Inconsistencies in Steady State. Thermodynamics
|
|
|
- Lawrence Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inconsistencies in Steady State Thermodynamics Ronald Dickman and Ricardo Motai Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais
2 OUTLINE Nonequilibrium steady states (NESS) Steady state thermodynamics (Oono-Paniconi, Sasa- Tasaki, Pradhan et al) Coexistence of NESS: definition of intensive variables effective temperature and chemical potential Weak exchange, virtual contact and virtual reservoirs Consistency and utility of intensive variables: zeroth law Driven NNE lattice gas: consistent definition of chemical potential Driven lattice gas with attractive interactions (KLS model): - need for effective temperature - violation of zeroth law
3 Coexistence of NESS Consider systems A and B in steady states (equilibrium or not) If A and B, at the same temperature, can exchange particles, and the net particle flux between them is zero, we say they coexist wrt particle exchange; we expect them to have the same value of chemical potential Analogous definition for coexistence wrt energy exchange, temperature If A is a particle reservoir of known chemical potential the zero-flux condition defines the chemical potential of B We study lattice gases with stochastic dynamics
4 Criteria for a valid chemical potential:
5 Virtual exchange Out of equilibrium, the stationary properties of the systems in contact in general depend on the rate of exchange of particles and/or energy. To define the situation precisely, we consider the limit of vanishing exchange rates. This is formalized in virtual exchange: determining the fluxes that would ensue if exchange were permitted, without actually transferring anything.
6 The flux is zero when the reservoir chemical potential equals that of the system Particle exchange with a virtual reservoir with chemical potential µ Choose a site at random, if vacant, insert particle w.p. If occupied, remove particle w.p. Mean particle flux per exchange attempt:
7 Application to driven NNE lattice gas In the NNE lattice gas a particle excludes nearest-neighbor sites a hard-core repulsive potential The model is athermal no characteristic energy Only µ = βµ is of interest Equilibrium dynamics: symmetric hopping attempts Nonequilibrium (driven) dynamics: there is a preferred hopping direction We study the model in the disordered phase
8 NNE Lattice Gas
9
10
11
12 DR IVE N L AT T IC E GAS WIT H AT T R AC T IVE INT E R AC T IONS : A F IR S T AT T E MPT Driven lattice gas or Katz-Lebowitz-Spohn (KLS) model with attractive nearest-neighbor interactions. The system evolves via a particle-conserving dynamics with a drive D = Di favoring particle displacements along the +x direction and inhibiting those in the opposite sense. The acceptance probability for a particle displacement Δx is p a = min{ 1, exp[ (ΔE D Δx)]} Energy of configuration C: E (C) = - Σ <i,j> σ i σ j
13 We attempt to describe coexistence between KLS systems using the approach employed for the NNE lattice gas. Given a system S with density ρ S, temperature T and drive D > 0, we determine µ S via the zero-current condition. We then examine the possibility of coexistence between S and a nondriven (equilibrium) system S 0 at temperature T, whose density is such that its chemical potential µ 0 equal to µ S
14
15 The results shown in Fig. 3 lead one to expect that if the two systems are initialized with the same density, ρ > 1/ 2, then particles will migrate from the driven to the undriven system, until the corresponding µ values are equal In fact, particles flow in the opposite sense! Equating the effective chemical potentials of a driven and an undriven KLS system, does not predict the stationary densities when thesesystems are allowed to exchange particles. The reason for this becomes apparent when we examine the energy transfer from the undriven to the driven system: on Average, particle exchanges transfer energy from the driven to the undriven system The nonzero energy flux implies that the two systems are not, in fact, at coexistence
16
17 On average, the drive increases the energy of the system, since it tends to increase the likelihood of transitions with ΔE > 0 more than those with ΔE < 0. Under steady conditions, the energy increase due to the drive is balanced by the energy transfer to the reservoir: this is the socalled housekeeping heat associated with the stationary operation of a driven system. Thus the reservoir temperature is merely a parameter in the definition of the transition probabilities; we shall refer to it as the nominal temperature T n The effective temperature, T e, of the driven system, if one can be defined, should be greater than T n. Define T e via zero energy flux under virtual exchange
18 The effective temperature and chemical potential of S are determined by the conditions: ρ S + (-j): density of vacant sites with j occupied neighbors ρ S - (j): density of occupied sites with j occupied neighbors
19
20 Let R be a reservoir with temperature and chemical potential equal to that of S, and let S 0 be an undriven (equilibrium) nearest-neighbor lattice gas with the same temperature and chemical potential as R and S. Since S 0 and R are in equilibrium, we have the detailed-balance relations, We now ask whether S and S 0 coexist, that is, whether the particle and energy fluxes between these systems are zero under virtual exchange. Using detailed balance, the fluxes (from the nondriven to the driven system) are given by
21
22 Now α (j) is an increasing function of j and has a different value for each j Thus the conditions <Δn> S S 0 = 0 and <ΔE> S S = 0 are in general 0 distinct from those that define µ and Te In general the four conditions cannot be satisfied simultaneously For example, for µ > 0, <Δn> S = 0 implies which is clearly different from the condition <Δn> S S 0 = 0. We have therefore demonstrated a violation of the zeroth law: although S and S 0 both coexist with R, in general they do not coexist with each other.
23 Numerically, the violations appear to be quite small in the KLS model above the critical temperature Simulations show violations of the same order of magnitude
24 S UMMARY We have examined, in concrete, operational terms, the possibility of devising a steady state thermodynamics for driven lattice gases. In the case of the lattice gas with nearest-neighbor exclusion, our definition of an effective chemical potential turns out to be fully consistent, obeying the zeroth law, and capable of predicting the coexistence densities of systems with distinct values of the drive We expect that this will be true of other models with purely excluded-volume interactions
25 Direct application of this approach to the KLS lattice gas clearly fails, motivating us to define an effective temperature T e We then explore the possibility of predicting coexistence using equality of the effective temperature and chemical potential A theoretical argument shows that the zeroth law is violated We are left without a consistent SST applicable to systems capable of exchanging particles and energy It appears that steady state thermodynamics is not viable for such systems
Thermodynamics and Phase Coexistence in Nonequilibrium Steady States
 Thermodynamics and Phase Coexistence in Nonequilibrium Steady States Ronald Dickman Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais R.D. & R. Motai, Phys Rev E 89, 032134 (2014) R.D., Phys Rev E 90, 062123 (2014)
Thermodynamics and Phase Coexistence in Nonequilibrium Steady States Ronald Dickman Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais R.D. & R. Motai, Phys Rev E 89, 032134 (2014) R.D., Phys Rev E 90, 062123 (2014)
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jan 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jan 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jan 2007](/thumbs/83/88963517.jpg) Colloids in a periodic potential: driven lattice gas in continuous space arxiv:cond-mat/0701076v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jan 2007 Fabricio Q. Potiguar and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade
Colloids in a periodic potential: driven lattice gas in continuous space arxiv:cond-mat/0701076v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jan 2007 Fabricio Q. Potiguar and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade
Zeroth law of thermodynamics for nonequilibrium steady states in contact
 Zeroth law of thermodynamics for nonequilibrium steady states in contact Sayani Chatterjee 1, Punyabrata Pradhan 1 and P. K. Mohanty 2,3 1 Department of Theoretical Sciences, S. N. Bose National Centre
Zeroth law of thermodynamics for nonequilibrium steady states in contact Sayani Chatterjee 1, Punyabrata Pradhan 1 and P. K. Mohanty 2,3 1 Department of Theoretical Sciences, S. N. Bose National Centre
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 2005](/thumbs/83/88963522.jpg) Driven lattice gas with nearest-neighbor exclusion: shear-like drive arxiv:cond-mat/57114v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 25 Fabricio Q. Potiguar and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade
Driven lattice gas with nearest-neighbor exclusion: shear-like drive arxiv:cond-mat/57114v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 25 Fabricio Q. Potiguar and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade
TOWARD THERMODYNAMICS FOR NONEQUILIBRIUM STEADY STATES OR TWO TWISTS IN THERMODYNAMICS FOR NONEQUILBRIUM STEADY STATES
 TOWARD THERMODYNAMICS FOR NONEQUILIBRIUM STEADY STATES OR TWO TWISTS IN THERMODYNAMICS FOR NONEQUILBRIUM STEADY STATES HAL TASAKI WITH T.S.KOMATSU, N.NAKAGAWA, S.SASA PRL 100, 230602 (2008) and papers
TOWARD THERMODYNAMICS FOR NONEQUILIBRIUM STEADY STATES OR TWO TWISTS IN THERMODYNAMICS FOR NONEQUILBRIUM STEADY STATES HAL TASAKI WITH T.S.KOMATSU, N.NAKAGAWA, S.SASA PRL 100, 230602 (2008) and papers
Open boundary conditions in stochastic transport processes with pair-factorized steady states
 Open boundary conditions in stochastic transport processes with pair-factorized steady states Hannes Nagel a, Darka Labavić b, Hildegard Meyer-Ortmanns b, Wolfhard Janke a a Institut für Theoretische Physik,
Open boundary conditions in stochastic transport processes with pair-factorized steady states Hannes Nagel a, Darka Labavić b, Hildegard Meyer-Ortmanns b, Wolfhard Janke a a Institut für Theoretische Physik,
Quasi-Stationary Simulation: the Subcritical Contact Process
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 6 685 Quasi-Stationary Simulation: the Subcritical Contact Process Marcelo Martins de Oliveira and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx,
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 6 685 Quasi-Stationary Simulation: the Subcritical Contact Process Marcelo Martins de Oliveira and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx,
Generalized Manna Sandpile Model with Height Restrictions
 75 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 26 Generalized Manna Sandpile Model with Height Restrictions Wellington Gomes Dantas and Jürgen F. Stilck Instituto de Física, Universidade
75 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 26 Generalized Manna Sandpile Model with Height Restrictions Wellington Gomes Dantas and Jürgen F. Stilck Instituto de Física, Universidade
Effect of Diffusing Disorder on an. Absorbing-State Phase Transition
 Effect of Diffusing Disorder on an Absorbing-State Phase Transition Ronald Dickman Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil Support: CNPq & Fapemig, Brazil OUTLINE Introduction: absorbing-state phase
Effect of Diffusing Disorder on an Absorbing-State Phase Transition Ronald Dickman Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil Support: CNPq & Fapemig, Brazil OUTLINE Introduction: absorbing-state phase
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 57 (2014 ) 77 81
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 57 (204 ) 77 8 27th Annual CSP Workshops on Recent Developments in Computer Simulation Studies in Condensed Matter Physics, CSP
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 57 (204 ) 77 8 27th Annual CSP Workshops on Recent Developments in Computer Simulation Studies in Condensed Matter Physics, CSP
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Sep 2000
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Sep 2000 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Sep 2000](/thumbs/92/109029912.jpg) technical note, cond-mat/0009244 arxiv:cond-mat/0009244v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Sep 2000 Jarzynski Relations for Quantum Systems and Some Applications Hal Tasaki 1 1 Introduction In a series of papers
technical note, cond-mat/0009244 arxiv:cond-mat/0009244v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Sep 2000 Jarzynski Relations for Quantum Systems and Some Applications Hal Tasaki 1 1 Introduction In a series of papers
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC)
 Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Department of Physics, Princeton University. Graduate Preliminary Examination Part II. Friday, May 10, :00 am - 12:00 noon
 Department of Physics, Princeton University Graduate Preliminary Examination Part II Friday, May 10, 2013 9:00 am - 12:00 noon Answer TWO out of the THREE questions in Section A (Quantum Mechanics) and
Department of Physics, Princeton University Graduate Preliminary Examination Part II Friday, May 10, 2013 9:00 am - 12:00 noon Answer TWO out of the THREE questions in Section A (Quantum Mechanics) and
I.D The Second Law Q C
 I.D he Second Law he historical development of thermodynamics follows the industrial revolution in the 19 th century, and the advent of heat engines. It is interesting to see how such practical considerations
I.D he Second Law he historical development of thermodynamics follows the industrial revolution in the 19 th century, and the advent of heat engines. It is interesting to see how such practical considerations
Diffusion in Dilute Alloys
 Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
The Kelvin-Planck statement of the second law
 The Kelvin-Planck statement of the second law It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and produce a net amount of work Q W E =ΔE net net net, mass
The Kelvin-Planck statement of the second law It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and produce a net amount of work Q W E =ΔE net net net, mass
Statistical Physics of The Symmetric Group. Mobolaji Williams Harvard Physics Oral Qualifying Exam Dec. 12, 2016
 Statistical Physics of The Symmetric Group Mobolaji Williams Harvard Physics Oral Qualifying Exam Dec. 12, 2016 1 Theoretical Physics of Living Systems Physics Particle Physics Condensed Matter Astrophysics
Statistical Physics of The Symmetric Group Mobolaji Williams Harvard Physics Oral Qualifying Exam Dec. 12, 2016 1 Theoretical Physics of Living Systems Physics Particle Physics Condensed Matter Astrophysics
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Oct 2007 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Oct 2007](/thumbs/72/66290493.jpg) arxiv:0707434v2 [cond-matstat-mech] 24 Oct 2007 Matrix Product Steady States as Superposition of Product Shock Measures in D Driven Systems F H Jafarpour and S R Masharian 2 Bu-Ali Sina University, Physics
arxiv:0707434v2 [cond-matstat-mech] 24 Oct 2007 Matrix Product Steady States as Superposition of Product Shock Measures in D Driven Systems F H Jafarpour and S R Masharian 2 Bu-Ali Sina University, Physics
Information Theory in Statistical Mechanics: Equilibrium and Beyond... Benjamin Good
 Information Theory in Statistical Mechanics: Equilibrium and Beyond... Benjamin Good Principle of Maximum Information Entropy Consider the following problem: we have a number of mutually exclusive outcomes
Information Theory in Statistical Mechanics: Equilibrium and Beyond... Benjamin Good Principle of Maximum Information Entropy Consider the following problem: we have a number of mutually exclusive outcomes
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Oct 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Oct 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Oct 2004](/thumbs/93/111728656.jpg) The Totally Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process with Langmuir Kinetics A. Parmeggiani,, T. Franosch,2, and E. Frey,2 arxiv:cond-mat/4834v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Oct 24 Hahn-Meitner Institut, Abteilung
The Totally Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process with Langmuir Kinetics A. Parmeggiani,, T. Franosch,2, and E. Frey,2 arxiv:cond-mat/4834v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Oct 24 Hahn-Meitner Institut, Abteilung
Introduction to a few basic concepts in thermoelectricity
 Introduction to a few basic concepts in thermoelectricity Giuliano Benenti Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems Univ. Insubria, Como, Italy 1 Irreversible thermodynamic Irreversible thermodynamics
Introduction to a few basic concepts in thermoelectricity Giuliano Benenti Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems Univ. Insubria, Como, Italy 1 Irreversible thermodynamic Irreversible thermodynamics
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC)
 Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter
 Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi University of Camerino, Italy Naples, 24 May,2017 Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi (2017) Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter 2017
Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi University of Camerino, Italy Naples, 24 May,2017 Umberto Marini Bettolo Marconi (2017) Statistical Mechanics of Active Matter 2017
Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners
 Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners Pavel Krapivsky Boston University Plan and Motivation Evolving limiting shapes in the context of Ising model endowed with T=0 spin-flip dynamics.
Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners Pavel Krapivsky Boston University Plan and Motivation Evolving limiting shapes in the context of Ising model endowed with T=0 spin-flip dynamics.
Lattice Versus Lennard-Jones Models with a Net Particle Flow
 Lattice Versus Lennard-Jones Models with a Net Particle Flow Manuel Díez-Minguito, Pedro L. Garrido, and Joaquín Marro Institute Carlos I for Theoretical and Computational Physics, and Departamento de
Lattice Versus Lennard-Jones Models with a Net Particle Flow Manuel Díez-Minguito, Pedro L. Garrido, and Joaquín Marro Institute Carlos I for Theoretical and Computational Physics, and Departamento de
Nonconservative Abelian sandpile model with the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld toppling rule
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 2000 Nonconservative Abelian sandpile model with the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld toppling rule Alexei Vázquez 1,2 1 Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 2000 Nonconservative Abelian sandpile model with the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld toppling rule Alexei Vázquez 1,2 1 Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical
CHEM Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 CHEM2011.03 Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall 2003 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction It is a matter of everyday observation that things tend to change in a certain direction.
CHEM2011.03 Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall 2003 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction It is a matter of everyday observation that things tend to change in a certain direction.
Lecture Outline Chapter 18. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
SPH 302 THERMODYNAMICS
 THERMODYNAMICS Nyongesa F. W., PhD. e-mail: fnyongesa@uonbi.ac.ke 1 Course Outline Lecture 1: Thermodynamic concepts & Zeroth Law Lecture 2: 1 ST Law Lecture 3: 2 ND Law Lecture 4: Entropy and 2 ND Law
THERMODYNAMICS Nyongesa F. W., PhD. e-mail: fnyongesa@uonbi.ac.ke 1 Course Outline Lecture 1: Thermodynamic concepts & Zeroth Law Lecture 2: 1 ST Law Lecture 3: 2 ND Law Lecture 4: Entropy and 2 ND Law
16. Working with the Langevin and Fokker-Planck equations
 16. Working with the Langevin and Fokker-Planck equations In the preceding Lecture, we have shown that given a Langevin equation (LE), it is possible to write down an equivalent Fokker-Planck equation
16. Working with the Langevin and Fokker-Planck equations In the preceding Lecture, we have shown that given a Langevin equation (LE), it is possible to write down an equivalent Fokker-Planck equation
CHAPTER 2 INTERATOMIC FORCES. atoms together in a solid?
 CHAPTER 2 INTERATOMIC FORCES What kind of force holds the atoms together in a solid? Interatomic Binding All of the mechanisms which cause bonding between the atoms derive from electrostatic interaction
CHAPTER 2 INTERATOMIC FORCES What kind of force holds the atoms together in a solid? Interatomic Binding All of the mechanisms which cause bonding between the atoms derive from electrostatic interaction
Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together.
 Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together. For example Nacl In the Nacl lattice, each Na atom is
Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together. For example Nacl In the Nacl lattice, each Na atom is
NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials. The Electrochemical Gradient
 NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials Communication by neurons is based on changes in the membrane s permeability to ions This depends on the presence of specific membrane ion channels and the presence
NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials Communication by neurons is based on changes in the membrane s permeability to ions This depends on the presence of specific membrane ion channels and the presence
Novel Phase Transitions in Biased Diffusion of Two Species.
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 32 (l), pp. 49-54 (1995) 1 October 1995 Novel Phase Transitions in Biased Diffusion of Two Species. G. KORNISS, B. SCHMITTMA" and R. K. P. ZIA Center for Stochastic
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 32 (l), pp. 49-54 (1995) 1 October 1995 Novel Phase Transitions in Biased Diffusion of Two Species. G. KORNISS, B. SCHMITTMA" and R. K. P. ZIA Center for Stochastic
Phase Diagram, Density, And Current Density Profiles Of Totally Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process For A Junction With Two Entrances and Two Exits
 Jurnal Materi dan Pembelajaran Fisika (JMPF) 38 Phase Diagram, Density, And Current Density Profiles Of Totally Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process For A Junction With Two Entrances and Two Exits M. Za
Jurnal Materi dan Pembelajaran Fisika (JMPF) 38 Phase Diagram, Density, And Current Density Profiles Of Totally Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process For A Junction With Two Entrances and Two Exits M. Za
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 53 (2014 ) Andressa A. Bertolazzo and Marcia C.
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 53 (2014 ) 7 15 Density and Diffusion Anomalies in a repulsive lattice gas Andressa A. Bertolazzo and Marcia C. Barbosa Instituto
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 53 (2014 ) 7 15 Density and Diffusion Anomalies in a repulsive lattice gas Andressa A. Bertolazzo and Marcia C. Barbosa Instituto
Spontaneous Change.! Although exothermic processes tend to be spontaneous, spontaneous reactions can be exothermic or endothermic:
 Spontaneous Change! Any process, once initiated, that continues without further intervention is spontaneous.! Although exothermic processes tend to be spontaneous, spontaneous reactions can be exothermic
Spontaneous Change! Any process, once initiated, that continues without further intervention is spontaneous.! Although exothermic processes tend to be spontaneous, spontaneous reactions can be exothermic
Navier-Stokes Equation: Principle of Conservation of Momentum
 Navier-tokes Equation: Principle of Conservation of Momentum R. hankar ubramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Newton formulated the principle of conservation
Navier-tokes Equation: Principle of Conservation of Momentum R. hankar ubramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Newton formulated the principle of conservation
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004](/thumbs/93/113057924.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0306501v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004 Exactly solvable models through the generalized empty interval method: multi-species and more-than-two-site interactions Amir Aghamohammadi 1 &
arxiv:cond-mat/0306501v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004 Exactly solvable models through the generalized empty interval method: multi-species and more-than-two-site interactions Amir Aghamohammadi 1 &
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Physical Modeling of Multiphase flow. Boltzmann method
 with lattice Boltzmann method Exa Corp., Burlington, MA, USA Feburary, 2011 Scope Scope Re-examine the non-ideal gas model in [Shan & Chen, Phys. Rev. E, (1993)] from the perspective of kinetic theory
with lattice Boltzmann method Exa Corp., Burlington, MA, USA Feburary, 2011 Scope Scope Re-examine the non-ideal gas model in [Shan & Chen, Phys. Rev. E, (1993)] from the perspective of kinetic theory
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Intermolecular Forces and Monte-Carlo Integration 열역학특수연구
 Intermolecular Forces and Monte-Carlo Integration 열역학특수연구 2003.3.28 Source of the lecture note. J.M.Prausnitz and others, Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equiliria Atkins, Physical Chemistry Lecture
Intermolecular Forces and Monte-Carlo Integration 열역학특수연구 2003.3.28 Source of the lecture note. J.M.Prausnitz and others, Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equiliria Atkins, Physical Chemistry Lecture
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS. IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5
 DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I
 Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: S. T. Cummins Photo: S. T. Cummins Announcements Today is our final class! We will first discuss more on Chapters 14-15 and then conduct a short
Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: S. T. Cummins Photo: S. T. Cummins Announcements Today is our final class! We will first discuss more on Chapters 14-15 and then conduct a short
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle. Irreversible Processes. Reversible Processes. Carnot Cycle
 Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Module 16. Diffusion in solids II. Lecture 16. Diffusion in solids II
 Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Dr.Salwa Alsaleh fac.ksu.edu.sa/salwams
 Dr.Salwa Alsaleh Salwams@ksu.edu.sa fac.ksu.edu.sa/salwams What is Temperature? It is the measurement of the AVERAGE kinetic energy of the particles of matter. Temperature We associate the concept of temperature
Dr.Salwa Alsaleh Salwams@ksu.edu.sa fac.ksu.edu.sa/salwams What is Temperature? It is the measurement of the AVERAGE kinetic energy of the particles of matter. Temperature We associate the concept of temperature
Introduction to Stochastic Thermodynamics: Application to Thermo- and Photo-electricity in small devices
 Université Libre de Bruxelles Center for Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems Introduction to Stochastic Thermodynamics: Application to Thermo- and Photo-electricity in small devices Massimiliano Esposito
Université Libre de Bruxelles Center for Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems Introduction to Stochastic Thermodynamics: Application to Thermo- and Photo-electricity in small devices Massimiliano Esposito
Gases and the Virial Expansion
 Gases and the irial Expansion February 7, 3 First task is to examine what ensemble theory tells us about simple systems via the thermodynamic connection Calculate thermodynamic quantities: average energy,
Gases and the irial Expansion February 7, 3 First task is to examine what ensemble theory tells us about simple systems via the thermodynamic connection Calculate thermodynamic quantities: average energy,
The Second Virial Coefficient & van der Waals Equation
 V.C The Second Virial Coefficient & van der Waals Equation Let us study the second virial coefficient B, for a typical gas using eq.v.33). As discussed before, the two-body potential is characterized by
V.C The Second Virial Coefficient & van der Waals Equation Let us study the second virial coefficient B, for a typical gas using eq.v.33). As discussed before, the two-body potential is characterized by
Mathematical Structures of Statistical Mechanics: from equilibrium to nonequilibrium and beyond Hao Ge
 Mathematical Structures of Statistical Mechanics: from equilibrium to nonequilibrium and beyond Hao Ge Beijing International Center for Mathematical Research and Biodynamic Optical Imaging Center Peking
Mathematical Structures of Statistical Mechanics: from equilibrium to nonequilibrium and beyond Hao Ge Beijing International Center for Mathematical Research and Biodynamic Optical Imaging Center Peking
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER
 FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER Lecture 2: Evaluating properties Pierwsza strona STATES OF THE MATTER Phase is a quantity is of matter that is homogeneous throughout in both chemical composition
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER Lecture 2: Evaluating properties Pierwsza strona STATES OF THE MATTER Phase is a quantity is of matter that is homogeneous throughout in both chemical composition
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 Feb 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 Feb 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 Feb 2010](/thumbs/82/85352313.jpg) Asymmetric Exclusion Process in a System of Interacting Brownian Particles José Eduardo de Oliveira Rodrigues and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Caixa
Asymmetric Exclusion Process in a System of Interacting Brownian Particles José Eduardo de Oliveira Rodrigues and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Caixa
T s change via collisions at boundary (not mechanical interaction)
 Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Lattice versus Lennard-Jones models with a net particle flow
 Lattice versus Lennard-Jones models with a net particle flow M. Díez-Minguito 1,2, P. L. Garrido 1,2, and J. Marro 1,2 1 Institute Carlos I for Theoretical and Computational Physics 2 Departamento de Electromagnetismo
Lattice versus Lennard-Jones models with a net particle flow M. Díez-Minguito 1,2, P. L. Garrido 1,2, and J. Marro 1,2 1 Institute Carlos I for Theoretical and Computational Physics 2 Departamento de Electromagnetismo
BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP
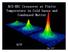 BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP May 2007 Cold Atom Collaborators: Qijin Chen J. Stajic (U Chicago; LANL) Yan He (U. Chicago) ChihChun Chien (U. Chicago)
BCS-BEC BEC Crossover at Finite Temperature in Cold Gases and Condensed Matter KITP May 2007 Cold Atom Collaborators: Qijin Chen J. Stajic (U Chicago; LANL) Yan He (U. Chicago) ChihChun Chien (U. Chicago)
Thouless conductance, Landauer-Büttiker currents and spectrum
 , Landauer-Büttiker currents and spectrum (Collaboration with V. Jakšić, Y. Last and C.-A. Pillet) L. Bruneau Univ. Cergy-Pontoise Marseille - June 13th, 2014 L. Bruneau, Landauer-Büttiker currents and
, Landauer-Büttiker currents and spectrum (Collaboration with V. Jakšić, Y. Last and C.-A. Pillet) L. Bruneau Univ. Cergy-Pontoise Marseille - June 13th, 2014 L. Bruneau, Landauer-Büttiker currents and
The fine-grained Gibbs entropy
 Chapter 12 The fine-grained Gibbs entropy 12.1 Introduction and definition The standard counterpart of thermodynamic entropy within Gibbsian SM is the socalled fine-grained entropy, or Gibbs entropy. It
Chapter 12 The fine-grained Gibbs entropy 12.1 Introduction and definition The standard counterpart of thermodynamic entropy within Gibbsian SM is the socalled fine-grained entropy, or Gibbs entropy. It
Effect of Magnet Geometry on the Magnetic Component of the Lorentz Force Equation
 Effect of Magnet Geometry on the Magnetic Component of the Lorentz Force Equation Author: Singer, Michael Date: 1 st May 2017 3 rd July 2018 Revision Abstract All forces in the universe are created from
Effect of Magnet Geometry on the Magnetic Component of the Lorentz Force Equation Author: Singer, Michael Date: 1 st May 2017 3 rd July 2018 Revision Abstract All forces in the universe are created from
Non equilibrium thermodynamic transformations. Giovanni Jona-Lasinio
 Non equilibrium thermodynamic transformations Giovanni Jona-Lasinio Kyoto, July 29, 2013 1. PRELIMINARIES 2. RARE FLUCTUATIONS 3. THERMODYNAMIC TRANSFORMATIONS 1. PRELIMINARIES Over the last ten years,
Non equilibrium thermodynamic transformations Giovanni Jona-Lasinio Kyoto, July 29, 2013 1. PRELIMINARIES 2. RARE FLUCTUATIONS 3. THERMODYNAMIC TRANSFORMATIONS 1. PRELIMINARIES Over the last ten years,
CHAPTER V. Brownian motion. V.1 Langevin dynamics
 CHAPTER V Brownian motion In this chapter, we study the very general paradigm provided by Brownian motion. Originally, this motion is that a heavy particle, called Brownian particle, immersed in a fluid
CHAPTER V Brownian motion In this chapter, we study the very general paradigm provided by Brownian motion. Originally, this motion is that a heavy particle, called Brownian particle, immersed in a fluid
Theory of Electromigration
 Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it
Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it
Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions
 134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 12 Jun 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 12 Jun 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 12 Jun 2007](/thumbs/90/103721986.jpg) TOPICAL REVIEW arxiv:0706.678v [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Jun 2007 Nonequilibrium Steady States of Matrix Product Form: A Solver s Guide Contents R. A. Blythe and M. R. Evans SUPA, School of Physics, University
TOPICAL REVIEW arxiv:0706.678v [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Jun 2007 Nonequilibrium Steady States of Matrix Product Form: A Solver s Guide Contents R. A. Blythe and M. R. Evans SUPA, School of Physics, University
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 17 Aug 1994
 Universality in the One-Dimensional Self-Organized Critical Forest-Fire Model Barbara Drossel, Siegfried Clar, and Franz Schwabl Institut für Theoretische Physik, arxiv:cond-mat/9408046v1 17 Aug 1994 Physik-Department
Universality in the One-Dimensional Self-Organized Critical Forest-Fire Model Barbara Drossel, Siegfried Clar, and Franz Schwabl Institut für Theoretische Physik, arxiv:cond-mat/9408046v1 17 Aug 1994 Physik-Department
8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation
 8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation So far we have considered only free particles - i.e. particles whose energy consists entirely of its kinetic energy. In general, however, a particle moves under
8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation So far we have considered only free particles - i.e. particles whose energy consists entirely of its kinetic energy. In general, however, a particle moves under
Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion
 Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm Anthony Trubiano April 11th, 2018 1 Introduction Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from a probability
Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm Anthony Trubiano April 11th, 2018 1 Introduction Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from a probability
V.E Mean Field Theory of Condensation
 V.E Mean Field heory of Condensation In principle, all properties of the interacting system, including phase separation, are contained within the thermodynamic potentials that can be obtained by evaluating
V.E Mean Field heory of Condensation In principle, all properties of the interacting system, including phase separation, are contained within the thermodynamic potentials that can be obtained by evaluating
Disorder and Entropy. Disorder and Entropy
 Disorder and Entropy Suppose I have 10 particles that can be in one of two states either the blue state or the red state. How many different ways can we arrange those particles among the states? All particles
Disorder and Entropy Suppose I have 10 particles that can be in one of two states either the blue state or the red state. How many different ways can we arrange those particles among the states? All particles
Immigration, integration and ghetto formation
 Immigration, integration and ghetto formation arxiv:cond-mat/0209242v1 10 Sep 2002 Hildegard Meyer-Ortmanns School of Engineering and Science International University Bremen P.O.Box 750561 D-28725 Bremen,
Immigration, integration and ghetto formation arxiv:cond-mat/0209242v1 10 Sep 2002 Hildegard Meyer-Ortmanns School of Engineering and Science International University Bremen P.O.Box 750561 D-28725 Bremen,
Thermodynamics. 1.1 Introduction. Thermodynamics is a phenomenological description of properties of macroscopic systems in thermal equilibrium.
 1 hermodynamics 1.1 Introduction hermodynamics is a phenomenological description of properties of macroscopic systems in thermal equilibrium. Imagine yourself as a post-newtonian physicist intent on understanding
1 hermodynamics 1.1 Introduction hermodynamics is a phenomenological description of properties of macroscopic systems in thermal equilibrium. Imagine yourself as a post-newtonian physicist intent on understanding
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Fusion Materials: Challenges and Opportunities (Recent Developments)
 Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Fusion Materials: Challenges and Opportunities (Recent Developments) Fei Gao gaofeium@umich.edu Limitations of MD Time scales Length scales (PBC help a lot) Accuracy of
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Fusion Materials: Challenges and Opportunities (Recent Developments) Fei Gao gaofeium@umich.edu Limitations of MD Time scales Length scales (PBC help a lot) Accuracy of
Effect of Magnet Geometry on the Magnetic Component of the Lorentz Force Equation
 Effect of Magnet Geometry on the Magnetic Component of the Lorentz Force Equation Author: Singer, Michael Date: 1st May 2017 email: singer43212@gmail.com Page 1 Abstract All forces in the universe are
Effect of Magnet Geometry on the Magnetic Component of the Lorentz Force Equation Author: Singer, Michael Date: 1st May 2017 email: singer43212@gmail.com Page 1 Abstract All forces in the universe are
The Phase Transition of the 2D-Ising Model
 The Phase Transition of the 2D-Ising Model Lilian Witthauer and Manuel Dieterle Summer Term 2007 Contents 1 2D-Ising Model 2 1.1 Calculation of the Physical Quantities............... 2 2 Location of the
The Phase Transition of the 2D-Ising Model Lilian Witthauer and Manuel Dieterle Summer Term 2007 Contents 1 2D-Ising Model 2 1.1 Calculation of the Physical Quantities............... 2 2 Location of the
Diffusion d une particule marquée dans un gaz dilué de sphères dures
 Diffusion d une particule marquée dans un gaz dilué de sphères dures Thierry Bodineau Isabelle Gallagher, Laure Saint-Raymond Journées MAS 2014 Outline. Particle Diffusion Introduction Diluted Gas of hard
Diffusion d une particule marquée dans un gaz dilué de sphères dures Thierry Bodineau Isabelle Gallagher, Laure Saint-Raymond Journées MAS 2014 Outline. Particle Diffusion Introduction Diluted Gas of hard
STATIONARY NON EQULIBRIUM STATES F STATES FROM A MICROSCOPIC AND A MACROSCOPIC POINT OF VIEW
 STATIONARY NON EQULIBRIUM STATES FROM A MICROSCOPIC AND A MACROSCOPIC POINT OF VIEW University of L Aquila 1 July 2014 GGI Firenze References L. Bertini; A. De Sole; D. G. ; G. Jona-Lasinio; C. Landim
STATIONARY NON EQULIBRIUM STATES FROM A MICROSCOPIC AND A MACROSCOPIC POINT OF VIEW University of L Aquila 1 July 2014 GGI Firenze References L. Bertini; A. De Sole; D. G. ; G. Jona-Lasinio; C. Landim
Avalanches, transport, and local equilibrium in self-organized criticality
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 998 Avalanches, transport, and local equilibrium in self-organized criticality Afshin Montakhab and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 998 Avalanches, transport, and local equilibrium in self-organized criticality Afshin Montakhab and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California,
Why quantum field theory?
 Why quantum field theory? It is often said that quantum field theory is the natural marriage of Einstein s special theory of relativity and the quantum theory. The point of this section will be to motivate
Why quantum field theory? It is often said that quantum field theory is the natural marriage of Einstein s special theory of relativity and the quantum theory. The point of this section will be to motivate
Nonintegrability and the Fourier heat conduction law
 Nonintegrability and the Fourier heat conduction law Giuliano Benenti Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems, Univ. Insubria, Como, Italy INFN, Milano, Italy In collaboration with: Shunda Chen, Giulio
Nonintegrability and the Fourier heat conduction law Giuliano Benenti Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems, Univ. Insubria, Como, Italy INFN, Milano, Italy In collaboration with: Shunda Chen, Giulio
ME 300 Thermodynamics II
 ME 300 Thermodynamics II Prof. S. H. Frankel Fall 2006 ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Week 1 Introduction/Motivation Review Unsteady analysis NEW! ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Today s Outline Introductions/motivations
ME 300 Thermodynamics II Prof. S. H. Frankel Fall 2006 ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Week 1 Introduction/Motivation Review Unsteady analysis NEW! ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Today s Outline Introductions/motivations
Field-induced vacancy localization in a driven lattice gas: Scaling of steady states
 Iowa State University From the SelectedWorks of Beate Schmittmann January 1, 2000 Field-induced vacancy localization in a driven lattice gas: Scaling of steady states M. Thies Beate Schmittmann, Iowa State
Iowa State University From the SelectedWorks of Beate Schmittmann January 1, 2000 Field-induced vacancy localization in a driven lattice gas: Scaling of steady states M. Thies Beate Schmittmann, Iowa State
Clusters and Percolation
 Chapter 6 Clusters and Percolation c 2012 by W. Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 5 November 2012 6.1 Introduction In this chapter we continue our investigation of nucleation near the spinodal. We
Chapter 6 Clusters and Percolation c 2012 by W. Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 5 November 2012 6.1 Introduction In this chapter we continue our investigation of nucleation near the spinodal. We
Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H. Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK expansion?
 ...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
...Thermodynamics Adiabats: How c P and c V get into the exponent PV γ Free expansion (Joule); Constant U Forced expansion (Joule-Kelvin); Constant H Joule-Kelvin coefficient - heating or cooling on JK
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Nov 2016](/thumbs/80/80475788.jpg) A traffic model with an absorbing-state phase transition M. L. L. Iannini, and Ronald Dickman, arxiv:1611.05307v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Nov 2016 Departamento de Física and National Institute of Science
A traffic model with an absorbing-state phase transition M. L. L. Iannini, and Ronald Dickman, arxiv:1611.05307v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Nov 2016 Departamento de Física and National Institute of Science
Math 5587 Lecture 2. Jeff Calder. August 31, Initial/boundary conditions and well-posedness
 Math 5587 Lecture 2 Jeff Calder August 31, 2016 1 Initial/boundary conditions and well-posedness 1.1 ODE vs PDE Recall that the general solutions of ODEs involve a number of arbitrary constants. Example
Math 5587 Lecture 2 Jeff Calder August 31, 2016 1 Initial/boundary conditions and well-posedness 1.1 ODE vs PDE Recall that the general solutions of ODEs involve a number of arbitrary constants. Example
Topological defects and its role in the phase transition of a dense defect system
 Topological defects and its role in the phase transition of a dense defect system Suman Sinha * and Soumen Kumar Roy Depatrment of Physics, Jadavpur University Kolkata- 70003, India Abstract Monte Carlo
Topological defects and its role in the phase transition of a dense defect system Suman Sinha * and Soumen Kumar Roy Depatrment of Physics, Jadavpur University Kolkata- 70003, India Abstract Monte Carlo
Fluctuations of intensive variables and non-equivalence of thermodynamic ensembles
 Fluctuations of intensive variables and non-equivalence of thermodynamic ensembles A. Ya. Shul'man V.A. Kotel'nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics of the RAS, Moscow, Russia 7th International
Fluctuations of intensive variables and non-equivalence of thermodynamic ensembles A. Ya. Shul'man V.A. Kotel'nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics of the RAS, Moscow, Russia 7th International
Energy minimization for the flow in ducts and networks
 Energy minimization for the flow in ducts and networks Taha Sochi University College London, Department of Physics & Astronomy, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT Email: t.sochi@ucl.ac.uk. Abstract The present
Energy minimization for the flow in ducts and networks Taha Sochi University College London, Department of Physics & Astronomy, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT Email: t.sochi@ucl.ac.uk. Abstract The present
Coarsening process in the 2d voter model
 Alessandro Tartaglia (LPTHE) Coarsening in the 2d voter model May 8, 2015 1 / 34 Coarsening process in the 2d voter model Alessandro Tartaglia LPTHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie alessandro.tartaglia91@gmail.com
Alessandro Tartaglia (LPTHE) Coarsening in the 2d voter model May 8, 2015 1 / 34 Coarsening process in the 2d voter model Alessandro Tartaglia LPTHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie alessandro.tartaglia91@gmail.com
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Aug 2015](/thumbs/90/102824791.jpg) arxiv:4.83v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Aug 25 Effect of diffusion in simple discontinuous absorbing transition models Salete Pianegonda Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Caixa
arxiv:4.83v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Aug 25 Effect of diffusion in simple discontinuous absorbing transition models Salete Pianegonda Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Caixa
Lecture 1 Modeling and simulation for the growth of thin films
 Lecture 1 Modeling and simulation for the growth of thin films Russel Caflisch Mathematics Department Materials Science and Engineering Department UCLA & IPAM www.math.ucla.edu/~material 1 Outline Epitaxial
Lecture 1 Modeling and simulation for the growth of thin films Russel Caflisch Mathematics Department Materials Science and Engineering Department UCLA & IPAM www.math.ucla.edu/~material 1 Outline Epitaxial
Thermodynamics. Basic concepts. Thermal equilibrium and temperature
 hermodynamics Basic concepts hermodynamics is a phenomenological description of macroscopic systems with many degrees of freedom. Its microscopic justication is provided by statistical mechanics. Equilibrium
hermodynamics Basic concepts hermodynamics is a phenomenological description of macroscopic systems with many degrees of freedom. Its microscopic justication is provided by statistical mechanics. Equilibrium
SPH 302 THERMODYNAMICS
 THERMODYNAMICS Nyongesa F. W., PhD. e-mail: fnyongesa@uonbi.ac.ke 1 Objectives Explain the Laws of thermodynamics & their significance Apply laws of thermodynamics to solve problems relating to energy
THERMODYNAMICS Nyongesa F. W., PhD. e-mail: fnyongesa@uonbi.ac.ke 1 Objectives Explain the Laws of thermodynamics & their significance Apply laws of thermodynamics to solve problems relating to energy
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
Quantum measurement theory and micro-macro consistency in nonequilibrium statistical mechanics
 Nagoya Winter Workshop on Quantum Information, Measurement, and Quantum Foundations (Nagoya, February 18-23, 2010) Quantum measurement theory and micro-macro consistency in nonequilibrium statistical mechanics
Nagoya Winter Workshop on Quantum Information, Measurement, and Quantum Foundations (Nagoya, February 18-23, 2010) Quantum measurement theory and micro-macro consistency in nonequilibrium statistical mechanics
Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences from Line Emission
 Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences from Line Emission Ø From line λ, can determine element, ionization state, and energy levels involved Ø From line shape, can determine bulk and thermal velocity and often
Plasma Spectroscopy Inferences from Line Emission Ø From line λ, can determine element, ionization state, and energy levels involved Ø From line shape, can determine bulk and thermal velocity and often
=1. The thinner contours continue to represent constant Q 2. 1/2 w *], except that w* rather than h* is considered
![=1. The thinner contours continue to represent constant Q 2. 1/2 w *], except that w* rather than h* is considered =1. The thinner contours continue to represent constant Q 2. 1/2 w *], except that w* rather than h* is considered](/thumbs/95/124168854.jpg) 5.4 Steady flow through a pure contraction. If the bottom remains horizontal (h*=constant=0, say) and the flow is choked only by contractions in the width of the rectangular channel then a new type of
5.4 Steady flow through a pure contraction. If the bottom remains horizontal (h*=constant=0, say) and the flow is choked only by contractions in the width of the rectangular channel then a new type of
