PHY231 Review. Lecturer is Prof. J. Huston
|
|
|
- Helen Ward
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHY231 Review Lecturer is Prof. J. Huston Final Exam, Thursday May 3, 8:00 10:00PM ANH 1281 (Anthony Hall) RCPD students: Thursday May 3, 5:00 9:00PM, BPS 3239 Alternate Final Exam, Tuesday May 1, 10:00 12:00 PM, BPS 3239; BY APPOINTMENT ONLY, and deadline has past.
2 Kinematics Review 1D motion equations for constant acceleration Velocity, Acceleration, Displacement, initial values at t = 0 v = v + o 1 x ( v + o v)t = 2 at 2 2 v = vo + 2ax x = vo t at 2 t = time relative to the start of the clock (t = 0) x = displacement over the time t v 0 = velocity at time t = 0 v = final velocity after time t or displacement x a = constant acceleration (typical units: m/s 2 )
3 Kinematics Review 2D motion equations for constant acceleration Velocities, Accelerations, Displacements, initial values at t = 0 x-direction y-direction v x = v ox + a x t x = 1 2 ( v + v ) t ox x v y = v oy + a y t y = 1 2 ( v + v ) t oy y v 2 x = v 2 ox + 2a x x v 2 y = v 2 oy + 2a y y x = v ox t a x t 2 y = v oy t a y t 2
4 FE-1. An eagle takes off from a tree branch on the side of a mountain and flies due west for 225 m in 19 s. Spying a mouse on the ground to the west, the eagle dives 441 m at an angle of 65 relative to the horizontal direction for 11 s to catch the mouse. Determine the eagle s average velocity for the thirty second interval. a) 19 m/s at 44 below the horizontal direction b) 22 m/s at 65 below the horizontal direction c) 19 m/s at 65 below the horizontal direction d) 22 m/s at 44 below the horizontal direction e) 25 m/s at 27 below the horizontal direction 225 m! 65 d 441 m
5 FE-1. An eagle takes off from a tree branch on the side of a mountain and flies due west for 225 m in 19 s. Spying a mouse on the ground to the west, the eagle dives 441 m at an angle of 65 relative to the horizontal direction for 11 s to catch the mouse. Determine the eagle s average velocity for the thirty second interval. a) 19 m/s at 44 below the horizontal direction b) 22 m/s at 65 below the horizontal direction c) 19 m/s at 65 below the horizontal direction d) 22 m/s at 44 below the horizontal direction e) 25 m/s at 27 below the horizontal direction x = x 1 + x 2 = ( cos65 )m = 411 m y = y 1 + y 2 = ( sin65 )m = 400 m v = d t = x2 + y 2 = 574 m = 19.1 m/s t 30 s! = tan "1 ( y / x) = tan " ( ) = m! d m
6 FE-2. A basketball is launched with an initial speed of 8.5 m/s and follows the trajectory shown. The ball enters the basket 0.92 s after it is launched. What are the distances x and y? Note: The drawing is not to scale. a) x = 6.3 m, y = 0.96 m b) x = 5.4 m, y = 0.73 m c) x = 5.7 m, y = 0.91 m d) x = 7.6 m, y = 1.1 m e) x = 6.0 m, y = 0.88 m
7 FE-2. A basketball is launched with an initial speed of 8.5 m/s and follows the trajectory shown. The ball enters the basket 0.92 s after it is launched. What are the distances x and y? Note: The drawing is not to scale. a) x = 6.3 m, y = 0.96 m b) x = 5.4 m, y = 0.73 m c) x = 5.7 m, y = 0.91 m d) x = 7.6 m, y = 1.1 m e) x = 6.0 m, y = 0.88 m x = v 0x t = v 0 t cos40 = ( 8.5m/s) ( 0.92 s)(0.77)= 6.0m y = v 0 y t! 1 2 gt 2 = ( 8.5m/s) ( 0.92s)sin 40! (0.5)(9.8m/s 2 )( 0.92s) 2 = 0.88m
8 linear rotational x! v a m F p " # I = mr 2 (point m)! = Fr sin" L = I# Gravitational PE PE G = mgh Conserved: Dynamics Review If W NC = 0, KE + PE linear! F = m a!! p = m v! W = Fscos! Conservation laws If F ext = 0, P =! p rotational = I "!! L = I #! W rot =!$ KE = 1 KE rot = 1 I# 2 2 mv2 2 W! "KE W rot! "KE! rot F!t "! p!!"t! # " L! Gravitational force: F G = Gm 1 m 2 / r 2 If! ext = 0, L = I"
9 FE-3. If an object is moving can you conclude there are forces acting on it? If an object is at rest, can you conclude there are no forces acting on it? Consider each of the following situations. In which one of the following cases, if any, are there no forces acting on the object? a) A bolt that came loose from a satellite in a circular orbit around the earth. b) After a gust of wind has blown through a tree, an apple falls to the ground. c) A man rests by leaning against a tall building in downtown Dallas. d) Sometime after her parachute opened, the sky diver fell toward the ground at a constant velocity. e) Forces are acting on all of the objects in choices a, b, c, and d.
10 FE-3. If an object is moving can you conclude there are forces acting on it? If an object is at rest, can you conclude there are no forces acting on it? Consider each of the following situations. In which one of the following cases, if any, are there no forces acting on the object? a) A bolt that came loose from a satellite in a circular orbit around the earth. b) After a gust of wind has blown through a tree, an apple falls to the ground. c) A man rests by leaning against a tall building in downtown Dallas. d) Sometime after her parachute opened, the sky diver fell toward the ground at a constant velocity. e) Forces are acting on all of the objects in choices a, b, c, and d.
11 FE-4. On a rainy evening, a truck is driving along a straight, level road at 25 m/s. The driver panics when a deer runs onto the road and locks the wheels while braking. If the coefficient of friction for the wheel/road interface is 0.68, how far does the truck slide before it stops? a) 55 m b) 47 m c) 41 m d) 36 m e) 32 m
12 FE-4. On a rainy evening, a truck is driving along a straight, level road at 25 m/s. The driver panics when a deer runs onto the road and locks the wheels while braking. If the coefficient of friction for the wheel/road interface is 0.68, how far does the truck slide before it stops? a) 55 m b) 47 m c) 41 m d) 36 m e) 32 m v 0 = +25 m/s, µ = 0.68, f =!µmg v 2 = v ax;!v 0 2 =!2µgx f m = a =!µg, v = 0 x = v 0 2 2µg = (0.68)(9.8) = 47m
13 FE-5. A truck is traveling with a constant speed of 15 m/s. When the truck follows a curve in the road, its centripetal acceleration is 4.0 m/s 2. What is the radius of the curve? a) 3.8 m b) 14 m c) 56 m c) 120 m e) 210 m
14 FE-5. A truck is traveling with a constant speed of 15 m/s. When the truck follows a curve in the road, its centripetal acceleration is 4.0 m/s 2. What is the radius of the curve? a) 3.8 m b) 14 m c) 56 m d) 120 m e) 210 m r = v2 a c = 225 m2 /s m/s 2 56 m
15 FE-6. The Rapid Rotor amusement ride is spinning fast enough that the floor beneath the rider drops away and the rider remains in place. If the Rotor speeds up until it is going twice as fast as it was previously, what is the effect on the frictional force on the rider? a) The frictional force is reduced to one-fourth of its previous value. b) The frictional force is the same as its previous value. c) The frictional force is reduced to one-half of its previous value. d) The frictional force is increased to twice its previous value. e) The frictional force is increased to four times its previous value.
16 FE-6. The Rapid Rotor amusement ride is spinning fast enough that the floor beneath the rider drops away and the rider remains in place. If the Rotor speeds up until it is going twice as fast as it was previously, what is the effect on the frictional force on the rider? f MAX = µf!, F! " = 4F!, but f = F G = mg a) The frictional force is reduced to one-fourth of its previous value. b) The frictional force is the same as its previous value. c) The frictional force is reduced to one-half of its previous value. d) The frictional force is increased to twice its previous value. e) The frictional force is increased to four times its previous value.
17 FE-7. Determine the amount of work done in firing a 2.0-kg projectile with an initial speed of 50 m/s. Neglect any effects due to air resistance a) 900 J b) 1600 J c) 2500 J d) 4900 J e) Need to know the launch angle
18 FE-7. Determine the amount of work done in firing a 2.0-kg projectile with an initial speed of 50 m/s. Neglect any effects due to air resistance a) 900 J W =!KE m = 2.0kg, v b) 1600 J 0 = 0, v = 50 m/s c) 2500 J = 1 2 mv2 = 1kg(50 m/s) 2 = 2500 J d) 4900 J e) Need to know the launch angle
19 FE-8. A roller coaster car travels down a hill and is moving at 18 m/s as it passes through a section of straight, horizontal track. The car then travels up another hill that has a maximum height of 15 m. If frictional effects are ignored, what is the speed of the car at the top of the hill? a) Can t make it up the hill. b) 0 m/s c) 5.5 m/s d) 9.0 m/s e) 18 m/s
20 FE-8. A roller coaster car travels down a hill and is moving at 18 m/s as it passes through a section of straight, horizontal track. The car then travels up another hill that has a maximum height of 15 m. If frictional effects are ignored, what is the speed of the car at the top of the hill? a) Can t make it up the hill. b) 0 m/s c) 5.5 m/s d) 9.0 m/s e) 18 m/s 1 mv 2 = 1 mv 2 + mgh f v f = v 0 2! 2gh = (18) 2! 2(9.8)(15) = 5.5 m/s
21 FE-9. A kg truck is accelerated from rest by a net force that decreases linearly with distance traveled. The graph shows this force. Using the information provided and work-energy methods, determine the approximate speed of the truck when the force is removed. a) 8.41 m/s b) 12.5 m/s c) 17.7 m/s d) 25.0 m/s e) 35.4 m/s (NOTE: kn)
22 FE-9. A kg truck is accelerated from rest by a net force that decreases linearly with distance traveled. The graph shows this force. Using the information provided and work-energy methods, determine the approximate speed of the truck when the force is removed. a) 8.41 m/s b) 12.5 m/s c) 17.7 m/s d) 25.0 m/s e) 35.4 m/s W net! Fs = ( 6.5"10 3 N)(150 m) = 975"10 3 J W net = #KE = 1 2 mv2 v = 2W net m = 1950 "103 J 12,500 kg = 12.5m/s
23 FE-10 A small asteroid collides with a planet. Which one of the following statements concerning what happens during the collision is correct? a) The asteroid exerts a smaller force on the planet than the planet exerts on the asteroid. b) The planet exerts a force on the asteroid, but the asteroid does not exert a force on the planet. c) The asteroid exerts the same amount of force on the planet as the planet exerts on the asteroid. d) The asteroid exerts a force on the planet, but the planet does not exert a force on the asteroid. e) The planet exerts a smaller force on the asteroid than the asteroid exerts on the planet.
24 FE-10 A small asteroid collides with a planet. Which one of the following statements concerning what happens during the collision is correct? a) The asteroid exerts a smaller force on the planet than the planet exerts on the asteroid. b) The planet exerts a force on the asteroid, but the asteroid does not exert a force on the planet. c) The asteroid exerts the same amount of force on the planet as the planet exerts on the asteroid. Newton's 3rd Law d) The asteroid exerts a force on the planet, but the planet does not exert a force on the asteroid. e) The planet exerts a smaller force on the asteroid than the asteroid exerts on the planet.
25 FE-11 Ryan, m = 45 kg, runs and jumps off a stationary, 168-kg floating platform on a lake. Ryan s horizontal velocity as he leaps is +2.7 m/s. Ignoring any frictional effects, what is the recoil velocity of the platform? a) 2.7 m/s b) m/s c) 1.4 m/s d) 0.72 m/s e) +2.7 m/s
26 FE-11 Ryan, m = 45 kg, runs and jumps off a stationary, 168-kg floating platform on a lake. Ryan s horizontal velocity as he leaps is +2.7 m/s. Ignoring any frictional effects, what is the recoil velocity of the platform? No external forces! momentum is conserved. a) 2.7 m/s b) m/s c) 1.4 m/s d) 0.72 m/s e) +2.7 m/s P i = P f 0 = p Ryan + p plat m plat v plat = "m Ryan v Ryan v plat = " m Ryan m plat v Ryan = " (+2.7m/s) ="0.72m/s
27 FE-12 A 4.0-m board is resting directly on top of a 4.0-m long table. The weight of the board is 340 N. An object with a weight of 170 N is placed at the right end of the board. What is the maximum horizontal distance that the board can be moved toward the right such that the board remains in equilibrium? a) 0.75 m b) 1.0 m c) 1.3 m d) 1.5 m e) 2.0 m 4.0 m
28 FE-12 A 4.0-m board is resting directly on top of a 4.0-m long table. The weight of the board is 340 N. An object with a weight of 170 N is placed at the right end of the board. What is the maximum horizontal distance that the board can be moved toward the right such that the board remains in equilibrium? a) 0.75 m b) 1.0 m c) 1.3 m d) 1.5 m e) 2.0 m x :amount that sticks out over the table for equilibrium:! b +! o = 0 = w b ( 1 2 L " x) " w o x x = 1 L! x L x w b w o w b 1 w b + w L = 340 (2m) = 1.3m 2 o
29 FE-13 A solid sphere of radius R rotates about an axis that is tangent to the sphere with an angular speed!. Under the action of internal forces, the radius of the sphere increases to 2R. What is the final angular speed of the sphere? a)! 0 / 4 b)! 0 / 2 c)! 0 d) 2! 0 e) 4! 0
30 FE-13 A solid sphere of radius R rotates about an axis that is tangent to the sphere with an angular speed! 0. Under the action of internal forces, the radius of the sphere increases to 2R. What is the final angular speed of the sphere? a)! 0 / 4 b)! 0 / 2 c)! 0 d) 2! 0 e) 4! 0 Only internal forces, angular momentum conserved. I 0! 0 = I f! f ; I 0 " mr 2 ; I f " m(2r) 2 = 4mR 2! f = I 0 I f! 0 = mr2 4mR 2! 0 =! 0 / 4
31 Hooke's Law Oscillations Springs & Oscillations F A = k x! = k m Restoring Force Angular frequency (! = 2" f = 2" T ) F R =!k x position velocity acceleration x = Acos(! t) v x =! A" sin("t) a x =! A" 2 cos"t Elastic PE Pendulum PE S = 1 2 kx2! pendulum = 2" T = g L Elastic Materials " F = Y!L % $ ' # & A L o Y is Young's modulus
32 FE-14 A steel ball is hung from a vertical ideal spring where it oscillates in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of m and an angular frequency of! rad/s. With time, t = 0, at the maximum vertical position, which one of the following expressions represents the acceleration, in m/s 2, of the ball as a function of time? a)!1.55 cos"t b) cos 2 "t c)! cos"t d)! 0.493cos 2 "t e)! 0.493cos"t
33 FE-14 A steel ball is hung from a vertical ideal spring where it oscillates in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of m and an angular frequency of! rad/s. With time, t = 0, at the maximum vertical position, which one of the following expressions represents the acceleration, in m/s 2, of the ball as a function of time? a)!1.55 cos"t b) cos 2 "t c)! cos"t d)! 0.493cos 2 "t e)! 0.493cos"t x = Acos!t; v = " A! sin!t a = " A! 2 cos!t; A = m,! = # rad/s A! 2 = (0.157 m)(# rad/s) 2 = 1.55 m/s 2 a = "1.55cos!t;
34 FE-15 In designing a spring loaded cannon, determine the spring constant required to launch a 2.0-kg ball with an initial speed of 1.2 m/s from a position where the spring is displaced 0.15 m from its equilibrium position. a) 16 N/m b) 32 N/m c) 64 N/m d) 130 N/m e) 180 N/m
35 FE-15 In designing a spring loaded cannon, determine the spring constant required to launch a 2.0-kg ball with an initial speed of 1.2 m/s from a position where the spring is displaced 0.15 m from its equilibrium position. a) 16 N/m b) 32 N/m c) 64 N/m d) 130 N/m e) 180 N/m E total = KE + PE is conserved E f = KE = 1 2 mv2 ; E i = PE S = 1 2 kx2 ; 1 2 mv2 = 1 2 kx2 k = mv2 x 2 = (2kg)(1.2 m/s)2 (0.15m) 2 = 130 N/m
36 Fluids Force derived from pressure on an area Pressure grows linearly with depth (h) Buoyant force = Weight of displaced fluid F = PA P 2 = P 1 +! gh F B =!Vg, where!v is the mass of displaced fluid Bernoulli's equation for a nonviscous, incompressible fluid Poiseuille's Law ( flow of viscous fluid) P 1 + 1!v 2 +!gy = P 2 + 1!v 2 +!gy πr Q = 4 ( P P ) 2 8η L 1
37 FE-16 Helium gas is confined within a chamber that has a moveable piston. The mass of the piston is 8.7 kg; and its radius is m. If the system is in equilibrium, what is the pressure exerted on the piston by the gas? a) 1.639!10 4 Pa b) 8.491!10 4 Pa c) 1.013!10 5 Pa d) 1.606!10 5 Pa e) 2.619!10 5 Pa
38 FE-16 Helium gas is confined within a chamber that has a moveable piston. The mass of the piston is 8.7 kg; and its radius is m. If the system is in equilibrium, what is the pressure exerted on the piston by the gas? a) 1.639!10 4 Pa b) 8.491!10 4 Pa c) 1.013!10 5 Pa d) 1.606!10 5 Pa e) 2.619!10 5 Pa P = F A = mg 8.7kg(9.8 N/kg) = 2!r 3.14(.013m) = "10 5 Pa
39 FE-17 An above ground water pump is used to extract water from a well. A pipe extends from the pump to the bottom of the well. What is the maximum depth from which water can be pumped? a) 19.6 m b) 39.2 m c) 10.3 m d) 101 m e) A big pump can lift an arbitrarily large column of water
40 FE-17 An above ground water pump is used to extract water from a well. A pipe extends from the pump to the bottom of the well. What is the maximum depth from which water can be pumped? (water density: 1x10 3 kg/m 3 ) (atmospheric pressure: 1.01x10 5 N/m 2 ) a) 19.6 m b) 39.2 m c) 10.3 m d) 101 m e) A big pump can lift an arbitrarily large column of water P =!Vg A =!gl L = P!g = 1.01"10 5 N/m 2 1"10 3 kg/m 3 = 10.3 m ( ) 9.8N/kg ( )
41 Temperature and Heat Kelvin temperature scale T K = T C Thermal Expansion!L = " L 0!T!V = "V 0!T Heat needed to make a temperature change to a solid or liquid Heat needed to make a phase change Q = mc!t Q = ml!t = ( T f " T ) i Mixing heat sources with no loss of heat ( ) ( )! Q =! mc"t +! ml = 0
42 FE-18 Elena s normal body temperature is 36.5 C. When she recently became ill, her body temperature increased to 38.0 C. What was the minimum amount of heat required for this increase in body temperature if her weight is 561 N? (specific heat 3500 J/kg C) a) 3.0!10 6 J b) 3.5!10 3 J c) 5.0!10 4 J d) 3.1!10 5 J e) 7.6!10 5 J
43 FE-18 Elena s normal body temperature is 36.5 C. When she recently became ill, her body temperature increased to 38.0 C. What was the minimum amount of heat required for this increase in body temperature if her weight is 561 N? (specific heat 3500 J/kg C) a) 3.0!10 6 J b) 3.5!10 3 J c) 5.0!10 4 J d) 3.1!10 5 J e) 7.6!10 5 J!T = ( 38 " 36.5) C = 1.5 C m = W / g = 561N (9.8 N/kg) = 60.2 kg Q = mc!t = ( 60.2 kg)(3500 J/kg #C)(1.5 C) = 3.1$10 5 J
44 FE-18 Elena s normal body temperature is 36.5 C. When she recently became ill, her body temperature increased to 38.0 C. What was the minimum amount of heat required for this increase in body temperature if her weight is 561 N? (specific heat 3500 J/kg C) a) 3.0!10 6 J b) 3.5!10 3 J c) 5.0!10 4 J d) 3.1!10 5 J e) 7.6!10 5 J!T = ( 38 " 36.5) C = 1.5 C m = W / g = 561N (9.8 N/kg) = 60.2 kg Q = mc!t = ( 60.2 kg)(3500 J/kg #C)(1.5 C) = 3.1$10 5 J
45 Ideal Gas Law & Thermodynamics Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt (or PV = NkT ) R = 8.31 J/ ( mole! K) k = 1.38 "10 #23 J/K Average Kinetic Energy is proportional to Temperature KE = 1 mv 2 2 rms = 3 2 kt (T in Kelvin) Internal Energy monoatomic Ideal Gas U = 3 2 nrt 1st Law:!U = Q "W W = P!V (isobaric) W = nrt ln(v f W = 3 2 nr(t i! T f ) (adiabatic) V i ) (isothermal) e Carnot = 1! T C T H!S = ( Q T ) R reversible
46 FE-19 An isobaric process is represented by which one of the following graphs? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E
47 FE-19 An isobaric process is represented by which one of the following graphs? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E
48 FE-20 An ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion. Determine which of the following expressions is true. a)!u is positive b)!u is negative c) Q is positive d) Q is negative e) Q = "W
49 FE-20 An ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion. Determine which of the following statements is true. a)!u is positive b)!u is negative c) Q is positive d) Q is negative e) Q = "W 1st Law:!U = Q "W U = 3 nrt 2!U = 3 nr!t = 0 (isothermal) 2 Q = W Expansion # W is positive # Q is positive.
DO NOT USE CELL PHONES. Good Luck!!!
 Phys 111 Exam October 17, 017 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phys 111 Exam October 17, 017 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Honor Physics Final Exam Review. What is the difference between series, parallel, and combination circuits?
 Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current.
Name Period Date Honor Physics Final Exam Review Circuits You should be able to: Calculate the total (net) resistance of a circuit. Calculate current in individual resistors and the total circuit current.
Wiley Plus. Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm!
 Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Phys 111 Exam 2 October 18, Name Section University ID
 Phys 111 Exam October 18, 016 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) Use your previous answer sheet and start with 1. Note problem number of the second exam
Phys 111 Exam October 18, 016 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) Use your previous answer sheet and start with 1. Note problem number of the second exam
Today s lecture. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics. Final Exam 041. Answer key - First choice is the correct answer
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics MSK Final Exam 041 Answer key - First choice is the correct answer Q1 A 20 kg uniform ladder is leaning against a frictionless wall
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Physics MSK Final Exam 041 Answer key - First choice is the correct answer Q1 A 20 kg uniform ladder is leaning against a frictionless wall
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book)
 PHYS 111-01 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book) 1. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO. NAME: (Given) (Family) 2. For the problems, write clearly and neatly and be sure to show your work. Answers without
PHYS 111-01 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book) 1. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO. NAME: (Given) (Family) 2. For the problems, write clearly and neatly and be sure to show your work. Answers without
Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy?
 Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Energy Conservation AP
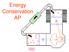 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Final Mock Exam PH 221-1D
 Final Mock Exam PH 221-1D April 18, 2015 You will have 2 hours to complete this exam. You must answer 8 questions to make a perfect score of 80. 1 Chapter Concept Summary Equations: Cutnell & Johnson
Final Mock Exam PH 221-1D April 18, 2015 You will have 2 hours to complete this exam. You must answer 8 questions to make a perfect score of 80. 1 Chapter Concept Summary Equations: Cutnell & Johnson
All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (1:30 PM 4:30 PM) Page 1 of 6 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
(1:30 PM 4:30 PM) Page 1 of 6 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
Phys 111 Exam 3 November 14, Name Section University ID
 Phys 111 Exam 3 November 14, 017 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phys 111 Exam 3 November 14, 017 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Slide 1 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (3:30 pm 6:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
(3:30 pm 6:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam
 South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
Question 1: In which one of the following situations does a car have a westward acceleration?
 Question 1: In which one of the following situations does a car have a westward acceleration? A. The car travels eastward and speeds up. B. The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. C. The car
Question 1: In which one of the following situations does a car have a westward acceleration? A. The car travels eastward and speeds up. B. The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. C. The car
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Q1. A) 46 m/s B) 21 m/s C) 17 m/s D) 52 m/s E) 82 m/s. Ans: v = ( ( 9 8) ( 98)
 Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Wednesday, May 24, 207 Page: Q. A hot-air balloon is ascending (going up) at the rate of 4 m/s and when the balloon is 98 m above the ground a package is dropped from it, vertically
Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Wednesday, May 24, 207 Page: Q. A hot-air balloon is ascending (going up) at the rate of 4 m/s and when the balloon is 98 m above the ground a package is dropped from it, vertically
AP Mechanics Summer Assignment
 2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
Phys 111 Final Exam December 16, 2015
 Phys 111 Final Exam December 16, 2015 61. The density of a solid object is defined as the ratio of the mass of the object to its volume. The dimension of density is A) [M]/[L]. B) [L] 3 /[M]. C) [M] /[L]
Phys 111 Final Exam December 16, 2015 61. The density of a solid object is defined as the ratio of the mass of the object to its volume. The dimension of density is A) [M]/[L]. B) [L] 3 /[M]. C) [M] /[L]
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (1:30 pm 4:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
(1:30 pm 4:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 2
 Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #4 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 22 ABC Quiz #4 Solutions Spring 207 I. (6 points) Corentine is driving her car of mass m around a curve when suddenly, all systems fail! The engine quits, she can t brake, she can t steer, and
Physics 22 ABC Quiz #4 Solutions Spring 207 I. (6 points) Corentine is driving her car of mass m around a curve when suddenly, all systems fail! The engine quits, she can t brake, she can t steer, and
Slide 1 / A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? 10 km 22.5 km 25 km 45 km 50 km
 Slide 1 / 96 1 train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? 10 km 22.5 km 25 km 45 km 50 km Slide 2 / 96 2 bicyclist moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. How long it will
Slide 1 / 96 1 train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? 10 km 22.5 km 25 km 45 km 50 km Slide 2 / 96 2 bicyclist moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s. How long it will
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Review - Chapter 1. Ans: 2.12m
 Review - Chapter 1 The distance d that a certain particle moves may be calculated from the expression d = at + bt 2 where a and b are constants; and t is the elapsed time. The dimensions of the quantities
Review - Chapter 1 The distance d that a certain particle moves may be calculated from the expression d = at + bt 2 where a and b are constants; and t is the elapsed time. The dimensions of the quantities
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
- 1 -APPH_MidTerm. Mid - Term Exam. Part 1: Write your answers to all multiple choice questions in this space. A B C D E A B C D E
 Name - 1 -APPH_MidTerm AP Physics Date Mid - Term Exam Part 1: Write your answers to all multiple choice questions in this space. 1) 2) 3) 10) 11) 19) 20) 4) 12) 21) 5) 13) 22) 6) 7) 14) 15) 23) 24) 8)
Name - 1 -APPH_MidTerm AP Physics Date Mid - Term Exam Part 1: Write your answers to all multiple choice questions in this space. 1) 2) 3) 10) 11) 19) 20) 4) 12) 21) 5) 13) 22) 6) 7) 14) 15) 23) 24) 8)
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first
 Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Final Exam April 26, 2016
 PHYS 050 Spring 016 Name: Final Exam April 6, 016 INSTRUCTIONS: a) No books or notes are permitted. b) You may use a calculator. c) You must solve all problems beginning with the equations on the Information
PHYS 050 Spring 016 Name: Final Exam April 6, 016 INSTRUCTIONS: a) No books or notes are permitted. b) You may use a calculator. c) You must solve all problems beginning with the equations on the Information
MODEL PAPER CLASS XI PHYSICS (GROUP 1) BLUEPRINT Name of chapter (1)
 sr. no. MODEL PAPER CLASS XI PHYSICS (GROUP ) BLUEPRINT Name of chapter VSAQ () SA-I (2) SA-II (3) Value based (4) LA(5) Total 70 Physical world and measurement 3 2 Kinematics 2 3,3 5 3 Laws of motion
sr. no. MODEL PAPER CLASS XI PHYSICS (GROUP ) BLUEPRINT Name of chapter VSAQ () SA-I (2) SA-II (3) Value based (4) LA(5) Total 70 Physical world and measurement 3 2 Kinematics 2 3,3 5 3 Laws of motion
Physics 53 Summer Final Exam. Solutions
 Final Exam Solutions In questions or problems not requiring numerical answers, express the answers in terms of the symbols given, and standard constants such as g. If numbers are required, use g = 10 m/s
Final Exam Solutions In questions or problems not requiring numerical answers, express the answers in terms of the symbols given, and standard constants such as g. If numbers are required, use g = 10 m/s
(1) +0.2 m/s (2) +0.4 m/s (3) +0.6 m/s (4) +1 m/s (5) +0.8 m/s
 77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
A. 50 N B. 100 N C. 20 N D. 0 N E. 500 N
 SQ1: A 0.05-kg tennis ball moving to the right with a speed of 10 m/s is struck by a tennis racket, causing it to move to the left with a speed of 10 m/s. If the ball remains in contact with the racquet
SQ1: A 0.05-kg tennis ball moving to the right with a speed of 10 m/s is struck by a tennis racket, causing it to move to the left with a speed of 10 m/s. If the ball remains in contact with the racquet
Mechanics. Time (s) Distance (m) Velocity (m/s) Acceleration (m/s 2 ) = + displacement/time.
 Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
PHYSICS 111 SPRING EXAM 2: March 6, 2018; 8:15-9:45 pm
 PHYSICS 111 SPRING 2018 EXAM 2: March 6, 2018; 8:15-9:45 pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 20 multiple-choice questions plus 1 extra credit question,
PHYSICS 111 SPRING 2018 EXAM 2: March 6, 2018; 8:15-9:45 pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 20 multiple-choice questions plus 1 extra credit question,
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy
 PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
5. A car moves with a constant speed in a clockwise direction around a circular path of radius r, as represented in the diagram above.
 1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
Jordan University of Science & Technology PHYS 101A Final exam First semester 2007
 Student Name Student ID Jordan University of Science & Technology PHYS 101A Final exam First semester 2007 Approximate your answer to those given for each question. Use this table to fill in your answer
Student Name Student ID Jordan University of Science & Technology PHYS 101A Final exam First semester 2007 Approximate your answer to those given for each question. Use this table to fill in your answer
4. Find the average velocities and average accelerations of a particle moving in 1-D given its position at various times.
 PHYSICS 201: TEST 1 STUDY SHEET 1. Convert a quantity from one set of units to another set of units. 2. Convert a 2-D vector from rectangular form (components) to polar form (magnitude and angle), or from
PHYSICS 201: TEST 1 STUDY SHEET 1. Convert a quantity from one set of units to another set of units. 2. Convert a 2-D vector from rectangular form (components) to polar form (magnitude and angle), or from
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam
 Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14)
 Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
AP Physics II Summer Packet
 Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes. Name
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Midterm Prep. 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?
 Name: ate: 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?. weight and kg. velocity and m/s. speed and m/s. acceleration and m 2 /s 2. 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at
Name: ate: 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?. weight and kg. velocity and m/s. speed and m/s. acceleration and m 2 /s 2. 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at
. d. v A v B. e. none of these.
 General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review
 Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 20, You cannot use CELL PHONES, ipad, IPOD... Good Luck!!! Name Section University ID
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 0, 016 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 0, 016 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
P211 Spring 2004 Form A
 1. A 2 kg block A traveling with a speed of 5 m/s as shown collides with a stationary 4 kg block B. After the collision, A is observed to travel at right angles with respect to the initial direction with
1. A 2 kg block A traveling with a speed of 5 m/s as shown collides with a stationary 4 kg block B. After the collision, A is observed to travel at right angles with respect to the initial direction with
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Newton s Second Law: in vector form Newton s Laws of Motion σ റF = m റa in component form σ F x = ma x σ F y = ma y in equilibrium and static situations a x = 0; a y = 0 Strategy for Solving
Chapter 4 Newton s Second Law: in vector form Newton s Laws of Motion σ റF = m റa in component form σ F x = ma x σ F y = ma y in equilibrium and static situations a x = 0; a y = 0 Strategy for Solving
Page 1. Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work!
 Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
 PAGE NO.: 1 of 6 + Formula Sheet Equal marks for all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
PAGE NO.: 1 of 6 + Formula Sheet Equal marks for all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms,
 43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
 CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
Solution Only gravity is doing work. Since gravity is a conservative force mechanical energy is conserved:
 8) roller coaster starts with a speed of 8.0 m/s at a point 45 m above the bottom of a dip (see figure). Neglecting friction, what will be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope,
8) roller coaster starts with a speed of 8.0 m/s at a point 45 m above the bottom of a dip (see figure). Neglecting friction, what will be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope,
Motion. Argument: (i) Forces are needed to keep things moving, because they stop when the forces are taken away (evidence horse pulling a carriage).
 1 Motion Aristotle s Study Aristotle s Law of Motion This law of motion was based on false assumptions. He believed that an object moved only if something was pushing it. His arguments were based on everyday
1 Motion Aristotle s Study Aristotle s Law of Motion This law of motion was based on false assumptions. He believed that an object moved only if something was pushing it. His arguments were based on everyday
The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest.
 T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
AP Physics B Summer Assignment
 BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
w = mg F g = τ = Frsinθ a c v f + at = v i F = ma F f p = mv W = Fd v f 2 = v i 2 + 2ad F t = Δ(mv) Impulse = F t KE = 1 2 mv 2 PE = mgh PE = 1 2 kx 2
 Wissahickon Physics Midterm x = x i + vt + 1 2 at 2 v f 2 = v i 2 + 2ad Name v f = v i + at Gm 1 m 2 w = mg F g = r 2 g = 9.8m/s 2 G = 6.67 10 11 (N m 2 /k g 2 ) F = ma F f = µn τ = Frsinθ a c = v 2 p
Wissahickon Physics Midterm x = x i + vt + 1 2 at 2 v f 2 = v i 2 + 2ad Name v f = v i + at Gm 1 m 2 w = mg F g = r 2 g = 9.8m/s 2 G = 6.67 10 11 (N m 2 /k g 2 ) F = ma F f = µn τ = Frsinθ a c = v 2 p
v (m/s) 10 d. displacement from 0-4 s 28 m e. time interval during which the net force is zero 0-2 s f. average velocity from 0-4 s 7 m/s x (m) 20
 Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Base your answers to questions 5 and 6 on the information below.
 1. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second
1. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second
St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School
 Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 18, You cannot use CELL PHONES, ipad, IPOD... Good Luck!!! Name Section University ID
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 18, 018 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 18, 018 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
PY205N Spring The vectors a, b, and c. are related by c = a b. The diagram below that best illustrates this relationship is (a) I
 PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
EXPERIENCE COLLEGE BEFORE COLLEGE
 Mechanics, Heat, and Sound (PHY302K) College Unit Week Dates Big Ideas Subject Learning Outcomes Assessments Apply algebra, vectors, and trigonometry in context. Employ units in problems. Course Mathematics
Mechanics, Heat, and Sound (PHY302K) College Unit Week Dates Big Ideas Subject Learning Outcomes Assessments Apply algebra, vectors, and trigonometry in context. Employ units in problems. Course Mathematics
PRACTICE QUESTION PAPER WITH SOLUTION CLASS XI PHYSICS
 PRACTICE QUESTION PAPER WITH SOLUTION CLASS XI PHYSICS. A given quantity has both magnitude and direction. Is it necessarily a vector? Justify your answer.. What is the rotational analogue of the force?.
PRACTICE QUESTION PAPER WITH SOLUTION CLASS XI PHYSICS. A given quantity has both magnitude and direction. Is it necessarily a vector? Justify your answer.. What is the rotational analogue of the force?.
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Circular motion Impulse and momentum 08-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 9 in textbook Prelecture due next Thursday HW#8 due NEXT Friday (extension!)
Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Circular motion Impulse and momentum 08-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 9 in textbook Prelecture due next Thursday HW#8 due NEXT Friday (extension!)
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems. Kinetic Energy and
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Kinetic energy Work Work-energy theorem Gravitational work Work of spring forces Power 1. A single force acts on a 5.0-kg object in such
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Kinetic energy Work Work-energy theorem Gravitational work Work of spring forces Power 1. A single force acts on a 5.0-kg object in such
Physics 101 Hour Exam 2 November 3, 2014
 Physics 101 Hour Exam 2 November 3, 2014 Last Name: First Name ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators cannot be shared. Please keep
Physics 101 Hour Exam 2 November 3, 2014 Last Name: First Name ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators cannot be shared. Please keep
*************************************************************************
 Your Name: TEST #3 Print clearly. There are 20 equally-weighted questions on this test (two-part problems count as two separate questions). There is only one correct answer per question. Clearly circle
Your Name: TEST #3 Print clearly. There are 20 equally-weighted questions on this test (two-part problems count as two separate questions). There is only one correct answer per question. Clearly circle
PSI AP Physics B Dynamics
 PSI AP Physics B Dynamics Multiple-Choice questions 1. After firing a cannon ball, the cannon moves in the opposite direction from the ball. This an example of: A. Newton s First Law B. Newton s Second
PSI AP Physics B Dynamics Multiple-Choice questions 1. After firing a cannon ball, the cannon moves in the opposite direction from the ball. This an example of: A. Newton s First Law B. Newton s Second
RELEASED FORM RELEASED. North Carolina Test of Physics
 Name Physics Form North arolina Test of Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina www.ncpublicschools.org State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction ivision of ccountability Services/North
Name Physics Form North arolina Test of Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina www.ncpublicschools.org State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction ivision of ccountability Services/North
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015
 95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
Physics 23 Exam 2 March 3, 2009
 Use the following to answer question 1: A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third
Use the following to answer question 1: A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
A B = AB cos θ = 100. = 6t. a(t) = d2 r(t) a(t = 2) = 12 ĵ
 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the Earth s surface and falls back to Earth. Which of the graphs below best symbolizes its speed v(t) as a function of time, neglecting air resistance: The answer
1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the Earth s surface and falls back to Earth. Which of the graphs below best symbolizes its speed v(t) as a function of time, neglecting air resistance: The answer
Slide 2 / 76. Slide 1 / 76. Slide 3 / 76. Slide 4 / 76. Slide 6 / 76. Slide 5 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems A 1,800 B 5,000 E 300,000
 Slide 1 / 76 Slide 2 / 76 1 driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate the sports car from 30 m/s to
Slide 1 / 76 Slide 2 / 76 1 driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate the sports car from 30 m/s to
Physics 207 Lecture 25. Lecture 25. HW11, Due Tuesday, May 6 th For Thursday, read through all of Chapter 18. Angular Momentum Exercise
 Lecture 5 Today Review: Exam covers Chapters 14-17 17 plus angular momentum, rolling motion & torque Assignment HW11, Due Tuesday, May 6 th For Thursday, read through all of Chapter 18 Physics 07: Lecture
Lecture 5 Today Review: Exam covers Chapters 14-17 17 plus angular momentum, rolling motion & torque Assignment HW11, Due Tuesday, May 6 th For Thursday, read through all of Chapter 18 Physics 07: Lecture
Suggested Solutions for 2011 J1 H2 Physics Paper Which of the following is a unit of pressure?
 Suggested s for 2011 J1 H2 Physics Paper 1 1. Which of the following is a unit of pressure? kg m s -1 kg m -1 s -2 kg m 2 s -2 kg m -2 s -1 [] P = Force/area Units of pressure, P = (kg m s -2 ) / m 2 =
Suggested s for 2011 J1 H2 Physics Paper 1 1. Which of the following is a unit of pressure? kg m s -1 kg m -1 s -2 kg m 2 s -2 kg m -2 s -1 [] P = Force/area Units of pressure, P = (kg m s -2 ) / m 2 =
St. Mary's H.S. Physics. Midterm Review
 Name Midterm Review St. Mary's H.S. Physics 1. If a car accelerates uniformly from rest to 15 meters per second over a distance of 100. meters, the magnitude of the car s acceleration is A) 0.15 m/s 2
Name Midterm Review St. Mary's H.S. Physics 1. If a car accelerates uniformly from rest to 15 meters per second over a distance of 100. meters, the magnitude of the car s acceleration is A) 0.15 m/s 2
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
Simon Fraser University 2000 April 18 Physics 100 Final Examination
 Simon Fraser University 2000 April 18 Physics 100 Final Examination This exam has two parts: Part A contains 25 multiple choice questions. Complete the bubbles for your name and student number on the multiple
Simon Fraser University 2000 April 18 Physics 100 Final Examination This exam has two parts: Part A contains 25 multiple choice questions. Complete the bubbles for your name and student number on the multiple
