REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, FALL 2016 ANSWER KEY
|
|
|
- Alaina Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, FALL 2016 ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutely complete review. For a complete review make sure that you know how to do all the homework assigned in the course up to and including that due on October 4, and all the worksheets up to and including those of week 4. Strive to solve all the problems on this review sheet by hand, except perhaps for the Alice, Bob and Carol problem which has not-so-pretty numbers. In general you are expected to solve problems on an exam by hand unless specific instructions to the contrary are supplied on the exam. On the first midterm exam we will permit use of the calculator only sparingly (just for scientific calculator functions like +,,,,, log, exp) but on later exams we will ease up and permit calculator use for row reduction and determinants in many cases. However, on all exams, for algebra and calculus work not involving matrices, we insist that you perform and show all the steps needed to justify your final answer by hand calculation. An answer key for this review sheet will be posted on the course web page gwanders/math2373 at 10:30am on Wednesday, October 5. There is also a link to this URL on the Moodle page. Problem 1 Standing in line at the supermarket I see Alice, Bob and Carol ahead of me in the express check-out lane. Alice buys 2 bags of chips, 3 diet sodas, 1 bag of circus peanuts and spends $5.54. Bob buys 3 bags of chips, 1 diet soda, 3 bags of circus peanuts and spends $7.13. Carol buys 1 bag of chips, 1 diet soda, 1 bag of circus peanuts and spends $2.97. Find the price for a bag of chips, for a diet soda and for a bag of circus peanuts. You may use your calculator for the numerical work. Use the x A 1 b method of solution. Identify A, x and b clearly. A x x x y z x y z price of bag of chips price of can of diet soda price of bag of circus peanuts x y z Alice s bill Bob s bill Carol s bill b Date: September 30,
2 2 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY Remark. Another way to solve these equations, different from the method we asked for in this problem, is the following: and hence rref Solve the system of equations price of chips price of diet soda price of circus peanuts Problem x y +5w 1 2x +z +w 3 using the standard method taught in class, which means: write out the augmented matrix for the system, reduce the augmented matrix to reduced row echelon form, and present the final answer in the format of Example 7 on pp (see the next-to-last displayed line in the example). Do your work entirely by hand. Explain each row operation using notation like R 2 R 2 3R 3, as in the textbook. The augmented matrix of the system is [ Applying R 1 R 1 /2, we get [ 1 1/2 0 5/2 1/ Applying R 2 R 2 2R 1, we get [ 1 1/2 0 5/2 1/ Applying R 2 R 2, we get [ 1 1/2 0 5/2 1/ which is in row echelon form. Finally, applying R1 R 1 R 2 /2, we get [ 1 0 1/2 1/2 3/2, which is in reduced row echelon form. The last matrix above corresponds to the pair of equations... x +z/2 +w/2 3/2 y z 6w 4,.,
3 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 3 The variables z and w are free since they appear in columns without pivots in the reduced row echelon matrix. Let z s and w t. Then, solving for the remaining variables x and y in terms of the parameters s and t, we get x s/2 t/2 + 3/2 and y s + 6t 4. The final answer written in the officially acceptable manner is x s/2 t/2 + 3/2 1/2 1/2 y z s + 6t 4 s s t 6 0 w t 0 1 where s and t may take any (real) values. Problem 3 The following matrix is not quite in row echelon form (i) Reduce the matrix to row echelon form. (At most two more steps are required.) Clearly identify which matrix is supposed to be in row echelon form. (ii) Then reduce the matrix all the way to reduced row echelon form. The last matrix you write down should be exactly in reduced row echelon form. Furthermore, every step of row-reduction should be explained by using notation like R2 R 2 3R 1, as in the textbook. (We are only asking for you to do row operations. You are not being asked to solve any equations.) 3/ , (given matrix) R4 R 4 R 3, R4 R (row echelon form) R3 R 3 R 4, R2 R 2 R 4, R1 R 1 R R 2 R 2 R 3, R 1 R 1 R 3
4 4 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY R1 R 1 R 2 Problem 4 (reduced row echelon form) Expand the following determinant along the third row. You need not evaluate the resulting 3 by 3 determinants, just get all the numbers in the right places, and get all the signs right. Then answer the same question except now expand along the second column checkerboard: expansion along row 3: expansion along column 2: ( 1) ( 6) +4 Solve the initial value problem column row ( 6) Problem t dt 4y + t5 sin t and y(1)
5 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 5 We start by rewriting the equation in the standard form and then calculate in standard fashion: dt 4 t y t4 sin t ( ) exp 4 dt/t exp ( 4 log t) t 4 d dt t 4 y sin t t 4 y cos t + C 2 y(1) cos(1) + C C 2 + cos(1) t 4 y cos t cos(1) y t 4 cos t + (2 + cos(1))t 4. Solve the initial value problem dt y + 1 2t + 8 Problem 6 and y(0) 3. We use the technique of separation of variables. y + 1 dt 2(t + 4) log y log t C 2 y + 1 e C t + 4 1/2 y + 1 C 1 (t + 4) 1/2 (C 1 ±e C, t + 4 > 0) 4 y(0) /2 C 1 C 1 2 y + 1 2(t + 4) 1/2 y 2(t + 4) 1/2 1. To double-check our work, note that y(0) 2(0 + 4) 1/
6 6 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY using old math professor s trick We always get rid of the absolute value bars the same way. So instead of repeating those moves every time, we organize the calculation as follows: y + 1 dt 2(t + 4) log(y + 1) 1 log(t + 4) + ln C 2 y + 1 C(t + 4) 1/2 4 y(0) /2 C C 2 y + 1 2(t + 4) 1/2 y 2(t + 4) 1/2 1. The old math professor s trick of writing ln C is just a shorthand for skipping over some steps that are always the same when you have logarithms on one or both sides of the equation after integrating. To further double-check our work let us verify that the function we found does indeed satisfy the given differential equation. dt y + 1 2t + 4 Indeed, this checks out (t + 4)1/2 1 (t + 4) 1/2. (2(t + 4)1/2 1) + 1 2(t + 4) Problem 7 (t + 4) 1/2. Find k such that the following system of homogeneous equations has infinitely many solutions: x y 0. 1 k 2 z 0 It is the same thing to solve the equation k 2 0 because in general, for a square matrix A, the system of equations A x 0 has infinitely many solutions if and only if det A 0. Using basketweave to evaluate the left side we get the equation 2 4 ( 2) ( 5) ( 3) k ( 5) ( 3) ( 2) 2 7 k 0 which simplifies to 7 + k 0. Thus the solution is k 7. Another way to solve the problem is to expand the
7 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 7 determinant along the third row: (1) k and then solve for k as before. + ( 2) k k 0 checkerboard: row 3 Find a, b, c, d, w, x, y and z. Problem d w x y z a b 12 c You must do all the work by hand, and justify the steps. Note: This problem is only long because there are so many variables. It is not particularly difficult to solve for any one particular variable. If you are in a hurry just solve for two or three of the variables. 0 [ a b 0 [ [ a 12 2a a a b y 27 c a + b b c c 27.
8 8 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 0 [ d d + 12 d 6. 0 [ w z w 27 2w w 27/2 0 [ x x 54 2x x 27. (watch out: next pitch is a curveball!) 1 [ y 27 c y 82 6y y y [ w z 2z z + 41 z Finally, here s the puzzle with the blanks all filled in: / /2 41/
9 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 9 Problem 9 (i) Find the general solution of the autonomous differential equation y (1 + y)(5 y). (ii) Also find the solution which satisfies the initial condition y(0) 7. (iii) Find the equilibrium solutions. (iv) Determine the stability of each equilibrium solution. (v) Sketch the direction field for the differential equation well enough to justify your determination of stability. First find the general solution. Start by separating variables (1 + y)(5 y) dt Partial fractions: 1 (1 + y)(5 y) A y B y 5 Multiply on both sides by (y + 1)(y 5) to get 1 A(y 5) + B(y + 1) Plug in y 1 to get A 1/6. Plug in y 5 to get B 1/6. We can rewrite the separated differential equation as 1 6 y y 5 dt Clear denominators: y + 1 y 5 6 dt Integrate on both sides and use the old math professor s trick: log(y + 1) log(y 5) 6t + ln C y + 1 ( ) y 5 Ce6t Solve for y: y + 1 yce 6t 5Ce 6t y(1 Ce 6t ) 5Ce 6t 1 y 5Ce6t + 1 Ce 6t 1 Next we solve the indicated initial value problem. Plug t 0 in earlier line marked with ( ) to get C. Thus y 20e6t + 1 4e 6t 1 is the solution satisfying y(0) 7. Equilibrium solutions are y 1 and y 5. (The numbers 1 and 5 are just the roots of (1 + y)(y 5) 0.) Looking at the dfield plot, we can see that y 5 is stable and y 1 is unstable. Using dfield here was overkill. Any legible sketch of the direction field which establishes where the slopes are positive and where the slopes are negative is good enough.
10 10 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 10 Figure 1. Direction field y (1 + y) (5 y) y t Problem 10 Find the least squares line y k + mx for the following data points. (1, 4), (3, 8), (4, 9), (6, 12). Do so by first expressing the two equations for the unknowns k and m in matrix form. You can do the numerical work with your calculator.. The inconsistent system of equations we wish that we could solve exactly (but cannot) is the following: [ k m In order to do the best we can by the method of least squares, we use the trick to left-multiply both sides by the transpose. [ [ k m [ After multiplying out using MATLAB or hand calculator, we get [ [ [ 4 14 k m
11 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 11 Finally, [ k m Thus the least squares line is [ [ [ y x. Here is a plot of the data points and the least squares line that fits these data points:. Figure 2. Least squares line and data points 15 y x y x (We just included this figure as an illustration. It is not an official part of the answer to this line-fitting problem.) Problem 11 The rate at which the amount of a radioactive substance changes is proportional to the amount present. At a certain time, a sample of a certain radioactive substance contains 40 mg. The same sample only contains 25 mg of the substance 50 years later. (i) How much of the substance will remain after 120 years? (ii) What is the half-life of the substance? Start with the differential equation.
12 12 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY Let y denote the amount of the substance in milligrams and let t denote the time in years measured from the time observations of the substance began. We are given that ky, y(0) 40, y(50) 25. dt Here k is a negative constant we need to determine. The general solution of the differential equation is y Ce kt. We have C 40 because y(0) 40. We have 40e 50k 25 because y(50) 25. Thus e 50k 25/40 5/8 and hence y 40(5/8) t/50. Some students may prefer to solve for k, so we present that route as well. From, say, the equation e 50k 5/8 above we get and hence k ln(5/8) y 40e t, which is an equivalent expression for the amount of substance at time t. We then have y(120) 40(5/8) 120/50 40 exp( ( )(120)) mg. which answers part (i) in several different formats any of one of which is acceptable but with the last being preferred since easiest to read. To answer part (ii) of the question we have to calculate the half-life T of the substance. This is determined by either of the following two equations: Solving the former we have Solving the latter we get 40(5/8) T/50 20 and 40e T 20 T 50 ln(1/2) ln(5/8) ln(1/2) years T ln( 1 2 ) years, which (no surprise) is the same answer. I solved this problem in two ways but in practice of course you only have to pick one way of solving and then stick with it. Problem 12 Initially an 800 gallon tank contains 400 gallons of water in which is dissolved 50 lbs of salt. Brine containing 4 lbs of salt per gallon enters the tank at the rate of 5 gallons per minute. The well mixed brine leaves the tank at the slower rate of 3 gallons per minute. (i) Find an expression for the number of pounds of salt in the tank at time t, until the tank overflows. (ii) How much salt is in the tank at the moment the tank overflows?
13 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 13 Let y y(t) be the amount (lbs) of salt in the tank at time t (min). We have to solve the initial value problem y(0) 50 and dt 4 lbs gal 5 gal y lbs min (5 3)t gal 3 gal. min }{{}}{{} rate in rate out After simplifying algebraically we get 3y t 20. y(0) 50 and dt + We now use the integrating factor method to finish up. ( ) ( ) 3 dt 3 dt exp exp exp t t ( 3 log(t + 200) 2 d dt (t + 200)3/2 y 20(t + 200) 3/2 (t + 200) 3/2 y 8(t + 200) 5/2 + C ) (t + 200) 3/ / /2 + C C 200 3/ /2 4, 384, 062. y 8(t + 200) 4, 384, 062/(t + 200) 3/2. The tank overflows when t 800 and hence t minutes. Plugging in t 200 we get y(200) 8( ) 4, 384, 062/( ) 3/ pounds of salt in the tank at the moment of overflow. Note: On an exam, to answer part (i) of the question, it would be okay to write, say, y 8(t + 200) + C/(t + 200) 3/2, where C 200 3/ /2, without simplifying C further. Problem 13 A steel ball with an initial temperature of 60 o F is placed in an oven which is maintained at 420 o F. After 4 minutes the temperature of the ball is 180 o F. (i) Find an expression for the temperature of the ball at time t. (ii) Find the surface temperature of the ball after 12 minutes. (iii) Find the time at which the ball will have a temperature of 350 o F. Start with the differential equation. Let y y(t) be the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit of the ball at time t in minutes after being placed in the oven. We know that k(420 y) dt by Newton s law of heating, where k > 0 is a constant we have to determine using the information given in the problem. We are also given that y(0) 60 and y(4) 180.
14 14 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY We solve using the integrating factor method. We start by rewriting the differential equation as + ky 420k. dt The integrating factor is exp( k dt) e kt. We then have d dt ekt y 420ke kt e kt y 420e kt + C y Ce kt. To get the constant C we use the initial value information: Thus we have y(0) C C 360. y e kt. To answer part (i) of the question, we are going to replace e kt by an expression in which the only variable is t. One way to do that is to solve for k and another way is to use algebra to get such an expression. We will show both ways, and we will show below how to pursue both ways to answer parts (ii) and (iii) of the question as well. We have It follows that 180 y(4) e 4k e 4k e kt y ( ) t/4 2, 3 ( ) t/ which answers part (i) of the question. We can also solve the equation e 4k 2 3 for k, obtaining k 1 ( ) 2 4 ln Then we get another (equivalent) answer for part (i), namely We then have y(12) y e t. ( ) 12/ exp( ) which answers part (ii) of the question both ways. Finally, to find the time T asked for in part (iii) we have to solve the equation ( ) T/4 2 y(t ) exp( T ) This can be rewritten ( ) T/4 2 exp( T ). 3 Solving by the usual precalculus methods, we get T 4 ln(7/36) ln(2/3) ln(7/36) minutes, which answers part (iii) of the question (in both ways).
15 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 15 Remark. Just so there is no misunderstanding: I solved the problem two different ways. When you are solving problems like this you only have to pick one of the ways and then stick with it. Find the determinant Problem by hand. Use whatever combination of methods seems the easiest. Explain each step of your calculation by a word or phrase (use the row operation R4 R 4 + 2R 1 ) (expand along third column) (expand along first column) (This is not the only possible solution.) Problem 15 Find the inverse of the following matrix You must show all work. You must use the textbook notation for row operations to explain each step. Check at least three times that you wrote out the correct starting matrix for your calculation.
16 16 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY We use the side-by-side method , R 2 R 2 + 2R 1, R 3 R 3 2R , hence:, R 3 R 3, R 2 R 2 + R 3, R 1 R 1 R 3, R 1 R 1 R Solve the system of equations Problem 16 5x 4 x 3 7, 4x 3 2x 2 + x 4 9, 2x 2 + x 4 x 3 17, x 1 + x 2 + x 3 + x 4 14 for x 3 using Cramer s Rule. You are expected first to rewrite the system of equations neatly, and then to express x 3 as a ratio of 4-by-4 determinants. You do not have to evaluate any determinants. The emphasis is on demonstrating that you know the pattern of Cramer s Rule. Note that the equations were written sloppily. You have to begin by rewriting the equations neatly, with each variable placed in its own column. x 3 +5x 4 7 2x 2 +4x 3 +x x 2 x 3 +x x 1 +x 2 +x 3 +x 4 14 Having written things out neatly, I can read off the required ratio of determinants easily: / x
17 REVIEW FOR MT1: ANSWER KEY 17 Problem 17 Find the inverse of the following matrix: [ Express all the entries of the inverse matrix as fractions, not as decimals. Solve this problem entirely by hand. Show all your work. [ [ [ 5/3 1/3 17/3 4/3.
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, SPRING 2019 UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, SPRING 209 UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be a complete review. For a complete review make sure that you know how
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, SPRING 209 UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be a complete review. For a complete review make sure that you know how
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, SPRING 2015 ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, SPRING 2015 ANSWER KEY Problem 1 Standing in line at the supermarket I see Alice, Bob and Carol ahead of me in the express check-out lane. Alice buys 2 bags of
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I MATH 2373, SPRING 2015 ANSWER KEY Problem 1 Standing in line at the supermarket I see Alice, Bob and Carol ahead of me in the express check-out lane. Alice buys 2 bags of
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1
 Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Math 2214 Solution Test 1D Spring 2015
 Math 2214 Solution Test 1D Spring 2015 Problem 1: A 600 gallon open top tank initially holds 300 gallons of fresh water. At t = 0, a brine solution containing 3 lbs of salt per gallon is poured into the
Math 2214 Solution Test 1D Spring 2015 Problem 1: A 600 gallon open top tank initially holds 300 gallons of fresh water. At t = 0, a brine solution containing 3 lbs of salt per gallon is poured into the
Math 392 Exam 1 Solutions Fall (10 pts) Find the general solution to the differential equation dy dt = 1
 Math 392 Exam 1 Solutions Fall 20104 1. (10 pts) Find the general solution to the differential equation = 1 y 2 t + 4ty = 1 t(y 2 + 4y). Hence (y 2 + 4y) = t y3 3 + 2y2 = ln t + c. 2. (8 pts) Perform Euler
Math 392 Exam 1 Solutions Fall 20104 1. (10 pts) Find the general solution to the differential equation = 1 y 2 t + 4ty = 1 t(y 2 + 4y). Hence (y 2 + 4y) = t y3 3 + 2y2 = ln t + c. 2. (8 pts) Perform Euler
Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018
 Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018 WHEN: Wednesday, September 26, in class (no notes, books, calculators I will supply a table of integrals) EXTRA OFFICE HOURS: Sunday, September 23 from 8:00 PM
Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018 WHEN: Wednesday, September 26, in class (no notes, books, calculators I will supply a table of integrals) EXTRA OFFICE HOURS: Sunday, September 23 from 8:00 PM
Math 314H EXAM I. 1. (28 points) The row reduced echelon form of the augmented matrix for the system. is the matrix
 Math 34H EXAM I Do all of the problems below. Point values for each of the problems are adjacent to the problem number. Calculators may be used to check your answer but not to arrive at your answer. That
Math 34H EXAM I Do all of the problems below. Point values for each of the problems are adjacent to the problem number. Calculators may be used to check your answer but not to arrive at your answer. That
Name: October 24, 2014 ID Number: Fall Midterm I. Number Total Points Points Obtained Total 40
 Math 307O: Introduction to Differential Equations Name: October 24, 204 ID Number: Fall 204 Midterm I Number Total Points Points Obtained 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 Total 40 Instructions.. Show all your work and box
Math 307O: Introduction to Differential Equations Name: October 24, 204 ID Number: Fall 204 Midterm I Number Total Points Points Obtained 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 Total 40 Instructions.. Show all your work and box
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
A 2. =... = c c N. 's arise from the three types of elementary row operations. If rref A = I its determinant is 1, and A = c 1
 Theorem: Let A n n Then A 1 exists if and only if det A 0 proof: We already know that A 1 exists if and only if the reduced row echelon form of A is the identity matrix Now, consider reducing A to its
Theorem: Let A n n Then A 1 exists if and only if det A 0 proof: We already know that A 1 exists if and only if the reduced row echelon form of A is the identity matrix Now, consider reducing A to its
1 Linear systems, existence, uniqueness
 Jor-el Briones / Math 2F, 25 Summer Session, Practice Midterm Page of 9 Linear systems, existence, uniqueness For each part, construct an augmented matrix for a linear system with the given properties,
Jor-el Briones / Math 2F, 25 Summer Session, Practice Midterm Page of 9 Linear systems, existence, uniqueness For each part, construct an augmented matrix for a linear system with the given properties,
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
MA 242 LINEAR ALGEBRA C1, Solutions to First Midterm Exam
 MA 242 LINEAR ALGEBRA C Solutions to First Midterm Exam Prof Nikola Popovic October 2 9:am - :am Problem ( points) Determine h and k such that the solution set of x + = k 4x + h = 8 (a) is empty (b) contains
MA 242 LINEAR ALGEBRA C Solutions to First Midterm Exam Prof Nikola Popovic October 2 9:am - :am Problem ( points) Determine h and k such that the solution set of x + = k 4x + h = 8 (a) is empty (b) contains
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework 7
 MATH22 Linear Algebra B Homework 7 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra and its Applications Pearson, 26 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
MATH22 Linear Algebra B Homework 7 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra and its Applications Pearson, 26 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
Chapter 2 Notes, Kohler & Johnson 2e
 Contents 2 First Order Differential Equations 2 2.1 First Order Equations - Existence and Uniqueness Theorems......... 2 2.2 Linear First Order Differential Equations.................... 5 2.2.1 First
Contents 2 First Order Differential Equations 2 2.1 First Order Equations - Existence and Uniqueness Theorems......... 2 2.2 Linear First Order Differential Equations.................... 5 2.2.1 First
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17
 Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17 July 8, 2017 Section 2.3 Problem 4. A tank with capacity of 500 gallons originally contains 200 gallons of water with 100 pounds of salt in solution. Water containing
Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17 July 8, 2017 Section 2.3 Problem 4. A tank with capacity of 500 gallons originally contains 200 gallons of water with 100 pounds of salt in solution. Water containing
Review for Exam Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions.
 Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
APPM 2360: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 2017
 APPM 36: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 17 On the front of your Bluebook write: (1) your name, () your instructor s name, (3) your recitation section number and () a grading table. Text books, class notes,
APPM 36: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 17 On the front of your Bluebook write: (1) your name, () your instructor s name, (3) your recitation section number and () a grading table. Text books, class notes,
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
4. Some Applications of first order linear differential
 September 9, 2012 4-1 4. Some Applications of first order linear differential Equations The modeling problem There are several steps required for modeling scientific phenomena 1. Data collection (experimentation)
September 9, 2012 4-1 4. Some Applications of first order linear differential Equations The modeling problem There are several steps required for modeling scientific phenomena 1. Data collection (experimentation)
REVIEW FOR MT3 ANSWER KEY MATH 2373, SPRING 2015
 REVIEW FOR MT3 ANSWER KEY MATH 373 SPRING 15 PROF. YOICHIRO MORI This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutel complete review. For completeness ou must also make sure that ou know how to
REVIEW FOR MT3 ANSWER KEY MATH 373 SPRING 15 PROF. YOICHIRO MORI This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutel complete review. For completeness ou must also make sure that ou know how to
Practice Midterm 1 Solutions Written by Victoria Kala July 10, 2017
 Practice Midterm 1 Solutions Written by Victoria Kala July 10, 2017 1. Use the slope field plotter link in Gauchospace to check your solution. 2. (a) Not linear because of the y 2 sin x term (b) Not linear
Practice Midterm 1 Solutions Written by Victoria Kala July 10, 2017 1. Use the slope field plotter link in Gauchospace to check your solution. 2. (a) Not linear because of the y 2 sin x term (b) Not linear
Math Applied Differential Equations
 Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Existence and Uniqueness The following theorem gives sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of a solution to the IVP for first order nonlinear
Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Existence and Uniqueness The following theorem gives sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of a solution to the IVP for first order nonlinear
Chapters 8.1 & 8.2 Practice Problems
 EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapters 8.1 & 8. Practice Problems Be able to verify that a given function is a solution to a differential equation. Given a description in words of how some quantity changes in time
EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapters 8.1 & 8. Practice Problems Be able to verify that a given function is a solution to a differential equation. Given a description in words of how some quantity changes in time
Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation
 Goals: Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation Solutions of linear system. Vectors, vector equation. Matrix equation. Math 112, Week 2 Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 1.3, 1.4, 1.5
Goals: Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation Solutions of linear system. Vectors, vector equation. Matrix equation. Math 112, Week 2 Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 1.3, 1.4, 1.5
Sample Questions, Exam 1 Math 244 Spring 2007
 Sample Questions, Exam Math 244 Spring 2007 Remember, on the exam you may use a calculator, but NOT one that can perform symbolic manipulation (remembering derivative and integral formulas are a part of
Sample Questions, Exam Math 244 Spring 2007 Remember, on the exam you may use a calculator, but NOT one that can perform symbolic manipulation (remembering derivative and integral formulas are a part of
MATH240: Linear Algebra Review for exam #1 6/10/2015 Page 1
 MATH24: Linear Algebra Review for exam # 6//25 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an exam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well
MATH24: Linear Algebra Review for exam # 6//25 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an exam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well
MA 262, Spring 2018, Midterm 1 Version 01 (Green)
 MA 262, Spring 2018, Midterm 1 Version 01 (Green) INSTRUCTIONS 1. Switch off your phone upon entering the exam room. 2. Do not open the exam booklet until you are instructed to do so. 3. Before you open
MA 262, Spring 2018, Midterm 1 Version 01 (Green) INSTRUCTIONS 1. Switch off your phone upon entering the exam room. 2. Do not open the exam booklet until you are instructed to do so. 3. Before you open
Solutions to Math 53 First Exam April 20, 2010
 Solutions to Math 53 First Exam April 0, 00. (5 points) Match the direction fields below with their differential equations. Also indicate which two equations do not have matches. No justification is necessary.
Solutions to Math 53 First Exam April 0, 00. (5 points) Match the direction fields below with their differential equations. Also indicate which two equations do not have matches. No justification is necessary.
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY. MATH 2610 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practice for test 1 solutions
 VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2610 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practice for test 1 solutions The first test will cover all material discussed up to (including) section 4.5. Important: The solutions below
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2610 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practice for test 1 solutions The first test will cover all material discussed up to (including) section 4.5. Important: The solutions below
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 2 Solutions
 MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2 Homework Assignment 2 Solutions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 60, Problem 2 Solution: Let M(t) be the mass (in grams) of salt in the tank after t minutes The initial-value
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2 Homework Assignment 2 Solutions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 60, Problem 2 Solution: Let M(t) be the mass (in grams) of salt in the tank after t minutes The initial-value
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices
 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices What is a Matrix? A matrix is a compact grid or array of numbers. It can be created from a system of equations and used to solve the system of equations.
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices What is a Matrix? A matrix is a compact grid or array of numbers. It can be created from a system of equations and used to solve the system of equations.
Math 20D Final Exam 8 December has eigenvalues 3, 3, 0 and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. ( 2) det
 Math D Final Exam 8 December 9. ( points) Show that the matrix 4 has eigenvalues 3, 3, and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. 4 λ det λ λ λ = (4 λ) det λ ( ) det + det λ = (4 λ)(( λ) 4) + ( λ + )
Math D Final Exam 8 December 9. ( points) Show that the matrix 4 has eigenvalues 3, 3, and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. 4 λ det λ λ λ = (4 λ) det λ ( ) det + det λ = (4 λ)(( λ) 4) + ( λ + )
Honors Advanced Mathematics Determinants page 1
 Determinants page 1 Determinants For every square matrix A, there is a number called the determinant of the matrix, denoted as det(a) or A. Sometimes the bars are written just around the numbers of the
Determinants page 1 Determinants For every square matrix A, there is a number called the determinant of the matrix, denoted as det(a) or A. Sometimes the bars are written just around the numbers of the
Do not write in this space. Problem Possible Score Number Points Total 48
 MTH 337. Name MTH 337. Differential Equations Exam II March 15, 2019 T. Judson Do not write in this space. Problem Possible Score Number Points 1 8 2 10 3 15 4 15 Total 48 Directions Please Read Carefully!
MTH 337. Name MTH 337. Differential Equations Exam II March 15, 2019 T. Judson Do not write in this space. Problem Possible Score Number Points 1 8 2 10 3 15 4 15 Total 48 Directions Please Read Carefully!
Name: Solutions Final Exam
 Instructions. Answer each of the questions on your own paper. Put your name on each page of your paper. Be sure to show your work so that partial credit can be adequately assessed. Credit will not be given
Instructions. Answer each of the questions on your own paper. Put your name on each page of your paper. Be sure to show your work so that partial credit can be adequately assessed. Credit will not be given
If you need more room, use the backs of the pages and indicate that you have done so.
 Math 125 Final Exam Winter 2018 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name Turn off and stow away all cell phones, watches, pagers, music players, and other similar devices.
Math 125 Final Exam Winter 2018 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name Turn off and stow away all cell phones, watches, pagers, music players, and other similar devices.
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
1. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal
 . Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
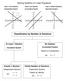 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
MATH 310, REVIEW SHEET 2
 MATH 310, REVIEW SHEET 2 These notes are a very short summary of the key topics in the book (and follow the book pretty closely). You should be familiar with everything on here, but it s not comprehensive,
MATH 310, REVIEW SHEET 2 These notes are a very short summary of the key topics in the book (and follow the book pretty closely). You should be familiar with everything on here, but it s not comprehensive,
California State University Northridge MATH 280: Applied Differential Equations Midterm Exam 1
 California State University Northridge MATH 280: Applied Differential Equations Midterm Exam 1 October 9, 2013. Duration: 75 Minutes. Instructor: Jing Li Student Name: Student number: Take your time to
California State University Northridge MATH 280: Applied Differential Equations Midterm Exam 1 October 9, 2013. Duration: 75 Minutes. Instructor: Jing Li Student Name: Student number: Take your time to
Homework 1.1 and 1.2 WITH SOLUTIONS
 Math 220 Linear Algebra (Spring 2018) Homework 1.1 and 1.2 WITH SOLUTIONS Due Thursday January 25 These will be graded in detail and will count as two (TA graded) homeworks. Be sure to start each of these
Math 220 Linear Algebra (Spring 2018) Homework 1.1 and 1.2 WITH SOLUTIONS Due Thursday January 25 These will be graded in detail and will count as two (TA graded) homeworks. Be sure to start each of these
Problem Set. Assignment #1. Math 3350, Spring Feb. 6, 2004 ANSWERS
 Problem Set Assignment #1 Math 3350, Spring 2004 Feb. 6, 2004 ANSWERS i Problem 1. [Section 1.4, Problem 4] A rocket is shot straight up. During the initial stages of flight is has acceleration 7t m /s
Problem Set Assignment #1 Math 3350, Spring 2004 Feb. 6, 2004 ANSWERS i Problem 1. [Section 1.4, Problem 4] A rocket is shot straight up. During the initial stages of flight is has acceleration 7t m /s
University of Ottawa
 University of Ottawa Department of Mathematics and Statistics MAT 1302B : Mathematical Methods II Professor: Hadi Salmasian First Midterm Exam Version A February 3, 2017 Surname First Name Student # DGD
University of Ottawa Department of Mathematics and Statistics MAT 1302B : Mathematical Methods II Professor: Hadi Salmasian First Midterm Exam Version A February 3, 2017 Surname First Name Student # DGD
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework Week 3. Be prepared to answer the following oral questions if asked in the supervision class
 MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework Week Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D. C. Lay Linear Algebra its Applications. Pearson, 2006. ISBN 0-521-2871-4. Normally, homework
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework Week Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D. C. Lay Linear Algebra its Applications. Pearson, 2006. ISBN 0-521-2871-4. Normally, homework
(a) x cos 3x dx We apply integration by parts. Take u = x, so that dv = cos 3x dx, v = 1 sin 3x, du = dx. Thus
 Math 128 Midterm Examination 2 October 21, 28 Name 6 problems, 112 (oops) points. Instructions: Show all work partial credit will be given, and Answers without work are worth credit without points. You
Math 128 Midterm Examination 2 October 21, 28 Name 6 problems, 112 (oops) points. Instructions: Show all work partial credit will be given, and Answers without work are worth credit without points. You
( ) ( ). ( ) " d#. ( ) " cos (%) " d%
 Math 22 Fall 2008 Solutions to Homework #6 Problems from Pages 404-407 (Section 76) 6 We will use the technique of Separation of Variables to solve the differential equation: dy d" = ey # sin 2 (") y #
Math 22 Fall 2008 Solutions to Homework #6 Problems from Pages 404-407 (Section 76) 6 We will use the technique of Separation of Variables to solve the differential equation: dy d" = ey # sin 2 (") y #
MATH 307 Introduction to Differential Equations Autumn 2017 Midterm Exam Monday November
 MATH 307 Introduction to Differential Equations Autumn 2017 Midterm Exam Monday November 6 2017 Name: Student ID Number: I understand it is against the rules to cheat or engage in other academic misconduct
MATH 307 Introduction to Differential Equations Autumn 2017 Midterm Exam Monday November 6 2017 Name: Student ID Number: I understand it is against the rules to cheat or engage in other academic misconduct
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Old Math 330 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
MATH 1207 R02 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SOLUTION
 MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
MATH 152 Exam 1-Solutions 135 pts. Write your answers on separate paper. You do not need to copy the questions. Show your work!!!
 MATH Exam -Solutions pts Write your answers on separate paper. You do not need to copy the questions. Show your work!!!. ( pts) Find the reduced row echelon form of the matrix Solution : 4 4 6 4 4 R R
MATH Exam -Solutions pts Write your answers on separate paper. You do not need to copy the questions. Show your work!!!. ( pts) Find the reduced row echelon form of the matrix Solution : 4 4 6 4 4 R R
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework 6. Be prepared to answer the following oral questions if asked in the supervision class:
 MATH0 Linear Algebra B Homework 6 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra its Applications Pearson, 006 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
MATH0 Linear Algebra B Homework 6 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra its Applications Pearson, 006 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
MATH 1553, C.J. JANKOWSKI MIDTERM 1
 MATH 155, C.J. JANKOWSKI MIDTERM 1 Name Section Please read all instructions carefully before beginning. You have 5 minutes to complete this exam. There are no aids of any kind (calculators, notes, text,
MATH 155, C.J. JANKOWSKI MIDTERM 1 Name Section Please read all instructions carefully before beginning. You have 5 minutes to complete this exam. There are no aids of any kind (calculators, notes, text,
7.1 Solving Systems of Equations
 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations. Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve:
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
MATH 3330 INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST 3 SPRING Test 3 will be in PKH 113 in class time, Tues April 21
 MATH INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST SPRING Test will be in PKH in class time, Tues April See above for date, time and location of Test It will last 7 minutes and is worth % of your course grade The material
MATH INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST SPRING Test will be in PKH in class time, Tues April See above for date, time and location of Test It will last 7 minutes and is worth % of your course grade The material
APPM 2360 Exam 2 Solutions Wednesday, March 9, 2016, 7:00pm 8:30pm
 APPM 2360 Exam 2 Solutions Wednesday, March 9, 206, 7:00pm 8:30pm ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: () your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) recitation section (4) your instructor s name, and (5)
APPM 2360 Exam 2 Solutions Wednesday, March 9, 206, 7:00pm 8:30pm ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: () your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) recitation section (4) your instructor s name, and (5)
Math Applied Differential Equations
 Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Basic Definitions and Concepts A differential equation is an equation that involves one or more of the derivatives (first derivative, second derivative,
Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Basic Definitions and Concepts A differential equation is an equation that involves one or more of the derivatives (first derivative, second derivative,
Math 308 Midterm Answers and Comments July 18, Part A. Short answer questions
 Math 308 Midterm Answers and Comments July 18, 2011 Part A. Short answer questions (1) Compute the determinant of the matrix a 3 3 1 1 2. 1 a 3 The determinant is 2a 2 12. Comments: Everyone seemed to
Math 308 Midterm Answers and Comments July 18, 2011 Part A. Short answer questions (1) Compute the determinant of the matrix a 3 3 1 1 2. 1 a 3 The determinant is 2a 2 12. Comments: Everyone seemed to
weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Exponentials and Natural Logarithms
 http://kumarmaths. weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Exponentials and Natural Logarithms Core Maths 3 Exponentials and natural Logarithms Page 1 Ln and Exponentials C3 Content By the end of this unit you
http://kumarmaths. weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Exponentials and Natural Logarithms Core Maths 3 Exponentials and natural Logarithms Page 1 Ln and Exponentials C3 Content By the end of this unit you
dy x a. Sketch the slope field for the points: (1,±1), (2,±1), ( 1, ±1), and (0,±1).
 Chapter 6. d x Given the differential equation: dx a. Sketch the slope field for the points: (,±), (,±), (, ±), and (0,±). b. Find the general solution for the given differential equation. c. Find the
Chapter 6. d x Given the differential equation: dx a. Sketch the slope field for the points: (,±), (,±), (, ±), and (0,±). b. Find the general solution for the given differential equation. c. Find the
Math 118, Fall 2014 Final Exam
 Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
Modeling with First Order ODEs (cont). Existence and Uniqueness of Solutions to First Order Linear IVP. Second Order ODEs
 Modeling with First Order ODEs (cont). Existence and Uniqueness of Solutions to First Order Linear IVP. Second Order ODEs September 18 22, 2017 Mixing Problem Yuliya Gorb Example: A tank with a capacity
Modeling with First Order ODEs (cont). Existence and Uniqueness of Solutions to First Order Linear IVP. Second Order ODEs September 18 22, 2017 Mixing Problem Yuliya Gorb Example: A tank with a capacity
Reduction to the associated homogeneous system via a particular solution
 June PURDUE UNIVERSITY Study Guide for the Credit Exam in (MA 5) Linear Algebra This study guide describes briefly the course materials to be covered in MA 5. In order to be qualified for the credit, one
June PURDUE UNIVERSITY Study Guide for the Credit Exam in (MA 5) Linear Algebra This study guide describes briefly the course materials to be covered in MA 5. In order to be qualified for the credit, one
MATH 54 - WORKSHEET 1 MONDAY 6/22
 MATH 54 - WORKSHEET 1 MONDAY 6/22 Row Operations: (1 (Replacement Add a multiple of one row to another row. (2 (Interchange Swap two rows. (3 (Scaling Multiply an entire row by a nonzero constant. A matrix
MATH 54 - WORKSHEET 1 MONDAY 6/22 Row Operations: (1 (Replacement Add a multiple of one row to another row. (2 (Interchange Swap two rows. (3 (Scaling Multiply an entire row by a nonzero constant. A matrix
Name Class. 5. Find the particular solution to given the general solution y C cos x and the. x 2 y
 10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
MAT 275 Test 1 SOLUTIONS, FORM A
 MAT 75 Test SOLUTIONS, FORM A The differential equation xy e x y + y 3 = x 7 is D neither linear nor homogeneous Solution: Linearity is ruinied by the y 3 term; homogeneity is ruined by the x 7 on the
MAT 75 Test SOLUTIONS, FORM A The differential equation xy e x y + y 3 = x 7 is D neither linear nor homogeneous Solution: Linearity is ruinied by the y 3 term; homogeneity is ruined by the x 7 on the
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Homework 1 Due: Wednesday, August 27. x + y + z = 1. x y = 3 x + y + z = c 2 2x + cz = 4
 Homework 1 Due: Wednesday, August 27 1. Find all values of c for which the linear system: (a) has no solutions. (b) has exactly one solution. (c) has infinitely many solutions. (d) is consistent. x + y
Homework 1 Due: Wednesday, August 27 1. Find all values of c for which the linear system: (a) has no solutions. (b) has exactly one solution. (c) has infinitely many solutions. (d) is consistent. x + y
Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay 2.5
 Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay 2.5 October, 20 You have seen that if we know the inverse A of a matrix A, we can easily solve the equation Ax = b. Solving a large number of equations Ax = b, Ax 2 =
Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay 2.5 October, 20 You have seen that if we know the inverse A of a matrix A, we can easily solve the equation Ax = b. Solving a large number of equations Ax = b, Ax 2 =
MATH 101: PRACTICE MIDTERM 2
 MATH : PRACTICE MIDTERM INSTRUCTOR: PROF. DRAGOS GHIOCA March 7, Duration of examination: 7 minutes This examination includes pages and 6 questions. You are responsible for ensuring that your copy of the
MATH : PRACTICE MIDTERM INSTRUCTOR: PROF. DRAGOS GHIOCA March 7, Duration of examination: 7 minutes This examination includes pages and 6 questions. You are responsible for ensuring that your copy of the
MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Differential Equations 7. An Introduction to Differential Equations Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions: What
Chapter 7 Differential Equations 7. An Introduction to Differential Equations Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions: What
LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
3.2 Systems of Two First Order Linear DE s
 Agenda Section 3.2 Reminders Lab 1 write-up due 9/26 or 9/28 Lab 2 prelab due 9/26 or 9/28 WebHW due 9/29 Office hours Tues, Thurs 1-2 pm (5852 East Hall) MathLab office hour Sun 7-8 pm (MathLab) 3.2 Systems
Agenda Section 3.2 Reminders Lab 1 write-up due 9/26 or 9/28 Lab 2 prelab due 9/26 or 9/28 WebHW due 9/29 Office hours Tues, Thurs 1-2 pm (5852 East Hall) MathLab office hour Sun 7-8 pm (MathLab) 3.2 Systems
Topic 14 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 Row reduction and subspaces 4. Goals. Be able to put a matrix into row reduced echelon form (RREF) using elementary row operations.. Know the definitions of null and column
Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 Row reduction and subspaces 4. Goals. Be able to put a matrix into row reduced echelon form (RREF) using elementary row operations.. Know the definitions of null and column
MATH 1553, SPRING 2018 SAMPLE MIDTERM 1: THROUGH SECTION 1.5
 MATH 553, SPRING 28 SAMPLE MIDTERM : THROUGH SECTION 5 Name Section Please read all instructions carefully before beginning You have 5 minutes to complete this exam There are no aids of any kind (calculators,
MATH 553, SPRING 28 SAMPLE MIDTERM : THROUGH SECTION 5 Name Section Please read all instructions carefully before beginning You have 5 minutes to complete this exam There are no aids of any kind (calculators,
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM II MATH 2373, FALL 2016 ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM II MATH 7, FALL 6 ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutely complete review. For completeness you must also make sure that you know how to do all
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM II MATH 7, FALL 6 ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutely complete review. For completeness you must also make sure that you know how to do all
2t t dt.. So the distance is (t2 +6) 3/2
 Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm
 Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm All course information is available on Moodle. Text: Nicholson, Linear algebra with applications, 7th edition. We shall cover Chapters 1,2,3,4,5:
Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm All course information is available on Moodle. Text: Nicholson, Linear algebra with applications, 7th edition. We shall cover Chapters 1,2,3,4,5:
Math 314 Lecture Notes Section 006 Fall 2006
 Math 314 Lecture Notes Section 006 Fall 2006 CHAPTER 1 Linear Systems of Equations First Day: (1) Welcome (2) Pass out information sheets (3) Take roll (4) Open up home page and have students do same
Math 314 Lecture Notes Section 006 Fall 2006 CHAPTER 1 Linear Systems of Equations First Day: (1) Welcome (2) Pass out information sheets (3) Take roll (4) Open up home page and have students do same
Spring 2015 Midterm 1 03/04/15 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman
 Math 0 Spring 05 Midterm 03/04/5 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print): Teaching Assistant This exam contains pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if
Math 0 Spring 05 Midterm 03/04/5 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print): Teaching Assistant This exam contains pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay
 October 15, 2010 Population growth Population growth If y = f (t) is the number of individuals in a population of animals or humans at time t, then it seems reasonable to expect that the rate of growth
October 15, 2010 Population growth Population growth If y = f (t) is the number of individuals in a population of animals or humans at time t, then it seems reasonable to expect that the rate of growth
APPM 2360: Final Exam 10:30am 1:00pm, May 6, 2015.
 APPM 23: Final Exam :3am :pm, May, 25. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: ) your name, 2) your student ID number, 3) lecture section, 4) your instructor s name, and 5) a grading table for eight questions.
APPM 23: Final Exam :3am :pm, May, 25. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: ) your name, 2) your student ID number, 3) lecture section, 4) your instructor s name, and 5) a grading table for eight questions.
Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations In the sciences and engineering, mathematical models are developed to aid in the understanding of physical phenomena. These models often yield an equation that
Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations In the sciences and engineering, mathematical models are developed to aid in the understanding of physical phenomena. These models often yield an equation that
It is convenient to think that solutions of differential equations consist of a family of functions (just like indefinite integrals ).
 Section 1.1 Direction Fields Key Terms/Ideas: Mathematical model Geometric behavior of solutions without solving the model using calculus Graphical description using direction fields Equilibrium solution
Section 1.1 Direction Fields Key Terms/Ideas: Mathematical model Geometric behavior of solutions without solving the model using calculus Graphical description using direction fields Equilibrium solution
Math 216 First Midterm 18 October, 2018
 Math 16 First Midterm 18 October, 018 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 16 First Midterm 18 October, 018 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
MATH 251 Examination I October 10, 2013 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 10, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 10, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Modeling with Differential Equations
 Modeling with Differential Equations 1. Exponential Growth and Decay models. Definition. A quantity y(t) is said to have an exponential growth model if it increases at a rate proportional to the amount
Modeling with Differential Equations 1. Exponential Growth and Decay models. Definition. A quantity y(t) is said to have an exponential growth model if it increases at a rate proportional to the amount
Math 1070 Exam 2. March 16, 2006
 Math 1070 Exam 2 Name: March 16, 2006 1. Solve each of the following systems of equations using the indicated method: (a) Solve by graphing (include a sketch of your graph, indicating the graphing window,
Math 1070 Exam 2 Name: March 16, 2006 1. Solve each of the following systems of equations using the indicated method: (a) Solve by graphing (include a sketch of your graph, indicating the graphing window,
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
Midterm 1 Review. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015
 Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
