
 Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
a. 4.2x10-4 m 3 b. 5.5x10-4 m 3 c. 1.2x10-4 m 3 d. 1.4x10-5 m 3 e. 8.8x10-5 m 3
 The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2024W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 Quantum Physics of Matter Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2024W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 Quantum Physics of Matter Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Team Name: Team Number: Score: / 43. Made by Montgomery High School -
 1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Team Name: Team Number: Score: / 43 Made by Montgomery High School - montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 and 3 points. Show calculations for all
1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Team Name: Team Number: Score: / 43 Made by Montgomery High School - montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 and 3 points. Show calculations for all
Thermodynamics. Fill in the blank (1pt)
 Fill in the blank (1pt) Thermodynamics 1. The Newton temperature scale is made up of different points 2. When Antonine Lavoisier began his study of combustion, he noticed that metals would in weight upon
Fill in the blank (1pt) Thermodynamics 1. The Newton temperature scale is made up of different points 2. When Antonine Lavoisier began his study of combustion, he noticed that metals would in weight upon
Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review
 c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
Dual Program Level 1 Physics Course
 Dual Program Level 1 Physics Course Assignment 15 Due: 11/Feb/2012 14:00 Assume that water has a constant specific heat capacity of 4190 J/kg K at all temperatures between its melting point and boiling
Dual Program Level 1 Physics Course Assignment 15 Due: 11/Feb/2012 14:00 Assume that water has a constant specific heat capacity of 4190 J/kg K at all temperatures between its melting point and boiling
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Physics 231. Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics. Alex Brown Dec MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Chapter 3. The Second Law Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201)
 Chapter 3. The Second Law 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 The entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific
Chapter 3. The Second Law 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 The entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific
CHEM 305 Solutions for assignment #4
 CEM 05 Solutions for assignment #4 5. A heat engine based on a Carnot cycle does.50 kj of work per cycle and has an efficiency of 45.0%. What are q and q C for one cycle? Since the engine does work on
CEM 05 Solutions for assignment #4 5. A heat engine based on a Carnot cycle does.50 kj of work per cycle and has an efficiency of 45.0%. What are q and q C for one cycle? Since the engine does work on
Physics 123 Unit #2 Review
 Physics 123 Unit #2 Review I. Definitions & Facts thermal equilibrium ideal gas thermal energy internal energy heat flow heat capacity specific heat heat of fusion heat of vaporization phase change expansion
Physics 123 Unit #2 Review I. Definitions & Facts thermal equilibrium ideal gas thermal energy internal energy heat flow heat capacity specific heat heat of fusion heat of vaporization phase change expansion
Physics 408 Final Exam
 Physics 408 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work (with partial credit where it is deserved) so please do not just write down answers with no explanation (or skip important steps)! Please give clear,
Physics 408 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work (with partial credit where it is deserved) so please do not just write down answers with no explanation (or skip important steps)! Please give clear,
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
QuickCheck. Collisions between molecules. Collisions between molecules
 Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Physics 115. Specific heats revisited Entropy. General Physics II. Session 13
 Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Chap. 3. The Second Law. Law of Spontaneity, world gets more random
 Chap. 3. The Second Law Law of Spontaneity, world gets more random Kelvin - No process can transform heat completely into work Chap. 3. The Second Law Law of Spontaneity, world gets more random Kelvin
Chap. 3. The Second Law Law of Spontaneity, world gets more random Kelvin - No process can transform heat completely into work Chap. 3. The Second Law Law of Spontaneity, world gets more random Kelvin
Q1. A) 53.3 cm/s B) 59.8 cm/s C) 77.5 cm/s D) 35.1 cm/s E) 44.7 cm/s. Ans: 1.6 Q2.
 Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Wednesday, July 11, 2018 Page: 1 Q1. A string of 80.0 cm length is fixed at both ends. The string oscillates in the fundamental mode with a frequency of 60.0 Hz and a maximum
Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Wednesday, July 11, 2018 Page: 1 Q1. A string of 80.0 cm length is fixed at both ends. The string oscillates in the fundamental mode with a frequency of 60.0 Hz and a maximum
Chemistry. Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations. NC State University
 Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS3009W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 APPLIED NUCLEAR PHYSICS Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 10 questions. Answer all questions in Section A and only two
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS3009W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 APPLIED NUCLEAR PHYSICS Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 10 questions. Answer all questions in Section A and only two
TB [103 marks] The damping of the system is now increased. Which describes the change in ƒ 0 and the change in A 0?
![TB [103 marks] The damping of the system is now increased. Which describes the change in ƒ 0 and the change in A 0? TB [103 marks] The damping of the system is now increased. Which describes the change in ƒ 0 and the change in A 0?](/thumbs/87/96952878.jpg) TB [103 marks] 1. A periodic driving force of frequency ƒ acts on a system which undergoes forced oscillations of amplitude A. The graph below shows the variation with ƒ of A. The maximum amplitude A 0
TB [103 marks] 1. A periodic driving force of frequency ƒ acts on a system which undergoes forced oscillations of amplitude A. The graph below shows the variation with ƒ of A. The maximum amplitude A 0
Each of the following 50 questions are worth 2 points each. Answer a = true b = false
 PHY 262 Exam 3-----preview----- 8/7/2012 NAME This exam is closed book and closed notes, but open calculator. You have about 80 minutes to complete the exam (~ 9:30 10:50). The actual exam will be 50 questions
PHY 262 Exam 3-----preview----- 8/7/2012 NAME This exam is closed book and closed notes, but open calculator. You have about 80 minutes to complete the exam (~ 9:30 10:50). The actual exam will be 50 questions
Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
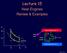 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3
![Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3 Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3](/thumbs/75/71840722.jpg) Ph70A Spring 004 Prof. Pui Lam SOLUTION Reading Assignment #3 :h.3: (3-3,5,6,7,8), h4: (4-,,4,5,6) Homework #3: First Law and Second of Thermodynamics Due: Monday 5/3/004.. A monatomic ideal gas is allowed
Ph70A Spring 004 Prof. Pui Lam SOLUTION Reading Assignment #3 :h.3: (3-3,5,6,7,8), h4: (4-,,4,5,6) Homework #3: First Law and Second of Thermodynamics Due: Monday 5/3/004.. A monatomic ideal gas is allowed
Collisions between molecules
 Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics
 Fall 004 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics November 1, 004 Calculators allowed. No books allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your name on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully. Do all
Fall 004 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics November 1, 004 Calculators allowed. No books allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your name on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully. Do all
Physics 2 week 7. Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Physics week 7 Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases 3.1. Ideal Gases 3.1.1. Experimental Laws and the Equation of State 3.1.. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3.. Mean Free Path 3.3. The Boltzmann Distribution
Physics week 7 Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases 3.1. Ideal Gases 3.1.1. Experimental Laws and the Equation of State 3.1.. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3.. Mean Free Path 3.3. The Boltzmann Distribution
Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gas Law
 Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gas Law The Density of copper is 8.9 E 3 kg/m^3 and each copper atom has a mass of 63 u, where 1u= 1.66 E -27 kg. Estimate the average distance between neighboring
Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gas Law The Density of copper is 8.9 E 3 kg/m^3 and each copper atom has a mass of 63 u, where 1u= 1.66 E -27 kg. Estimate the average distance between neighboring
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
HEAT- I Part - A C D A B. Te m p. Heat input
 e m p HE- I Part -. solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. he temperature of the material is changing with heat input as shown in the graph. Study the graph carefully and answer the following
e m p HE- I Part -. solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. he temperature of the material is changing with heat input as shown in the graph. Study the graph carefully and answer the following
HEAT, WORK, AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 HET, WORK, ND THE FIRST LW OF THERMODYNMICS 8 EXERCISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET We identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The problem involves calculating
HET, WORK, ND THE FIRST LW OF THERMODYNMICS 8 EXERCISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET We identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The problem involves calculating
PY Introduction to thermodynamics and statistical physics Summer Examination suggested solutions Dr. Asaf Pe er
 PY2104 - Introduction to thermodynamics and statistical physics Summer Examination 2014 - suggested solutions Dr. Asaf Pe er 1) Onemoleofwater(H 2 O)isbeingheatedfrom 20 Cto+80 C,atconstant atmospheric
PY2104 - Introduction to thermodynamics and statistical physics Summer Examination 2014 - suggested solutions Dr. Asaf Pe er 1) Onemoleofwater(H 2 O)isbeingheatedfrom 20 Cto+80 C,atconstant atmospheric
= 1906J/0.872deg = 2186J/deg
 Physical Chemistry 2 2006 Homework assignment 2 Problem 1: he heat of combustion of caffeine was determined by first burning benzoic acid and then caffeine. In both cases the calorimeter was filled with
Physical Chemistry 2 2006 Homework assignment 2 Problem 1: he heat of combustion of caffeine was determined by first burning benzoic acid and then caffeine. In both cases the calorimeter was filled with
