Chapter 21 The Electric Field 1: Discrete Charge Distributions
|
|
|
- Russell Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
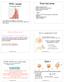
1 hapte The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions onceptual Poblems 3 Two point paticles that have chages of + and 3 ae sepaated b distance d. (a) Use field lines to sketch the electic field in the neighbohood of this sstem. (b) Daw the field lines at distances much geate than d fom the chages. Detemine the oncept (a) We can use the ules fo dawing electic field lines to daw the electic field lines fo this sstem. In the field-line sketch we ve assigned field lines to each chage. (b) At distances much geate than the sepaation distance between the two chages, the sstem of two chaged bodies will look like a single chage of and the field patten will be that due to a point chage of. Fou field lines have been assigned to each chage. (a) (b) 7 Two molecules have dipole moments of eual magnitude. The dipole moments ae oiented in vaious configuations as shown in Figue -34. Detemine the electic-field diection at each of the numbeed locations. Explain ou answes. omment [EPM]: Detemine the oncept Figue -3 shows the electic field due to a single dipole, whee the dipole moment is diected towad the ight. The electic field due two a pai of dipoles can be obtained b supeposing the two electic fields. 3 (a) down up up (b) up ight left (c) down up up (d) down up up
2 hapte hage 3 What is the total chage of all of the potons in. kg of cabon? Pictue the Poblem We can find the numbe of coulombs of positive chage thee ae in. kg of cabon fomq 6ne, whee n is the numbe of atoms in. kg of cabon and the facto of 6 is pesent to account fo the pesence of 6 potons in each atom. We can find the numbe of atoms in. kg of cabon b setting up a popotion elating Avogado s numbe, the mass of cabon, and the molecula mass of cabon to n. See Appendix fo the mola mass of cabon. Expess the positive chage in tems of the electonic chage, the numbe of potons pe atom, and the numbe of atoms in. kg of cabon: Q 6n e Using a popotion, elate the numbe of atoms in. kg of cabon n, to Avogado s numbe and the molecula mass M of cabon: n m N M A n N Am M Substitute fo n to obtain: 6N Ame Q M Substitute numeical values and evaluate Q: 6 6. Q 3 atoms 9 (. kg)(.6 ) mol kg. mol oulomb s Law 7 Thee point chages ae on the x-axis: 6. μ is at x 3. m, 4. μ is at the oigin, and 3 6. μ is at x 3. m. Find the electic foce on.
3 The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 3 Pictue the Poblem exets an attactive electic foce F, on point chage and 3 exets a epulsive electic foce F 3, on point chage. We can find the net electic foce on b adding these foces (that is, b using the supeposition pinciple). F 3, F 3, μ 4.μ Expess the net foce acting on : F F, + F3, Expess the foce that exets on : F, k, 3 6.μ Expess the foce that 3 exets on k 3 F ( 3, ) : 3, x, m Substitute and simplif to obtain: F k k 3, 3, 3 k, 3, Substitute numeical values and evaluate F : F 9 4. μ 6. μ ( )( ) N m / 6. μ (.5 N) ( ) ( ) 3.m 6.m 35 Five identical point chages, each having chage Q, ae euall spaced on a semicicle of adius R as shown in Figue -37. Find the foce (in tems of k, Q, and R) on a chage located euidistant fom the five othe chages. Pictue the Poblem B consideing the smmet of the aa of chaged point paticles, we can see that the component of the foce on is zeo. We can appl oulomb s law and the pinciple of supeposition of foces to find the net foce acting on. Expess the net foce acting on the point chage : F F + F Q on x axis, Q at 45,
4 4 hapte Expess the foce on point chage due to the point chage Q on the x axis: Expess the net foce on point chage due to the point chages at 45 : F Q on x axis, F Q at 45, kq R kq cos45 R kq R Substitute fo F F to obtain: Q at 45, Qon xaxis, The Electic Field and F kq kq + R R kq ( + ) R 37 A point chage of 4. μ is at the oigin. What is the magnitude and diection of the electic field on the x axis at (a) x 6. m, and (b) x m? (c) Sketch the function E x vesus x fo both positive and negative values of x. (Remembe that E x is negative when E points in the x diection.) Pictue the Poblem Let epesent the point chage at the oigin and use oulomb s law fo E due to a point chage to find the electic field at x 6. m and m. (a) Expess the electic field at a point P located a distance x fom a point chage : E k x ˆ ( x ) P, Evaluate this expession fo x 6. m: E (.m) N m ( 6.m) ( 4. μ) (. kn/) (b) Evaluate E at x m: E 9 N m ( m) ( m) ( 4. μ) ( ) (.36 kn/)
5 The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 5 (c) The following gaph was plotted using a speadsheet pogam: E x (kn/) E x (N/) x (m) 4 Two point chages and both have a chage eual to +6. n and ae on the axis at +3. cm and 3. cm espectivel. (a) What is the magnitude and diection of the electic field on the x axis at x 4. cm? (b) What is the foce exeted on a thid chage. n when it is placed on the x axis at x 4. cm? Deleted: Pictue the Poblem The diagam shows the locations of the point chages and and the point on the x axis at which we ae to find E. Fom smmet consideations we can conclude that the component of E at an point on the x axis is zeo. We can use oulomb s law fo the electic field due to point chages and the pinciple of supeposition fo fields to find the field at an point on the x axis and F E to find the foce on a point chage placed on the x axis at x 4. cm., cm n θ 4. θ x, cm E n
6 6 hapte (a) Letting, expess the x- component of the electic field due to one point chage as a function of the distance fom eithe point chage to the point of inteest: Expess E x fo both chages: E E x x k cosθ k cos θ Substitute fo cosθ and, substitute numeical values, and evaluate to obtain: E ( 4. cm) x k.4m k (.4 m) 9 ( N m / )( 6.n)(.4 m) 3 [(.3 m) + (.4 m) ] ( 34.5kN/) ( 35kN/) 3 The magnitude and diection of the electic field at x 4. cm is: (b) Appl F E to find the foce on a point chage placed on the x axis at x 4. cm: 35 F (.n)( 34.5kN/) ( 69 μn) 47 Two point paticles, each having a chage, sit on the base of an euilateal tiangle that has sides of length L as shown in Figue -38. A thid point paticle that has a chage eual to sits at the apex of the tiangle. Whee must a fouth point paticle that has a chage eual to be placed in ode that the electic field at the cente of the tiangle be zeo? (The cente is in the plane of the tiangle and euidistant fom the thee vetices.) Pictue the Poblem The electic field of 4 th chaged point paticle must cancel the sum of the electic fields due to the othe thee chaged point paticles. B smmet, the position of the 4 th chaged point paticle must lie on the vetical centeline of the tiangle. Using tigonomet, one can show that the cente of an euilateal tiangle is a distance L 3 fom each vetex, whee L is the length of the side of the tiangle. Note that the x components of the fields due to the base chaged paticles cancel each othe, so we onl need concen ouselves with the components of the fields due to the chaged point paticles at the vetices of the tiangle. hoose a coodinate sstem in which the oigin is at the midpoint of the base of the tiangle, the +x diection is to the ight, and the + diection is upwad. Deleted: Note that the x components of the electic field vectos add up to zeo.
7 The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 7 3 L 3 E 6 E L 3 L 3 6 E 3 x Expess the condition that must be satisfied if the electic field at the cente of the tiangle is to be zeo: E i i to 4 Substituting fo E, E, E 3, and E 4 ields: ( ) k( ) k( ) k L 3 cos6 ˆj + L 3 cos6 ˆj L 3 ˆ k j + ˆj Solving fo ields: ± The positive solution coesponds to the 4 th point paticle being a distance L 3 above the base of the tiangle, whee it poduces the same stength and same diection electic field caused b the thee chages at the cones of the tiangle. So the chaged point paticle must be placed a distance L 3 below the midpoint of the tiangle. Point hages in Electic Fields 5 The acceleation of a paticle in an electic field depends on /m (the chage-to-mass atio of the paticle). (a) ompute /m fo an electon. (b) What is the magnitude and diection of the acceleation of an electon in a unifom electic field that has a magnitude of N/? (c) ompute the time it takes fo an electon placed at est in a unifom electic field that has a magnitude of N/ to each a speed of.c. (When the speed of an electon appoaches the speed of light c, elativistic kinematics must be used to calculate its motion, but at speeds L 3 Deleted: Because the positive solution coesponds to the 4 th chage being at the cente of the tiangle, it follows that:... [] Deleted: The chaged point paticle must be placed a distance eual to the length of the side of the tiangle divided b the suae oot of thee below the midpoint of the base of the tiangle, whee L is the length of a side of the tiangle.
8 8 hapte of.c o less, non-elativistic kinematics is sufficientl accuate fo most puposes.) (d) How fa does the electon tavel in that time? Pictue the Poblem We can use Newton s second law of motion to find the acceleation of the electon in the unifom electic field and constant-acceleation euations to find the time euied fo it to each a speed of.c and the distance it tavels while acuiing this speed. (a) Use data found at the back of ou text to compute e/m fo an electon: e m e kg /kg (b) Appl Newton s second law to elate the acceleation of the electon to the electic field: Substitute numeical values and evaluate a: F ee a net m a e m e 9 (.6 )( N/) m/s m/s kg The diection of the acceleation of an electon is opposite the electic field. (c) Using the definition of acceleation, elate the time euied fo an electon to each.c to its acceleation: Substitute numeical values and evaluate Δt: (d) Use a constant-acceleation euation to expess the distance the electon tavels in a given time inteval: Substitute numeical values and evaluate Δx: v.c Δ t a a 8 ( m/s)..998 t.759 Δ 3.μs Δx v Δt + i a ( Δt) o, because v i, Δx a Δt ( ) m/s.74 μs 3 (.759 m/s )(.74 s) Δx μ.3m Deleted: Page Beak Deleted: Δx v Δt ( v v o, because v i, Δx vf Δt av i + Deleted: (d) The distance the electon tavels in a given time inteval is the poduct of its aveage speed and the elapsed time: Deleted: Substitute numeical values and evaluate Δx:... [] f
9 The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 9 57 An electon stats at the position shown in Figue -39 with an initial speed v 5. 6 m/s at 45º to the x axis. The electic field is in the + diection and has a magnitude of N/. The black lines in the figue ae chaged metal plates. On which plate and at what location will the electon stike? Pictue the Poblem We can use constant-acceleation euations to expess the x and coodinates of the electon in tems of the paamete t and Newton s second law to expess the constant acceleation in tems of the electic field. Eliminating the paamete will ield an euation fo as a function of x,, and m. We can decide whethe the electon will stike the uppe plate b finding the maximum value of its coodinate. Should we find that it does not stike the uppe plate, we can detemine whee it stikes the lowe plate b setting (x). Ignoe an effects of gavitational foces. Expess the x and coodinates of the electon as functions of time: Appl Newton s second law to elate the acceleation of the electon to the net foce acting on it: Substitute in the -coodinate euation to obtain: Eliminate the paamete t between the two euations to obtain: To find max, set d/dx fo extema: Solve fo x to obtain: Substitute x in (x) and simplif to obtain max : x ( v cosθ )t and ( ) v sinθ t a t F a net, me ee m e ( v sin ) t t θ ee m ( x) ( tanθ ) x x d dx x' e ee () m v cos θ ee tanθ x' mev cos θ fo extema mev sin θ (See emak below.) ee max mev sin θ ee e
10 hapte Substitute numeical values and evaluate max : 3 6 ( 9.9 kg)( 5. m/s) sin 9 3 (.6 )( 3.5 N/) 45 max. cm and, because the plates ae sepaated b cm, the electon does not stike the uppe plate. To detemine whee the electon will stike the lowe plate, set in euation () and solve fo x to obtain: mev sin θ x ee Substitute numeical values and evaluate x: x 3 6 ( 9.9 kg)( 5. m/s) 9 3 (.6 )( 3.5 N/) sin 9 4.cm Deleted: Remaks: x is an extemum, that is, eithe a maximum o a minimum. To show that it is a maximum we need to show that d /dx, evaluated at x, is negative. A simple altenative is to use ou gaphing calculato to show that the gaph of (x) is a maximum at x. Yet anothe altenative is to ecognize that, because euation () is uadatic and the coefficient of x is negative, its gaph is a paabola that opens downwad. Geneal Poblems 6 Show that it is onl possible to place one isolated poton in an odina empt coffee cup b consideing the following situation. Assume the fist poton is fixed at the bottom of the cup. Detemine the distance diectl above this poton whee a second poton would be in euilibium. ompae this distance to the depth of an odina coffee cup to complete the agument. Pictue the Poblem Euilibium of the second poton euies that the sum of the electic and gavitational foces acting on it be zeo. Let the upwad diection be the + diection and appl the condition fo euilibium to the second poton. Appl F to the second poton: Fe + Fg o kp mpg h h kp m g p omment [EPM]: DAVID: M coffee mug is moe than 5 in high, so I changed mug to cup. omment [MSOffice3]: At close distances, potons will bind togethe b the stong nuclea foce. This uestion confuses students. omment [EPM4]: To the best of m knowledge, Helium- does not exist. Deleted:
11 Substitute numeical values and evaluate h: The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions h N m 9 (.6 ) 7 (.673 kg)( 9.8 m/s ) cm 5 in This sepaation of about 5 in is geate than the height of a tpical coffee cup. Thus the fist poton will epel the second one out of the cup and the maximum numbe of potons in the cup is one. 65 A positive chage Q is to be divided into two positive point chages and. Show that, fo a given sepaation D, the foce exeted b one chage on the othe is geatest if Q. Pictue the Poblem We can use oulomb s law to expess the foce exeted on one chage b the othe and then set the deivative of this expession eual to zeo to find the distibution of the chage that maximizes this foce. Using oulomb s law, expess the foce that eithe chage exets on the othe: k F D Expess in tems of Q and : Q Substitute fo to obtain: k ( Q ) F D Diffeentiate F with espect to and set this deivative eual to zeo fo exteme values: Solve fo to obtain: df d k d D d k D fo extema [ ( Q )] [ ( ) + Q ] Q Q Q
12 hapte To detemine whethe a maximum o a minimum exists at Q, diffeentiate F a second time and evaluate this deivative at Q : d F k d [ Q ] d D d k ( ) D < independentl of. Q maximizes F. 69 A igid.-m-long od is pivoted about its cente (Figue -4). A chage 5. 7 is placed on one end of the od, and a chage is placed a distance d. cm diectl below it. (a) What is the foce exeted b on? (b) What is the toue (measued about the otation axis) due to that foce? (c) To countebalance the attaction between the two chages, we hang a block 5. cm fom the pivot as shown. What value should we choose fo the mass of the block? (d) We now move the block and hang it a distance of 5. cm fom the balance point, on the same side of the balance as the chage. Keeping the same, and d the same, what value should we choose fo to keep this appaatus in balance? Pictue the Poblem We can use oulomb s law, the definition of toue, and the condition fo otational euilibium to find the electostatic foce between the two chaged bodies, the toue this foce poduces about an axis though the cente of the od, and the mass euied to maintain euilibium when it is located eithe 5. cm to the ight o to the left of the mid-point of the od. (a) Using oulomb s law, expess the electic foce between the two chages: k F d Substitute numeical values and evaluate F: F 9 7 ( N m / )( 5. ) (. m).47 N.5 N (b) The toue (measued about the otation axis) due to the foce F is: Substitute numeical values and evaluate τ: τ Fl τ (.47 N)(.5 m).4 N m counteclockwise.. N m, (c) Appl τ cente of to the od: the od τ τ mgl' m gl' Deleted:
13 Substitute numeical values and The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 3 m.4 N m evaluate m: ( 9.8m/s )(.5 m ).4583 kg 45.8g (d) Appl τ cente of to the od: τ + mgl' the od Substitute fo τ to obtain: Fl + mgl' Substituting fo F gives: k ' d l + mg ' d mgl' ' k l whee is the euied chage. Substitute numeical values and evaluate : ' (.m) (.458kg)( 9.8m/s )(.5 m) ( N m / )( 5. )(.5m) 7 Two point chages have a total chage of μ and ae sepaated b.6 m. (a) Find the chage of each paticle if the paticles epel each othe with a foce of N. (b) Find the foce on each paticle if the chage on each paticle is μ. Pictue the Poblem Let the numeal denote one of the point chages and the numeal the othe. Knowing the total chage on the two sphees, we can use oulomb s law to find the chage on each of them. A second application of oulomb s law when the sphees ca the same chage and ae.6 m apat will ield the foce each exets on the othe. (a) Use oulomb s law to expess the epulsive foce each point chage exets on the othe: Expess in tems of the total chage and : k F, Q Substitute fo to obtain: k ( Q ) F,
14 4 hapte Substitute numeical values to obtain: N 9 ( N m / )[( μ) ] (.6m) Simplif to obtain the uadatic euation: Use the uadatic fomula o ou gaphing calculato to obtain: Hence the chages on the paticles ae: (b) Use oulomb s law to expess the epulsive foce each point chage exets on the othe when μ: ( μ) + 486( ) + μ 7.9 and 7μ μ 7.9 μ and 7 μ k F, Substitute numeical values and evaluate F: F ( ) ( N m / ) 9 μ (.6m) 5 N 77 Figue -46 shows a dumbbell consisting of two identical small paticles, each of mass m, attached to the ends of a thin (massless) od of length a that is pivoted at its cente. The paticles ca chages of + and, and the dumbbell is located in a unifom electic field E. Show that fo small values of the angle θ between the diection of the dipole and the diection of the electic field, the sstem displas a otational fom of simple hamonic motion, and obtain an expession fo the peiod of that motion. Pictue the Poblem We can appl Newton s second law in otational fom to obtain the diffeential euation of motion of the dipole and then use the small angle appoximation sinθ θ to show that the dipole expeiences a linea estoing toue and, hence, will expeience simple hamonic motion. Appl τ Iα to the dipole: d θ pe sinθ I dt whee τ is negative because acts in such a diection as to decease θ.
15 The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 5 Fo small values of θ, sinθ θ d θ peθ I and: dt Expess the moment of inetia of the dipole: Relate the dipole moment of the dipole to its chage and the chage sepaation: Substitute fo p and I to obtain: Expess the peiod of a simple hamonic oscillato: I ma p a d θ ma aeθ dt o d θ E θ dt ma the diffeential euation fo a simple hamonic oscillato with angula feuenc ω E ma. π T ω Substitute fo ω and simplif to obtain: T π ma E 79 An electon (chage e, mass m) and a positon (chage +e, mass m) evolve aound thei common cente of mass unde the influence of thei attactive coulomb foce. Find the speed v of each paticle in tems of e, m, k, and thei sepaation distance L. Pictue the Poblem The foces the electon and the poton exet on each othe constitute an action-and-eaction pai. Because the magnitudes of thei chages ae eual and thei masses ae the same, we find the speed of each paticle b finding the speed of eithe one. We ll appl oulomb s foce law fo point chages and Newton s second law to elate v to e, m, k, and thei sepaation distance L. Appl Newton s second law to the positon to obtain: ke L v ke m mv L L
16 6 hapte Solving fo v gives: v ke ml 85 Duing a famous expeiment in 99, Enest Ruthefod shot doubl ionized helium nuclei (also known as alpha paticles) at a gold foil. He discoveed that vituall all of the mass of an atom esides in an extemel compact nucleus. Suppose that duing such an expeiment, an alpha paticle fa fom the foil has an initial kinetic eneg of 5. MeV. If the alpha paticle is aimed diectl at the gold nucleus, and the onl foce acting on it is the electic foce of epulsion exeted on it b the gold nucleus, how close will it appoach the gold nucleus befoe tuning back? That is, what is the minimum cente-to-cente sepaation of the alpha paticle and the gold nucleus? omment [MSOffice5]: What???? Pictue the Poblem The wok done b the electic field of the gold nucleus changes the kinetic eneg of the alpha paticle eventuall binging it to est. We can appl the wok-kinetic eneg theoem to deive an expession fo the distance of closest appoach. Because the epulsive oulomb foce F e vaies with distance, we ll have to evaluate Fe d in ode to find the wok done on the alpha paticles b this foce. Appl the wok-kinetic eneg theoem to the alpha paticle to obtain: min Wnet Fe d ΔK o, because min min k e Fe d K f, min d 58ke K ( )( 79e) i d and Evaluating the integal ields: min 58ke 58ke min K i Solve fo min and simplif to obtain: 58ke min K i
17 The Electic Field : Discete hage Distibutions 7 Substitute numeical values and evaluate min : min 9 N m Mev ev 9 (.6 ) 9 J m 87 In Poblem 86, thee is a desciption of the Millikan expeiment used to detemine the chage on the electon. Duing the expeiment, a switch is used to evese the diection of the electic field without changing its magnitude, so that one can measue the teminal speed of the micosphee both as it is moving upwad and as it is moving downwad. Let v u epesent the teminal speed when the paticle is moving up, and v d the teminal speed when moving down. (a) If we let u v u + v d, show that 3πηu E, whee is the micosphee s net chage. Fo the pupose of detemining, what advantage does measuing both v u and v d have ove measuing onl one teminal speed? (b) Because chage is uantized, u can onl change b steps of magnitude N, whee N is an intege. Using the data fom Poblem 86, calculate Δu. Pictue the Poblem The fee bod diagam shows the foces acting on the micosphee of mass m and having an excess chage of Ne when the electic field is downwad. Unde teminal-speed conditions the sphee is in euilibium unde the influence of the electic foce F e, its weight mg, and the dag foce F d. We can appl Newton s second law, unde teminalspeed conditions, to elate the numbe of excess chages N on the sphee to its mass and, using Stokes law, to its teminal speed. (a) Appl Newton s second law to the micosphee when the electic field is downwad: Substitute fo F e and obtain: F d, teminal to F e mg Fd ma o, because a, F mg F m, Ne e d,teminal F e mg F d E mg 6πη vu o, because Ne, NeE mg 6πη vu
18 8 hapte Solve fo v u to obtain: With the field pointing upwad, the electic foce is downwad and the application of Newton s second law to the micosphee ields: Solve fo v d to obtain: v u F NeE mg () 6πη d, teminal Fe mg o 6πη vd NeE mg v d NeE + mg () 6πη Add euations () and () and simplif to obtain: NeE mg NeE + mg NeE E u vu + vd + 6πη 6πη 3πη 3πη Measuing both v u and v d has the advantage that ou don t need to know the mass of the micosphee. (b) Letting Δu epesent the change in the teminal speed of the micosphee due to a gain (o loss) of one electon we have: Δ + u v N v N Noting that Δv will be the same whethe the micosphee is moving upwad o downwad, expess its teminal speed when it is moving upwad with N electonic chages on it: v N NeE mg 6πη Expess its teminal speed upwad when it has N + electonic chages: v N + ( N + ) ee mg 6πη Substitute and simplif to obtain: ( N + ) Substitute numeical values and evaluate Δu: Δu 6πη ee 6πη ee mg NeE mg 6πη 9 4 (.6 )( 6. N/) 5 π (.8 Pa m)( 5.5 m) Δu 7 6 5μm/s
19 Page 7: [] Deleted Lea Mills 9/3/7 7:5: PM Because the positive solution coesponds to the 4 th chage being at the cente of the tiangle, it follows that: L 3 Page 8: [] Deleted Lea Mills 9/3/7 7:54: PM Substitute numeical values and evaluate Δx: 8 [(.)(.998 m/s) ](.74 s).3m Δx μ
7.2. Coulomb s Law. The Electric Force
 Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Electrostatics. 1. Show does the force between two point charges change if the dielectric constant of the medium in which they are kept increase?
 Electostatics 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of the medium in which they ae kept incease? 2. A chaged od P attacts od R whee as P epels anothe chaged od
Electostatics 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of the medium in which they ae kept incease? 2. A chaged od P attacts od R whee as P epels anothe chaged od
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
ELECTRIC CHARGE AND ELECTRIC FIELD
 LCTRIC CHARG AND LCTRIC FILD (a) IDNTIFY and ST UP: Use the chage of one electon ( 6 C) to find the numbe of electons euied to poduce the net chage XCUT: The numbe of ecess electons needed to poduce net
LCTRIC CHARG AND LCTRIC FILD (a) IDNTIFY and ST UP: Use the chage of one electon ( 6 C) to find the numbe of electons euied to poduce the net chage XCUT: The numbe of ecess electons needed to poduce net
anubhavclasses.wordpress.com CBSE Solved Test Papers PHYSICS Class XII Chapter : Electrostatics
 CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
Electrostatics. 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative object: excess of electrons
 Electostatics IB 12 1) electic chage: 2 types of electic chage: positive and negative 2) chaging by fiction: tansfe of electons fom one object to anothe 3) positive object: lack of electons negative object:
Electostatics IB 12 1) electic chage: 2 types of electic chage: positive and negative 2) chaging by fiction: tansfe of electons fom one object to anothe 3) positive object: lack of electons negative object:
Chapter 22: Electric Fields. 22-1: What is physics? General physics II (22102) Dr. Iyad SAADEDDIN. 22-2: The Electric Field (E)
 Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Chapter 22 The Electric Field II: Continuous Charge Distributions
 Chapte The lectic Field II: Continuous Chage Distibutions A ing of adius a has a chage distibution on it that vaies as l(q) l sin q, as shown in Figue -9. (a) What is the diection of the electic field
Chapte The lectic Field II: Continuous Chage Distibutions A ing of adius a has a chage distibution on it that vaies as l(q) l sin q, as shown in Figue -9. (a) What is the diection of the electic field
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Problem Solutions
 Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
Physics 11 Chapter 20: Electric Fields and Forces
 Physics Chapte 0: Electic Fields and Foces Yesteday is not ous to ecove, but tomoow is ous to win o lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the futue. When I am depessed
Physics Chapte 0: Electic Fields and Foces Yesteday is not ous to ecove, but tomoow is ous to win o lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the futue. When I am depessed
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam)
 (Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
Physics C Rotational Motion Name: ANSWER KEY_ AP Review Packet
 Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
20-9 ELECTRIC FIELD LINES 20-9 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL. Answers to the Conceptual Questions. Chapter 20 Electricity 241
 Chapte 0 Electicity 41 0-9 ELECTRIC IELD LINES Goals Illustate the concept of electic field lines. Content The electic field can be symbolized by lines of foce thoughout space. The electic field is stonge
Chapte 0 Electicity 41 0-9 ELECTRIC IELD LINES Goals Illustate the concept of electic field lines. Content The electic field can be symbolized by lines of foce thoughout space. The electic field is stonge
Electricity Revision ELECTRICITY REVISION KEY CONCEPTS TERMINOLOGY & DEFINITION. Physical Sciences X-Sheets
 Electicity Revision KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on the following: Stating and apply Coulomb s Law. Defining electical field stength and applying the deived equations. Dawing electical field
Electicity Revision KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on the following: Stating and apply Coulomb s Law. Defining electical field stength and applying the deived equations. Dawing electical field
AP Physics - Coulomb's Law
 AP Physics - oulomb's Law We ve leaned that electons have a minus one chage and potons have a positive one chage. This plus and minus one business doesn t wok vey well when we go in and ty to do the old
AP Physics - oulomb's Law We ve leaned that electons have a minus one chage and potons have a positive one chage. This plus and minus one business doesn t wok vey well when we go in and ty to do the old
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics Courseware Physics II Electric Field and Force
 Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
The Millikan Experiment: Determining the Elementary Charge
 LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
4. Compare the electric force holding the electron in orbit ( r = 0.53
 Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
16.1 Permanent magnets
 Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electric Charge and Field
 lectic Chage and ield Chapte 6 (Giancoli) All sections ecept 6.0 (Gauss s law) Compaison between the lectic and the Gavitational foces Both have long ange, The electic chage of an object plas the same
lectic Chage and ield Chapte 6 (Giancoli) All sections ecept 6.0 (Gauss s law) Compaison between the lectic and the Gavitational foces Both have long ange, The electic chage of an object plas the same
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Magnetic Field. Conference 6. Physics 102 General Physics II
 Physics 102 Confeence 6 Magnetic Field Confeence 6 Physics 102 Geneal Physics II Monday, Mach 3d, 2014 6.1 Quiz Poblem 6.1 Think about the magnetic field associated with an infinite, cuent caying wie.
Physics 102 Confeence 6 Magnetic Field Confeence 6 Physics 102 Geneal Physics II Monday, Mach 3d, 2014 6.1 Quiz Poblem 6.1 Think about the magnetic field associated with an infinite, cuent caying wie.
PHYSICS 272 Electric & Magnetic Interactions
 PHYS 7: Matte and Inteactions II -- Electic And Magnetic Inteactions http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic_pogams/couses/phys7/ PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Lectue 3 Chaged Objects; Polaization
PHYS 7: Matte and Inteactions II -- Electic And Magnetic Inteactions http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic_pogams/couses/phys7/ PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Lectue 3 Chaged Objects; Polaization
17.1 Electric Potential Energy. Equipotential Lines. PE = energy associated with an arrangement of objects that exert forces on each other
 Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
15 B1 1. Figure 1. At what speed would the car have to travel for resonant oscillations to occur? Comment on your answer.
 Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) F:EasteHolidaysAssignmentAns.doc Easte Holidays Assignment Answe Fom 6B Subject: Physics. (a) State the conditions fo a body to undego simple hamonic motion. ( mak) (a)
Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) F:EasteHolidaysAssignmentAns.doc Easte Holidays Assignment Answe Fom 6B Subject: Physics. (a) State the conditions fo a body to undego simple hamonic motion. ( mak) (a)
3.8.1 Electric Potential Due to a System of Two Charges. Figure Electric dipole
 3.8 Solved Poblems 3.8.1 Electic Potential Due to a System o Two Chages Conside a system o two chages shown in Figue 3.8.1. Figue 3.8.1 Electic dipole Find the electic potential at an abitay point on the
3.8 Solved Poblems 3.8.1 Electic Potential Due to a System o Two Chages Conside a system o two chages shown in Figue 3.8.1. Figue 3.8.1 Electic dipole Find the electic potential at an abitay point on the
Physics 4A Chapter 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane
 Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics Electrostatics: Coulomb s Law
 A C U L T Y O E D U C A T I O N Depatment of Cuiculum and Pedagogy Physics Electostatics: Coulomb s Law Science and Mathematics Education Reseach Goup Suppoted by UBC Teaching and Leaning Enhancement und
A C U L T Y O E D U C A T I O N Depatment of Cuiculum and Pedagogy Physics Electostatics: Coulomb s Law Science and Mathematics Education Reseach Goup Suppoted by UBC Teaching and Leaning Enhancement und
Chapter 4. Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapter 7-8 Rotational Motion
 Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Circular Motion & Torque Test Review. The period is the amount of time it takes for an object to travel around a circular path once.
 Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Electric Field. y s +q. Point charge: Uniformly charged sphere: Dipole: for r>>s :! ! E = 1. q 1 r 2 ˆr. E sphere. at <0,r,0> at <0,0,r>
 Electic Field Point chage: E " ˆ Unifomly chaged sphee: E sphee E sphee " Q ˆ fo >R (outside) fo >s : E " s 3,, at z y s + x Dipole moment: p s E E s "#,, 3 s "#,, 3 at
Electic Field Point chage: E " ˆ Unifomly chaged sphee: E sphee E sphee " Q ˆ fo >R (outside) fo >s : E " s 3,, at z y s + x Dipole moment: p s E E s "#,, 3 s "#,, 3 at
CHAPTER 25 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
 CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
PHYS 1114, Lecture 21, March 6 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
EELE 3331 Electromagnetic I Chapter 4. Electrostatic fields. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
UNIT 3:Electrostatics
 The study of electic chages at est, the foces between them and the electic fields associated with them. UNIT 3:lectostatics S7 3. lectic Chages and Consevation of chages The electic chage has the following
The study of electic chages at est, the foces between them and the electic fields associated with them. UNIT 3:lectostatics S7 3. lectic Chages and Consevation of chages The electic chage has the following
ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FORCES
 ELECTRIC CHARGES AND ORCES 5 Conceptual Questions 5.1. An insulato can be chaged. Plastic is an insulato. A plastic od can be chaged by ubbing it with wool. 5.. A conducto can be chaged. A conducto can
ELECTRIC CHARGES AND ORCES 5 Conceptual Questions 5.1. An insulato can be chaged. Plastic is an insulato. A plastic od can be chaged by ubbing it with wool. 5.. A conducto can be chaged. A conducto can
Phys 201A. Homework 5 Solutions
 Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
AP-C WEP. h. Students should be able to recognize and solve problems that call for application both of conservation of energy and Newton s Laws.
 AP-C WEP 1. Wok a. Calculate the wok done by a specified constant foce on an object that undegoes a specified displacement. b. Relate the wok done by a foce to the aea unde a gaph of foce as a function
AP-C WEP 1. Wok a. Calculate the wok done by a specified constant foce on an object that undegoes a specified displacement. b. Relate the wok done by a foce to the aea unde a gaph of foce as a function
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Centripetal Force OBJECTIVE INTRODUCTION APPARATUS THEORY
 Centipetal Foce OBJECTIVE To veify that a mass moving in cicula motion expeiences a foce diected towad the cente of its cicula path. To detemine how the mass, velocity, and adius affect a paticle's centipetal
Centipetal Foce OBJECTIVE To veify that a mass moving in cicula motion expeiences a foce diected towad the cente of its cicula path. To detemine how the mass, velocity, and adius affect a paticle's centipetal
06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page ) A body A of mass M while falling vetically downwads unde gavity beaks into two pats, a body B of mass ( / ) M and a body C of mass ( / ) M. The cente of mass of bodies B and
06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page ) A body A of mass M while falling vetically downwads unde gavity beaks into two pats, a body B of mass ( / ) M and a body C of mass ( / ) M. The cente of mass of bodies B and
Charges, Coulomb s Law, and Electric Fields
 Q&E -1 Chages, Coulomb s Law, and Electic ields Some expeimental facts: Expeimental fact 1: Electic chage comes in two types, which we call (+) and (). An atom consists of a heavy (+) chaged nucleus suounded
Q&E -1 Chages, Coulomb s Law, and Electic ields Some expeimental facts: Expeimental fact 1: Electic chage comes in two types, which we call (+) and (). An atom consists of a heavy (+) chaged nucleus suounded
KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION
 EPER S AWS OF PANETARY MOTION 1. Intoduction We ae now in a position to apply what we have leaned about the coss poduct and vecto valued functions to deive eple s aws of planetay motion. These laws wee
EPER S AWS OF PANETARY MOTION 1. Intoduction We ae now in a position to apply what we have leaned about the coss poduct and vecto valued functions to deive eple s aws of planetay motion. These laws wee
Physics NYB problem set 5 solution
 Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
From last times. MTE1 results. Quiz 1. GAUSS LAW for any closed surface. What is the Electric Flux? How to calculate Electric Flux?
 om last times MTE1 esults Mean 75% = 90/120 Electic chages and foce Electic ield and was to calculate it Motion of chages in E-field Gauss Law Toda: Moe on Gauss law and conductos in electostatic equilibium
om last times MTE1 esults Mean 75% = 90/120 Electic chages and foce Electic ield and was to calculate it Motion of chages in E-field Gauss Law Toda: Moe on Gauss law and conductos in electostatic equilibium
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
Rotational Motion. Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart
 Rotational Motion & Angula Momentum Rotational Motion Evey quantity that we have studied with tanslational motion has a otational countepat TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angula Position Velocity
Rotational Motion & Angula Momentum Rotational Motion Evey quantity that we have studied with tanslational motion has a otational countepat TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angula Position Velocity
b) (5) What average force magnitude was applied by the students working together?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
ELECTROSTATICS::BHSEC MCQ 1. A. B. C. D.
 ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
to point uphill and to be equal to its maximum value, in which case f s, max = μsfn
 Chapte 6 16. (a) In this situation, we take f s to point uphill and to be equal to its maximum value, in which case f s, max = μsf applies, whee μ s = 0.5. pplying ewton s second law to the block of mass
Chapte 6 16. (a) In this situation, we take f s to point uphill and to be equal to its maximum value, in which case f s, max = μsf applies, whee μ s = 0.5. pplying ewton s second law to the block of mass
F g. = G mm. m 1. = 7.0 kg m 2. = 5.5 kg r = 0.60 m G = N m 2 kg 2 = = N
 Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
! E da = 4πkQ enc, has E under the integral sign, so it is not ordinarily an
 Physics 142 Electostatics 2 Page 1 Electostatics 2 Electicity is just oganized lightning. Geoge Calin A tick that sometimes woks: calculating E fom Gauss s law Gauss s law,! E da = 4πkQ enc, has E unde
Physics 142 Electostatics 2 Page 1 Electostatics 2 Electicity is just oganized lightning. Geoge Calin A tick that sometimes woks: calculating E fom Gauss s law Gauss s law,! E da = 4πkQ enc, has E unde
Multiple choice questions [100 points] As shown in the figure, a mass M is hanging by three massless strings from the ceiling of a room.
![Multiple choice questions [100 points] As shown in the figure, a mass M is hanging by three massless strings from the ceiling of a room. Multiple choice questions [100 points] As shown in the figure, a mass M is hanging by three massless strings from the ceiling of a room.](/thumbs/94/119386670.jpg) Multiple choice questions [00 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefully. Fill the coect ule on you scanton sheet. Each coect answe is woth 4 points. Each question has exactly
Multiple choice questions [00 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefully. Fill the coect ule on you scanton sheet. Each coect answe is woth 4 points. Each question has exactly
PHYS 2135 Exam I February 13, 2018
 Exam Total /200 PHYS 2135 Exam I Febuay 13, 2018 Name: Recitation Section: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each Choose the best o most nealy coect answe Fo questions 6-9, solutions must begin
Exam Total /200 PHYS 2135 Exam I Febuay 13, 2018 Name: Recitation Section: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each Choose the best o most nealy coect answe Fo questions 6-9, solutions must begin
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
AP Physics Electric Potential Energy
 AP Physics lectic Potential negy Review of some vital peviously coveed mateial. The impotance of the ealie concepts will be made clea as we poceed. Wok takes place when a foce acts ove a distance. W F
AP Physics lectic Potential negy Review of some vital peviously coveed mateial. The impotance of the ealie concepts will be made clea as we poceed. Wok takes place when a foce acts ove a distance. W F
- 5 - TEST 1R. This is the repeat version of TEST 1, which was held during Session.
 - 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
- 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
Electric Field, Potential Energy, & Voltage
 Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
CHECK YOUR GRASP. +q +2q A B. D 2q +q
 J-Physics XCIS 1 CHCK YOU GASP SLCT TH COCT ALTNATIV (ONLY ON COCT ANSW) 1. Using mass (M), length (L), time (T) and cuent as fundamental uantities, the dimension of pemittivity is : ML T A M 1 L T 4 A
J-Physics XCIS 1 CHCK YOU GASP SLCT TH COCT ALTNATIV (ONLY ON COCT ANSW) 1. Using mass (M), length (L), time (T) and cuent as fundamental uantities, the dimension of pemittivity is : ML T A M 1 L T 4 A
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE Physics Department Tutorial: Electric Fields (solutions)
 JJ 5 H Physics (646) Electic Fields_tutsoln JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE Physics Depatment Tutoial: Electic Fields (solutions) No Solution LO Electic field stength at a point in an electic field is defined as
JJ 5 H Physics (646) Electic Fields_tutsoln JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE Physics Depatment Tutoial: Electic Fields (solutions) No Solution LO Electic field stength at a point in an electic field is defined as
Phys102 Second Major-182 Zero Version Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1
 Monday, Mach 5, 019 Page: 1 Q1. Figue 1 shows thee pais of identical conducting sphees that ae to be touched togethe and then sepaated. The initial chages on them befoe the touch ae indicated. Rank the
Monday, Mach 5, 019 Page: 1 Q1. Figue 1 shows thee pais of identical conducting sphees that ae to be touched togethe and then sepaated. The initial chages on them befoe the touch ae indicated. Rank the
 Page 1 of 6 Physics II Exam 1 155 points Name Discussion day/time Pat I. Questions 110. 8 points each. Multiple choice: Fo full cedit, cicle only the coect answe. Fo half cedit, cicle the coect answe and
Page 1 of 6 Physics II Exam 1 155 points Name Discussion day/time Pat I. Questions 110. 8 points each. Multiple choice: Fo full cedit, cicle only the coect answe. Fo half cedit, cicle the coect answe and
Between any two masses, there exists a mutual attractive force.
 YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit 2) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit 2) Circular Motion
 AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) Cicula Motion No. kill Done 1 Know that cicula motion efes to motion in a cicle of constant adius Know that cicula motion is conveniently descibed
AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) AH Mechanics Checklist (Unit ) Cicula Motion No. kill Done 1 Know that cicula motion efes to motion in a cicle of constant adius Know that cicula motion is conveniently descibed
PHYSICS 272H Electric & Magnetic Interactions
 PHYSICS 7H Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Physics couse home page: http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic-pogams/couses/all_couses.php Blackboad Lean: https://mycouses.pudue.edu/webapps/login/ Couse Content
PHYSICS 7H Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Physics couse home page: http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic-pogams/couses/all_couses.php Blackboad Lean: https://mycouses.pudue.edu/webapps/login/ Couse Content
Phys 201A. Homework 6 Solutions. F A and F r. B. According to Newton s second law, ( ) ( )2. j = ( 6.0 m / s 2 )ˆ i ( 10.4m / s 2 )ˆ j.
 7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
4.[1pt] Two small spheres with charges -4 C and -9 C are held 9.5 m apart. Find the magnitude of the force between them.
![4.[1pt] Two small spheres with charges -4 C and -9 C are held 9.5 m apart. Find the magnitude of the force between them. 4.[1pt] Two small spheres with charges -4 C and -9 C are held 9.5 m apart. Find the magnitude of the force between them.](/thumbs/75/72362800.jpg) . [pt] A peson scuffing he feet on a wool ug on a y ay accumulates a net chage of - 4.uC. How many ecess electons oes this peson get? Coect, compute gets:.63e+4. [pt] By how much oes he mass incease? Coect,
. [pt] A peson scuffing he feet on a wool ug on a y ay accumulates a net chage of - 4.uC. How many ecess electons oes this peson get? Coect, compute gets:.63e+4. [pt] By how much oes he mass incease? Coect,
Look over Chapter 22 sections 1-8 Examples 2, 4, 5, Look over Chapter 16 sections 7-9 examples 6, 7, 8, 9. Things To Know 1/22/2008 PHYS 2212
 PHYS 1 Look ove Chapte sections 1-8 xamples, 4, 5, PHYS 111 Look ove Chapte 16 sections 7-9 examples 6, 7, 8, 9 Things To Know 1) What is an lectic field. ) How to calculate the electic field fo a point
PHYS 1 Look ove Chapte sections 1-8 xamples, 4, 5, PHYS 111 Look ove Chapte 16 sections 7-9 examples 6, 7, 8, 9 Things To Know 1) What is an lectic field. ) How to calculate the electic field fo a point
Electric Forces: Coulomb s Law
 Electic Foces: Coulomb s Law All the matte aound you contains chaged paticles, and it is the electic foces between these chaged paticles that detemine the stength of the mateials and the popeties of the
Electic Foces: Coulomb s Law All the matte aound you contains chaged paticles, and it is the electic foces between these chaged paticles that detemine the stength of the mateials and the popeties of the
( ) ( ) Review of Force. Review of Force. r = =... Example 1. What is the dot product for F r. Solution: Example 2 ( )
 : PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
: PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapter Sixteen: Electric Charge and Electric Fields
 Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
 CHAPTER 0 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE 7 0. ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic
CHAPTER 0 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE 7 0. ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8. Lab 5. Magnetism
 Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Objects usually are charged up through the transfer of electrons from one object to the other.
 1 Pat 1: Electic Foce 1.1: Review of Vectos Review you vectos! You should know how to convet fom pola fom to component fom and vice vesa add and subtact vectos multiply vectos by scalas Find the esultant
1 Pat 1: Electic Foce 1.1: Review of Vectos Review you vectos! You should know how to convet fom pola fom to component fom and vice vesa add and subtact vectos multiply vectos by scalas Find the esultant
PHYS Summer Professor Caillault Homework Solutions. Chapter 5
 PHYS 1111 - Summe 2007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 5 7. Pictue the Poblem: The ball is acceleated hoizontally fom est to 98 mi/h ove a distance of 1.7 m. Stategy: Use equation 2-12 to
PHYS 1111 - Summe 2007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 5 7. Pictue the Poblem: The ball is acceleated hoizontally fom est to 98 mi/h ove a distance of 1.7 m. Stategy: Use equation 2-12 to
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Objectives: After finishing this unit you should be able to:
 lectic Field 7 Objectives: Afte finishing this unit you should be able to: Define the electic field and explain what detemines its magnitude and diection. Wite and apply fomulas fo the electic field intensity
lectic Field 7 Objectives: Afte finishing this unit you should be able to: Define the electic field and explain what detemines its magnitude and diection. Wite and apply fomulas fo the electic field intensity
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Lab 10: Newton s Second Law in Rotation
 Lab 10: Newton s Second Law in Rotation We can descibe the motion of objects that otate (i.e. spin on an axis, like a popelle o a doo) using the same definitions, adapted fo otational motion, that we have
Lab 10: Newton s Second Law in Rotation We can descibe the motion of objects that otate (i.e. spin on an axis, like a popelle o a doo) using the same definitions, adapted fo otational motion, that we have
Physics 111 Lecture 5 Circular Motion
 Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 207 Lecture 5. Lecture 5
 Lectue 5 Goals: Addess sstems with multiple acceleations in 2- dimensions (including linea, pojectile and cicula motion) Discen diffeent efeence fames and undestand how the elate to paticle motion in stationa
Lectue 5 Goals: Addess sstems with multiple acceleations in 2- dimensions (including linea, pojectile and cicula motion) Discen diffeent efeence fames and undestand how the elate to paticle motion in stationa
Section 26 The Laws of Rotational Motion
 Physics 24A Class Notes Section 26 The Laws of otational Motion What do objects do and why do they do it? They otate and we have established the quantities needed to descibe this motion. We now need to
Physics 24A Class Notes Section 26 The Laws of otational Motion What do objects do and why do they do it? They otate and we have established the quantities needed to descibe this motion. We now need to
Central Force Motion
 Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Unit 6 Test Review Gravitation & Oscillation Chapters 13 & 15
 A.P. Physics C Unit 6 Test Review Gavitation & Oscillation Chaptes 13 & 15 * In studying fo you test, make sue to study this eview sheet along with you quizzes and homewok assignments. Multiple Choice
A.P. Physics C Unit 6 Test Review Gavitation & Oscillation Chaptes 13 & 15 * In studying fo you test, make sue to study this eview sheet along with you quizzes and homewok assignments. Multiple Choice
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homework (Answers)
 Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Solutions to Problems : Chapter 19 Problems appeared on the end of chapter 19 of the Textbook
 Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
Physics 202, Lecture 2
 Physics 202, Lectue 2 Todays Topics Electic Foce and Electic Fields Electic Chages and Electic Foces Coulomb's Law Physical Field The Electic Field Electic Field Lines Motion of Chaged Paticle in Electic
Physics 202, Lectue 2 Todays Topics Electic Foce and Electic Fields Electic Chages and Electic Foces Coulomb's Law Physical Field The Electic Field Electic Field Lines Motion of Chaged Paticle in Electic
The geometric construction of Ewald sphere and Bragg condition:
 The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
Physics 111. Ch 12: Gravity. Newton s Universal Gravity. R - hat. the equation. = Gm 1 m 2. F g 2 1. ˆr 2 1. Gravity G =
 ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
