HW 2 Help cm sin 60 =12.5 cm 10.8 cm cm sin 30 =12.5 cm 6.25 cm 2. We can check the answer by using the Pythagorean Theorem:
|
|
|
- Marylou Robinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HW Help 8.OGANIZE AND PLAN opposite funtion sin hpotenuse Gien the hpotenuse and the anles we will use the trionometri to sole for eah of the unknown sides. We note that the 60 is the anle opposite the lon side L beause it is a wider anle and 30 is the anle opposite the short side. We are interested in the unknown sides so we will use a little alebra to find that opposite = hpotenuse sin. We should also reall the sin of the ommon anles used in this problem (table 3.1). sin 30 = 1/ and sin 60 3 /. OLVE Applin our trionometri relation for riht trianles we find: and EFLECT (1.5 m). L L m sin 60 =1.5 m 10.8 m m sin 30 =1.5 m 6.5 m We an hek the answer b usin the Pthaorean Theorem: 3. OGANIZE AND PLAN We need to find the riht trianle lurkin within the problem. From where ou are the peak of the mountain is aboe the horizon. The map puts ou a horizontal distane from the peak. o ou hae an anle and a side adjaent to the anle. We need to find the side opposite the anle to find the heiht, aboe the present eleation. The eleation will then be the eleation of the ar at the point of measurement, plus the lenth of the side opposite the anle. The trionometri funtion that relates the two thins we know to the side we don t is the tanent funtion: tan =. Isolatin for the unknown alue ields: = tan OLVE The heiht aboe the urrent eleation is: = tan = 5.0 km tab 3.1 = 1.35 km The peak s eleation is then 1350 m m = 930 m EFLECT This eleation is a respetabl sized peak, thouh one of the smaller ones in the ok Mountains.
2 36. OGANIZE AND PLAN We are ien a displaement etor in ardinal diretions, the time it takes to traerse the displaement and asked to find the displaement and the aerae eloit. The first part is just onertin the ardinal diretions to the Cartesian form. We reall that North, outh, East and West orrespond to the unit etors i ˆ, i ˆ, ĵ and ˆ, j respetiel. The aerae eloit (whih we remember is a etor) will be determined b diidin the displaement etor b the time of traersal. We are asked to find the aerae eloit in units of m/s so we will also need to onert minutes to seonds. OLVE Mappin the ardinal diretions to the Cartesian unit etors ields displaement r in Cartesian form: Conertin 0 min t s we hae The aerae eloit is then: r 150 miˆ900 mˆj 60 s 1 1 min 0 min so 60 s min 100 s r 1 (150 miˆ900 m ˆj) 1.04 m/siˆ0.75 m/sˆj T 100 s or, in ardinal diretions 1.04 m/s east and 0.75 m/s south. EFLECT This problem required two tpes of onersions: minutes to seonds and ardinal diretions to Cartesian form. Aquirin skill in unit onersions will be somethin ou thank ourself for the rest of our life. ubtratin etors is ahieed b ombinin like terms where the unit etors are treated as ariables. The differene between etors 1 and is a etor ien b 1 ˆ ˆ ( 1 ) i ( 1 ) j 39.OGANIZE AND PLAN OLVE r r ( r r ) i ˆ ( r r ) ˆ j ( ) mi ( ) m j 5.95 mi 6.05 m j r r EFLECT in is important when subtratin omponents and sometimes an be trik. You an alwas hek the answer b drawin the etors tail to tail and obtainin r 1 r b drawin a etor startin at r and endin at r 1. Unlike addition, r 1 r r r so order 1 matters.
3 48. OGANIZE AND PLAN There is a distintion between distane traeled and displaement. Distane traeled is the readin on the odometer of the ar (assumin it started at zero at the beinnin of the rae). Displaement is the displaement etor beinnin at the start and endin at the loation of interest. The distane traelled will just be the ar of a irle whih is ien b frations of a irumferene. The irumferene of a irle is C =. One-quarter lap is orresponds C C to, one-half lap and one whole lap C. 4 The displaement is a etor and requires both manitude and diretion. The displaement etor d an be obtained b alulatin the differene between the final position etor and the initial position etor, d rf ri. One we hae the position etors at the start, at one-quarter lap, one-half lab and one full lap it is a straiht forward matter to alulate the etor differene. OLVE Distane traeled: C quarter lap: 393 m half lap: 4 C 785 m full lap: C 1570 m Position etors in omponent form (r, r ) at: start: (50 m, 0) quarter lap: (0, 50 m) half lap: ( 50 m, 0) full lap: (50 m, 0) Displaement etors from start to quarter lap: (0,50 m) (50 m,0) ( 50 m,50 m) 50 mi ˆ 50 mˆj half lap: ( 50 m,0) (50 m,0) ( 500 m,0)=500 mˆ i full lap: (50 m,0) (50 m,0) ( 0,0)= 0 EFLECT This problem reinfores the differene between distane traeled (a salar quantit) and displaement. The stark differene is seen between the distane traeled to o all the wa around, one irumferene; and the displaement assoiated with endin upwhere ou started, zero.
4 The aerae aeleration oer an duration of time requires the differene between the eloities at the start and end of the duration as well as the duration itself. The eloities are obtained from the speed and diretion at the beinnin of the rae and 1/4 of the wa around the irle. If the rae starts with ars fain due north (whih will all the ĵ diretion) then 1/4 of the wa around the irle the ar will be fain due west (whih we will all the î diretion) (see fiure below). 58.OGANIZE AND PLAN! f = ( ı) N! i = N ae trak The time is determined b usin rate time = distane. We an use the eometr of the problem to determine the total distane traeled and we are ien the rate of trael oer this distane. The aeleration is then just obtained b diidin the hane in eloit b the time. We also note that the units are km/h. To obtain an answer that we an ompare to eperiene we want to onert eerthin to meters and seonds. OLVE The differene in eloities is: ˆ ˆ 90 km / h 1000 m 1 hr 90 km / h( i j) ( iˆ ˆj) 5 m /s( iˆ ˆj) 1 km 3600 s The path lenth d of this part of the rae is 1/4 the irumferene of a irle: km d π 1.96 km. 4 d 1.96 km The time of trael is t hr 78 s 90 km / hr The aerae aeleration is: 5 m /s( iˆ ˆj) a ˆ ˆ a 0.31 m/s ( i j) t 78 s EFLECT The aerae aeleration is direted toward the south-west diretion whih jibes with the piture and the trajetor of the ar around the trak. The manitude of the aeleration is 0.45 ms or about 5% the aeleration due to rait on the Earth.
5 63. OGANIZE AND PLAN Gien the initial eloit we an use the relationships deried in question 11 to find the rane and the time of fliht. The rane is ien b 0 T. The time of fliht was deried to be 0 The maimum heiht an be determined b onsiderin that half the time time of fliht is spent oin up and half is spent oin down when the launh eleation is the same as the landin eleation. When the projetile is at the ape of the path the omponent of the eloit in the ertial diretion is zero. Usin equation 3.19a with zero initial eloit in 1 the diretion of aeleration ( t ) and takin the oriin of the oordinate sstem as the ape. The distane of the fall in Known: iˆ ˆj i OLVE The rane is: The time of fliht is: 7 m/s(os45 sin45 ) The maimum heiht is: 0. T t will ie us the maimum heiht. 00 (7) m /s 74 m 9.8 m/s 0 (7) m /s T 3.9 s 9.8 m/s s 9.8 m /s ( ) 19 m t EFLECT The distane between home-plate and the outfield wall is approimatel 400 ft. The rane found aboe is onsistent with a fl-ball hit into the outfield. The time of fliht is also onsistent with the eperiene of wathin a ball ame and timin the time from bat to loe of a fl-ball.
6 66. OGANIZE AND PLAN Gien the initial eloit we an use the relationships deried in question 11 to find the rane and the time of fliht. The rane is ien b 00 sinos where is the launh anle from the horizontal and is the speed. We are asked to determine if an initial eloit and launh anle will result in a rane that is less than 5 m. We shall etrat 0 and 0 from the ien information: i (0 m/s,15 ) to obtain whether or not the ball will be in or out of the ourt. Gien a rane and a launh anle, determination of the speed is just alebrai manipulation of the relationship aboe: sinos and 0 0 m /s os m/s Preliminar alulations: 0 0 m/s sin m/s OLVE Proof that the ball will land in pla: The rane of the struk tennis ball is 5.18 m/s19.3 m/s 0 m 5 m 9.8 m/s The maimum eloit that will result in a ball in pla is: ma 9.8 m /s 5 m m/s sin15os15 EFLECT Another appliation of the rane formula. It is interestin to note that m/s differene in the eloit of the ball omin off the raket makes the different between in and out of the ourt. Great tennis plaers must hae done er well in their phsis lasses.
7 We hae deeloped the rane equation ien the horizontal and ertial omponents of the eloit: 70.OGANIZE AND PLAN 0 0 This problem is stated in a wa that allows a straihtforward appliation of this equations. OLVE The rane of the lon jumper is: 3.85 m/s7.5 m/s 5.89 m 9.8 m/s EFLECT The worlds reord for women s lon jump in 198 was 5.98 meters. Toda is 7.5 meters. A distane of 5.89 m is a respetable and reasonable distane. 8.OGANIZE AND PLAN The equation for the entripetal aeleration is a limit on the allowed alue for a 1.0 ms leadin to the inequalit: olin for : r a ma a min ma a ma ar. We are ien Notes on units: We will standardize the units in the problem to meters and seonds. OLVE m 1 hr 100 km hr m s km 3600 s (7.8 ms) min 773 m min a 1 ms Minimum radius of urature is EFLECT A larer radius of urature an aommodate faster speeds or lower entripetal aeleration.
MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS
 MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS 3 CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS. (a) Surace area is a scalar; (b) position o point on Earth s surace is a ector; (c) centripetal acceleration is a ector; (d) the number o paes in this book
MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS 3 CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS. (a) Surace area is a scalar; (b) position o point on Earth s surace is a ector; (c) centripetal acceleration is a ector; (d) the number o paes in this book
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Position and Displacement. Average Velocity. Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions
 PC11 Fndamentals of Physis I Letres 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions A/Prof Tay Sen Chan 1 Grond Rles Swith off yor handphone and paer Swith off yor laptop ompter and keep it No talkin while letre is oin
PC11 Fndamentals of Physis I Letres 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions A/Prof Tay Sen Chan 1 Grond Rles Swith off yor handphone and paer Swith off yor laptop ompter and keep it No talkin while letre is oin
Announcements. Today s class. The Lorentz transformation. Lorentz transformation (Relativistic version of Galileo transformation)
 Announements Reading for Monda:. -.5 HW 3 is posted. Due net Wed. noon. The Frida was a TYPO! IT I DUE WEDNEDAY! Toda s lass Lorent transformation Doppler shift First Midterm is on the 6 th. Will oer relatiit
Announements Reading for Monda:. -.5 HW 3 is posted. Due net Wed. noon. The Frida was a TYPO! IT I DUE WEDNEDAY! Toda s lass Lorent transformation Doppler shift First Midterm is on the 6 th. Will oer relatiit
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 11
 8.0 (E&M) Leture Topis: Introdution to Speial Relatiit Length ontration and Time dilation Lorentz transformations Veloit transformation Speial relatiit Read for the hallenge? Speial relatiit seems eas
8.0 (E&M) Leture Topis: Introdution to Speial Relatiit Length ontration and Time dilation Lorentz transformations Veloit transformation Speial relatiit Read for the hallenge? Speial relatiit seems eas
Physics 6C. Special Relativity. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physis 6C Speial Relatiity Two Main Ideas The Postulates of Speial Relatiity Light traels at the same speed in all inertial referene frames. Laws of physis yield idential results in all inertial referene
Physis 6C Speial Relatiity Two Main Ideas The Postulates of Speial Relatiity Light traels at the same speed in all inertial referene frames. Laws of physis yield idential results in all inertial referene
Projectiles 6D. 1 At maximum height, h, the vertical component of velocity, vy = 0, a = g, s h, v 0 R( ) sin. v u 2as sin 2. U h. as required.
 Projectiles 6D 1 At maimum heiht, h, the ertical component of elocit, = 0 R( ): u u sin, a =, s h, 0 u as 0 sin h sin h sin h Resolin the initial elocit horizontall and erticall R( ) u 1cos R u 1sin a
Projectiles 6D 1 At maimum heiht, h, the ertical component of elocit, = 0 R( ): u u sin, a =, s h, 0 u as 0 sin h sin h sin h Resolin the initial elocit horizontall and erticall R( ) u 1cos R u 1sin a
v( t) g 2 v 0 sin θ ( ) ( ) g t ( ) = 0
 PROJECTILE MOTION Velocity We seek to explore the velocity of the projectile, includin its final value as it hits the round, or a taret above the round. The anle made by the velocity vector with the local
PROJECTILE MOTION Velocity We seek to explore the velocity of the projectile, includin its final value as it hits the round, or a taret above the round. The anle made by the velocity vector with the local
(a) 1m s -2 (b) 2 m s -2 (c) zero (d) -1 m s -2
 11 th Physics - Unit 2 Kinematics Solutions for the Textbook Problems One Marks 1. Which one of the followin Cartesian coordinate system is not followed in physics? 5. If a particle has neative velocity
11 th Physics - Unit 2 Kinematics Solutions for the Textbook Problems One Marks 1. Which one of the followin Cartesian coordinate system is not followed in physics? 5. If a particle has neative velocity
Firing an Ideal Projectile
 92 Chapter 13: Vector-Valued Functions and Motion in Space 13.2 Modelin Projectile Motion 921 r at time t v v cos i a j (a) v sin j Newton s second law of motion sas that the force actin on the projectile
92 Chapter 13: Vector-Valued Functions and Motion in Space 13.2 Modelin Projectile Motion 921 r at time t v v cos i a j (a) v sin j Newton s second law of motion sas that the force actin on the projectile
The Lorenz Transform
 The Lorenz Transform Flameno Chuk Keyser Part I The Einstein/Bergmann deriation of the Lorentz Transform I follow the deriation of the Lorentz Transform, following Peter S Bergmann in Introdution to the
The Lorenz Transform Flameno Chuk Keyser Part I The Einstein/Bergmann deriation of the Lorentz Transform I follow the deriation of the Lorentz Transform, following Peter S Bergmann in Introdution to the
If the speed of light were smaller than it is, would relativistic phenomena be more or less conspicuous than they are now?
 Physis 07 Problem. If the speed of light were smaller than it is, would relatiisti phenomena be more or less onspiuous than they are now? All of the phenomena of speial relatiity depend upon the fator
Physis 07 Problem. If the speed of light were smaller than it is, would relatiisti phenomena be more or less onspiuous than they are now? All of the phenomena of speial relatiity depend upon the fator
Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Text: Chapters 6 & 7, except 7.5 & 7.6
 Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Tet: Chapters 6 & 7, ecept 7.5 & 7.6 It is time to etend the definitions we developed in Note 03 to describe motion in 2D space. In doin so we shall find
Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Tet: Chapters 6 & 7, ecept 7.5 & 7.6 It is time to etend the definitions we developed in Note 03 to describe motion in 2D space. In doin so we shall find
Precalculus Notes: Unit 6 Law of Sines & Cosines, Vectors, & Complex Numbers. A can be rewritten as B
 Date: 6.1 Law of Sines Syllaus Ojetie: 3.5 Te student will sole appliation prolems inoling triangles (Law of Sines). Deriing te Law of Sines: Consider te two triangles. a C In te aute triangle, sin and
Date: 6.1 Law of Sines Syllaus Ojetie: 3.5 Te student will sole appliation prolems inoling triangles (Law of Sines). Deriing te Law of Sines: Consider te two triangles. a C In te aute triangle, sin and
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.10
 Camride Physis for the IB Diploma Answers to Courseook questions Chapter. 1 a y = OP = 1 t = 0.05 m = 0.0 = 00 m s 1 0. The time to fall to the floor is iven y y = 1 t t = y = 1.3 = 0.51 s. The horizontal
Camride Physis for the IB Diploma Answers to Courseook questions Chapter. 1 a y = OP = 1 t = 0.05 m = 0.0 = 00 m s 1 0. The time to fall to the floor is iven y y = 1 t t = y = 1.3 = 0.51 s. The horizontal
Get Solution of These Packages & Learn by Video Tutorials on PROJECTILE MOTION
 FREE Download Study Packae from website: www.tekoclasses.com & www.mathsbysuha.com Get Solution of These Packaes & Learn by Video Tutorials on www.mathsbysuha.com. BASIC CONCEPT :. PROJECTILE PROJECTILE
FREE Download Study Packae from website: www.tekoclasses.com & www.mathsbysuha.com Get Solution of These Packaes & Learn by Video Tutorials on www.mathsbysuha.com. BASIC CONCEPT :. PROJECTILE PROJECTILE
Agenda 2/12/2017. Modern Physics for Frommies V Gravitation Lecture 6. Special Relativity Einstein s Postulates. Einstein s Postulates
 /1/17 Fromm Institute for Lifelong Learning Uniersit of San Franiso Modern Phsis for Frommies V Graitation Leture 6 Agenda Speial Relatiit Einstein s Postulates 15 Februar 17 Modern Phsis V Leture 6 1
/1/17 Fromm Institute for Lifelong Learning Uniersit of San Franiso Modern Phsis for Frommies V Graitation Leture 6 Agenda Speial Relatiit Einstein s Postulates 15 Februar 17 Modern Phsis V Leture 6 1
MOTION IN 2-DIMENSION (Projectile & Circular motion And Vectors)
 MOTION IN -DIMENSION (Projectile & Circular motion nd Vectors) INTRODUCTION The motion of an object is called two dimensional, if two of the three co-ordinates required to specif the position of the object
MOTION IN -DIMENSION (Projectile & Circular motion nd Vectors) INTRODUCTION The motion of an object is called two dimensional, if two of the three co-ordinates required to specif the position of the object
ECE507 - Plasma Physics and Applications
 ECE57 - Plasma Phsis and Appliations Leture 4 Prof. Jorge Roa and Dr. Fernando Tomasel Department of Eletrial and Computer Engineering Constant, uniform Let s align with the -ais, so = k. Then we an write
ECE57 - Plasma Phsis and Appliations Leture 4 Prof. Jorge Roa and Dr. Fernando Tomasel Department of Eletrial and Computer Engineering Constant, uniform Let s align with the -ais, so = k. Then we an write
REVIEW: Going from ONE to TWO Dimensions with Kinematics. Review of one dimension, constant acceleration kinematics. v x (t) = v x0 + a x t
 Lecture 5: Projectile motion, uniform circular motion 1 REVIEW: Goin from ONE to TWO Dimensions with Kinematics In Lecture 2, we studied the motion of a particle in just one dimension. The concepts of
Lecture 5: Projectile motion, uniform circular motion 1 REVIEW: Goin from ONE to TWO Dimensions with Kinematics In Lecture 2, we studied the motion of a particle in just one dimension. The concepts of
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS] CHAPTER NO. 4 In this chapter we are oin to discuss motion in projectile
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS] CHAPTER NO. 4 In this chapter we are oin to discuss motion in projectile
Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 2 - Solutions
 Physics 11 Fall 01 Practice Problems - s 1. True or false (inore any effects due to air resistance): (a) When a projectile is fired horizontally, it takes the same amount of time to reach the round as
Physics 11 Fall 01 Practice Problems - s 1. True or false (inore any effects due to air resistance): (a) When a projectile is fired horizontally, it takes the same amount of time to reach the round as
Lesson 3: Free fall, Vectors, Motion in a plane (sections )
 Lesson 3: Free fall, Vectors, Motion in a plane (sections.6-3.5) Last time we looked at position s. time and acceleration s. time graphs. Since the instantaneous elocit is lim t 0 t the (instantaneous)
Lesson 3: Free fall, Vectors, Motion in a plane (sections.6-3.5) Last time we looked at position s. time and acceleration s. time graphs. Since the instantaneous elocit is lim t 0 t the (instantaneous)
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 4. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 35.
 Rutgers Uniersit Department of Phsics & Astronom 01:750:271 Honors Phsics I Fall 2015 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 35 4. Motion in two and three dimensions Goals: To stud position, elocit, and acceleration ectors
Rutgers Uniersit Department of Phsics & Astronom 01:750:271 Honors Phsics I Fall 2015 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 35 4. Motion in two and three dimensions Goals: To stud position, elocit, and acceleration ectors
Velocity and Accceleration in Different Coordinate system
 Velocity & cceleration in different coordinate system Chapter Velocity and ccceleration in Different Coordinate system In physics basic laws are first introdced for a point partile and then laws are etended
Velocity & cceleration in different coordinate system Chapter Velocity and ccceleration in Different Coordinate system In physics basic laws are first introdced for a point partile and then laws are etended
Einstein s theory of special relativity
 Einstein s theory of speial relatiity Announements: First homework assignment is online. You will need to read about time dilation (1.8) to answer problem #3 and for the definition of γ for problem #4.
Einstein s theory of speial relatiity Announements: First homework assignment is online. You will need to read about time dilation (1.8) to answer problem #3 and for the definition of γ for problem #4.
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Position and Displacement. Average Velocity. Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions
 PC11 Fundamentals of Physics I Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions Dr Tay Sen Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch off your handphone and paer Switch off your laptop computer and keep it No talkin while lecture
PC11 Fundamentals of Physics I Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions Dr Tay Sen Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch off your handphone and paer Switch off your laptop computer and keep it No talkin while lecture
Relativistic Analysis of Doppler Effect and Aberration based on Vectorial Lorentz Transformations
 Uniersidad Central de Venezuela From the SeletedWorks of Jorge A Frano June, Relatiisti Analysis of Doppler Effet and Aberration based on Vetorial Lorentz Transformations Jorge A Frano, Uniersidad Central
Uniersidad Central de Venezuela From the SeletedWorks of Jorge A Frano June, Relatiisti Analysis of Doppler Effet and Aberration based on Vetorial Lorentz Transformations Jorge A Frano, Uniersidad Central
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Sprin 2009 Problem Set 2 Solutions The followin three problems are due 20 January 2009 at the beinnin of class. 1. (H,R,&W 4.39)
UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Sprin 2009 Problem Set 2 Solutions The followin three problems are due 20 January 2009 at the beinnin of class. 1. (H,R,&W 4.39)
Parametric Equations
 Parametric Equations Suppose a cricket jumps off of the round with an initial velocity v 0 at an anle θ. If we take his initial position as the oriin, his horizontal and vertical positions follow the equations:
Parametric Equations Suppose a cricket jumps off of the round with an initial velocity v 0 at an anle θ. If we take his initial position as the oriin, his horizontal and vertical positions follow the equations:
Get the frictional force from the normal force. Use dynamics to get the normal force.
 . L F n µ k L =00 t µ k = 0.60 = 0 o = 050 lb F n +y +x x = sin y = cos = µf n Is the initial elocity o the car reater than 30 mph? Approach: Use conseration o enery. System: car Initial time: beore you
. L F n µ k L =00 t µ k = 0.60 = 0 o = 050 lb F n +y +x x = sin y = cos = µf n Is the initial elocity o the car reater than 30 mph? Approach: Use conseration o enery. System: car Initial time: beore you
PSI AP Physics C Kinematics 2D. Multiple Choice Questions
 PSI AP Physics C Kinematics D Multiple Choice Questions 1. A tennis ball is thrown off a cliff 10 m above the round with an initial horizontal velocity of 5 m/s as shown above. The time between the ball
PSI AP Physics C Kinematics D Multiple Choice Questions 1. A tennis ball is thrown off a cliff 10 m above the round with an initial horizontal velocity of 5 m/s as shown above. The time between the ball
The Material Traces Determination and Significance of Reprinted Belt Conveyor Gui-Yu LIN 1,a*, Zhao-Yong LI 2,b, Yu ZHOU 3,c, Chao ZHANG 1,d
 International Conferene on Mehanis and Ciil Enineerin (ICMCE 014) The Material Traes Determination and Sinifiane of Reprinted Belt Coneyor Gui-Yu LIN 1,a*, Zhao-Yon LI,b, Yu ZHOU 3,, Chao ZHANG 1,d 1 Liaonin
International Conferene on Mehanis and Ciil Enineerin (ICMCE 014) The Material Traes Determination and Sinifiane of Reprinted Belt Coneyor Gui-Yu LIN 1,a*, Zhao-Yon LI,b, Yu ZHOU 3,, Chao ZHANG 1,d 1 Liaonin
Chapter 3. Vectors. θ that the vector forms with i ˆ is 15. I. Vectors and Scalars
 Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Special Relativity Simply Debunked in Five Steps!
 Speial Relatiity Simply Debunked in Fie Steps! Radwan M. Kassir Abstrat The speed of light postulate is losely examined from the perspetie of two inertial referene frames unprimed ( stationary ) and primed
Speial Relatiity Simply Debunked in Fie Steps! Radwan M. Kassir Abstrat The speed of light postulate is losely examined from the perspetie of two inertial referene frames unprimed ( stationary ) and primed
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 2 - Solutions Wednesday January 26, 2011
 Physics 18 Sprin 011 Homework - s Wednesday January 6, 011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be ivin partial credit, be sure to attempt all the
Physics 18 Sprin 011 Homework - s Wednesday January 6, 011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be ivin partial credit, be sure to attempt all the
Phys207: Lecture 04. Today s Agenda 3-D Kinematics Independence of x and y components Baseball projectile Shoot the monkey Uniform circular motion
 Phys7: Lecture 4 Reminders All Discussion and Lab sections start meetin this week Homework is posted on course website Solutions to preious hwks will be posted Thursday mornins Today s Aenda 3-D Kinematics
Phys7: Lecture 4 Reminders All Discussion and Lab sections start meetin this week Homework is posted on course website Solutions to preious hwks will be posted Thursday mornins Today s Aenda 3-D Kinematics
Chapter 4 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
 Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Volume Charge Density in Most General Lorentz Transformation
 Publiations Aailable Online J. Si. Res. 8(), 59-65 (016) JOURNA OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH www.banglajol.info/inde.php/jsr Volume Charge Densit in Most General orent Transformation S. A. Bhuian *, A. R. Baiid
Publiations Aailable Online J. Si. Res. 8(), 59-65 (016) JOURNA OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH www.banglajol.info/inde.php/jsr Volume Charge Densit in Most General orent Transformation S. A. Bhuian *, A. R. Baiid
Prince Sultan University Physics Department First Semester 2012 /2013. PHY 105 First Major Exam Allowed Time: 60 min
 Prince Sultan University Physics Department First Semester 01 /01 PHY 105 First Major Exam Allowed Time: 60 min Student Name: 1. Write your name in the specified space NOW.. Any paper without name will
Prince Sultan University Physics Department First Semester 01 /01 PHY 105 First Major Exam Allowed Time: 60 min Student Name: 1. Write your name in the specified space NOW.. Any paper without name will
KINEMATICS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS ENGINEERING PAPER
 KINEMATICS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS ENGINEERING PAPER. A body is projected vertically upwards at time t = 0 and is seen at a heiht at time t and t seconds durin its fliht. The maximum heiht attained is [ =
KINEMATICS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS ENGINEERING PAPER. A body is projected vertically upwards at time t = 0 and is seen at a heiht at time t and t seconds durin its fliht. The maximum heiht attained is [ =
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics. Physics 8.01x Fall Term 2001 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01x Fall Term 2001 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem 1: We define a vertical coordinate system with positive upwards. The only forces actin
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01x Fall Term 2001 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem 1: We define a vertical coordinate system with positive upwards. The only forces actin
Physics 43 HW 2 Chapter 39 Problems given from 7 th Edition
 Physis 3 HW Chater 39 Problems gien from 7 th Edition Problems:, 7,, 9, 1, 0,,, 9, 33, 35, 3, 0, 5,. How fast must a meter stik be moing if its length is measured to shrink to 0.500 m? P39. L = L L Taking
Physis 3 HW Chater 39 Problems gien from 7 th Edition Problems:, 7,, 9, 1, 0,,, 9, 33, 35, 3, 0, 5,. How fast must a meter stik be moing if its length is measured to shrink to 0.500 m? P39. L = L L Taking
Answer Key 8 th Grade Geometry Honors Summer 2018 Mathematics Packet
 Answer Ke 8 th Grade Geometr Honors Summer 08 Mathematics Packet [] [B] [] You will never reach point B. [] a. raph 4. raph c. raph d. raph [4] $7.78 [] 4% [6] 6 4 % decrease [7] A population is a roup
Answer Ke 8 th Grade Geometr Honors Summer 08 Mathematics Packet [] [B] [] You will never reach point B. [] a. raph 4. raph c. raph d. raph [4] $7.78 [] 4% [6] 6 4 % decrease [7] A population is a roup
Solving Right Triangles Using Trigonometry Examples
 Solving Right Triangles Using Trigonometry Eamples 1. To solve a triangle means to find all the missing measures of the triangle. The trigonometri ratios an be used to solve a triangle. The ratio used
Solving Right Triangles Using Trigonometry Eamples 1. To solve a triangle means to find all the missing measures of the triangle. The trigonometri ratios an be used to solve a triangle. The ratio used
This Week. Next Week
 This Week Tutorial and Test 1, in the lab (chapters 1 and 2) Next Week Experiment 1: Measurement of Lenth and Mass WileyPLUS Assinment 1 now available Due Monday, October 5 at 11:00 pm Chapters 2 & 3 28
This Week Tutorial and Test 1, in the lab (chapters 1 and 2) Next Week Experiment 1: Measurement of Lenth and Mass WileyPLUS Assinment 1 now available Due Monday, October 5 at 11:00 pm Chapters 2 & 3 28
Announcements. Review: Lorentz & velocity transformations (relativistic version of Galileo) Transformations (in 1D) Some examples
 Announeents Reading for Monda: Chapter.6-. First Mid-ter is in das (Feb. 9 th, 7:30p). It will oer Chapters &. Reiew: Lorentz & eloit transforations (relatiisti ersion of Galileo) Transforations (in D)
Announeents Reading for Monda: Chapter.6-. First Mid-ter is in das (Feb. 9 th, 7:30p). It will oer Chapters &. Reiew: Lorentz & eloit transforations (relatiisti ersion of Galileo) Transforations (in D)
Chapter 35. Special Theory of Relativity (1905)
 Chapter 35 Speial Theory of Relatiity (1905) 1. Postulates of the Speial Theory of Relatiity: A. The laws of physis are the same in all oordinate systems either at rest or moing at onstant eloity with
Chapter 35 Speial Theory of Relatiity (1905) 1. Postulates of the Speial Theory of Relatiity: A. The laws of physis are the same in all oordinate systems either at rest or moing at onstant eloity with
Energizing Math with Engineering Applications
 Enerizin Math with Enineerin Applications Understandin the Math behind Launchin a Straw-Rocket throuh the use of Simulations. Activity created by Ira Rosenthal (rosenthi@palmbeachstate.edu) as part of
Enerizin Math with Enineerin Applications Understandin the Math behind Launchin a Straw-Rocket throuh the use of Simulations. Activity created by Ira Rosenthal (rosenthi@palmbeachstate.edu) as part of
PHYS 1114, Lecture 9, February 6 Contents:
 PHYS 4, Lecture 9, February 6 Contents: Continued with projectile motion: The kicko problem in football was treated analytically, obtainin formulas for maimum heiht and rane in terms of initial speed and
PHYS 4, Lecture 9, February 6 Contents: Continued with projectile motion: The kicko problem in football was treated analytically, obtainin formulas for maimum heiht and rane in terms of initial speed and
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Coordinate Systems. Cartesian Coordinate System. Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors.
 PC1221 Fundamentals of Phsics I Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors Dr Ta Seng Chuan 1 Ground ules Switch off our handphone and pager Switch off our laptop computer and keep it No talking while lecture is going on
PC1221 Fundamentals of Phsics I Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors Dr Ta Seng Chuan 1 Ground ules Switch off our handphone and pager Switch off our laptop computer and keep it No talking while lecture is going on
(a) Taking the derivative of the position vector with respect to time, we have, in SI units (m/s),
 Chapter 4 Student Solutions Manual. We apply Eq. 4- and Eq. 4-6. (a) Taking the deriatie of the position ector with respect to time, we hae, in SI units (m/s), d ˆ = (i + 4t ˆj + tk) ˆ = 8tˆj + k ˆ. dt
Chapter 4 Student Solutions Manual. We apply Eq. 4- and Eq. 4-6. (a) Taking the deriatie of the position ector with respect to time, we hae, in SI units (m/s), d ˆ = (i + 4t ˆj + tk) ˆ = 8tˆj + k ˆ. dt
Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 PH 1-1D Spring 013 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Lectures 5,6,7 Chapter 4 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions In this chapter
PH 1-1D Spring 013 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Lectures 5,6,7 Chapter 4 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions In this chapter
P6.5 (a) static friction. v r. = r ( 30.0 cm )( 980 cm s ) P6.15 Let the tension at the lowest point be T.
 Q65 The speed chanes The tanential orce component causes tanential acceleration Q69 I would not accept that statement or two reasons First, to be beyond the pull o raity, one would hae to be ininitely
Q65 The speed chanes The tanential orce component causes tanential acceleration Q69 I would not accept that statement or two reasons First, to be beyond the pull o raity, one would hae to be ininitely
Today: Review of SR. Einstein s Postulates of Relativity (Abbreviated versions) Let's start with a few important concepts
 Today: eiew of Eam: Tomorrow, 7:30-9:00pm, DUANE GB30 You an bring paper (etter format written on both sides with whateer you think might help you during the eam. But you annot bring the tetbook or leture
Today: eiew of Eam: Tomorrow, 7:30-9:00pm, DUANE GB30 You an bring paper (etter format written on both sides with whateer you think might help you during the eam. But you annot bring the tetbook or leture
jfpr% ekuo /kez iz.ksrk ln~xq# Jh j.knksm+nklth egkjkt
 Phone : 0 903 903 7779, 98930 58881 Kinematics Pae: 1 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] uha kjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k fla ladyi dj] lrs foifr usd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj jk[ks
Phone : 0 903 903 7779, 98930 58881 Kinematics Pae: 1 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] uha kjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k fla ladyi dj] lrs foifr usd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj jk[ks
Green s function for the wave equation
 Green s funtion for the wave equation Non relativisti ase 1 The wave equations In the Lorentz Gauge, the wave equations for the potentials in Lorentz Gauge Gaussian units are: r 2 A 1 2 A 2 t = 4π 2 j
Green s funtion for the wave equation Non relativisti ase 1 The wave equations In the Lorentz Gauge, the wave equations for the potentials in Lorentz Gauge Gaussian units are: r 2 A 1 2 A 2 t = 4π 2 j
(a)!! d = 17 m [W 63 S]!! d opposite. (b)!! d = 79 cm [E 56 N] = 79 cm [W 56 S] (c)!! d = 44 km [S 27 E] = 44 km [N 27 W] metres. 3.
![(a)!! d = 17 m [W 63 S]!! d opposite. (b)!! d = 79 cm [E 56 N] = 79 cm [W 56 S] (c)!! d = 44 km [S 27 E] = 44 km [N 27 W] metres. 3. (a)!! d = 17 m [W 63 S]!! d opposite. (b)!! d = 79 cm [E 56 N] = 79 cm [W 56 S] (c)!! d = 44 km [S 27 E] = 44 km [N 27 W] metres. 3.](/thumbs/87/95551963.jpg) Chapter Reiew, pages 90 95 Knowledge 1. (b). (d) 3. (b) 4. (a) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (c) 8. (a) 9. (a) 10. False. A diagram with a scale of 1 cm : 10 cm means that 1 cm on the diagram represents 10 cm in real
Chapter Reiew, pages 90 95 Knowledge 1. (b). (d) 3. (b) 4. (a) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (c) 8. (a) 9. (a) 10. False. A diagram with a scale of 1 cm : 10 cm means that 1 cm on the diagram represents 10 cm in real
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit I Kinematics: Chapter 2 Solutions
 Pearson Phsics Leel 0 Unit I Kinematics: Chapter Solutions Student Book page 71 Skills Practice Students answers will ar but ma consist of: (a) scale 1 cm : 1 m; ector will be 5 cm long scale 1 m forward
Pearson Phsics Leel 0 Unit I Kinematics: Chapter Solutions Student Book page 71 Skills Practice Students answers will ar but ma consist of: (a) scale 1 cm : 1 m; ector will be 5 cm long scale 1 m forward
Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 PH 1-A Fall 014 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Lectures 4,5 Chapter 4 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions In this chapter
PH 1-A Fall 014 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Lectures 4,5 Chapter 4 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions In this chapter
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 4 Homework
 Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 4 Homework Chapter 4 Questions: 4, 1, 1 Exercises & Problems: 5, 11, 3, 7, 8, 58, 67, 77, 87, 11 Answers to Questions: Q 4-4 (a) all tie (b) 1 and tie (the rocket is shot
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 4 Homework Chapter 4 Questions: 4, 1, 1 Exercises & Problems: 5, 11, 3, 7, 8, 58, 67, 77, 87, 11 Answers to Questions: Q 4-4 (a) all tie (b) 1 and tie (the rocket is shot
PHYS 100: Lecture 4 PROJECTILE MOTION. y = (v 0 /v T ) x (g/2v T2 )x 2. Velocity of Train v T. Physics 100 Lecture 4, Slide y(m)
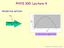 PHYS : Lecture 4 PROJECTILE MOTION.4. Velocity of Train T y(m).8.6.4. 5 5 x(m) y ( / T ) x (/ T )x Physics Lecture 4, Slide Music Who is the Artist? A) Miles Dais B) Wynton Marsalis C) Chris Botti D) Nina
PHYS : Lecture 4 PROJECTILE MOTION.4. Velocity of Train T y(m).8.6.4. 5 5 x(m) y ( / T ) x (/ T )x Physics Lecture 4, Slide Music Who is the Artist? A) Miles Dais B) Wynton Marsalis C) Chris Botti D) Nina
SPECTRUM OF THE COMA CLUSTER RADIO HALO SYNCHROTRON RADIATION
 SPECTRUM OF THE COMA CLUSTER RADIO HALO SYNCHROTRON RADIATION OUTLINE OF THE LESSON REMINDER SPECIAL RELATIVITY: BEAMING, RELATIVISTIC LARMOR FORMULA CYCLOTRON EMISSION SYNCHROTRON POWER AND SPECTRUM EMITTED
SPECTRUM OF THE COMA CLUSTER RADIO HALO SYNCHROTRON RADIATION OUTLINE OF THE LESSON REMINDER SPECIAL RELATIVITY: BEAMING, RELATIVISTIC LARMOR FORMULA CYCLOTRON EMISSION SYNCHROTRON POWER AND SPECTRUM EMITTED
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 PART I CHAPTER P Preparation for Calulus Setion P. Graphs and Models...................... Setion P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............. 7 Setion P. Funtions and Their Graphs.................
PART I CHAPTER P Preparation for Calulus Setion P. Graphs and Models...................... Setion P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............. 7 Setion P. Funtions and Their Graphs.................
If velocity of A relative to ground = velocity of B relative to ground = the velocity of A relative to B =
 L Physis MC nswers Year:1989 Question Number: 3,0,,4,6,9,30,31,36,40,4 1989MC (3) If eloity of relatie to ground = and eloity of relatie to ground =, then the eloity of relatie to = X X Y Y Suppose that
L Physis MC nswers Year:1989 Question Number: 3,0,,4,6,9,30,31,36,40,4 1989MC (3) If eloity of relatie to ground = and eloity of relatie to ground =, then the eloity of relatie to = X X Y Y Suppose that
Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane
 Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane Introduce ectors and scalars. Vectors hae direction as well as magnitude. The are represented b arrows. The arrow points in the direction of the ector and its length is related
Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane Introduce ectors and scalars. Vectors hae direction as well as magnitude. The are represented b arrows. The arrow points in the direction of the ector and its length is related
PHYSICS FOR THE IB DIPLOMA CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Option A Relatiity A The beginnings of relatiity Learning objeties It is said that Albert Einstein, as a boy, asked himself what would happen if he held a mirror in front of himself and ran forward at
Option A Relatiity A The beginnings of relatiity Learning objeties It is said that Albert Einstein, as a boy, asked himself what would happen if he held a mirror in front of himself and ran forward at
PES 1110 Fall 2013, Spendier Lecture 5/Page 1
 PES 1110 Fall 2013, Spendier Lecture 5/Page 1 Toda: - Announcements: Quiz moved to net Monda, Sept 9th due to website glitch! - Finish chapter 3: Vectors - Chapter 4: Motion in 2D and 3D (sections 4.1-4.4)
PES 1110 Fall 2013, Spendier Lecture 5/Page 1 Toda: - Announcements: Quiz moved to net Monda, Sept 9th due to website glitch! - Finish chapter 3: Vectors - Chapter 4: Motion in 2D and 3D (sections 4.1-4.4)
Kinematics in two Dimensions
 Lecure 5 Chaper 4 Phsics I Kinemaics in wo Dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teachin/phsicsi PHYS.141 Lecure 5 Danlo Deparmen of Phsics and Applied Phsics Toda we are oin o discuss:
Lecure 5 Chaper 4 Phsics I Kinemaics in wo Dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teachin/phsicsi PHYS.141 Lecure 5 Danlo Deparmen of Phsics and Applied Phsics Toda we are oin o discuss:
1 CHAPTER 7 PROJECTILES. 7.1 No Air Resistance
 CHAPTER 7 PROJECTILES 7 No Air Resistance We suppose that a particle is projected from a point O at the oriin of a coordinate system, the y-axis bein vertical and the x-axis directed alon the round The
CHAPTER 7 PROJECTILES 7 No Air Resistance We suppose that a particle is projected from a point O at the oriin of a coordinate system, the y-axis bein vertical and the x-axis directed alon the round The
arxiv:physics/ Oct 2002
 Dedution of Lorentz Transformation from the eistene of absolute rest. Dedution of the speed of light in any frame of referene. Rodrigo de Abreu Centro de Eletrodinâmia e Departamento de Físia do IST Abstrat
Dedution of Lorentz Transformation from the eistene of absolute rest. Dedution of the speed of light in any frame of referene. Rodrigo de Abreu Centro de Eletrodinâmia e Departamento de Físia do IST Abstrat
Electromagnetic Theory Prof. Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctorphys on YouTube Chapter B Notes. Special Relativity. B1. The Rotation Matrix
 Eletromagneti Theory Prof. Ruiz, UNC Asheille, dotorphys on YouTube Chapter B Notes. Speial Relatiity B1. The Rotation Matrix There are two pairs of axes below. The prime axes are rotated with respet to
Eletromagneti Theory Prof. Ruiz, UNC Asheille, dotorphys on YouTube Chapter B Notes. Speial Relatiity B1. The Rotation Matrix There are two pairs of axes below. The prime axes are rotated with respet to
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 03 Due: February 08, 2008 Name:
 Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 03 Due: ebruary 08, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., bo in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 03 Due: ebruary 08, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., bo in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
LECTURE 2 Geometrical Properties of Rod Cross Sections (Part 2) 1 Moments of Inertia Transformation with Parallel Transfer of Axes.
 V. DEMENKO MECHNCS OF MTERLS 05 LECTURE Geometrial Properties of Rod Cross Setions (Part ) Moments of nertia Transformation with Parallel Transfer of xes. Parallel-xes Theorems S Given: a b = S = 0. z
V. DEMENKO MECHNCS OF MTERLS 05 LECTURE Geometrial Properties of Rod Cross Setions (Part ) Moments of nertia Transformation with Parallel Transfer of xes. Parallel-xes Theorems S Given: a b = S = 0. z
Lecture 3 - Lorentz Transformations
 Leture - Lorentz Transformations A Puzzle... Example A ruler is positioned perpendiular to a wall. A stik of length L flies by at speed v. It travels in front of the ruler, so that it obsures part of the
Leture - Lorentz Transformations A Puzzle... Example A ruler is positioned perpendiular to a wall. A stik of length L flies by at speed v. It travels in front of the ruler, so that it obsures part of the
2.2 Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions
 .. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION OF VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS133. Differentiation and Interation of Vector-Valued Functions Simply put, we differentiate and interate vector functions by differentiatin
.. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION OF VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS133. Differentiation and Interation of Vector-Valued Functions Simply put, we differentiate and interate vector functions by differentiatin
Phys101 First Major-111 Zero Version Monday, October 17, 2011 Page: 1
 Monday, October 17, 011 Page: 1 Q1. 1 b The speed-time relation of a moving particle is given by: v = at +, where v is the speed, t t + c is the time and a, b, c are constants. The dimensional formulae
Monday, October 17, 011 Page: 1 Q1. 1 b The speed-time relation of a moving particle is given by: v = at +, where v is the speed, t t + c is the time and a, b, c are constants. The dimensional formulae
ANALYZE In all three cases (a) (c), the reading on the scale is. w = mg = (11.0 kg) (9.8 m/s 2 ) = 108 N.
 Chapter 5 1. We are only concerned with horizontal forces in this problem (ravity plays no direct role). We take East as the +x direction and North as +y. This calculation is efficiently implemented on
Chapter 5 1. We are only concerned with horizontal forces in this problem (ravity plays no direct role). We take East as the +x direction and North as +y. This calculation is efficiently implemented on
the equations for the motion of the particle are written as
 Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 02 Due: ebruary 01, 2008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, ie, box in, star, etc, and write neatly There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work please use lots
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 02 Due: ebruary 01, 2008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, ie, box in, star, etc, and write neatly There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work please use lots
Mathematics Extension 1 Time allowed: 2 hours (plus 5 minutes reading time)
 Name: Teacher: Class: FORT STREET HIGH SCHOOL 0 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE ASSESSMENT TASK : TRIAL HSC Mathematics Extension Time allowed: hours (plus 5 minutes readin time) Syllabus Assessment Area
Name: Teacher: Class: FORT STREET HIGH SCHOOL 0 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE ASSESSMENT TASK : TRIAL HSC Mathematics Extension Time allowed: hours (plus 5 minutes readin time) Syllabus Assessment Area
Exam 2A Solution. 1. A baseball is thrown vertically upward and feels no air resistance. As it is rising
 Exam 2A Solution 1. A baseball is thrown vertically upward and feels no air resistance. As it is risin Solution: Possible answers: A) both its momentum and its mechanical enery are conserved - incorrect.
Exam 2A Solution 1. A baseball is thrown vertically upward and feels no air resistance. As it is risin Solution: Possible answers: A) both its momentum and its mechanical enery are conserved - incorrect.
Remarks Around Lorentz Transformation
 Remarks Around Lorentz Transformation Arm Boris Nima arm.boris@gmail.om Abstrat After diagonalizing the Lorentz Matrix, we find the frame where the Dira equation is one derivation and we alulate the speed
Remarks Around Lorentz Transformation Arm Boris Nima arm.boris@gmail.om Abstrat After diagonalizing the Lorentz Matrix, we find the frame where the Dira equation is one derivation and we alulate the speed
SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I
 University of California, Berkeley Physics 7A Sprin 009 (Yury Kolomensky) SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I Maximum score: 100 points 1. (15 points) Race Stratey Two swimmers need to et from
University of California, Berkeley Physics 7A Sprin 009 (Yury Kolomensky) SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I Maximum score: 100 points 1. (15 points) Race Stratey Two swimmers need to et from
UNDERSTAND MOTION IN ONE AND TWO DIMENSIONS
 SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 UNDERSTAND MOTION IN ONE AND TWO DIMENSIONS MECHANICS Skill 1.1 Calculating displacement, aerage elocity, instantaneous elocity, and acceleration in a gien frame of reference
SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 UNDERSTAND MOTION IN ONE AND TWO DIMENSIONS MECHANICS Skill 1.1 Calculating displacement, aerage elocity, instantaneous elocity, and acceleration in a gien frame of reference
The Lorentz Transform 2
 The Lorentz Transform Chuk Keyser 1/4/13 (Work in Progress) Most reent update: 1/16/13 Forward When I was a junior at UCSB in the 196 s, I took a ourse in Modern Physis that desribed the Speial Theory
The Lorentz Transform Chuk Keyser 1/4/13 (Work in Progress) Most reent update: 1/16/13 Forward When I was a junior at UCSB in the 196 s, I took a ourse in Modern Physis that desribed the Speial Theory
The Geometric Interpretation of Some Mathematical Expressions Containing the Riemann ζ-function
 Mathematis Letters 6; (6): 4-46 http://www.sienepublishinggroup.om/j/ml doi:.648/j.ml.66. The Geometri Interpretation of Some Mathematial Epressions Containing the Riemann ζ-funtion Yuriy N. Zayko Department
Mathematis Letters 6; (6): 4-46 http://www.sienepublishinggroup.om/j/ml doi:.648/j.ml.66. The Geometri Interpretation of Some Mathematial Epressions Containing the Riemann ζ-funtion Yuriy N. Zayko Department
Chapter 1: Kinematics of Particles
 Chapter 1: Kinematics of Particles 1.1 INTRODUCTION Mechanics the state of rest of motion of bodies subjected to the action of forces Static equilibrium of a body that is either at rest or moes with constant
Chapter 1: Kinematics of Particles 1.1 INTRODUCTION Mechanics the state of rest of motion of bodies subjected to the action of forces Static equilibrium of a body that is either at rest or moes with constant
PROJECTILE MOTION. ( ) g y 0. Equations ( ) General time of flight (TOF) General range. Angle for maximum range ("optimum angle")
 PROJECTILE MOTION Equations General time of fliht (TOF) T sin θ y 0 sin( θ) General rane R cos( θ) T R cos θ sin( θ) sin( θ) y 0 Anle for maximum rane ("optimum anle") θ opt atan y 0 atan v f atan v f
PROJECTILE MOTION Equations General time of fliht (TOF) T sin θ y 0 sin( θ) General rane R cos( θ) T R cos θ sin( θ) sin( θ) y 0 Anle for maximum rane ("optimum anle") θ opt atan y 0 atan v f atan v f
F = F x x + F y. y + F z
 ECTION 6: etor Calulus MATH20411 You met vetors in the first year. etor alulus is essentially alulus on vetors. We will need to differentiate vetors and perform integrals involving vetors. In partiular,
ECTION 6: etor Calulus MATH20411 You met vetors in the first year. etor alulus is essentially alulus on vetors. We will need to differentiate vetors and perform integrals involving vetors. In partiular,
1. Linear Motion. Table of Contents. 1.1 Linear Motion: Velocity Time Graphs (Multi Stage) 1.2 Linear Motion: Velocity Time Graphs (Up and Down)
 . LINEAR MOTION www.mathspoints.ie. Linear Motion Table of Contents. Linear Motion: Velocity Time Graphs (Multi Stage). Linear Motion: Velocity Time Graphs (Up and Down).3 Linear Motion: Common Initial
. LINEAR MOTION www.mathspoints.ie. Linear Motion Table of Contents. Linear Motion: Velocity Time Graphs (Multi Stage). Linear Motion: Velocity Time Graphs (Up and Down).3 Linear Motion: Common Initial
Introduction to vectors
 Lecture 4 Introduction to vectors Course website: http://facult.uml.edu/andri_danlov/teaching/phsicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danlov2013/phsics1fall.html 95.141, Fall 2013, Lecture 3 Outline
Lecture 4 Introduction to vectors Course website: http://facult.uml.edu/andri_danlov/teaching/phsicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danlov2013/phsics1fall.html 95.141, Fall 2013, Lecture 3 Outline
Green s function for the wave equation
 Green s funtion for the wave equation Non-relativisti ase January 2019 1 The wave equations In the Lorentz Gauge, the wave equations for the potentials are (Notes 1 eqns 43 and 44): 1 2 A 2 2 2 A = µ 0
Green s funtion for the wave equation Non-relativisti ase January 2019 1 The wave equations In the Lorentz Gauge, the wave equations for the potentials are (Notes 1 eqns 43 and 44): 1 2 A 2 2 2 A = µ 0
METHOD OF IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
 J-Phsis MTHOD OF IMPULS ND MOMNTUM Until now, we hae studied kineatis of partiles, Newton s laws of otion and ethods of work and energ. Newton s laws of otion desribe relation between fores ating on a
J-Phsis MTHOD OF IMPULS ND MOMNTUM Until now, we hae studied kineatis of partiles, Newton s laws of otion and ethods of work and energ. Newton s laws of otion desribe relation between fores ating on a
Class XII - Physics Electromagnetic Waves Chapter-wise Problems
 Class XII - Physis Eletromagneti Waves Chapter-wise Problems Multiple Choie Question :- 8 One requires ev of energy to dissoiate a arbon monoxide moleule into arbon and oxygen atoms The minimum frequeny
Class XII - Physis Eletromagneti Waves Chapter-wise Problems Multiple Choie Question :- 8 One requires ev of energy to dissoiate a arbon monoxide moleule into arbon and oxygen atoms The minimum frequeny
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics. Summer Lecture 2 Velocity and Momentum Read:
 PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics Summer 2010 p sys F net t E W Q sys surr surr L sys net t Lecture 2 Velocity and Momentum Read: 1.6-1.9 Math Experience A) Currently taking Calculus B) Currently taking Calculus
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics Summer 2010 p sys F net t E W Q sys surr surr L sys net t Lecture 2 Velocity and Momentum Read: 1.6-1.9 Math Experience A) Currently taking Calculus B) Currently taking Calculus
Millennium Relativity Acceleration Composition. The Relativistic Relationship between Acceleration and Uniform Motion
 Millennium Relativity Aeleration Composition he Relativisti Relationship between Aeleration and niform Motion Copyright 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat he relativisti priniples developed throughout the six
Millennium Relativity Aeleration Composition he Relativisti Relationship between Aeleration and niform Motion Copyright 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat he relativisti priniples developed throughout the six
UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 8 Kik off with CAS 8 Introdution to vetors 8 Operations on vetors Vetors 8 Magnitude, diretion and omponents of vetors 85 i, j notation 86 Appliations of vetors 87 Review 8 8 Kik off with CAS Eploring
8 Kik off with CAS 8 Introdution to vetors 8 Operations on vetors Vetors 8 Magnitude, diretion and omponents of vetors 85 i, j notation 86 Appliations of vetors 87 Review 8 8 Kik off with CAS Eploring
Physics 101. Vectors. Lecture 2. h0r33fy. EMU Physics Department. Assist. Prof. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN
 Phsics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors ssist. Prof. Dr. li ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department h0r33f www.aovgun.com Coordinate Sstems qcartesian coordinate sstem qpolar coordinate sstem qfrom Cartesian to Polar coordinate
Phsics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors ssist. Prof. Dr. li ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department h0r33f www.aovgun.com Coordinate Sstems qcartesian coordinate sstem qpolar coordinate sstem qfrom Cartesian to Polar coordinate
1. SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES WHEN TWO WAVES OCCUPY THE SAME AREA IN SPACE THEY FORM A NEW WAVE WHICH IS THE MATHEMATICAL SUM OF THE TWO SEPARATE WAVES.
 FW C:\hysis\13 leture\h 18 interferene dse standin rous.dox ae 1 of 13 1. SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES WHEN TWO WAVES OCCUPY THE SAME AREA IN SPACE THEY FORM A NEW WAVE WHICH IS THE MATHEMATICAL SUM OF THE TWO
FW C:\hysis\13 leture\h 18 interferene dse standin rous.dox ae 1 of 13 1. SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES WHEN TWO WAVES OCCUPY THE SAME AREA IN SPACE THEY FORM A NEW WAVE WHICH IS THE MATHEMATICAL SUM OF THE TWO
3. THE SOLUTION OF TRANSFORMATION PARAMETERS
 Deartment of Geosatial Siene. HE SOLUION OF RANSFORMAION PARAMEERS Coordinate transformations, as used in ratie, are models desribing the assumed mathematial relationshis between oints in two retangular
Deartment of Geosatial Siene. HE SOLUION OF RANSFORMAION PARAMEERS Coordinate transformations, as used in ratie, are models desribing the assumed mathematial relationshis between oints in two retangular
Simultaneity. CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity 2. Gedanken (Thought) experiments. The complete Lorentz Transformation. Re-evaluation of Time!
 CHAPTER Speial Theory of Relatiity. The Need for Aether. The Mihelson-Morley Eperiment.3 Einstein s Postulates.4 The Lorentz Transformation.5 Time Dilation and Length Contration.6 Addition of Veloities.7
CHAPTER Speial Theory of Relatiity. The Need for Aether. The Mihelson-Morley Eperiment.3 Einstein s Postulates.4 The Lorentz Transformation.5 Time Dilation and Length Contration.6 Addition of Veloities.7
