25/01/2014. Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power. Work of a force. Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (First part) Work = Force x Displacement
|
|
|
- Gregory Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5/0/04 Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power King Saud University College o Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. Phys 45 (General Physics) Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (Part ) Week n 5 This presentation has been prepared by: Pr. Nabil BEN NESSIB We will learn in this chapter 4: Work and Energy Kinetic energy Potential energy Dissipative orces Power Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (irst part) We will learn in this irst part o chapter 4: Work and Energy Kinetic energy Potential energy Work o a orce The work done by a orce is deined as the product o the orce component and the displacement. Work = orce x Displacement In the S.I., work is in Joule (J), J = N xm. θ 3 Δx W(). x cos() x i and x are in the same direction: W() x 4
2 5/0/04 Work o a orce Example 5. Work o a orce Example 5. When a man carries a bucket o water دلو من الماء) ) horizontally at constant velocity, the orce does no work on the bucket: Displacement is horizontal and orce is vertical. cos 90 = 0 so W = 0 Work can be positive or negative: θ = 0, W > 0 Δx θ = 80, W < Work done against gravity Work done by multiple orces Example 5.3 Work (joules) W = mgh Mass (kg) Height object raised (m) W() mg. mg x mgcos(90) x 0 W() R. R x R cos(90) x 0 R θ Gravity (m/s ) W(). x cos() x m g Δx W W()()() mg W Rcos() W x net 7 8
3 5/0/04 Video 0 o Week 05: Work and energy Kinetic energy The total work done on an object by all the orces acting upon it is equal to the variation o its kinetic energy. W() net KE KE KEi We have: v a x v v so a x and W x ma x vi i i net net The kinetic energy o an object having a mass m and a velocity v is: KE 9 0 Kinetic energy Remember that: So: The KE is always positive. KE I the mass is doubled the KE is also doubled, but i the velocity is doubled the KE is quadrupled (KE is proportional to the square o the velocity). Kinetic energy Example 5.4 I the surace is smooth what is the speed o the block at the bottom o the incline? We have: W()() W0() R W mg sin(38) W mg mgl net KE KEi 0 L So: v glsin(38) gh m/s 3
4 5/0/04 Potential energy An object can store energy as the result o its position. Energy is the ability to do work, so one o the energy orm is the potential energy. This stored energy o position is reerred to as potential energy. Potential energy is the stored energy o position possessed by an object. Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object as the result o its vertical position or height. The energy is stored as the result o the gravitational attraction o the Earth or the object. Reerence level or potential energy The reerence level is a location where the gravitational potential energy is zero. It must be chosen or each problem. The choice is arbitrary since the change in the potential energy is the important quantity. Once the position is chosen, it must remain ixed or the entire problem. PEgrav mgh where h is the height o the object. h 3 4 Total mechanical energy (TME) The total amount o mechanical energy is merely the sum o the potential energy and the kinetic energy. This sum is simply reerred to as the total mechanical energy (abbreviated TME). TME KE PE mgh Law o conservation o energy The total amount o mechanical energy is merely the sum o the potential energy and the kinetic energy. Or: TME i TME KEi PEi KE PE No new energy is created and no existing energy is destroyed. This is the principle o conservation o energy
5 5/0/04 Law o conservation o energy Example 5.5 I the surace is smooth what is the velocity at B i the initial velocity at A is zero? Video 0 o Week 05: Work and energy We will treat the problem with the law o conservation o energy: TMEA TMEB A mgha 0 mghb v g h h 4 m/s A B 0 m B 7 8 Conservative orce Video 03 o Week 05: Kinetic and potential energies Any orce that has the property that the work it does is the same or all paths between any two given points is said to be conservative orce. Gravitational, electrical and spring orces are examples o conservative orces. riction and many other orces are not conservative
6 5/0/04 Summary o week 05 Quiz or week 05 Work o a orce is: W(). x cos() x Kinetic and potential energies are respectively: KE PEgrav mgh A orce is conservative when its work between two points is independent o the path between the two points. Gravitational orce is conservative but riction is not. 6
Energy present in a variety of forms. Energy can be transformed form one form to another Energy is conserved (isolated system) ENERGY
 ENERGY Energy present in a variety of forms Mechanical energy Chemical energy Nuclear energy Electromagnetic energy Energy can be transformed form one form to another Energy is conserved (isolated system)
ENERGY Energy present in a variety of forms Mechanical energy Chemical energy Nuclear energy Electromagnetic energy Energy can be transformed form one form to another Energy is conserved (isolated system)
Physics 111 Lecture 6 Work-Energy -Power Dr.Ali ÖVGÜN
 Physics 111 Lecture 6 Work-Energy -Power Dr.Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Why Energy? q Why do we need a concept o energy? q The energy approach to describing motion is particularly useul
Physics 111 Lecture 6 Work-Energy -Power Dr.Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Why Energy? q Why do we need a concept o energy? q The energy approach to describing motion is particularly useul
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy. No Recitation Quiz this week
 Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Physics 231 Lecture 9
 Physics 31 Lecture 9 Mi Main points o today s lecture: Potential energy: ΔPE = PE PE = mg ( y ) 0 y 0 Conservation o energy E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Reading Quiz 3. I you raise an object to a greater
Physics 31 Lecture 9 Mi Main points o today s lecture: Potential energy: ΔPE = PE PE = mg ( y ) 0 y 0 Conservation o energy E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Reading Quiz 3. I you raise an object to a greater
0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 2
 0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 2 Work, Power, Energy Work If a force is applied to a body, which then moves, we say the force does work. In 1D, if the force is constant with magnitude F, and the body moves
0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 2 Work, Power, Energy Work If a force is applied to a body, which then moves, we say the force does work. In 1D, if the force is constant with magnitude F, and the body moves
One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s
 One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s v x t Position x Meters Speed v m/s v t Length l Meters
One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s v x t Position x Meters Speed v m/s v t Length l Meters
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
FORCE, WORK, ENERGY & POWER
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) PHYS 101 - LECTURE 5 FORCE, WORK, ENERGY & POWER DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM 1 What change the state of object is called force. We mean by saying state, shape or position of the
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) PHYS 101 - LECTURE 5 FORCE, WORK, ENERGY & POWER DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM 1 What change the state of object is called force. We mean by saying state, shape or position of the
Physics 121. Tuesday, February 19, Physics 121. Tuesday, February 19, Physics 121. Course announcements. Topics:
 Physics 121. Tuesday, ebruary 19, 2008. avy Lt. Ron Candiloro's /A-18 Hornet creates a shock wave as he breaks the sound barrier July 7. The shock wave is visible as a large cloud o condensation ormed
Physics 121. Tuesday, ebruary 19, 2008. avy Lt. Ron Candiloro's /A-18 Hornet creates a shock wave as he breaks the sound barrier July 7. The shock wave is visible as a large cloud o condensation ormed
5-2 Energy. Potential and Kinetic Energy. Energy: The ability to do work. Vocabulary
 5-2 Energy Potential and Kinetic Energy Vocabulary Energy: The ability to do work. There are many dierent types o energy. This chapter will ocus on only mechanical energy, or the energy related to position
5-2 Energy Potential and Kinetic Energy Vocabulary Energy: The ability to do work. There are many dierent types o energy. This chapter will ocus on only mechanical energy, or the energy related to position
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY. Chapter 6 (cont.)
 KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
Physics 231 Lecture 12
 Physics 31 Lecture 1 Work energy theorem W Potential energy o gravity: ΔPE total = = PE KE PE KE 0 mg Conservation o energy ( y ) 0 y 0 E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Potential energy o a spring = PE = 1 kx
Physics 31 Lecture 1 Work energy theorem W Potential energy o gravity: ΔPE total = = PE KE PE KE 0 mg Conservation o energy ( y ) 0 y 0 E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Potential energy o a spring = PE = 1 kx
Work changes Energy. Do Work Son!
 1 Work changes Energy Do Work Son! 2 Do Work Son! 3 Work Energy Relationship 2 types of energy kinetic : energy of an object in motion potential: stored energy due to position or stored in a spring Work
1 Work changes Energy Do Work Son! 2 Do Work Son! 3 Work Energy Relationship 2 types of energy kinetic : energy of an object in motion potential: stored energy due to position or stored in a spring Work
There are two types of forces: conservative (gravity, spring force) nonconservative (friction)
 Chapter 8: Conservation o Energy There are two types o orces: conservative (gravity, spring orce) nonconservative (riction) Conservative Forces Conservative Force the work done by the orce on an object
Chapter 8: Conservation o Energy There are two types o orces: conservative (gravity, spring orce) nonconservative (riction) Conservative Forces Conservative Force the work done by the orce on an object
Work and Energy continued
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy continued 6.2 The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy Chapters 1 5 Motion equations were been developed, that relate the concepts of velocity, speed, displacement, time, and
Chapter 6 Work and Energy continued 6.2 The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy Chapters 1 5 Motion equations were been developed, that relate the concepts of velocity, speed, displacement, time, and
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
The Long List of Things to Memorize
 8 th Grade Physics BASIS Peoria Pre Comprehensive Exam Prep The Long List of Things to Memorize How to use this guide o This is a list of items that must be memorized in order to have success on the precomprehensive
8 th Grade Physics BASIS Peoria Pre Comprehensive Exam Prep The Long List of Things to Memorize How to use this guide o This is a list of items that must be memorized in order to have success on the precomprehensive
Work and Energy. chapter 7
 chapter 7 Work and Energy Work Work in one dimension: (Section 7.1, part 1) The following two problems involve pulleys and may be used after Example 2 in Section 7.1: 1. twood machine 2. Raising m by a
chapter 7 Work and Energy Work Work in one dimension: (Section 7.1, part 1) The following two problems involve pulleys and may be used after Example 2 in Section 7.1: 1. twood machine 2. Raising m by a
W = F Δx or W = F Δx cosθ
 WORK AND ENERGY When a force acts upon an object to cause a displacement of the object, it is said that work was done upon the object. In order for a force to qualify as having done work on an object,
WORK AND ENERGY When a force acts upon an object to cause a displacement of the object, it is said that work was done upon the object. In order for a force to qualify as having done work on an object,
Chapter 5: Energy. Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy
 Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Chapter 4. Energy. Work Power Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy. W = Fs Work = (force)(distance)
 Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Gravitational Potential Energy (filled in)
 Name: Date: 4/3 Period: Unit 5 Gravitational Potential Energy (filled in) Essential Questions: Why is energy and work useful to learn? What does work mean in physics? What does energy mean in physics?
Name: Date: 4/3 Period: Unit 5 Gravitational Potential Energy (filled in) Essential Questions: Why is energy and work useful to learn? What does work mean in physics? What does energy mean in physics?
The content contained in all sections of chapter 6 of the textbook is included on the AP Physics B exam.
 WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system is always
WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system is always
Physics 2414 Group Exercise 8. Conservation of Energy
 Physics 244 Group Exercise 8 Name : OUID : Name 2: OUID 2: Name 3: OUID 3: Name 4: OUID 4: Section Number: Solutions Solutions Conservation of Energy A mass m moves from point i to point f under the action
Physics 244 Group Exercise 8 Name : OUID : Name 2: OUID 2: Name 3: OUID 3: Name 4: OUID 4: Section Number: Solutions Solutions Conservation of Energy A mass m moves from point i to point f under the action
Work Up an Incline. Work = Force x Distance. Push up: 1500J. What is the PE at the top? mg = 500N. An incline is a simple machine!
 Quick Question Work Up an Incline The block o ice weighs 500 Newtons. How much work does it take to push it up the incline compared to liting it straight up? Ignore riction. Work Up an Incline Work = Force
Quick Question Work Up an Incline The block o ice weighs 500 Newtons. How much work does it take to push it up the incline compared to liting it straight up? Ignore riction. Work Up an Incline Work = Force
Work and energy. 15 m. c. Find the work done by the normal force exerted by the incline on the crate.
 Work and energy 1. A 10.0-kg crate is pulled 15.0 m up along a frictionless incline as shown in the figure below. The crate starts at rest and has a final speed of 6.00 m/s. motor 15 m 5 a. Draw the free-body
Work and energy 1. A 10.0-kg crate is pulled 15.0 m up along a frictionless incline as shown in the figure below. The crate starts at rest and has a final speed of 6.00 m/s. motor 15 m 5 a. Draw the free-body
Lecture 10. Potential energy and conservation of energy
 Lecture 10 Potential energy and conservation of energy Today s Topics: Potential Energy and work done by conservative forces Work done by nonconservative forces Conservation of mechanical energy Potential
Lecture 10 Potential energy and conservation of energy Today s Topics: Potential Energy and work done by conservative forces Work done by nonconservative forces Conservation of mechanical energy Potential
Other Examples of Energy Transfer
 Chapter 7 Work and Energy Overview energy. Study work as defined in physics. Relate work to kinetic energy. Consider work done by a variable force. Study potential energy. Understand energy conservation.
Chapter 7 Work and Energy Overview energy. Study work as defined in physics. Relate work to kinetic energy. Consider work done by a variable force. Study potential energy. Understand energy conservation.
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
Units are important anyway
 Ch. 1 Units -- SI System (length m, Mass Kg and Time s). Dimensions -- First check of Mathematical relation. Trigonometry -- Cosine, Sine and Tangent functions. -- Pythagorean Theorem Scalar and Vector
Ch. 1 Units -- SI System (length m, Mass Kg and Time s). Dimensions -- First check of Mathematical relation. Trigonometry -- Cosine, Sine and Tangent functions. -- Pythagorean Theorem Scalar and Vector
WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work scalar W = F S Cosθ Unit of work in SI system Work done by a constant force
 WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work Let a force be applied on a body so that the body gets displaced. Then work is said to be done. So work is said to be done if the point of application of force gets displaced.
WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work Let a force be applied on a body so that the body gets displaced. Then work is said to be done. So work is said to be done if the point of application of force gets displaced.
Chapters 10 & 11: Energy
 Chapters 10 & 11: Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not
Chapters 10 & 11: Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not
Lesson 5. Luis Anchordoqui. Physics 168. Tuesday, September 26, 17
 Lesson 5 Physics 168 1 C. B.-Champagne Luis Anchordoqui 2 2 Work Done by a Constant Force distance moved times component of force in direction of displacement W = Fd cos 3 Work Done by a Constant Force
Lesson 5 Physics 168 1 C. B.-Champagne Luis Anchordoqui 2 2 Work Done by a Constant Force distance moved times component of force in direction of displacement W = Fd cos 3 Work Done by a Constant Force
PHYS 221 General Physics II
 PHYS 221 General Physics II Elec. Potential Energy, Voltage, Equipotentials Spring 2015 Assigned Reading: 18.1 18.3 Lecture 4 Review: Gauss Law Last Lecture E q enc o E EAcos Gauss Law Very useful to determine
PHYS 221 General Physics II Elec. Potential Energy, Voltage, Equipotentials Spring 2015 Assigned Reading: 18.1 18.3 Lecture 4 Review: Gauss Law Last Lecture E q enc o E EAcos Gauss Law Very useful to determine
Lesson 4 Momentum and Energy
 Lesson 4 Momentum and Energy Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The previous lessons concentrated on the forces that cause objects to change motion. Lesson 4 will introduce momentum and energy, as
Lesson 4 Momentum and Energy Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The previous lessons concentrated on the forces that cause objects to change motion. Lesson 4 will introduce momentum and energy, as
XI PHYSICS. M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WORK, POWER AND ENERGY] CHAPTER NO. 7 A little concept of vector mathematics is applied here
XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WORK, POWER AND ENERGY] CHAPTER NO. 7 A little concept of vector mathematics is applied here
Slide. King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 8: POTENTIAL ENERGY LECTURE NO.
 Slide King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 8: POTENTIAL ENERGY LECTURE NO. 11 THIS PRESENTATION HAS EEN PREPARED Y: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED
Slide King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 8: POTENTIAL ENERGY LECTURE NO. 11 THIS PRESENTATION HAS EEN PREPARED Y: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED
GIANCOLI LESSON 6-1, WORK DONE BY A CONSTANT FORCE LESSON 6-2, WORK DONE BY A VARYING FORCE
 AP PHYSICS GIANCOLI LESSON 6-1, ORK DONE BY A CONSTANT ORCE LESSON 6-2, ORK DONE BY A VARYING ORCE Big Idea(s): The interactions of an object with other objects can be described by forces. Interactions
AP PHYSICS GIANCOLI LESSON 6-1, ORK DONE BY A CONSTANT ORCE LESSON 6-2, ORK DONE BY A VARYING ORCE Big Idea(s): The interactions of an object with other objects can be described by forces. Interactions
Essentially, the amount of work accomplished can be determined two ways:
 1 Work and Energy Work is done on an object that can exert a resisting force and is only accomplished if that object will move. In particular, we can describe work done by a specific object (where a force
1 Work and Energy Work is done on an object that can exert a resisting force and is only accomplished if that object will move. In particular, we can describe work done by a specific object (where a force
Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum
 Physics 101 Lecture 1 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net external
Physics 101 Lecture 1 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net external
Chapter 6. Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy The Ideal Spring HOOKE S LAW: RESTORING FORCE OF AN IDEAL SPRING The restoring orce on an ideal spring is F x = k x SI unit or k: N/m The Ideal Spring Example: A Tire Pressure
Chapter 6 Work and Energy The Ideal Spring HOOKE S LAW: RESTORING FORCE OF AN IDEAL SPRING The restoring orce on an ideal spring is F x = k x SI unit or k: N/m The Ideal Spring Example: A Tire Pressure
WORK, POWER AND ENERGY
 WORK, POWER AND ENERGY Important Points:. Dot Product: a) Scalar product is defined as the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. The dot product of two vectors
WORK, POWER AND ENERGY Important Points:. Dot Product: a) Scalar product is defined as the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. The dot product of two vectors
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN -3: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: The fundamental concept of energy lays the basis upon which much of
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN -3: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: The fundamental concept of energy lays the basis upon which much of
Chapter 10: Energy and Work. Slide 10-2
 Chapter 10: Energy and Work Slide 10-2 Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy K U g U s Thermal Energy Other forms include E th E chem E nuclear The Basic Energy Model An exchange of energy between the system
Chapter 10: Energy and Work Slide 10-2 Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy K U g U s Thermal Energy Other forms include E th E chem E nuclear The Basic Energy Model An exchange of energy between the system
Chapter 5 Work and Energy
 Chapter 5 Work and Energy Work and Kinetic Energy Work W in 1D Motion: by a Constant orce by a Varying orce Kinetic Energy, KE: the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy E and Its Conservation Potential
Chapter 5 Work and Energy Work and Kinetic Energy Work W in 1D Motion: by a Constant orce by a Varying orce Kinetic Energy, KE: the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy E and Its Conservation Potential
CBSE Class 9 Work Energy and Power Quick Study Chapter Note
 CBSE Class 9 Work Energy and Power Quick Study Chapter Note Work: In our daily life anything that makes us tired is known as work. For example, reading, writing, painting, walking, etc. In physics work
CBSE Class 9 Work Energy and Power Quick Study Chapter Note Work: In our daily life anything that makes us tired is known as work. For example, reading, writing, painting, walking, etc. In physics work
Conservative vs. Non-conservative forces Gravitational Potential Energy. Conservation of Mechanical energy
 Next topic Conservative vs. Non-conservative forces Gravitational Potential Energy Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical energy Work done by non-conservative forces and changes in mechanical energy
Next topic Conservative vs. Non-conservative forces Gravitational Potential Energy Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical energy Work done by non-conservative forces and changes in mechanical energy
Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work
 Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric potential energy Relate it to work Ex: charge in uniform electric field, point charges Apply these concepts
Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric potential energy Relate it to work Ex: charge in uniform electric field, point charges Apply these concepts
Potential Energy. Serway 7.6, 7.7;
 Potential Energy Conservative and non-conservative forces Gravitational and elastic potential energy Mechanical Energy Serway 7.6, 7.7; 8.1 8.2 Practice problems: Serway chapter 7, problems 41, 43 chapter
Potential Energy Conservative and non-conservative forces Gravitational and elastic potential energy Mechanical Energy Serway 7.6, 7.7; 8.1 8.2 Practice problems: Serway chapter 7, problems 41, 43 chapter
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 7 Energy Name: Lab Partner: Section: 7.1 Purpose In this experiment, energy and work will be explored. The relationship between total energy, kinetic energy and potential energy will be observed.
Chapter 7 Energy Name: Lab Partner: Section: 7.1 Purpose In this experiment, energy and work will be explored. The relationship between total energy, kinetic energy and potential energy will be observed.
Slide. King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept.
 Slide King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 7: ENERGY AND ENERGY TRANSFER LECTURE NO. 11 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR
Slide King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 7: ENERGY AND ENERGY TRANSFER LECTURE NO. 11 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR
ENERGY. Conservative Forces Non-Conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Power
 ENERGY Conservative Forces Non-Conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Power Conservative Forces A force is conservative if the work it does on an object moving between two points is independent
ENERGY Conservative Forces Non-Conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Power Conservative Forces A force is conservative if the work it does on an object moving between two points is independent
PHY 101. Work and Kinetic Energy 7.1 Work Done by a Constant Force
 PHY 101 DR M. A. ELERUJA KINETIC ENERGY AND WORK POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY CENTRE OF MASS AND LINEAR MOMENTUM Work is done by a force acting on an object when the point of application
PHY 101 DR M. A. ELERUJA KINETIC ENERGY AND WORK POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY CENTRE OF MASS AND LINEAR MOMENTUM Work is done by a force acting on an object when the point of application
Machines: Can You lift a car?
 Work=Force x Distance 10 m Units of work Nt-m=joules How much work? Machines: Can You lift a car? The ratio of the input force to the output force is called the Mechanical Advantage MA=5000/50=100 1 =
Work=Force x Distance 10 m Units of work Nt-m=joules How much work? Machines: Can You lift a car? The ratio of the input force to the output force is called the Mechanical Advantage MA=5000/50=100 1 =
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy Units of Chapter 6 Work Done by a Constant Force Work Done by a Varying Force Kinetic Energy, and the Work-Energy Principle Potential Energy Conservative and Nonconservative Forces
Chapter 6 Work and Energy Units of Chapter 6 Work Done by a Constant Force Work Done by a Varying Force Kinetic Energy, and the Work-Energy Principle Potential Energy Conservative and Nonconservative Forces
l1, l2, l3, ln l1 + l2 + l3 + ln
 Work done by a constant force: Consider an object undergoes a displacement S along a straight line while acted on a force F that makes an angle θ with S as shown The work done W by the agent is the product
Work done by a constant force: Consider an object undergoes a displacement S along a straight line while acted on a force F that makes an angle θ with S as shown The work done W by the agent is the product
Purpose of the experiment
 Work and Energy PES 1160 General Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment What is Work and how is related to Force? To understand the work done by a constant force and a variable force. To see how gravitational
Work and Energy PES 1160 General Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment What is Work and how is related to Force? To understand the work done by a constant force and a variable force. To see how gravitational
Chapter 6. Work and Kinetic Energy. Richard Feynman Nobel Prize in physics (1965)
 Chapter 6 ork and Kinetic Energy 1 Deinitions ebster s dictionary: Energy the capacity to do work ork the transer o energy Richard Feynman Nobel Prize in physics (1965) The Feynman Lectures on Physics....in
Chapter 6 ork and Kinetic Energy 1 Deinitions ebster s dictionary: Energy the capacity to do work ork the transer o energy Richard Feynman Nobel Prize in physics (1965) The Feynman Lectures on Physics....in
Conservation of Mechanical Energy 8.01
 Conservation o Mechanical Energy 8.01 Non-Conservative Forces Work done on the object by the orce depends on the path taken by the object Example: riction on an object moving on a level surace F riction
Conservation o Mechanical Energy 8.01 Non-Conservative Forces Work done on the object by the orce depends on the path taken by the object Example: riction on an object moving on a level surace F riction
Fs (30.0 N)(50.0 m) The magnitude of the force that the shopper exerts is f 48.0 N cos 29.0 cos 29.0 b. The work done by the pushing force F is
 Chapter 6: Problems 5, 6, 8, 38, 43, 49 & 53 5. ssm Suppose in Figure 6. that +1.1 1 3 J o work is done by the orce F (magnitude 3. N) in moving the suitcase a distance o 5. m. At what angle θ is the orce
Chapter 6: Problems 5, 6, 8, 38, 43, 49 & 53 5. ssm Suppose in Figure 6. that +1.1 1 3 J o work is done by the orce F (magnitude 3. N) in moving the suitcase a distance o 5. m. At what angle θ is the orce
TPS for Problem Solving Dr. Edward Prather
 TPS for Problem Solving Dr. Edward Prather University of Arizona Center for Astronomy Education (CAE) http://astronomy101.jpl.nasa.gov Insights from the Univ. of Arizona AAU STEM reform effort in Physics
TPS for Problem Solving Dr. Edward Prather University of Arizona Center for Astronomy Education (CAE) http://astronomy101.jpl.nasa.gov Insights from the Univ. of Arizona AAU STEM reform effort in Physics
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 6
 CHAPTER 6 1. Because there is no acceleration, the contact orce must have the same magnitude as the weight. The displacement in the direction o this orce is the vertical displacement. Thus, W = F Æy =
CHAPTER 6 1. Because there is no acceleration, the contact orce must have the same magnitude as the weight. The displacement in the direction o this orce is the vertical displacement. Thus, W = F Æy =
Tutorial 1 Calculating the Kinetic Energy of a Moving Object
 5. Energy As you learned in Section 5.1, mechanical work is done by applying orces on objects and displacing them. How are people, machines, and Earth able to do mechanical work? The answer is energy:
5. Energy As you learned in Section 5.1, mechanical work is done by applying orces on objects and displacing them. How are people, machines, and Earth able to do mechanical work? The answer is energy:
Lecture 12 (Kinetic Energy) Physics Spring 2017 Douglas Fields
 Lecture 12 (Kinetic Energy) Physics 160-02 Spring 2017 Douglas Fields Your Toolbox so far: Vectors Components, vector addition, etc. Position, velocity, acceleration Constant acceleration equations Newton
Lecture 12 (Kinetic Energy) Physics 160-02 Spring 2017 Douglas Fields Your Toolbox so far: Vectors Components, vector addition, etc. Position, velocity, acceleration Constant acceleration equations Newton
Physics 231. Topic 5: Energy and Work. Alex Brown October 2, MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 5: Energy and Work Alex Brown October 2, 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 What s up? (Friday Sept 26) 1) The correction exam is now open. The exam grades will be sent out after that on
Physics 231 Topic 5: Energy and Work Alex Brown October 2, 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 What s up? (Friday Sept 26) 1) The correction exam is now open. The exam grades will be sent out after that on
Forces and two masses.
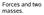 Forces and two masses. Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a +a M 1 M 2 Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a T +a m 1 a=t m 1 g 1 M 1 M 2 T m 2 a=m 2 g T 2 w 1 =m 1 g w 2 =m 2
Forces and two masses. Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a +a M 1 M 2 Atwood's Machine frictionless, massless pulley +a T +a m 1 a=t m 1 g 1 M 1 M 2 T m 2 a=m 2 g T 2 w 1 =m 1 g w 2 =m 2
CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
Power: Sources of Energy
 Chapter 5 Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Chapter 5 Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Work Done by a Constant Force
 Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
CHAPTER 13.3 AND 13.4 ENERGY
 CHAPTER 13.3 AND 13.4 ENERGY Section 13.3 Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy
CHAPTER 13.3 AND 13.4 ENERGY Section 13.3 Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy
In an avalanche, a mass of loose snow, soil, or rock suddenly gives way and slides down the side of a mountain.
 ENERGY Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy depends on Objective 4: What is non-mechanical
ENERGY Energy Objective 1: What is the relationship between energy and work? Objective 2: Identify the energy of position. Objective 3: The factors that kinetic energy depends on Objective 4: What is non-mechanical
Mechanics and Heat. Chapter 5: Work and Energy. Dr. Rashid Hamdan
 Mechanics and Heat Chapter 5: Work and Energy Dr. Rashid Hamdan 5.1 Work Done by a Constant Force Work Done by a Constant Force A force is said to do work if, when acting on a body, there is a displacement
Mechanics and Heat Chapter 5: Work and Energy Dr. Rashid Hamdan 5.1 Work Done by a Constant Force Work Done by a Constant Force A force is said to do work if, when acting on a body, there is a displacement
11th Grade. Review for General Exam-3. decreases. smaller than. remains the same
 1. An object is thrown horizontally with a speed of v from point M and hits point E on the vertical wall after t seconds as shown in the figure. (Ignore air friction.). Two objects M and S are thrown as
1. An object is thrown horizontally with a speed of v from point M and hits point E on the vertical wall after t seconds as shown in the figure. (Ignore air friction.). Two objects M and S are thrown as
Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department o Physics 8. Spring 4 Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation o Mechanical Energy D.1 Conservative and Non-conservative Force... D.1.1 Introduction...
MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department o Physics 8. Spring 4 Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation o Mechanical Energy D.1 Conservative and Non-conservative Force... D.1.1 Introduction...
5.3. Conservation of Energy
 5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
General Physics I Work & Energy
 General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes
 Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 3.1 & 3.3 & 3.4 - Energy, Work, and Power Energy, Work, and Power You need to know what energy, work, and power is, and the units for energy and
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 3.1 & 3.3 & 3.4 - Energy, Work, and Power Energy, Work, and Power You need to know what energy, work, and power is, and the units for energy and
Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power
 Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
Physics 201, Review 2
 Physics 01, Review Important Notes: v This review does not replace your own preparation efforts v The review is not meant to be complete. v Exercises used in this review do not form a test problem pool.
Physics 01, Review Important Notes: v This review does not replace your own preparation efforts v The review is not meant to be complete. v Exercises used in this review do not form a test problem pool.
In-Class Problems 20-21: Work and Kinetic Energy Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004 In-Class Problems 20-21: Work and Kinetic Energy Solutions In-Class-Problem 20 Calculating Work Integrals a) Work
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004 In-Class Problems 20-21: Work and Kinetic Energy Solutions In-Class-Problem 20 Calculating Work Integrals a) Work
Potential energy functions used in Chapter 7
 Potential energy functions used in Chapter 7 CHAPTER 7 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Conservation of mechanical energy Conservation of total energy of a system Examples Origin of friction Gravitational potential
Potential energy functions used in Chapter 7 CHAPTER 7 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Conservation of mechanical energy Conservation of total energy of a system Examples Origin of friction Gravitational potential
Physics 111. Lecture 15 (Walker: 7.1-2) Work & Energy March 2, Wednesday - Midterm 1
 Physics 111 Lecture 15 (Walker: 7.1-2) Work & Energy March 2, 2009 Wednesday - Midterm 1 Lecture 15 1/25 Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement:
Physics 111 Lecture 15 (Walker: 7.1-2) Work & Energy March 2, 2009 Wednesday - Midterm 1 Lecture 15 1/25 Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement:
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Introduction to Energy. Energy Approach to Problems. Lectures 13 and 14. Energy and Energy Transfer
 PC11 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer A/Pro Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
PC11 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer A/Pro Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
WORK ENERGY AND POWER
 WORK ENERGY AND POWER WORK PHYSICAL DEINITION When the point of application of force moves in the direction of the applied force under its effect then work is said to be done. MATHEMATICAL DEINITION O
WORK ENERGY AND POWER WORK PHYSICAL DEINITION When the point of application of force moves in the direction of the applied force under its effect then work is said to be done. MATHEMATICAL DEINITION O
In vertical circular motion the gravitational force must also be considered.
 Vertical Circular Motion In vertical circular motion the gravitational force must also be considered. An example of vertical circular motion is the vertical loop-the-loop motorcycle stunt. Normally, the
Vertical Circular Motion In vertical circular motion the gravitational force must also be considered. An example of vertical circular motion is the vertical loop-the-loop motorcycle stunt. Normally, the
grav mgr, where r is the radius of the bowl and grav W mgr kg 9.8 m s m J.
 Phys 0 Homework 9 Solutions 3. (a) The force of ity is constant, so the work it does is given by W F d, where F is the force and d is the displacement. The force is vertically downward and has magnitude
Phys 0 Homework 9 Solutions 3. (a) The force of ity is constant, so the work it does is given by W F d, where F is the force and d is the displacement. The force is vertically downward and has magnitude
Physics 2514 Lecture 34
 Physics 2514 Lecture 34 P. Gutierrez Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Oklahoma Physics 2514 p. 1/13 Information Information needed for the exam Exam will be in the same format as the practice
Physics 2514 Lecture 34 P. Gutierrez Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Oklahoma Physics 2514 p. 1/13 Information Information needed for the exam Exam will be in the same format as the practice
Physics 1A, Summer 2011, Summer Session 1 Quiz 3, Version A 1
 Physics 1A, Summer 2011, Summer Session 1 Quiz 3, Version A 1 Closed book and closed notes. No work needs to be shown. 1. Three rocks are thrown with identical speeds from the top of the same building.
Physics 1A, Summer 2011, Summer Session 1 Quiz 3, Version A 1 Closed book and closed notes. No work needs to be shown. 1. Three rocks are thrown with identical speeds from the top of the same building.
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Introduction to Energy. Energy Approach to Problems. Lectures 13 and 14. Energy and Energy Transfer
 PC1221 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer Dr Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
PC1221 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer Dr Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Physics 131
 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Energy Chemical bonding Intermolecular Interactions 1 Physics 131 Quiz 11 60 50 Q 1.1 11 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D 2 18 Q 1.2
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Energy Chemical bonding Intermolecular Interactions 1 Physics 131 Quiz 11 60 50 Q 1.1 11 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D 2 18 Q 1.2
Chapter 1: Mathematical Concepts and Vectors
 Chapter 1: Mathematical Concepts and Vectors giga G 1 9 mega M 1 6 kilo k 1 3 centi c 1 - milli m 1-3 micro μ 1-6 nano n 1-9 1 in =.54 cm 1 m = 1 cm = 3.81 t 1 mi = 58 t = 169 m 1 hr = 36 s 1 day = 86,4
Chapter 1: Mathematical Concepts and Vectors giga G 1 9 mega M 1 6 kilo k 1 3 centi c 1 - milli m 1-3 micro μ 1-6 nano n 1-9 1 in =.54 cm 1 m = 1 cm = 3.81 t 1 mi = 58 t = 169 m 1 hr = 36 s 1 day = 86,4
King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept.
 King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 7:Energy and Energy Transfer Presented by Nouf Saad Alkathran Imagine a system consisting of a book
King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 7:Energy and Energy Transfer Presented by Nouf Saad Alkathran Imagine a system consisting of a book
Ch 5 Work and Energy
 Ch 5 Work and Energy Energy Provide a different (scalar) approach to solving some physics problems. Work Links the energy approach to the force (Newton s Laws) approach. Mechanical energy Kinetic energy
Ch 5 Work and Energy Energy Provide a different (scalar) approach to solving some physics problems. Work Links the energy approach to the force (Newton s Laws) approach. Mechanical energy Kinetic energy
Kinetic Energy and Work
 Kinetic Energy and Work 8.01 W06D1 Today s Readings: Chapter 13 The Concept of Energy and Conservation of Energy, Sections 13.1-13.8 Announcements Problem Set 4 due Week 6 Tuesday at 9 pm in box outside
Kinetic Energy and Work 8.01 W06D1 Today s Readings: Chapter 13 The Concept of Energy and Conservation of Energy, Sections 13.1-13.8 Announcements Problem Set 4 due Week 6 Tuesday at 9 pm in box outside
Conservation of Energy and Momentum
 Conservation of Energy and Momentum Three criteria for Work There must be a force. There must be a displacement, d. The force must have a component parallel to the displacement. Work, W = F x d, W = Fd
Conservation of Energy and Momentum Three criteria for Work There must be a force. There must be a displacement, d. The force must have a component parallel to the displacement. Work, W = F x d, W = Fd
PH201 Chapter 7 Solutions
 PH0 Chapter 7 Solutions 7.6. Set Up: Use W F s ( F cos ) s Calculate the work done by each force. In each case, identify the angle In part (d), the net work is the algebraic sum of the work done by each
PH0 Chapter 7 Solutions 7.6. Set Up: Use W F s ( F cos ) s Calculate the work done by each force. In each case, identify the angle In part (d), the net work is the algebraic sum of the work done by each
This chapter covers all kinds of problems having to do with work in physics terms. Work
 Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
Chapter 7 Working the Physics Way In This Chapter Understanding work Working with net force Calculating kinetic energy Handling potential energy Relating kinetic energy to work This chapter covers all
