Physics 111 Lecture 6 Work-Energy -Power Dr.Ali ÖVGÜN
|
|
|
- Barry Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 111 Lecture 6 Work-Energy -Power Dr.Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department
2 Why Energy? q Why do we need a concept o energy? q The energy approach to describing motion is particularly useul when Newton s Laws are diicult or impossible to use. q Energy is a scalar quantity. It does not have a direction associated with it. October 7-13, 013
3 Kinetic Energy q Kinetic Energy is energy associated with the state o motion o an object q For an object moving with a speed o v K = 1 mv q SI unit: joule (J) 1 joule = 1 J = 1 kg m /s October 7-13, 013
4 Kinetic Energy or Various Objects KE = 1 mv October 7-13, 013
5 K = 1 mv Why? October 7-13, 013
6 Work W q Start with 1 mv 1 mv 0 = FxΔx Work W q Work provides a link between orce and energy q Work done on an object is transerred to/rom it q I W > 0, energy added: transerred to the object q I W < 0, energy taken away: transerred rom the object October 7-13, 013
7 Deinition o Work W q The work, W, done by a constant orce on an object is deined as the product o the component o the orce along the direction o displacement and the magnitude o the displacement W ( F cosθ )Δ x n F is the magnitude o the orce n Δ x is the magnitude o the object s displacement n θ is the angle between =!! F Δ x!! F and Δx October 7-13, 013
8 Work Unit q This gives no inormation about n the time it took or the displacement to occur n the velocity or acceleration o the object q Work is a scalar quantity q SI Unit n Newton meter = Joule n N m = J mv n J = kg m / s = ( kg m / s ) m W ( F cosθ )Δ x = 1 1 mv0 = ( F cosθ ) Δx!! F Δ x October 7-13, 013
9 Work: + or -? q Work can be positive, negative, or zero. The sign o the work depends on the direction o the orce relative to the displacement!! W ( F cosφ) s = F s q Work positive: i 90 > φ> 0 q Work negative: i 180 > φ> 90 q Work zero: W = 0 i φ= 90 q Work maximum i φ= 0 q Work minimum i φ = 180 October 7-13, 013
10 Work done by a Gravitational Force q Gravitational Force n Magnitude: mg n Direction: downwards to the Earth s center q Work done by Gravitational Force r r W = FΔ rcosθ = F Δ W net = 1 mv 1 mv 0 W g = mgδr cosθ November 3, 008
11 Example: When Work is Zero q A man carries a bucket o water horizontally at constant velocity. q The orce does no work on the bucket q Displacement is horizontal q Force is vertical q cos 90 = 0 W ( F cosθ ) Δx October 7-13, 013
12 Example: Work Can Be Positive or Negative q Work is positive when liting the box q Work would be negative i lowering the box n The orce would still be upward, but the displacement would be downward October 7-13, 013
13 Work Done by a Constant q Force The work W done a system by an agent exerting a constant orce on the system is the product o the magnitude F o the orce, the magnitude Δr o the displacement o the point o application o the orce, and cosθ, where θ is the angle between the orce and displacement vectors: W!! F Δr = FΔr cosθ W I W III I III F! = 0 Δr! F! Δr! = FΔr F! Δr! II W II W IV = FΔr F! Δr! IV = FΔr cosθ October 7-13, 013
14 Work and Force q An Eskimo returning pulls a sled as shown. The total mass o the sled is 50.0 kg, and he exerts a orce o N on the sled by pulling on the rope. How much work does he do on the sled i θ = 30 and he pulls the sled 5.0 m? W = ( F cosθ ) Δx = ( = J N)(cos30! )(5.0m) October 7-13, 013
15 Work Done by Multiple Forces q I more than one orce acts on an object, then the total work is equal to the algebraic sum o the work done by the individual orces W net = W by individual orces n Remember work is a scalar, so this is the algebraic sum W net = W + W + W = ( F cosθ ) Δr g N F October 7-13, 013
16 Problem Solving Strategy q Identiy the initial and inal positions o the body, and draw a ree body diagram showing and labeling all the orces acting on the body q Choose a coordinate system q List the unknown and known quantities, and decide which unknowns are your target variables q Calculate the work done by each orce. Be sure to check signs. Add the amounts o work done by each orce to ind the net (total) work W net q Check whether your answer makes sense October 7-13, 013
17 Kinetic Energy q Kinetic energy associated with the motion o an object 1 K = mv q Scalar quantity with the same unit as work q Work is related to kinetic energy 1 mv 1 mv 0 = F netδ x W = KE KE = ΔKE net i October 7-13, 013
18 Work-Energy Theorem q When work is done by a net orce on an object and the only change in the object is its speed, the work done is equal to the change in the object s kinetic energy W net = K K i = ΔK n Speed will increase i work is positive n Speed will decrease i work is negative W net = 1 mv 1 mv 0 October 7-13, 013
19 Potential Energy q Potential energy is associated with the position o the object q Gravitational Potential Energy is the energy associated with the relative position o an object in space near the Earth s surace q The gravitational potential energy n n n n PE mgy m is the mass o an object g is the acceleration o gravity y is the vertical position o the mass relative the surace o the Earth SI unit: joule (J) November 3, 008
20 Reerence Levels q A location where the gravitational potential energy is zero must be chosen or each problem n The choice is arbitrary since the change in the potential energy is the important quantity n Choose a convenient location or the zero reerence height n oten the Earth s surace n may be some other point suggested by the problem n Once the position is chosen, it must remain ixed or the entire problem November 3, 008
21 q PE = mgy q W g = mg( y Work and Gravitational = FΔy cosθ = q Units o Potential Energy are the same as those o Work and Kinetic Energy W grav ity Potential Energy y i = ) PE mg( y i i PE y )cos0 November 3, 008
22 xtended Work-Energy Theorem q The work-energy theorem can be extended to include potential energy: Wnet = KE KEi = ΔKE W grav ity PE q I we only have gravitational orce, then KE KE i = = q The sum o the kinetic energy and the gravitational potential energy remains constant at all time and hence is a conserved quantity PE i i KE + PE = PE + i PE PE KE i W net = W gravity November 3, 008
23 Extended Work-Energy Theorem q We denote the total mechanical energy by q Since E = KE + PE KE + PE = PE + i KE i q The total mechanical energy is conserved and remains the same at all times 1 1 mv i + mgyi = mv + mgy q I there is riction orce PE + KE = E + KE + PE E i i Lostbyriction Lostbyriction = d November 3, 008
24 Problem-Solving Strategy q Deine the system q Select the location o zero gravitational potential energy n Do not change this location while solving the problem q Identiy two points the object o interest moves between n One point should be where inormation is given n The other point should be where you want to ind out something November 3, 008
25 Platorm Diver q A diver o mass m drops rom a board 10.0 m above the water s surace. Neglect air resistance. q (a) Find is speed 5.0 m above the water surace q (b) Find his speed as he hits the water November 3, 008
26 Platorm Diver q (a) Find is speed 5.0 m above the water surace 1 1 mv i + mgyi = mv + mgy gy i = v + mgy v = g( y i y ) = (9.8m / s )(10m 5m) = 9.9m / s q (b) Find his speed as he hits the water mgy i = mv + 0 v = gyi =14m / s November 3, 008
27 Power q Work does not depend on time interval q The rate at which energy is transerred is important in the design and use o practical device q The time rate o energy transer is called power q The average power is given by W P = Δt n when the method o energy transer is work October 7-13, 013
28 Units o Power qthe SI unit o power is called the watt n 1 watt = 1 joule / second = 1 kg. m / s 3 qa unit o power in the US Customary system is horsepower n 1 hp = 550 t. lb/s = 746 W qunits o power can also be used to express units o work or energy n 1 kwh = (1000 W)(3600 s) = 3.6 x10 6 J October 7-13, 013
29 Problems October 7-13, 013
30 October 7-13, 013
31 October 7-13, 013
32 October 7-13, 013
33 October 7-13, 013
Physics 101 Lecture 7 Kinetic Energy and Work
 Phsics 101 Lecture 7 Kinetic Energ and Work Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department www.aovgun.com Wh Energ? q Wh do we need a concept of energ? q The energ approach to describing motion is particularl useful
Phsics 101 Lecture 7 Kinetic Energ and Work Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department www.aovgun.com Wh Energ? q Wh do we need a concept of energ? q The energ approach to describing motion is particularl useful
Physics 231 Lecture 9
 Physics 31 Lecture 9 Mi Main points o today s lecture: Potential energy: ΔPE = PE PE = mg ( y ) 0 y 0 Conservation o energy E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Reading Quiz 3. I you raise an object to a greater
Physics 31 Lecture 9 Mi Main points o today s lecture: Potential energy: ΔPE = PE PE = mg ( y ) 0 y 0 Conservation o energy E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Reading Quiz 3. I you raise an object to a greater
Energy present in a variety of forms. Energy can be transformed form one form to another Energy is conserved (isolated system) ENERGY
 ENERGY Energy present in a variety of forms Mechanical energy Chemical energy Nuclear energy Electromagnetic energy Energy can be transformed form one form to another Energy is conserved (isolated system)
ENERGY Energy present in a variety of forms Mechanical energy Chemical energy Nuclear energy Electromagnetic energy Energy can be transformed form one form to another Energy is conserved (isolated system)
Mechanics and Heat. Chapter 5: Work and Energy. Dr. Rashid Hamdan
 Mechanics and Heat Chapter 5: Work and Energy Dr. Rashid Hamdan 5.1 Work Done by a Constant Force Work Done by a Constant Force A force is said to do work if, when acting on a body, there is a displacement
Mechanics and Heat Chapter 5: Work and Energy Dr. Rashid Hamdan 5.1 Work Done by a Constant Force Work Done by a Constant Force A force is said to do work if, when acting on a body, there is a displacement
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
Physics 231 Lecture 12
 Physics 31 Lecture 1 Work energy theorem W Potential energy o gravity: ΔPE total = = PE KE PE KE 0 mg Conservation o energy ( y ) 0 y 0 E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Potential energy o a spring = PE = 1 kx
Physics 31 Lecture 1 Work energy theorem W Potential energy o gravity: ΔPE total = = PE KE PE KE 0 mg Conservation o energy ( y ) 0 y 0 E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Potential energy o a spring = PE = 1 kx
Chapter 5: Energy. Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy
 Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Physics 111. Lecture 15 (Walker: 7.1-2) Work & Energy March 2, Wednesday - Midterm 1
 Physics 111 Lecture 15 (Walker: 7.1-2) Work & Energy March 2, 2009 Wednesday - Midterm 1 Lecture 15 1/25 Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement:
Physics 111 Lecture 15 (Walker: 7.1-2) Work & Energy March 2, 2009 Wednesday - Midterm 1 Lecture 15 1/25 Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement:
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Introduction to Energy. Energy Approach to Problems. Lectures 13 and 14. Energy and Energy Transfer
 PC1221 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer Dr Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
PC1221 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer Dr Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work
 Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work Like other undamental concepts, energy is harder to deine in words than in equations. It is closely linked to the concept o orce. Conservation o Energy is one o Nature
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work Like other undamental concepts, energy is harder to deine in words than in equations. It is closely linked to the concept o orce. Conservation o Energy is one o Nature
Chapter 4. Energy. Work Power Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy. W = Fs Work = (force)(distance)
 Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Chapter 4 Energy In This Chapter: Work Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Work Work is a measure of the amount of change (in a general sense) that a force produces when it acts on a
Physics 2010 Work and Energy Recitation Activity 5 (Week 9)
 Physics 2010 Work and Energy Recitation Activity 5 (Week 9) Name Section Tues Wed Thu 8am 10am 12pm 2pm 1. The figure at right shows a hand pushing a block as it moves through a displacement Δ! s. a) Suppose
Physics 2010 Work and Energy Recitation Activity 5 (Week 9) Name Section Tues Wed Thu 8am 10am 12pm 2pm 1. The figure at right shows a hand pushing a block as it moves through a displacement Δ! s. a) Suppose
25/01/2014. Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power. Work of a force. Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (First part) Work = Force x Displacement
 5/0/04 Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power King Saud University College o Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. Phys 45 (General Physics) Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (Part ) Week n 5 This presentation
5/0/04 Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power King Saud University College o Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. Phys 45 (General Physics) Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (Part ) Week n 5 This presentation
Chapter 6. Work and Kinetic Energy. Richard Feynman Nobel Prize in physics (1965)
 Chapter 6 ork and Kinetic Energy 1 Deinitions ebster s dictionary: Energy the capacity to do work ork the transer o energy Richard Feynman Nobel Prize in physics (1965) The Feynman Lectures on Physics....in
Chapter 6 ork and Kinetic Energy 1 Deinitions ebster s dictionary: Energy the capacity to do work ork the transer o energy Richard Feynman Nobel Prize in physics (1965) The Feynman Lectures on Physics....in
Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum
 Physics 101 Lecture 1 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net external
Physics 101 Lecture 1 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net external
Chapter 6. Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy The Ideal Spring HOOKE S LAW: RESTORING FORCE OF AN IDEAL SPRING The restoring orce on an ideal spring is F x = k x SI unit or k: N/m The Ideal Spring Example: A Tire Pressure
Chapter 6 Work and Energy The Ideal Spring HOOKE S LAW: RESTORING FORCE OF AN IDEAL SPRING The restoring orce on an ideal spring is F x = k x SI unit or k: N/m The Ideal Spring Example: A Tire Pressure
Chapter 7 Work and Kinetic Energy. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 7 Work and Kinetic Energy Units of Chapter 7 Work Done by a Constant Force Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem Work Done by a Variable Force Power 7-1 Work Done by a Constant Force The definition
Chapter 7 Work and Kinetic Energy Units of Chapter 7 Work Done by a Constant Force Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem Work Done by a Variable Force Power 7-1 Work Done by a Constant Force The definition
Which iceboat crosses the finish line with more kinetic energy (KE)?
 Two iceboats (one of mass m, one of mass 2m) hold a race on a frictionless, horizontal, frozen lake. Both iceboats start at rest, and the wind exerts the same constant force on both iceboats. Which iceboat
Two iceboats (one of mass m, one of mass 2m) hold a race on a frictionless, horizontal, frozen lake. Both iceboats start at rest, and the wind exerts the same constant force on both iceboats. Which iceboat
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Lectures 13 and 14. Energy and Energy Transfer. Dr Tay Seng Chuan
 PC1221 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer Dr Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
PC1221 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer Dr Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Introduction to Energy. Energy Approach to Problems. Lectures 13 and 14. Energy and Energy Transfer
 PC11 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer A/Pro Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
PC11 Fundamentals o Physics I Lectures 13 and 14 Energy and Energy Transer A/Pro Tay Seng Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch o your handphone and pager Switch o your laptop computer and keep it No talking while
One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s
 One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s v x t Position x Meters Speed v m/s v t Length l Meters
One-Dimensional Motion Review IMPORTANT QUANTITIES Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Name Symbol Units Basic Equation Time t Seconds Velocity v m/s v x t Position x Meters Speed v m/s v t Length l Meters
Fs (30.0 N)(50.0 m) The magnitude of the force that the shopper exerts is f 48.0 N cos 29.0 cos 29.0 b. The work done by the pushing force F is
 Chapter 6: Problems 5, 6, 8, 38, 43, 49 & 53 5. ssm Suppose in Figure 6. that +1.1 1 3 J o work is done by the orce F (magnitude 3. N) in moving the suitcase a distance o 5. m. At what angle θ is the orce
Chapter 6: Problems 5, 6, 8, 38, 43, 49 & 53 5. ssm Suppose in Figure 6. that +1.1 1 3 J o work is done by the orce F (magnitude 3. N) in moving the suitcase a distance o 5. m. At what angle θ is the orce
Lecture 3. > Potential Energy. > Conservation of Energy. > Power. (Source: Serway; Giancoli) Villacorta--DLSUM-SCIENVP-L Term01
 Lecture 3 > Potential Energy > Conservation of Energy > Power (Source: Serway; Giancoli) 1 Conservative & Nonconservative Forces > Conservative forces allow objects to lose energy through work and gain
Lecture 3 > Potential Energy > Conservation of Energy > Power (Source: Serway; Giancoli) 1 Conservative & Nonconservative Forces > Conservative forces allow objects to lose energy through work and gain
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy. No Recitation Quiz this week
 Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Power: Sources of Energy
 Chapter 7: Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Chapter 7: Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Chapter 5 Work and Energy
 Chapter 5 Work and Energy Work and Kinetic Energy Work W in 1D Motion: by a Constant orce by a Varying orce Kinetic Energy, KE: the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy E and Its Conservation Potential
Chapter 5 Work and Energy Work and Kinetic Energy Work W in 1D Motion: by a Constant orce by a Varying orce Kinetic Energy, KE: the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy E and Its Conservation Potential
( ) = ( ) W net = ΔKE = KE f KE i W F. F d x. KE = 1 2 mv2. Note: Work is the dot product of F and d. Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem
 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem KE = 1 2 mv2 W F change in the kinetic energy of an object F d x net work done on the particle ( ) = ( ) W net = ΔKE = KE f KE i Note: Work is the dot product of F and d W g
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem KE = 1 2 mv2 W F change in the kinetic energy of an object F d x net work done on the particle ( ) = ( ) W net = ΔKE = KE f KE i Note: Work is the dot product of F and d W g
There are two types of forces: conservative (gravity, spring force) nonconservative (friction)
 Chapter 8: Conservation o Energy There are two types o orces: conservative (gravity, spring orce) nonconservative (riction) Conservative Forces Conservative Force the work done by the orce on an object
Chapter 8: Conservation o Energy There are two types o orces: conservative (gravity, spring orce) nonconservative (riction) Conservative Forces Conservative Force the work done by the orce on an object
Chapter 5 Gravitation Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 5 Gravitation Chapter 6 Work and Energy Chapter 5 (5.6) Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation (5.7) Gravity Near the Earth s Surface Chapter 6 (today) Work Done by a Constant Force Kinetic Energy,
Chapter 5 Gravitation Chapter 6 Work and Energy Chapter 5 (5.6) Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation (5.7) Gravity Near the Earth s Surface Chapter 6 (today) Work Done by a Constant Force Kinetic Energy,
Conservation of Energy and Momentum
 Conservation of Energy and Momentum Three criteria for Work There must be a force. There must be a displacement, d. The force must have a component parallel to the displacement. Work, W = F x d, W = Fd
Conservation of Energy and Momentum Three criteria for Work There must be a force. There must be a displacement, d. The force must have a component parallel to the displacement. Work, W = F x d, W = Fd
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Chapter 5. Work and Energy. continued
 Chapter 5 Work and Energy continued 5.2 Work on a Spring & Work by a Spring HOOKE S LAW Force Required to Distort an Ideal Spring The force applied to an ideal spring is proportional to the displacement
Chapter 5 Work and Energy continued 5.2 Work on a Spring & Work by a Spring HOOKE S LAW Force Required to Distort an Ideal Spring The force applied to an ideal spring is proportional to the displacement
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Lecture 9. > Potential Energy. > Conservation of Energy. > Power. (Source: Serway; Giancoli) Villacorta--DLSUM-BIOPHY1-L Term01
 Lecture 9 > Potential Energy > Conservation of Energy > Power (Source: Serway; Giancoli) 1 Conservative & Nonconservative Forces > The various ways work and energy appear in some processes lead to two
Lecture 9 > Potential Energy > Conservation of Energy > Power (Source: Serway; Giancoli) 1 Conservative & Nonconservative Forces > The various ways work and energy appear in some processes lead to two
The Electric Potential Energy
 Lecture 6 Chapter 25 The Electric Potential Energy Course website: http://aculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 25: Section 25.1 Electric Potential Energy
Lecture 6 Chapter 25 The Electric Potential Energy Course website: http://aculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 25: Section 25.1 Electric Potential Energy
Lecture 7 Chapter 7 Work Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 7 Chapter 7 Work Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy -- The money of physics Demo: Elastic Collisions Objects of equal mass exchange momentum in elastic collisions. 1 Demo: Blaster Balls
Lecture 7 Chapter 7 Work Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy -- The money of physics Demo: Elastic Collisions Objects of equal mass exchange momentum in elastic collisions. 1 Demo: Blaster Balls
Physics Unit 4:Work & Energy Name:
 Name: Review and Preview We have come a long way in our study of mechanics. We started with the concepts of displacement and time, and built up to the more complex quantities of velocity and acceleration.
Name: Review and Preview We have come a long way in our study of mechanics. We started with the concepts of displacement and time, and built up to the more complex quantities of velocity and acceleration.
CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
Units are important anyway
 Ch. 1 Units -- SI System (length m, Mass Kg and Time s). Dimensions -- First check of Mathematical relation. Trigonometry -- Cosine, Sine and Tangent functions. -- Pythagorean Theorem Scalar and Vector
Ch. 1 Units -- SI System (length m, Mass Kg and Time s). Dimensions -- First check of Mathematical relation. Trigonometry -- Cosine, Sine and Tangent functions. -- Pythagorean Theorem Scalar and Vector
Forces of Friction Contact between bodies with a relative velocity produces friction opposite
 Forces of Friction Contact between bodies with a relative velocity produces friction Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic
Forces of Friction Contact between bodies with a relative velocity produces friction Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic
The Electric. Potential Energy
 Lecture 7 Chapter 25 The Electric Ok, let s move to scalar quantities. Potential Energy I am sick and tired o your orces, ields!!! Course website: http://aculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii
Lecture 7 Chapter 25 The Electric Ok, let s move to scalar quantities. Potential Energy I am sick and tired o your orces, ields!!! Course website: http://aculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii
Physics 111. Lecture 18 (Walker: 8.3-4) Energy Conservation I March 11, Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 Physics 111 Lecture 18 (Walker: 8.3-4) Energy Conservation I March 11, 2009 Lecture 18 1/24 Conservation o Mechanical Energy Deinition o mechanical energy: (8-6) I the only work done in going rom the initial
Physics 111 Lecture 18 (Walker: 8.3-4) Energy Conservation I March 11, 2009 Lecture 18 1/24 Conservation o Mechanical Energy Deinition o mechanical energy: (8-6) I the only work done in going rom the initial
Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department o Physics 8. Spring 4 Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation o Mechanical Energy D.1 Conservative and Non-conservative Force... D.1.1 Introduction...
MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department o Physics 8. Spring 4 Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation o Mechanical Energy D.1 Conservative and Non-conservative Force... D.1.1 Introduction...
Work Up an Incline. Work = Force x Distance. Push up: 1500J. What is the PE at the top? mg = 500N. An incline is a simple machine!
 Quick Question Work Up an Incline The block o ice weighs 500 Newtons. How much work does it take to push it up the incline compared to liting it straight up? Ignore riction. Work Up an Incline Work = Force
Quick Question Work Up an Incline The block o ice weighs 500 Newtons. How much work does it take to push it up the incline compared to liting it straight up? Ignore riction. Work Up an Incline Work = Force
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power
 Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 17
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 17 Chapter 6: Conservation of Energy 6.7 Elastic Potential Energy 6.8 Power Chapter 7: Linear Momentum 7.1 A Vector Conservation Law 7. Momentum Lecture 17 Purdue University, Physics
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 17 Chapter 6: Conservation of Energy 6.7 Elastic Potential Energy 6.8 Power Chapter 7: Linear Momentum 7.1 A Vector Conservation Law 7. Momentum Lecture 17 Purdue University, Physics
Physics 1A Lecture 6B. "If the only tool you have is a hammer, every problem looks like a nail. --Abraham Maslow
 Physics 1A Lecture 6B "If the only tool you have is a hammer, every problem looks like a nail. --Abraham Maslow Work Let s assume a constant force F acts on a rolling ball in a trough at an angle θ over
Physics 1A Lecture 6B "If the only tool you have is a hammer, every problem looks like a nail. --Abraham Maslow Work Let s assume a constant force F acts on a rolling ball in a trough at an angle θ over
Kinetic Energy and Work
 Kinetic Energy and Work 8.01 W06D1 Today s Readings: Chapter 13 The Concept of Energy and Conservation of Energy, Sections 13.1-13.8 Announcements Problem Set 4 due Week 6 Tuesday at 9 pm in box outside
Kinetic Energy and Work 8.01 W06D1 Today s Readings: Chapter 13 The Concept of Energy and Conservation of Energy, Sections 13.1-13.8 Announcements Problem Set 4 due Week 6 Tuesday at 9 pm in box outside
Work Done by a Constant Force
 Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
Work and Energy Work Done by a Constant Force In physics, work is described by what is accomplished when a force acts on an object, and the object moves through a distance. The work done by a constant
ENERGY. Conservative Forces Non-Conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Power
 ENERGY Conservative Forces Non-Conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Power Conservative Forces A force is conservative if the work it does on an object moving between two points is independent
ENERGY Conservative Forces Non-Conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Power Conservative Forces A force is conservative if the work it does on an object moving between two points is independent
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 07: WORK & ENERGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO ENERGY & ENERGY FORMS ENERGY: A physical quantity without a precise definition. We don't know exactly WHAT it is, but we know HOW it works. - Energy "exists" in many forms;
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO ENERGY & ENERGY FORMS ENERGY: A physical quantity without a precise definition. We don't know exactly WHAT it is, but we know HOW it works. - Energy "exists" in many forms;
. According to the workenergy theorem (Equation 6.3), the work done by the net external force W catapult
 1. REASONING The work done by the catapult catapult is one contribution to the work done by the net external force that changes the kinetic energy of the plane. The other contribution is the work done
1. REASONING The work done by the catapult catapult is one contribution to the work done by the net external force that changes the kinetic energy of the plane. The other contribution is the work done
Be on time Switch off mobile phones. Put away laptops. Being present = Participating actively
 A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
Lecture III. Introduction to Mechanics, Heat, and Sound /FIC 318
 Introduction to Mechanics, Heat, and Sound /FIC 318 Lecture III Motion in two dimensions projectile motion The Laws of Motion Forces, Newton s first law Inertia, Newton s second law Newton s third law
Introduction to Mechanics, Heat, and Sound /FIC 318 Lecture III Motion in two dimensions projectile motion The Laws of Motion Forces, Newton s first law Inertia, Newton s second law Newton s third law
Conservation of Mechanical Energy 8.01
 Conservation o Mechanical Energy 8.01 Non-Conservative Forces Work done on the object by the orce depends on the path taken by the object Example: riction on an object moving on a level surace F riction
Conservation o Mechanical Energy 8.01 Non-Conservative Forces Work done on the object by the orce depends on the path taken by the object Example: riction on an object moving on a level surace F riction
Physics 101 Lecture 10 Rotation
 Physics 101 Lecture 10 Rotation Assist. Pro. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Rotational Motion Angular Position and Radians Angular Velocity Angular Acceleration Rigid Object under
Physics 101 Lecture 10 Rotation Assist. Pro. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Rotational Motion Angular Position and Radians Angular Velocity Angular Acceleration Rigid Object under
Chapter 8. Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Conservation of Energy Energy Review Kinetic Energy Associated with movement of members of a system Potential Energy Determined by the configuration of the system Gravitational and Elastic Potential
Chapter 8 Conservation of Energy Energy Review Kinetic Energy Associated with movement of members of a system Potential Energy Determined by the configuration of the system Gravitational and Elastic Potential
Tutorial 1 Calculating the Kinetic Energy of a Moving Object
 5. Energy As you learned in Section 5.1, mechanical work is done by applying orces on objects and displacing them. How are people, machines, and Earth able to do mechanical work? The answer is energy:
5. Energy As you learned in Section 5.1, mechanical work is done by applying orces on objects and displacing them. How are people, machines, and Earth able to do mechanical work? The answer is energy:
Other Examples of Energy Transfer
 Chapter 7 Work and Energy Overview energy. Study work as defined in physics. Relate work to kinetic energy. Consider work done by a variable force. Study potential energy. Understand energy conservation.
Chapter 7 Work and Energy Overview energy. Study work as defined in physics. Relate work to kinetic energy. Consider work done by a variable force. Study potential energy. Understand energy conservation.
Lectures Chapter 6 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Work and Energy Lectures 16-17 Chapter 6 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 Work and Energy: Work done by a constant force Constant pushing force F pointing in the same direction
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Work and Energy Lectures 16-17 Chapter 6 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 Work and Energy: Work done by a constant force Constant pushing force F pointing in the same direction
Work and Energy continued
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy continued 6.2 The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy Chapters 1 5 Motion equations were been developed, that relate the concepts of velocity, speed, displacement, time, and
Chapter 6 Work and Energy continued 6.2 The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy Chapters 1 5 Motion equations were been developed, that relate the concepts of velocity, speed, displacement, time, and
Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws
 Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws Other Important Aspects of the Second Law: Note that = ma is a vector equation, i.e., it is equivalent to saying: = ma x y z = ma = ma An object accelerates in the same
Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws Other Important Aspects of the Second Law: Note that = ma is a vector equation, i.e., it is equivalent to saying: = ma x y z = ma = ma An object accelerates in the same
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
Chapter 5. Work and Energy. continued
 Chapter 5 Work and Energy continued 5.2 Work on a Spring & Work by a Spring Work done by applied force stretching (or compressing) a spring. Force is changing while stretching so use the average force.
Chapter 5 Work and Energy continued 5.2 Work on a Spring & Work by a Spring Work done by applied force stretching (or compressing) a spring. Force is changing while stretching so use the average force.
Physics 10 Lecture 7A. "Energy and persistence conquer all things. --Benjamin Franklin
 Physics 10 Lecture 7A "Energy and persistence conquer all things. --Benjamin Franklin Quiz 1 Info It will be a Scantron test covering Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. A list of equations, constants, and
Physics 10 Lecture 7A "Energy and persistence conquer all things. --Benjamin Franklin Quiz 1 Info It will be a Scantron test covering Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. A list of equations, constants, and
The Laws of Motion. Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples
 The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4 Main points of last lecture Scalars vs. Vectors Vectors A: (A x, A y ) or A & θ Addition/Subtraction Projectile Motion X-direction: a x = 0 (v x = constant)
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4 Main points of last lecture Scalars vs. Vectors Vectors A: (A x, A y ) or A & θ Addition/Subtraction Projectile Motion X-direction: a x = 0 (v x = constant)
Physics 1A Lecture 4B. "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig inches per second. --J. Hart
 Physics 1A Lecture 4B "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig 39.37 inches per second. --J. Hart Types of Forces There are many types of forces that we will apply in this class, let s discuss
Physics 1A Lecture 4B "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig 39.37 inches per second. --J. Hart Types of Forces There are many types of forces that we will apply in this class, let s discuss
Chapter 4. Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion. That is, describing why objects move
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal orce, Tension, riction ree-body
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal orce, Tension, riction ree-body
Isaac Newton ( ) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity
 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Chapter 4. The Laws of Motion. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Dr. Armen Kocharian Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical
Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Dr. Armen Kocharian Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture 7. Forces. Important note: First Exam is next Tuesday, Feb. 6, 8:15-9:45 pm (see link on Canvas for locations)
 Lecture 7 Forces Important note: First Exam is next Tuesday, Feb. 6, 8:15-9:45 pm (see link on Canvas for locations) Today s Topics: Forces The gravitational force The normal force Frictional Forces Next
Lecture 7 Forces Important note: First Exam is next Tuesday, Feb. 6, 8:15-9:45 pm (see link on Canvas for locations) Today s Topics: Forces The gravitational force The normal force Frictional Forces Next
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
13.7 Power Applied by a Constant Force
 13.7 Power Applied by a Constant Force Suppose that an applied force F a acts on a body during a time interval Δt, and the displacement of the point of application of the force is in the x -direction by
13.7 Power Applied by a Constant Force Suppose that an applied force F a acts on a body during a time interval Δt, and the displacement of the point of application of the force is in the x -direction by
Newton s First Law and IRFs
 Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
Physics 121. Tuesday, February 19, Physics 121. Tuesday, February 19, Physics 121. Course announcements. Topics:
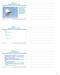 Physics 121. Tuesday, ebruary 19, 2008. avy Lt. Ron Candiloro's /A-18 Hornet creates a shock wave as he breaks the sound barrier July 7. The shock wave is visible as a large cloud o condensation ormed
Physics 121. Tuesday, ebruary 19, 2008. avy Lt. Ron Candiloro's /A-18 Hornet creates a shock wave as he breaks the sound barrier July 7. The shock wave is visible as a large cloud o condensation ormed
Chapter 7 Kinetic Energy and Work
 Prof. Dr. I. Nasser Chapter7_I 14/11/017 Chapter 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Energy: Measure of the ability of a body or system to do work or produce a change, expressed usually in joules or kilowatt hours
Prof. Dr. I. Nasser Chapter7_I 14/11/017 Chapter 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Energy: Measure of the ability of a body or system to do work or produce a change, expressed usually in joules or kilowatt hours
AP PHYSICS 1. Energy 2016 EDITION
 AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
Physics 11 HW #6 Solutions
 Physics HW #6 Solutions Chapter 6: Focus On Concepts:,,, Probles: 8, 4, 4, 43, 5, 54, 66, 8, 85 Focus On Concepts 6- (b) Work is positive when the orce has a coponent in the direction o the displaceent.
Physics HW #6 Solutions Chapter 6: Focus On Concepts:,,, Probles: 8, 4, 4, 43, 5, 54, 66, 8, 85 Focus On Concepts 6- (b) Work is positive when the orce has a coponent in the direction o the displaceent.
PHY 101. Work and Kinetic Energy 7.1 Work Done by a Constant Force
 PHY 101 DR M. A. ELERUJA KINETIC ENERGY AND WORK POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY CENTRE OF MASS AND LINEAR MOMENTUM Work is done by a force acting on an object when the point of application
PHY 101 DR M. A. ELERUJA KINETIC ENERGY AND WORK POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY CENTRE OF MASS AND LINEAR MOMENTUM Work is done by a force acting on an object when the point of application
Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy
 Welcome back to Physics 15 Today s agenda: Work Power Physics 15 Spring 017 Lecture 10-1 1 Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy For an object of mass m near the surface of the earth: U g = mgh h is height
Welcome back to Physics 15 Today s agenda: Work Power Physics 15 Spring 017 Lecture 10-1 1 Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy For an object of mass m near the surface of the earth: U g = mgh h is height
Physics 1401V October 28, 2016 Prof. James Kakalios Quiz No. 2
 This is a closed book, closed notes, quiz. Only simple (non-programmable, nongraphing) calculators are permitted. Define all symbols and justify all mathematical expressions used. Make sure to state all
This is a closed book, closed notes, quiz. Only simple (non-programmable, nongraphing) calculators are permitted. Define all symbols and justify all mathematical expressions used. Make sure to state all
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW QUICK REFERENCE. Important Terms
 Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
Pre-AP Physics Chapter 1 Notes Yockers JHS 2008
 Pre-AP Physics Chapter 1 Notes Yockers JHS 2008 Standards o Length, Mass, and Time ( - length quantities) - mass - time Derived Quantities: Examples Dimensional Analysis useul to check equations and to
Pre-AP Physics Chapter 1 Notes Yockers JHS 2008 Standards o Length, Mass, and Time ( - length quantities) - mass - time Derived Quantities: Examples Dimensional Analysis useul to check equations and to
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Section 1 Changes in Motion. Chapter 4. Preview. Objectives Force Force Diagrams
 Section 1 Changes in Motion Preview Objectives Force Force Diagrams Section 1 Changes in Motion Objectives Describe how force affects the motion of an object. Interpret and construct free body diagrams.
Section 1 Changes in Motion Preview Objectives Force Force Diagrams Section 1 Changes in Motion Objectives Describe how force affects the motion of an object. Interpret and construct free body diagrams.
Physics 111. Applying Newton s Laws. Lecture 9 (Walker: 5.4-5) Newton s Third Law Free Body Diagram Solving 2-D Force Problems Weight & Gravity
 Phsics 111 Lecture 9 (Walker: 5.4-5) Newton s Third Law ree Bod Diagram Solving -D orce Problems Weight & Gravit Sept. 1, 009 Quiz Wednesda - Chaps. 3 & 4 Lecture 9 1/6 Newton s Third Law of Motion orces
Phsics 111 Lecture 9 (Walker: 5.4-5) Newton s Third Law ree Bod Diagram Solving -D orce Problems Weight & Gravit Sept. 1, 009 Quiz Wednesda - Chaps. 3 & 4 Lecture 9 1/6 Newton s Third Law of Motion orces
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 6
 CHAPTER 6 1. Because there is no acceleration, the contact orce must have the same magnitude as the weight. The displacement in the direction o this orce is the vertical displacement. Thus, W = F Æy =
CHAPTER 6 1. Because there is no acceleration, the contact orce must have the same magnitude as the weight. The displacement in the direction o this orce is the vertical displacement. Thus, W = F Æy =
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work
 Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work Conservation of Energy is one of Nature s fundamental laws that is not violated. Energy can take on different forms in a given system. This chapter we will discuss work
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work Conservation of Energy is one of Nature s fundamental laws that is not violated. Energy can take on different forms in a given system. This chapter we will discuss work
Chapter 3: Force, Work and Energy
 Chapter 3: Force and Force Equilibrium Chapter 3: Force, Work and Energy Chapter 3: Force, Work and Energy 3.1 Mass and Weight 3.2 Newton's Law of Gravitation 3.3 Force and Newton's 3 Laws of Motion 3.4
Chapter 3: Force and Force Equilibrium Chapter 3: Force, Work and Energy Chapter 3: Force, Work and Energy 3.1 Mass and Weight 3.2 Newton's Law of Gravitation 3.3 Force and Newton's 3 Laws of Motion 3.4
XI PHYSICS. M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WORK, POWER AND ENERGY] CHAPTER NO. 7 A little concept of vector mathematics is applied here
XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WORK, POWER AND ENERGY] CHAPTER NO. 7 A little concept of vector mathematics is applied here
6.0 Energy Conservation. 6.1 Work
 Phys 300/301 Physics: Algebra/Trig Eugene Hecht, 3e. Prepared 1/09/05 6.0 Energy Conservation After Newtonian mechanics came a lull in the state of mechanical physics. In the beginning of the 1800 s, the
Phys 300/301 Physics: Algebra/Trig Eugene Hecht, 3e. Prepared 1/09/05 6.0 Energy Conservation After Newtonian mechanics came a lull in the state of mechanical physics. In the beginning of the 1800 s, the
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 Changes in Motion. Section 2 Newton's First Law. Section 3 Newton's Second and Third Laws
 Forces and the Laws of Motion Table of Contents Section 1 Changes in Motion Section 2 Newton's First Law Section 3 Newton's Second and Third Laws Section 4 Everyday Forces Section 1 Changes in Motion Objectives
Forces and the Laws of Motion Table of Contents Section 1 Changes in Motion Section 2 Newton's First Law Section 3 Newton's Second and Third Laws Section 4 Everyday Forces Section 1 Changes in Motion Objectives
Sometimes (like on AP test) you will see the equation like this:
 Work, Energy & Momentum Notes Chapter 5 & 6 The two types of energy we will be working with in this unit are: (K in book KE): Energy associated with of an object. (U in book PE): Energy associated with
Work, Energy & Momentum Notes Chapter 5 & 6 The two types of energy we will be working with in this unit are: (K in book KE): Energy associated with of an object. (U in book PE): Energy associated with
Worksheet for Exploration 6.1: An Operational Definition of Work
 Worksheet for Exploration 6.1: An Operational Definition of Work This Exploration allows you to discover how work causes changes in kinetic energy. Restart. Drag "handy" to the front and/or the back of
Worksheet for Exploration 6.1: An Operational Definition of Work This Exploration allows you to discover how work causes changes in kinetic energy. Restart. Drag "handy" to the front and/or the back of
The relationship between force and distance has a name. WORK
 EWP The relationship between force and distance has a name. WORK WORK - the product of the net force and distance through which an object moves in the direction of the net force. W=F d where W=work joules
EWP The relationship between force and distance has a name. WORK WORK - the product of the net force and distance through which an object moves in the direction of the net force. W=F d where W=work joules
Chapters 5-6. Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Applications
 Chapters 5-6 Dynamics: orces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Applications That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal,
Chapters 5-6 Dynamics: orces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Applications That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal,
