7.1 Solving Systems of Equations
|
|
|
- Moses Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities. Solution of a System of Linear Equations: the ordered pair xy, where the lines intersect A solution can be substituted into both equations to make true statements Special Cases: If the graphs of the equations in a system are parallel (do not intersect), then the system has NO SOLUTION. Systems with no solution are called inconsistent. Systems with solutions are called consistent. If the graphs of the equations in a system are the same line (coincident), then the system has INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS. Systems with infinite solutions are called dependent. Note: If the graphs are not coincident and intersect, then the system has EXACTLY ONE SOLUTION. Consistent solution(s) Inconsistent Ø Dependent ( ) Independent (1 or Ø) Systems of equations that are dependent graph lines that are coincident. Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Ex 1: Graph and determine the point of intersection. 3 x y 4 xy 6 Graph both lines on the same coordinate plane. The lines intersect at. Page 1 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
2 Solving a System by Graphing (not linear) Ex : Graph and find the solution of the system. Graph both functions on the same coordinate plane. 3xy 6 y ln x1 The solution of the system is the point at which the functions intersect: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Substitution 3x y 7 Ex 3: Solve using substitution. 6x y 8 Step One: Solve one of the equations for one of the variables (if necessary). Note: You may choose which variable to solve for. Step Two: Substitute the expression from Step One into the other equation of the system and solve for the other variable. Note: Both variables were eliminated, and the resulting equation is an untrue statement. Solving Nonlinear Systems by Substitution Ex 4: Solve the system. x y y x Step One: Solve one of the equations for one of the variables (if necessary) Step Two: Substitute the expression from Step One into the other equation of the system and solve for the other variable. Note: We solved for x instead of substituting the expression for y to avoid a high-degree polynomial equation to solve. Step Three: Substitute the value from Step Two into the equation from Step One and solve for the remaining variable. Step Four: Write your answer as an ordered pair and check in both of the original equations. Page of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
3 Ex. 5 A total of $1,000 is invested in two funds paying 9% and 11% simple interest. The yearly interest is $1180. How much is invested at each rate? Ex. 6 Break-Even Analysis A small business invests $10,000 in equipment to produce a new soft drink. Each bottle of the soft drink costs $0.65 to produce and is sold for $1.0. How many bottles must be sold before the business breaks even? Page 3 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
4 Date: 7. Solving Linear Systems by Linear Combinations (Elimination) Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities. Solve the systems using Elimination: Step One: Write the two equations in standard form. Ex. 1 5x 6y 3 3x6y 48 Step Two: Multiply one or both of the equations by a constant to obtain coefficients that are opposites for one of the variables. Step Three: Add the two equations from Step Two. One of the variable terms should be eliminated. Solve for the remaining variable. Ex 7xy 10 7x y 16 Step Four: Substitute the value from Step Three into either one of the original equations to solve for the other variable. Step Five: Write your answer as an ordered pair and check in the original system Ex 3 x18y 9 4x18y 7 Ex. 4 5x3y 1 4x 6y 10 Page 4 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
5 Ex. 5 5x3y 9 x 5y 3 Ex. 6 15x y 31 4x6y 11 Ex. 7 9x 6y 0 1x 8y 0 Ex. 8 x y 6 4xy 5. Ex 9 3y 5x 9 x 5y 3 Page 5 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
6 Application Problems Systems of Equations Ex 10: Three gallons of a mixture is 60% water by volume. Determine the number of gallons of water that must be added to bring the mixture to 75% water. Assign labels: w = gallons of water; t = total gallons of mixture Write a system: Amount (gallons) Value (percent water) Solve the system: Rewrite second equation. Use substitution. Ex 11: A machine takes 3 minutes to form a bowl and minutes to form a plate. The material costs $0.5 for a bowl and $0.0 for a plate. How many bowls and plates were made if the machine ran for 8 hours and $44 was spent on materials? Assign labels: b = # of bowls; p = # of plates Write a system: Time (Multiply by 60 to change hours to minutes.) Money Solve the system: Rewrite equations. Use elimination. You Try: x y 6 1. Solve the system: x y x y x 6 (Hint: You do not need to substitute for a single variable. You can use an expression.). A car radiator contains 10 quarts of a 30% antifreeze solution. How many quarts will have to be replaced with pure antifreeze if the resulting solution is to be 50% antifreeze? Reflection: Explain how you would choose the most efficient method for solving a system of equations. Page 6 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
7 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.3 Multivariable Linear Systems Syllabus Objective: 8.4 The student will solve application problems involving matrix operations with and without technology. Triangular Form of a System: an equivalent form of a system from which the solution is easy to read; all lead coefficients are equal to 1 x y z 7 Ex 1: Solve the system in triangular form. y z 7 z 3 Use back substitution: Write solution as an ordered triple: Gaussian Elimination: transforming a system to triangular form by Select Equations. Eliminate a variable. Replace one of the Equation. Select Equations. Eliminate the same variable. Replace one Equation. Repeat until you have a Triangular Form 3,,1 (one equ. in 3 var., one equ in var., 1 equ in 1 var.) x y z 0 Eq. I Ex : Solve the system using Gaussian Elimination. x y z 3 Eq. II x y 3z 7 Eq. III Note: Calculator Trick Rref: Magic Bullet Note: All variables were eliminated, and the result is a false statement. Therefore, this system has NO SOLUTION. Special Systems: A linear system can have exactly one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solution. x y z 4 Ex 3: Solve the system. 3x 6y 3z 7 x y 4z Page 7 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
8 Date: B4 Solving Inequalities Solving a Linear Inequality: Ex.1: Solve and graph the solution on the number line. Express the solution in interval notation. 5x 8 x 3 or Note: When multiplying or dividing by a negative number, you must flip the inequality sign. Interval notation: Solving a Compound Inequality: Ex.: Solve and graph. Express in interval notation x Solving an Absolute Value Inequality If x If x a, then a x a. Or x is between a and a. a, then x a or x a. Ex.3: Solve the inequality. x 4 1 Since the absolute value is less than 1, the value of the expression inside the absolute value must be between 1 and 1. Solve the compound inequality. *Have students pick a value within the interval to verify that it is a solution to the original inequality. Ex.4: Solve the inequality and verify your solution graphically. x 3 7 Since the absolute value is greater than or equal to 7, the value of the expression inside the absolute value must be less than or equal to 7 or greater than or equal to 7. Page 8 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
9 Solve the compound inequality. We can see that the graph of y x 3 is greater than or equal to the graph of y 7 when xor x 5. Solving Quadratic Inequalities Algebraic Method (sign chart) Ex.5: Solve the inequality. x 6x 8 0 Solve the equation to find the zeros. Make a sign chart using test values between and outside of the zeros. + + The solutions to the inequality are the x-values that make the expression positive (greater than zero). Set notation: Graphing Method Ex.6: Solve the inequality graphically. x 5x 0 Because the graph is below the x-axis y 0 between x = and x =.851, the solution, written in interval notation is: Page 9 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
10 Projectile Motion: When an object is launched vertically from an initial height of s 0 feet and an initial velocity of v 0 feet per second, then the vertical position s of the object t seconds after it is launched is s 16t v0t s0. Ex.7: A ball is thrown straight up from ground level with an initial velocity of 59 ft/sec. When will the ball s height above the ground be more than 30 ft? Write the equation of the height of the ball. Write an inequality to model the question. Solve by graphing. The ball s height will be more than ft when seconds. You Try: Solve the quadratic inequality algebraically. Then verify your answer graphically. x 7x 30 0 Page 10 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
11 Sample SAT Question(s): Taken from College Board online practice problems. 1. If y x 3 and x, which of the following represents all the possible values for y? (A) y 7 (B) y 7 (C) y 5 (D) y 5 (E) 5 y 7. The figure above shows the graph of a quadratic function in the xy-plane. Of all the points xy, on the graph, for what value of x is the value of y greatest? 3. At a snack bar, a customer who orders a small soda gets a cup containing c ounces of soda, where 1 c is at least 1 but no more than 1. Which of the following describes all possible values of c? A. B. C. D. E c 1 c 1 1 c c c Reflection: Can a quadratic and/or absolute value inequality have no solutions or one solution? Explain your answer with an example. Page 11 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
12 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.3 Continued: Partial Fraction Decomposition Syllabus Objective: 8.5 The student will use partial fractions to decompose rational expressions with distinct linear factors. Recall: To add the rational expressions 3 3 x 3 x 4 5x 1 x 4 x 3 x 4 x 3 x x1 3, we must find a common denominator. x4 x 3 or a c ad bc b d bd 5x 1 What if we wanted to go from the sum,, back to the addends, x x1 Partial Fraction Decomposition: writing rational expressions as the sum of simpler ones Steps Case I: Distinct (no repeated) Linear Factors in the Denominator 1. Factor the denominator.. Write the factors as a sum. 3. Clear the fractions (multiply by the LCD). 4. Write and solve the resulting system of equations. 5. Write the resulting partial fractions. 5x 10 Ex 1: Find the partial fraction decomposition of x 3x 1. Factor the denominator: 5x 10 x 3x. Write the factors as a sum. 5x 10 A B x 1 x x 1 x 3. Clear the fractions. 3 x4 x 3? 4. Write and solve the system. 5. Write the resulting partial fractions. Solution: Page 1 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
13 Steps Case II: Repeated Linear Factors in the Denominator 1. Factor the denominator.. Write the factors as a sum. Any repeated factors, A A1 A An... n n f f f f 3. Clear the fractions (multiply by the LCD). 4. Write and solve the resulting system of equations. 5. Write the resulting partial fractions. x Ex : Write as a decomposition of partial fractions. x x1 x 1. Factor the denominator. x x1 n f will be written as n factors in the fractions.. Write the factors as a sum. Any repeated factors, x A B x1 x 1 x1 n f will be written as n factors in the fractions. 3. Clear the fractions (multiply by the LCD). 4. Write and solve the resulting system of equations. 5. Write the resulting partial fractions. Page 13 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
14 Steps Case III: Irreducible Distinct Quadratic Factors in the Denominator 1. Factor the denominator.. Write the factors as a sum. Any irreducible quadratic factor in the denominator must have a linear expression in the numerator, i.e. ax b. 3. Clear the fractions (multiply by the LCD). 4. Write and solve the resulting system of equations. 5. Write the resulting partial fractions. Ex 3: Find the partial fraction decomposition of 1. Factor the denominator (difference of two cubes). 8x 5x18. 3 x 8 8x 5x18 3 x 8. Write the factors as a sum. Any irreducible quadratic factor in the denominator must have a linear expression in the numerator, i.e. ax b. 8x 5x18 x x x 4 3. Clear the fractions (multiply by the LCD). 4. Write and solve the resulting system of equations. 5. Write the resulting partial fractions. Page 14 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
15 Irreducible Quadratic Factors Improper Fractions: use long division to write in the form Ex 4: Find the partial fraction decomposition. 4x 6 4x 1 x x 3 Long Division: x x 4x 9x x Decompose: 4x 6 A x Bx 4x 6 Ax A Bx 4x 6 A B x A 3 4x 9x x 3 7 4x 1 x x x x A 3 A B 4 3 B 4 A 6 B 7 r x qx d x 3 4x 9x x x x 4x 6 A B x x x x 4x x x x x REFLECTION: Are partial fraction decompositions always unique? Explain. Page 15 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
16 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices F Linear Programming Syllabus Objective:.1 The student will graph relations or functions, including real-world applications. Half-Plane: the graph of a linear inequality Number Line Coordinate Plane & Open dot Dotted (dashed) line & Closed (solid) dot Solid Line Note: You can use a test point to determine which half-plane to shade. Ex 1: Draw the graph of the inequality. y3x 4 Graph the line y3x 4, or y3x 4. The line will be dashed because it is a < sign. Pick a test point: 0,0 y3x true Shade the half-plane that contains the test point. Solution of a System of Inequalities: the intersection of the solutions of all of the inequalities in the system; common solutions to all x 4 Ex : Graph and determine if the solution is bounded or unbounded. y 3 x y 4 3, : x y 3 3 x y To be sure we shaded the correct region, use a test point. The region is bounded. Page 16 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
17 Ex 3: Graph the system of inequalities and state if the solution is bounded or unbounded. 1 y x 1 x 1 Ex 4: Solve the system of inequalities. The region is unbounded. y x1 3 x y 9 y x1 3: vertex at 1,3 ; opens down; shade above x y 9 : circle with center 0,0 ; radius = 3; shade inside Solution is the shaded region they have in common. Linear Programming: decision making by finding a minimum or maximum value of a linear function given a set of constraints Constraints: a system of linear inequalities Feasible Region: the solution set found using the constraints Objective Function: an equation applied to a feasible region that we want to minimize or maximize Vertex Points: the corner points of the feasible region The maximum or minimum of a linear programming problem always occurs at a vertex point. Solving a Linear Programming Problem Write the system of inequalities that represent the constraints. Graph the feasible region. Write the objective function. Test the vertex points in the objective function and answer the question. Page 17 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
18 Ex 5: Mrs. Meservey is baking as many cakes and pies as possible using the 18 eggs and 15 cups of milk she has on hand. Her cake recipe requires eggs and 1 cup of milk. Her pie recipe requires 1 egg and 1.5 cups of milk. How many cakes and pies should she make? Constraints: C: number of cakes; P: number of pies Graph: Objective Function: Maximum: Ex 6: It takes hours to manufacture a pair of skis and 1 hour for a snowboard. The finishing time for both is 1 hours. The maximum time available for manufacturing is 40 hours and for finishing is 3 hours each week. The profit for a pair of skis is $70 and the profit for a snowboard is $50. The manufacturer must produce at least 8 snowboards every week because of a contract with a sporting goods store. Find the maximum profit. Constraints: k: number of pairs of skis; w: number of snowboards Graph: Objective Function: Maximum Profit: Page 18 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
19 You Try: Write a system of inequalities that represents the graph. REFLECTION: What does the feasible region represent in a linear programming problem? How are the corner points special? Page 19 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
20 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.4 Matrices and Systems of Equations The student will find the order of Matrices, write an augmented matrix, use elementary row operations, Gaussian Elimination with Back-Substitution, and use Row Echelon Form. Matrix: a rectangular arrangement of numbers (called entries) in rows and columns. Plural of matrix: matrices Dimensions (Order) of a Matrix: Number of Rows (by) Number of Columns A = Entry/Element a 3 = (row 3, column ) Square Matrix: a matrix with the same number of rows and columns Ex1: Determine the order of the matrix. Is it a square matrix? Identify b B Order: Rows by Columns No, it is not a square matrix. b : Element in row, column 4 4 Coefficient Matrix of a System: The coefficient matrix of the system a1 b1 c1 is a b c. a 3 b3 c3 Augmented Matrix of a System: The augmented matrix of the system a1 b1 c1 d1 is a b c d. a 3 b3 c3 d3 a x b y c z d a x b y c z d a x b y c z d a x b y c z d a x b y c z d a x b y c z d Page 0 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
21 Row Echelon Form of a Matrix: the augmented matrix that corresponds to the triangular form of the original system of equations rows consisting entirely of zeros (if any) occur at the bottom of the matrix the first entry in any row with nonzero entries is 1 the column subscript of the leading 1 entries increases as the row subscript increases (the leading 1 s move to the right as we move down the rows) For Example, the triangular system x y z 3 yz 4 z 3 as an augmented matrix: We will write a system as an augmented matrix, then use Elementary Row Operations to put the matrix in Row Echelon Form to solve the system. Elementary Row Operations: interchange rows multiply all elements of a row by a nonzero number add a multiple of one row to any other row Note: These are the same strategies we used in Gaussian Elimination! Tip: Start in the lower left corner of the matrix. 3x y z 5 Ex: Solve the system using an augmented matrix in row echelon form. x y z 4 Write as an augmented matrix: Perform the elementary row operations: x 3y z 3 R1 R 3R1 R R1 R3 R3 R 4R R3 1 R3 Row Echelon Form! 7 Triangular Form of System: Solution of System (use back substitution): Reduced Row Echelon Form: every column that has a leading 1 has zeros elsewhere Ex3: Write the augmented matrix above in reduced row echelon form R3 R R3 R1 R R1 Reduced Row Echelon Form Solution of system is the last column! Page 1 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
22 Special Case: Infinite Solutions Ex4: Solve the system. 1 R1 R3 R3 R R3 3 x y 3 1 yz 0 x y 1 Notice that the last row in the matrix represents the equation 0 = 0, so we know there are infinitely many solutions. We can represent these solutions as an ordered triple in terms of z. y z 0 y z Solutions: x y 3z 1 x y 3z 1 x z 3z 1 x z 1 Reflection: Page of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
23 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.5 Operations with Matrices The student will use matrix addition, scalar multiplication, matrix multiplication. Adding and Subtracting Matrices: matrices must have the same order Add or subtract corresponding elements. Multiplying by a Scalar: multiply all elements of the matrix by the scalar Ex: Perform the operations Multiply by the scalar: Add the matrices: Matrix Multiplication: In order to multiply matrices, the number of columns in the first matrix must equal the number of rows in the second matrix. The product matrix will have the same number of rows of the first matrix and the same number of columns of the second matrix. Matrix multiplication is NOT commutative. ( AB BA for all matrices A and B.) Let A be an mnmatrix, and B be an n pmatrix. The product AB exists, and will have the dimensions m p. 3 Ex 3: Find the product AB (if possible). A 1 5 B Step One: Determine if the product exists. If it does, find its dimensions. Matrix A is a 3 matrix. Matrix B is a matrix. The number of columns in matrix A equals the number of rows in matrix B. Therefore, the product exists and will be a 3 matrix. Step Two: Multiply each entry in the rows of matrix A to each entry in the columns of matrix B. Then find the sum of these products. Page 3 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
24 Ex 4: Find the product BA (if possible) of the matrices from the previous example. Step One: Determine if the product exists. If it does, find its dimensions. Matrix B is a matrix. Matrix A is a 3 matrix. The number of columns in Matrix B does not equal the number of rows in matrix A. Therefore, the product BA does not exist. Matrices on the Graphing Calculator Ex 5: Evaluate the product from the previous example on the graphing calculator Ex6: Find the product AC if A and C 8 (if possible) Matrix A is a 4 3 matrix. Matrix C is a 3 1 matrix. The number of columns in matrix A equals the number of rows in matrix C. Therefore, the product AC exists, and has the dimensions 4 1. Application Problem Multiplying Matrices Ex: A school is selling tickets to a school play. They sell tickets for $5 for balcony seating and $7 for floor seating. The school sells 60 balcony seats and 5 floor seats to parents and relatives. They also sell 40 balcony seats and 50 floor seats to students. Set up the school s profit as a product of two matrices. Seat Matrix Ticket Price Matrix = Profit Non-Student Tickets Balcony Price Seat Matrix: Ticket Price Matrix: Student Tickets Floor Price Multiply the matrices: Non-Student Profit Student Profit You Try: Find the product CA using the matrices 5 6 A 4 1 and 4 3 C Reflection: Is matrix multiplication commutative? Explain why or why not. Page 4 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
25 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix 8.3 The student will find the inverse of a given square matrix. Solve equations using inverse matrices. Recall: Identity of Addition: a 0 a Identity of Multiplication: a1 a Matrix Identity of Addition: 0 0 Matrix Identity of Multiplication: Ex1: Find and Recall: Additive Inverse: a a 0 Multiplicative Inverse: a b a b 0 0 Additive Inverse (matrices): c d c d a 1 a a A c b d Determinant of a Matrix: If, then Ex: Find the determinant of each matrix. a.) 3 1 b.) 1 4 det A A ad bc. c.) Nonsingular Matrix: a matrix that has a nonzero determinant Inverse of a Matrix: If The product of a A c b d, then A d A c 1 1 b, A 0 a A A A A 0 1, the multiplicative identity. Note: If A 0, then A does not have an inverse. Be careful with notation. of matrix A, NOT the reciprocal of matrix A. 1 A means the inverse Page 5 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
26 4 1 Ex3: Find the inverse of B 6. Verify your answer. Evaluate the determinant: Write the inverse: Verify by multiplying: Ex4: Calculate the determinant of the matrix on the calculator. Then find the inverse and verify. 0 1 A Enter the matrix into the calculator. On the home screen, find the determinant. det( can be found in the Matrix Math menu. Find the inverse: Verify: 1 Recall: Inverses can be used to solve the equation ax b. x b a a1x b1 y c1 Solving Systems Using Inverses: The system a x b y c the solution of the system is Note: The matrix a a x a b c y a b c. 1 1 b b is called the coefficient matrix. can be written as a1 b1 x c1 a b y c. So Page 6 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
27 4x y 4 Ex5: Solve the system 6xy 3 Write as a matrix equation: using the inverse matrix. Find the inverse of the coefficient matrix: Multiply both sides by the inverse: Note: Multiplying the coefficient matrix by its inverse results in the identity matrix. Solving a System Using Inverse Matrices x y z w 4 x y z 0 Ex6: Solve the system. 3x y z w 6 x y z w 1 Write as a matrix equation: Enter the coefficient matrix as Matrix A and the constant matrix as Matrix B. Multiply 1 A B. Solution: Page 7 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
28 Application Problems Ex7: A man borrows a total of $10,000; some at 18%, 15%, and 9%. He borrows 3 times as much at 15% as he borrows at 18%, and the total interest on all of the loans is $ How much did he borrow at each percentage rate? Assign labels: x = amount borrowed at 18%; y = amount at 15%; z = amount at 9% Write a system: Total amount borrowed: Total interest: Other information given: Solve by inverses: He borrowed $175 at 18%, $385 at 15%, and $4900 at 9%. You Try: Find the 1 A. Then verify that it is the inverse of A. 6 A 1 5. Reflection: Which matrix operation(s) are commutative? Explain. Page 8 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
29 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.7 The Determinant of a Square Matrix Syllabus Objectives: 8. The student will calculate the determinant of a square matrix. Evaluating Review: Find the Determinant of a x Matrix: Determinant of a 3 3 Matrix: Lattice Method Ex1: Evaluate the determinant Rewrite the first two columns to the right of the 3 rd column: Multiply along the diagonals. Find the sum of the products of the diagonals from left to right and the opposite of the products of the diagonals from right to left OR,,,, Ex. You Try: Evaluate the determinant Application: Finding the Area of a Triangle Using Determinants The area of a triangle with vertices,,,, and, x y x y x y is x1 y1 1 1 x y 1. x y Note: The ± sign indicates that we need to choose which sign will make this a positive number. Ex3: Find the area of a triangle whose vertices are the points 1,, 3, 4, and 0,6. Area = Solution: Because the determinant is positive, we will use the positive answer for the area of the triangle, sq. units. Page 9 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
30 Date: 7.8 Applicatoin of Matrices and Determinants Students will use Cramer s Rule to solve systems of equations. Solving a Linear System Using Cramer s Rule Linear System: a x b y c a x b y c a D = a b b 1 1 D x c c b 1 1 b D y a a c 1 1 c Cramer s Rule Solution of a Linear System: x D x and y D y D D, D 0 Note: Constant matrix replaces the column of the coefficients of the variable being solved for. x 7y 3 Ex1: Solve the system of equations using Cramer s Rule. 3x5y 17 Check: Solution: Solving a System of Three Equations and Three Unknowns with Cramer s Rule a x b y c z d a b c d b c a d c a x b y c d a x b y c d d a b c a b c x d d b c d b c y d a d c a d c z a b d d a b d a b d d x x d d y y d d z z d Ex: Solve the system using Cramer s Rule. x 3y z 1 x 6y z 3 3x 5y z 4 Solution: (Check this on your own in the original three equations.) Note: We could also use Cramer s Rule to find x and y, then substitute these values into one of the original equations to find z. Page 30 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
31 Ex3: Determine the quadratic function that contains the points 1,3,,10, &, 6. Quadratic function: Substitute each ordered pair into y ax bx c We must find a, b, and c. Solve on graphing calculator. Solution: y ax bx c. 1,3 : 3 a b c,10 : 10 4a b c, 6 : 6 4a b c You Try: A piggy bank contains quarters, dimes, and nickels. The number of dimes is 1 less than the number of nickels. The number of nickels is more than twice the number of quarters. The coins are worth $5.70. How many nickels are there? Refection: Page 31 of 31 Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic: Larson Chapter 7
degree -6x 3 + 5x 3 Coefficients:
 Date P3 Polynomials and Factoring leading coefficient degree -6 3 + 5 3 constant term coefficients Degree: the largest sum of eponents in a term Polynomial: a n n + a n-1 n-1 + + a 1 + a 0 where a n 0
Date P3 Polynomials and Factoring leading coefficient degree -6 3 + 5 3 constant term coefficients Degree: the largest sum of eponents in a term Polynomial: a n n + a n-1 n-1 + + a 1 + a 0 where a n 0
Dependent ( ) Independent (1 or Ø) These lines coincide so they are a.k.a coincident.
 Notes #3- Date: 7.1 Solving Systems of Two Equations (568) The solution to a system of linear equations is the ordered pair (x, y) where the lines intersect! A solution can be substituted into both equations
Notes #3- Date: 7.1 Solving Systems of Two Equations (568) The solution to a system of linear equations is the ordered pair (x, y) where the lines intersect! A solution can be substituted into both equations
Algebra II Notes Unit Four: Matrices and Determinants
 Syllabus Objectives: 4. The student will organize data using matrices. 4.2 The student will simplify matrix expressions using the properties of matrices. Matrix: a rectangular arrangement of numbers (called
Syllabus Objectives: 4. The student will organize data using matrices. 4.2 The student will simplify matrix expressions using the properties of matrices. Matrix: a rectangular arrangement of numbers (called
Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 9. Systems of Equations Solve the system of equations below. By this we mean, find pair(s) of numbers (x, y) (if possible) that satisfy both equations.
Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 9. Systems of Equations Solve the system of equations below. By this we mean, find pair(s) of numbers (x, y) (if possible) that satisfy both equations.
Systems of Equations and Inequalities. College Algebra
 Systems of Equations and Inequalities College Algebra System of Linear Equations There are three types of systems of linear equations in two variables, and three types of solutions. 1. An independent system
Systems of Equations and Inequalities College Algebra System of Linear Equations There are three types of systems of linear equations in two variables, and three types of solutions. 1. An independent system
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations
 6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
y in both equations.
 Syllabus Objective: 3.1 The student will solve systems of linear equations in two or three variables using graphing, substitution, and linear combinations. System of Two Linear Equations: a set of two
Syllabus Objective: 3.1 The student will solve systems of linear equations in two or three variables using graphing, substitution, and linear combinations. System of Two Linear Equations: a set of two
Chapter 7 Linear Systems and Matrices
 Chapter 7 Linear Systems and Matrices Overview: 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations 7.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 7.3 Multivariable Linear Systems 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations What
Chapter 7 Linear Systems and Matrices Overview: 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations 7.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 7.3 Multivariable Linear Systems 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations What
Precalculus Notes: Unit P Prerequisite Skills
 Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
The Method of Substitution. Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. The Method of Substitution. Example 2.
 The Method of Substitution Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations Precalculus 7.1 Here is an example of a system of two equations in two unknowns. Equation 1 x + y = 5 Equation 3x y = 4 A solution of
The Method of Substitution Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations Precalculus 7.1 Here is an example of a system of two equations in two unknowns. Equation 1 x + y = 5 Equation 3x y = 4 A solution of
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables
 9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
NOTES. [Type the document subtitle] Math 0310
![NOTES. [Type the document subtitle] Math 0310 NOTES. [Type the document subtitle] Math 0310](/thumbs/79/79061464.jpg) NOTES [Type the document subtitle] Math 010 Cartesian Coordinate System We use a rectangular coordinate system to help us map out relations. The coordinate grid has a horizontal axis and a vertical axis.
NOTES [Type the document subtitle] Math 010 Cartesian Coordinate System We use a rectangular coordinate system to help us map out relations. The coordinate grid has a horizontal axis and a vertical axis.
Algebra & Trig. I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
2.1 Quadratic Functions
 Date:.1 Quadratic Functions Precalculus Notes: Unit Polynomial Functions Objective: The student will sketch the graph of a quadratic equation. The student will write the equation of a quadratic function.
Date:.1 Quadratic Functions Precalculus Notes: Unit Polynomial Functions Objective: The student will sketch the graph of a quadratic equation. The student will write the equation of a quadratic function.
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2. where a, b, c, d, h, and k are real numbers and neither a and b nor c and d are both zero.
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Math Analysis Notes Mrs. Atkinson 1
 Name: Math Analysis Chapter 7 Notes Day 6: Section 7-1 Solving Systems of Equations with Two Variables; Sections 7-1: Solving Systems of Equations with Two Variables Solving Systems of equations with two
Name: Math Analysis Chapter 7 Notes Day 6: Section 7-1 Solving Systems of Equations with Two Variables; Sections 7-1: Solving Systems of Equations with Two Variables Solving Systems of equations with two
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming
 Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
You solved systems of equations algebraically and represented data using matrices. (Lessons 0-5 and 0-6)
 You solved systems of equations algebraically and represented data using matrices. (Lessons 0-5 and 0-6) Solve systems of linear equations using matrices and Gaussian elimination. Solve systems of linear
You solved systems of equations algebraically and represented data using matrices. (Lessons 0-5 and 0-6) Solve systems of linear equations using matrices and Gaussian elimination. Solve systems of linear
MAC1105-College Algebra. Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices
 MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
Introduction to Systems of Equations
 Systems of Equations 1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Remember, we are finding a point of intersection x 2y 5 2x y 4 1. A golfer scored only 4 s and 5 s in a round of 18 holes. His score was 80.
Systems of Equations 1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Remember, we are finding a point of intersection x 2y 5 2x y 4 1. A golfer scored only 4 s and 5 s in a round of 18 holes. His score was 80.
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers
 Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Order of Operations. Real numbers
 Order of Operations When simplifying algebraic expressions we use the following order: 1. Perform operations within a parenthesis. 2. Evaluate exponents. 3. Multiply and divide from left to right. 4. Add
Order of Operations When simplifying algebraic expressions we use the following order: 1. Perform operations within a parenthesis. 2. Evaluate exponents. 3. Multiply and divide from left to right. 4. Add
Answers to Sample Exam Problems
 Math Answers to Sample Exam Problems () Find the absolute value, reciprocal, opposite of a if a = 9; a = ; Absolute value: 9 = 9; = ; Reciprocal: 9 ; ; Opposite: 9; () Commutative law; Associative law;
Math Answers to Sample Exam Problems () Find the absolute value, reciprocal, opposite of a if a = 9; a = ; Absolute value: 9 = 9; = ; Reciprocal: 9 ; ; Opposite: 9; () Commutative law; Associative law;
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 5.1.1 5.1.4 Students have been solving equations since Algebra 1. Now they focus on what a solution means, both algebraically and graphically. By understanding the nature of
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 5.1.1 5.1.4 Students have been solving equations since Algebra 1. Now they focus on what a solution means, both algebraically and graphically. By understanding the nature of
Equations and Inequalities
 Equations and Inequalities Figure 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE 1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs Linear Equations in One Variable Models and Applications Comple Numbers Quadratic Equations 6 Other Types
Equations and Inequalities Figure 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE 1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs Linear Equations in One Variable Models and Applications Comple Numbers Quadratic Equations 6 Other Types
Math 101, Basic Algebra. Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 2 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions 2 Terms, coefficients, like terms, combining like terms, simplifying
Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 2 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions 2 Terms, coefficients, like terms, combining like terms, simplifying
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Compressed Approach
 College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Compressed Approach 978-1-63545-059-0 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Compressed Approach 978-1-63545-059-0 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
Glossary. Glossary Hawkes Learning Systems. All rights reserved.
 A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute triangle A triangle in which all three angles are acute Addends The
A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute triangle A triangle in which all three angles are acute Addends The
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
An equation is a statement that states that two expressions are equal. For example:
 Section 0.1: Linear Equations Solving linear equation in one variable: An equation is a statement that states that two expressions are equal. For example: (1) 513 (2) 16 (3) 4252 (4) 64153 To solve the
Section 0.1: Linear Equations Solving linear equation in one variable: An equation is a statement that states that two expressions are equal. For example: (1) 513 (2) 16 (3) 4252 (4) 64153 To solve the
Math 1314 Week #14 Notes
 Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: Targeted Review
 College Algebra with Corequisite Support: Targeted Review 978-1-63545-056-9 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: Targeted Review 978-1-63545-056-9 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities
 Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Blended Approach
 College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Blended Approach 978-1-63545-058-3 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Blended Approach 978-1-63545-058-3 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
Reference Material /Formulas for Pre-Calculus CP/ H Summer Packet
 Reference Material /Formulas for Pre-Calculus CP/ H Summer Packet Week # 1 Order of Operations Step 1 Evaluate expressions inside grouping symbols. Order of Step 2 Evaluate all powers. Operations Step
Reference Material /Formulas for Pre-Calculus CP/ H Summer Packet Week # 1 Order of Operations Step 1 Evaluate expressions inside grouping symbols. Order of Step 2 Evaluate all powers. Operations Step
FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA 1 (Students entering Geometry)
 FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA (Students entering Geometry) Dear Parent/Guardian and Student, Name: Date: Period: Attached you will find a review packet of skills which each student is expected
FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA (Students entering Geometry) Dear Parent/Guardian and Student, Name: Date: Period: Attached you will find a review packet of skills which each student is expected
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1)
 ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent
1 4 3 A Scalar Multiplication
 1 Matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of variables or constants in horizontal rows and vertical columns, usually enclosed in brackets. In a matrix, the numbers or data are organized so that each position
1 Matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of variables or constants in horizontal rows and vertical columns, usually enclosed in brackets. In a matrix, the numbers or data are organized so that each position
Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries. Lesson Goal: Mastery 70% or higher
 Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries For every lesson, you need to: Read through the LESSON REVIEW which is located below or on the last page of the lesson and 3-hole punch into your MATH BINDER. Read and work
Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries For every lesson, you need to: Read through the LESSON REVIEW which is located below or on the last page of the lesson and 3-hole punch into your MATH BINDER. Read and work
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
1 Chapter 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models
 1 Chapter 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models 1.1 Introduction to Graphing 1.1.1 Know how to graph an equation Eample 1. Create a table of values and graph the equation y = 1. f() 6 1 0 1 f() 3 0 1 0 3 4
1 Chapter 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models 1.1 Introduction to Graphing 1.1.1 Know how to graph an equation Eample 1. Create a table of values and graph the equation y = 1. f() 6 1 0 1 f() 3 0 1 0 3 4
Review questions for Math 111 final. Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points
 Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points 1. True or False questions (17 pts) a. Common Logarithmic functions cross the y axis at (0,1) b. A square matrix has as many
Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points 1. True or False questions (17 pts) a. Common Logarithmic functions cross the y axis at (0,1) b. A square matrix has as many
Chapter 7 Linear Systems
 Chapter 7 Linear Systems Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Multivariable Linear Systems Vocabulary Systems of equations Substitution
Chapter 7 Linear Systems Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Multivariable Linear Systems Vocabulary Systems of equations Substitution
Foundations of Mathematics
 Foundations of Mathematics 978-1-63545-087-3 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Lynn Marecek, Santa Ana College
Foundations of Mathematics 978-1-63545-087-3 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Lynn Marecek, Santa Ana College
When using interval notation use instead of open circles, and use instead of solid dots.
 P.1 Real Numbers PreCalculus P.1 REAL NUMBERS Learning Targets for P1 1. Describe an interval on the number line using inequalities. Describe an interval on the number line using interval notation (closed
P.1 Real Numbers PreCalculus P.1 REAL NUMBERS Learning Targets for P1 1. Describe an interval on the number line using inequalities. Describe an interval on the number line using interval notation (closed
June If you want, you may scan your assignment and convert it to a.pdf file and it to me.
 Summer Assignment Pre-Calculus Honors June 2016 Dear Student: This assignment is a mandatory part of the Pre-Calculus Honors course. Students who do not complete the assignment will be placed in the regular
Summer Assignment Pre-Calculus Honors June 2016 Dear Student: This assignment is a mandatory part of the Pre-Calculus Honors course. Students who do not complete the assignment will be placed in the regular
1) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-1) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-1)(2) =
 Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Algebra 1. Math Review Packet. Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals
 Algebra 1 Math Review Packet Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals 2017 Math in the Middle 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive
Algebra 1 Math Review Packet Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals 2017 Math in the Middle 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive
Solving Multi-Step Equations
 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive property. 2. Combine like terms within each side of the equal sign. Solving Multi-Step Equations 3. Add/subtract terms to both sides of the equation to get the
1. Clear parentheses using the distributive property. 2. Combine like terms within each side of the equal sign. Solving Multi-Step Equations 3. Add/subtract terms to both sides of the equation to get the
Section September 6, If n = 3, 4, 5,..., the polynomial is called a cubic, quartic, quintic, etc.
 Section 2.1-2.2 September 6, 2017 1 Polynomials Definition. A polynomial is an expression of the form a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a 1 x + a 0 where each a 0, a 1,, a n are real numbers, a n 0, and n is a
Section 2.1-2.2 September 6, 2017 1 Polynomials Definition. A polynomial is an expression of the form a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a 1 x + a 0 where each a 0, a 1,, a n are real numbers, a n 0, and n is a
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 1 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 2015 03 24 2 Table of Contents Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solve Systems by Elimination Choosing your Strategy Solving Systems of
1 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 2015 03 24 2 Table of Contents Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solve Systems by Elimination Choosing your Strategy Solving Systems of
BLITZER LEARNING GUIDE SAMPLE
 BLITZER LEARNING GUIDE SAMPLE Section 5.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Procrastination makes you sick! Researchers compared college students who were procrastinators and nonprocrastinators.
BLITZER LEARNING GUIDE SAMPLE Section 5.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Procrastination makes you sick! Researchers compared college students who were procrastinators and nonprocrastinators.
Numbers and Operations Review
 C H A P T E R 5 Numbers and Operations Review This chapter reviews key concepts of numbers and operations that you need to know for the SAT. Throughout the chapter are sample questions in the style of
C H A P T E R 5 Numbers and Operations Review This chapter reviews key concepts of numbers and operations that you need to know for the SAT. Throughout the chapter are sample questions in the style of
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Break Even. Example. 240x x This is when total cost equals total revenue.
 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Gauss-Jordan elimination ( used in the videos below) stops when the augmented coefficient
 To review these matrix methods for solving systems of linear equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering all the basic
To review these matrix methods for solving systems of linear equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering all the basic
1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices
 1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices We can represent a system of linear equations using an augmented matrix. In general, a matrix is just a rectangular arrays
1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices We can represent a system of linear equations using an augmented matrix. In general, a matrix is just a rectangular arrays
SUMMER REVIEW PACKET. Name:
 Wylie East HIGH SCHOOL SUMMER REVIEW PACKET For students entering Regular PRECALCULUS Name: Welcome to Pre-Calculus. The following packet needs to be finished and ready to be turned the first week of the
Wylie East HIGH SCHOOL SUMMER REVIEW PACKET For students entering Regular PRECALCULUS Name: Welcome to Pre-Calculus. The following packet needs to be finished and ready to be turned the first week of the
Key Vocabulary. Vocabulary Check. 4. If a system has no solution, it is said to be inconsistent. 7. Each number in a matrix is called a(n) dimension.
 Study Guide and Review Study Guide Key Concepts Systems of Equations (Lessons - through -4) A system with a graph of two intersecting lines has one solution and is consistent and independent. Graphing
Study Guide and Review Study Guide Key Concepts Systems of Equations (Lessons - through -4) A system with a graph of two intersecting lines has one solution and is consistent and independent. Graphing
Algebra II Notes Unit One. Syllabus Objective 1.1 The student will differentiate among subsets of the real number system.
 Syllabus Objective 1.1 The student will differentiate among subsets of the real number system. Real Numbers: Numbers that can be graphed on the number line Ex:,!10, 2, 8,4.2," Put the numbers in order
Syllabus Objective 1.1 The student will differentiate among subsets of the real number system. Real Numbers: Numbers that can be graphed on the number line Ex:,!10, 2, 8,4.2," Put the numbers in order
Study Guide for Math 095
 Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics. The Basics of Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
College Algebra To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com
 College Algebra 978-1-63545-097-2 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Text Jay Abramson, Arizona State University
College Algebra 978-1-63545-097-2 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Text Jay Abramson, Arizona State University
College Algebra. Chapter 6. Mary Stangler Center for Academic Success
 College Algebra Chapter 6 Note: This review is composed of questions similar to those in the chapter review at the end of chapter 6. This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from chapter 6. It
College Algebra Chapter 6 Note: This review is composed of questions similar to those in the chapter review at the end of chapter 6. This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from chapter 6. It
System of Equations: An Introduction
 System of Equations: An Introduction Many books on linear algebra will introduce matrices via systems of linear equations. We tried a different approach. We hope this way you will appreciate matrices as
System of Equations: An Introduction Many books on linear algebra will introduce matrices via systems of linear equations. We tried a different approach. We hope this way you will appreciate matrices as
A2TH MIDTERM REVIEW (at home) CHAPTER 1/2 NUMBERS/FUNCTIONS. 2) Solve the inequality, write the solution set, and graph in the specified domain:
 A2TH MIDTERM REVIEW (at home) )Simplify 3 2[ 2x 3(x + 4) 3(4 x) ] CHAPTER /2 NUMBERS/FUNCTIONS 2) Solve the inequality, write the solution set, and graph in the specified domain: a) 5x 3< 22 {integers}
A2TH MIDTERM REVIEW (at home) )Simplify 3 2[ 2x 3(x + 4) 3(4 x) ] CHAPTER /2 NUMBERS/FUNCTIONS 2) Solve the inequality, write the solution set, and graph in the specified domain: a) 5x 3< 22 {integers}
8 Systems of Linear Equations
 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.1 Systems of linear equations in two variables To solve a system of linear equations of the form { a1 x + b 1 y = c 1 x + y = c 2 means to find all its solutions (all pairs
8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.1 Systems of linear equations in two variables To solve a system of linear equations of the form { a1 x + b 1 y = c 1 x + y = c 2 means to find all its solutions (all pairs
Math 0031, Final Exam Study Guide December 7, 2015
 Math 0031, Final Exam Study Guide December 7, 2015 Chapter 1. Equations of a line: (a) Standard Form: A y + B x = C. (b) Point-slope Form: y y 0 = m (x x 0 ), where m is the slope and (x 0, y 0 ) is a
Math 0031, Final Exam Study Guide December 7, 2015 Chapter 1. Equations of a line: (a) Standard Form: A y + B x = C. (b) Point-slope Form: y y 0 = m (x x 0 ), where m is the slope and (x 0, y 0 ) is a
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities
 Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 217-pilot)
 Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10024 Sp 11 213 Topics (was 217-pilot) College Algebra, 9th Ed. [open all close all] R-Basic Algebra Operations Section R.1 Integers and rational numbers Rational and irrational
Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10024 Sp 11 213 Topics (was 217-pilot) College Algebra, 9th Ed. [open all close all] R-Basic Algebra Operations Section R.1 Integers and rational numbers Rational and irrational
Systems of Equations. Red Company. Blue Company. cost. 30 minutes. Copyright 2003 Hanlonmath 1
 Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
5.2 MULTIPLICATION OF POLYNOMIALS. section. Multiplying Monomials with the Product Rule
 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials (5 9) 231 98. Height difference. A red ball and a green ball are simultaneously tossed into the air. The red ball is given an initial velocity of 96 feet per second, and
5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials (5 9) 231 98. Height difference. A red ball and a green ball are simultaneously tossed into the air. The red ball is given an initial velocity of 96 feet per second, and
Study Guide-Quarter 1 Test
 Study Guide-Quarter 1 Test This is a summary of the material covered in all the units you have studied this marking quarter. To make sure that you are fully prepared for this test, you should re-read your
Study Guide-Quarter 1 Test This is a summary of the material covered in all the units you have studied this marking quarter. To make sure that you are fully prepared for this test, you should re-read your
SUMMER MATH PACKET College Algebra and Trigonometry A COURSE 235 and Pre-Calculus A COURSE 241
 SUMMER MATH PACKET College Algebra and Trigonometry A COURSE 35 and Pre-Calculus A COURSE 41 Revised May 017 MATH SUMMER PACKET INSTRUCTIONS Attached you will find a packet of exciting math problems for
SUMMER MATH PACKET College Algebra and Trigonometry A COURSE 35 and Pre-Calculus A COURSE 41 Revised May 017 MATH SUMMER PACKET INSTRUCTIONS Attached you will find a packet of exciting math problems for
3. Replace any row by the sum of that row and a constant multiple of any other row.
 Section. Solution of Linear Systems by Gauss-Jordan Method A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers, letters, symbols or algebraic expressions. A matrix with m rows and n columns has size or
Section. Solution of Linear Systems by Gauss-Jordan Method A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers, letters, symbols or algebraic expressions. A matrix with m rows and n columns has size or
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
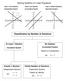 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Elementary and Intermediate Algebra
 Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 978-1-63545-106-1 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Lynn Marecek, Santa
Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 978-1-63545-106-1 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Lynn Marecek, Santa
Relationships Between Planes
 Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Student ID: Exam: RR - SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS; INEQUALITIES. 1. Graph the inequality y 3.
 Student ID: 21745663 Exam: 050353RR - SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS; INEQUALITIES When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit
Student ID: 21745663 Exam: 050353RR - SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS; INEQUALITIES When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit
Chapter 1: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 : Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
Algebra 2 Notes Systems of Equations and Inequalities Unit 03d. Operations with Matrices
 Operations with Matrices Big Idea Organizing data into a matrix can make analysis and interpretation much easier. Operations such as addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication can be performed on
Operations with Matrices Big Idea Organizing data into a matrix can make analysis and interpretation much easier. Operations such as addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication can be performed on
Partial Fraction Decomposition
 Partial Fraction Decomposition As algebra students we have learned how to add and subtract fractions such as the one show below, but we probably have not been taught how to break the answer back apart
Partial Fraction Decomposition As algebra students we have learned how to add and subtract fractions such as the one show below, but we probably have not been taught how to break the answer back apart
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix
 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
5x 2 = 10. x 1 + 7(2) = 4. x 1 3x 2 = 4. 3x 1 + 9x 2 = 8
 1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
H.Alg 2 Notes: Day1: Solving Systems of Equations (Sections ) Activity: Text p. 116
 H.Alg 2 Notes: Day: Solving Systems of Equations (Sections 3.-3.3) Activity: Text p. 6 Systems of Equations: A set of or more equations using the same. The graph of each equation is a line. Solutions of
H.Alg 2 Notes: Day: Solving Systems of Equations (Sections 3.-3.3) Activity: Text p. 6 Systems of Equations: A set of or more equations using the same. The graph of each equation is a line. Solutions of
PreCalculus. Curriculum (447 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Intermediate Algebra
 Intermediate Algebra 978-1-63545-084-2 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) Openstax Lyn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Intermediate Algebra 978-1-63545-084-2 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) Openstax Lyn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
1. Graph the system of equations and tell the solution. 1. Solution
 Algebra Reporting Strand 4: Systems of Equations & Inequalities Subunit 4a: Solving Systems of Equations Review Name: Period: Date: Read all the directions carefully, put your answers in the blanks provided,
Algebra Reporting Strand 4: Systems of Equations & Inequalities Subunit 4a: Solving Systems of Equations Review Name: Period: Date: Read all the directions carefully, put your answers in the blanks provided,
0-2. 2) Plot the points and connect them. X
 1) Pam s Pie Pantry had 2 backorders for cherry pies. Pam can bake 3 pies every hour. Fill in the blanks. Hours 0-2 Pies Practice 6C 2) Plot the points and connect them. 3) Write an equation for the line.
1) Pam s Pie Pantry had 2 backorders for cherry pies. Pam can bake 3 pies every hour. Fill in the blanks. Hours 0-2 Pies Practice 6C 2) Plot the points and connect them. 3) Write an equation for the line.
(MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R)
 College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
Name: Section Registered In:
 Name: Section Registered In: Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 21, 2006 60 points possible 1. (a) (3pts) Define what it means for a linear system to be inconsistent. Solution: A linear system is inconsistent
Name: Section Registered In: Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 21, 2006 60 points possible 1. (a) (3pts) Define what it means for a linear system to be inconsistent. Solution: A linear system is inconsistent
The ACCUPLACER (Elementary Algebra) is a 12 question placement exam. Its purpose is to make sure you are put in the appropriate math course.
 About the ACCUPLACER Test The ACCUPLACER (Elementary Algebra) is a 12 question placement exam. Its purpose is to make sure you are put in the appropriate math course. A student whose score is 67 or higher
About the ACCUPLACER Test The ACCUPLACER (Elementary Algebra) is a 12 question placement exam. Its purpose is to make sure you are put in the appropriate math course. A student whose score is 67 or higher
Math 4: Advanced Algebra Ms. Sheppard-Brick B Quiz Review Learning Targets
 5B Quiz Review Learning Targets 4.6 5.9 Key Facts We learned two ways to solve a system of equations using algebra: o The substitution method! Pick one equation and solve for either x or y! Take that result
5B Quiz Review Learning Targets 4.6 5.9 Key Facts We learned two ways to solve a system of equations using algebra: o The substitution method! Pick one equation and solve for either x or y! Take that result
Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions
 19 Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions (Textbook Lessons 1.1 1.2) Graphing Quadratic Function A function defined by an equation of the form, The graph is a U-shape called a. Standard Form Vertex Form
19 Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions (Textbook Lessons 1.1 1.2) Graphing Quadratic Function A function defined by an equation of the form, The graph is a U-shape called a. Standard Form Vertex Form
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing 1. Graph and solve systems of linear equations in two variables. Solution of a system of linear equations
 3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Objectives 1. Graph and solve systems of linear equations in two variables. Key Terms System of linear equations Solution of a system of linear equations Check whether
3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Objectives 1. Graph and solve systems of linear equations in two variables. Key Terms System of linear equations Solution of a system of linear equations Check whether
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1)
 ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent independent
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent independent
Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 261-pilot)
 Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10023 Sp 11 253 Topics (was 261-pilot) Intermediate Algebra (2011), 3rd Ed. [open all close all] R-Review of Basic Algebraic Concepts Section R.2 Ordering integers Plotting
Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10023 Sp 11 253 Topics (was 261-pilot) Intermediate Algebra (2011), 3rd Ed. [open all close all] R-Review of Basic Algebraic Concepts Section R.2 Ordering integers Plotting
Solve by factoring and applying the Zero Product Property. Review Solving Quadratic Equations. Three methods to solve equations of the
 Hartfield College Algebra (Version 2015b - Thomas Hartfield) Unit ONE Page - 1 - of 26 Topic 0: Review Solving Quadratic Equations Three methods to solve equations of the form ax 2 bx c 0. 1. Factoring
Hartfield College Algebra (Version 2015b - Thomas Hartfield) Unit ONE Page - 1 - of 26 Topic 0: Review Solving Quadratic Equations Three methods to solve equations of the form ax 2 bx c 0. 1. Factoring
