M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
|
|
|
- Darcy Ashley Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H Q. Let A ( ) 4 and B 3 3 Compute (if possible) : AB and BA ( ) 4 AB 3 3 ( ) ( ) ( ) BA Q. Compute The determinant 3 3 Solution () : Using Sarrus Method (6+4+9) (++8) Solution () : Using The definition (6 ) (9 )+3(3 4) alfadhel@ksu.edu.sa
2 Q.3 Find all the elements of the conic section x y +x and sketch it. x x y x x+ y + ( (x ) y + ) The conic section is a parabola opens upwards. ( The vertex is V, ). 4a a 4. The focus is F (, + ) (,). The equation of the directrix is y y x y x 3 F 3 V y Q.4 Find the standard equation of the ellipse with vertex (,) and with foci (,) and (,), and then sketch it. The equation of the ellipse has the form (x h) a The center of the ellipse is the mid-point of the two foci. + (y k) b.
3 ( + The center is P, + ) (6,), hence h 6 and k. The two foci lie on a line parallel to the x-axis, hence a > b c is the distance between the center and one of the foci, hence c 4 a is the distance between the center (6,) and the vertex V (,), hence a 5. c a b 4 5 b b b 3. The equation of the ellipse is (x 6) 5 The other vertex is V (,). + (y ) 9. The end-points of the minor axis are W (6,5) and W (6, ) x 6 y W F P F V V 6 W Q.5 Solve by Cramer s Rule the following linear system ( ) ( ) ( ) A, A x, A 4 y 4 A 3 ( ) ( 3 ) ( 3) 5 A x (3 ) ( 3 4) 3 ( ) 5 A y 3 4 ( 4) (3 ) { x 3y 3 x + y 4 3
4 x A x 5 A 5 3 y A y A 5 5 The solution of the linear system is ( ) x y ( ) 3 4
5 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the Second Mid-Term Exam First semester H Q. Solve by Gauss Elimination method the linear system : x + 3y + z x y 3z 3 3x 4y z 5 The augmented matrix is 3 3 R 3 3 +R R +R 3 3R +R 3 6z z y +z y + y 7 R x+3y +z x 3+4 x+ x x The solution of the linear system is y. z Q. Compute the integrals : (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) xe x dx x+ (x+)(x 3) dx 4x(x +3) 3 dx x lnx dx x (x ) dx alfadhel@ksu.edu.sa 5
6 (a) Using integration by parts : u x du dx dv e x dx v e x xe x dx [xe x ] e x dx [xe x ] [ex ] [( e ) ( e )] [ e e ] (e ) (e ) e e+ (b) Using the method of partial fractions : x+ (x+)(x 3) A x+ + A x 3 x+ A (x 3)+A (x+) Put x : + A ( 3) 5A A 5 Put x 3 : 3+ A (3+) 4 5A A 4 5 ( x+ 4 ) (x+)(x 3) dx 5 x+ + 5 dx x 3 5 x+ dx+ 4 5 x 3 dx 5 ln x ln x 3 +c (c) Using the formula [f(x)] n f (x) dx [f(x)]n+ +c, where n n+ 4x(x +3) 3 dx (x +3) 3 4x dx (x +3) 4 +c 4 (d) Using integration by parts : u lnx du x dx dv x dx v x x lnx dx x x lnx x lnx x dx x dx x lnx x +c (e) Using the method of partial fractions : x (x ) A (x ) + A (x ) 6
7 x A (x )+A A x A +A Comparing the coefficients of both sides A A +A +A A ( ) x (x ) dx x + (x ) dx x dx+ (x ) x dx+ (x ) dx ln x + (x ) +c Q.3 (a) Sketch the region R determined by the curves : y x, x, x and y. (b) Find the area of the region R. (a) y x is a parabola opens upwards with vertex (,). x is a straight line parallel to the y-axis and passes through (,). x is a straight line parallel to the y-axis and passes through (,). y is the x-axis. 4 3 y x 3 x x (b) Area [ x x 3 dx 3 ]
8 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 3 Solution of the Final Exam First semester H 5 3 Q. (a) Compute AB and BA for A 3 3 and B (b) Compute the determinant 3 3. (c) Solve by Cramer s rule : 4x y x 3y 5 3 (a) AB BA (b) Solution (): Using Sarrus Method (3++6) (7+4+) 33 3 Solution (): R +R alfadhel@ksu.edu.sa 8
9 3R +R R +R 3 3 Solution (3) : Using the definition of the determinant (3 4) ( 6)+3 ( 9) + (c) Using Cramer s rule : ( ) ( ) ( ) 4 4 A, A 3 x, A 3 y A 4 3 (4 3) ( ) ( ) + A x 3 ( 3) ( ) 6 4 A y 4 (4 ) ( ) 8 x A x A y A y A The solution of the linear system is ( ) x y ( ) Q. (a) Find the standard equation of the ellipse with foci (,3) and (6,3) and the length of its major axis is, and then sketch it. (b) Find The elements of the conic section 9x 4y 6y 8x 43 (a) The standard equation of the ellipse is (x h) a The center P (h,k) is located between the two foci. ( +6 The center is P (h,k), 3+3 ) (,3) + (y k) b The major axis (where the two foci are located) is parallel to the x-axis, hence a > b. The length of the major axis equals means a a 5. 9
10 c is the distance between the two foci, hence c 4 c a b 6 5 b b b 3 The standard equation of the ellipse is (x ) 5 The vertices are V ( 3,3) and V (7,3) + (y 3) 9 The end-points of the minor axis are W (,6) and W (,) x y W F P F V 3 V W (b) 9x 4y 6y 8x 43 9x 8x 4y 6y 43 9(x x) 4(y +4y) 43 By completing the square 9(x x+) 4(y +4y +4) (x ) 4(y +) 36 9(x ) 36 (x ) 4 4(y +) 36 (y +) 9 The conic section is a hyperbola with transverse axis parallel to the x-axis. The ceneter is P (, ). a 4 a and b 9 b 3. c a +b c 3. The vertices are V (, ) and V (3, ).
11 ( The foci are F ) ( 3, and F + ) 3,. The equations of the asymptotes are L : y + 3 (x ) and L : y + 3 (x ) L L P F V V F 5 9x 4y 6y 8x 43 Q.3 (a) Compute the integrals : (i) x dx (ii) x lnx dx (iii) +6x+ (b) Find the area of the surface delimited by the curves : y, x, x 4 and y x+5. x (x+)(x ) dx (c) The region R between the curves y, y x, and y x + is rotated about the y-axis to form a solid of revolution S. Find the volume of S. (a) (i) x +6x+ dx f (x) Using the formula [f(x)] +a dx ( ) f(x) a tan +c a x dx +6x+ (x +6x+9)+ dx
12 (x+3) + dx tan (x+3)+c (ii) x lnx dx Using integration by parts u lnx dv x dx du x dx v x3 3 x lnx dx x3 3 lnx x 3 x 3 dx x3 3 lnx x dx x3 3 3 lnx 3 (iii) x (x+)(x ) dx Using the method of partial fractions (x+)(x ) A x+ + A x x 3 3 +c (x )(x+) dx (x+)(x ) A (x ) (x+)(x ) + A (x+) (x+)(x ) A (x )+A (x+) Put x then A A Put x then A A ( ) (x+)(x ) dx x+ + dx x x+ dx+ x dx ln x+ + ln x +c (b) y is the x-axis. x is the y-axis. x 4 is a straight line parallel to the y-axis and passes through (4,). y x+5 (y 5) x is the upper-half of the parabola with vertex (,5) and opens to the right
13 7 y x 5 5 x 4 4 Area 4 ( 3 (4) ( x+5 ) dx [x 3 ) 3 +5x ] 4 ( 3 ()3 +5 ) 3 [ ] 4 3 x3 +5x (8) (c) y x y x y is the x-axis. y x+ is a straight line passes through (,) and its slope is -. y x is a parabola opens upwards with vertex (,). Points of intersection of y x and y x+ : 3
14 x x+ x +x (x+)(x ) x, x Points of intersection are (,4) and (,). Using Washer Method : In this case y x+ x y + and y x x y Volume π ( ( y +) ( y) ) dy π [ ] y π (y 3 5y +4) dy π 3 5y +4y [( π 3 5 ) ] ( ) ( +) π 6 (4 4y +y y) dy 6 π Q.4 (a) Find f x and f y for the function f(x,y) x y 3 +ye x + x x+y (b) Solve the differential equation x dy dx y x e x (a) f x f x xy3 +ye x + (x+y) x(+) (x+y) xy 3 +ye x y + (x+y) f y 3x y +e x + (x+y) x(+) (x+y) 3x y +e x x (x+y) (b) x dy dx y x e x xy y x e x y x y xex It is a first-order linear differential equation. P(x) x and Q(x) xex The integrating factor is: u(x) P(x) dx e x dx e lnx e lnx x x The general solution of the differential equation is : y u(x) Q(x) dx u(x) x x xe x dx x x(e x +c) xe x +cx e x dx 4
15 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 4 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam Second semester H Q. Let A ( ) 4 and B 3 4 Compute (if possible) : AB and BA ( ) 4 AB 3 4 ( ) ( ) ( ) BA Q. Compute The determinant Solution () : Using Sarrus Method (6+8+) (3++8) Solution () : Using The definition (6 ) (9 4)+4(3 8) alfadhel@ksu.edu.sa 5
16 Q.3 Find all the elements of the conic section y 4y 4x+4 and sketch it. By completing the square y 4y 4x+4 y 4y +4 4x+4+4 y 4y +4 4x+8 (y ) 4(x+) The conic section is a parabola opens to the right. The vertex is V(,). 4a 4 a 4 4. The focus is F( +,) (,). The equation of the directrix is x 3 y 4y 4x 4 V F x 3 3 Q.4 Find the standard equation of the ellipse with vertex (,4) and with foci (,4) and (,4), and then sketch it. The equation of the ellipse has the form (x h) a + (y k) b. The center of the ellipse is the mid-point of the two foci. ( + The center is P, 4+4 ) (6,4), hence h 6 and k. 6
17 The two foci lie on a line parallel to the x-axis, hence a > b c is the distance between the center and one of the foci, hence c 4 a is the distance between the center (6,4) and the vertex V (,4), hence a 5. c a b 4 5 b b b 3. The equation of the ellipse is (x 6) 5 The other vertex is V (,4). + (y 4) 9. The end-points of the minor axis are W (6,7) and W (6,) 7 W x 6 5 y P V F F V W 6 Q.5 Solve by Cramer s Rule the following linear system { 4x 3y x + y 3 ( ) ( ) ( ) A, A x, A 3 y 3 A 4 3 (4 ) ( 3) 4 ( 6) 4+6 A x 3 3 ( ) (3 3) ( 9) +9 A y 4 3 (4 3) ( ) x A x A 7
18 y A y A The solution of the linear system is ( ) x y ( ) 8
19 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 5 Solution of the Second Mid-Term Exam Second semester H Q. Find the area of the surface bounded by the curves : y x + and y 3. y x + y x is a parabola opens upwards with vertex (,). y 3 is a straight line parallel to the x-axis and passes through (,3). Points of intersection of y x + and y 3 : x + 3 x x ±. y x 3 y 3 Area ] [x x3 3 [ 3 (x +) ] dx ( ) ( 3 3 ( x ) dx ) 3 ( ) Q. Compute the integrals : x+5 (a) (x+)(x+) dx x+3 (b) x +3x+6 dx 3 (c) x +x+5 dx 5 alfadhel@ksu.edu.sa 9
20 (d) (e) (f) 3x sin(x 3 +3) dx xcosx dx x(x +) 5 dx (a) x+5 (x+)(x+) dx Using the method of partial fractions: x+5 (x+)(x+) A x+ + A x+ x+5 A (x+)+a (x+) Put x : ( )+5 A ( +) A A Put x : ( )+5 A ( +) A +5 3 ( x+5 (x+)(x+) dx x+ + 3 ) dx x+ x+ dx+3 dx ln x+ +3ln x+ +c x+ (b) (c) x+3 x +3x+6 dx Using the formula f (x) f(x) dx ln f(x) +c x+3 x +3x+6 dx ln x +3x+6 +c 3 x +x+5 dx Using the formula 3 x +x+5 dx 3 3 tan ( x+ f (x) a +[f(x)] dx ( f(x) a tan a (x +x+)+4 dx 3 ) +c 3 tan ( x+ ) +c ) +c, where a > (x+) + dx (d) 3x sin(x 3 +3) dx
21 Using the formula sin(f(x)) f (x) dx cos(f(x))+c 3x sin(x 3 +3) dx sin(x 3 +3) (3x ) dx cos(x 3 +3)+c (e) xcosx dx Using integration by parts : u x dv cosx dx du dx v sinx xcosx dx xsinx sinx dx xsinx ( cosx)+c xsinx+cosx+c (f) x(x +) 5 dx Using the formula [f(x)] n f (x) dx [f(x)]n+ +c, where n n+ x(x +) 5 dx (x +) 5 (x) dx (x +) 6 +c 6 Q.3 Find the area of the srface bounded by the curves : y x, y and y x+ y x y x is the upper half of a parabola opens to the right with vertex (,). y x+ is a straight line passes through (,) with slope -. y is the x-axis. y x y x and y x+ x y + Points of intersection of x y and x y + : y y + y +y (y +)(y ) y, y
22 y x y x Area [( y +) y ] dy ( y y +) dy ( 3 ) + ( +) ] [ y3 3 y +y Another solution : Area [ 3 ] x dx+ ( x+) dx [ + ( +4) ( + )] [ x 3 3 ] ] + [ x +x
23 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 6 Solution of the Final Exam Second semester H Q. (a) Compute BA+AB for A and B 3 3 (b) Compute the determinant 3 4. x + y + z 3 (c) Solve by Gauss Elimination Method : x y z x + y z 3 (a) BA AB BA+AB (b) Using Sarrus Method (++) ( 6 9+) 4 ( 5) alfadhel@ksu.edu.sa 3
24 (c) Using Gauss Elimination Method 3 R+R 3 R +R 3 R +R z z y +z y + y 3 3 R x+y +z 3 x++ 3 x x The solution of the linear system is y z Q. Find all the elements of the two following conic sections and sketch their graphs : (a) 9y +4x +8y 8x 3 (b) 9x 4y 6y 8x 43 (a) 9y +4x +8y 8x 3 4x 8x+9y +8y 3 4(x x)+9(y +y) 3 By completing the square 4(x x+)+9(y +y +) (x ) +9(y +) 36 4(x ) + 36 (x ) + 9 9(y +) 36 (y +) 4 The conic sectionis an ellipse with center P (, ) a 9 a 3 and b 4 b c a b c 5 4
25 The vertices are V (, ) and V (4, ) The Foci are F ( 5, ) and F ( + 5, ) The end-points of the minor axis are W (,) and W (, 3) W V F P F V 3 W x y 9 4 (b) 9x 4y 6y 8x 43 9x 8x 4y 6y 43 9(x x) 4(y +4y) 43 By completing the square 9(x x+) 4(y +4y +4) (x ) 4(y +) 36 9(x ) 36 (x ) 4 4(y +) 36 (y +) 9 The conic section is a hyperbola with transverse axis parallel to the x-axis. The ceneter is P (, ). a 4 a and b 9 b 3. c a +b c 3. The vertices are V (, ) and V (3, ). ( The foci are F ) ( 3, and F + ) 3,. The equations of the asymptotes are L : y + 3 (x ) and 5
26 L : y + 3 (x ) L L F P V V F 5 9x 4y 6y 8x 43 Q.3 (a) Compute the integrals : (i) dx (ii) xsinx dx (iii) (x )(x+) (b) Find the area of the region delimited by the curves : y and y x +. x 4 x 4x+5 dx (c) The region R in the first quadrant lying between the curves y and y x is rotated about the x-axis to form a solid of revolution S. Find the volume of S. (a) (i) (x )(x+) dx Using the method of partial fractions (x )(x+) A x + A x+ A (x+)+a (x ) Put x : A A Put x : A A (x )(x+) x + x+ 6
27 (x )(x+) dx x dx (ii) xsinx dx x+ Using integration by parts ( x + ) x+ dx dx ln x ln x+ +c u x dv sinx dx du dx v cosx xsinx dx xcosx cosx dx xcosx+ cosx dx xcosx+sinx+c x 4 (iii) x 4x+5 dx Using the formula f (x) f(x) dx ln f(x) +c x 4 x 4x+5 dx ln x 4x+5 +c (b) y is a straight line parallel to the x-axis and passes through (,) y x + y x is a parabola with vertex (,) and opens upwards Points of intersection of y and y x + : x + x (x )(x+) x, x y x y Area ( 3 [ (x +) ] dx ) ( 3 ( x ) dx ) 3 ( ) ] [x x
28 (c) y is the x-axis. y x (y ) x is a parabola opens downwards with vertex (,). Points of intersection of y x and y : x x (x )(x+) x, x y x y Using Disk Method : Volume π [( π ( x ) dx π ) ] ( +) ( x +x 4 ) dx 5 +3 π π ] [x x 3 + x5 5 Q.4 (a) Find f x, f y and f z for the function f(x,y,z) x y 3 +z 5 ye y (b) Solve the differential equation xdy +y dx, y() (a) f x xy 3 + xy 3 f y x (3y )+z 5 ( e y +ye y ) 3x y +z 5 (e y +ye y ) f z +5z 4 ye y 5z 4 ye y (b) xdy +y dx x dy y dx y dy x dx y dy x dx It is a separable differential equation 8
29 y dy x dx y ln x +c y ln x +c The general solution of the differential equation is : y ln x +c y() ln()+c +c c c The particular solution of the differential equation is : y ln x + 9
M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
 M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
Circles. Example 2: Write an equation for a circle if the enpoints of a diameter are at ( 4,5) and (6, 3).
 Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conic Sections. Geometry - Conics ~1~ NJCTL.org. Write the following equations in standard form.
 Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Note: Final Exam is at 10:45 on Tuesday, 5/3/11 (This is the Final Exam time reserved for our labs). From Practice Test I
 MA Practice Final Answers in Red 4/8/ and 4/9/ Name Note: Final Exam is at :45 on Tuesday, 5// (This is the Final Exam time reserved for our labs). From Practice Test I Consider the integral 5 x dx. Sketch
MA Practice Final Answers in Red 4/8/ and 4/9/ Name Note: Final Exam is at :45 on Tuesday, 5// (This is the Final Exam time reserved for our labs). From Practice Test I Consider the integral 5 x dx. Sketch
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
ALGEBRA 2 X. Final Exam. Review Packet
 ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
Final Examination 201-NYA-05 May 18, 2018
 . ( points) Evaluate each of the following limits. 3x x + (a) lim x x 3 8 x + sin(5x) (b) lim x sin(x) (c) lim x π/3 + sec x ( (d) x x + 5x ) (e) lim x 5 x lim x 5 + x 6. (3 points) What value of c makes
. ( points) Evaluate each of the following limits. 3x x + (a) lim x x 3 8 x + sin(5x) (b) lim x sin(x) (c) lim x π/3 + sec x ( (d) x x + 5x ) (e) lim x 5 x lim x 5 + x 6. (3 points) What value of c makes
MTH 111, Math for Architects, Exam I, Summer 2013
 Name, ID Math for Architects MTH 111 summer 2013, 1 4 copyright Ayman Badawi 2013 MTH 111, Math for Architects, Exam I, Summer 2013 Ayman Badawi QUESTION 1. Given 12x = y 2 4y 20. Find the vertex, the
Name, ID Math for Architects MTH 111 summer 2013, 1 4 copyright Ayman Badawi 2013 MTH 111, Math for Architects, Exam I, Summer 2013 Ayman Badawi QUESTION 1. Given 12x = y 2 4y 20. Find the vertex, the
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
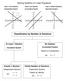 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Exam 3 Solutions. Multiple Choice Questions
 MA 4 Exam 3 Solutions Fall 26 Exam 3 Solutions Multiple Choice Questions. The average value of the function f (x) = x + sin(x) on the interval [, 2π] is: A. 2π 2 2π B. π 2π 2 + 2π 4π 2 2π 4π 2 + 2π 2.
MA 4 Exam 3 Solutions Fall 26 Exam 3 Solutions Multiple Choice Questions. The average value of the function f (x) = x + sin(x) on the interval [, 2π] is: A. 2π 2 2π B. π 2π 2 + 2π 4π 2 2π 4π 2 + 2π 2.
y 1 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 ) 2 A circle is a set of points P in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, called the center.
 Ch 12. Conic Sections Circles, Parabolas, Ellipses & Hyperbolas The formulas for the conic sections are derived by using the distance formula, which was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. If you know
Ch 12. Conic Sections Circles, Parabolas, Ellipses & Hyperbolas The formulas for the conic sections are derived by using the distance formula, which was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. If you know
Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material
 Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material Math114 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky April 26, 2017 Math114 Lecture 37 1/ 11 Outline 1 Conic Sections Math114 Lecture 37 2/ 11 Outline 1
Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material Math114 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky April 26, 2017 Math114 Lecture 37 1/ 11 Outline 1 Conic Sections Math114 Lecture 37 2/ 11 Outline 1
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
Math 10C - Fall Final Exam
 Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Spring 2015 Sample Final Exam
 Math 1151 Spring 2015 Sample Final Exam Final Exam on 4/30/14 Name (Print): Time Limit on Final: 105 Minutes Go on carmen.osu.edu to see where your final exam will be. NOTE: This exam is much longer than
Math 1151 Spring 2015 Sample Final Exam Final Exam on 4/30/14 Name (Print): Time Limit on Final: 105 Minutes Go on carmen.osu.edu to see where your final exam will be. NOTE: This exam is much longer than
Math 226 Calculus Spring 2016 Practice Exam 1. (1) (10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = f(x) have inverse function x = f 1 (y).
 Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Integration by Parts
 Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review.
 Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
5 t + t2 4. (ii) f(x) = ln(x 2 1). (iii) f(x) = e 2x 2e x + 3 4
 Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane
 3110 General Mathematics 1 31 10 General Mathematics For the students from Pharmaceutical Faculty 1/004 Instructor: Dr Wattana Toutip (ดร.ว ฒนา เถาว ท พย ) Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane Overview:
3110 General Mathematics 1 31 10 General Mathematics For the students from Pharmaceutical Faculty 1/004 Instructor: Dr Wattana Toutip (ดร.ว ฒนา เถาว ท พย ) Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane Overview:
3.4 Conic sections. Such type of curves are called conics, because they arise from different slices through a cone
 3.4 Conic sections Next we consider the objects resulting from ax 2 + bxy + cy 2 + + ey + f = 0. Such type of curves are called conics, because they arise from different slices through a cone Circles belong
3.4 Conic sections Next we consider the objects resulting from ax 2 + bxy + cy 2 + + ey + f = 0. Such type of curves are called conics, because they arise from different slices through a cone Circles belong
1. (5 points) Use the change-of-base formula to evaluate the following logarithm. Round your answer to four decimal places.
 Millersville University Name Answer Key Department of Mathematics MATH 160, Precalculus, Final Examination December 14, 2011, 10:15A-12:15P Please answer the following questions. Answers without justifying
Millersville University Name Answer Key Department of Mathematics MATH 160, Precalculus, Final Examination December 14, 2011, 10:15A-12:15P Please answer the following questions. Answers without justifying
Ch 9/10/11/12 Exam Review
 Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
Indefinite Integration
 Indefinite Integration 1 An antiderivative of a function y = f(x) defined on some interval (a, b) is called any function F(x) whose derivative at any point of this interval is equal to f(x): F'(x) = f(x)
Indefinite Integration 1 An antiderivative of a function y = f(x) defined on some interval (a, b) is called any function F(x) whose derivative at any point of this interval is equal to f(x): F'(x) = f(x)
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1
 Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
The Distance Formula. The Midpoint Formula
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
e x3 dx dy. 0 y x 2, 0 x 1.
 Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
SCORE. Exam 3. MA 114 Exam 3 Fall 2016
 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used. You may use a graphing
Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used. You may use a graphing
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
Solutions to Exam 2, Math 10560
 Solutions to Exam, Math 6. Which of the following expressions gives the partial fraction decomposition of the function x + x + f(x = (x (x (x +? Solution: Notice that (x is not an irreducile factor. If
Solutions to Exam, Math 6. Which of the following expressions gives the partial fraction decomposition of the function x + x + f(x = (x (x (x +? Solution: Notice that (x is not an irreducile factor. If
ECONOMICS 207 SPRING 2006 LABORATORY EXERCISE 5 KEY. 8 = 10(5x 2) = 9(3x + 8), x 50x 20 = 27x x = 92 x = 4. 8x 2 22x + 15 = 0 (2x 3)(4x 5) = 0
 ECONOMICS 07 SPRING 006 LABORATORY EXERCISE 5 KEY Problem. Solve the following equations for x. a 5x 3x + 8 = 9 0 5x 3x + 8 9 8 = 0(5x ) = 9(3x + 8), x 0 3 50x 0 = 7x + 7 3x = 9 x = 4 b 8x x + 5 = 0 8x
ECONOMICS 07 SPRING 006 LABORATORY EXERCISE 5 KEY Problem. Solve the following equations for x. a 5x 3x + 8 = 9 0 5x 3x + 8 9 8 = 0(5x ) = 9(3x + 8), x 0 3 50x 0 = 7x + 7 3x = 9 x = 4 b 8x x + 5 = 0 8x
Logs and Exponential functions e, ln, solving exponential functions, solving log and exponential equations, properties of logs
 Page 1 AM1 Final Exam Review Packet TOPICS Complex Numbers, Vectors, and Parametric Equations Change back and forth from and to polar and rectangular forms. Raise a term in polar form to a power (DeMoivre).
Page 1 AM1 Final Exam Review Packet TOPICS Complex Numbers, Vectors, and Parametric Equations Change back and forth from and to polar and rectangular forms. Raise a term in polar form to a power (DeMoivre).
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
Math 222 Spring 2013 Exam 3 Review Problem Answers
 . (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
. (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
Math 190 (Calculus II) Final Review
 Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
2) ( 8 points) The point 1/4 of the way from (1, 3, 1) and (7, 9, 9) is
 MATH 6 FALL 6 FIRST EXAM SEPTEMBER 8, 6 SOLUTIONS ) ( points) The center and the radius of the sphere given by x + y + z = x + 3y are A) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ B) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ C)
MATH 6 FALL 6 FIRST EXAM SEPTEMBER 8, 6 SOLUTIONS ) ( points) The center and the radius of the sphere given by x + y + z = x + 3y are A) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ B) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ C)
Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves
 Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves 7.1 Ellipse An ellipse is a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane the sum of whose distances r1 and r from two fixed
Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves 7.1 Ellipse An ellipse is a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane the sum of whose distances r1 and r from two fixed
Math 180, Exam 2, Practice Fall 2009 Problem 1 Solution. f(x) = arcsin(2x + 1) = sin 1 (3x + 1), lnx
 Math 80, Exam, Practice Fall 009 Problem Solution. Differentiate the functions: (do not simplify) f(x) = x ln(x + ), f(x) = xe x f(x) = arcsin(x + ) = sin (3x + ), f(x) = e3x lnx Solution: For the first
Math 80, Exam, Practice Fall 009 Problem Solution. Differentiate the functions: (do not simplify) f(x) = x ln(x + ), f(x) = xe x f(x) = arcsin(x + ) = sin (3x + ), f(x) = e3x lnx Solution: For the first
Review: Exam Material to be covered: 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5 plus review of u, du substitution.
 Review: Exam. Goals for this portion of the course: Be able to compute the area between curves, the volume of solids of revolution, and understand the mean value of a function. We had three basic volumes:
Review: Exam. Goals for this portion of the course: Be able to compute the area between curves, the volume of solids of revolution, and understand the mean value of a function. We had three basic volumes:
SCORE. Exam 3. MA 114 Exam 3 Fall 2016
 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used. You may use a graphing
Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used. You may use a graphing
Foundations of Calculus. November 18, 2014
 Foundations of Calculus November 18, 2014 Contents 1 Conic Sections 3 11 A review of the coordinate system 3 12 Conic Sections 4 121 Circle 4 122 Parabola 5 123 Ellipse 5 124 Hyperbola 6 2 Review of Functions
Foundations of Calculus November 18, 2014 Contents 1 Conic Sections 3 11 A review of the coordinate system 3 12 Conic Sections 4 121 Circle 4 122 Parabola 5 123 Ellipse 5 124 Hyperbola 6 2 Review of Functions
Ma 221 Homework Solutions Due Date: January 24, 2012
 Ma Homewk Solutions Due Date: January, 0. pg. 3 #, 3, 6,, 5, 7 9,, 3;.3 p.5-55 #, 3, 5, 7, 0, 7, 9, (Underlined problems are handed in) In problems, and 5, determine whether the given differential equation
Ma Homewk Solutions Due Date: January, 0. pg. 3 #, 3, 6,, 5, 7 9,, 3;.3 p.5-55 #, 3, 5, 7, 0, 7, 9, (Underlined problems are handed in) In problems, and 5, determine whether the given differential equation
MATH 162. Midterm Exam 1 - Solutions February 22, 2007
 MATH 62 Midterm Exam - Solutions February 22, 27. (8 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) x sin(x 4 + 7) dx Solution: Let u = x 4 + 7, then du = 4x dx and x sin(x 4 + 7) dx = 4 sin(u) du = 4 [
MATH 62 Midterm Exam - Solutions February 22, 27. (8 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) x sin(x 4 + 7) dx Solution: Let u = x 4 + 7, then du = 4x dx and x sin(x 4 + 7) dx = 4 sin(u) du = 4 [
CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH
 CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS 4 Conics Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS GRAPHICALLY Parabola Ellipse Circle Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING
CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS 4 Conics Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS GRAPHICALLY Parabola Ellipse Circle Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING
Math 108, Solution of Midterm Exam 3
 Math 108, Solution of Midterm Exam 3 1 Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve x 3 +y 3 = xy at the point (1,1). Solution. Differentiating both sides of the given equation with respect to x,
Math 108, Solution of Midterm Exam 3 1 Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve x 3 +y 3 = xy at the point (1,1). Solution. Differentiating both sides of the given equation with respect to x,
Math 180, Final Exam, Fall 2012 Problem 1 Solution
 Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola
 Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
EXAM. Exam #1. Math 3350 Summer II, July 21, 2000 ANSWERS
 EXAM Exam #1 Math 3350 Summer II, 2000 July 21, 2000 ANSWERS i 100 pts. Problem 1. 1. In each part, find the general solution of the differential equation. dx = x2 e y We use the following sequence of
EXAM Exam #1 Math 3350 Summer II, 2000 July 21, 2000 ANSWERS i 100 pts. Problem 1. 1. In each part, find the general solution of the differential equation. dx = x2 e y We use the following sequence of
Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations
 Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations Section 10.1 Geometry of Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola a. Geometric Definition b. Parabola c. Ellipse d. Hyperbola e. Translations f.
Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations Section 10.1 Geometry of Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola a. Geometric Definition b. Parabola c. Ellipse d. Hyperbola e. Translations f.
1 x. II. CHAPTER 2: (A) Graphing Rational Functions: Show Asymptotes using dotted lines, Intercepts, Holes(Coordinates, if any.)
 FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
104Math. Find the equation of the parabola and sketch it in the exercises 10-18:
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY COLEGE OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS Math Prof Messaoud Bounkhel List of Eercises: Chapter [Parabola] Find the elements of the parabola and sketch it in the eercises -9: ( )
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY COLEGE OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS Math Prof Messaoud Bounkhel List of Eercises: Chapter [Parabola] Find the elements of the parabola and sketch it in the eercises -9: ( )
1. 4 2y 1 2 = x = x 1 2 x + 1 = x x + 1 = x = 6. w = 2. 5 x
 .... VII x + x + = x x x 8 x x = x + a = a + x x = x + x x Solve the absolute value equations.. z = 8. x + 7 =. x =. x =. y = 7 + y VIII Solve the exponential equations.. 0 x = 000. 0 x+ = 00. x+ = 8.
.... VII x + x + = x x x 8 x x = x + a = a + x x = x + x x Solve the absolute value equations.. z = 8. x + 7 =. x =. x =. y = 7 + y VIII Solve the exponential equations.. 0 x = 000. 0 x+ = 00. x+ = 8.
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
MATH-1420 Review Concepts (Haugen)
 MATH-40 Review Concepts (Haugen) Unit : Equations, Inequalities, Functions, and Graphs Rational Expressions Determine the domain of a rational expression Simplify rational expressions -factor and then
MATH-40 Review Concepts (Haugen) Unit : Equations, Inequalities, Functions, and Graphs Rational Expressions Determine the domain of a rational expression Simplify rational expressions -factor and then
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 5
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Practice Problems for the Final Exam
 Math 114 Spring 2017 Practice Problems for the Final Exam 1. The planes 3x + 2y + z = 6 and x + y = 2 intersect in a line l. Find the distance from the origin to l. (Answer: 24 3 ) 2. Find the area of
Math 114 Spring 2017 Practice Problems for the Final Exam 1. The planes 3x + 2y + z = 6 and x + y = 2 intersect in a line l. Find the distance from the origin to l. (Answer: 24 3 ) 2. Find the area of
Solutions to Exam 1, Math Solution. Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists. Recall that (f 1 ) (a) =
 Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic concepts: Find y(x) where x is the independent and y the dependent varible, based on an equation involving x, y(x), y 0 (x),...e.g.: y 00 (x) = 1+y(x) y0 (x) 1+x or,
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic concepts: Find y(x) where x is the independent and y the dependent varible, based on an equation involving x, y(x), y 0 (x),...e.g.: y 00 (x) = 1+y(x) y0 (x) 1+x or,
c) xy 3 = cos(7x +5y), y 0 = y3 + 7 sin(7x +5y) 3xy sin(7x +5y) d) xe y = sin(xy), y 0 = ey + y cos(xy) x(e y cos(xy)) e) y = x ln(3x + 5), y 0
 Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
Integrated Calculus II Exam 1 Solutions 2/6/4
 Integrated Calculus II Exam Solutions /6/ Question Determine the following integrals: te t dt. We integrate by parts: u = t, du = dt, dv = e t dt, v = dv = e t dt = e t, te t dt = udv = uv vdu = te t (
Integrated Calculus II Exam Solutions /6/ Question Determine the following integrals: te t dt. We integrate by parts: u = t, du = dt, dv = e t dt, v = dv = e t dt = e t, te t dt = udv = uv vdu = te t (
CIRCLES: #1. What is an equation of the circle at the origin and radius 12?
 1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
Hour Exam #2 Math 3 Oct. 31, 2012
 Hour Exam #2 Math 3 Oct. 31, 2012 Name (Print): Last First On this, the second of the two Math 3 hour-long exams in Fall 2012, and on the final examination I will work individually, neither giving nor
Hour Exam #2 Math 3 Oct. 31, 2012 Name (Print): Last First On this, the second of the two Math 3 hour-long exams in Fall 2012, and on the final examination I will work individually, neither giving nor
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
Math 250 Skills Assessment Test
 Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Calculus II/III Summer Packet
 Calculus II/III Summer Packet First of all, have a great summer! Enjoy your time away from school. Come back fired up and ready to learn. I know that I will be ready to have a great year of calculus with
Calculus II/III Summer Packet First of all, have a great summer! Enjoy your time away from school. Come back fired up and ready to learn. I know that I will be ready to have a great year of calculus with
Access to Science, Engineering and Agriculture: Mathematics 2 MATH00040 Chapter 4 Solutions
 Access to Science, Engineering and Agriculture: Mathematics MATH4 Chapter 4 Solutions In all these solutions, c will represent an arbitrary constant.. (a) Since f(x) 5 is a constant, 5dx 5x] 5. (b) Since
Access to Science, Engineering and Agriculture: Mathematics MATH4 Chapter 4 Solutions In all these solutions, c will represent an arbitrary constant.. (a) Since f(x) 5 is a constant, 5dx 5x] 5. (b) Since
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila February 9, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila February 9, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
MATH 151, FALL SEMESTER 2011 COMMON EXAMINATION 3 - VERSION B - SOLUTIONS
 Name (print): Signature: MATH 5, FALL SEMESTER 0 COMMON EXAMINATION - VERSION B - SOLUTIONS Instructor s name: Section No: Part Multiple Choice ( questions, points each, No Calculators) Write your name,
Name (print): Signature: MATH 5, FALL SEMESTER 0 COMMON EXAMINATION - VERSION B - SOLUTIONS Instructor s name: Section No: Part Multiple Choice ( questions, points each, No Calculators) Write your name,
1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to
 SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
Exam 4 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 4 Spring Section and/or TA:
 Exam 4 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may
Exam 4 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may
Functions and Equations
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Euclid eworkshop # Functions and Equations c 006 CANADIAN
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Euclid eworkshop # Functions and Equations c 006 CANADIAN
Limit. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 9 Limit Limit is the foundation of calculus that it is so useful to understand more complicating chapters of calculus. Besides, Mathematics has black hole scenarios (dividing by zero, going to
Chapter 9 Limit Limit is the foundation of calculus that it is so useful to understand more complicating chapters of calculus. Besides, Mathematics has black hole scenarios (dividing by zero, going to
Mth Review Problems for Test 2 Stewart 8e Chapter 3. For Test #2 study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.
 For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
Name: AK-Nummer: Ergänzungsprüfung January 29, 2016
 INSTRUCTIONS: The test has a total of 32 pages including this title page and 9 questions which are marked out of 10 points; ensure that you do not omit a page by mistake. Please write your name and AK-Nummer
INSTRUCTIONS: The test has a total of 32 pages including this title page and 9 questions which are marked out of 10 points; ensure that you do not omit a page by mistake. Please write your name and AK-Nummer
Math 259 Winter Solutions to Homework # We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9.
 Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
DAY 139 EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA
 DAY 139 EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA INTRODUCTION In our prior conic sections lessons, we discussed in detail the two conic sections, the parabola, and the ellipse. The hyperbola is another conic section we
DAY 139 EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA INTRODUCTION In our prior conic sections lessons, we discussed in detail the two conic sections, the parabola, and the ellipse. The hyperbola is another conic section we
Conic Sections Session 3: Hyperbola
 Conic Sections Session 3: Hyperbola Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 3: Hyperbola Oct 2017 1 / 16 Problem 3.1 1 Recall that an ellipse is defined as the locus of points P such that
Conic Sections Session 3: Hyperbola Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 3: Hyperbola Oct 2017 1 / 16 Problem 3.1 1 Recall that an ellipse is defined as the locus of points P such that
MATH 115 Precalculus Spring, 2015, V1.2
 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Solve, and express the answer in interval notation: 6 5x 4. 1. A. (, 2] [2/5, ) B. [2/5, 2] C. (, 2/5] D. (, 2/5] [2, ) 2. Which of the following polynomials has a graph which exhibits
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Solve, and express the answer in interval notation: 6 5x 4. 1. A. (, 2] [2/5, ) B. [2/5, 2] C. (, 2/5] D. (, 2/5] [2, ) 2. Which of the following polynomials has a graph which exhibits
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems. Answers
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems Answers. A 988 AB # 48%. D 998 AB #4 5%. E 998 BC # % 5. C 99 AB # % 6. B 998 AB #80 48% 7. C 99 AB #7 65% 8. C 998 AB # 69% 9. B 99 BC # 75% 0. C 998 BC # 80%.
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems Answers. A 988 AB # 48%. D 998 AB #4 5%. E 998 BC # % 5. C 99 AB # % 6. B 998 AB #80 48% 7. C 99 AB #7 65% 8. C 998 AB # 69% 9. B 99 BC # 75% 0. C 998 BC # 80%.
APPLIED MATHEMATICS. Part 1: Ordinary Differential Equations. Wu-ting Tsai
 APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 1: Ordinary Differential Equations Contents 1 First Order Differential Equations 3 1.1 Basic Concepts and Ideas................... 4 1.2 Separable Differential Equations................
APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 1: Ordinary Differential Equations Contents 1 First Order Differential Equations 3 1.1 Basic Concepts and Ideas................... 4 1.2 Separable Differential Equations................
CP Pre-Calculus Summer Packet
 Page CP Pre-Calculus Summer Packet Name: Ø Do all work on a separate sheet of paper. Number your problems and show your work when appropriate. Ø This packet will count as your first homework assignment
Page CP Pre-Calculus Summer Packet Name: Ø Do all work on a separate sheet of paper. Number your problems and show your work when appropriate. Ø This packet will count as your first homework assignment
In general, the formula is S f ds = D f(φ(u, v)) Φ u Φ v da. To compute surface area, we choose f = 1. We compute
 alculus III Test 3 ample Problem Answers/olutions 1. Express the area of the surface Φ(u, v) u cosv, u sinv, 2v, with domain u 1, v 2π, as a double integral in u and v. o not evaluate the integral. In
alculus III Test 3 ample Problem Answers/olutions 1. Express the area of the surface Φ(u, v) u cosv, u sinv, 2v, with domain u 1, v 2π, as a double integral in u and v. o not evaluate the integral. In
MATHEMATICS Code No. 13 INSTRUCTIONS
 DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO COMBINED COMPETITIVE (PRELIMINARY) EXAMINATION, 00 Serial No. MATHEMATICS Code No. A Time Allowed : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 00 INSTRUCTIONS.
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO COMBINED COMPETITIVE (PRELIMINARY) EXAMINATION, 00 Serial No. MATHEMATICS Code No. A Time Allowed : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 00 INSTRUCTIONS.
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES 10.5 Conic Sections In this section, we will learn: How to derive standard equations for conic sections. CONIC SECTIONS
10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES 10.5 Conic Sections In this section, we will learn: How to derive standard equations for conic sections. CONIC SECTIONS
Mathematics 1052, Calculus II Exam 1, April 3rd, 2010
 Mathematics 5, Calculus II Exam, April 3rd,. (8 points) If an unknown function y satisfies the equation y = x 3 x + 4 with the condition that y()=, then what is y? Solution: We must integrate y against
Mathematics 5, Calculus II Exam, April 3rd,. (8 points) If an unknown function y satisfies the equation y = x 3 x + 4 with the condition that y()=, then what is y? Solution: We must integrate y against
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Final Exam 2011 Winter Term 2 Solutions
 . (a Find the radius of convergence of the series: ( k k+ x k. Solution: Using the Ratio Test, we get: L = lim a k+ a k = lim ( k+ k+ x k+ ( k k+ x k = lim x = x. Note that the series converges for L
. (a Find the radius of convergence of the series: ( k k+ x k. Solution: Using the Ratio Test, we get: L = lim a k+ a k = lim ( k+ k+ x k+ ( k k+ x k = lim x = x. Note that the series converges for L
Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA 2132 Final Practice Answers Fall 2012
 Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA Final Practice Answers Fall Studying from past or sample exams is NOT recommended. If you do, it should be only AFTER you know how to do all of the homework and worksheet
Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA Final Practice Answers Fall Studying from past or sample exams is NOT recommended. If you do, it should be only AFTER you know how to do all of the homework and worksheet
Math 16A, Summer 2009 Exam #2 Name: Solutions. Problem Total Score / 120. (x 2 2x + 1) + (e x + x)(2x 2)
 Math 16A, Summer 2009 Exam #2 Name: Solutions Each Problem is worth 10 points. You must show work to get credit. Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Total Score / 120 Problem 1. Compute the derivatives
Math 16A, Summer 2009 Exam #2 Name: Solutions Each Problem is worth 10 points. You must show work to get credit. Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Total Score / 120 Problem 1. Compute the derivatives
MA FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 December 13, Section # and recitation time
 MA 16500 FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 December 13, 2017 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet). 2. Check
MA 16500 FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 December 13, 2017 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet). 2. Check
(c) Find the equation of the degree 3 polynomial that has the same y-value, slope, curvature, and third derivative as ln(x + 1) at x = 0.
 Chapter 7 Challenge problems Example. (a) Find the equation of the tangent line for ln(x + ) at x = 0. (b) Find the equation of the parabola that is tangent to ln(x + ) at x = 0 (i.e. the parabola has
Chapter 7 Challenge problems Example. (a) Find the equation of the tangent line for ln(x + ) at x = 0. (b) Find the equation of the parabola that is tangent to ln(x + ) at x = 0 (i.e. the parabola has
a x a y = a x+y a x a = y ax y (a x ) r = a rx and log a (xy) = log a (x) + log a (y) log a ( x y ) = log a(x) log a (y) log a (x r ) = r log a (x).
 You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
MA1021 Calculus I B Term, Sign:
 MA1021 Calculus I B Term, 2014 Final Exam Print Name: Sign: Write up your solutions neatly and show all your work. 1. (28 pts) Compute each of the following derivatives: You do not have to simplify your
MA1021 Calculus I B Term, 2014 Final Exam Print Name: Sign: Write up your solutions neatly and show all your work. 1. (28 pts) Compute each of the following derivatives: You do not have to simplify your
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON MATH03W SEMESTER EXAMINATION 0/ MATHEMATICS FOR ELECTRONIC & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Duration: 0 min This paper has two parts, part A and part B. Answer all questions from part
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON MATH03W SEMESTER EXAMINATION 0/ MATHEMATICS FOR ELECTRONIC & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Duration: 0 min This paper has two parts, part A and part B. Answer all questions from part
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 2 Limits 2.1 The Tangent Problems The word tangent is derived from the Latin word tangens, which means touching. A tangent line to a curve is a line that touches the curve and a secant line is a line that
2 Limits 2.1 The Tangent Problems The word tangent is derived from the Latin word tangens, which means touching. A tangent line to a curve is a line that touches the curve and a secant line is a line that
