P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles
|
|
|
- Derrick Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk Last modified: 11 th August 2017
2 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: Practise questions by chapter, including past paper Edexcel questions and extension questions (e.g. MAT). Teachers: you can create student accounts (or students can register themselves).
3 Chapter Overview From this chapter onwards, the majority of the theory you will learn is new since GCSE. 1:: Equation of a circle The diameter of a circle is AB where A and B have the coordinates 2,5 and 8,13. Determine the equation of the circle. 2:: Intersections of lines + circles Show that the line y = x 7 does not meet the circle x y 2 = 33 NEW! since GCSE You should already know the equation x 2 + y 2 = r 2 for a circle centred at the origin, but not a circle centred at a specified point. 3:: Chords, tangents and perpendicular bisectors. A circle C has the equation x y = 10. Find the equations of the two possible tangents whose gradient is -3. 4:: Circumscribing Triangles Find the equation of the circle that passes through the points A 8,1, B 4,5, C 4,9.
4 Midpoints and Perpendicular Bisectors Later in the chapter you will need to find the perpendicular bisector of a chord of a circle. What two properties does a perpendicular bisector of two points A and B have? perpendicular bisector chord A 2,5 M 4, 6 B 6,7 Just find the mean of the x values and the mean of the y values. 1. It passes through the midpoint of AB. 2. It is perpendicular to AB. Equation? m AB = 2 4 = 1 2 m = 2 y 6 = 2 x 4
5 Test Your Understanding Find the perpendicular bisector of the line AB where A and B have the coordinates: a) A 4,7, B 10,17 b) A x 1, y 1, B x 2, y 2 A line segment AB is the diameter of a circle with centre 5, 4. If A has coordinates 1, 2, what are the coordinates of B? a M 7,12 m AB = 10 6 = 5 3 y 12 = 3 5 x 7 m = 3 5 A 1, 2 M 5, 4 b M x 1 + y 1 2, x 2 + y 2 2 m AB = y 2 y 1 m x 2 x = x 1 x 2 1 y 2 y 1 y x 2 + y 2 = x 1 x 2 x x 1 + y 1 2 y 2 y 1 2 Fro Note: Do not try to memorise this! We could use the formula x 1 +x 2 2, y 1+y 2 2 B, but it is easy to see from the diagram that whatever movement there is from A to M, we can continue to get to B = = 6 B 9, 6
6 Exercise 6A/6B Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page 115,
7 Equation of a circle y r (x, y) r y x r x Recall that a line can be a set of points x, y that satisfy some equation. Suppose we have a point x, y on a circle centred at the origin, with radius r. What equation must x, y satisfy? (Hint: draw a right-angled triangle inside your circle, with one vertex at the origin and another at the circumference) x 2 + y 2 = r 2
8 Equation of a circle y (a, b) r (x, y) x Now suppose we shift the circle so it s now centred at a, b. What s the equation now? (Hint: What would the sides of this rightangled triangle be now?)! The equation of a circle with centre a, b and radius r is: x a 2 + y b 2 = r 2
9 Quickfire Questions Centre Radius Equation (0,0) 5 x 2 + y 2 = 25 (1,2) 6 (x 1)2 + (y 2)2 = 36 ( 3,5) 1 (x + 3)2 + (y 5)2 = 1 ( 5,2) 7 (x + 5)2 + (y 2)2 = 49 ( 6,0) 4 x y 2 = 16 (1, 1) 3 (x 1)2 + (y + 1)2 = 3 ( 2,3) 2 2 (x + 2)2 + (y 3)2 = 8
10 Finding the equation using points A 5,8 A line segment AB is the diameter of a circle, where A and B have coordinates 5,8 and 7,4 respectively. Determine the equation of the circle. B 7,4 Hint: What two things do we need to use the circle formula? Centre: C 1, 6 We can use the distance BC or AC as the radius. Using B 7, 4 and M 1, 6 r = = 40 = 2 10 x y 6 2 = 40
11 Test Your Understanding Edexcel C2 Jan 2005 Q2 a) 9, 5 b) r = = 52 x y 5 2 = 52
12 Completing the square When the equation of a circle is in the form x a 2 + y b 2 = r 2, we can instantly read off the centre a, b and the radius r. But what if the equation wasn t in this form? Find the centre and radius of the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 6x + 2y 6 = 0 Hint: Have we seen a method in a previous chapter that allows us to turn a x 2 term and a x term into a single expression involving x? x 2 6x + y 2 + 2y 6 = 0 x y = 0 x y = 16 Rearrange terms so that x terms are together and y terms are together. Complete the square! Textbook Note: There s a truly awful method, initially presented in the textbook, that allows you to find the centre/radius without completing the square. Don t even contemplate using it.
13 Further Example Edexcel C2 June 2012 Q3a,b x 2 20x + y 2 16y = 0 x y = 0 x y 8 2 = 25 C 10,8, r = 25 = 5
14 Exercise 6C Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page Extension: [MAT B] The point on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 6x + 8y = 75 which is closest to the origin, is at what distance from the origin? x y = 100 C 3, 4, r = 10 The closest point P lies on the line between the circle centre and the origin. Since 3, 4 is 5 away from the origin, the distance between the origin and P must be 10 5 = 5 3, 4 [MAT D] The point on the circle x y 4 2 = 4 which is closest to the circle x y 1 2 = 1 has what coordinates? 2 3 Drawing the circles on the same axes, and drawing a straight line connecting their centres, the point is where the straight line intersects the first circle. The circle centres are 5 apart, so we need to go 2 5 of the way across this line, giving (3. 4, 2. 8) k b [MAT I] Let a and b be positive real numbers. If x 2 + y 2 1 then the largest that ax + by can equal is what? Give your expression in terms of a and b. Many MAT questions consider maximising an expression in terms of x and y. Consider for example the simple case x + y = k. As we increase k, the line stays in the same direction but sweeps across: y k, and therefore x + y, increase as we move in this direction. x If we similarly consider the line ax + by = k, ax + by is therefore maximised when the line is tangent to the unit circle. 1 k a k b k 2 a 2 + k2 b 2 1 k a Using similar triangles, we can obtain k = a 2 + b 2
15 Intersections of Lines and Circles Recall that to consider the intersection of two lines, we attempt to solve them simultaneously by substitution, potentially using the discriminant to show that there are no solutions (and hence no points of intersection). 2 intersections (such a line is known as a secant of the circle) Show that the line y = x + 3 never intersects the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 = 1. Using substitution: x 2 + x = 1 x 2 + x 2 + 6x + 9 = 1 2x 2 + 6x + 8 = 0 x 2 + 3x + 4 = 0 Discriminant: a = 1, b = 3, c = = 7 7 < 0 therefore no solutions. 1 intersections (such a line is known as a tangent of the circle) 0 intersections
16 Test Your Understanding Find the points of intersection where the line y = x + 6 meets x 2 + y 3 2 = 29. x 2 + x = 29 x 2 + x 2 + 6x + 9 = 29 2x 2 + 6x 20 = 0 x 2 + 3x 10 = 0 x + 5 x 2 = 0 x = 5 or x = 2 y = 1 or y = 8 5, 1, 2,8 Using an algebraic (and not geometric) method, determine the k such that the line y = x + k touches the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 = 1. x 2 + x + k 2 = 1 x 2 + x 2 + 2kx + k 2 = 1 2x 2 + 2kx + k 2 1 = 0 If the line touches the circle, one point of intersection and therefore one solution. Discriminant: a = 2, b = 2k, c = k 2 1 4k k 2 1 = 0 4k 2 8k = 0 4k 2 8 = 0 k = ± 2
17 Exercise 6D Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Page 122
18 Tangents, Chords, Perpendicular Bisectors There are two circle theorems that are of particular relevance to problems in this chapter, the latter you might be less familiar with: The tangent is perpendicular to the radius (at the point of intersection). Why this will help: If we knew the centre of the circle and the point of intersection, we can easily find the gradient of the radius, and thus the gradient and hence equation of the tangent. The perpendicular bisector of any chord passes through the centre of the circle. Why this will help: The first thing we did in this chapter is find the equation of the perpendicular bisector. If we had two chords, and hence found two bisectors, we could find the point of intersection, which would be the centre of the circle.
19 Examples Note that the GCSE syllabus had questions like this, except with circles centred at the origin only. The circle C has equation x y 7 2 = 100. a) Verify the point P 11,1 lies on C. b) Find an equation of the tangent to C at the point P, giving your answer in the form ax + by + c = 0 a) = = 100 b) Circle centre: 3,7 Gradient of radius: m r = = 3 4 m t = 4 3 y 1 = 4 x y 3 = 4 x 11 3y 3 = 4x 44 4x 3y 41 = 0 Fro Tip: Use subscripting of variables to make clear to the examiner (and yourself!) what you re calculating. A circle C has equation x y = 10 The line l is a tangent to the circle and has gradient -3. Find two possible equations for l, giving your answers in the form y = mx + c. This time we have the gradient, but don t have the points where the tangent(s) intersect the radius. 4, 4 Equation of radius/diameter: y + 4 = 1 3 x 4 y = 1 16 x 3 3 Intersecting with circle: x x = 10 Solving results in the points 1, 5, 7, 3. Then equations of tangents: y + 5 = 3 x 1 y = 3x 2 y + 3 = 3 x 7 y = 3x + 18
20 Determining the Circle Centre The points P and Q lie on a circle with centre C, as shown in the diagram. The point P has coordinates ( 8, 2) and the point Q has coordinates 2, 6. M is the midpoint of the line segment PQ. The line l passes through the points M and C. a) Find an equation for l. b) Given that the y-coordinate of C is -9: i) show that the x-coordinate of C is -5. ii) find an equation of the circle. P 8, 2 C M y x Q 2, 6 a b c l We know the line going through the midpoint of a chord and a centre of the circle is the perpendicular bisector of the chord. M( 3, 4) m PQ = 4 = 2 m 10 5 MC = 5 Fro Exam Tip: If you re not asked 2 for the equation in a particular Equation of l: y + 4 = 5 x + 3 form, just leave it as it is. 2 When y = 9: = 5 x + 3 x = 5 C( 5, 9) 2 Use either PC or CQ for the radius. r = PC = = 58 x y = 58
21 Test Your Understanding A circle has centre C 3,5, and goes through the point P(6,9). Find the equation of the tangent of the circle at the point P, giving your equation in the form ax + by + c = 0 where a, b, c are integers.. m r = 4 3 m t = 3 4 y 9 = 3 4 x 6 4y 36 = 3 x 6 4y 36 = 3x x + 4y 54 = 0 A circle passes through the points A(0,0) and B 4,2. The centre of the circle has x value -1. Determine the equation of the circle. m AB = 2 4 = 1 m 2 = 2 M 2,1 Equation of perpendicular bisector of chord: y 1 = 2 x 2 When x = 1: y 1 = y 1 = 6 y = 7 Centre: C( 1,7) Radius (using length AC): = 50 x y 7 2 = 50
22 Exercise 6E Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Pages Extension: [MAT A] Which of the following lines is a tangent to the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 = 4? A) x + y = 2 B) y = x 2 2 C) x = 2 D) y = 2 x Solution: B. Note that we could avoid using algebra by using a suitable diagram and simple use of Pythagoras to get the yintercept. Mark scheme on next slide. 2 3 [AEA 2006 Q4] The line with equation y = mx is a tangent to the circle C 1 with equation x y 7 2 = 13 (a) Show that m satisfies the equation 3m m + 36 = 0 The tangents from the origin O to C 1 touch C 1 at the points A and B. (b) Find the coordinates of the points A and B. Another circle C 2 has equation x 2 + y 2 = 13. The tangents from the point 4, 7 to C 2 touch it at the points P and Q. (c) Find the coordinates of either the point P or the point Q. Mark scheme on next slide. [STEP 2005 Q6] (i) (ii) The point A has coordinates 5,16 and the point B has coordinates 4, 4. The variable P has coordinates x, y and moves on a path such that AP = 2BP. Show that the Cartesian equation of the path of P is x y 2 = 100. The point C has coordinates a, 0 and the point D has coordinates b, 0. The variable point Q moves on a path such that QC = k QD, where k > 1. Given that the path of Q is the same as the path of P, show that a + 7 b + 7 = a b Show further that a + 7 (This is not a tangent/chord question but is worthwhile regardless!) b + 7 = 100, in the case a b.
23 Mark Scheme for Extension Question 2
24 Mark Scheme for Extension Question 3
25 Triangles in Circles We d say: The triangle inscribes the circle. (A shape inscribes another if it is inside and its boundaries touch but do not intersect the outer shape) The circle circumscribes the triangle. If the circumscribing shape is a circle, it is known as the circumcircle of the triangle. The centre of a circumcircle is known as the circumcentre.
26 Triangles in Circles B A C If ABC = 90 then: AC is the diameter of the circumcircle of triangle ABC. Similarly if AC is the diameter of a circle: ABC = 90 therefore AB is perpendicular to BC. AB 2 + BC 2 = AC 2 Given three points/a triangle we can find the centre of the circumcircle by: Finding the equation of the perpendicular bisectors of two different sides. Find the point of intersection of the two bisectors.
27 Example C 4,9 [Textbook] The points A 8,1, B 4,5, C 4,9 lie on a circle. a) Show that AB is a diameter of the circle. B 4,5 A 8,1 Method 1: Show that AC 2 + BC 2 = AB 2 Method 2: (not in textbook!) Show that AC is perpendicular to BC. AC = = 80 BC = = 80 AB = = = 160 Therefore AB is the diameter. m AC = 8 4 = 2 m CB = 4 8 = = 1 AC is perpendicular to BC Therefore AB is the diameter. b) Hence find the equation of the circle. Centre is midpoint of AB: M 2,3 Radius: r = AM = = 40 x y 3 2 = 40
28 Example The points A 0,2, B 2,0, C 8,18 lie on the circumference of a circle. Determine the equation of the circle. C 8,18 Perpendicular bisector of AB: By inspection, y = x A 0,2 Perpendicular bisector of AC: Midpoint: 4,10 B 2,0 m AC = 16 8 = 2 m = 1 2 y 10 = 1 2 x 4 Solving simultaneously with y = x: x 10 = 1 2 x 4 2x 20 = x + 4 3x = 24 x = 8 y = 8 Centre is (8,8). Using A and centre of circle: r = = 10 Equation of circle: x y 8 2 = 100
29 Exercise 6F Pearson Pure Mathematics Year 1/AS Pages Extension: 1 [STEP 2009 Q8 Edited] If equation of the circle C is x 2t 2 + y t 2 = t 2, where t is a positive number, it can be shown that C touches the line y = 0 as well as the line 3y = 4x. Find the equation of the incircle of the triangle formed by the lines y = 0, 3y = 4x and 4y + 3x = 15. Note: The incircle of a triangle is the circle, lying totally inside the triangle, that touches all three sides. Solution: x y 1 2 = 1
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle.
 Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
Circles, Mixed Exercise 6
 Circles, Mixed Exercise 6 a QR is the diameter of the circle so the centre, C, is the midpoint of QR ( 5) 0 Midpoint = +, + = (, 6) C(, 6) b Radius = of diameter = of QR = of ( x x ) + ( y y ) = of ( 5
Circles, Mixed Exercise 6 a QR is the diameter of the circle so the centre, C, is the midpoint of QR ( 5) 0 Midpoint = +, + = (, 6) C(, 6) b Radius = of diameter = of QR = of ( x x ) + ( y y ) = of ( 5
P1 Chapter 3 :: Equations and Inequalities
 P1 Chapter 3 :: Equations and Inequalities jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 26 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 3 :: Equations and Inequalities jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 26 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 11 :: Vectors
 P1 Chapter 11 :: Vectors jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 21 st August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 11 :: Vectors jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 21 st August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry
 Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
AQA IGCSE FM "Full Coverage": Equations of Circles
 AQA IGCSE FM "Full Coverage": Equations of Circles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each AQA IGCSE Further Maths topic. This worksheet was automatically
AQA IGCSE FM "Full Coverage": Equations of Circles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each AQA IGCSE Further Maths topic. This worksheet was automatically
A-Level Notes CORE 1
 A-Level Notes CORE 1 Basic algebra Glossary Coefficient For example, in the expression x³ 3x² x + 4, the coefficient of x³ is, the coefficient of x² is 3, and the coefficient of x is 1. (The final 4 is
A-Level Notes CORE 1 Basic algebra Glossary Coefficient For example, in the expression x³ 3x² x + 4, the coefficient of x³ is, the coefficient of x² is 3, and the coefficient of x is 1. (The final 4 is
P1 Chapter 1 :: Algebraic Expressions
 P1 Chapter 1 :: Algebraic Expressions jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 26 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 1 :: Algebraic Expressions jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 26 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
The Not-Formula Book for C1
 Not The Not-Formula Book for C1 Everything you need to know for Core 1 that won t be in the formula book Examination Board: AQA Brief This document is intended as an aid for revision. Although it includes
Not The Not-Formula Book for C1 Everything you need to know for Core 1 that won t be in the formula book Examination Board: AQA Brief This document is intended as an aid for revision. Although it includes
Recognise the Equation of a Circle. Solve Problems about Circles Centred at O. Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes
 1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
b UVW is a right-angled triangle, therefore VW is the diameter of the circle. Centre of circle = Midpoint of VW = (8 2) + ( 2 6) = 100
 Circles 6F a U(, 8), V(7, 7) and W(, ) UV = ( x x ) ( y y ) = (7 ) (7 8) = 8 VW = ( 7) ( 7) = 64 UW = ( ) ( 8) = 8 Use Pythagoras' theorem to show UV UW = VW 8 8 = 64 = VW Therefore, UVW is a right-angled
Circles 6F a U(, 8), V(7, 7) and W(, ) UV = ( x x ) ( y y ) = (7 ) (7 8) = 8 VW = ( 7) ( 7) = 64 UW = ( ) ( 8) = 8 Use Pythagoras' theorem to show UV UW = VW 8 8 = 64 = VW Therefore, UVW is a right-angled
"Full Coverage": Pythagoras Theorem
 "Full Coverage": Pythagoras Theorem This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated by the
"Full Coverage": Pythagoras Theorem This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated by the
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
Circles. hsn.uk.net. Contents. Circles 1
 hsn.uk.net Circles Contents Circles 1 1 Representing a Circle A 1 Testing a Point A 3 The General Equation of a Circle A 4 Intersection of a Line and a Circle A 4 5 Tangents to Circles A 5 6 Equations
hsn.uk.net Circles Contents Circles 1 1 Representing a Circle A 1 Testing a Point A 3 The General Equation of a Circle A 4 Intersection of a Line and a Circle A 4 5 Tangents to Circles A 5 6 Equations
The gradient of the radius from the centre of the circle ( 1, 6) to (2, 3) is: ( 6)
 Circles 6E a (x + ) + (y + 6) = r, (, ) Substitute x = and y = into the equation (x + ) + (y + 6) = r + + + 6 = r ( ) ( ) 9 + 8 = r r = 90 = 0 b The line has equation x + y = 0 y = x + y = x + The gradient
Circles 6E a (x + ) + (y + 6) = r, (, ) Substitute x = and y = into the equation (x + ) + (y + 6) = r + + + 6 = r ( ) ( ) 9 + 8 = r r = 90 = 0 b The line has equation x + y = 0 y = x + y = x + The gradient
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet
 Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Maharashtra Board Class X Mathematics - Geometry Board Paper 2014 Solution. Time: 2 hours Total Marks: 40
 Maharashtra Board Class X Mathematics - Geometry Board Paper 04 Solution Time: hours Total Marks: 40 Note: - () All questions are compulsory. () Use of calculator is not allowed.. i. Ratio of the areas
Maharashtra Board Class X Mathematics - Geometry Board Paper 04 Solution Time: hours Total Marks: 40 Note: - () All questions are compulsory. () Use of calculator is not allowed.. i. Ratio of the areas
MEI Core 1. Basic Algebra. Section 1: Basic algebraic manipulation and solving simple equations. Manipulating algebraic expressions
 MEI Core Basic Algebra Section : Basic algebraic manipulation and solving simple equations Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Manipulating algebraic expressions Collecting like terms
MEI Core Basic Algebra Section : Basic algebraic manipulation and solving simple equations Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Manipulating algebraic expressions Collecting like terms
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook
 Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Straight line graphs Parallel and Perpendicular lines. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Straight line graphs A LEVEL LINKS Scheme of work: a. Straight-line
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Straight line graphs Parallel and Perpendicular lines. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Straight line graphs A LEVEL LINKS Scheme of work: a. Straight-line
CBSE X Mathematics 2012 Solution (SET 1) Section B
 CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Section B Q11. Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation x kx + k = 0 has equal roots. Given equation is x kx k 0 For the given equation to have equal
CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Section B Q11. Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation x kx + k = 0 has equal roots. Given equation is x kx k 0 For the given equation to have equal
+ 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 if S
 CIRCLE DEFINITIONS A circle is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point, called the centre, is always a constant. The distance r from the centre is called the
CIRCLE DEFINITIONS A circle is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point, called the centre, is always a constant. The distance r from the centre is called the
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 2: Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane
 Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test : Coordinate in the (x, y) plane Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a Use of the gradient formula to begin attempt to find k. k 1 ( ) or 1 (k 4) ( k 1) (i.e.
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test : Coordinate in the (x, y) plane Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a Use of the gradient formula to begin attempt to find k. k 1 ( ) or 1 (k 4) ( k 1) (i.e.
Example 1: Finding angle measures: I ll do one: We ll do one together: You try one: ML and MN are tangent to circle O. Find the value of x
 Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
(D) (A) Q.3 To which of the following circles, the line y x + 3 = 0 is normal at the point ? 2 (A) 2
 CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
Circles - Edexcel Past Exam Questions. (a) the coordinates of A, (b) the radius of C,
 - Edecel Past Eam Questions 1. The circle C, with centre at the point A, has equation 2 + 2 10 + 9 = 0. Find (a) the coordinates of A, (b) the radius of C, (2) (2) (c) the coordinates of the points at
- Edecel Past Eam Questions 1. The circle C, with centre at the point A, has equation 2 + 2 10 + 9 = 0. Find (a) the coordinates of A, (b) the radius of C, (2) (2) (c) the coordinates of the points at
5 Find an equation of the circle in which AB is a diameter in each case. a A (1, 2) B (3, 2) b A ( 7, 2) B (1, 8) c A (1, 1) B (4, 0)
 C2 CRDINATE GEMETRY Worksheet A 1 Write down an equation of the circle with the given centre and radius in each case. a centre (0, 0) radius 5 b centre (1, 3) radius 2 c centre (4, 6) radius 1 1 d centre
C2 CRDINATE GEMETRY Worksheet A 1 Write down an equation of the circle with the given centre and radius in each case. a centre (0, 0) radius 5 b centre (1, 3) radius 2 c centre (4, 6) radius 1 1 d centre
S56 (5.3) Recurrence Relations.notebook September 09, 2015
 Daily Practice 31.8.2015 Q1. Write down the equation of a circle with centre (-1, 4) and radius 5 Q2. Given the circle with equation (x 4) 2 + (y + 5) 2 = 40. Find the equation of the tangent to this circle
Daily Practice 31.8.2015 Q1. Write down the equation of a circle with centre (-1, 4) and radius 5 Q2. Given the circle with equation (x 4) 2 + (y + 5) 2 = 40. Find the equation of the tangent to this circle
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 1 C1 2015-2016 Name: Page C1 workbook contents Indices and Surds Simultaneous equations Quadratics Inequalities Graphs Arithmetic series
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 1 C1 2015-2016 Name: Page C1 workbook contents Indices and Surds Simultaneous equations Quadratics Inequalities Graphs Arithmetic series
9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations
 www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
LLT Education Services
 8. The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle. (a) 4 cm (b) 3 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 5 cm 9. From a point P, 10 cm away from the
8. The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle. (a) 4 cm (b) 3 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 5 cm 9. From a point P, 10 cm away from the
Around the corner. Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h
 Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
"Full Coverage": Curved Graphs ...
 "Full Coverage": Curved Graphs This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated by the DrFrostMaths
"Full Coverage": Curved Graphs This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated by the DrFrostMaths
Plane geometry Circles: Problems with some Solutions
 The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
Equation of a Straight Line (H)
 Equation of a Straight Line (H) A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks: 1. The line L1 is shown in the diagram below.
Equation of a Straight Line (H) A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks: 1. The line L1 is shown in the diagram below.
Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Algebra and Functions
 Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test : Algebra and Functions Simplify 6 4, giving your answer in the form p 8 q, where p and q are positive rational numbers. f( x) x ( k 8) x (8k ) a Find the discriminant
Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test : Algebra and Functions Simplify 6 4, giving your answer in the form p 8 q, where p and q are positive rational numbers. f( x) x ( k 8) x (8k ) a Find the discriminant
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
C-1. Snezana Lawrence
 C-1 Snezana Lawrence These materials have been written by Dr. Snezana Lawrence made possible by funding from Gatsby Technical Education projects (GTEP) as part of a Gatsby Teacher Fellowship ad-hoc bursary
C-1 Snezana Lawrence These materials have been written by Dr. Snezana Lawrence made possible by funding from Gatsby Technical Education projects (GTEP) as part of a Gatsby Teacher Fellowship ad-hoc bursary
Integrated Math II. IM2.1.2 Interpret given situations as functions in graphs, formulas, and words.
 Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS
 DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) Show by using the discriminant that the graph of the curve with equation y = x 4x + 10, does not cross the x axis. proof Question (**) Show that the quadratic
DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) Show by using the discriminant that the graph of the curve with equation y = x 4x + 10, does not cross the x axis. proof Question (**) Show that the quadratic
Geometry JWR. Monday September 29, 2003
 Geometry JWR Monday September 29, 2003 1 Foundations In this section we see how to view geometry as algebra. The ideas here should be familiar to the reader who has learned some analytic geometry (including
Geometry JWR Monday September 29, 2003 1 Foundations In this section we see how to view geometry as algebra. The ideas here should be familiar to the reader who has learned some analytic geometry (including
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes
 Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #1. Wednesday, 13 September. [10 minutes] 1. Suppose you are given a line (segment) AB. Using
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #1. Wednesday, 13 September. [10 minutes] 1. Suppose you are given a line (segment) AB. Using
( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear.
 Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Additional Mathematics Lines and circles
 Additional Mathematics Lines and circles Topic assessment 1 The points A and B have coordinates ( ) and (4 respectively. Calculate (i) The gradient of the line AB [1] The length of the line AB [] (iii)
Additional Mathematics Lines and circles Topic assessment 1 The points A and B have coordinates ( ) and (4 respectively. Calculate (i) The gradient of the line AB [1] The length of the line AB [] (iii)
Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus MATHEMATICS. Class X examination in 2011 and onwards. SSC Part-II (Class X)
 Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus MATHEMATICS Class X examination in 2011 and onwards SSC Part-II (Class X) 15. Algebraic Manipulation: 15.1.1 Find highest common factor (H.C.F) and least
Secondary School Certificate Examination Syllabus MATHEMATICS Class X examination in 2011 and onwards SSC Part-II (Class X) 15. Algebraic Manipulation: 15.1.1 Find highest common factor (H.C.F) and least
Review exercise 2. 1 The equation of the line is: = 5 a The gradient of l1 is 3. y y x x. So the gradient of l2 is. The equation of line l2 is: y =
 Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad Training Problems
 Singapore International athematical Olympiad Training Problems 18 January 2003 1 Let be a point on the segment Squares D and EF are erected on the same side of with F lying on The circumcircles of D and
Singapore International athematical Olympiad Training Problems 18 January 2003 1 Let be a point on the segment Squares D and EF are erected on the same side of with F lying on The circumcircles of D and
P1 Chapter 14 :: Exponentials & Logarithms
 P1 Chapter 14 :: Exponentials & Logarithms jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 28 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 14 :: Exponentials & Logarithms jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 28 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
16 circles. what goes around...
 16 circles. what goes around... 2 lesson 16 this is the first of two lessons dealing with circles. this lesson gives some basic definitions and some elementary theorems, the most important of which is
16 circles. what goes around... 2 lesson 16 this is the first of two lessons dealing with circles. this lesson gives some basic definitions and some elementary theorems, the most important of which is
Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse
 Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 2: Ellipse Oct 2017 1 / 24 Introduction Problem 2.1 Let A, F 1 and F 2 be three points that form a triangle F 2
Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 2: Ellipse Oct 2017 1 / 24 Introduction Problem 2.1 Let A, F 1 and F 2 be three points that form a triangle F 2
Trans Web Educational Services Pvt. Ltd B 147,1st Floor, Sec-6, NOIDA, UP
 Solved Examples Example 1: Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle formed by the lines x + y = 6, 2x + y = 4, x + 2y = 5. Method 1. Consider the equation (x + y 6) (2x + y 4) + λ 1
Solved Examples Example 1: Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle formed by the lines x + y = 6, 2x + y = 4, x + 2y = 5. Method 1. Consider the equation (x + y 6) (2x + y 4) + λ 1
UNIT 3 CIRCLES AND VOLUME Lesson 1: Introducing Circles Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
1 2n. i=1. 2m+1 i = m, while. 2m + 1 = 1. is the best possible for any odd n.
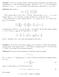 Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
Free Sample set of investigative questions
 Free Sample set of investigative questions SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS: Year Contents Unit Topic : Combinatorics Task : Extended investigation: Relationships in Pascal s Triangle 3 Task : In-class investigation:
Free Sample set of investigative questions SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS: Year Contents Unit Topic : Combinatorics Task : Extended investigation: Relationships in Pascal s Triangle 3 Task : In-class investigation:
EdExcel Further Pure 2
 EdExcel Further Pure 2 Complex Numbers Section : Loci in the Argand diagram Multiple Choice Test Questions 1 are about the following loci: P: z i = 2 Q: z i = z R: arg( z i) = S: z i = 2 z 1) Which of
EdExcel Further Pure 2 Complex Numbers Section : Loci in the Argand diagram Multiple Choice Test Questions 1 are about the following loci: P: z i = 2 Q: z i = z R: arg( z i) = S: z i = 2 z 1) Which of
"Full Coverage": Non-Right Angled Triangles
 "Full Coverage": Non-Right Angled Triangles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated
"Full Coverage": Non-Right Angled Triangles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated
Unit 8. ANALYTIC GEOMETRY.
 Unit 8. ANALYTIC GEOMETRY. 1. VECTORS IN THE PLANE A vector is a line segment running from point A (tail) to point B (head). 1.1 DIRECTION OF A VECTOR The direction of a vector is the direction of the
Unit 8. ANALYTIC GEOMETRY. 1. VECTORS IN THE PLANE A vector is a line segment running from point A (tail) to point B (head). 1.1 DIRECTION OF A VECTOR The direction of a vector is the direction of the
Chapter 3. The angle bisectors. 3.1 The angle bisector theorem
 hapter 3 The angle bisectors 3.1 The angle bisector theorem Theorem 3.1 (ngle bisector theorem). The bisectors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If
hapter 3 The angle bisectors 3.1 The angle bisector theorem Theorem 3.1 (ngle bisector theorem). The bisectors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If
Fly-eye Sensors and Circles
 Fly-eye Sensors and Circles Description: Part of the research conducted in the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at the University of Wyoming involves a sensor platform based on the function
Fly-eye Sensors and Circles Description: Part of the research conducted in the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at the University of Wyoming involves a sensor platform based on the function
Power Round: Geometry Revisited
 Power Round: Geometry Revisited Stobaeus (one of Euclid s students): But what shall I get by learning these things? Euclid to his slave: Give him three pence, since he must make gain out of what he learns.
Power Round: Geometry Revisited Stobaeus (one of Euclid s students): But what shall I get by learning these things? Euclid to his slave: Give him three pence, since he must make gain out of what he learns.
Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1
 BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 1999 2000 Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1 Zvezdelina Stankova-Frenkel UC Berkeley and Mills College Note: All objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual
BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 1999 2000 Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1 Zvezdelina Stankova-Frenkel UC Berkeley and Mills College Note: All objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual
Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle. x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0. which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c =
 Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c = a) 11 b) -13 c) 24 d) 100 Solution: Any circle concentric with x 2 +
Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c = a) 11 b) -13 c) 24 d) 100 Solution: Any circle concentric with x 2 +
NAME: Date: HOMEWORK: C1. Question Obtained. Total/100 A 80 B 70 C 60 D 50 E 40 U 39
 NAME: Date: HOMEWORK: C1 Question Obtained 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Total/100 A 80 B 70 C 60 D 50 E 40 U 39 1. Figure 2 y A(1, 7) B(20, 7) D(8, 2) O x C(p, q) The points A(1, 7), B(20, 7) and C(p, q) form
NAME: Date: HOMEWORK: C1 Question Obtained 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Total/100 A 80 B 70 C 60 D 50 E 40 U 39 1. Figure 2 y A(1, 7) B(20, 7) D(8, 2) O x C(p, q) The points A(1, 7), B(20, 7) and C(p, q) form
"Full Coverage": Trigonometry of Right-Angled Triangles
 "Full Coverage": Trigonometry of Right-Angled Triangles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically
"Full Coverage": Trigonometry of Right-Angled Triangles This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically
Geometry Honors Homework
 Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
Senior Math Circles February 11, 2009 Conics II
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles February 11, 2009 Conics II Locus Problems The word locus is sometimes synonymous with
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles February 11, 2009 Conics II Locus Problems The word locus is sometimes synonymous with
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
PRACTICE EXAM IV Sections 6.1, 6.2, 8.1 8.4 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For a circle, the constant ratio of the circumference C to length of diameter d is represented by the number.
Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
Homework Assignments Math /02 Fall 2017
 Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2017 Assignment 1 Due date : Wednesday, August 30 Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22,
Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2017 Assignment 1 Due date : Wednesday, August 30 Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22,
Math : Analytic Geometry
 7 EP-Program - Strisuksa School - Roi-et Math : Analytic Geometry Dr.Wattana Toutip - Department of Mathematics Khon Kaen University 00 :Wattana Toutip wattou@kku.ac.th http://home.kku.ac.th/wattou 7 Analytic
7 EP-Program - Strisuksa School - Roi-et Math : Analytic Geometry Dr.Wattana Toutip - Department of Mathematics Khon Kaen University 00 :Wattana Toutip wattou@kku.ac.th http://home.kku.ac.th/wattou 7 Analytic
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
TARGET : JEE 2013 SCORE. JEE (Advanced) Home Assignment # 03. Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad
 TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A*
 Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A* 1380 / 2381 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number.
Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A* 1380 / 2381 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number.
P1 Chapter 4 :: Graphs & Transformations
 P1 Chapter 4 :: Graphs & Transformations jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 14 th September 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 4 :: Graphs & Transformations jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 14 th September 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle.
 Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Higher Mathematics Course Notes
 Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
Chapter-wise questions
 hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
Topic Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities Resources On-Line Resources
 UNIT 3 Trigonometry and Vectors (P1) Recommended Prior Knowledge. Students will need an understanding and proficiency in the algebraic techniques from either O Level Mathematics or IGCSE Mathematics. Context.
UNIT 3 Trigonometry and Vectors (P1) Recommended Prior Knowledge. Students will need an understanding and proficiency in the algebraic techniques from either O Level Mathematics or IGCSE Mathematics. Context.
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning. Progressive Mathematics Initiative
 Slide 1 / 150 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Slide 1 / 150 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Newbattle Community High School Higher Mathematics. Key Facts Q&A
 Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing to take turns reading a random question
Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing to take turns reading a random question
MT - w A.P. SET CODE MT - w - MATHEMATICS (71) GEOMETRY- SET - A (E) Time : 2 Hours Preliminary Model Answer Paper Max.
 .P. SET CODE.. Solve NY FIVE of the following : (i) ( BE) ( BD) ( BE) ( BD) BE D 6 9 MT - w 07 00 - MT - w - MTHEMTICS (7) GEOMETRY- (E) Time : Hours Preliminary Model nswer Paper Max. Marks : 40 [Triangles
.P. SET CODE.. Solve NY FIVE of the following : (i) ( BE) ( BD) ( BE) ( BD) BE D 6 9 MT - w 07 00 - MT - w - MTHEMTICS (7) GEOMETRY- (E) Time : Hours Preliminary Model nswer Paper Max. Marks : 40 [Triangles
Circle. Paper 1 Section A. Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks. 5. A circle has equation. 4. The point P( 2, 4) lies on the circle
 PSf Circle Paper 1 Section A Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks. 1. A circle has equation ( 3) 2 + ( + 4) 2 = 20. Find the gradient of the tangent to the circle at the point (1, 0).
PSf Circle Paper 1 Section A Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks. 1. A circle has equation ( 3) 2 + ( + 4) 2 = 20. Find the gradient of the tangent to the circle at the point (1, 0).
Homework Assignments Math /02 Fall 2014
 Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2014 Assignment 1 Due date : Friday, September 5 6th Edition Problem Set Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14,
Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2014 Assignment 1 Due date : Friday, September 5 6th Edition Problem Set Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14,
= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]
![= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ] = 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]](/thumbs/74/71228184.jpg) STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER)
 BY:Prof. RAHUL MISHRA Class :- X QNo. VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CIRCLES Subject :- Maths General Instructions Questions M:9999907099,9818932244 1 In the adjoining figures, PQ
BY:Prof. RAHUL MISHRA Class :- X QNo. VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CIRCLES Subject :- Maths General Instructions Questions M:9999907099,9818932244 1 In the adjoining figures, PQ
Berkeley Math Circle, May
 Berkeley Math Circle, May 1-7 2000 COMPLEX NUMBERS IN GEOMETRY ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA FRENKEL, MILLS COLLEGE 1. Let O be a point in the plane of ABC. Points A 1, B 1, C 1 are the images of A, B, C under symmetry
Berkeley Math Circle, May 1-7 2000 COMPLEX NUMBERS IN GEOMETRY ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA FRENKEL, MILLS COLLEGE 1. Let O be a point in the plane of ABC. Points A 1, B 1, C 1 are the images of A, B, C under symmetry
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars
 SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics
 King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics Modules Algebra, Geometry and Calculus. Materials Text book: Mathematics for A-Level Hodder Education. needed Calculator. Progress objectives
King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics Modules Algebra, Geometry and Calculus. Materials Text book: Mathematics for A-Level Hodder Education. needed Calculator. Progress objectives
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1
 Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
Add Math (4047/02) Year t years $P
 Add Math (4047/0) Requirement : Answer all questions Total marks : 100 Duration : hour 30 minutes 1. The price, $P, of a company share on 1 st January has been increasing each year from 1995 to 015. The
Add Math (4047/0) Requirement : Answer all questions Total marks : 100 Duration : hour 30 minutes 1. The price, $P, of a company share on 1 st January has been increasing each year from 1995 to 015. The
This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic.
 Higher Portfolio Circle Higher 10. Circle Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic. R1 I can use the distance formula to find the distance between
Higher Portfolio Circle Higher 10. Circle Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic. R1 I can use the distance formula to find the distance between
Mathematics AQA Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (MPC1) January 2010
 Link to past paper on AQA website: http://store.aqa.org.uk/qual/gce/pdf/aqa-mpc1-w-qp-jan10.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are
Link to past paper on AQA website: http://store.aqa.org.uk/qual/gce/pdf/aqa-mpc1-w-qp-jan10.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are
REVISED GCSE Scheme of Work Mathematics Higher Unit 4. For First Teaching September 2010 For First Examination Summer 2011
 REVISED GCSE Scheme of Work Mathematics Higher Unit 4 For First Teaching September 2010 For First Examination Summer 2011 Version 1: 28 April 10 Version 1: 28 April 10 Unit T4 Version 1: 28 April 10 Unit
REVISED GCSE Scheme of Work Mathematics Higher Unit 4 For First Teaching September 2010 For First Examination Summer 2011 Version 1: 28 April 10 Version 1: 28 April 10 Unit T4 Version 1: 28 April 10 Unit
Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge
 The Canadian Mathematical Society in collaboration with The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING presents the Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge Wednesday, November, 006 Supported by: Solutions
The Canadian Mathematical Society in collaboration with The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING presents the Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge Wednesday, November, 006 Supported by: Solutions
ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS.
 ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS. A B X Z Y A MINOR arc is LESS than 1/2 way around the circle. A MAJOR arc is MORE than 1/2 way around
ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS. A B X Z Y A MINOR arc is LESS than 1/2 way around the circle. A MAJOR arc is MORE than 1/2 way around
Geometry in the Complex Plane
 Geometry in the Complex Plane Hongyi Chen UNC Awards Banquet 016 All Geometry is Algebra Many geometry problems can be solved using a purely algebraic approach - by placing the geometric diagram on a coordinate
Geometry in the Complex Plane Hongyi Chen UNC Awards Banquet 016 All Geometry is Algebra Many geometry problems can be solved using a purely algebraic approach - by placing the geometric diagram on a coordinate
Ch 10 Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the diagram shown, the measure of ADC is a. 55 b. 70 c. 90 d. 180 2. What is the measure
Ch 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the diagram shown, the measure of ADC is a. 55 b. 70 c. 90 d. 180 2. What is the measure
AS MATHEMATICS HOMEWORK C1
 Student Teacher AS MATHEMATICS HOMEWORK C September 05 City and Islington Sixth Form College Mathematics Department www.candimaths.uk HOMEWORK INTRODUCTION You should attempt all the questions. If you
Student Teacher AS MATHEMATICS HOMEWORK C September 05 City and Islington Sixth Form College Mathematics Department www.candimaths.uk HOMEWORK INTRODUCTION You should attempt all the questions. If you
MT - MATHEMATICS (71) GEOMETRY - PRELIM II - PAPER - 1 (E)
 04 00 eat No. MT - MTHEMTI (7) GEOMETY - PELIM II - PPE - (E) Time : Hours (Pages 3) Max. Marks : 40 Note : (i) ll questions are compulsory. Use of calculator is not allowed. Q.. olve NY FIVE of the following
04 00 eat No. MT - MTHEMTI (7) GEOMETY - PELIM II - PPE - (E) Time : Hours (Pages 3) Max. Marks : 40 Note : (i) ll questions are compulsory. Use of calculator is not allowed. Q.. olve NY FIVE of the following
Regent College. Maths Department. Core Mathematics 4. Vectors
 Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 4 Vectors Page 1 Vectors By the end of this unit you should be able to find: a unit vector in the direction of a. the distance between two points (x 1,
Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 4 Vectors Page 1 Vectors By the end of this unit you should be able to find: a unit vector in the direction of a. the distance between two points (x 1,
