CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
|
|
|
- Ann Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai
2 Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole Chapter 1. Section 1.10 and Chapter 11 Section
3 LECTURE 3. PLANE GEOMETRY The purpose of this lecture is to review some high school plane geometry: Algebra Geometry. We will discuss lines and quadratic curves (conic sections) in the plane.
4 Coordinate (Cartesian) Plane
5 Construction of Coordinates As we identify points on a line with the real numbers, we can identify points in a (Euclidean) plane with ordered pairs of numbers to form the coordinate plane or Cartesian plane, which is done by drawing two perpendicular real lines that intersect at 0 on each line. The horizontal line with positive direction to the right is called the x-axis and the other line with positive direction pointing upward is called the y-axis. The point of intersection of the two axes is called the origin O. These two axes divide the plane into four quadrants, labeled I, II, III and IV. Any point P on the plan can be labeled by a unique ordered pairs of numbers (a, b). a is called the x-coordinate of P and b is called the y-coordinate of P.
6
7 The Distance Formula Definition By using the Pythagorean theorem, define distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2
8 Graphs Equations in Two Variables In this section, we only treat lines and quadratic curves of standard forms. The more general cases will will be discussed in Calculus!
9 Line Equations Definition The slope m of a nonvertical line that passes through the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) is m = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 Consequently, the slope of a horizontal line is 0. The slope of a vertical line is not defined. Vertical Line Equation: x = c, where c is a fixed real number. Point-Slope Equation: The line equation that through the point (x 1, y 1 ) and has slope m is y y 1 = m(x x 1 ). Horizonal Line Equation: y = c, where c R is fixed.
10 Line Equations The line equation that through the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is y y 1 = ( y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 ) (x x 1 ) which is called Two-Points Form of a line equation. y y 1 = m(x x 1 ) y = mx + b, b = y 1 mx 1. The (red) equation is called Slope-Intercept Form of a line equation with slope m and y-intercept b. Together Theorem The graph of a linear equation ax + by + c = 0 (a and b are not both 0 a 2 + b 2 0) is a line. Conversely, Every line is the graph of a linear equation.
11 Facts about The Slopes of Two Lines Theorem 1. Two nonvertical lines are parallel if and only if they have the same slope.
12 Facts about The Slopes of Two Lines 2. Two lines have slopes m 1 and m 2 are perpendicular if and only if m 1 m 2 = 1. The horizonal lines y = c 1 are perpendicular the the vertical lines x = c 2 for any fixed c 1, c 2 R.
13 Graphing Regions in Coordinate Plane Describe and sketch regions given by the following each set: 1. {(x, y) R 2 2x y 3}
14 Graphing Regions in Coordinate Plane 2. {(x, y) R 2 2x + y < 3}
15 Graphing Regions in Coordinate Plane 3. {(x, y) R 2 2x y 3 and 2x + y < 3}
16 Digression The coordinate of intersecting point of two lines are found by solving the system of two linear equations 2x 3y = 3 (1) 2x + 3y = 3 (2) (1) + (2) 4x = 6 x = 3 2. With x = 3 2 plugging into (1) 3 3y = 3 y = 0. Hence ( 3, 0) is the coordinate of the intersecting point. 2
17 Writing the set of region given by the graph The line on the left L 1 passes through ( 3 2, 0) and (0, 3) and the line on the right L 2 passes through ( 5 2, 0) and (0, 5), using the two-points form of line a equation:
18 Writing the set of region given by the graph L 1 y 3 = (x 0) x 2y = 6 L 2 y ( 5) = 0 ( 5) (x 0) x 2y = 10 Since the region lies between them and the lines are solid, the set is {(x, y) R 2 6 x 2y 10} = {(x, y) R 2 x 2y 2 8} because 6 x 2y 10 8 (x 2y) 2 8 x 2y 2 8. See
19 Writing the set of region given by the graph
20 Circles The equation of a circle with center at (a, b) and radius r is (x a) 2 + (y b) 2 = r 2 This is called the standard form for equation of the circle. In particular, if the center is O(0, 0), then the equation is x 2 + y 2 = r 2.
21 Examples 1. Graph x 2 + y 2 = 25
22 Examples 2. Show that the equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x 6y + 7 = 0 represent a circle, and find the center and radius of the circle. 0 = x 2 + y 2 + 2x 6y + 7 = (x 2 + 2x + 1) + (y 2 6y + 9) + (7 1 9) = (x + 1) 2 + (y 3) 2 3 [x ( 1)] 2 + (y 3) 2 = ( 3) 2. Hence the equation represents a circle of radius 3 and centered at ( 1, 3).
23 Parabolas Geometric Definition of a Parabola A parabola is the set of points in the plane that are equidistance from a fixed point F (called focus) and a fixed line l (called directrix).
24 Equations of Parabolas With vertex V at the origin O(0, 0), two cases to consider here: 1. The focus F(0, p) and the directrix l equation is given by y = p. If P(x, y) is a point on the parabola, then d(f, P) = x 2 + (y p) 2 and the distance from P to l is y ( p) = y + p. Hence x 2 + (y p) 2 = y + p x 2 + (y p) 2 = y + p 2 = (y + p) 2 x 2 + y 2 2py + p 2 = y 2 + 2py + p 2 x 2 = 4py. Two possibilities: (a) p > 0, the parabola opens upward; (b) p < 0, the parabola opens downward. 2. The focus F(p, 0) and the directrix l equation is given by x = p. If P(x, y) is a point on the parabola, as before, we can have y 2 = 4px. Two possibilities: (a) p > 0, the parabola opens rightward; (b)p < 0, the parabola opens leftward.
25 Examples of Parabolas
26 Examples of Parabolas
27 Examples of Parabolas
28 Examples of Parabolas
29 Examples of Parabolas
30 Ellipse Geometric Definition of a Ellipse A ellipse is the set of points in the plane that the sum of whose distances from two fixed point F 1 and F 2 (called foci) is a positive constant 2a > d(f 1, F2) = 2c > 0.
31 Equations of Ellipses Let the 2a > 0 be the sum of distance the sum of whose distances from two fixed point F 1 and F 2. Then if P(x, y) is any point on the ellipse, then we have Consider the following cases: d(p, F 1 ) + d(p, F 2 ) = 2a 1. If the foci F 1 ( c, 0), F 2 (c, 0) (c > 0) are placed on the x-axis, using the Distance Formula, we see that the equation is x 2 a 2 + y 2 b 2 = 1 where b 2 = a 2 c 2 (with b > 0 and so a > b). The major axis is horizontal of length 2a and the minor axis is vertical of length 2b.
32 Equations of Ellipses 2. If the foci F 1 (0, c), F 2 (0, c) (c > 0) are placed on the x-axis, the equation is x 2 b 2 + y 2 a 2 = 1 The major axis is vertical of length 2a and the minor axis is horizontal of length 2b.
33 Hyperbolas Geometric Definition of a Hyperbola A hyperbola is the set of points in the plane that the difference of whose distances from two fixed point F 1 and F 2 (called foci) is a positive constant 2a > 0.
34 Equations of Hyperbolas Let the 2a > 0 be the sum of distance the sum of whose distances from two fixed point F 1 and F 2. Then if P(x, y) is any point on the hyperbola, then we have Consider the following cases: d(p, F 1 ) d(p, F 2 ) = ±2a 1. If the foci F 1 ( c, 0), F 2 (c, 0) (c > a) are placed on the x-axis, using the Distance Formula, we see that the equation is x 2 a 2 y 2 b 2 = 1 where b 2 = c 2 a 2 (with b > 0 and so a > b). The transverse axis is horizontal of length 2a. See
35
36 Equations of Hyperbolas 2. If the foci F 1 (0, c), F 2 (0, c) (c > 0) are placed on the x-axis, the equation is x 2 b 2 + y 2 a 2 = 1 The transverse axis is vertical of length 2a. See
37
y 1 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 ) 2 A circle is a set of points P in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, called the center.
 Ch 12. Conic Sections Circles, Parabolas, Ellipses & Hyperbolas The formulas for the conic sections are derived by using the distance formula, which was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. If you know
Ch 12. Conic Sections Circles, Parabolas, Ellipses & Hyperbolas The formulas for the conic sections are derived by using the distance formula, which was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. If you know
CIRCLES: #1. What is an equation of the circle at the origin and radius 12?
 1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Circles. Example 2: Write an equation for a circle if the enpoints of a diameter are at ( 4,5) and (6, 3).
 Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1
 Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
The Distance Formula. The Midpoint Formula
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Conic Sections. Geometry - Conics ~1~ NJCTL.org. Write the following equations in standard form.
 Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila February 9, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila February 9, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES 10.5 Conic Sections In this section, we will learn: How to derive standard equations for conic sections. CONIC SECTIONS
10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES 10.5 Conic Sections In this section, we will learn: How to derive standard equations for conic sections. CONIC SECTIONS
CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH
 CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS 4 Conics Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS GRAPHICALLY Parabola Ellipse Circle Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING
CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS 4 Conics Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS GRAPHICALLY Parabola Ellipse Circle Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING
Math Conic Sections
 Math 114 - Conic Sections Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 13, 2017 Bill of Fare Why Conic Sections? Parabolas Ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Goals of This Lecture By the end of this lecture,
Math 114 - Conic Sections Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 13, 2017 Bill of Fare Why Conic Sections? Parabolas Ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Goals of This Lecture By the end of this lecture,
Table of contents. Jakayla Robbins & Beth Kelly (UK) Precalculus Notes Fall / 53
 Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
ALGEBRA 2 X. Final Exam. Review Packet
 ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
Standard Form of Conics
 When we teach linear equations in Algebra1, we teach the simplest linear function (the mother function) as y = x. We then usually lead to the understanding of the effects of the slope and the y-intercept
When we teach linear equations in Algebra1, we teach the simplest linear function (the mother function) as y = x. We then usually lead to the understanding of the effects of the slope and the y-intercept
Algebra 2 Unit 9 (Chapter 9)
 Algebra Unit 9 (Chapter 9) 0. Spiral Review Worksheet 0. Find verte, line of symmetry, focus and directri of a parabola. (Section 9.) Worksheet 5. Find the center and radius of a circle. (Section 9.3)
Algebra Unit 9 (Chapter 9) 0. Spiral Review Worksheet 0. Find verte, line of symmetry, focus and directri of a parabola. (Section 9.) Worksheet 5. Find the center and radius of a circle. (Section 9.3)
9.1 Circles and Parabolas. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
The coordinates of the vertex of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the parabola opens upward. If a < 0, the parabola opens downward.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 8 Quadratic Relations in Vertex Form The expression y ax p q defines a quadratic relation in form. The coordinates of the of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 8 Quadratic Relations in Vertex Form The expression y ax p q defines a quadratic relation in form. The coordinates of the of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the
MATH-1420 Review Concepts (Haugen)
 MATH-40 Review Concepts (Haugen) Unit : Equations, Inequalities, Functions, and Graphs Rational Expressions Determine the domain of a rational expression Simplify rational expressions -factor and then
MATH-40 Review Concepts (Haugen) Unit : Equations, Inequalities, Functions, and Graphs Rational Expressions Determine the domain of a rational expression Simplify rational expressions -factor and then
Precalculus 1, 161. Spring 2018 CRN Section 009. Time: S, 12:30 p.m. - 3:35 p.m. Room BR-11
 Precalculus 1, 161 Spring 2018 CRN 11996 Section 009 Time: S, 12:30 p.m. - 3:35 p.m. Room BR-11 SYLLABUS Catalog description Functions and relations and their graphs, transformations and symmetries; composition
Precalculus 1, 161 Spring 2018 CRN 11996 Section 009 Time: S, 12:30 p.m. - 3:35 p.m. Room BR-11 SYLLABUS Catalog description Functions and relations and their graphs, transformations and symmetries; composition
Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane
 3110 General Mathematics 1 31 10 General Mathematics For the students from Pharmaceutical Faculty 1/004 Instructor: Dr Wattana Toutip (ดร.ว ฒนา เถาว ท พย ) Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane Overview:
3110 General Mathematics 1 31 10 General Mathematics For the students from Pharmaceutical Faculty 1/004 Instructor: Dr Wattana Toutip (ดร.ว ฒนา เถาว ท พย ) Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane Overview:
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
Chapter 1: Precalculus Review
 : Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
: Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
DAY 139 EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA
 DAY 139 EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA INTRODUCTION In our prior conic sections lessons, we discussed in detail the two conic sections, the parabola, and the ellipse. The hyperbola is another conic section we
DAY 139 EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA INTRODUCTION In our prior conic sections lessons, we discussed in detail the two conic sections, the parabola, and the ellipse. The hyperbola is another conic section we
Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections 3.1, 3.3, and 3.5
 Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 11 Worksheet Sections 3.1, 3.3, and 3.5 1. For f(x) = 5x + (a) Determine the slope and the y-intercept. f(x) = 5x + is of the form y = mx
Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 11 Worksheet Sections 3.1, 3.3, and 3.5 1. For f(x) = 5x + (a) Determine the slope and the y-intercept. f(x) = 5x + is of the form y = mx
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Advanced Math A Units and s Advanced Math A Unit 1 Functions and Math Models (7 days) 10% of grade s 1. I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Advanced Math A Units and s Advanced Math A Unit 1 Functions and Math Models (7 days) 10% of grade s 1. I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description
Mathematics Precalculus: Academic Unit 7: Conics
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Conics are models of real-life situations. Conics have many reflective properties that are used in every day situations Conics work can be simplified
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Conics are models of real-life situations. Conics have many reflective properties that are used in every day situations Conics work can be simplified
REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS
 REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS 8.1 8. Equations of Loci Refer to the Key Concepts on page 598. 1. Sketch the locus of points in the plane that are cm from a circle of radius 5 cm.. a) How are the lines y = x 3
REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS 8.1 8. Equations of Loci Refer to the Key Concepts on page 598. 1. Sketch the locus of points in the plane that are cm from a circle of radius 5 cm.. a) How are the lines y = x 3
April 30, Name: Amy s Solutions. Discussion Section: N/A. Discussion TA: N/A
 Math 1151, April 30, 010 Exam 3 (in-class) Name: Amy s Solutions Discussion Section: N/A Discussion TA: N/A This exam has 8 multiple-choice problems, each worth 5 points. When you have decided on a correct
Math 1151, April 30, 010 Exam 3 (in-class) Name: Amy s Solutions Discussion Section: N/A Discussion TA: N/A This exam has 8 multiple-choice problems, each worth 5 points. When you have decided on a correct
Lesson 9 Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions
 Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions Graph the following system of linear inequalities: { y > 1 2 x 5 3x + 2y 14 a What are three points that are solutions to the system of inequalities? b Is the point
Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions Graph the following system of linear inequalities: { y > 1 2 x 5 3x + 2y 14 a What are three points that are solutions to the system of inequalities? b Is the point
Page 1
 Pacing Chart Unit Week Day CCSS Standards Objective I Can Statements 121 CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.1 Prove that all circles are similar. Prove that all circles are similar. I can prove that all circles
Pacing Chart Unit Week Day CCSS Standards Objective I Can Statements 121 CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.1 Prove that all circles are similar. Prove that all circles are similar. I can prove that all circles
The Geometry. Mathematics 15: Lecture 20. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. November 6, 2006
 The Geometry Mathematics 15: Lecture 20 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 6, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) The Geometry November 6, 2006 1 / 18 René Descartes 1596-1650 Dan Sloughter (Furman
The Geometry Mathematics 15: Lecture 20 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 6, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) The Geometry November 6, 2006 1 / 18 René Descartes 1596-1650 Dan Sloughter (Furman
Math 1012 Precalculus Functions Final Exam Review Page 1 of 5
 Math 1012 Precalculus Functions Final Exam Review Page 1 of 5 Final Exam Preparation The final exam will be 10 questions long, some with two parts. Material for the final can be drawn from anything we
Math 1012 Precalculus Functions Final Exam Review Page 1 of 5 Final Exam Preparation The final exam will be 10 questions long, some with two parts. Material for the final can be drawn from anything we
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola
 Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW
 NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW Algebra II Honors is a full-year, high school math course intended for the student who has successfully completed the prerequisite course Algebra I. This course focuses on algebraic
NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW Algebra II Honors is a full-year, high school math course intended for the student who has successfully completed the prerequisite course Algebra I. This course focuses on algebraic
30 Wyner Math Academy I Fall 2015
 30 Wyner Math Academy I Fall 2015 CHAPTER FOUR: QUADRATICS AND FACTORING Review November 9 Test November 16 The most common functions in math at this level are quadratic functions, whose graphs are parabolas.
30 Wyner Math Academy I Fall 2015 CHAPTER FOUR: QUADRATICS AND FACTORING Review November 9 Test November 16 The most common functions in math at this level are quadratic functions, whose graphs are parabolas.
Chapter P. Prerequisites. Slide P- 1. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Algebra 2 (3 rd Quad Expectations) CCSS covered Key Vocabulary Vertical
 Algebra 2 (3 rd Quad Expectations) CCSS covered Key Vocabulary Vertical Chapter (McGraw-Hill Algebra 2) Chapter 7 (Suggested Pacing 14 Days) Lesson 7-1: Graphing Exponential Functions Lesson 7-2: Solving
Algebra 2 (3 rd Quad Expectations) CCSS covered Key Vocabulary Vertical Chapter (McGraw-Hill Algebra 2) Chapter 7 (Suggested Pacing 14 Days) Lesson 7-1: Graphing Exponential Functions Lesson 7-2: Solving
Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material
 Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material Math114 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky April 26, 2017 Math114 Lecture 37 1/ 11 Outline 1 Conic Sections Math114 Lecture 37 2/ 11 Outline 1
Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material Math114 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky April 26, 2017 Math114 Lecture 37 1/ 11 Outline 1 Conic Sections Math114 Lecture 37 2/ 11 Outline 1
RF2 Unit Test # 2 Review Quadratics (Chapter 6) 1. What is the degree of a quadratic function?
 RF Unit Test # Review Quadratics (Chapter 6) 1. What is the degree of a quadratic function? Name: a. 1 b. c. 3 d. 0. What is the -intercept for = 3x + x 5? a. 5 b. 5 c. d. 3 3. Which set of data is correct
RF Unit Test # Review Quadratics (Chapter 6) 1. What is the degree of a quadratic function? Name: a. 1 b. c. 3 d. 0. What is the -intercept for = 3x + x 5? a. 5 b. 5 c. d. 3 3. Which set of data is correct
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
8.6 Translate and Classify Conic Sections
 8.6 Translate and Classify Conic Sections Where are the symmetric lines of conic sections? What is the general 2 nd degree equation for any conic? What information can the discriminant tell you about a
8.6 Translate and Classify Conic Sections Where are the symmetric lines of conic sections? What is the general 2 nd degree equation for any conic? What information can the discriminant tell you about a
Centerville High School Curriculum Mapping Algebra II 1 st Nine Weeks
 Centerville High School Curriculum Mapping Algebra II 1 st Nine Weeks Chapter/ Lesson Common Core Standard(s) 1-1 SMP1 1. How do you use a number line to graph and order real numbers? 2. How do you identify
Centerville High School Curriculum Mapping Algebra II 1 st Nine Weeks Chapter/ Lesson Common Core Standard(s) 1-1 SMP1 1. How do you use a number line to graph and order real numbers? 2. How do you identify
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8)
 Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Aldine I.S.D. Benchmark Targets/ Algebra 2 SUMMER 2004
 ASSURANCES: By the end of Algebra 2, the student will be able to: 1. Solve systems of equations or inequalities in two or more variables. 2. Graph rational functions and solve rational equations and inequalities.
ASSURANCES: By the end of Algebra 2, the student will be able to: 1. Solve systems of equations or inequalities in two or more variables. 2. Graph rational functions and solve rational equations and inequalities.
Ch 9/10/11/12 Exam Review
 Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET
 SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root. Ans. (D) x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
Portable Assisted Study Sequence ALGEBRA IIB
 SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
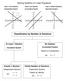 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Name Period. Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles. Standard: G-GPE.1. Objective:
 Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
1) The line has a slope of ) The line passes through (2, 11) and. 6) r(x) = x + 4. From memory match each equation with its graph.
 Review Test 2 Math 1314 Name Write an equation of the line satisfying the given conditions. Write the answer in standard form. 1) The line has a slope of - 2 7 and contains the point (3, 1). Use the point-slope
Review Test 2 Math 1314 Name Write an equation of the line satisfying the given conditions. Write the answer in standard form. 1) The line has a slope of - 2 7 and contains the point (3, 1). Use the point-slope
Algebra II Curriculum Guide Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA
 Algebra II Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Algebra II Prerequisite: Successful completion of Geometry This course continues and reinforces the mathematical material learned in Algebra I. It deals with
Algebra II Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Algebra II Prerequisite: Successful completion of Geometry This course continues and reinforces the mathematical material learned in Algebra I. It deals with
Precalculus 1, 161. Fall 2018 CRN Section 010. Time: Saturday, 9:00 a.m. 12:05 p.m. Room BR-11
 Precalculus 1, 161 Fall 018 CRN 4066 Section 010 Time: Saturday, 9:00 a.m. 1:05 p.m. Room BR-11 SYLLABUS Catalog description Functions and relations and their graphs, transformations and symmetries; composition
Precalculus 1, 161 Fall 018 CRN 4066 Section 010 Time: Saturday, 9:00 a.m. 1:05 p.m. Room BR-11 SYLLABUS Catalog description Functions and relations and their graphs, transformations and symmetries; composition
1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to
 SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
Pre-Calculus EOC Review 2016
 Pre-Calculus EOC Review 2016 Name The Exam 50 questions, multiple choice, paper and pencil. I. Limits 8 questions a. (1) decide if a function is continuous at a point b. (1) understand continuity in terms
Pre-Calculus EOC Review 2016 Name The Exam 50 questions, multiple choice, paper and pencil. I. Limits 8 questions a. (1) decide if a function is continuous at a point b. (1) understand continuity in terms
Pre Calculus Gary Community School Corporation Unit Planning Map
 UNIT/TIME FRAME STANDARDS Functions and Graphs (6 weeks) PC.F.1: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
UNIT/TIME FRAME STANDARDS Functions and Graphs (6 weeks) PC.F.1: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
Sect The Slope-Intercept Form
 0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
1 Quadratic Functions
 Unit 1 Quadratic Functions Lecture Notes Introductory Algebra Page 1 of 8 1 Quadratic Functions In this unit we will learn many of the algebraic techniques used to work with the quadratic function fx)
Unit 1 Quadratic Functions Lecture Notes Introductory Algebra Page 1 of 8 1 Quadratic Functions In this unit we will learn many of the algebraic techniques used to work with the quadratic function fx)
Utah Math Standards for College Prep Mathematics
 A Correlation of 8 th Edition 2016 To the A Correlation of, 8 th Edition to the Resource Title:, 8 th Edition Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN: SE: 9780133941753/ 9780133969078/
A Correlation of 8 th Edition 2016 To the A Correlation of, 8 th Edition to the Resource Title:, 8 th Edition Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN: SE: 9780133941753/ 9780133969078/
Basic Surveying Week 3, Lesson 2 Semester 2017/18/2 Vectors, equation of line, circle, ellipse
 Basic Surveying Week 3, Lesson Semester 017/18/ Vectors, equation of line, circle, ellipse 1. Introduction In surveying calculations, we use the two or three dimensional coordinates of points or objects
Basic Surveying Week 3, Lesson Semester 017/18/ Vectors, equation of line, circle, ellipse 1. Introduction In surveying calculations, we use the two or three dimensional coordinates of points or objects
Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves
 Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves 7.1 Ellipse An ellipse is a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane the sum of whose distances r1 and r from two fixed
Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves 7.1 Ellipse An ellipse is a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane the sum of whose distances r1 and r from two fixed
7. The set of all points for which the x and y coordinates are negative is quadrant III.
 SECTION - 67 CHAPTER Section -. To each point P in the plane there corresponds a single ordered pair of numbers (a, b) called the coordinates of the point. To each ordered pair of numbers (a, b) there
SECTION - 67 CHAPTER Section -. To each point P in the plane there corresponds a single ordered pair of numbers (a, b) called the coordinates of the point. To each ordered pair of numbers (a, b) there
Algebra II Honors Curriculum Guide Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA
 Algebra II Honors Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Algebra II Honors Prerequisite: Successful completion of Geometry Honors This course continues and reinforces the mathematical material learned in
Algebra II Honors Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Algebra II Honors Prerequisite: Successful completion of Geometry Honors This course continues and reinforces the mathematical material learned in
Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry. 9.3 The Parabola. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.3 The Parabola Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Graph parabolas with vertices at the origin. Write equations of parabolas in
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.3 The Parabola Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Graph parabolas with vertices at the origin. Write equations of parabolas in
Section 1.6. Functions
 Section 1.6 Functions Definitions Relation, Domain, Range, and Function The table describes a relationship between the variables x and y. This relationship is also described graphically. x y 3 2 4 1 5
Section 1.6 Functions Definitions Relation, Domain, Range, and Function The table describes a relationship between the variables x and y. This relationship is also described graphically. x y 3 2 4 1 5
2-7 Solving Quadratic Inequalities. ax 2 + bx + c > 0 (a 0)
 Quadratic Inequalities In One Variable LOOKS LIKE a quadratic equation but Doesn t have an equal sign (=) Has an inequality sign (>,
Quadratic Inequalities In One Variable LOOKS LIKE a quadratic equation but Doesn t have an equal sign (=) Has an inequality sign (>,
UMUC MATH-107 Final Exam Information
 UMUC MATH-07 Final Exam Information What should you know for the final exam? Here are some highlights of textbook material you should study in preparation for the final exam. Review this material from
UMUC MATH-07 Final Exam Information What should you know for the final exam? Here are some highlights of textbook material you should study in preparation for the final exam. Review this material from
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ALGEBRA II
 UNIT: Review of Basic Algebra Skills as Needed SR1 and any Supplemental Materials UNIT : What skills from Algebra I are used in Algebra II? Review Algebra I Skills as Needed SR1 and any additional resources
UNIT: Review of Basic Algebra Skills as Needed SR1 and any Supplemental Materials UNIT : What skills from Algebra I are used in Algebra II? Review Algebra I Skills as Needed SR1 and any additional resources
Conic Sections: THE ELLIPSE
 Conic Sections: THE ELLIPSE An ellipse is the set of all points,such that the sum of the distance between, and two distinct points is a constant. These two distinct points are called the foci (plural of
Conic Sections: THE ELLIPSE An ellipse is the set of all points,such that the sum of the distance between, and two distinct points is a constant. These two distinct points are called the foci (plural of
Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
RADNOR TOWNSHIP SCHOOL DISTRICT Course Overview Seminar Algebra 2 ( )
 RADNOR TOWNSHIP SCHOOL DISTRICT Course Overview Seminar Algebra 2 (05040430) General Information Prerequisite: Seminar Geometry Honors with a grade of C or teacher recommendation. Length: Full Year Format:
RADNOR TOWNSHIP SCHOOL DISTRICT Course Overview Seminar Algebra 2 (05040430) General Information Prerequisite: Seminar Geometry Honors with a grade of C or teacher recommendation. Length: Full Year Format:
STEM-Prep Pathway SLOs
 STEM-Prep Pathway SLOs Background: The STEM-Prep subgroup of the MMPT adopts a variation of the student learning outcomes for STEM from the courses Reasoning with Functions I and Reasoning with Functions
STEM-Prep Pathway SLOs Background: The STEM-Prep subgroup of the MMPT adopts a variation of the student learning outcomes for STEM from the courses Reasoning with Functions I and Reasoning with Functions
Homework. Basic properties of real numbers. Adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing real numbers. Solve one step inequalities with integers.
 Morgan County School District Re-3 A.P. Calculus August What is the language of algebra? Graphing real numbers. Comparing and ordering real numbers. Finding absolute value. September How do you solve one
Morgan County School District Re-3 A.P. Calculus August What is the language of algebra? Graphing real numbers. Comparing and ordering real numbers. Finding absolute value. September How do you solve one
MA 110 Algebra and Trigonometry for Calculus Spring 2017 Exam 1 Tuesday, 7 February Multiple Choice Answers EXAMPLE A B C D E.
 MA 110 Algebra and Trigonometry for Calculus Spring 2017 Exam 1 Tuesday, 7 February 2017 Multiple Choice Answers EXAMPLE A B C D E Question Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: This exam has ten
MA 110 Algebra and Trigonometry for Calculus Spring 2017 Exam 1 Tuesday, 7 February 2017 Multiple Choice Answers EXAMPLE A B C D E Question Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: This exam has ten
Section 1.4 Circles. Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form.
 1 Section 1. Circles Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form. We begin by giving a definition of a circle: Definition: A Circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from
1 Section 1. Circles Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form. We begin by giving a definition of a circle: Definition: A Circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS
 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic functions. Write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of functions. Find minimum and
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic functions. Write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of functions. Find minimum and
For all questions, answer choice E. NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 For all questions, answer choice " means none of the above answers is correct. 1. The sum of the integers 1 through n can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. What is the product of the non-zero coefficients
For all questions, answer choice " means none of the above answers is correct. 1. The sum of the integers 1 through n can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. What is the product of the non-zero coefficients
Utah Core State Standards for Mathematics - Precalculus
 A Correlation of A Graphical Approach to Precalculus with Limits A Unit Circle Approach 6 th Edition, 2015 to the Resource Title: with Limits 6th Edition Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice
A Correlation of A Graphical Approach to Precalculus with Limits A Unit Circle Approach 6 th Edition, 2015 to the Resource Title: with Limits 6th Edition Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice
1.2 Graphs and Lines. Cartesian Coordinate System
 1.2 Graphs and Lines Cartesian Coordinate System Note that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the points in a plane and the elements in the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) of real numbers. Graphs
1.2 Graphs and Lines Cartesian Coordinate System Note that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the points in a plane and the elements in the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) of real numbers. Graphs
SISD Unit Bundles of TEKS/SEs and Pacing Guide Algebra 2
 SISD Unit Bundles of TEKS/SEs and Pacing Guide Algebra 2 UNIT 0 - Preparing for Advanced Algebra Estimated 6 Days TEKS Identify the domain and range of functions. Use the FOIL (First, Outside, Inside,
SISD Unit Bundles of TEKS/SEs and Pacing Guide Algebra 2 UNIT 0 - Preparing for Advanced Algebra Estimated 6 Days TEKS Identify the domain and range of functions. Use the FOIL (First, Outside, Inside,
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
PreCalculus. Curriculum (637 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review.
 Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 435-436 H Q. Let A ( ) 4 and B 3 3 Compute (if possible) : AB and BA ( ) 4 AB 3 3 ( ) ( ) ++ 4+4+ 4
M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 435-436 H Q. Let A ( ) 4 and B 3 3 Compute (if possible) : AB and BA ( ) 4 AB 3 3 ( ) ( ) ++ 4+4+ 4
Conic section. Ans: c. Ans: a. Ans: c. Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ. 1. A circle
 Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review
 Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Pure Math 30: Explained! 81
 4 www.puremath30.com 81 Part I: General Form General Form of a Conic: Ax + Cy + Dx + Ey + F = 0 A & C are useful in finding out which conic is produced: A = C Circle AC > 0 Ellipse A or C = 0 Parabola
4 www.puremath30.com 81 Part I: General Form General Form of a Conic: Ax + Cy + Dx + Ey + F = 0 A & C are useful in finding out which conic is produced: A = C Circle AC > 0 Ellipse A or C = 0 Parabola
Roots are: Solving Quadratics. Graph: y = 2x 2 2 y = x 2 x 12 y = x 2 + 6x + 9 y = x 2 + 6x + 3. real, rational. real, rational. real, rational, equal
 Solving Quadratics Graph: y = 2x 2 2 y = x 2 x 12 y = x 2 + 6x + 9 y = x 2 + 6x + 3 Roots are: real, rational real, rational real, rational, equal real, irrational 1 To find the roots algebraically, make
Solving Quadratics Graph: y = 2x 2 2 y = x 2 x 12 y = x 2 + 6x + 9 y = x 2 + 6x + 3 Roots are: real, rational real, rational real, rational, equal real, irrational 1 To find the roots algebraically, make
Math 1152: Precalculus Algebra Section 4 Time: TR 14:30 16:20 Place: L305 Instructor: J. Jang Office: B019g Phone:
 Math 115: Precalculus Algebra Section 4 Time: TR 14:30 16:0 Place: L305 Instructor: J. Jang Office: B019g Phone: 33 5786 Email: jjang@langara.bc.ca Office hours: TBA Prerequisite: C- in Principles of Math
Math 115: Precalculus Algebra Section 4 Time: TR 14:30 16:0 Place: L305 Instructor: J. Jang Office: B019g Phone: 33 5786 Email: jjang@langara.bc.ca Office hours: TBA Prerequisite: C- in Principles of Math
Chapter 10 Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates Conics and Calculus
 Chapter 10 Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates 10.1 Conics and Calculus 1. Parabola A parabola is the set of all points x, y ( ) that are equidistant from a fixed line and a fixed point
Chapter 10 Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates 10.1 Conics and Calculus 1. Parabola A parabola is the set of all points x, y ( ) that are equidistant from a fixed line and a fixed point
8.8 Conics With Equations in the Form
 8.8 Conics With Equations in the Form ax + b + gx + f + c = 0 The CF-18 Hornet is a supersonic jet flown in Canada. It has a maximum speed of Mach 1.8. The speed of sound is Mach 1. When a plane like the
8.8 Conics With Equations in the Form ax + b + gx + f + c = 0 The CF-18 Hornet is a supersonic jet flown in Canada. It has a maximum speed of Mach 1.8. The speed of sound is Mach 1. When a plane like the
ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where
 Chapter P Prerequisites Section P.1 Real Numbers Real numbers The set of numbers formed by joining the set of rational numbers and the set of irrational numbers. Real number line A line used to graphically
Chapter P Prerequisites Section P.1 Real Numbers Real numbers The set of numbers formed by joining the set of rational numbers and the set of irrational numbers. Real number line A line used to graphically
C.3 Nonlinear Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 50 section C3 C.3 Nonlinear Systems of Equations and Inequalities In section E, we discussed methods of solving systems of two linear equations. Recall that solutions to such systems are the intercepts
50 section C3 C.3 Nonlinear Systems of Equations and Inequalities In section E, we discussed methods of solving systems of two linear equations. Recall that solutions to such systems are the intercepts
Quadratic Functions. and Equations
 Name: Quadratic Functions and Equations 1. + x 2 is a parabola 2. - x 2 is a parabola 3. A quadratic function is in the form ax 2 + bx + c, where a and is the y-intercept 4. Equation of the Axis of Symmetry
Name: Quadratic Functions and Equations 1. + x 2 is a parabola 2. - x 2 is a parabola 3. A quadratic function is in the form ax 2 + bx + c, where a and is the y-intercept 4. Equation of the Axis of Symmetry
1. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y 3x
 MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
