Power Control for a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell
|
|
|
- Lucas Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Power Control for a Polymer lectrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Donald J. Chmielewski Kevin Lauzze Department of Chemical and nvironmental ngineering Illinois Institute of Technology Presented at the Annual Meeting of the AICh: November 005
2 Outline PMFC Model Mat. & nergy Balances and lectrochemistry Operating Characteristics Controller Design Power Set-Point Tracking Temperature / Humidity Regulation Oxygen Regulation
3 What is a Fuel Cell? H Air Answer: Fuel Cell lectric Power H O A device that converts fuel directly into electrical power
4 Polymer lectrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell (PMFC) H H H H e - e - O H + N H H + O O H + H O N O O N H O H O N N H O H O Generated power due to enthalpy released by the reaction: H + ½ O H O H Anode H + lectrolyte O Cathode H O (H ~ 58 kcal/mole H )
5 The Fuel Cell Stack Stack Current Flow Fuel Flow Air Flow
6 Dynamic Model of PMFC Cooling Air In Anode H In Solid Material H H + H + H + H + H + Insulator Current Collector O N Jacket xhaust Cathode Air in Parameters based on 50 kw scale. Pure hydrogen feed H + H + H + H O Cathode xhaust Air cooling is assumed. MA cell
7 Material Balances in the Cathode V V V F cat cat cat cat dc H dt dc O dt dc C dt N O F in cat F F C F in cat in cat in cat C C 1 C in O in N in H O r H O F F A F cat cat mem cat C C O C N H O 1 r H r H O O A A mem mem
8 Cathode Chamber Gas Cooling Jacket Gas dt V jac dt Solid Material nergy Balances sol C V UA ( T T ) UA p sol V sol cat dt dt dt dt cat cat F F in cat in jac T T cat in cat in jac UA ( Tamb Tsol ) QgenAmem eff cat F F cat jac T T cat sol jac UA C p UA C p jac cat jac ( T ( Tsol Tcat jac T sol ) ) ( T T ) jac sol
9 Rates Rate of Reaction: (production of water per area of membrane) r H O j F Heat Generation Rate: (per area of membrane) Q gen ( H f, H O) r HO P e Power Generation: (electrical energy generation rate per area of membrane) Pe j cell
10 Load Current Density Depends on the Load Fuel Cell R int I=j*A cell cell The fuel cell looks like a battery to the DC o electrical world.
11 Changing the Reaction Rate load load = o - R int *I r H O I / n A F mem o Battery I -R int R int load R load load = R load *I I DC o
12 lectrochemistry cell ner act ohm mt
13 lectrochemistry cell ner act ohm mt Nernst Potential: ner o RT sol F ln P H P H P 1/ O O
14 lectrochemistry cell ner act ohm mt Ohmic Loss: ohm IR ja mem t A mem mem ~ ionic conductivity of the membrane depends on humidification levels
15 Ohmic Resistance Ionic conductivity,, increases with humidity RH x H P O sat P ( T) x HO = 0.35
16 Partial PMFC Polarization Curve cell ner act ohm mt 0 000
17 PMFC Polarization Curve cell ner act ohm mt 0 000
18 PMFC Polarization Curve cell ner act ohm mt Activation Loss: act 1 RT F sol ln Mass Transfer Loss: mt RT F o ( s) o j / j j j ( C / C ) o 1 ln sol ( s) CO / C O o o O O
19 Surface Concentrations Mass Transfer Rate : (assuming O is the rate limiting species) ( 1/ ) r K C ( s) C H O O O Mass Transfer Coefficient : K K 1e o ( RH 1)/ ~ porosity coefficient
20 Mass Transfer Coefficient Flooding Resistance via the MTC x Relative Humidity (%)
21 fficient Operation Ionic conductivity,, increases with humidity x w = 0.35
22 Outline PMFC Model Mat. & nergy Balances and lectrochemistry Operating Characteristics Controller Design Power Set-Point Tracking Temperature / Humidity Regulation Oxygen Regulation
23 Power Set-Point Tracking Transportation Applications (sp) Power Controller MV PMFC
24 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Selecting the Power Output P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
25 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Selecting the Power Output P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
26 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Selecting the Power Output P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
27 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Selecting the Power Output P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
28 + - Power Controller PI j (sp) + - PI cell PMFC j (sp)
29 + - Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Power Controller PI j (sp) + - PI cell PMFC j (sp) P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
30 + - Power Controller j (sp) + - PI cell PMFC j PI (sp) Cooling Air In Anode H In Solid Material H H + H + Insulator Current Collector O Jacket xhaust Cathode Air in H + H + H + H + H + H + MA cell N H O Cathode xhaust
31 Power Density (watts/cm ) Power Controller P P e (sp) e Time (seconds)
32 Current Density (ma/cm ) Cell Voltage (V) Power Controller 30 0 j cell Time (seconds)
33 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Current Density (ma/cm ) Cell Voltage (V) Power Controller 30 0 j P e cell Time (seconds) cell Current Density (ma/cm )
34 Temperature (Celsius) Relative Humidity (%) Power Controller Flooding T cat RH Time (seconds)
35 Power Density (watts/cm ) Power Controller (sp) Time (seconds)
36 Current Density (ma/cm ) Cell Voltage (V) Power Controller Failure 400 cell j Time (seconds)
37 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Power Controller Failure P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
38 Power Density (watts/cm ) Power Controller (sp) Time (seconds)
39 Temperature (Celsius) Relative Humidity (%) Power Controller Failure RH T cat Time (seconds)
40 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) Power Controller Failure P e cell Current Density (ma/cm )
41 Temperature / RH Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC T cat (sp) PI + - PI F jac T cat RH + - RH (sp)
42 Temperature / RH Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC T cat (sp) PI + - PI F jac T cat RH + - RH (sp)
43 Temperature / RH Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC T cat (sp) PI + - PI F jac T cat RH + - RH (sp)
44 Temperature / RH Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC T cat (sp) PI + - PI F jac T cat RH Cooling Air In Insulator Jacket xhaust + - RH (sp) Anode H In Solid Material H H + H + H + H + H + Current Collector O N Cathode Air in H + H + H + H O Cathode xhaust MA cell
45 Power Density (watts/cm ) Temperature / RH Controller P (sp) e Time (seconds)
46 Temperature (Celsius) Relative Humidity (%) Temperature / RH Controller T cat RH (sp) T cat Time (seconds) 85 80
47 Oxygen Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC F jac RH, T cat RH (sp) RH Controller PI F cat (sp) x O x O + -
48 Oxygen Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC F jac RH, T cat RH (sp) RH Controller PI F cat (sp) x O x O + -
49 Oxygen Controller (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC F jac RH, T cat RH (sp) RH Controller PI F cat Cooling Air In Insulator Jacket xhaust (sp) x O + - x O Anode H In Solid Material H H + H + Current Collector O Cathode Air in H + H + H + N H + H + H + H O Cathode xhaust MA cell
50 Power Density (watts/cm ) Oxygen Controller P (sp) e Time (seconds)
51 Mole fraction of oxygen Oxygen Controller Time (seconds)
52 Oxygen Controller Relative Humidity (%) Temperature (Celsius) Time (seconds)
53 Cell Voltage (V) Power Density (watts/cm ) fficient Operation Definition of fficiency: P e cell eq Current Density (ma/cm ) cell where eq H f, H F O
54 fficiency (%) + - Available Power and fficiency 75 PI j (sp) + - PI cell PMFC j 70 Power Control (sp) Power Density (watts/cm )
55 fficiency (%) Available Power and fficiency Power Control T cat (sp) PI (sp) Power Controller + - PI cell, j F jac PMFC T cat RH + - RH (sp) Power & Humidity Control Power Density (watts/cm )
56 fficiency (%) Available Power and fficiency 75 Power, Humidity & Oxygen Control (sp) Power Controller cell, j PMFC F jac RH, T cat RH (sp) RH Controller PI F cat 70 Power Control (sp) x O + - x O Power & Humidity Control Power Density (watts/cm )
57 Acknowledgements Students: Ayman Al-Qattan Janet Ruettiger Collaborators: Said Al-Hallaj Vijay Ramani Jai Prakash Yongyou Hu J. Robert Selman Satish Parulekar Funding: Argonne National Laboratory Graduate College, IIT Armour College of ngineering, IIT Department of Chemical & nvironmental ngineering, IIT
The Impact of Hydration Dynamics on the Control of a PEM Fuel Cell
 The Impact of Hydration Dynamics on the Control of a PM Fuel Cell Syed K. Ahmed Donald J. Chmielewski Department of Chemical and nvironmental ngineering Illinois Institute of Technology Presented at the
The Impact of Hydration Dynamics on the Control of a PM Fuel Cell Syed K. Ahmed Donald J. Chmielewski Department of Chemical and nvironmental ngineering Illinois Institute of Technology Presented at the
Dynamics and Control of Membrane Hydration in a PEMFC
 Dynamics and Control of Membrane Hydration in a PMFC Syed K. Ahmed Donald J. Chmielewski Department of Chemical and Biological ngineering Presented at the American Control Conference: June 009 Outline
Dynamics and Control of Membrane Hydration in a PMFC Syed K. Ahmed Donald J. Chmielewski Department of Chemical and Biological ngineering Presented at the American Control Conference: June 009 Outline
Figure 1. Schematic of Scriber Associates Model 850C fuel cell system.
 Objective of the fuel cell experiments: To familiarize the working principles and performance characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Experimental Procedures Instrumentation A Scriber Associates
Objective of the fuel cell experiments: To familiarize the working principles and performance characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Experimental Procedures Instrumentation A Scriber Associates
Power System and Controller Design for Hybrid Fuel Cell Vehicles
 Power System and Controller Design for Hybrid Fuel Cell Vehicles Syed K. Ahmed Donald J. Chmielewski Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Illinois Institute of Technology Presented at the
Power System and Controller Design for Hybrid Fuel Cell Vehicles Syed K. Ahmed Donald J. Chmielewski Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering Illinois Institute of Technology Presented at the
SCIENCES & TECHNOLOGY
 Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 22 (2): 645-655 (2014) SCIENCES & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Numerical Modelling of Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell: Effects of Gas Flow Direction
Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 22 (2): 645-655 (2014) SCIENCES & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Numerical Modelling of Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell: Effects of Gas Flow Direction
Performance Investigation on Electrochemical Compressor with Ammonia
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Performance Investigation on Electrochemical Compressor with Ammonia Ye Tao University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Performance Investigation on Electrochemical Compressor with Ammonia Ye Tao University
Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources)
 Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources) 1. Primary (single-discharge) batteries. => finite quantity of the reactants 2. Secondary or rechargeable batteries => regeneration of the original reactants by
Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources) 1. Primary (single-discharge) batteries. => finite quantity of the reactants 2. Secondary or rechargeable batteries => regeneration of the original reactants by
Electrochemical Equipment Design for Hybrid Vehicles
 ower to Motor (kw) Speed (mph) Electrochemical Equipment Design for Hybrid Vehicles Syed K. Ahmed, Benja. Omell and Donald J. Chmielewski 6 4 Cooling Air In Anode In (H, H O) Solid Material H H O Insulator
ower to Motor (kw) Speed (mph) Electrochemical Equipment Design for Hybrid Vehicles Syed K. Ahmed, Benja. Omell and Donald J. Chmielewski 6 4 Cooling Air In Anode In (H, H O) Solid Material H H O Insulator
Simulation of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stack Using an Electronic Equivalent Circuit Model
 imulation of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel ell tack Using an Electroc Equivalent ircuit Model JP U TOIT AN HvZ PIENAAR* epartment of Applied Electrocs and Electroc ommucations Vaal Uversity of Technology,
imulation of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel ell tack Using an Electroc Equivalent ircuit Model JP U TOIT AN HvZ PIENAAR* epartment of Applied Electrocs and Electroc ommucations Vaal Uversity of Technology,
Control of Proton Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Systems. Dr. M. Grujicic Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Control of Proton Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Systems Dr. M. Grujicic 4 Department of Mechanical Engineering OUTLINE. Feedforward Control, Fuel Cell System. Feedback Control, Fuel Cell System W Cp Supply
Control of Proton Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Systems Dr. M. Grujicic 4 Department of Mechanical Engineering OUTLINE. Feedforward Control, Fuel Cell System. Feedback Control, Fuel Cell System W Cp Supply
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells
 Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
DISCLAIMER. Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. Images are produced from the best available original document.
 ; i i : L4 0 t DSCLAMER Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. mages are produced from the best available original document. EVALUATON OF THE HUMDFCATON REQTJREMENTS OF
; i i : L4 0 t DSCLAMER Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. mages are produced from the best available original document. EVALUATON OF THE HUMDFCATON REQTJREMENTS OF
D DAVID PUBLISHING. 1. Introduction. Akira Nishimura 1, Masashi Baba 1, Kotaro Osada 1, Takenori Fukuoka 1, Masafumi Hirota 1 and Eric Hu 2
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering () - doi:./-/.. D DAVID PUBLISHING Temperature Distributions in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Simulated by an D Multi-plate Heat-Transfer Model and
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering () - doi:./-/.. D DAVID PUBLISHING Temperature Distributions in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Simulated by an D Multi-plate Heat-Transfer Model and
Diagnosis of PEMFC operation using EIS
 Diagnosis of PEMFC operation using EIS Electrical Research Institute Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Group Félix Loyola, Ulises Cano-Castillo ucano@iie.org.mx International Symposium on DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS FOR FUEL
Diagnosis of PEMFC operation using EIS Electrical Research Institute Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Group Félix Loyola, Ulises Cano-Castillo ucano@iie.org.mx International Symposium on DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS FOR FUEL
ELECTROCHEMICAL COMPRESSION OF PRODUCT HYDROGEN FROM PEM ELECTROLYZER STACK
 ELECTROCHEMICAL COMPRESSION OF PRODUCT HYDROGEN FROM PEM ELECTROLYZER STACK N.V. Dale 1,*, C. Y. Biaku 1, M. D. Mann 1, H. Salehfar 2, A. J. Peters 2 Abstract The low volumetric energy density of hydrogen
ELECTROCHEMICAL COMPRESSION OF PRODUCT HYDROGEN FROM PEM ELECTROLYZER STACK N.V. Dale 1,*, C. Y. Biaku 1, M. D. Mann 1, H. Salehfar 2, A. J. Peters 2 Abstract The low volumetric energy density of hydrogen
Electrochemical Cell - Basics
 Electrochemical Cell - Basics The electrochemical cell e - (a) Load (b) Load e - M + M + Negative electrode Positive electrode Negative electrode Positive electrode Cathode Anode Anode Cathode Anode Anode
Electrochemical Cell - Basics The electrochemical cell e - (a) Load (b) Load e - M + M + Negative electrode Positive electrode Negative electrode Positive electrode Cathode Anode Anode Cathode Anode Anode
Appendix A Electric Vehicle PEM Fuel Cell Stack Parameters
 Appendix A Electric Vehicle PEM Fuel Cell Stack Parameters A.1 Return Manifold Polynomial Fitting Table A.1 Return manifold polynomial fitting Parameter Value Return manifold parameter p 0 0.001248 kg/s
Appendix A Electric Vehicle PEM Fuel Cell Stack Parameters A.1 Return Manifold Polynomial Fitting Table A.1 Return manifold polynomial fitting Parameter Value Return manifold parameter p 0 0.001248 kg/s
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17653 Supplementary Methods Electronic transport mechanism in H-SNO In pristine RNO, pronounced electron-phonon interaction results in polaron formation that dominates the electronic
doi:10.1038/nature17653 Supplementary Methods Electronic transport mechanism in H-SNO In pristine RNO, pronounced electron-phonon interaction results in polaron formation that dominates the electronic
Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications. Pfaffenwaldring 6, Stuttgart, Germany
 Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications S. Altmann a,b, T. Kaz b, K. A. Friedrich a,b a Institute of Thermodynamics and Thermal Engineering, University Stuttgart,
Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications S. Altmann a,b, T. Kaz b, K. A. Friedrich a,b a Institute of Thermodynamics and Thermal Engineering, University Stuttgart,
Polarization analysis and microstructural characterization of SOFC anode and electrolyte supported cells
 Polarization analysis and microstructural characterization of SOFC anode and electrolyte supported cells Lanzini A., Leone P., Santarelli M., Asinari P., Calì M. Dipartimento di Energetica. Politecnico
Polarization analysis and microstructural characterization of SOFC anode and electrolyte supported cells Lanzini A., Leone P., Santarelli M., Asinari P., Calì M. Dipartimento di Energetica. Politecnico
Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering
 Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Experimental Characterization Methodology for the Identification of Voltage Losses of PEMFC: Applied to an Open Cathode Stack
 Experimental Characterization Methodology for the Identification of Voltage Losses of PEMFC: Applied to an Open Cathode Stack A. Husar *, S. Strahl, J. Riera Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial
Experimental Characterization Methodology for the Identification of Voltage Losses of PEMFC: Applied to an Open Cathode Stack A. Husar *, S. Strahl, J. Riera Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Lakshminarayanan V 1, Karthikeyan P 2, D. S. Kiran Kumar 1 and SMK Dhilip Kumar 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, KGiSL Institute
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Lakshminarayanan V 1, Karthikeyan P 2, D. S. Kiran Kumar 1 and SMK Dhilip Kumar 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, KGiSL Institute
FUEL CELLS: INTRODUCTION
 FUEL CELLS: INTRODUCTION M. OLIVIER marjorie.olivier@fpms.ac.be 19/5/8 A SIMPLE FUEL CELL Two electrochemical half reactions : H 1 O H + + H + e + + e H O These reactions are spatially separated: Electrons:
FUEL CELLS: INTRODUCTION M. OLIVIER marjorie.olivier@fpms.ac.be 19/5/8 A SIMPLE FUEL CELL Two electrochemical half reactions : H 1 O H + + H + e + + e H O These reactions are spatially separated: Electrons:
Modeling and Simulation of a PEM Fuel Cell System Under Various Temperature Conditions
 nd WSEAS/IASME International Conference on RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES (RES'08) Corfu, Greece, October 6-8, 008 Modelg and Simulation of a EM Fuel Cell System Under Various Temperature Conditions A. A. SALAM,
nd WSEAS/IASME International Conference on RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES (RES'08) Corfu, Greece, October 6-8, 008 Modelg and Simulation of a EM Fuel Cell System Under Various Temperature Conditions A. A. SALAM,
17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited
 Chapter Outline 17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited 17.2 Electrochemical Cells 17.3 Standard Potentials 17.4 Chemical Energy and Electrical Work 17.5 A Reference Point: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode 17.6
Chapter Outline 17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited 17.2 Electrochemical Cells 17.3 Standard Potentials 17.4 Chemical Energy and Electrical Work 17.5 A Reference Point: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode 17.6
Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering
 Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Performance Analysis of a Two phase Non-isothermal PEM Fuel Cell
 Performance Analysis of a Two phase Non-isothermal PEM Fuel Cell A. H. Sadoughi 1 and A. Asnaghi 2 and M. J. Kermani 3 1, 2 Ms Student of Mechanical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology Tehran,
Performance Analysis of a Two phase Non-isothermal PEM Fuel Cell A. H. Sadoughi 1 and A. Asnaghi 2 and M. J. Kermani 3 1, 2 Ms Student of Mechanical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology Tehran,
Chapter 18. Direct Current Circuits
 Chapter 18 Direct Current Circuits Sources of emf The source that maintains the current in a closed circuit is called a source of emf Any devices that increase the potential energy of charges circulating
Chapter 18 Direct Current Circuits Sources of emf The source that maintains the current in a closed circuit is called a source of emf Any devices that increase the potential energy of charges circulating
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice Hall,
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice Hall,
Prof. Mario L. Ferrari
 Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy Lesson II Lesson II: fuel cells (electrochemistry)
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy Lesson II Lesson II: fuel cells (electrochemistry)
Basic Concepts of Electrochemistry
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electricity-driven Chemistry or Chemistry-driven Electricity Electricity: Chemistry (redox): charge flow (electrons, holes, ions) reduction = electron uptake oxidation = electron loss
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electricity-driven Chemistry or Chemistry-driven Electricity Electricity: Chemistry (redox): charge flow (electrons, holes, ions) reduction = electron uptake oxidation = electron loss
Non-linear Predictive Control with Multi Design Variables for PEM-FC
 Non-linear Predictive Control with Multi Design Variables for PEM-FC A. Shokuhi-Rad, M. Naghash-Zadegan, N. Nariman-Zadeh, A. Jamali, A.Hajilu Abstract Designing of a non-linear controller base on model
Non-linear Predictive Control with Multi Design Variables for PEM-FC A. Shokuhi-Rad, M. Naghash-Zadegan, N. Nariman-Zadeh, A. Jamali, A.Hajilu Abstract Designing of a non-linear controller base on model
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO. FINAL EXAM, APRIL 28, hours. EXAMINER D.W. Kirk,
 Page 1 of 11 PRINT FIRST NAME LAST NAME STUDENT NUMBER UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FINAL EXAM, APRIL 28, 2017 2.5 hours CHE 469F - FUEL CELLS and ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS Do all questions. The marks add up to
Page 1 of 11 PRINT FIRST NAME LAST NAME STUDENT NUMBER UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FINAL EXAM, APRIL 28, 2017 2.5 hours CHE 469F - FUEL CELLS and ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS Do all questions. The marks add up to
Modelling fuel cells in start-up and reactant starvation conditions
 Modelling fuel cells in start-up and reactant starvation conditions Brian Wetton Radu Bradean Keith Promislow Jean St Pierre Mathematics Department University of British Columbia www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton
Modelling fuel cells in start-up and reactant starvation conditions Brian Wetton Radu Bradean Keith Promislow Jean St Pierre Mathematics Department University of British Columbia www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton
Current and Resistance
 Current and Resistance 1 Define the current. Understand the microscopic description of current. Discuss the rat at which the power transfer to a device in an electric current. 2 2-1 Electric current 2-2
Current and Resistance 1 Define the current. Understand the microscopic description of current. Discuss the rat at which the power transfer to a device in an electric current. 2 2-1 Electric current 2-2
Electrode Potentials and Their Measurement
 Electrochemistry Electrode Potentials and Their Measurement Cu(s) + 2Ag + (aq) Cu(s) + Zn 2+ (aq) Cu 2+ (aq) + 2 Ag(s) No reaction Zn(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) Cu(s) + Zn 2+ (aq) In this reaction: Zn (s) g Zn 2+
Electrochemistry Electrode Potentials and Their Measurement Cu(s) + 2Ag + (aq) Cu(s) + Zn 2+ (aq) Cu 2+ (aq) + 2 Ag(s) No reaction Zn(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) Cu(s) + Zn 2+ (aq) In this reaction: Zn (s) g Zn 2+
Electrochemistry. The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy.
 Electrochemistry The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction: involves a transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. oxidation:
Electrochemistry The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction: involves a transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. oxidation:
H are designed for these purposes. The fuzzy logic control scheme is employed for the design of the two controllers.
 An Intelligent Control of Solid oxide Fuel cell voltage Kanhu Charan Bhuyan and Kamalakanta Mahapatra Dept of ECE, National Institute of Technology-Rourkela, India-7698 Email: kanhu6@gmail.com, kmaha@rediffmail.com
An Intelligent Control of Solid oxide Fuel cell voltage Kanhu Charan Bhuyan and Kamalakanta Mahapatra Dept of ECE, National Institute of Technology-Rourkela, India-7698 Email: kanhu6@gmail.com, kmaha@rediffmail.com
ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF PERFORMANCE OF A PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL IN MOBILE APPLICATIONS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 015, vol.0, No., pp.319-38 DOI: 10.1515/ijame-015-001 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF PERFORMANCE OF A PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 015, vol.0, No., pp.319-38 DOI: 10.1515/ijame-015-001 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF PERFORMANCE OF A PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL
Electrochemical System
 Electrochemical System Topic Outcomes Week Topic Topic Outcomes 8-10 Electrochemical systems It is expected that students are able to: Electrochemical system and its thermodynamics Chemical reactions in
Electrochemical System Topic Outcomes Week Topic Topic Outcomes 8-10 Electrochemical systems It is expected that students are able to: Electrochemical system and its thermodynamics Chemical reactions in
Reacting Gas Mixtures
 Reacting Gas Mixtures Reading Problems 15-1 15-7 15-21, 15-32, 15-51, 15-61, 15-74 15-83, 15-91, 15-93, 15-98 Introduction thermodynamic analysis of reactive mixtures is primarily an extension of the principles
Reacting Gas Mixtures Reading Problems 15-1 15-7 15-21, 15-32, 15-51, 15-61, 15-74 15-83, 15-91, 15-93, 15-98 Introduction thermodynamic analysis of reactive mixtures is primarily an extension of the principles
Computational model of a PEM fuel cell with serpentine gas flow channels
 Journal of Power Sources 130 (2004) 149 157 Computational model of a PEM fuel cell with serpentine gas flow channels Phong Thanh Nguyen, Torsten Berning 1, Ned Djilali Institute for Integrated Energy Systems,
Journal of Power Sources 130 (2004) 149 157 Computational model of a PEM fuel cell with serpentine gas flow channels Phong Thanh Nguyen, Torsten Berning 1, Ned Djilali Institute for Integrated Energy Systems,
Sliding Mode Control for Stabilizing of Boost Converter in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
 BUGARAN ACADEMY OF SCENCES CYBERNETCS AND NFORMATON TECHNOOGES Volume 13, No 4 Sofia 013 Print SSN: 1311-970; Online SSN: 1314-4081 DO: 10.478/cait-013-0060 Sliding Mode Control for Stabilizing of Boost
BUGARAN ACADEMY OF SCENCES CYBERNETCS AND NFORMATON TECHNOOGES Volume 13, No 4 Sofia 013 Print SSN: 1311-970; Online SSN: 1314-4081 DO: 10.478/cait-013-0060 Sliding Mode Control for Stabilizing of Boost
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Material Structure Grading in the Direction Normal to the Electrode/Electrolyte Interface using COMSOL Multiphysics
 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Material Structure Grading in the Direction Normal to the Electrode/Electrolyte Interface using COMSOL Multiphysics M. Andersson*, B. Sundén, Department of Energy Sciences, Lund University,
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Material Structure Grading in the Direction Normal to the Electrode/Electrolyte Interface using COMSOL Multiphysics M. Andersson*, B. Sundén, Department of Energy Sciences, Lund University,
Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts
 Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts Raja Swaidan The Cooper Union Advisor: Dr. Branko N. Popov Electrochemical Engineering 26 July 2007 Overview of Research Studied
Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts Raja Swaidan The Cooper Union Advisor: Dr. Branko N. Popov Electrochemical Engineering 26 July 2007 Overview of Research Studied
Forced Convectional Heat Transfer in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: An Analytical Treatment.
 Ionics 9 (2003) 83 Forced Convectional Heat Transfer in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: An Analytical Treatment. F.A. Coutelieris 1, A.K. Demin 2, S.L. Douvartzides 1 and P.E. Tsiakaras 1 1 University of Thessalia,
Ionics 9 (2003) 83 Forced Convectional Heat Transfer in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: An Analytical Treatment. F.A. Coutelieris 1, A.K. Demin 2, S.L. Douvartzides 1 and P.E. Tsiakaras 1 1 University of Thessalia,
Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example)
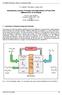 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
Fernando O. Raineri. Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby).
 Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Fuel Cells Activation polarization
 Fuel Cells The principle of fuel cells Oxygen and hydrogen, when mixed together in the presence of enough activation energy have a natural tendency to react and form water, because the Gibbs free energy
Fuel Cells The principle of fuel cells Oxygen and hydrogen, when mixed together in the presence of enough activation energy have a natural tendency to react and form water, because the Gibbs free energy
Modeling as a tool for understanding the MEA. Henrik Ekström Utö Summer School, June 22 nd 2010
 Modeling as a tool for understanding the MEA Henrik Ekström Utö Summer School, June 22 nd 2010 COMSOL Multiphysics and Electrochemistry Modeling The software is based on the finite element method A number
Modeling as a tool for understanding the MEA Henrik Ekström Utö Summer School, June 22 nd 2010 COMSOL Multiphysics and Electrochemistry Modeling The software is based on the finite element method A number
Oxygen Transfer Model in Cathode GDL of PEM Fuel Cell for Estimation of Cathode Overpotential
 Oxygen Transfer Model in Cathode GDL of PEM Fuel Cell for Estimation of Cathode Overpotential Abstract... The mathematical model involving kinetics and mass transfer in a PEM fuel cell cathode is developed
Oxygen Transfer Model in Cathode GDL of PEM Fuel Cell for Estimation of Cathode Overpotential Abstract... The mathematical model involving kinetics and mass transfer in a PEM fuel cell cathode is developed
Fuel Cell System Model: Auxiliary Components
 2 Fuel Cell System Model: Auxiliary Components Models developed specifically for control studies have certain characteristics. Important characteristics such as dynamic (transient) effects are included
2 Fuel Cell System Model: Auxiliary Components Models developed specifically for control studies have certain characteristics. Important characteristics such as dynamic (transient) effects are included
THERMAL ELECTROCHEMICAL DYNAMIC MODELING OF SEALED LEAD ACID BATTERIES. Kevin Siniard
 THERMAL ELECTROCHEMICAL DYNAMIC MODELING OF SEALED LEAD ACID BATTERIES Except where reference is made to the work of others, the work described in this thesis is my own or was done in collaboration with
THERMAL ELECTROCHEMICAL DYNAMIC MODELING OF SEALED LEAD ACID BATTERIES Except where reference is made to the work of others, the work described in this thesis is my own or was done in collaboration with
Effect of Varying Electrolyte Conductivity on the Electrochemical Behavior of Porous Electrodes
 A984 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 52 5 A984-A988 2005 003-465/2005/525/A984/5/$7.00 The Electrochemical Society, Inc. Effect of Varying Electrolyte Conductivity on the Electrochemical Behavior
A984 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 52 5 A984-A988 2005 003-465/2005/525/A984/5/$7.00 The Electrochemical Society, Inc. Effect of Varying Electrolyte Conductivity on the Electrochemical Behavior
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry. Chapter 20 Problems. Electrochemistry 7/3/2012. Problems 15, 17, 19, 23, 27, 29, 33, 39, 59
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chapter 20 Problems
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chapter 20 Problems
CFD Analysis of PEM Fuel Cell
 CFD Analysis of PEM Fuel Cell Group Seminar Munir Khan Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University Outline 1 Geometry 2 Mathematical Model 3 Results 4 Conclusions I 5 Pore Scale
CFD Analysis of PEM Fuel Cell Group Seminar Munir Khan Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University Outline 1 Geometry 2 Mathematical Model 3 Results 4 Conclusions I 5 Pore Scale
January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells
 January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells Fuel Cells Instructor James M. Fenton, Professor, Chemical Engineering University of Connecticut Teaching Assistants: 1.
January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells Fuel Cells Instructor James M. Fenton, Professor, Chemical Engineering University of Connecticut Teaching Assistants: 1.
Unraveling Fuel Cell Electrical Measurements
 A G R E A T E R M E A S U R E O F C O N F I D E N C E Unraveling Fuel Cell Electrical Measurements James Niemann, Keithley Instruments, Inc. ducting, catalyzed anode and cathode electrodes. See Figure
A G R E A T E R M E A S U R E O F C O N F I D E N C E Unraveling Fuel Cell Electrical Measurements James Niemann, Keithley Instruments, Inc. ducting, catalyzed anode and cathode electrodes. See Figure
ELEC 103. Objectives
 ELEC 103 Voltage, Current, and Resistance Objectives Define voltage and discuss its characteristics Define current and discuss its characteristics Define resistance and discuss its characteristics Identify
ELEC 103 Voltage, Current, and Resistance Objectives Define voltage and discuss its characteristics Define current and discuss its characteristics Define resistance and discuss its characteristics Identify
Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA, 16802
 Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells using Fluent Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park,
Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells using Fluent Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park,
Simulation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by using ANSYS Fluent
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by using ANSYS Fluent To cite this article: Asifa Awan et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by using ANSYS Fluent To cite this article: Asifa Awan et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Appendix A Potassium Formate Property Calculations
 Appendix A Potassium Formate Property Calculations A.1 Potassium Formate Vapour Pressure This section describes the routine used to calculate the vapour pressure of the potassium formate solution (p sol
Appendix A Potassium Formate Property Calculations A.1 Potassium Formate Vapour Pressure This section describes the routine used to calculate the vapour pressure of the potassium formate solution (p sol
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS. Checklist. Exam Questions
 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Checklist Make sure you can. State Ohm's law in words. Determine relationship between current, potential difference and resistance at constant temperature using a simple circuit Draw,
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Checklist Make sure you can. State Ohm's law in words. Determine relationship between current, potential difference and resistance at constant temperature using a simple circuit Draw,
Computational Analysis of Heat Transfer in Air-cooled Fuel Cells
 Proceedings of ASME 2011, 5th International Conference on Energy Sustainability & 9th Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology Conference, ESFuelCell2011 August 7-10, 2011, Washington, DC, USA ESFuelCell2011-54794
Proceedings of ASME 2011, 5th International Conference on Energy Sustainability & 9th Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology Conference, ESFuelCell2011 August 7-10, 2011, Washington, DC, USA ESFuelCell2011-54794
RESISTANCE AND NETWORKS
 PURPOSE The purpose of this laboratory is to learn to construct simple circuits; and, to become familiar with the use of power supplies and the digital multimeter. to experimentally find the equivalent
PURPOSE The purpose of this laboratory is to learn to construct simple circuits; and, to become familiar with the use of power supplies and the digital multimeter. to experimentally find the equivalent
MP ) 12:40-2:40 3:00-4:00 PM
 PHY294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 handwritten problem per week) Problem 29.77 (already assigned) will
PHY294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 handwritten problem per week) Problem 29.77 (already assigned) will
Physics 102 Lab 4: Circuit Algebra and Effective Resistance Dr. Timothy C. Black Spring, 2005
 Physics 02 Lab 4: Circuit Algebra and Effective Resistance Dr. Timothy C. Black Spring, 2005 Theoretical Discussion The Junction Rule: Since charge is conserved, charge is neither created or destroyed
Physics 02 Lab 4: Circuit Algebra and Effective Resistance Dr. Timothy C. Black Spring, 2005 Theoretical Discussion The Junction Rule: Since charge is conserved, charge is neither created or destroyed
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Engineering A COMPUTATIONAL MODEL FOR ASSESSING IMPACT OF INTERFACIAL
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering A COMPUTATIONAL MODEL FOR ASSESSING IMPACT OF INTERFACIAL MORPHOLOGY ON POLYMER ELECTROLYTE FUEL CELL PERFORMANCE A Thesis in
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering A COMPUTATIONAL MODEL FOR ASSESSING IMPACT OF INTERFACIAL MORPHOLOGY ON POLYMER ELECTROLYTE FUEL CELL PERFORMANCE A Thesis in
Galvanic cells. Galvanic cells (2) Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Baron Volta. John Frederic Daniell
 A quote of the week (or camel of the week): I have no special talents. I am only passionately curious Albert Einstein Physical Chemistry EPM/7 1 Galvanic cells Galvanic cells are devices permitting direct
A quote of the week (or camel of the week): I have no special talents. I am only passionately curious Albert Einstein Physical Chemistry EPM/7 1 Galvanic cells Galvanic cells are devices permitting direct
Three-Dimensional Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells and Stacks
 INL/CON-08-14297 PREPRINT Three-Dimensional Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells and Stacks 8 th European SOFC Forum Grant Hawkes James O Brien Carl Stoots Stephen Herring
INL/CON-08-14297 PREPRINT Three-Dimensional Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells and Stacks 8 th European SOFC Forum Grant Hawkes James O Brien Carl Stoots Stephen Herring
 Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
8. ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS. n Electrode Reactions and Electrode Potentials a. H 2 2H + + 2e. Cl 2 + 2e 2Cl. H 2 + Cl 2 2H + + 2Cl ; z = 2
 8. ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS n Electrode Reactions and Electrode Potentials 8.1. a. H H + + e Cl + e Cl H + Cl H + + Cl ; z = E = E RT F ln ( a H +a Cl ) b. Hg(l)+ Cl Hg Cl + e H + + e H Hg + H + + Cl Hg Cl
8. ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS n Electrode Reactions and Electrode Potentials 8.1. a. H H + + e Cl + e Cl H + Cl H + + Cl ; z = E = E RT F ln ( a H +a Cl ) b. Hg(l)+ Cl Hg Cl + e H + + e H Hg + H + + Cl Hg Cl
Reliability of Flexible Termination Ceramic Capacitors in Temperature-Humidity-Bias Conditions. Michael H. Azarian, Ph.D
 inemi Medical TIG Forum November 14, 2008 FDA, Silver Spring, Maryland Reliability of Flexible Termination Ceramic Capacitors in Temperature-Humidity-Bias Conditions Michael H. Azarian, Ph.D (CALCE) College
inemi Medical TIG Forum November 14, 2008 FDA, Silver Spring, Maryland Reliability of Flexible Termination Ceramic Capacitors in Temperature-Humidity-Bias Conditions Michael H. Azarian, Ph.D (CALCE) College
Estimation of approximate activation energy loss and mass transfer coefficient from a polarization curve of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29(9), 1158-1162 (2012) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-012-0006-3 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Estimation of approximate activation energy loss and mass transfer coefficient from a polarization curve
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29(9), 1158-1162 (2012) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-012-0006-3 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Estimation of approximate activation energy loss and mass transfer coefficient from a polarization curve
Numerical simulation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell
 CHAPTER 6 Numerical simulation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell T.C. Jen, T.Z. Yan & Q.H. Chen Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, USA. Abstract This chapter presents
CHAPTER 6 Numerical simulation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell T.C. Jen, T.Z. Yan & Q.H. Chen Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, USA. Abstract This chapter presents
A Bayesian network fault diagnostic system for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
 Journal of Power Sources 165 (2007) 267 278 A Bayesian network fault diagnostic system for proton exchange membrane fuel cells Luis Alberto M. Riascos a,, Marcelo G. Simoes b, Paulo E. Miyagi c a Federal
Journal of Power Sources 165 (2007) 267 278 A Bayesian network fault diagnostic system for proton exchange membrane fuel cells Luis Alberto M. Riascos a,, Marcelo G. Simoes b, Paulo E. Miyagi c a Federal
Hydrogen production by electrolysis. Ann Cornell, Department of Chemical Engineering, KTH
 Hydrogen production by electrolysis Ann Cornell, Department of Chemical Engineering, KTH amco@kth.se Sources for hydrogen International Energy Agency. Technology Roadmap Hydrogen and Fuel Cells, 2015
Hydrogen production by electrolysis Ann Cornell, Department of Chemical Engineering, KTH amco@kth.se Sources for hydrogen International Energy Agency. Technology Roadmap Hydrogen and Fuel Cells, 2015
i i ne. (1) i The potential difference, which is always defined to be the potential of the electrode minus the potential of the electrolyte, is ln( a
 We re going to calculate the open circuit voltage of two types of electrochemical system: polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells and lead-acid batteries. To do this, we re going to make use of two
We re going to calculate the open circuit voltage of two types of electrochemical system: polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells and lead-acid batteries. To do this, we re going to make use of two
MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL
 MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL R. Gopikaramanan, R. Praburaja and S. Bhaskar Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, School of Electrical and Computing
MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL R. Gopikaramanan, R. Praburaja and S. Bhaskar Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, School of Electrical and Computing
Chapters 24/25: Current, Circuits & Ohm s law Thursday September 29 th **Register your iclickers**
 Chapters 24/25: Current, Circuits & Ohm s law Thursday September 29 th **Register your iclickers** Conductors under dynamic conditions Current, current density, drift velocity Ohm s law Types of conductor
Chapters 24/25: Current, Circuits & Ohm s law Thursday September 29 th **Register your iclickers** Conductors under dynamic conditions Current, current density, drift velocity Ohm s law Types of conductor
Answer Key. Chapter 23. c. What is the current through each resistor?
 Chapter 23. Three 2.0- resistors are connected in series to a 50.0- power source. a. What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? R R R 2 R 3 2.0 2.0 2.0 36.0 b. What is the current in the circuit?
Chapter 23. Three 2.0- resistors are connected in series to a 50.0- power source. a. What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? R R R 2 R 3 2.0 2.0 2.0 36.0 b. What is the current in the circuit?
Iranian Journal of Hydrogen & Fuel Cell 2(2017) Iranian Journal of Hydrogen & Fuel Cell IJHFC. Journal homepage://ijhfc.irost.
 Iranian Journal of Hydrogen & Fuel Cell (017) 153-165 Iranian Journal of Hydrogen & Fuel Cell IJHFC Journal homepage://ijhfc.irost.ir Effect of CO in the ormatted fuel on the performance of Polymer Electrolyte
Iranian Journal of Hydrogen & Fuel Cell (017) 153-165 Iranian Journal of Hydrogen & Fuel Cell IJHFC Journal homepage://ijhfc.irost.ir Effect of CO in the ormatted fuel on the performance of Polymer Electrolyte
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics
 MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
Chapter 19: Electrochemistry I. Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta
 Chapter 19: Electrochemistry I Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta 2 Electrochemistry The study of the relationships between electrical processes and chemical processes Batteries, electroplating, fuel cells, hydrogen
Chapter 19: Electrochemistry I Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta 2 Electrochemistry The study of the relationships between electrical processes and chemical processes Batteries, electroplating, fuel cells, hydrogen
Supporting Information: Robust production of purified H 2 in a stable, self-regulating, and continuously operating solar fuel generator
 Supporting Information: Robust production of purified H 2 in a stable, self-regulating, and continuously operating solar fuel generator Miguel A. Modestino, Karl A. Walczak, Alan Berger, Christopher M.
Supporting Information: Robust production of purified H 2 in a stable, self-regulating, and continuously operating solar fuel generator Miguel A. Modestino, Karl A. Walczak, Alan Berger, Christopher M.
Gas Transport and Electrochemistry in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes
 Gas Transport and Electrochemistry in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes Wilson K. S. Chiu University of Connecticut Overview of Research Activities Heat & Mass Transfer with Chemical Rxns: CVD Nanomaterials
Gas Transport and Electrochemistry in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes Wilson K. S. Chiu University of Connecticut Overview of Research Activities Heat & Mass Transfer with Chemical Rxns: CVD Nanomaterials
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Electricity
 Electricity Electric Charge There are two fundamental charges in the universe. Positive (proton) has a charge of +1.60 x 10-19 C Negative (electron) has a charge of 1.60 x 10-19 C There is one general
Electricity Electric Charge There are two fundamental charges in the universe. Positive (proton) has a charge of +1.60 x 10-19 C Negative (electron) has a charge of 1.60 x 10-19 C There is one general
LABORATORY REPORT SHEET. Name Date Sect Cell 1. Predicted potential for cell reaction (using Nernst equation)
 LABORATORY REPORT SHEET Experiment 22-026 Cell 1 Cathode half-reaction Anode half-reaction Overall chemical reaction How does your experimental potential compare with the calculated value (i.e. % error)?
LABORATORY REPORT SHEET Experiment 22-026 Cell 1 Cathode half-reaction Anode half-reaction Overall chemical reaction How does your experimental potential compare with the calculated value (i.e. % error)?
Electrochemistry. Goal: Understand basic electrochemical reactions. Half Cell Reactions Nernst Equation Pourbaix Diagrams.
 Electrochemistry Goal: Understand basic electrochemical reactions Concepts: Electrochemical Cell Half Cell Reactions Nernst Equation Pourbaix Diagrams Homework: Applications Battery potential calculation
Electrochemistry Goal: Understand basic electrochemical reactions Concepts: Electrochemical Cell Half Cell Reactions Nernst Equation Pourbaix Diagrams Homework: Applications Battery potential calculation
ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Fuel Cells Module Manual
 ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Fuel Cells Module Manual April 2009 Copyright c 2009 by ANSYS, Inc. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or otherwise used in any form without express written
ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Fuel Cells Module Manual April 2009 Copyright c 2009 by ANSYS, Inc. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or otherwise used in any form without express written
The Fuel Cell An Ideal Chemical Engineering Undergraduate Experiment
 Revised as of July 14, 2003 The Fuel Cell An Ideal Chemical Engineering Undergraduate Experiment Jung-Chou Lin, H. Russell Kunz, James M. Fenton, Suzanne S. Fenton Department of Chemical Engineering University
Revised as of July 14, 2003 The Fuel Cell An Ideal Chemical Engineering Undergraduate Experiment Jung-Chou Lin, H. Russell Kunz, James M. Fenton, Suzanne S. Fenton Department of Chemical Engineering University
FUEL CELLS in energy technology (4)
 Fuel Cells 1 FUEL CELLS in energy technology (4) Werner Schindler Department of Physics Nonequilibrium Chemical Physics TU Munich summer term 213 Fuel Cells 2 Nernst equation and its application to fuel
Fuel Cells 1 FUEL CELLS in energy technology (4) Werner Schindler Department of Physics Nonequilibrium Chemical Physics TU Munich summer term 213 Fuel Cells 2 Nernst equation and its application to fuel
Electrochemistry objectives
 Electrochemistry objectives 1) Understand how a voltaic and electrolytic cell work 2) Be able to tell which substance is being oxidized and reduced and where it is occuring the anode or cathode 3) Students
Electrochemistry objectives 1) Understand how a voltaic and electrolytic cell work 2) Be able to tell which substance is being oxidized and reduced and where it is occuring the anode or cathode 3) Students
Electrode Kinetics 1
 Electrode Kinetics 1 Background Consider the reaction given below: A B (1) Let k f and k b are the rate constants of the forward and backward reactions 2 Reaction rates Rate of the forward reaction is
Electrode Kinetics 1 Background Consider the reaction given below: A B (1) Let k f and k b are the rate constants of the forward and backward reactions 2 Reaction rates Rate of the forward reaction is
Chapter 25 Current Resistance, and Electromotive Force
 Chapter 25 Current Resistance, and Electromotive Force 1 Current In previous chapters we investigated the properties of charges at rest. In this chapter we want to investigate the properties of charges
Chapter 25 Current Resistance, and Electromotive Force 1 Current In previous chapters we investigated the properties of charges at rest. In this chapter we want to investigate the properties of charges
8 TH GRADE MATHEMATICS:
 8 TH GRADE MATHEMATICS: AIM: USING OHM S LAW TO SOLVE MATH PROBLEMS HOME WORK: HANDOUT BY MR. AKOMAH ENCHANCING STUDENTS SKILLS IN INVERESE OPERATION USING OHMS LAW : Students will 1.Become aware of Ohm's
8 TH GRADE MATHEMATICS: AIM: USING OHM S LAW TO SOLVE MATH PROBLEMS HOME WORK: HANDOUT BY MR. AKOMAH ENCHANCING STUDENTS SKILLS IN INVERESE OPERATION USING OHMS LAW : Students will 1.Become aware of Ohm's
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Engineering COMPUTATIONAL EXPLORATION OF HIGH POWER OPERATION IN POROUS FLOW
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering COMPUTATIONAL EXPLORATION OF HIGH POWER OPERATION IN POROUS FLOW FIELD POLYMER ELECTROLYTE FUEL CELLS WITH A VALIDATED MODEL
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering COMPUTATIONAL EXPLORATION OF HIGH POWER OPERATION IN POROUS FLOW FIELD POLYMER ELECTROLYTE FUEL CELLS WITH A VALIDATED MODEL
V.A.11 Development of Ultra-Low Platinum Alloy Cathode Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
 V.A.11 Development of Ultra-Low Platinum Alloy Cathode Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Branko N. Popov University of South Carolina (USC) 301 Main Street Columbia, SC 29208 Phone:
V.A.11 Development of Ultra-Low Platinum Alloy Cathode Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Branko N. Popov University of South Carolina (USC) 301 Main Street Columbia, SC 29208 Phone:
