CHAPTER 6 Applications of Integration
|
|
|
- Jane Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves Section. Volume: The Disk Method Section. Volume: The Shell Method Section. Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution Section. Work Section. Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids Section.7 Fluid Pressure and Fluid Force Review Eercises Problem Solving
2 CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Solutions to Even-Numbered Eercises. A Area of a Region Between Two Curves d d. A d. d.. A d d. sec cos d 7 ( ), (, ) (, ) 7 π ( ) (, ) π, ( ) π, π ( ) π, π. f. g A Matches (a) (, ) (, ) A d 7 d 7 7 (, ) ( ), (, ) (, )
3 Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves. The points of intersection are given b when, A d d 7. The points of intersection are given b: when, A f g d d d (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). A d. (, ).... (,.). The points of intersection are given b (, ) (, ),, A d (, )
4 Chapter Applications of Integration. The points of intersection are given b: when, A f g d d d (, ) (, ). A f g d d d 7. (, ) 7. A d (, ) ln ln.7 (, ). The point of intersection is given b: Numerical Approimation:. (, ) when A f g d d d. The points of intersection are given b: when, ± A d d Numerical Approimation:. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, )
5 Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7. f, g The points of intersection are given b: g.. when,,, A d d 7 Numerical Approimation: A ln ln. Numerical Approimation:. sin cos π (, ) d. ( )., (, ) A cos sin d. f d A d. A sec tan d sec.77 π π ( ) π, (, ). From the graph we see that f and g intersect twice at and. A g f d (, ) d ln. ln (, ). A (, ) cos sin sin cos d (π, )
6 Chapter Applications of Integration. ln A d ln (,.) (, ) ln.. (a) e,,, (b) A e d. No, it cannot be evaluated b hand. (c). = e. F t dt t t (a) F (b). F e d e e e (a) F F (b) F e.7 (c) (c) F F e e.. A d d 7 7 d 7 d = (, ) (, ) = + (, ) =
7 Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves. f f,, At f. Tangent line: or (, ) = + f () = + ( ), The tangent line intersects f at. A d arctan. Answers will var. See page 7... on, on, Both functions smmetric to origin d d. Thus, d. A d (, ) (, ) (, ). Proposal is better, since the cummulative deficit (the area under the curve) is less.. A d b b d b b d b b b b ( ( b), b ) ( b, b) b b.
8 7 Chapter Applications of Integration 7. lim n i i where and i i is the same as n n d. f () = (, ) (, ) t.t 7..t.t dt.t.t dt.t.t billion $.7 billion 7. % : P, e.t %: P, e.t Difference in profits over ears:,e.t,e.t dt, e.t e.t.. Note: Using a graphing utilit ou obtain $,.,...7,. $, 7. The curves intersect at the point where the slope of equals that of,.. k (a) The value of k is given b... k k..... (b). Area d... d (a) (b) A.. V A.. m (c) V., pounds. True
9 Section. Volume: The Disk Method 7 Section.. V.. Volume: The Disk Method d d V d d. V d. d ± V V d. d d d.,, (a) R, r V d (b) R, r V d (c) R, r V d d d (d) R, r V d d
10 7 Chapter Applications of Integration., intersect at, and,. (a) R, r V d d (b) R, r V d d. R, r. V 7 d (, ) d 7 R, r sec V sec d ln sec tan tan ln ln ln 7. sec sec d π π π π π. R, r V d
11 Section. Volume: The Disk Method 7. R r,. V d d ln ln ln R, r V d d ln. ln. R r,. V d d R e, r V e d e d e e.. V d d d d (, )
12 7 Chapter Applications of Integration..,,, V d d V 7 (, ) 7 cos d.7. V ln d.. V arctan. d.. A. or V d Matches (b) b V a A d c A d. (a) z (b) z (c) z a < c < b.. R r r h, h V r h d r h h r h h r h = r h r ( h, r) h
13 . r, r V r d h r r d r r h r r r h h r r h h h r r h h r R r, r. (a) (b) Set Section. Volume: The Disk Method 7 V d Let < c < and set c d c c. c c Thus, when, the solid is divided into two parts of equal volume. c c d, To find the other value, set of the volume). Then d (one third of the volume). Then c, c. d d (two thirds h d, d, d. The -values that divide the solid into three parts of equal volume are and......,.,. V.. <.... d.. d.... cubic centimeters..... (a) First find where b intersects the parabola: b b b b b V b d b d b b b b d b d z b b b b b b b b CONTINUED
14 7 Chapter Applications of Integration. CONTINUED (b) graph of Vb b b (c) Vb b b Vb > b is a relative minimum. Minimum Volume is 7.7 for b.7. (a) V f d Simpson s Rule: b a, V cm n (b) f..... (c) V f d. cm. V m. (b) A bh V d Base of Cross Section (a) A b V d CONTINUED
15 Section. Volume: The Disk Method 77. CONTINUED (c) A r (d) V d A bh V d. The cross sections are squares. B smmetr, we can set up an integral for an eighth of the volume and multipl b. A b r r V r d r r r. R V r R r d R r R r R r d R r Rr R r R r R r R r R R r a :. (a) When represents a square. (b) When A a : a a represents a circle. a a d a a d a = a = To approimate the volume of the solid, form n slices, each of whose area is approimated b the integral above. Then sum the volumes of these n slices.
16 7 Chapter Applications of Integration Section. Volume: The Shell Method. p. p h V d d h V d d. p. p h V d h V d. p h V d d. p h sin V sin d sin d cos π π π π. p p on,. p h V d d h V d d
17 Section. Volume: The Shell Method 7. p h V d d. p h V d d. (a) Disk (b) Shell R, r V d d R, r V d d ln ln (c) Disk R, r V d. (a) Disk (b) Same as part a b smmetr R a r a V a d a a a a a d ( a, ) (, a) ( a, ) (, a) (, a) ( a, ) a a 7 a 7 a a a 7 a a a
18 Chapter Applications of Integration. (a) z (b) z (c) z a < c < b. represents the volume of the solid generated b revolving the region bounded b,, and about the -ais b using the Shell Method. d d represents this same volume b using the Disk Method. d. (a) (b) V d. Disk Method. (a). tan,,, Volume Matches (e) (b) V e d. π π. Total volume of the hemisphere is r. B the Shell Method, p, h. Find such that d d.. Diameter:.
19 Section. Volume: The Shell Method. r V R r d r r r R r d r d r r R r r r r r R. (a) (b) b Area region ab n a n d lim R n lim n n lim n abn b ab n a n n b ab n a bn n ab n n ab n n R n n ab n b n n n n abn n n (c) Disk Method: (d) b V ab n a n d b a lim R n lim n a b n a b n b n n d n n b bn n ab n n R n b ab n n n ab n n n n n n n lim b ab n n (e) As n, the graph approaches the line.. (a) V f d,7 cubic feet (b) Top line: Bottom line: V d d d,,,7 cubic feet (Note that Simpson s Rule is eact for this problem.) d
20 Chapter Applications of Integration Section. Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution.,, 7,. (a) d 7 (b) 7 s d 7,, s d ,, 7 7 s d 7 d d,, b s d a d d 77.. e e. (a), e e,, e e,, s e e d e e d e e e e.7 (b) L d (c) L.. (a), (b) = + (c) L. L d
21 Section. Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution = cos. (a) cos, (b) sin (c). sin L sin d. (a) ln, (b) (c) L.7 L d. (a),, (b) d d (c) L.! L d d Alternativel, ou can convert to a function of.. d d L d d Although this integral is undefined at, a graphing utilit still gives L.. d d tan d s Matches (e) = tan ( π, ( (, ) π π. f,, (a) (b) d. d. (c) s d.7 (d).7
22 Chapter Applications of Integration. Let ln, e, and d Equivalentl, e,, and d e, Numericall, both integrals ield L. e L d. L e d e d.. e e e e e e e e s e e d e e d e e e 7 ft e Thus, there are 7 7 square feet of roofing on the barn cosh..7 sinh.. s.7 sinh. d. (Use Simpson s Rule with n or a graphing utilit.).. s d d arcsin arcsin arcsin 7. s 7.,, S d d 7.
23 Section. Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution.,, S d.,, S d d ln,, e e S d e d.. The precalculus formula is the distance formula between two points. The representative element is i i i i i.. The surface of revolution given b f will be larger. r is larger for f.. r r r r r S r r r r d r r r d r r r r. From Eercise 7 we have: a r S r d r a d r rr a r rr a r r r a rh where h is the height of the zone h r r h + = r
24 Chapter Applications of Integration. (a) We approimate the volume b summing disks of thickness and circumference C i equal to the average of the given circumferences: V i (b) The lateral surface area of a frustum of a right circular cone is sr r. For the first frustum, S.. Adding the si frustums together, S r i i cubic inches C i C i i (c) r (d) V r d 7. cubic inches S r r d 7. square inches h r R s. Individual project, see Eercise,.. (a) (b) Ellipse:, + = L d (c) You cannot evaluate this definite integral, since the integrand is not defined at. Simpson s Rule will not work for the same reason. Also, the integrand does not have an elementar antiderivative.. Essa
25 Section. Work 7 Section. Work. W Fd, ft lb. W Fd 7,, ft lb b W. F d is the work done b a force F moving an object along a straight line from a to b. a. (a) (b) W 7 W W (c) (d) W ft lbs d ft lbs. d d 7 7 d ft lbs d 7 ft lbs W d in lb. ft lb.. F k. F k k7 k 7 7 F d 7 W n cm Nm d W 7. k d k k 7 W d 7 k..7 ft lbs k k W d ft lb h,, W d,, h,, h lim W, miton. h ft lb,. Weight on surface of moon: tons Weight varies inversel as the square of distance from the center of the moon. Therefore, F k k k. W.. d.. mi ton. ft lb
26 Chapter Applications of Integration. The bottom half had to be pumped a greater distance then the top half.. Volume of disk: Weight of disk: Distance the disk of water is moved: W d,,, newton meters. Volume of disk: 7 Weight of disk:. Distance: (a) W. d.. ft lb (b) W. d. 7.7 ft lb. Volume of each laer: Weight of each laer:. Distance: W. d. d. (, ) =. ft lb. Volume of laer: V Weight of laer: W Distance:. W. d... d. d The second integral is zero since the integrand is odd and the limits of integration are smmetric to the origin. The first integral represents the area of a semicircle of radius. Thus, the work is W, ft lb,. ft lb. Ground level
27 Section. Work. The lower feet of chain are raised feet with a constant force. W ft lb The top feet will be raised with variable force. Weight of section: Distance: W d W W W 7 7 ft lb 7 ft lb. The work required to lift the chain is 7. ft lb (from Eercise ). The work required to lift the -pound load is W 7. The work required to lift the chain with a -pound load attached is W ft lbs. W d ft lb. Work to pull up the ball: W, ft lb. Work to pull up the cable: force is variable Weight per section: Distance: W d ft lb p k V k W k V dv ln V ln 7. ft lb W W W,, ft lb. (a) (b) W FD, ft lbs W,,,,,. ft lb (c) F,.,. 7,7.,..7, (d) F when. feet. F is a maimum when. feet. (e) W F d,. ft lbs. W e d, ft lb. W sinh d 7. ft lb
28 Chapter Applications of Integration Section. Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids The center of mass is translated k units as well.. (Person on left) feet.,, m (, ). m (, ) m (, ). 7. 7, 7, 7 m (, ) m (, ) m (, ) m (, ). m M M m M M m d d d d d ( ),,,
29 Section. Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids. m M M m M M m,, d d d d d (, ). m d 7 d M M d d d d d d M m ; M m,, (, ) ( ), (, )
30 Chapter Applications of Integration. m d B smmetr, M and. M d (, ),, 7. m M M M m d d d (, ). M m,, m M M M m d d d d d (, ) M m,,. A M M d ln ln d d
31 . A M d d M b smmetr. d d Section. Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids. m M M e e d.7 e d e d.7 e d.7 (, ) M m. M m.. Therefore, the centroid is.,.. m M M m d. d. b smmetr. Therefore, the centroid is,.. d.. A bh ac A ac ac ac c ab c a d ac ab c c a ac c b c a b c d c c c, b a, c c b c a b c d ac abc a c b a This is the point of intersection of the diagonals. = c b (, ) ( b, c) (, ) ( a + b, c) ( a, ) = c b ( a)
32 Chapter Applications of Integration. b smmetr. A r A r r r,, r r r d r r r r r r r A d A,, 7 d d d d d 7 r r. (a) M b smmetr (c) M n b because b n is an odd function. M n b n b b n n b n b b n bnn n n n bnn A n b n b b n d b n b n n b d n b b n d n b b n n b b n bnn n n b n b n n bnn M A n bnn n n n b nn n n b b n d (b) > b because there is more area above b than below. (d) n n (e) lim lim n n n b b (f) As n, the figure gets narrower. n b b b = n n b 7 b = b 7b
33 Section. Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids. Let f be the top curve, given b l d. The bottom curve is d..... f...7. (a) d.... Area f d d M.7... f.7.77 M A.77.,,.7 f d f d d f d d.7 (b) f...7 (c) d..7. M A,,. d.... Centroids of the given regions: and Area: A ,,,, 7 7 7, m m m,,. m 7 7, P, 7 m 7 7 B smmetr,. 7, P, m , m,,,.
34 Chapter Applications of Integration. Centroids of the given regions:, and,. V ra Mass:,,.,. A d M d d (, ) Let u, u, du d: u u du M M A 7 7 u u du u u (, ) r V ra.. A planar lamina is a thin flat plate of constant densit. The center of mass, is the balancing point on the lamina.. Let R be a region in a plane and let L be a line such that L does not intersect the interior of R. If r is the distance between the centroid of R and L, then the volume V of the solid of revolution formed b revolving R about L is V ra where A is the area of R.. The centroid of the circle is,. The distance traveled b the centroid is. The arc length of the circle is also. Therefore, S. C d
35 Section.7 Fluid Pressure and Fluid Force 7 Section.7 Fluid Pressure and Fluid Force. F PA. lb. F.h.h.,. lb. h. L F. d.. Force is one-third that of Eercise. d 7. lb h L F. d.. lb. h L F. d. d. 7. lb. h L lower part L upper part F d,, d +, Newtons
36 Chapter Applications of Integration. h. L F d 7, Newtons h L F.7 d.7 d.7 7. lb. h L F.7 d.7 d (, ).7.7. lb. h L F d The second integral is zero since it is an odd function and the limits of integration are smmetric to the origin. The first integral is twice the area of a semicircle of radius. Thus, the force is.7. lb. d d. (a) F wkr lbs. (a) (b) F wkr. lbs F wkhb. lbs (b) F wkhb. 7, lbs
37 Review Eercises for Chapter. From Eercise : F 7. lb. h. Solving for, ou obtain. L F. d. d. lb h L 7 7 F. 7 d.7 d 7.7 lb. Fluid pressure is the force per unit of area eerted b a fluid over the surface of a bod.. The left window eperiences the greater fluid force because its centroid is lower. Review Eercises for Chapter. A d. (, ) (, ) A d d d (, ) (, )
38 Chapter Applications of Integration. A d. d (, ) A csc d ln csc cot ln ln. π ( ) ( ) π,, (, ) π π π π π. A 7 cos d cos sin sin 7 ( ( ) 7π, ) π, d. Point of intersection is given b:.7..7 A d.7. π, ( ) (.7,.). A d. d. (, ) (, ) (, ) A d d (, ) (, )
39 . A d d A d (, ) (, ) Review Eercises for Chapter. (a) R t..7 t. e.t (b) R t. e.t Difference R t R t dt 7. billion dollars. (a) Shell V d (b) Shell V d d (c) Disk V d (d) Disk V d d 7
40 Chapter Applications of Integration. (a) Shell a V b a a d b a a a d b a a a a b (b) Disk V a b a a a ab b a a d (, b) a + b = (, b) a + b = ( a, ) ( a, ). Disk V d arctan. Disk V e d e d e e e. (a) Disk V d d (b) Shell u u d u du V d u u du u u u du 7 u7 u u
41 Review Eercises for Chapter. A bh a a. a a V a d a a a a a Since a, we have a. Thus, s d a. meters. a a a. Since f tan has f sec, this integral represents the length of the graph of tan from to. This length is a little over unit. Answers (b).. S d d. F k k k F W d in lb.7 ft lb. We know that dv galmin galmin dt 7. galft 7. ft min V r h h dv dt dh dt dv dt 7.. ftmin. Depth of water:.t Time to drain well: t minutes. gallons pumped Volume of water pumped in Eercise :.7 gallons.7 dh dt.7 7 Work 7 ft ton
42 Chapter Applications of Integration. (a) Weight of section of cable: Distance: W d, ft lb ft ton (b) Work to move pounds feet verticall: Total work work for drawing up the cable work of lifting the load ft ton ft ton 7 ft ton, ft lb ft ton.. b W F d a F,, W d d 7,, 7 ft lbs A d A d d d d (, ). A d A d d (, ) 7 7,,
Math 122 Fall Solutions to Homework #5. ( ) 2 " ln x. y = x 2
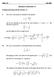 Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration
 Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids 7.7 Fluid Pressure
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids 7.7 Fluid Pressure
AP Calculus AB/BC ilearnmath.net
 CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
(a) Use washer cross sections: a washer has
 Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w
Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w
1993 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. C) 2
 Cal II- Final Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Epress the following logarithm as specified. ) ln 4. in terms of ln and
Cal II- Final Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Epress the following logarithm as specified. ) ln 4. in terms of ln and
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
Review Exercises for Chapter 3. Review Exercises for Chapter r v 0 2. v ft sec. x 1 2 x dx f x x 99.4.
 Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
2016 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration 1 = 80 0 = 80. dx 1 + x 2 = arctan x] k2
![2016 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration 1 = 80 0 = 80. dx 1 + x 2 = arctan x] k2 2016 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration 1 = 80 0 = 80. dx 1 + x 2 = arctan x] k2](/thumbs/96/127235785.jpg) 6 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration. A. 3 3 7 6 6 3 ] 3 6 6 3. B. For quadratic functions, Simpson s Rule is eact. Thus, 3. D.. B. lim 5 3 + ) 3 + ] 5 8 8 cot θ) dθ csc θ ) dθ cot θ θ + C n k n + k n lim
6 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration. A. 3 3 7 6 6 3 ] 3 6 6 3. B. For quadratic functions, Simpson s Rule is eact. Thus, 3. D.. B. lim 5 3 + ) 3 + ] 5 8 8 cot θ) dθ csc θ ) dθ cot θ θ + C n k n + k n lim
1993 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
Practice Questions From Calculus II. 0. State the following calculus rules (these are many of the key rules from Test 1 topics).
 Math 132. Practice Questions From Calculus II I. Topics Covered in Test I 0. State the following calculus rules (these are many of the key rules from Test 1 topics). (Trapezoidal Rule) b a f(x) dx (Fundamental
Math 132. Practice Questions From Calculus II I. Topics Covered in Test I 0. State the following calculus rules (these are many of the key rules from Test 1 topics). (Trapezoidal Rule) b a f(x) dx (Fundamental
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability
 1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: Unlimited and Continuous! (21 points)
 BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: United and Continuous! ( points) For #- below, find the its, if they eist.(#- are pt each) ) 7 ) 9 9 ) 5 ) 8 For #5-7, eplain why
BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: United and Continuous! ( points) For #- below, find the its, if they eist.(#- are pt each) ) 7 ) 9 9 ) 5 ) 8 For #5-7, eplain why
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (169 points)
 AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (69 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (69 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
CHAPTER 11 Vector-Valued Functions
 CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
MAC 2311 Chapter 5 Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function
 MAC Chapter Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
MAC Chapter Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Department of Mathematical x 1 x 2 1
 Contents Limits. Basic Factoring Eample....................................... One-Sided Limit........................................... 3.3 Squeeze Theorem.......................................... 4.4
Contents Limits. Basic Factoring Eample....................................... One-Sided Limit........................................... 3.3 Squeeze Theorem.......................................... 4.4
3 Applications of Derivatives Instantaneous Rates of Change Optimization Related Rates... 13
 Contents Limits Derivatives 3. Difference Quotients......................................... 3. Average Rate of Change...................................... 4.3 Derivative Rules...........................................
Contents Limits Derivatives 3. Difference Quotients......................................... 3. Average Rate of Change...................................... 4.3 Derivative Rules...........................................
Math 190 (Calculus II) Final Review
 Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
MA 114 Worksheet #01: Integration by parts
 Fall 8 MA 4 Worksheet Thursday, 3 August 8 MA 4 Worksheet #: Integration by parts. For each of the following integrals, determine if it is best evaluated by integration by parts or by substitution. If
Fall 8 MA 4 Worksheet Thursday, 3 August 8 MA 4 Worksheet #: Integration by parts. For each of the following integrals, determine if it is best evaluated by integration by parts or by substitution. If
( afa, ( )) [ 12, ]. Math 226 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION
![( afa, ( )) [ 12, ]. Math 226 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION ( afa, ( )) [ 12, ]. Math 226 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION](/thumbs/86/93981005.jpg) Math 6 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION A curve is rectifiable if it has a finite arc length. It is sufficient that f be continuous on [ab, ] in order for f to be rectifiable between
Math 6 Notes Section 7.4 ARC LENGTH AND SURFACES OF REVOLUTION A curve is rectifiable if it has a finite arc length. It is sufficient that f be continuous on [ab, ] in order for f to be rectifiable between
Chapter 6 Notes, Stewart 8e
 Contents 6. Area between curves........................................ 6.. Area between the curve and the -ais.......................... 6.. Overview of Area of a Region Between Two Curves...................
Contents 6. Area between curves........................................ 6.. Area between the curve and the -ais.......................... 6.. Overview of Area of a Region Between Two Curves...................
Math 1431 Final Exam Review. 1. Find the following limits (if they exist): lim. lim. lim. lim. sin. lim. cos. lim. lim. lim. n n.
 . Find the following its (if they eist: sin 7 a. 0 9 5 b. 0 tan( 8 c. 4 d. e. f. sin h0 h h cos h0 h h Math 4 Final Eam Review g. h. i. j. k. cos 0 n nn e 0 n arctan( 0 4 l. 0 sin(4 m. cot 0 = n. = o.
. Find the following its (if they eist: sin 7 a. 0 9 5 b. 0 tan( 8 c. 4 d. e. f. sin h0 h h cos h0 h h Math 4 Final Eam Review g. h. i. j. k. cos 0 n nn e 0 n arctan( 0 4 l. 0 sin(4 m. cot 0 = n. = o.
Chapter 2 Section 3. Partial Derivatives
 Chapter Section 3 Partial Derivatives Deinition. Let be a unction o two variables and. The partial derivative o with respect to is the unction, denoted b D1 1 such that its value at an point (,) in the
Chapter Section 3 Partial Derivatives Deinition. Let be a unction o two variables and. The partial derivative o with respect to is the unction, denoted b D1 1 such that its value at an point (,) in the
Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
1 x 3 3x. x 1 2x 1. 2x 1 2x 1. 2x 1 2x 1. x 2 +4x 1 j. lim. x3 +2x x 5. x2 9
 MATHEMATICS 57 Final Eamination Review Problems. Let f 5. Find each of the following. a. fa+b b. f f. Find the domain of each function. a. f b. g +. The graph of f + is the same as the graph of g ecept
MATHEMATICS 57 Final Eamination Review Problems. Let f 5. Find each of the following. a. fa+b b. f f. Find the domain of each function. a. f b. g +. The graph of f + is the same as the graph of g ecept
A = (cosh x sinh x) dx = (sinh x cosh x) = sinh1 cosh1 sinh 0 + cosh 0 =
 Calculus 7 Review Consider the region between curves y= cosh, y= sinh, =, =.. Find the area of the region. e + e e e Solution. Recall that cosh = and sinh =, whence sinh cosh. Therefore the area is given
Calculus 7 Review Consider the region between curves y= cosh, y= sinh, =, =.. Find the area of the region. e + e e e Solution. Recall that cosh = and sinh =, whence sinh cosh. Therefore the area is given
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions
 CHAPTER 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Differentiation.... 9 Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Integration...... 98
CHAPTER 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Differentiation.... 9 Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Integration...... 98
Math 113 (Calculus II) Final Exam KEY
 Math (Calculus II) Final Exam KEY Short Answer. Fill in the blank with the appropriate answer.. (0 points) a. Let y = f (x) for x [a, b]. Give the formula for the length of the curve formed by the b graph
Math (Calculus II) Final Exam KEY Short Answer. Fill in the blank with the appropriate answer.. (0 points) a. Let y = f (x) for x [a, b]. Give the formula for the length of the curve formed by the b graph
lim x c) lim 7. Using the guidelines discussed in class (domain, intercepts, symmetry, asymptotes, and sign analysis to
 Math 7 REVIEW Part I: Problems Using the precise definition of the it, show that [Find the that works for any arbitrarily chosen positive and show that it works] Determine the that will most likely work
Math 7 REVIEW Part I: Problems Using the precise definition of the it, show that [Find the that works for any arbitrarily chosen positive and show that it works] Determine the that will most likely work
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS
 SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
I. Degrees and Radians minutes equal 1 degree seconds equal 1 minute. 3. Also, 3600 seconds equal 1 degree. 3.
 0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
Math 2250 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions. f(x) = ln x x. 1 x. lim. lim. x x = lim. = lim 2
 Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
1. By the Product Rule, in conjunction with the Chain Rule, we compute the derivative as follows: and. So the slopes of the tangent lines to the curve
 MAT 11 Solutions TH Eam 3 1. By the Product Rule, in conjunction with the Chain Rule, we compute the derivative as follows: Therefore, d 5 5 d d 5 5 d 1 5 1 3 51 5 5 and 5 5 5 ( ) 3 d 1 3 5 ( ) So the
MAT 11 Solutions TH Eam 3 1. By the Product Rule, in conjunction with the Chain Rule, we compute the derivative as follows: Therefore, d 5 5 d d 5 5 d 1 5 1 3 51 5 5 and 5 5 5 ( ) 3 d 1 3 5 ( ) So the
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
2. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-2, 3), B(4, y), 2 3
 . Find an equation for the line that contains the points (, -) and (6, 9).. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-, ), B(4, y), m.. Find an equation for the line
. Find an equation for the line that contains the points (, -) and (6, 9).. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-, ), B(4, y), m.. Find an equation for the line
Answers to Some Sample Problems
 Answers to Some Sample Problems. Use rules of differentiation to evaluate the derivatives of the following functions of : cos( 3 ) ln(5 7 sin(3)) 3 5 +9 8 3 e 3 h 3 e i sin( 3 )3 +[ ln ] cos( 3 ) [ln(5)
Answers to Some Sample Problems. Use rules of differentiation to evaluate the derivatives of the following functions of : cos( 3 ) ln(5 7 sin(3)) 3 5 +9 8 3 e 3 h 3 e i sin( 3 )3 +[ ln ] cos( 3 ) [ln(5)
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
Review: A Cross Section of the Midterm. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review: A Cross Section of the Midterm Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the limit, if it eists. 4 + ) lim - - ) A) - B) -
Review: A Cross Section of the Midterm Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the limit, if it eists. 4 + ) lim - - ) A) - B) -
Chapter 8. Applications of Definite Integrals. π π. 1 and 2. The graph is. x 2x + 3 = 0 has no real solutions, since
 Chapter 8 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 8 Accumulation and Net Change (pp 8 96) Eploration Revisiting Eample t 8 st () 8 + + t + 8 s () 8+ + 8 s () 8+ + 6 and The graph is + + Section 8 7
Chapter 8 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 8 Accumulation and Net Change (pp 8 96) Eploration Revisiting Eample t 8 st () 8 + + t + 8 s () 8+ + 8 s () 8+ + 6 and The graph is + + Section 8 7
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 Chapter 5 Review 95 (c) f( ) f ( 7) ( 7) 7 6 + ( 6 7) 7 6. 96 Chapter 5 Review Eercises (pp. 60 6). y y ( ) + ( )( ) + ( ) The first derivative has a zero at. 6 Critical point value: y 9 Endpoint values:
Chapter 5 Review 95 (c) f( ) f ( 7) ( 7) 7 6 + ( 6 7) 7 6. 96 Chapter 5 Review Eercises (pp. 60 6). y y ( ) + ( )( ) + ( ) The first derivative has a zero at. 6 Critical point value: y 9 Endpoint values:
MATH 150/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions. Name Class. (a) (b) ln x (c) (a) (b) (c) 1 x. y e (a) 0 (b) y.
 90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
CHAPTER 4 Trigonometry
 CHAPTER Trigonometr Section. Radian and Degree Measure You should know the following basic facts about angles, their measurement, and their applications. Tpes of Angles: (a) Acute: Measure between 0 and
CHAPTER Trigonometr Section. Radian and Degree Measure You should know the following basic facts about angles, their measurement, and their applications. Tpes of Angles: (a) Acute: Measure between 0 and
Calculus 1 - Lab ) f(x) = 1 x. 3.8) f(x) = arcsin( x+1., prove the equality cosh 2 x sinh 2 x = 1. Calculus 1 - Lab ) lim. 2.
 ) Solve the following inequalities.) ++.) 4 >.) Calculus - Lab { + > + 5 + < +. ) Graph the functions f() =, g() = + +, h() = cos( ), r() = +. ) Find the domain of the following functions.) f() = +.) f()
) Solve the following inequalities.) ++.) 4 >.) Calculus - Lab { + > + 5 + < +. ) Graph the functions f() =, g() = + +, h() = cos( ), r() = +. ) Find the domain of the following functions.) f() = +.) f()
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS
 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
Virginia Tech Math 1226 : Past CTE problems
 Virginia Tech Math 16 : Past CTE problems 1. It requires 1 in-pounds of work to stretch a spring from its natural length of 1 in to a length of 1 in. How much additional work (in inch-pounds) is done in
Virginia Tech Math 16 : Past CTE problems 1. It requires 1 in-pounds of work to stretch a spring from its natural length of 1 in to a length of 1 in. How much additional work (in inch-pounds) is done in
CHAPTER 6 Differential Equations
 CHAPTER 6 Differential Equations Section 6. Slope Fields and Euler s Method.............. 55 Section 6. Differential Equations: Growth and Deca........ 557 Section 6. Separation of Variables and the Logistic
CHAPTER 6 Differential Equations Section 6. Slope Fields and Euler s Method.............. 55 Section 6. Differential Equations: Growth and Deca........ 557 Section 6. Separation of Variables and the Logistic
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models...................... Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................. Section
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models...................... Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................. Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine from the graph whether the function has an absolute etreme values on the interval
Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine from the graph whether the function has an absolute etreme values on the interval
Fitting Integrands to Basic Rules
 6_8.qd // : PM Page 8 8 CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8. Basic Integration Rules Review proceres for fitting an integrand to one of the basic integration
6_8.qd // : PM Page 8 8 CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8. Basic Integration Rules Review proceres for fitting an integrand to one of the basic integration
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
(c) cos Arctan ( 3) ( ) PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER
 PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
Fitting Integrands to Basic Rules. x x 2 9 dx. Solution a. Use the Arctangent Rule and let u x and a dx arctan x 3 C. 2 du u.
 58 CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8 Basic Integration Rules Review proceres for fitting an integrand to one of the basic integration rules Fitting Integrands
58 CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8 Basic Integration Rules Review proceres for fitting an integrand to one of the basic integration rules Fitting Integrands
EXERCISES Chapter 15: Multiple Integrals. Evaluating Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates
 08 Chapter 5: Multiple Integrals EXERCISES 5.6 Evaluating Integrals in Clindrical Evaluate the clindrical coordinate integrals in Eercises 6... 3. 4. 5. 6. Changing Order of Integration in Clindrical The
08 Chapter 5: Multiple Integrals EXERCISES 5.6 Evaluating Integrals in Clindrical Evaluate the clindrical coordinate integrals in Eercises 6... 3. 4. 5. 6. Changing Order of Integration in Clindrical The
2008 CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of Questions 28 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION
 8 CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of Questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION Directions: Solve each of the following problems. After eamining the form
8 CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of Questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION Directions: Solve each of the following problems. After eamining the form
Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers x for which f (x) is a real number.
 997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
Integrals. D. DeTurck. January 1, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Integrals 1 / 61
 Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Answer Key 1973 BC 1969 BC 24. A 14. A 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. C 28. D 29. C 30. D 31. C 13. C 12. D 12. E 3. A 32. B 27. E 34. C 14. D 25. B 26.
 Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
Math 1710 Final Review 1 1
 Math 7 Final Review. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove 3 (2 2 +)=4. 2. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove +7 2 + =3. 3. Use the ɛ-δ definition of it to prove (32 +5 ) = 3. 4. Prove that if f() =
Math 7 Final Review. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove 3 (2 2 +)=4. 2. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove +7 2 + =3. 3. Use the ɛ-δ definition of it to prove (32 +5 ) = 3. 4. Prove that if f() =
1. Find A and B so that f x Axe Bx. has a local minimum of 6 when. x 2.
 . Find A and B so that f Ae B has a local minimum of 6 when.. The graph below is the graph of f, the derivative of f; The domain of the derivative is 5 6. Note there is a cusp when =, a horizontal tangent
. Find A and B so that f Ae B has a local minimum of 6 when.. The graph below is the graph of f, the derivative of f; The domain of the derivative is 5 6. Note there is a cusp when =, a horizontal tangent
AP Calculus BC : The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 AP Calculus BC 415 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Tuesday, November 5, 008 Homework Answers 6. (a) approimately 0.5 (b) approimately 1 (c) approimately 1.75 38. 4 40. 5 50. 17 Introduction In
AP Calculus BC 415 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Tuesday, November 5, 008 Homework Answers 6. (a) approimately 0.5 (b) approimately 1 (c) approimately 1.75 38. 4 40. 5 50. 17 Introduction In
Calculus 1: A Large and In Charge Review Solutions
 Calculus : A Large and n Charge Review Solutions use the symbol which is shorthand for the phrase there eists.. We use the formula that Average Rate of Change is given by f(b) f(a) b a (a) (b) 5 = 3 =
Calculus : A Large and n Charge Review Solutions use the symbol which is shorthand for the phrase there eists.. We use the formula that Average Rate of Change is given by f(b) f(a) b a (a) (b) 5 = 3 =
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
C) 2 D) 4 E) 6. ? A) 0 B) 1 C) 1 D) The limit does not exist.
 . The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric equations = t, y = t t + are A) =, y = B) = only C) =, y = D) = only E) =, y =. What are the coordinates of the inflection point on the graph of y = ( +
. The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric equations = t, y = t t + are A) =, y = B) = only C) =, y = D) = only E) =, y =. What are the coordinates of the inflection point on the graph of y = ( +
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
Ex. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative exponents or complex fractions in your answers.
 CALCULUS AB THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS AND REVIEW E. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in your answers. 4 (a) y 4 e 5 f sin (b) sec (c) g 5 (d) y 4
CALCULUS AB THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS AND REVIEW E. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in your answers. 4 (a) y 4 e 5 f sin (b) sec (c) g 5 (d) y 4
Review Sheet for Exam 1 SOLUTIONS
 Math b Review Sheet for Eam SOLUTIONS The first Math b midterm will be Tuesday, February 8th, 7 9 p.m. Location: Schwartz Auditorium Room ) The eam will cover: Section 3.6: Inverse Trig Appendi F: Sigma
Math b Review Sheet for Eam SOLUTIONS The first Math b midterm will be Tuesday, February 8th, 7 9 p.m. Location: Schwartz Auditorium Room ) The eam will cover: Section 3.6: Inverse Trig Appendi F: Sigma
MATH 150/GRACEY EXAM 2 PRACTICE/CHAPTER 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 0/GRACEY EXAM PRACTICE/CHAPTER Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the indicated derivative. ) Find if = 8 sin. A) = 8
MATH 0/GRACEY EXAM PRACTICE/CHAPTER Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the indicated derivative. ) Find if = 8 sin. A) = 8
Math 122 Fall Handout 15: Review Problems for the Cumulative Final Exam
 Math 122 Fall 2008 Handout 15: Review Problems for the Cumulative Final Exam The topics that will be covered on Final Exam are as follows. Integration formulas. U-substitution. Integration by parts. Integration
Math 122 Fall 2008 Handout 15: Review Problems for the Cumulative Final Exam The topics that will be covered on Final Exam are as follows. Integration formulas. U-substitution. Integration by parts. Integration
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration
 Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.4 Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.4 Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 1300, Calculus 1
 Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 300, Calculus. For what values of is the graph of y = 5 5 both increasing and concave up? >. 2. Where does the tangent line to y = 2 through (0, ) intersect
Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 300, Calculus. For what values of is the graph of y = 5 5 both increasing and concave up? >. 2. Where does the tangent line to y = 2 through (0, ) intersect
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Third Annual NCMATYC Math Competition November 16, Calculus Test
 Third Annual NCMATYC Math Competition November 6, 0 Calculus Test Please do NOT open this booklet until given the signal to begin. You have 90 minutes to complete this 0-question multiple choice calculus
Third Annual NCMATYC Math Competition November 6, 0 Calculus Test Please do NOT open this booklet until given the signal to begin. You have 90 minutes to complete this 0-question multiple choice calculus
Chapter Start Thinking. 10π 31.4 cm. 1. 5π 15.7 cm 2. 5 π 7.9 cm π 13.1 cm Warm Up , 8π 2. 90,15π 3.
 x = 8andx = 7 8. x = andx = 7. x = 0. x = 10 x = 11. x = 18. x =. x = 8 x = 1. x = x = 1 8. x = 175. 0. 5 8.. 8. 1. 18 8. a. x + 11 b. c. 11 d. 17. (, ) 50. 5 15 7, 5, 11, 1 7, 5 1, 5 1 1, 11, 5 75 58.
x = 8andx = 7 8. x = andx = 7. x = 0. x = 10 x = 11. x = 18. x =. x = 8 x = 1. x = x = 1 8. x = 175. 0. 5 8.. 8. 1. 18 8. a. x + 11 b. c. 11 d. 17. (, ) 50. 5 15 7, 5, 11, 1 7, 5 1, 5 1 1, 11, 5 75 58.
Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test
 Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 3 Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test. f 8 3. 3, Decreasing on:, 3 3 3,,, Decreasing
Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 3 Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test. f 8 3. 3, Decreasing on:, 3 3 3,,, Decreasing
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE. MTH06 Review Sheet y 6 2x + 5 y.
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab
Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus
 Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Infinite Limits. Let f be the function given by. f x 3 x 2.
 0_005.qd //0 :07 PM Page 8 SECTION.5 Infinite Limits 8, as Section.5, as + f() = f increases and decreases without bound as approaches. Figure.9 Infinite Limits Determine infinite its from the left and
0_005.qd //0 :07 PM Page 8 SECTION.5 Infinite Limits 8, as Section.5, as + f() = f increases and decreases without bound as approaches. Figure.9 Infinite Limits Determine infinite its from the left and
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 --review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the area of the shaded region. ) f() = + - ) 0 0 (, 8) 0 (0, 0) - - - - - - -0
--review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the area of the shaded region. ) f() = + - ) 0 0 (, 8) 0 (0, 0) - - - - - - -0
Math 262 Exam 1 - Practice Problems. 1. Find the area between the given curves:
 Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
ANOTHER FIVE QUESTIONS:
 No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
Final Exam Review / AP Calculus AB
 Chapter : Final Eam Review / AP Calculus AB Use the graph to find each limit. 1) lim f(), lim f(), and lim π - π + π f 5 4 1 y - - -1 - - -4-5 ) lim f(), - lim f(), and + lim f 8 6 4 y -4 - - -1-1 4 5-4
Chapter : Final Eam Review / AP Calculus AB Use the graph to find each limit. 1) lim f(), lim f(), and lim π - π + π f 5 4 1 y - - -1 - - -4-5 ) lim f(), - lim f(), and + lim f 8 6 4 y -4 - - -1-1 4 5-4
171, Calculus 1. Summer 1, CRN 50248, Section 001. Time: MTWR, 6:30 p.m. 8:30 p.m. Room: BR-43. CRN 50248, Section 002
 171, Calculus 1 Summer 1, 018 CRN 5048, Section 001 Time: MTWR, 6:0 p.m. 8:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CRN 5048, Section 00 Time: MTWR, 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CONTENTS Syllabus Reviews for tests 1 Review
171, Calculus 1 Summer 1, 018 CRN 5048, Section 001 Time: MTWR, 6:0 p.m. 8:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CRN 5048, Section 00 Time: MTWR, 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CONTENTS Syllabus Reviews for tests 1 Review
y sin n x dx cos x sin n 1 x n 1 y sin n 2 x cos 2 x dx y sin n xdx cos x sin n 1 x n 1 y sin n 2 x dx n 1 y sin n x dx
 SECTION 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS 57 EXAPLE 6 Prove the reduction formula N Equation 7 is called a reduction formula because the eponent n has been reduced to n and n. 7 sin n n cos sinn n n sin n where
SECTION 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS 57 EXAPLE 6 Prove the reduction formula N Equation 7 is called a reduction formula because the eponent n has been reduced to n and n. 7 sin n n cos sinn n n sin n where
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
y=1/4 x x=4y y=x 3 x=y 1/3 Example: 3.1 (1/2, 1/8) (1/2, 1/8) Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded by y = 1 x and y = x3
 Eample: 3.1 Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded b 1 and 3 4 First find the points of intersection of the two curves: clearl the curves intersect at (, ) and at 1 4 3 1, 1 8 Select a strip at
Eample: 3.1 Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded b 1 and 3 4 First find the points of intersection of the two curves: clearl the curves intersect at (, ) and at 1 4 3 1, 1 8 Select a strip at
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND LOGS
 PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND LOGS Calculus Lesson- Derivatives of Eponentials and Logs Name: Date: Objective: to learn how to find the derivative of an eponential or logarithmic function Finding
PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND LOGS Calculus Lesson- Derivatives of Eponentials and Logs Name: Date: Objective: to learn how to find the derivative of an eponential or logarithmic function Finding
Integration. 5.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration. Suppose that f(x) = 5x 4. Can we find a function F (x) whose derivative is f(x)?
 5 Integration 5. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Suppose that f() = 5 4. Can we find a function F () whose derivative is f()? Definition. A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval
5 Integration 5. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Suppose that f() = 5 4. Can we find a function F () whose derivative is f()? Definition. A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
