CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
|
|
|
- Blanche McLaughlin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change Section P. Functions and Their Graphs Section P. Fitting Models to Data Review Eercises Problem Solving
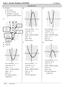
2 CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models.. 9 -intercept:, -intercepts:,,, -intercept:, -intercept:, Matches graph. Matches graph (d)... -intercepts:,,, -intercepts:,,,,, -intercept:, -intercept:, Matches graph (a). Matches graph (, 7) (, ) (, ) 8 8 (, ) 8 (, ) (, ) 8 (, ) (, ) (, ) (, )
3 ) Section P. Graphs and Models 9.. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 8 (9, ) (, ) (, ) 8.. Undef. Undef. ), ) (, ) (, ), ) (, ) (, ) ), ) ), ) (, ), ), ) (, ) ) ). Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl =. Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl = Note that when. Note that when or.
4 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 7. (., ) (,.7) (a),,.7,,.7 (a).,.,.7,., and,, 9.. -intercept: ;, -intercept: ;, -intercepts: -intercepts:, ;,,,, ±;,, ±,.. -intercept: ;, -intercept: ;, -intercepts: -intercept: ;,, ±;, ; ±,.. -intercept: None. cannot equal. -intercept: ;, -intercept: -intercepts: ;,, ;,,,. -intercept: ;, -intercept: ;,
5 Section P. Graphs and Models. -intercept: ;, 7. Smmetric with respect to the -ais since. -intercept: Note: ± ;, is an etraneous solution. 8. No smmetr with respect to either ais or the origin. 9. Smmetric with respect to the -ais since.. Smmetric with respect to the origin since. Smmetric with respect to the origin since... Smmetric with respect to the -ais since.. No smmetr with respect to either ais or the origin.. Smmetric with respect to the origin since.. Smmetric with respect to the origin since.. is smmetric with respect to the -ais since. 7. is smmetric with respect to the -ais since. 8. is smmetric with respect to the -ais 9. since. Intercepts:,,, Smmetr: none (, ),
6 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus... Intercepts:,,, Intercepts: 8,,, Intercepts:,,, Smmetr: none Smmetr: none Smmetr: none (, ) (, ) 8 (, ) (8, ) 8 (, ) (, )... Intercepts: Intercept:, Intercepts:,,,,, Smmetr: -ais,,, 9 Smmetr: -ais Smmetr: none (, ) (, ) (, ) 9 (, ) (, 9) 8 8 (, ) Intercepts:,,, Intercepts:,,, Intercepts:,,,,, Smmetr: none Smmetr: none Smmetr: origin ( ), (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 9.. Intercepts:,,, Smmetr: none Domain: (, ) (, ) 9 Intercepts:,,,,, Smmetr: -ais Domain:, (, ) (,) (, )
7 Section P. Graphs and Models 7.. Intercept:, Smmetr: origin. Intercepts:,,,,, Smmetr: -ais Intercepts: none Smmetr: origin (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). Intercept:, Smmetr: -ais.. Intercepts:,,,,, Smmetr: -ais Intercepts:,,, Smmetr: none (, ) 8 (, ) 8 (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) ± 9 Intercepts:,,,, 9, Smmetr: -ais (, ) ( 9, ) (, ) ± Intercepts:,,,,,,, Smmetr: origin and both aes Domain:, (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 9. Intercepts: Smmetr: -ais,,,,, ± (, ) (, ) (, ) 8. 8 Intercept: 8 ± 8, Smmetr: -ais 8 (, ). The corresponding -value is. Point of intersection:,
8 8 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus.. 7 The corresponding -value is., The corresponding -values are (for ) and (for ). Points of intersection:,,, Point of intersection:,.. or The corresponding -values are and. Points of intersection:,,, or The corresponding -values are and. Points of intersection:,,, or The corresponding -values are and. Points of intersection:,,,,, or The corresponding -values are,, and. Points of intersection:,,,,, or The corresponding -values are and. Points of intersection:,,,,,,,,,, = + (, ) (, ) (, ) 8 = +
9 Section P. Graphs and Models ,,,,,,, = + (, ) (, ) (, ) = = + (, ) 7 = (, ) Points of intersection: Analticall,,,,,.,,,,.7 7. Points of intersection:, Analticall,,, 7 (, ) = (, ) 8 = - + or or. Hence,,,,. 7. (a) Using a graphing utilit, ou obtain.7t.8t.. 7. (a).t.t 7 For, t and 7. For, t and.. 7 acres. 7. C R.,.9..9,..8,8,,.8,8.,, Use the Quadratic Formula. units The other root, 99, does not satisf the equation R C. This problem can also be solved b using a graphing utilit and finding the intersection of the graphs of C and R.
10 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 7.,77.7 If the diameter is doubled, the resistance is changed b approimatel a factor of. For instance,. and (other answers possible) 78. (other answers possible) 79. (i) k matches. Use, 7: 7 k k, thus,. (ii) k matches (d). Use, 9: 9 k k, thus,. (iii) k matches (a). Use, : k k, thus,. (iv) k matches. Use, : k k, thus,. 8. (a) If, is on the graph, then so is, b -ais smmetr. Since, is on the graph, then so is, b -ais smmetr. Hence, the graph is smmetric with respect to the origin. The converse is not true. For eample, has origin smmetr but is not smmetric with respect to either the -ais or the -ais. Assume that the graph has -ais and origin smmetr. If, is on the graph, so is, b -ais smmetr. Since, is on the graph, then so is,, b origin smmetr. Therefore, the graph is smmetric with respect to the -ais. The argument is similar for -ais and origin smmetr. 8. False; -ais smmetr means that if, is on the graph, then, is also on the graph. 8. True 8. True; the -intercepts are b ± b ac, a. 8. True; the -intercept is b a, Circle of radius and center, (, ) (, ) (, ) 8. Distance from the origin K Distance from, K, K K K K K K Note: This is the equation of a circle!
11 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change. m. m. m. m. m. m 7. m is undefined. 8. (, ) m = m = m = m = (, ) m = m = m = 9. m (, ) 7 (, ). m. m. m undefined (, ) (,) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). m (, ) (, ). m ( ) 7, 8 ( ),. Since the slope is, the line is horizontal and its equation is. Therefore, three additional points are,,,, and,.. Since the slope is undefined, the line is vertical and its equation is. Therefore, three additional points are,,,, and,. 7. The equation of this line is 7. Therefore, three additional points are and,.,,,, 8. The equation of this line is. Therefore, three additional points are and,.,,,,
12 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 9. (a) Slope ft ft B the Pthagorean Theorem,. feet.. (a) m indicates that the revenues increase b in one da. m indicates that the revenues increase b in one da. m indicates that the revenues do not change from one da to the net.. (a). (a) r Population (in millions) Year ( 99) t 8 t The slopes of the line segments are: The population increased least rapidl between and. The slopes are: The rate changed most rapidl between and seconds. The change is. mphsec... Therefore, the slope is m and the -intercept is,. Therefore, the slope is m and the -intercept is,... The line is vertical. Therefore, the slope is undefined and there is no -intercept. The line is horizontal. Therefore, the slope is m and the -intercept is, (, ) (, )
13 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change (, ) (, ) (, ).. m. m (, ) 8 (, ) (, ) 8 8 (, ) 8 (,). m (, ) (, ). m (, ) (, ) m (, 8) 8 (, ) 8. m 9. m 8 Undefined 7 (, ) Vertical line (, ) (, 8) (, )
14 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. m. m 7. m (, ) (, ) 7 (, ) (, ) 7 ( ) 7, 8 ( ),.. m b a (, ) b a b b b a a b (, b) ( a, ).. 7. a a a a a a 8. a 9. a a a. a a
15 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change... (, ) (a) The lines do not appear perpendicular. The lines appear perpendicular. The lines are perpendicular because their slopes and are negative reciprocals of each other. You must use a square setting in order for perpendicular lines to appear perpendicular. Answers depend on calculator used. 8. (a) The lines do not appear perpendicular. The lines appear perpendicular. The lines are perpendicular because their slopes and are negative reciprocals of each other. You must use a square setting in order for perpendicular lines to appear perpendicular. Answers depend on calculator used (a) m (a) 7 m
16 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus (a) m 7 8 (a) m The given line is vertical.. (a) (a). The slope is. V when t.. The slope is.. V when t. V t t V.t.t 8 7. The slope is. V, when t. 8. The slope is. V, when t. V t, t 8, V t, t 7, 9. (, ) 7., (, ) (, ) (, ) 9 9 You can use the graphing utilit to determine that the points of intersection are, and,. Analticall,,,. The slope of the line joining, and, is m. Hence, an equation of the line is. You can use the graphing utilit to determine that the points of intersection are, and,. Analticall,,,. The slope of the line joining, and, is m. Hence, an equation of the line is.
17 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change 7 7. m 7. m m m m m The points are not collinear. m m The points are not collinear. 7. Equations of perpendicular bisectors: c c a b c a b c Setting the right-hand sides of the two equations equal and solving for ields. Letting in either equation gives the point of intersection:, a b c c. a b ( b, c) b a This point lies on the third perpendicular bisector,. ( ) (, ) b a, c a b c ( a, ) ( a, ) 7. Equations of medians: c b Solving simultaneousl, the point of intersection is b, c. c a a b c a a b 7. Equations of altitudes: a b a c b a b a c Solving simultaneousl, the point of intersection is b, a b c. ( ) b a, c ( a, ) ( b, c) ( ) a + b, c (, ) ( a, ) ( a, ) ( b, c) ( a, ) 7. The slope of the line segment from to b, a b b is:, c c m a b c c b b a b c c b The slope of the line segment from to, a b c b is:, c c a b c bc m a b c c c b m m Therefore, the points are collinear. a b c c c b a b c bc
18 8 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 77. Find the equation of the line through the points, 78. and,. m 8 9 F 9 C C. If 7, C.7 $9.8. or F 9C For F 7, C.. F 9 C C 9F 79. (a) W.7. W. 9. Using a graphing utilit, the point of intersection is Analticall,, 7. (, 7) Both jobs pa $7 per hour if units are produced. For someone who can produce more than units per hour, the second offer would pa more. For a worker who produces less than units per hour, the first offer pas more. 8. (a) Depreciation per ear: 87 $ where $ ears 8. (a) Two points are, 8 and 7,. The slope is 8. (a) quiz score, test score m 8 7. p 8 p 7 8 or p If 7, (d) The slope shows the average increase in eam score for each unit increase in quiz score. (e) The points would shift verticall upward units. The new regression line would have a -intercept greater than before: If p, units. If p 9, 9 9 units.
19 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change 9 8. The tangent line is perpendicular to the line joining the point, and the center,. 8. The tangent line is perpendicular to the line joining the point, and the center of the circle,,. (, ) (, ) 8 (, ) (, ) Slope of the line joining, and, is. The equation of the tangent line is 9. 9 Slope of the line joining, and, is. Tangent line: 8. d 8. d d 88. d A point on the line is,. The distance from the point, to is d. 9. A point on the line is,. The distance from the point, to is d If A, then B C is the horizontal line CB. The distance to, is d C B B C B A B C. A B If B, then A C is the vertical line CA. The distance to, is d C A A C A A B C. A B (Note that A and B cannot both be zero.) CONTINUED
20 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 9. CONTINUED The slope of the line A B C is AB. The equation of the line through, perpendicular to A B C is: B A A A B B B A B A The point of intersection of these two lines is: A B C A AB AC B A B A B AB B AB A B AC B AB A B C AB B BC AC B AB A B B A B A AB A AB A A B BC AB A () () (B adding equations () and ()) () () (B adding equations () and ()) BC AB A A B AC B AB, BC AB A point of intersection A B A B The distance between, and this point gives us the distance between, and the line A B C. d AC B AB A B BC AB A A B AC AB A AC B A A B A B C A B A B A B C A B A B BC AB B A B BC A B A B 9. m m d A B C A B m m 9 9 m m The distance is when m. In this case, the line contains the point,. (, ) 8
21 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change 9. For simplicit, let the vertices of the rhombus be,, a,, b, c, and a b, c, as shown in the figure. The slopes of the diagonals are then ( b, c) ( a + b, c) m and m c c a b b a. Since the sides of the rhombus are equal, and we have a b c, (, ) ( a, ) m m c a b c b a c b a c c. Therefore, the diagonals are perpendicular. 9. For simplicit, let the vertices of the quadrilateral be,, a,, b, c, and d, e, as shown in the figure. The midpoints of the sides are a,, a b, c, b d, c e and, d, e. ( ) d, e ( d, e) ( ) b + d, c + e ( b, c) ( ) a + b, c The slope of the opposite sides are equal: (, ) ( ) a, ( a, ) c a b a c e e b d d c b e a d c a b c e b d e a d Therefore, the figure is a paralleogram. 9. Consider the figure below in which the four points are collinear. Since the triangles are similar, the result immediatel follows. 9. If m m, then m m. Let L be a line with slope m that is perpendicular to L. Then m m. Hence, m m L and L are parallel. Therefore, L and L are also perpendicular. (, ) (, ) ( *, * ) ( *, * ) 97. True. a b c a b c b m a b 98. False; if m is positive, then m m is negative. b a c b a c a m b a m m
22 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Functions and Their Graphs. (a) Domain of f:. (a) Domain of Range of f: Domain of g: Range of g: f g f g for (d) f for (e) g for, and Range of g: f g f g for and (d) f for, (e) f: Range of f: Domain of g: g for. (a) f. (a) f f 9 f b b f 9 f, undefined (d) f (d) f. (a) g g g (d) gt t t t. (a) (d) g g 9 8 gc c c c c gt t t t t t 8t t 7. (a) f cos cos f f cos cos cos cos 8. (a) f sin f sin f sin 9. f f,. f f,. f f,. f f,
23 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs. h. Domain:, Range:, g. Domain:, Range:, t f t sec t k t k Domain: all t k, k an integer Range:,,. ht cot t 7. Domain: all t k, k an integer Range:, f Domain:,, Range:,, 8. g Domain:,, Range:,, 9. f. and and Domain: f. Domain: or Domain:,, g cos cos cos Domain: all n, n an integer. h sin. f. g sin Domain: all n, n, n integer sin Domain: all Domain: all ±. f, <,. f,, > (a) f (a) f f f f f (d) f t t t (d) f s s s 8s (Note: t for all t) (Note: s > for all s) Domain:, Domain:, Range:,, Range:,
24 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 7. f (a), <, f 8. f,, > (a) f f f f f (d) f b b b (d) f Domain:, Domain:, Range:,, Range:, 9. f. g. h Domain:, Domain:,, Domain:, Range:, Range:,, Range:, 8. f. f 9. f Domain:, Domain:, Domain:, Range:, Range:, Range:,,.8 8 -intercept:, -intercept:, (, ( (, ). gt sin t. Domain:, Range:, t h cos Domain:, Range:, π π θ
25 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs 7. The student travels during the first mimin 8. minutes. The student is stationar for the following minutes. Finall, the student travels mimin during the final minutes. d t t t t 9. ±. is not a function of. Some vertical lines intersect the graph twice. is a function of. Vertical lines intersect the graph at most once.. is a function of. Vertical lines intersect the graph at most once.. ± is not a function of. Some vertical lines intersect the graph twice.. ±. is not a function of since there are two values of for some. is a function of since there is one value of for each.. ±. is not a function of since there are two values of for some. is a function of since there is one value of for each. 7. f is a horizontal shift 8. f is a vertical shift 9. f is a reflection in units to the left. Matches d. units downward. Matches b. the -ais, a reflection in the -ais, and a vertical shift downward units. Matches c.. f is a horizontal. f is a horizontal. f is a horizontal shift units to the right, followed b a reflection in the -ais. Matches a. shift to the left units, and a vertical shift upward units. Matches e. shift to the right unit, and a vertical shift upward units. Matches g.. (a) The graph is shifted units to the left. The graph is shifted unit to the right. The graph is shifted units upward. 8 CONTINUED
26 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. CONTINUED (d) The graph is shifted units downward. (e) The graph is stretched verticall b a factor of. (f) The graph is stretched verticall b a factor of (a) g f g f g f g f g f Shift f right units 7 (, ) (, ) Shift f left units 7 (, ) (, ) Vertical shift upwards units (, ) (, ) (d) g f (e) g f (f) g f Vertical shift down unit g f g f g f g f (, ) (, ) (, ) ( ), ( ), (, ). (a) Vertical shift units upward Reflection about the -ais Horizontal shift units to the right. (a) h sin is a horizontal shift units to the left, followed b a vertical shift unit upwards. h sin is a horizontal shift unit to the right followed b a reflection about the -ais.
27 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs 7 7. (a) f g f g f g g f g (d) f g f (e) f g f (f ) g f g, 8. f sin, g (a) (d) (e) fg f sin fg f sin g f g g f gsin g fg f sin (f ) g f gsin sin 9. f, g. f g f g f, Domain:, g f g f g Domain:, No. Their domains are different. f g g f for. f, g cos f g fg f cos cos Domain:, g f g cos Domain:, No, f g g f.. f, g f g f g f Domain: all ± g f g f g 9 9 Domain: all No, f g g f.. f g f Domain:, g f g You can find the domain of g f b determining the intervals where and are both positive, or both negative Domain:,,,. (a) f g fg f g f g g f g, which is undefined (d) f g fg f (e) g f g f g (f ) fg f, which is undefined
28 8 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. A rt Art A.t.t.t A rt represents the area of the circle at time t.. F Let h, g and f. Then, f g h fg f F. [Other answers possible]. F sin Let f, g sin and h. Then, f g h fg fsin sin F. [Other answers possible] 7. f f 8. Even f f Odd 9. f cos cos f Odd 7. f sin sin sin sin sin sin Even 7. (a) If f is even, then is on the graph., 7. (a) If f is even, then, 9 is on the graph. If f is odd, then, is on the graph. If f is odd, then, 9 is on the graph. 7. f is even because the graph is smmetric about the -ais. g is neither even nor odd. h is odd because the graph is smmetric about the origin. 7. (a) If f is even, then the graph is smmetric about the - ais. If f is odd, then the graph is smmetric about the origin. f f 7. Slope (, ) f, (, )
29 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs 9 7. Slope (, ) (, ) 77. f, f, 78. f, 79. Matches (ii). The function is g c. Since, 8. Matches (i). The function is f c. Since, satisfies the equation, c. Thus, g. satisfies the equation, c. Thus, f. 8. Matches (iv). The function is r c, since it must be 8. Matches (iii). The function is h c. Since, undefined at. Since, satisfies the equation, satisfies the equation, c. Thus, h. c. Thus, r. 8. (a) T, T If Ht Tt, then the program would turn on (and off) one hour later. If Ht Tt, then the overall temperature would be reduced degree. 8. (a) For each time t, there corresponds a depth d. 8. (a) A Domain: t Range: d d t A acresfarm t 8. (a) H
30 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 87. f If <, then f. If <, then f. If, then f. Thus,, f,, < <. 88. p has one zero. p has three zeros. Ever cubic polnomial has at least one zero. Given p A B C D, we have p as and p as if A >. Furthermore, p as and p as if A <. Since the graph has no breaks, the graph must cross the -ais at least one time. p p 89. f a n n... a a a n n... a a f Odd 9. f a n n a n n... a a a n n a n n... a a f Even 9. Let F f g where f and g are even. Then F f g f g F. Thus, F is even. Let F f g where f and g are odd. Then Thus, F f g f g f g F. F is even. 9. Let F f g where f is even and g is odd. Then Thus, F f g f g f g F. F is odd. 9. (a) V Domain: < < The dimensions for maimum volume are cm. length and width volume The dimensions for maimum volume appear to be cm.
31 Section P. Fitting Models to Data 9. B equating slopes,, L. 9. False; let f. Then f f 9, but. 9. True 97. True, the function is even. 98. False; let f. Then f 9 and f. Thus, f f. 99. First consider the portion of R in the first quadrant:, and ; shown below. B smmetr, ou obtain the entire region R: (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) The area of this region is. The area of R is. [9th competition, Problem A, 988]. Let g c be a constant polnomial. Then fg fc and g f c. Thus, fc c. Since this is true for all real numbers c, f is the identit function: f. Section P. Fitting Models to Data. Quadratic function. Trigonometric function. Linear function. No relationship. (a),. (a) 9 Yes. The cancer mortalit increases linearl with increased eposure to the carcinogenic substance. If, then. No, the relationship does not appear to be linear. Quiz scores are dependent on several variables such as stud time, class attendance, etc. These variables ma change from one quiz to the net.
32 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus 7. (a) d.f or F.d. 8. (a) s 9.7t. F =. d+. The model fits well. If F, then d.. cm. The model fits well. If t., s. meterssecond. 9. (a) Using a graphing utilit,..8. r.88 correlation coefficient = (a) Linear model: H.t.9 8 The data indicates that greater per capita electricit consumption tends to correspond to greater per capita gross national product. The data for Hong Kong, Venezuela and South Korea differ most from the linear model. (d) Removing the data 8,.9,,.7 and 7, 7., ou obtain the model..8 with r.98. The fit is ver good. When t, H (a).t.t.887t..9t.7.97t.797. (a) S When, S 8.98 pounds. For t,. centsmile.. (a) Linear:.8t 8. Cubic:.89t.t.8t. 9 (d).8t.8t.7 9 The cubic model is better. (e) For t : Linear model 9. million Cubic model. million (f ) Answers will var.
33 Section P. Fitting Models to Data. (a) t.7s.9s.7. (a) The curve levels off for s <. If., horsepower. (d) t.s.s.8 (e) The model is better for low speeds.. (a) T.98 p. p.8p. 7. (a) Yes, is a function of t. At each time t, there is one and onl one displacement. The amplitude is approimatel.... For T F, p 8.9 pounds per square inch. (d) The model is based on data up to pounds per square inch. The period is approimatel.7... One model is. sint. (d) (.,.) (.7,.).9 8. (a) Ht 8..8 sin t.8 One model is Ct 8 7 sin t.. (d) The average in Honolulu is 8.. The average in Chicago is 8. (e) The period is months ( ear). (f ) Chicago has greater variabilit 7 > Answers will var.. Answers will var.
34 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus Review Eercises for Chapter P.,, -intercept -intercept., -intercept,,,, -intercepts., -intercept. and are both impossible. No intercepts., -intercept. Smmetric with respect to -ais since.. Smmetric with respect to -ais since Slope: -intercept:, Slope: -intercept:..... Slope: -intercept:, 8 7
35 Review Eercises for Chapter P... Domain:, Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl = Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl = 7 8 Point:, 8. 7 No real solution No points of intersection The graphs of and 7 do not intersect. 9. You need factors and.. Multipl b to obtain origin smmetr. k (a) k k and k k and 8 8 k an k will do! (d) k k. ( ), ( ),. 8 (7, ) (7, ). t t t 7 Slope 7 7 The line is vertical and has no slope.
36 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. t 8 t.. Horizontal line 9 t t t (, ) 8 8 (, ) 8 7. (, ) m is undefined. Line is vertical. (, ) 8 9. (a) Slope of line is (d) 7. (a) 7 m Slope of perpendicular line is. (d) m 9. The slope is 8. V 8t,. V 8, $99
37 Review Eercises for Chapter P 7. (a) C 9.t.t,..7t, R t t.7t, 7.t, t.8 hours to break even Not a function of since there are two values of for some. ±... 9 Function of since there is one value for for each. Function of since there is one value of for each. Not a function of since there are two values of for some f (a) f does not eist. f f,, 8. (a) f 8 (because ) f < f 9. (a) Domain: or,. f and g Range:, (a) f g Domain: all or,, Range: all or,, f g g f g Domain: all or, Range: all or,
38 8 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. (a) f c, c,, f c, c,, c c c c c c f c, c,, (d) f c, c,, c c c c c c. f (, ) (, ) (a) The graph of g is obtained from f b a vertical shift down unit, followed b a reflection in the -ais: g f The graph of g is obtained from f b a vertical shift upwards of and a horizontal shift of to the right. g f. (a) Odd powers: f, g, h Even powers: f, g, h h g h g f f The graphs of f, g, and h all rise to the right and fall to the left. As the degree increases, the graph rises and falls more steepl. All three graphs pass through the points,,,, and,. The graphs of f, g, and h all rise to the left and to the right. As the degree increases, the graph rises more steepl. All three graphs pass through the points,,,, and,. 7 will look like h, but rise and fall even more steepl. 8 will look like h, but rise even more steepl.. (a) f g h 8
39 Problem Solving for Chapter P 9. (a) Domain: < < A Maimum area is A. In general, the maimum area is attained when the rectangle is a square. In this case,.. For compan (a) the profit rose rapidl for the first ear, and then leveled off. For the second compan, the profit dropped, and then rose again later. 7. (a) (cubic), negative leading coefficient (quartic), positive leading coefficient (quadratic), negative leading coefficient (d), positive leading coefficient 8. (a)..7 7 The data point 7, is probabl an error. Without this point, the new model is (a) Yes, is a function of t. At each time t, there is one and onl one displacement. The amplitude is approimatel.... The period is approimatel.. One model is (d). (.,.) cos. t cos.7t.. (.,.) Problem Solving for Chapter P. (a) 8 Slope of line from, to, is Slope of tangent line is. Hence,. Center:, Radius: Slope of line from, to, is. Slope of tangent line is Hence,. 9 Tangent line (d) 9 9 Intersection:, 9 Tangent line
40 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. Let m be a tangent line to the circle from the point,. Then m m m Setting the discriminant b ac equal to zero, m m m m m m ± Tangent lines: and.. H,, < (a) H H H (d) H (e) H (f ) H
41 Problem Solving for Chapter P. (a) f f f (d) f (e) f f (f ) (g) f. (a) Domain: < < A A A m is the maimum. m, m Maimum of m at m, m.
42 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. (a) A Domain: < < 7 Maimum of 7 ft at ft, 7. ft. A 7 7 A 7 square feet is the maimum area, where ft and 7. ft. 7. The length of the trip in the water is, and the length of the trip over land is. Hence, the total time is T hours. 8. Let d be the distance from the starting point to the beach. Average speed distance time d d d 8 kmhr 9. (a) Slope 9. Slope of tangent line is less than. Slope. Slope of tangent line is greater than.. Slope.. Slope of tangent line is less than... (d) Slope h h f h f h h h h h, h (e) Letting h get closer and closer to, the slope approaches. Hence, the slope at, is.
43 Problem Solving for Chapter P. (, ) (a) (d) (e) Slope Slope Slope h h Slope of tangent line is greater than 9. Slope of tangent line is less than.. Slope.. f h f h h h h h h h h Slope of tangent line is greater than h, h h h. As h gets closer to, the slope gets closer to The slope is at the point,..... (a) 9 I I 9 ± I I ± 8., Circle of radius 8 and center,. 8
44 Chapter P Preparation for Calculus. (a) I ki k k 8 k If k, then is a vertical line. Assume k. 8 k k k k 8 k k k k k, Circle As k k becomes ver large, and k k. The center of the circle gets closer to,, and its radius approaches. If k,. d d (, ) (, ) (, ) Let. Then or. Thus,,,, and, are on the curve.. f (a) Domain: all Range: all f f f Domain: all, f f f f Domain: all, (d) The graph is not a line. It has holes at, and,.
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 PART I CHAPTER P Preparation for Calulus Setion P. Graphs and Models...................... Setion P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............. 7 Setion P. Funtions and Their Graphs.................
PART I CHAPTER P Preparation for Calulus Setion P. Graphs and Models...................... Setion P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............. 7 Setion P. Funtions and Their Graphs.................
CHAPTER 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
Review Exercises for Chapter 3. Review Exercises for Chapter r v 0 2. v ft sec. x 1 2 x dx f x x 99.4.
 Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Answers to All Exercises. Appendix C ( ) ( ) Section C.1 (page C7) APPENDICES. Answers to All Exercises Ans1
 Answers to All Eercises Ans Answers to All Eercises Appendi C Section C. (page C). Cartesian. Distance Formula. Midpoint Formula. ( h) + ( k) = r, center, radius. c. f. a. d. e. b. A: (, ); B: (, ); C:
Answers to All Eercises Ans Answers to All Eercises Appendi C Section C. (page C). Cartesian. Distance Formula. Midpoint Formula. ( h) + ( k) = r, center, radius. c. f. a. d. e. b. A: (, ); B: (, ); C:
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus
 Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER 3 Polynomial Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test
 Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 3 Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test. f 8 3. 3, Decreasing on:, 3 3 3,,, Decreasing
Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 3 Section 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test. f 8 3. 3, Decreasing on:, 3 3 3,,, Decreasing
CHAPTER 3 Graphs and Functions
 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
C H A P T E R 3 Polynomial Functions
 C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
 Review Eercises for Chapter 7 Review Eercises for Chapter. (a) Vertical stretch Vertical stretch and a reflection in the -ais Vertical shift two units upward (a) Horizontal shift two units to the left.
Review Eercises for Chapter 7 Review Eercises for Chapter. (a) Vertical stretch Vertical stretch and a reflection in the -ais Vertical shift two units upward (a) Horizontal shift two units to the left.
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
P.4 Lines in the Plane
 28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
Graphing Calculator Computations 2
 Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Sample Questions to the Final Exam in Math 1111 Chapter 2 Section 2.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs
 Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
CHAPTER 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
Chapter 1 Graph of Functions
 Graph of Functions Chapter Graph of Functions. Rectangular Coordinate Sstem and Plotting points The Coordinate Plane Quadrant II Quadrant I (0,0) Quadrant III Quadrant IV Figure. The aes divide the plane
Graph of Functions Chapter Graph of Functions. Rectangular Coordinate Sstem and Plotting points The Coordinate Plane Quadrant II Quadrant I (0,0) Quadrant III Quadrant IV Figure. The aes divide the plane
6.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing Algebra 2
 10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing Algebra Goal 1: Write functions in quadratic form Goal : Graph quadratic functions Goal 3: Solve quadratic equations b graphing. Quadratic Function: Eample 1:
10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing Algebra Goal 1: Write functions in quadratic form Goal : Graph quadratic functions Goal 3: Solve quadratic equations b graphing. Quadratic Function: Eample 1:
Math 121. Practice Questions Chapters 2 and 3 Fall Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint.
 Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
ZETA MATHS. Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
y = f(x + 4) a) Example: A repeating X by using two linear equations y = ±x. b) Example: y = f(x - 3). The translation is
 Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
/ =0. (c) Section P.3 Functions and Their Graphs. (c) g(-2) = 5-(-2) 2 = 5-4 = 1. (e) g(x) = 0 for x = -I, 1 and 2. 2.
 Section P,3 Functions and Their Graphs 3 Section P.3 Functions and Their Graphs. (a) Domain off." -4 < x < 4 ~ [-4, 4] Range off:-3 < y < 5 ~ [-3, 5] Domain of g: -3 < x < 3 ~ [-3, 3] Range of g: -4
Section P,3 Functions and Their Graphs 3 Section P.3 Functions and Their Graphs. (a) Domain off." -4 < x < 4 ~ [-4, 4] Range off:-3 < y < 5 ~ [-3, 5] Domain of g: -3 < x < 3 ~ [-3, 3] Range of g: -4
Chapter 2 Polynomial, Power, and Rational Functions
 Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
MATH 115: Final Exam Review. Can you find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (1.1)
 MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
18. (a) S(t) = sin(0.5080t- 2.07) (b) ~oo. (c)
 Review Exercises fr Chapter P 5 1. (a) T =.985 x 10-p - 0.01p + 5.8p + 1.1 50 18. (a) S(t) = 5.7 + 5.7 sin(0.5080t-.07) ~ 0 110 150 (c) Fr T = 00 F, p,~ 8.9 lb/in.. (d) The mdel is based n data up t 100
Review Exercises fr Chapter P 5 1. (a) T =.985 x 10-p - 0.01p + 5.8p + 1.1 50 18. (a) S(t) = 5.7 + 5.7 sin(0.5080t-.07) ~ 0 110 150 (c) Fr T = 00 F, p,~ 8.9 lb/in.. (d) The mdel is based n data up t 100
c) domain {x R, x 3}, range {y R}
 Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 0390) Final Exam Oct 2009
 Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
Review Exercises for Chapter 4
 0 Chapter Trigonometr Review Eercises for Chapter. 0. radian.. radians... The angle lies in Quadrant II. (c) Coterminal angles: Quadrant I (c) 0 The angle lies in Quadrant II. (c) Coterminal angles: 0.
0 Chapter Trigonometr Review Eercises for Chapter. 0. radian.. radians... The angle lies in Quadrant II. (c) Coterminal angles: Quadrant I (c) 0 The angle lies in Quadrant II. (c) Coterminal angles: 0.
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT. Dear future Calculus AB student
 AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
( 1 3, 3 4 ) Selected Answers SECTION P.2. Quick Review P.1. Exercises P.1. Quick Review P.2. Exercises P.2 SELECTED ANSWERS 895
 44_Demana_SEANS_pp89-04 /4/06 8:00 AM Page 89 SELECTED ANSWERS 89 Selected Answers Quick Review P.. {,,, 4,, 6}. {,, }. (a) 87.7 (b) 4.7 7. ;.7 9. 0,,,, 4,, 6 Eercises P.. 4.6 (terminating)..6 (repeating).
44_Demana_SEANS_pp89-04 /4/06 8:00 AM Page 89 SELECTED ANSWERS 89 Selected Answers Quick Review P.. {,,, 4,, 6}. {,, }. (a) 87.7 (b) 4.7 7. ;.7 9. 0,,,, 4,, 6 Eercises P.. 4.6 (terminating)..6 (repeating).
c) Words: The cost of a taxicab is $2.00 for the first 1/4 of a mile and $1.00 for each additional 1/8 of a mile.
 Functions Definition: A function f, defined from a set A to a set B, is a rule that associates with each element of the set A one, and onl one, element of the set B. Eamples: a) Graphs: b) Tables: 0 50
Functions Definition: A function f, defined from a set A to a set B, is a rule that associates with each element of the set A one, and onl one, element of the set B. Eamples: a) Graphs: b) Tables: 0 50
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
KEY IDEAS. Chapter 1 Function Transformations. 1.1 Horizontal and Vertical Translations Pre-Calculus 12 Student Workbook MHR 1
 Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
The standard form of the equation of a circle is based on the distance formula. The distance formula, in turn, is based on the Pythagorean Theorem.
 Unit, Lesson. Deriving the Equation of a Circle The graph of an equation in and is the set of all points (, ) in a coordinate plane that satisf the equation. Some equations have graphs with precise geometric
Unit, Lesson. Deriving the Equation of a Circle The graph of an equation in and is the set of all points (, ) in a coordinate plane that satisf the equation. Some equations have graphs with precise geometric
CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
CHAPTER 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
CHAPTER 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions
 CHAPTER 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Differentiation.... 9 Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Integration...... 98
CHAPTER 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Differentiation.... 9 Section 5. The Natural Logarithmic Function: Integration...... 98
Infinite Limits. Let f be the function given by. f x 3 x 2.
 0_005.qd //0 :07 PM Page 8 SECTION.5 Infinite Limits 8, as Section.5, as + f() = f increases and decreases without bound as approaches. Figure.9 Infinite Limits Determine infinite its from the left and
0_005.qd //0 :07 PM Page 8 SECTION.5 Infinite Limits 8, as Section.5, as + f() = f increases and decreases without bound as approaches. Figure.9 Infinite Limits Determine infinite its from the left and
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
1 k. cos tan? Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. 1. A sequence is defined by the recurrence relation u 2u 1, u 3.
 Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Lawrence High School s AP Calculus AB 2018 Summer Assignment
 s AP Calculus AB 2018 Summer Assignment To incoming AP Calculus AB students, To be best prepared for your AP Calculus AB course, you will complete this summer review assignment, which you will submit on
s AP Calculus AB 2018 Summer Assignment To incoming AP Calculus AB students, To be best prepared for your AP Calculus AB course, you will complete this summer review assignment, which you will submit on
Sample Final Exam Problems Solutions Math 107
 Sample Final Eam Problems Solutions Math 107 1 (a) We first factor the numerator and the denominator of the function to obtain f() = (3 + 1)( 4) 4( 1) i To locate vertical asymptotes, we eamine all locations
Sample Final Eam Problems Solutions Math 107 1 (a) We first factor the numerator and the denominator of the function to obtain f() = (3 + 1)( 4) 4( 1) i To locate vertical asymptotes, we eamine all locations
Chapter 6: Extending Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Etending Periodic Functions Lesson 6.. 6-. a. The graphs of y = sin and y = intersect at many points, so there must be more than one solution to the equation. b. There are two solutions. From
Chapter 6: Etending Periodic Functions Lesson 6.. 6-. a. The graphs of y = sin and y = intersect at many points, so there must be more than one solution to the equation. b. There are two solutions. From
STANDARD FORM is a QUADRATIC FUNCTION and its graph is a PARABOLA. The domain of a quadratic function is the set of all real numbers.
 EXERCISE 2-3 Things to remember: 1. QUADRATIC FUNCTION If a, b, and c are real numbers with a 0, then the function f() = a 2 + b + c STANDARD FORM is a QUADRATIC FUNCTION and its graph is a PARABOLA. The
EXERCISE 2-3 Things to remember: 1. QUADRATIC FUNCTION If a, b, and c are real numbers with a 0, then the function f() = a 2 + b + c STANDARD FORM is a QUADRATIC FUNCTION and its graph is a PARABOLA. The
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
Name Please print your name as it appears on the class roster.
 Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Practice for the Final Eam MAC 1 Sullivan Version 1 (2007) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
Practice for the Final Eam MAC 1 Sullivan Version 1 (2007) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
Math 123 Summary of Important Algebra & Trigonometry Concepts Chapter 1 & Appendix D, Stewart, Calculus Early Transcendentals
 Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. D) D: (-, 0) (0, )
 Midterm Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the domain and graph the function. ) G(t) = t - 3 ) 3 - -3 - - 3 - - -3
Midterm Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the domain and graph the function. ) G(t) = t - 3 ) 3 - -3 - - 3 - - -3
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. ( x x ) ( y y ) (1 7) ( 1 2) x x y y 100. ( 6) ( 3) x ( y 6) a. 101.
 Chapter Functions and Graphs... ( ) ( y y ) ( 7) ( ) y y y ( 6) ( ) 6 9 5 5 6y 6y 6y9 9 ( y ) y y Solution set:. 5. a. h, k 6, r ; ( ) [ y( 6)] ( ) ( y6) ( y6) b. ( ) ( y) [ ( )] ( y) So in the standard
Chapter Functions and Graphs... ( ) ( y y ) ( 7) ( ) y y y ( 6) ( ) 6 9 5 5 6y 6y 6y9 9 ( y ) y y Solution set:. 5. a. h, k 6, r ; ( ) [ y( 6)] ( ) ( y6) ( y6) b. ( ) ( y) [ ( )] ( y) So in the standard
Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions
 Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
For Thought. 3.1 Exercises 142 CHAPTER 3 POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. 1. False, the range of y = x 2 is [0, ).
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space. Coordinates in Space
 0_110.qd 11//0 : PM Page 77 SECTION 11. Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space 77 -plane Section 11. -plane -plane The three-dimensional coordinate sstem Figure 11.1 Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space
0_110.qd 11//0 : PM Page 77 SECTION 11. Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space 77 -plane Section 11. -plane -plane The three-dimensional coordinate sstem Figure 11.1 Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space
AP Calculus AB/BC ilearnmath.net
 CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
Mathematics. Mathematics 1. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN21000
 Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still Notes. For
Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still Notes. For
CHAPTER 6 Applications of Integration
 PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
CHAPTER 2 Functions and Their Graphs
 CHAPTER Functions and Teir Graps Section. Linear Equations in Two Variables............ 9 Section. Functions......................... 0 Section. Analzing Graps of Functions............. Section. A Librar
CHAPTER Functions and Teir Graps Section. Linear Equations in Two Variables............ 9 Section. Functions......................... 0 Section. Analzing Graps of Functions............. Section. A Librar
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
The Coordinate Plane. Circles and Polygons on the Coordinate Plane. LESSON 13.1 Skills Practice. Problem Set
 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
Basic Math Formulas. Unit circle. and. Arithmetic operations (ab means a b) Powers and roots. a(b + c)= ab + ac
 Basic Math Formulas Arithmetic operations (ab means ab) Powers and roots a(b + c)= ab + ac a+b c = a b c + c a b + c d = ad+bc bd a b = a c d b d c a c = ac b d bd a b = a+b ( a ) b = ab (y) a = a y a
Basic Math Formulas Arithmetic operations (ab means ab) Powers and roots a(b + c)= ab + ac a+b c = a b c + c a b + c d = ad+bc bd a b = a c d b d c a c = ac b d bd a b = a+b ( a ) b = ab (y) a = a y a
Unit 4 Practice Problem ANSWERS
 Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
C H A P T E R 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 C H A P T E R Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs........ 7 Section. Properties of Logarithms.................
C H A P T E R Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs........ 7 Section. Properties of Logarithms.................
Linear Equation Theory - 2
 Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Lesson º-60º-90º: 1 2, a: log 3 (5m) b: log 6. c: not possible d: log(10) = Degree 4; Graph shown at right.
 Lesson 9.1.1 9-. a: The shape would be stretched verticall. In other words, there would be a larger distance between the lowest and highest points of the curve. b: Each repeating section would be longer.
Lesson 9.1.1 9-. a: The shape would be stretched verticall. In other words, there would be a larger distance between the lowest and highest points of the curve. b: Each repeating section would be longer.
Section 2.5: Graphs of Functions
 Section.5: Graphs of Functions Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, ou will be able to: Sketch the graph of a piecewise function containing an of the librar functions. o Polnomial functions of degree
Section.5: Graphs of Functions Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, ou will be able to: Sketch the graph of a piecewise function containing an of the librar functions. o Polnomial functions of degree
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. 3Quadratics. Chapter 3. Objectives
 Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
1. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. b)
 Eam Review Unit 0:. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. (,),(,),(,),(5,) a) { }. For each of the following, sketch the relation and
Eam Review Unit 0:. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. (,),(,),(,),(5,) a) { }. For each of the following, sketch the relation and
5.6 RATIOnAl FUnCTIOnS. Using Arrow notation. learning ObjeCTIveS
 CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
MHF4U1 ASSIGNMENT CHAPTER 1
 K: /39 I: /35 A: /6 Multiple Choice [K: 1 mark each = 33 total marks] Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An equation representing a function that etends from
K: /39 I: /35 A: /6 Multiple Choice [K: 1 mark each = 33 total marks] Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An equation representing a function that etends from
6 p p } 5. x 26 x 5 x 3 5 x Product of powers property x4 y x 3 y 2 6
 Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Answer Explanations. The SAT Subject Tests. Mathematics Level 1 & 2 TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE
 The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
CHAPTER 2 Solving Equations and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
Special Mathematics Notes
 Special Mathematics Notes Tetbook: Classroom Mathematics Stds 9 & 10 CHAPTER 6 Trigonometr Trigonometr is a stud of measurements of sides of triangles as related to the angles, and the application of this
Special Mathematics Notes Tetbook: Classroom Mathematics Stds 9 & 10 CHAPTER 6 Trigonometr Trigonometr is a stud of measurements of sides of triangles as related to the angles, and the application of this
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question
 Midterm Review 0 Precalculu Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question ) A graph of a function g is shown below. Find g(0). (-, ) (-, 0) - -
Midterm Review 0 Precalculu Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question ) A graph of a function g is shown below. Find g(0). (-, ) (-, 0) - -
( ) ( ) SECTION 1.1, Page ( x 3) 5 = 4( x 5) = 7. x = = = x x+ 0.12(4000 x) = 432
 CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
Practice Final A. Miller Spring 89 Math Find the limits: a. lim x 1. c. lim x 0 (1 + x) 1/x. f. lim x 0
 Practice Final A. Miller Spring 89 Math 221 1. Find the limits: a. lim 1 ln() 1 b. lim 0 ln (3+ )2 9) c. lim 0 (1 + ) 1/ d. lim 2 +1 e e. lim 0 (sec()) 1 2 sec() 1 g. lim 0. 2. Find the integrals: a. ln(
Practice Final A. Miller Spring 89 Math 221 1. Find the limits: a. lim 1 ln() 1 b. lim 0 ln (3+ )2 9) c. lim 0 (1 + ) 1/ d. lim 2 +1 e e. lim 0 (sec()) 1 2 sec() 1 g. lim 0. 2. Find the integrals: a. ln(
APPENDIXES. B Coordinate Geometry and Lines C. D Trigonometry E F. G The Logarithm Defined as an Integral H Complex Numbers I
 APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
1 (C) 1 e. Q.3 The angle between the tangent lines to the graph of the function f (x) = ( 2t 5)dt at the points where (C) (A) 0 (B) 1/2 (C) 1 (D) 3
 [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Point 'A' lies on the curve y e and has the coordinate (, ) where > 0. Point B has the coordinates (, 0). If 'O' is the origin then the maimum area of the triangle AOB is (A)
[STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Point 'A' lies on the curve y e and has the coordinate (, ) where > 0. Point B has the coordinates (, 0). If 'O' is the origin then the maimum area of the triangle AOB is (A)
Selected Answers and Solutions Go to Hotmath.com for step-by-step solutions of most odd-numbered exercises free of charge.
 Go to Hotmath.com for step-b-step solutions of most odd-numbered eercises free of charge. CHAPTER Functions from a Calculus Perspective Chapter Get Read. - -. - - - -. - 7. = + 9. = ± - 7. = - - 9. D =
Go to Hotmath.com for step-b-step solutions of most odd-numbered eercises free of charge. CHAPTER Functions from a Calculus Perspective Chapter Get Read. - -. - - - -. - 7. = + 9. = ± - 7. = - - 9. D =
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
AP Calculus Summer Homework MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AP Calculus Summer Homework 2015-2016 Part 2 Name Score MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
AP Calculus Summer Homework 2015-2016 Part 2 Name Score MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
NEXT-GENERATION Advanced Algebra and Functions
 NEXT-GENERATIN Advanced Algebra and Functions Sample Questions The College Board The College Board is a mission-driven not-for-profit organization that connects students to college success and opportunit.
NEXT-GENERATIN Advanced Algebra and Functions Sample Questions The College Board The College Board is a mission-driven not-for-profit organization that connects students to college success and opportunit.
