Physics 213. Practice Final Exam Spring The next two questions pertain to the following situation:
|
|
|
- Cecil Elvin Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The next two questions pertain to the following situation: Consider the following two systems: A: three interacting harmonic oscillators with total energy 6ε. B: two interacting harmonic oscillators, with total energy 4ε. 1. What is the ratio of entropies for the two systems? a. σ A /σ B = 0 b. σ A /σ B = 0.86 c. σ A /σ B = 1 d. σ A /σ B = 2.07 e. σ A /σ B = Now the systems are brought into contact and allowed to reach equilibrium. The increase in entropy due to the process is a. 0 b c of 31 pages
2 3. Two types of atoms have energy levels as shown in the figure. All of the excited states are at the same energy, E 2, but atoms of type 1 have three states at that energy, while atoms of type 2 have only one. A box of gas Type 1 Type 2 contains both types of atoms in equilibrium at temperature, T. Compare the probability that an atom of type 1 is in its ground state (i.e., has energy E 1 ) with the probability that an atom of type 2 is in its ground state. a. Atoms of type 1 are more likely to be in the ground state. b. Atoms of type 2 are more likely to be in the ground state. c. Atoms of the two types are equally likely to be in the ground state. E 2 E 1 2 of 31 pages
3 The next three questions are related: Consider a large collection of spins with dipole moment μ = 1 x J/Tesla). 4. If B = 1 Tesla, for what temperature will twice as many spins be pointing up (along the field) as down? a. T = 2.1 K b. T = 5.2 K c. T = 14.5 K d. T = 23.7 K e. T = 88.4 K 5. Assuming there are N spins, what is the heat capacity in the limit of high temperature? *Note: This problem may be longer/more difficult; therefore, you may want to do it last.* a. b. C C V V 2 2 B 2 kt Nk T B 2 2 c. CV 2 d. e. N B kt 2 2 N B CV 2 kt 2 Nk T CV B 3 of 31 pages
4 4 of 31 pages
5 Consider a large collection of spins with dipole moment μ = 1 x J/Tesla). 6. Now let there be 10 6 spins and let B go to zero. After the spins have completely randomized, approximately what is the probability of observing N up N down = 1000? a. P = 5 x 10-2 b. P = 5 x 10-3 c. P = 5 x 10-4 d. P = 5 x 10-5 e. P = 5 x of 31 pages
6 The next two questions pertain to the following situation: 6 of 31 pages
7 7 of 31 pages
8 7. A box of total volume V initially has an insulating partition, which separates N Ar Argon atoms (monatomic, each with mass m Ar ) at initial temperature T Ar from N N2 nitrogen molecules (diatomic, each with mass m N2 ) at initial temperature T N2. The partition is suddenly removed, and the gases allowed to equilibrate. The final temperature T f is 3N T 5N T Ar Ar N 2 N 2 a. Tf 3NAr 5NN 2 N ArTAr NN 2TN 2 b. Tf NAr NN 2 5N ArTAr 3NN 2TN 2 c. Tf 5NAr 3NN 2 3N ArTAr 5NN 2TN 2 d. Tf 3NAr 5NN 2 N ArTAr NN 2TN 2 e. Tf NAr NN 2 8 of 31 pages
9 9 of 31 pages
10 ' ' 8. If U Ar and U N 2 are the final energies of each component, which of the following is true in equilibrium: a. U N ' Ar U N ' N 2 Ar N 2 b. ' U Ar ' U N 2 c. 2 2 mar v Ar mn 2 v N 2 9. The vibrational mode of the N 2 molecule acts like a harmonic oscillator with energy spacing, = ev. Estimate the probability that a molecule of N 2 in equilibrium at room temperature (T = 300 K) is in the first excited vibrational state (not the ground state). a. Probability = b. Probability = c. Probability = d. Probability = e. Probability = of 31 pages
11 10. As absolute temperature goes to zero, the heat capacity of N one-dimensional harmonic oscillators approaches a. 0 b. 1 2 Nk c. Nk 11 of 31 pages
12 The next two problems are related: 11. Consider a 2-dimensional gas, in which particles are allowed to move only in a plane. In this case, the probability density is given by P(E) = (kt) -1 e -E/kT. If the particles have mass of kg, at T = 300 K approximately what fraction of the particles have an energy between and ev? a b c d e What is the root-mean-square velocity of the particles in this 2-d gas? a. v 0 b. c. v v rms rms rms 2kT m 3kT m 12 of 31 pages
13 The next two problems are related: 13. A molecule has one electronic state with energy E 0, and four with energy E 1 = E ev. At T = 273K, what is the relative number of molecules at each energy level? 0.03 ev E 1 E 0 a. N 1 < N 0 b. N 1 > N 0 c. The answer cannot be determined from the information given. 14. What is the average energy of a molecule in the previous case? a ev b ev c ev 13 of 31 pages
14 The next two problems are related: A sphere of radius 1m is released into deep space (away from the sun), with an initial temperature of 72 C. 15. What is the wavelength of the peak in the blackbody radiation from the sphere? a. 830 nm b. 8.4 micrometers c. 40 micrometers 16. Approximating the sphere as a perfect black body, and assuming its heat capacity is 10 4 J/K, about how long does the sphere take to cool to 335 K? a s b. 0.1 s c. 1 s d. 10 s e. 100 s 14 of 31 pages
15 15 of 31 pages
16 17. Brick A has mass m A = 1 kg, with specific heat c A = 1000J/kg-K, initially at temperature T A = 100 K. Brick B has mass m B = 2 kg, with specific heat c B = 2000J/kg-K, initially at temperature T B = 200 K. The bricks are put in thermal contact with each other (but are isolated from the rest of the world). After the two-brick system reaches thermal equilibrium, by how much, S tot, has their total entropy changed? a. S tot = -81 J/K b. S tot = 0.0 J/K c. S tot = 81 J/K d. S tot = 166 J/K e. S tot = 1009 J/K 16 of 31 pages
17 The next two problems are related: A substance has the following chemical potential vs T diagram at a particular pressure. T(K) a b c d e 18. Which of the points corresponds to a substance that is in thermal equilibrium? a. b. c. d. e. 19. Which of the points corresponds to a substance that is about to sublime? a. b. c. d. e. 17 of 31 pages
18 20. Calculate the chemical potential,, of Argon gas at room temperature, T = 300 K, and atmospheric pressure, p = Pa. Ignore the effect of external forces, such as gravity. a. = ev b. = ev c. = 0 ev d. = ev e. = ev 21. A container holds N total gas molecules in equilibrium at two different heights as pictured. What is the relationship between the chemical potentials of the molecules at height h 1 and h 2 = 2h 1? a) 1 = 2 /4 b) 1 = 2 /2 c) 1 = 2 d) 1 2 = 2 e) 1 = of 31 pages
19 22. The gas molecules are 80% N 2 and 20% O 2 at sea level, i.e., n N2 /n O2 = 4. Neglecting the effects of thermal mixing, at what height is the ratio n N2 /n O2 = 1? (Assume a constant temperature T = 260 K.) a. 33 km b. 76 km c. There is no altitude above sea level where the ratio is of 31 pages
20 The next two problems are related: 23. A window is made of two layers of material that have different thermal conductivities, 2 > 1. The temperature on one side of the window is higher than the other: T 2 > T 1. Which orientation of the window (see the figure) T 1 T 2 T 1 T 2 gives more heat flow through the H window? A H B a. H A > H B (A has more heat flow.) b. H A = H B (The heat flows are equal.) c. H A < H B (B has more heat flow.) Orientation A Orientation B 24. Now consider that the layers have equal thickness, and 2 = 3 1. The temperatures T 1 = 10 C and T 2 = 20 C. What is the relative temperature T i at the interface between the two layers? a C b. 15 C c C d. 18 C e. 20 C T T i T 2 20 of 31 pages
21 25. Compare the isothermal V and adiabatic expansions 1 from V 1 = 0.04 m 3 to V 2 = 0.08 m 3 of two moles of an ideal diatomic gas, as shown in the figure. Both processes end up at the same state, T 2 = 300 K, and p 2 = 62.3 kpa. Calculate the ratio, W I /W A, of the work done by the two processes (isothermal divided by adiabatic). a. W I /W A = 0.40 b. W I /W A = 0.87 c. W I /W A = 1.40 d. W I /W A = 2.00 e. W I /W A = 3.46 p 2,V 2,T 2 21 of 31 pages
22 26. A Carnot heat engine achieves 33.3% efficiency when operating between temperatures T h and T c. If it is operated as a refrigerator operating between the same two reservoirs, how much work, W, must we supply in order to remove 1 kj of heat from the cold reservoir? a. W = 500 J b. W = 666 J c. W = 1 kj d. W = 2 kj e. W = 3 kj 22 of 31 pages
23 27. The following chemical reaction occurs: 2N 2 O 5 4NO 2 + O 2. Which of the following correctly expresses the relationship between the chemical potentials of all three species? a) 2 N2O 4 5 NO 2 O2 b) 2 N2O 4 5 NO 2 O2 c) 2 4 N2O 5 NO 2 O2 d) N2O 5 NO 2 O2 e) 2 N2O 4 5 NO 2 O2 28. Two identical blocks each have heat capacity 100 J/K. One block is at temperature 500K and the other is at temperature 100K. Which block has the higher free energy relative to the environment at 300 K? a) the cold block b) the hot block c) they have the same free energy 23 of 31 pages
24 29. A block of material has a temperature-dependent heat capacity given by C V (T) = 5 J/K + T (2 J/K 2 ). How much does the entropy of this object change as its temperature is increased from 10ºC to 40ºC at constant volume? a) 66.9 J/K b) 60.5 J/K c) 0.50 J/K d) 60.5 J/K e) 66.9 J/K 24 of 31 pages
25 30. The star Rigel (in the constellation Orion) is a blue supergiant. It is very large (R Rigel =70R Sun ) and very bright, i.e., has very high total radiated power P Rigel /P Sun = 80,000). How much hotter is it than the sun? That is, what is the ratio, T Rigel /T Sun? a. T Rigel /T Sun = 2 b. T Rigel /T Sun = 16 c. T Rigel /T Sun = 70 d. T Rigel /T Sun = 4,900 e. T Rigel /T Sun = 78, of 31 pages
26 31. The semiconductor silicon (Si) has a band gap of 1.14 ev. The quantum density associated with its valence and conduction bands is 1.72 x /m 2. How many free holes are there in the valence band at 300K if a density of /m 3 phosphorous atoms (electron donors) are added to the crystal? a) n h = 2.1 x 10 7 /m 3 b) n h = 2.1 x 10 9 /m 3 c) n h = 2.1 x /m 3 26 of 31 pages
27 32. A 1-liter (non-elastic) balloon is filled with pure helium gas. The balloon is in a room 10x10x10m at 300 K and 1 atm. (Assume the air in the room is all nitrogen and oxygen molecules.) Now we pop the balloon, allowing the He to diffuse throughout the room. By what amount does the Free energy of the He gas change? a) J b) -691 J c) 0 d) J e) J 27 of 31 pages
28 The next two problems are related: 33. Argon (molecular weight 40 g/mole) is a monatomic compound. If liquid argon is confined to a container and held at a constant temperature of 80.5 K, what is the approximate vapor pressure of gaseous argon, assuming the liquid has no entropy and a binding energy of 0.1 ev? [Note: At 1 atm, the boiling point is 87.3 K.] a) 2 atm b) 0.2 atm c) 0.02 atm d) atm e) atm 34. The measured value of the latent heat of vaporization of argon (at 1 atm) is 6.43 kj/mol. Use this to estimate the binding energy. a) ev b) ev c) ev d) 0.11 ev e) 0.4 ev 28 of 31 pages
29 The next two questions pertain to the following situation: In a hydrogen atom, the electron (e) is electrostatically bound to the proton (p) with an energy 13.6 ev. Inside a star, the density is ~10 24 /m 3, and the temperature is 7000 K. 35. *Note: This problem may be longer/more difficult; therefore, you may want to do it last.* What is the density of free electrons (and protons)? You may assume that n H = 1 x m -3 and that m H = m p = 1836 m e. a. 6.0 x m -3 b. 2.7 x m -3 c. 5.1 x m -3 d. 2.1 x m -3 e. 4.7 x m Which of the following would increase the fraction of unbound protons? a. increase the temperature. b. increase the pressure. c. increasing the binding energy. 29 of 31 pages
30 1 d 2 b 3 b 4 a 5 d 6 c 7 d 8 c 9 b 10 a 11 b 12 b 13 b 14 b 15 b 16 d 17 d 18 a 19 b 20 b 21 c 22 c 23 b 24 c 25 b 26 a 27 a 28 a 29 d 30 a 31 c 32 a 33 b 34 b 35 e 36 a 30 of 31 pages
31 31 of 31 pages
2. Estimate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 4 kg of Aluminum from 20 C to 30 C
 1. A circular rod of length L = 2 meter and diameter d=2 cm is composed of a material with a heat conductivity of! = 6 W/m-K. One end is held at 100 C, the other at 0 C. At what rate does the bar conduct
1. A circular rod of length L = 2 meter and diameter d=2 cm is composed of a material with a heat conductivity of! = 6 W/m-K. One end is held at 100 C, the other at 0 C. At what rate does the bar conduct
Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Physics 213 Final Exam Spring 2014 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. This is a closed book exam. You have 2 hours
Physics 213 Final Exam Spring 2014 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. This is a closed book exam. You have 2 hours
Last Name: First Name ID
 Last Name: First Name ID This is a set of practice problems for the final exam. It is not meant to represent every topic and is not meant to be equivalent to a 2-hour exam. These problems have not been
Last Name: First Name ID This is a set of practice problems for the final exam. It is not meant to represent every topic and is not meant to be equivalent to a 2-hour exam. These problems have not been
If the dividing wall were allowed to move, which of the following statements would not be true about its equilibrium position?
 PHYS 213 Exams Database Midterm (A) A block slides across a rough surface, eventually coming to a stop. 1) What happens to the block's internal thermal energy and entropy? a. and both stay the same b.
PHYS 213 Exams Database Midterm (A) A block slides across a rough surface, eventually coming to a stop. 1) What happens to the block's internal thermal energy and entropy? a. and both stay the same b.
a. 4.2x10-4 m 3 b. 5.5x10-4 m 3 c. 1.2x10-4 m 3 d. 1.4x10-5 m 3 e. 8.8x10-5 m 3
 The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers!
 AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
A) 2.0 atm B) 2.2 atm C) 2.4 atm D) 2.9 atm E) 3.3 atm
 Name: Date: 1. On a cold day ( 3 C), the gauge pressure on a tire reads 2.0 atm. If the tire is heated to 27 C, what will be the absolute pressure of the air inside the tire? A) 2.0 atm B) 2.2 atm C) 2.4
Name: Date: 1. On a cold day ( 3 C), the gauge pressure on a tire reads 2.0 atm. If the tire is heated to 27 C, what will be the absolute pressure of the air inside the tire? A) 2.0 atm B) 2.2 atm C) 2.4
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Dual Program Level 1 Physics Course
 Dual Program Level 1 Physics Course Assignment 15 Due: 11/Feb/2012 14:00 Assume that water has a constant specific heat capacity of 4190 J/kg K at all temperatures between its melting point and boiling
Dual Program Level 1 Physics Course Assignment 15 Due: 11/Feb/2012 14:00 Assume that water has a constant specific heat capacity of 4190 J/kg K at all temperatures between its melting point and boiling
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam. Review Lecture
 Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam Review Lecture The next two questions pertain to the following situation. A container of air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen molecules) is initially at 300 K and atmospheric
Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam Review Lecture The next two questions pertain to the following situation. A container of air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen molecules) is initially at 300 K and atmospheric
7. (2) Of these elements, which has the greatest number of atoms in a mole? a. hydrogen (H) b. oxygen (O) c. iron (Fe) d. gold (Au) e. all tie.
 General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.)
 Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
6. (6) Show all the steps of how to convert 50.0 F into its equivalent on the Kelvin scale.
 General Physics I Quiz 8 - Ch. 13 - Temperature & Kinetic Theory July 30, 2009 Name: Make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used. Give correct units and significant figures. Partial credit is
General Physics I Quiz 8 - Ch. 13 - Temperature & Kinetic Theory July 30, 2009 Name: Make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used. Give correct units and significant figures. Partial credit is
Chapter 19 Entropy Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 20-1
 Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. E.g., gas scaling, intro to the ideal gas law, pressure cooker,
Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. E.g., gas scaling, intro to the ideal gas law, pressure cooker,
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law
 Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state X along the path XYZX as shown in the PV-diagram.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
First major ( 043 ) a) 180 degrees b) 90 degrees c) 135 degrees d) 45 degrees e) 270 degrees
 First major ( 043 ) 1) The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by y(x,t) = y m sin( kx ωt ϕ ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of zero and is moving
First major ( 043 ) 1) The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by y(x,t) = y m sin( kx ωt ϕ ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of zero and is moving
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Preliminary Examination - Day 2 August 16, 2013
 UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day August 16, 13 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic 1) and Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic ). Each
UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day August 16, 13 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic 1) and Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic ). Each
Chemistry Lab Fairfax High School Invitational January 7, Team Number: High School: Team Members Names:
 Chemistry Lab Fairfax High School Invitational January 7, 2017 Team Number: High School: Team Members Names: Reference Values: Gas Constant, R = 8.314 J mol -1 K -1 Gas Constant, R = 0.08206 L atm mol
Chemistry Lab Fairfax High School Invitational January 7, 2017 Team Number: High School: Team Members Names: Reference Values: Gas Constant, R = 8.314 J mol -1 K -1 Gas Constant, R = 0.08206 L atm mol
First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Mechanical Equivalent of Heat Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Expansion of Solids
 Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Chapter 19 Entropy Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 20-1
 Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems for Ch. 19/20 Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. How to calculate energy required for a given T
Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems for Ch. 19/20 Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. How to calculate energy required for a given T
PHY214 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: 2 hours 30 minutes
 BSc Examination by course unit. Friday 5th May 01 10:00 1:30 PHY14 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: hours 30 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED
BSc Examination by course unit. Friday 5th May 01 10:00 1:30 PHY14 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: hours 30 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3. Temperature & Heat
 Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics Specific Heat (Capacity) Specific Heat Latent Heat
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics Specific Heat (Capacity) Specific Heat Latent Heat
T ice T water T water = T ice =0 0 C. e =1
 Given 1 kg of water at 100 0 C and a very large (very very large) block of ice at 0 0 C. A reversible heat engine absorbs heat from the water and expels heat to the ice until work can no longer be extracted
Given 1 kg of water at 100 0 C and a very large (very very large) block of ice at 0 0 C. A reversible heat engine absorbs heat from the water and expels heat to the ice until work can no longer be extracted
Chapter 12. Temperature and Heat. continued
 Chapter 12 Temperature and Heat continued 12.3 The Ideal Gas Law THE IDEAL GAS LAW The absolute pressure of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature and the number of moles (n) of
Chapter 12 Temperature and Heat continued 12.3 The Ideal Gas Law THE IDEAL GAS LAW The absolute pressure of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature and the number of moles (n) of
What is Temperature?
 What is Temperature? Observation: When objects are placed near each other, they may change, even if no work is done. (Example: when you put water from the hot tap next to water from the cold tap, they
What is Temperature? Observation: When objects are placed near each other, they may change, even if no work is done. (Example: when you put water from the hot tap next to water from the cold tap, they
Introduction to thermodynamics
 Chapter 6 Introduction to thermodynamics Topics First law of thermodynamics Definitions of internal energy and work done, leading to du = dq + dw Heat capacities, C p = C V + R Reversible and irreversible
Chapter 6 Introduction to thermodynamics Topics First law of thermodynamics Definitions of internal energy and work done, leading to du = dq + dw Heat capacities, C p = C V + R Reversible and irreversible
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 52 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW 1. Water at a temperature of 0 C is kept in a thermally insulated container.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 52 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW 1. Water at a temperature of 0 C is kept in a thermally insulated container.
S15--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch13_14_15 PRACTICE
 Name: Class: Date: S5--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch3_4_5 PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is a thermodynamic
Name: Class: Date: S5--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch3_4_5 PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is a thermodynamic
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics
 Name: Date: Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics 1. The kelvin temperature of an object is a measure of A. the total energy of the molecules of the object. B. the total kinetic energy of the molecules of
Name: Date: Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics 1. The kelvin temperature of an object is a measure of A. the total energy of the molecules of the object. B. the total kinetic energy of the molecules of
QuickCheck. Collisions between molecules. Collisions between molecules
 Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
(2) The volume of molecules is negligible in comparison to the volume of gas. (3) Molecules of a gas moves randomly in all direction.
 9.1 Kinetic Theory of Gases : Assumption (1) The molecules of a gas are identical, spherical and perfectly elastic point masses. (2) The volume of molecules is negligible in comparison to the volume of
9.1 Kinetic Theory of Gases : Assumption (1) The molecules of a gas are identical, spherical and perfectly elastic point masses. (2) The volume of molecules is negligible in comparison to the volume of
Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics. Preliminary Ph.D. Qualifying Exam. Summer 2009
 Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics Preliminary Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Summer 2009 (Choose 4 of the following 6 problems) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics Preliminary Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Summer 2009 (Choose 4 of the following 6 problems) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Physics 4230 Final Exam, Spring 2004 M.Dubson This is a 2.5 hour exam. Budget your time appropriately. Good luck!
 1 Physics 4230 Final Exam, Spring 2004 M.Dubson This is a 2.5 hour exam. Budget your time appropriately. Good luck! For all problems, show your reasoning clearly. In general, there will be little or no
1 Physics 4230 Final Exam, Spring 2004 M.Dubson This is a 2.5 hour exam. Budget your time appropriately. Good luck! For all problems, show your reasoning clearly. In general, there will be little or no
Exam 4. P201 Fall 2006, Instructor: Prof. Abanov 11/28/06. (print in big block letters )
 Exam 4 P201 Fall 2006, Instructor: Prof. Abanov 11/28/06 Name Section (print in big block letters ) Your grade: Problem 1. One end of a horizontal rope is attached to a prong of an electrically driven
Exam 4 P201 Fall 2006, Instructor: Prof. Abanov 11/28/06 Name Section (print in big block letters ) Your grade: Problem 1. One end of a horizontal rope is attached to a prong of an electrically driven
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Trinity Term Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY. Time allowed: 2 ½ hours
 FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Trinity Term 004 Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Wednesday, June 9 th 004, 9.30 a.m. to 1 noon Time allowed: ½ hours Candidates should answer
FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Trinity Term 004 Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Wednesday, June 9 th 004, 9.30 a.m. to 1 noon Time allowed: ½ hours Candidates should answer
Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, L π
 Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, 013 1. a. Define the chemical potential µ. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if µ 1 =µ. You may start with F =
Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, 013 1. a. Define the chemical potential µ. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if µ 1 =µ. You may start with F =
 第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
Collisions between molecules
 Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Physics 1501 Lecture 35
 Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
S = S(f) S(i) dq rev /T. ds = dq rev /T
 In 1855, Clausius proved the following (it is actually a corollary to Clausius Theorem ): If a system changes between two equilibrium states, i and f, the integral dq rev /T is the same for any reversible
In 1855, Clausius proved the following (it is actually a corollary to Clausius Theorem ): If a system changes between two equilibrium states, i and f, the integral dq rev /T is the same for any reversible
Temperature and Thermometers. Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. Most materials expand when heated.
 Heat Energy Temperature and Thermometers Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. Most materials expand when heated. Thermometers are instruments designed to measure temperature. In order
Heat Energy Temperature and Thermometers Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is. Most materials expand when heated. Thermometers are instruments designed to measure temperature. In order
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Physics 119A Final Examination
 First letter of last name Name: Perm #: Email: Physics 119A Final Examination Thursday 10 December, 2009 Question 1 / 25 Question 2 / 25 Question 3 / 15 Question 4 / 20 Question 5 / 15 BONUS Total / 100
First letter of last name Name: Perm #: Email: Physics 119A Final Examination Thursday 10 December, 2009 Question 1 / 25 Question 2 / 25 Question 3 / 15 Question 4 / 20 Question 5 / 15 BONUS Total / 100
CHAPTER 13. States of Matter. Kinetic = motion. Polar vs. Nonpolar. Gases. Hon Chem 13.notebook
 CHAPTER 13 States of Matter States that the tiny particles in all forms of matter are in constant motion. Kinetic = motion A gas is composed of particles, usually molecules or atoms, with negligible volume
CHAPTER 13 States of Matter States that the tiny particles in all forms of matter are in constant motion. Kinetic = motion A gas is composed of particles, usually molecules or atoms, with negligible volume
Physics 231. Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics. Alex Brown Dec MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Ideal Gas Behavior. NC State University
 Chemistry 331 Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Behavior NC State University Macroscopic variables P, T Pressure is a force per unit area (P= F/A) The force arises from the change in momentum as particles hit an object
Chemistry 331 Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Behavior NC State University Macroscopic variables P, T Pressure is a force per unit area (P= F/A) The force arises from the change in momentum as particles hit an object
KINETIC THEORY. was the original mean square velocity of the gas. (d) will be different on the top wall and bottom wall of the vessel.
 Chapter Thirteen KINETIC THEORY MCQ I 13.1 A cubic vessel (with faces horizontal + vertical) contains an ideal gas at NTP. The vessel is being carried by a rocket which is moving at a speed of 500m s 1
Chapter Thirteen KINETIC THEORY MCQ I 13.1 A cubic vessel (with faces horizontal + vertical) contains an ideal gas at NTP. The vessel is being carried by a rocket which is moving at a speed of 500m s 1
Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source
Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source
ASSIGNMENT SHEET #4 PART I APQ ANSWERS
 ASSIGNMENT SHEET #4 PART I APQ ANSWERS 5 a. (Recall: combustion means adding oxygen gas to) C 5 H 12 + 8 O 2 5 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O b. 2.50 g C 5 H 12 72.15 g/mole C 5 H 12 0.035 mole C 5 H 12 0.035 mole C 5
ASSIGNMENT SHEET #4 PART I APQ ANSWERS 5 a. (Recall: combustion means adding oxygen gas to) C 5 H 12 + 8 O 2 5 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O b. 2.50 g C 5 H 12 72.15 g/mole C 5 H 12 0.035 mole C 5 H 12 0.035 mole C 5
SI units, is given by: y = cos (46t - 12x). The frequency of the wave, in SI units, is closest to: A) 46 B) 100 C) 140 D) 23 E) 69
 Exam Name Email Perm# Tel # Remember to write all work in yoru Bluebook as well as put the answer on your Scantron MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Exam Name Email Perm# Tel # Remember to write all work in yoru Bluebook as well as put the answer on your Scantron MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
Quiz C&J page 316 (top), Check Your Understanding #6:... use a straw
 Quiz on Chapter 11 Quiz 9 1. C&J page 316 (top), Check Your Understanding #6:... use a straw Quiz 9 1. C&J page 316 (top), Check Your Understanding #6:... use a straw 2. What volume of helium has the same
Quiz on Chapter 11 Quiz 9 1. C&J page 316 (top), Check Your Understanding #6:... use a straw Quiz 9 1. C&J page 316 (top), Check Your Understanding #6:... use a straw 2. What volume of helium has the same
ME 262A - Physical Gas Dynamics 1996 Final Exam: Open Book Portion. h = 6.62 x J s Energy conversion factor: 1 calorie = 4.
 Name: ME 262A - Physical Gas Dynamics 1996 Final Exam: Open Book Portion Useful data and information: k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s Energy conversion factor: 1 calorie = 4.2 J 1. (40 points)
Name: ME 262A - Physical Gas Dynamics 1996 Final Exam: Open Book Portion Useful data and information: k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s Energy conversion factor: 1 calorie = 4.2 J 1. (40 points)
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS ( MARK). Write two condition when real gases obey the ideal gas equation ( nrt). n number of mole.. If the number of molecule in a container is
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS ( MARK). Write two condition when real gases obey the ideal gas equation ( nrt). n number of mole.. If the number of molecule in a container is
Chapter 10. Thermal Physics. Thermodynamic Quantities: Volume V and Mass Density ρ Pressure P Temperature T: Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermodynamic Quantities: Volume V and Mass Density ρ Pressure P Temperature T: Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion of Solids and Liquids Ideal
Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermodynamic Quantities: Volume V and Mass Density ρ Pressure P Temperature T: Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion of Solids and Liquids Ideal
Atomic Mass and Atomic Mass Number. Moles and Molar Mass. Moles and Molar Mass
 Atomic Mass and Atomic Mass Number The mass of an atom is determined primarily by its most massive constituents: protons and neutrons in its nucleus. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons is called
Atomic Mass and Atomic Mass Number The mass of an atom is determined primarily by its most massive constituents: protons and neutrons in its nucleus. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons is called
Rate of Heating and Cooling
 Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Each of the following questions (1-15) is worth 6 points
 Name: ----------------------------------------------- S. I. D.: ------------------------------------ Physics 0 Final Exam (Version A) Summer 06 HIS EXAM CONAINS 36 QUESIONS. ANSWERS ARE ROUNDED. PICK HE
Name: ----------------------------------------------- S. I. D.: ------------------------------------ Physics 0 Final Exam (Version A) Summer 06 HIS EXAM CONAINS 36 QUESIONS. ANSWERS ARE ROUNDED. PICK HE
Chapter 10, Thermal Physics
 CHAPTER 10 1. If it is given that 546 K equals 273 C, then it follows that 400 K equals: a. 127 C b. 150 C c. 473 C d. 1 200 C 2. A steel wire, 150 m long at 10 C, has a coefficient of linear expansion
CHAPTER 10 1. If it is given that 546 K equals 273 C, then it follows that 400 K equals: a. 127 C b. 150 C c. 473 C d. 1 200 C 2. A steel wire, 150 m long at 10 C, has a coefficient of linear expansion
Solutions Midterm Exam 3 December 12, Match the above shown players of the best baseball team in the world with the following names:
 Problem 1 (2.5 points) 1 2 3 4 Match the above shown players of the best baseball team in the world with the following names: A. Derek Jeter B. Mariano Rivera C. Johnny Damon D. Jorge Posada 1234 = a.
Problem 1 (2.5 points) 1 2 3 4 Match the above shown players of the best baseball team in the world with the following names: A. Derek Jeter B. Mariano Rivera C. Johnny Damon D. Jorge Posada 1234 = a.
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
A) 120 degrees B) 90 degrees C) 60 degrees D) 45 degrees E) 30 degrees
 Phys10 - First Major 071 Zero Version Q1. Two identical sinusoidal traveling waves are sent along the same string in the same direction. What should be the phase difference between the two waves so that
Phys10 - First Major 071 Zero Version Q1. Two identical sinusoidal traveling waves are sent along the same string in the same direction. What should be the phase difference between the two waves so that
MP203 Statistical and Thermal Physics. Jon-Ivar Skullerud and James Smith
 MP203 Statistical and Thermal Physics Jon-Ivar Skullerud and James Smith October 3, 2017 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Temperature and thermal equilibrium.................... 4 1.1.1 The zeroth law of
MP203 Statistical and Thermal Physics Jon-Ivar Skullerud and James Smith October 3, 2017 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Temperature and thermal equilibrium.................... 4 1.1.1 The zeroth law of
Gases and IMFs Unit Exam Review Guide
 Gases and IMFs Unit Exam Review Guide The following review guide does not necessarily contain all topics that will appear on the test. Make sure to review all notes and concepts from this unit. This review
Gases and IMFs Unit Exam Review Guide The following review guide does not necessarily contain all topics that will appear on the test. Make sure to review all notes and concepts from this unit. This review
Physics 231 Topic 12: Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases Alex Brown Nov
 Physics 231 Topic 12: Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases Alex Brown Nov 18-23 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 homework 3 rd midterm final Thursday 8-10 pm makeup Friday final 9-11 am MSU
Physics 231 Topic 12: Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases Alex Brown Nov 18-23 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 homework 3 rd midterm final Thursday 8-10 pm makeup Friday final 9-11 am MSU
Each of the following 50 questions are worth 2 points each. Answer a = true b = false
 PHY 262 Exam 3-----preview----- 8/7/2012 NAME This exam is closed book and closed notes, but open calculator. You have about 80 minutes to complete the exam (~ 9:30 10:50). The actual exam will be 50 questions
PHY 262 Exam 3-----preview----- 8/7/2012 NAME This exam is closed book and closed notes, but open calculator. You have about 80 minutes to complete the exam (~ 9:30 10:50). The actual exam will be 50 questions
Physics 111. Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, Latent Heats
 Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Lecture 25 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas
 Lecture 5 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular collisions
Lecture 5 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular collisions
BCIT Fall Chem Exam #1
 BCIT Fall 2012 Chem 3615 Exam #1 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
BCIT Fall 2012 Chem 3615 Exam #1 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
Handout 10: Heat and heat transfer. Heat capacity
 1 Handout 10: Heat and heat transfer Heat capacity Consider an experiment in Figure 1. Heater is inserted into a solid substance of mass m and the temperature rise T degrees Celsius is measured by a thermometer.
1 Handout 10: Heat and heat transfer Heat capacity Consider an experiment in Figure 1. Heater is inserted into a solid substance of mass m and the temperature rise T degrees Celsius is measured by a thermometer.
CHEMISTRY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST STATES OF MATTER TEST CODE:
 Chemsitry States of Matter Multiple Choice 017074 CHEMISTRY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST STATES OF MATTER TEST CODE: 017074 Directions: Each group of questions below consists of five lettered answers followed by
Chemsitry States of Matter Multiple Choice 017074 CHEMISTRY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST STATES OF MATTER TEST CODE: 017074 Directions: Each group of questions below consists of five lettered answers followed by
18.13 Review & Summary
 5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
Although different gasses may differ widely in their chemical properties, they share many physical properties
 IV. Gases (text Chapter 9) A. Overview of Chapter 9 B. Properties of gases 1. Ideal gas law 2. Dalton s law of partial pressures, etc. C. Kinetic Theory 1. Particulate model of gases. 2. Temperature and
IV. Gases (text Chapter 9) A. Overview of Chapter 9 B. Properties of gases 1. Ideal gas law 2. Dalton s law of partial pressures, etc. C. Kinetic Theory 1. Particulate model of gases. 2. Temperature and
Handout 11: Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat. Ideal gas law
 Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
Irreversible Processes
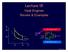 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016
 Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016 1. Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) A and B B) A and C C) B and C D) B and D 2. At STP, which physical property of aluminum always
Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016 1. Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) A and B B) A and C C) B and C D) B and D 2. At STP, which physical property of aluminum always
Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the Third Law
 Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the hird Law We have already noted that heat capacity and entropy have the same units. We will explore further the relationship between heat capacity and entropy. We
Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the hird Law We have already noted that heat capacity and entropy have the same units. We will explore further the relationship between heat capacity and entropy. We
Physics 408 Final Exam
 Physics 408 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work (with partial credit where it is deserved) so please do not just write down answers with no explanation (or skip important steps)! Please give clear,
Physics 408 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work (with partial credit where it is deserved) so please do not just write down answers with no explanation (or skip important steps)! Please give clear,
(prev) (top) (next) (Throughout, we will assume the processes involve an ideal gas with constant n.)
 1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
Phys102 First Major-182 Zero Version Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday, February 14, 2019 Page: 1
 Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday February 14 2019 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows a graph of a wave traveling to the left along a string at a speed of 34 m/s. At this instant what is the transverse velocity
Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday February 14 2019 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows a graph of a wave traveling to the left along a string at a speed of 34 m/s. At this instant what is the transverse velocity
S6. (a) State what is meant by an ideal gas...
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
People s Physics book 3e
 The Big Ideas Heat is a form of energy transfer. It can change the kinetic energy of a substance. For example, the average molecular kinetic energy of gas molecules is related to temperature. A heat engine
The Big Ideas Heat is a form of energy transfer. It can change the kinetic energy of a substance. For example, the average molecular kinetic energy of gas molecules is related to temperature. A heat engine
Physics 622. T.R. Lemberger. Jan. 2003
 Physics 622. T.R. Lemberger. Jan. 2003 Connections between thermodynamic quantities: enthalpy, entropy, energy, and microscopic quantities: kinetic and bonding energies. Useful formulas for one mole of
Physics 622. T.R. Lemberger. Jan. 2003 Connections between thermodynamic quantities: enthalpy, entropy, energy, and microscopic quantities: kinetic and bonding energies. Useful formulas for one mole of
(Heat capacity c is also called specific heat) this means that the heat capacity number c for water is 1 calorie/gram-k.
 Lecture 23: Ideal Gas Law and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1 (REVIEW) Chapter 17: Heat Transfer Origin of the calorie unit A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature
Lecture 23: Ideal Gas Law and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1 (REVIEW) Chapter 17: Heat Transfer Origin of the calorie unit A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature
