Lecture 6. What is contrast? Eyes: < 5% - can t detect <10% - difficult Enhance digital image electronically I I C I
|
|
|
- Elaine Farmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phae Contrat
2 Lecture 6 Scattering/Amplitude Contrat BF/DF: thickne, tilt Low-medium magnification Application Crytal defect: dilocation, tacking fault, phae boundarie, precipitate, defect cluter Contrat: g, type of the fault, it depth in the crytal Quantitative determination of b Reolution: trongly excited: 10 nm; weak beam: 1nm Phae Contrat: High magnification Highly coherent beam Large defocuing Reolution: nm Reliable interpretation: Simulation What i contrat? C I I I 1 1 Difference in intenity between two adjacent area I I Eye: < 5% - can t detect <10% - difficult Enhance digital image electronically 1
3 Interference Effect Frenel fringe around a hole in a carbon foil The dicovery of carbon nanotube Single atom and cluter of atom of tungten on the urface of a few atomic layer of graphite
4 Effect of two beam reaching the image Aperture: two beam (the incident and one diffracted) exp Unit amplitude ik r expik r g exp ik r 1g expi k r expik r 1g expig r int R exp i g R g t t Along x: perpendicular to the diffracting plane The total intenity ditribution: I 1 R R co g r 1 R x Rin t d -Lattice reolved (the reolving power of the microcope?) - At leat one order + the incident - More beam: harpen the detail - The viibility: orientation and thickne in inn t n R g t t g n 0 - The poition of the fringe: no imple relation to the poition of atomic plane (Next page) The fringe: not obervable Periodicity: d
5 Lattice Fringe: Thickne and Orientation Thickne variation change the contrat: no imple relation to the atomic plane (111) Lattice fringe Sodium faujaite, d = 1.44 nm Similar effect, when change
6 Summary of Theory A coherent ource of illumination Very thin < 3nm Two or more beam recombined to produce intenity difference from point to point Intrumental factor, phae plate High gun brightne Medium acceleration V, low C Parallel beam illumination: the illumination aperture < 0.1 mrad Highly table - Accelerating Voltage~ 1ppm: low energy preading - Vibration-free mechanical tability Coma-free on-axi alignment Sample height and orientation Simulate through-thickne-through-focu Phae hift ariing : at the pecimen ~ cattering the pherical aberration the defocu of the objective len
7 Phae Shift: Specimen Path difference relative to the wave front in vacuum r E E E E E 0 nr 1dz V rdz 0 Variation in n from point to point acro the pecimen n(r) atomic potential The exit wave amplitude: r rexpi r Ignore the local amplitude modulation: ~1 r 1 i r 1 i r me r h p r V rdz p Strong-phae object Weak-phae object The projected pecimen potential
8 Lack of Contrat at exact focu A phae hift of 90 o between the direct and cattered wave (thin ample) For thin ample, c << I I i ~ I i c i The phae object i inviible If the phae of the cattered wave can be hifted by a further 90 o I i c i I i c 0 Empirical method to enhance the contrat of image Knife edge blocking half of the tranvere patial frequencie Reducing the ize of the objective aperture limited reolution Introducing a focuing error (defocu) Uual method in HRTEM Simple intervention in the BFP (Schlieren contrat) Appeared from time to time Ue of BFP phae plate Optical
9 Phae hift: Intrumental Factor Spherical aberration: Wave front: equal phae Ray: trajectorie orthogonal to the wave front Two ray: R, R+dR Optical path difference due d dr to the angular deviation Total path difference or the phae hift relative to the optical axi Part of the outer zone of a len at a ditance R from the optical axi W R 0 d R 0 dr Angular deviation!!
10 Phae hift: Intrumental Factor Spherical aberration Change of pecimen poition Change of focal length f R C b M C b r f ar a f fr f f a Total angular deviation: The phae hift: z C f R a f f R C dr W R f R underfocu 0, a f z Scherzer formula
11 Phae hift: Intrumental Factor The wave aberration: C and Introducing reduced coordinate * C 1/ 4 ; z * z C 1/ The reduced wave aberration: * *4 * * W 4 z Scattered wave are hifted with a phae of 90 o. Scherzer focu: z * 1 W ha the value 90o over a relatively broad range of cattering angle
12 Image formation Abbe Theory A r B Plane wave: exp ik r 0 u Exit wave: e r ~ 0 a r exp ir expik r r: radiu vector in the pecimen plane q f F q r exp iq r ds S e Fourier tranform q: radiu vector in the diffraction plane Pupil function: aberration/aperture/defocu m 1 M 1 M r Fqexpiq r d q r m S Invere Fourier tranform 1 M r FqH qexpiq r d q S H q exp iw qm q
13 Contrat-Tranfer Function CTF: The imaging propertie of an objective len Independent of any particular pecimen tructure A pecimen with a ingle patial frequency (q = 1/d) The exit wave: 1 The Fourier tranform: F q q iq x 1 coqx i coqx... q The image: x m 1 q iq exp iw qexp iqx 1 q iq exp iw q The intenity: Ix x q q 1 m 1 co 1 D q W q q coiqx inw q q coiqx coiqx B( q) coiqx q q... co iqx D(q) : the CTF of the amplitude tructure of the pecimen B(q): the CTF of the phae tructure * * * * in 4 * B( ) inw z Ideal CTF: B = for all *
14 CTF: Defocu Poitive phae contrat Broad band o patial frequencie with the ame ign of the CTF No main tranfer band for z 0 Negative phae contrat Pa through zero: tranfer gap, for correponding q, no information reache the image Scherzer reolution/point reolution The firt zero: The maximum k for which phae coherency i preerved at Scherzer defocu d p 4 C 3 6
15 Influence of Energy Spread and Illumination Aperture Energy preading: E= 1- ev(thermionic); (Field Emiion) Finite ize of the gun: illumination aperture i. ( i << o, partially patially coherent) E reult in f: electron with different f uperpoed incoherently at the image I x 1 B( q) K q coiqx c q Envelope function: K c q q H exp 4 H C c E 1 E / E0 E 1 E / E 0 Information limit: the damped CTF goe to 0 Chromatic aberration Energy pread Fluctuation in high voltage Beam convergence Spatial incoherence Damp the CTF for increaing q
16 Contrat Tranfer Function (PCTF) Univeral curve Independent of pecimen and microcope Ocillatory nature Depending on: Envelope function: Coherent/partially coherent illumination» Temporal: Focal pread» Spatial: finite divergence» Not affect the poition of the zeroe Focu Scaling factor ued for pecific objective len/beam energy Recap: CTF
17 Reolution Limit Interpretable image reolution: tructural/point re At optimum(scherzer) defocu: PCTF larget band of patial frequencie without any phae reveral the firt zero Intrumental reolution: information limit Envelop function: cut-off 15% for image proceing Fine detail preent, not directly interpretable Focal Serie Recontruction Lattice-fringe reolution: finet pacing' that can be obtained obolete Fine tructure may not contain atomic information
18 Lattice and atomic imaging Comparatively very few lattice image are directly interpretable in term of atomic arrangement Phae reveral: difficult to achieve optimum image defocu Bet focu can be achieved by uing: edge for Frenel/a defect Knowledge of focal tep ize Small-unit-cell material A few diffracted beam contributing Fourier/Self-image: identical image occur periodically in defocu d / Contrat reveral by a half period Thick ample Dynamical complexity In the vicinity of the thickne extinction contour Low direct beam Strong diffraction between diffracted beam: dominating the image contrat Dumbbell different from the projected atomic eparation except for highly pecific thickne and defocu cannot be interpreted a atomic poition
19 Application: an example Accommodation of lattice mifit: Stre relieve reult in: interfacial mifit dilocation Cro ection of Ge/Si(001) heterointerface 1. J. N. Stirman, P. A. Crozier, D. J. Smith, F. Phillipp, G. Brill and S. Sivananthan, Appl. Phy. Lett. 84 (14), (004).
20 Apendix
21 Outline High Reolution TEM Elementary principle of Phae Contrat Weak-phae Object Approximation Multi-lice Method Peudo-weak-phae Object Approximation Reolving Power Application of HRTEM Identify crytal tructure Microtructure and defect Example of HRTEM Recent Progre of HRTEM
22 Brief Hitory of HRTEM 1949 Scherzer: Fundamental HRTEM Contrat Theory 1956 Menter: Experimental obervation TEM: Mechanical, thermal and electrical tabilitie 1930, exceeded the reolution of VLM 1970, the firt tructure image 1980, 0. nm, interpretable reolution limit Mid-1990, FEG information limit 0.1 nm
0 of the same magnitude. If we don t use an OA and ignore any damping, the CTF is
 1 4. Image Simulation Influence of C Spherical aberration break the ymmetry that would otherwie exit between overfocu and underfocu. One reult i that the fringe in the FT of the CTF are generally farther
1 4. Image Simulation Influence of C Spherical aberration break the ymmetry that would otherwie exit between overfocu and underfocu. One reult i that the fringe in the FT of the CTF are generally farther
CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Imaging
 CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Imaging 2016.10 Yanling Ge Outline Planar Defects Image strain field WBDF microscopy HRTEM information theory Discuss of question homework? Planar Defects - Internal Interface
CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Imaging 2016.10 Yanling Ge Outline Planar Defects Image strain field WBDF microscopy HRTEM information theory Discuss of question homework? Planar Defects - Internal Interface
Determination of the local contrast of interference fringe patterns using continuous wavelet transform
 Determination of the local contrat of interference fringe pattern uing continuou wavelet tranform Jong Kwang Hyok, Kim Chol Su Intitute of Optic, Department of Phyic, Kim Il Sung Univerity, Pyongyang,
Determination of the local contrat of interference fringe pattern uing continuou wavelet tranform Jong Kwang Hyok, Kim Chol Su Intitute of Optic, Department of Phyic, Kim Il Sung Univerity, Pyongyang,
Spatial Frequency and Transfer Function. columns of atoms, where the electrostatic potential is higher than in vacuum
 Image Formation Spatial Frequency and Transfer Function consider thin TEM specimen columns of atoms, where the electrostatic potential is higher than in vacuum electrons accelerate when entering the specimen
Image Formation Spatial Frequency and Transfer Function consider thin TEM specimen columns of atoms, where the electrostatic potential is higher than in vacuum electrons accelerate when entering the specimen
Demonstration of inverse scattering in optical coherence tomography
 Demontration of invere cattering in optical coherence tomography Tyler S. Ralton a,b, Dan Mark a,b, P. Scott Carney a,b, and Stephen A. Boppart a,b,c,* a Beckman ntitute for Advanced Science and Technology
Demontration of invere cattering in optical coherence tomography Tyler S. Ralton a,b, Dan Mark a,b, P. Scott Carney a,b, and Stephen A. Boppart a,b,c,* a Beckman ntitute for Advanced Science and Technology
Transmission Electron Microscopy
 L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
High-Resolution. Transmission. Electron Microscopy
 Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Design and Correction of optical Systems
 Design and Correction of optical Systems Part 10: Performance criteria 1 Summer term 01 Herbert Gross Overview 1. Basics 01-04-18. Materials 01-04-5 3. Components 01-05-0 4. Paraxial optics 01-05-09 5.
Design and Correction of optical Systems Part 10: Performance criteria 1 Summer term 01 Herbert Gross Overview 1. Basics 01-04-18. Materials 01-04-5 3. Components 01-05-0 4. Paraxial optics 01-05-09 5.
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 24
 Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 4 d (110) Final Exam Notice Time and Date: :30 4:30 PM, Wednesday, Dec. 10, 08. Place: Classroom CHEM-10 Coverage: All contents after midterm Open note Term project is due today
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 4 d (110) Final Exam Notice Time and Date: :30 4:30 PM, Wednesday, Dec. 10, 08. Place: Classroom CHEM-10 Coverage: All contents after midterm Open note Term project is due today
Lecture 3 Basic radiometric quantities.
 Lecture 3 Baic radiometric quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation.. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field: Definition,
Lecture 3 Baic radiometric quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation.. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field: Definition,
Linear Systems. : object : image. Describes the output of a linear system. input. output. Impulse response function
 Linear Systems Describes the output of a linear system Gx FxHx- xdx FxHx F x G x x output input Impulse response function H x xhx- xdx x If the microscope is a linear system: : object : image G x S F x
Linear Systems Describes the output of a linear system Gx FxHx- xdx FxHx F x G x x output input Impulse response function H x xhx- xdx x If the microscope is a linear system: : object : image G x S F x
CHEM 681 Seminar Mingqi Zhao April 20, 1998 Room 2104, 4:00 p.m. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: theories and applications
 CHEM 681 Seminar Mingqi Zhao April 20, 1998 Room 2104, 4:00 p.m. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: theories and applications In materials science, people are always interested in viewing
CHEM 681 Seminar Mingqi Zhao April 20, 1998 Room 2104, 4:00 p.m. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: theories and applications In materials science, people are always interested in viewing
1. Basic introduction to electromagnetic field. wave properties and particulate properties.
 Lecture Baic Radiometric Quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation. Objective:. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field:
Lecture Baic Radiometric Quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation. Objective:. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field:
Experimental methods in Physics. Electron Microscopy. Basic Techniques (MEP-I) SEM, TEM
 Experimental methods in Physics Electron Microscopy Basic Techniques (MEP-I) SEM, TEM Advanced Techniques (MEP-II) HR-TEM, STEM Analytical-TEM 3D-Microscopy Spring 2012 Experimental Methods in Physics
Experimental methods in Physics Electron Microscopy Basic Techniques (MEP-I) SEM, TEM Advanced Techniques (MEP-II) HR-TEM, STEM Analytical-TEM 3D-Microscopy Spring 2012 Experimental Methods in Physics
Physical Principles of Electron Microscopy. 2. Electron Optics
 Physical Principles of Electron Microscopy 2. Electron Optics Ray Egerton University of Alberta and National Institute of Nanotechnology Edmonton, Canada www.tem-eels.ca regerton@ualberta.ca Properties
Physical Principles of Electron Microscopy 2. Electron Optics Ray Egerton University of Alberta and National Institute of Nanotechnology Edmonton, Canada www.tem-eels.ca regerton@ualberta.ca Properties
Notes adapted from Prof. P. Lewis
 UCL DEPARTMENT OF EORAPHY EO141/ EO351 Principle & Practice of Remote Sening (PPRS) Radiative Tranfer Theory at optical wavelength applied to vegetation canopie: part 2 Dr. Mathia (Mat) Diney UCL eography
UCL DEPARTMENT OF EORAPHY EO141/ EO351 Principle & Practice of Remote Sening (PPRS) Radiative Tranfer Theory at optical wavelength applied to vegetation canopie: part 2 Dr. Mathia (Mat) Diney UCL eography
Radiometric properties of media. Mathieu Hébert
 1 Radiometric propertie of media Mathieu Hébert Aborbing media 2 Seawater i blue due to wavelength-dependent aborption http://www.webexhibit.org/caueofcolor/5b.html Almot all media are aborbing. The trength
1 Radiometric propertie of media Mathieu Hébert Aborbing media 2 Seawater i blue due to wavelength-dependent aborption http://www.webexhibit.org/caueofcolor/5b.html Almot all media are aborbing. The trength
Weak-Beam Dark-Field Technique
 Basic Idea recall bright-field contrast of dislocations: specimen close to Bragg condition, s î 0 Weak-Beam Dark-Field Technique near the dislocation core, some planes curved to s = 0 ) strong Bragg reflection
Basic Idea recall bright-field contrast of dislocations: specimen close to Bragg condition, s î 0 Weak-Beam Dark-Field Technique near the dislocation core, some planes curved to s = 0 ) strong Bragg reflection
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanic Phyic 151 Lecture 7 Scattering Problem (Chapter 3) What We Did Lat Time Dicued Central Force Problem l Problem i reduced to one equation mr = + f () r 3 mr Analyzed qualitative behavior Unbounded,
Mechanic Phyic 151 Lecture 7 Scattering Problem (Chapter 3) What We Did Lat Time Dicued Central Force Problem l Problem i reduced to one equation mr = + f () r 3 mr Analyzed qualitative behavior Unbounded,
Transmission Electron Microscope. Experimental Instruction
 Transmission Electron Microscope Experimental Instruction In advanced practical course [F-Praktikum] Date: April 2017 Contents 1 Task 3 2 Theoretical Basics 3 2.1 Bragg Diffraction......................................
Transmission Electron Microscope Experimental Instruction In advanced practical course [F-Praktikum] Date: April 2017 Contents 1 Task 3 2 Theoretical Basics 3 2.1 Bragg Diffraction......................................
h which looks like the classical version, because we used a modified kinetic energy
 1 0. Phase Contrast More on phase contrast The wave number of a high-energy electron in the vacuum can be written menr k h which looks like the classical version, because we used a modified kinetic energy
1 0. Phase Contrast More on phase contrast The wave number of a high-energy electron in the vacuum can be written menr k h which looks like the classical version, because we used a modified kinetic energy
Dislocation networks in graphite
 Dislocation networks in graphite High Resolution Microscop With Reference to Lattice Fringe Imaging in a TEM f f r Real space Specimen Reciprocal space hr Point spread function Diffraction pattern Back
Dislocation networks in graphite High Resolution Microscop With Reference to Lattice Fringe Imaging in a TEM f f r Real space Specimen Reciprocal space hr Point spread function Diffraction pattern Back
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory. ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy
 Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Advanced Digital Signal Processing. Stationary/nonstationary signals. Time-Frequency Analysis... Some nonstationary signals. Time-Frequency Analysis
 Advanced Digital ignal Proceing Prof. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Time-Frequency Analyi http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin 2 tationary/nontationary ignal Time-Frequency Analyi Fourier Tranform
Advanced Digital ignal Proceing Prof. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Time-Frequency Analyi http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin 2 tationary/nontationary ignal Time-Frequency Analyi Fourier Tranform
Overflow from last lecture: Ewald construction and Brillouin zones Structure factor
 Lecture 5: Overflow from lat lecture: Ewald contruction and Brillouin zone Structure factor Review Conider direct lattice defined by vector R = u 1 a 1 + u 2 a 2 + u 3 a 3 where u 1, u 2, u 3 are integer
Lecture 5: Overflow from lat lecture: Ewald contruction and Brillouin zone Structure factor Review Conider direct lattice defined by vector R = u 1 a 1 + u 2 a 2 + u 3 a 3 where u 1, u 2, u 3 are integer
Emittance limitations due to collective effects for the TOTEM beams
 LHC Project ote 45 June 0, 004 Elia.Metral@cern.ch Andre.Verdier@cern.ch Emittance limitation due to collective effect for the TOTEM beam E. Métral and A. Verdier, AB-ABP, CER Keyword: TOTEM, collective
LHC Project ote 45 June 0, 004 Elia.Metral@cern.ch Andre.Verdier@cern.ch Emittance limitation due to collective effect for the TOTEM beam E. Métral and A. Verdier, AB-ABP, CER Keyword: TOTEM, collective
III.9. THE HYSTERESIS CYCLE OF FERROELECTRIC SUBSTANCES
 III.9. THE HYSTERESIS CYCLE OF FERROELECTRIC SBSTANCES. Work purpoe The analyi of the behaviour of a ferroelectric ubtance placed in an eternal electric field; the dependence of the electrical polariation
III.9. THE HYSTERESIS CYCLE OF FERROELECTRIC SBSTANCES. Work purpoe The analyi of the behaviour of a ferroelectric ubtance placed in an eternal electric field; the dependence of the electrical polariation
High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy
 Chapter 2 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy The most fundamental imaging mode of a transmission electron microscope is realized by illuminating an electron-transparent specimen with a broad
Chapter 2 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy The most fundamental imaging mode of a transmission electron microscope is realized by illuminating an electron-transparent specimen with a broad
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND PHOTONS
 CHAPTER ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND PHOTONS Problem.1 Find the magnitude and direction of the induced electric field of Example.1 at r = 5.00 cm if the magnetic field change at a contant rate from 0.500
CHAPTER ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND PHOTONS Problem.1 Find the magnitude and direction of the induced electric field of Example.1 at r = 5.00 cm if the magnetic field change at a contant rate from 0.500
Gaussian Plane Waves Plane waves have flat emag field in x,y Tend to get distorted by diffraction into spherical plane waves and Gaussian Spherical
 Gauian Plane Wave Plane ave have lat ema ield in x,y Tend to et ditorted by diraction into pherical plane ave and Gauian Spherical Wave E ield intenity ollo: U ( ) x y u( x, y,r,t ) exp i ω t Kr R R here
Gauian Plane Wave Plane ave have lat ema ield in x,y Tend to et ditorted by diraction into pherical plane ave and Gauian Spherical Wave E ield intenity ollo: U ( ) x y u( x, y,r,t ) exp i ω t Kr R R here
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
2.71. Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Optics Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab
 Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab Lab #6 - Interference Microscopes The purpose of this lab is to observe the samples provided using two different interference microscopes --
Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab Lab #6 - Interference Microscopes The purpose of this lab is to observe the samples provided using two different interference microscopes --
Analysis of cavitating flow through a venturi
 Vol. 0(), pp. 67-7, June, 0 DOI: 0.897/SRE0.60 Article Number:BFBED8 ISSN 99-8 Copyright 0 Author() retain the copyright of thi article http://www.academicjournal.org/sre Scientific Reearch and Eay Full
Vol. 0(), pp. 67-7, June, 0 DOI: 0.897/SRE0.60 Article Number:BFBED8 ISSN 99-8 Copyright 0 Author() retain the copyright of thi article http://www.academicjournal.org/sre Scientific Reearch and Eay Full
Laser Optics-II. ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh 1
 Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005
 Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Laser Speckle and Applications in Optics
 Laser Speckle and Applications in Optics M. FRANCON Optics Laboratory Faculty of Sciences University of Paris Paris, France Translated by HENRI H. ARSENAULT Department of Physics Laval University Quebec,
Laser Speckle and Applications in Optics M. FRANCON Optics Laboratory Faculty of Sciences University of Paris Paris, France Translated by HENRI H. ARSENAULT Department of Physics Laval University Quebec,
Generalized Gouy phase for focused partially coherent light and its implications for interferometry
 Pang et al. Vol. 29, No. 6 / June 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 989 Generalized Gouy phae for focued partially coherent light and it implication for interferometry Xiaoyan Pang, 1 David G. Ficher, 2 and Taco
Pang et al. Vol. 29, No. 6 / June 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 989 Generalized Gouy phae for focued partially coherent light and it implication for interferometry Xiaoyan Pang, 1 David G. Ficher, 2 and Taco
Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials
 Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY. Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University
 DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
Chapter 2 Sampling and Quantization. In order to investigate sampling and quantization, the difference between analog
 Chapter Sampling and Quantization.1 Analog and Digital Signal In order to invetigate ampling and quantization, the difference between analog and digital ignal mut be undertood. Analog ignal conit of continuou
Chapter Sampling and Quantization.1 Analog and Digital Signal In order to invetigate ampling and quantization, the difference between analog and digital ignal mut be undertood. Analog ignal conit of continuou
A Comparison of Correlations for Heat Transfer from Inclined Pipes
 A Comparion of Correlation for Heat Tranfer from Inclined Pipe Krihperad Manohar Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The Univerity of the Wet Indie St. Augutine, Trinidad and Tobago
A Comparion of Correlation for Heat Tranfer from Inclined Pipe Krihperad Manohar Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The Univerity of the Wet Indie St. Augutine, Trinidad and Tobago
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.014.108 Supplementary Information "Spin angular momentum and tunable polarization in high harmonic generation" Avner Fleicher, Ofer Kfir, Tzvi Dikin, Pavel Sidorenko, and Oren Cohen
DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.014.108 Supplementary Information "Spin angular momentum and tunable polarization in high harmonic generation" Avner Fleicher, Ofer Kfir, Tzvi Dikin, Pavel Sidorenko, and Oren Cohen
Kai Yi! University of Iowa. on behalf of the CMS Collaboration
 Kai Yi! Univerity of Iowa on behalf of the CMS Collaboration Outline Motivation! The CMS detector and Jet Recontruction! Monojet + MET! Dijet Reonance! Multijet Reonance! Multijet Tranvere Momentum Sum
Kai Yi! Univerity of Iowa on behalf of the CMS Collaboration Outline Motivation! The CMS detector and Jet Recontruction! Monojet + MET! Dijet Reonance! Multijet Reonance! Multijet Tranvere Momentum Sum
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Liquid-like peudoelaticity of ub-10-nm crytalline ilver particle Jun Sun 1,*, Longbing He 1,*, Yu-Chieh Lo 2,5*, Tao Xu 1, Hengchang Bi 1, Litao Sun 1, Ze Zhang 3, Scott X. Mao 2,4, Ju Li 2 1 SEU-FEI Nano-Pico
Liquid-like peudoelaticity of ub-10-nm crytalline ilver particle Jun Sun 1,*, Longbing He 1,*, Yu-Chieh Lo 2,5*, Tao Xu 1, Hengchang Bi 1, Litao Sun 1, Ze Zhang 3, Scott X. Mao 2,4, Ju Li 2 1 SEU-FEI Nano-Pico
Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.710 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.710 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 10
 EELE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 10 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Ilamic Univerity of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 01 1 Electromagnetic wave propagation A changing magnetic
EELE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 10 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Ilamic Univerity of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 01 1 Electromagnetic wave propagation A changing magnetic
The Influence of Landau Damping on Multi Bunch Instabilities
 Univerität Dortmund The Influence of Landau Damping on Multi Bunch Intabilitie A Baic Coure on Landau Damping + A Few Implication Prof. Dr. Thoma Wei Department of Phyic / Dortmund Univerity Riezlern,
Univerität Dortmund The Influence of Landau Damping on Multi Bunch Intabilitie A Baic Coure on Landau Damping + A Few Implication Prof. Dr. Thoma Wei Department of Phyic / Dortmund Univerity Riezlern,
Part 1 - Basic Interferometers for Optical Testing
 Part 1 - Basic Interferometers for Optical Testing Two Beam Interference Fizeau and Twyman-Green interferometers Basic techniques for testing flat and spherical surfaces Mach-Zehnder Zehnder,, Scatterplate
Part 1 - Basic Interferometers for Optical Testing Two Beam Interference Fizeau and Twyman-Green interferometers Basic techniques for testing flat and spherical surfaces Mach-Zehnder Zehnder,, Scatterplate
Sampling and the Discrete Fourier Transform
 Sampling and the Dicrete Fourier Tranform Sampling Method Sampling i mot commonly done with two device, the ample-and-hold (S/H) and the analog-to-digital-converter (ADC) The S/H acquire a CT ignal at
Sampling and the Dicrete Fourier Tranform Sampling Method Sampling i mot commonly done with two device, the ample-and-hold (S/H) and the analog-to-digital-converter (ADC) The S/H acquire a CT ignal at
April 10th-12th, 2017
 Thomas LaGrange, Ph.D. Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist Introduction: Basics of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) TEM Doctoral Course MS-637 April 10th-12th, 2017 Outline 1. What is microcopy?
Thomas LaGrange, Ph.D. Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist Introduction: Basics of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) TEM Doctoral Course MS-637 April 10th-12th, 2017 Outline 1. What is microcopy?
Introduction to aberrations OPTI518 Lecture 5
 Introduction to aberrations OPTI518 Lecture 5 Second-order terms 1 Second-order terms W H W W H W H W, cos 2 2 000 200 111 020 Piston Change of image location Change of magnification 2 Reference for OPD
Introduction to aberrations OPTI518 Lecture 5 Second-order terms 1 Second-order terms W H W W H W H W, cos 2 2 000 200 111 020 Piston Change of image location Change of magnification 2 Reference for OPD
SMALL-SIGNAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT OF THE EUROPEAN POWER SYSTEM BASED ON ADVANCED NEURAL NETWORK METHOD
 SMALL-SIGNAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT OF THE EUROPEAN POWER SYSTEM BASED ON ADVANCED NEURAL NETWORK METHOD S.P. Teeuwen, I. Erlich U. Bachmann Univerity of Duiburg, Germany Department of Electrical Power Sytem
SMALL-SIGNAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT OF THE EUROPEAN POWER SYSTEM BASED ON ADVANCED NEURAL NETWORK METHOD S.P. Teeuwen, I. Erlich U. Bachmann Univerity of Duiburg, Germany Department of Electrical Power Sytem
Recent progress in fire-structure analysis
 EJSE Special Iue: Selected Key Note paper from MDCMS 1 1t International Conference on Modern Deign, Contruction and Maintenance of Structure - Hanoi, Vietnam, December 2007 Recent progre in fire-tructure
EJSE Special Iue: Selected Key Note paper from MDCMS 1 1t International Conference on Modern Deign, Contruction and Maintenance of Structure - Hanoi, Vietnam, December 2007 Recent progre in fire-tructure
Imaging through scattering medium by adaptive non-linear digital processing
 www.nature.com/cientificreport Received: 5 April 018 Accepted: 1 June 018 Publihed: xx xx xxxx OPEN Imaging through cattering medium by adaptive non-linear digital proceing Sawata Mukherjee & Joeph Roen
www.nature.com/cientificreport Received: 5 April 018 Accepted: 1 June 018 Publihed: xx xx xxxx OPEN Imaging through cattering medium by adaptive non-linear digital proceing Sawata Mukherjee & Joeph Roen
Electron microscopy in molecular cell biology I
 Electron microscopy in molecular cell biology I Electron optics and image formation Werner Kühlbrandt Max Planck Institute of Biophysics chemistry biology Objects of interest Galaxy 10 6 light years 10
Electron microscopy in molecular cell biology I Electron optics and image formation Werner Kühlbrandt Max Planck Institute of Biophysics chemistry biology Objects of interest Galaxy 10 6 light years 10
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
4.6 Principal trajectories in terms of amplitude and phase function
 4.6 Principal trajectorie in term of amplitude and phae function We denote with C() and S() the coinelike and inelike trajectorie relative to the tart point = : C( ) = S( ) = C( ) = S( ) = Both can be
4.6 Principal trajectorie in term of amplitude and phae function We denote with C() and S() the coinelike and inelike trajectorie relative to the tart point = : C( ) = S( ) = C( ) = S( ) = Both can be
Bogoliubov Transformation in Classical Mechanics
 Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
The use of connected masks for reconstructing the single particle image from X-ray diffraction data
 Mathematical Biology and Bioinformatic 2015. V. 10. Suppl. P. t1 t19. doi: 10.17537/2015.10.t1 The tranlation of original article Lunin V.Y., Lunina N.L., Petrova T.E. Matematichekaya biologiya i bioinformatika.
Mathematical Biology and Bioinformatic 2015. V. 10. Suppl. P. t1 t19. doi: 10.17537/2015.10.t1 The tranlation of original article Lunin V.Y., Lunina N.L., Petrova T.E. Matematichekaya biologiya i bioinformatika.
Medical Imaging. Transmission Measurement
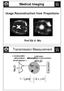 Medical Imaging Image Recontruction from Projection Prof Ed X. Wu Tranmiion Meaurement ( meaurable unknown attenuation, aborption cro-ection hadowgram ) I(ϕ,ξ) µ(x,) I = I o exp A(x, )dl L X-ra ource X-Ra
Medical Imaging Image Recontruction from Projection Prof Ed X. Wu Tranmiion Meaurement ( meaurable unknown attenuation, aborption cro-ection hadowgram ) I(ϕ,ξ) µ(x,) I = I o exp A(x, )dl L X-ra ource X-Ra
Lecture 23 Date:
 Lecture 3 Date: 4.4.16 Plane Wave in Free Space and Good Conductor Power and Poynting Vector Wave Propagation in Loy Dielectric Wave propagating in z-direction and having only x-component i given by: E
Lecture 3 Date: 4.4.16 Plane Wave in Free Space and Good Conductor Power and Poynting Vector Wave Propagation in Loy Dielectric Wave propagating in z-direction and having only x-component i given by: E
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
* AIT-4: Aberrations. Copyright 2006, Regents of University of California
 Advanced Issues and Technology (AIT) Modules Purpose: Explain the top advanced issues and concepts in optical projection printing and electron-beam lithography. AIT-: LER and Chemically Amplified Resists
Advanced Issues and Technology (AIT) Modules Purpose: Explain the top advanced issues and concepts in optical projection printing and electron-beam lithography. AIT-: LER and Chemically Amplified Resists
31. Diffraction: a few important illustrations
 31. Diffraction: a few important illustrations Babinet s Principle Diffraction gratings X-ray diffraction: Bragg scattering and crystal structures A lens transforms a Fresnel diffraction problem into a
31. Diffraction: a few important illustrations Babinet s Principle Diffraction gratings X-ray diffraction: Bragg scattering and crystal structures A lens transforms a Fresnel diffraction problem into a
AP5301/ Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions.
 Review Problems on Optical Microscopy AP5301/8301-2015 1. Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions. 2. Compare the focal lengths of two glass converging lenses, one with
Review Problems on Optical Microscopy AP5301/8301-2015 1. Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions. 2. Compare the focal lengths of two glass converging lenses, one with
PHY410 Optics Exam #3
 PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging
 Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging Contents Introduction Symbols and definitions Part A Diffraction and imaging of elastically scattered electrons Chapter 1. Basic kinematical
Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging Contents Introduction Symbols and definitions Part A Diffraction and imaging of elastically scattered electrons Chapter 1. Basic kinematical
An Image-encoded Mach-Zehnder Joint Transform Correlator for Polychromatic Pattern Recognition with Multi-level Quantized Reference Functions
 Proceeding of the International MultiConference of Engineer and Computer Scientit 008 Vol I IMECS 008, 19-1 March, 008, Hong Kong An Image-encoded Mach-Zehnder Joint Tranform Correlator for Polychromatic
Proceeding of the International MultiConference of Engineer and Computer Scientit 008 Vol I IMECS 008, 19-1 March, 008, Hong Kong An Image-encoded Mach-Zehnder Joint Tranform Correlator for Polychromatic
Chapter K - Problems
 Chapter K - Problem Blinn College - Phyic 2426 - Terry Honan Problem K. A He-Ne (helium-neon) laer ha a wavelength of 632.8 nm. If thi i hot at an incident angle of 55 into a gla block with index n =.52
Chapter K - Problem Blinn College - Phyic 2426 - Terry Honan Problem K. A He-Ne (helium-neon) laer ha a wavelength of 632.8 nm. If thi i hot at an incident angle of 55 into a gla block with index n =.52
A system of two lenses is achromatic when the separation between them is
 L e c t u r e 1 5 1 Eyepieces Single eye lens in a telescope / microscope produces spherical and chromatic aberrations. The field of view is also narrow. The eye lens is replaced by a system of lenses
L e c t u r e 1 5 1 Eyepieces Single eye lens in a telescope / microscope produces spherical and chromatic aberrations. The field of view is also narrow. The eye lens is replaced by a system of lenses
Lecture 10 Filtering: Applied Concepts
 Lecture Filtering: Applied Concept In the previou two lecture, you have learned about finite-impule-repone (FIR) and infinite-impule-repone (IIR) filter. In thee lecture, we introduced the concept of filtering
Lecture Filtering: Applied Concept In the previou two lecture, you have learned about finite-impule-repone (FIR) and infinite-impule-repone (IIR) filter. In thee lecture, we introduced the concept of filtering
Lecture 15 - Current. A Puzzle... Advanced Section: Image Charge for Spheres. Image Charge for a Grounded Spherical Shell
 Lecture 15 - Current Puzzle... Suppoe an infinite grounded conducting plane lie at z = 0. charge q i located at a height h above the conducting plane. Show in three different way that the potential below
Lecture 15 - Current Puzzle... Suppoe an infinite grounded conducting plane lie at z = 0. charge q i located at a height h above the conducting plane. Show in three different way that the potential below
Wolfgang Hofle. CERN CAS Darmstadt, October W. Hofle feedback systems
 Wolfgang Hofle Wolfgang.Hofle@cern.ch CERN CAS Darmtadt, October 9 Feedback i a mechanim that influence a ytem by looping back an output to the input a concept which i found in abundance in nature and
Wolfgang Hofle Wolfgang.Hofle@cern.ch CERN CAS Darmtadt, October 9 Feedback i a mechanim that influence a ytem by looping back an output to the input a concept which i found in abundance in nature and
Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED TEM RHEED
 Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED: Low Energy Electron Diffraction SPA-LEED: Spot Profile Analysis Low Energy Electron diffraction RHEED: Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction TEM: Transmission
Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED: Low Energy Electron Diffraction SPA-LEED: Spot Profile Analysis Low Energy Electron diffraction RHEED: Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction TEM: Transmission
n The visual examination of the image of a point source is one of the most basic and important tests that can be performed.
 8.2.11 Star Test n The visual examination of the image of a point source is one of the most basic and important tests that can be performed. Interpretation of the image is to a large degree a matter of
8.2.11 Star Test n The visual examination of the image of a point source is one of the most basic and important tests that can be performed. Interpretation of the image is to a large degree a matter of
USPAS Course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linear Accelerators
 USPAS Coure on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linear Accelerator G. A. Krafft and L. Merminga Jefferon Lab I. Bazarov Cornell Lecture 6 7 March 005 Lecture Outline. Invariant Ellipe Generated by a Unimodular
USPAS Coure on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linear Accelerator G. A. Krafft and L. Merminga Jefferon Lab I. Bazarov Cornell Lecture 6 7 March 005 Lecture Outline. Invariant Ellipe Generated by a Unimodular
No-load And Blocked Rotor Test On An Induction Machine
 No-load And Blocked Rotor Tet On An Induction Machine Aim To etimate magnetization and leakage impedance parameter of induction machine uing no-load and blocked rotor tet Theory An induction machine in
No-load And Blocked Rotor Tet On An Induction Machine Aim To etimate magnetization and leakage impedance parameter of induction machine uing no-load and blocked rotor tet Theory An induction machine in
Supplementary Information Free-space creation of ultralong anti-diffracting beam with multiple energy oscillations adjusted using optical pen
 Supplementary Information Free-pace creation of ultralong anti-diffracting beam with multiple energy ocillation aduted uing optical pen Weng et al. Supplementary Figure Normalized light intenity of ideal
Supplementary Information Free-pace creation of ultralong anti-diffracting beam with multiple energy ocillation aduted uing optical pen Weng et al. Supplementary Figure Normalized light intenity of ideal
A Single Particle Thermal Model for Lithium Ion Batteries
 A Single Particle Thermal Model for Lithium Ion Batterie R. Painter* 1, B. Berryhill 1, L. Sharpe 2 and S. Keith Hargrove 2 1 Civil Engineering, Tenneee State Univerity, Nahville, TN, USA 2 Mechanical
A Single Particle Thermal Model for Lithium Ion Batterie R. Painter* 1, B. Berryhill 1, L. Sharpe 2 and S. Keith Hargrove 2 1 Civil Engineering, Tenneee State Univerity, Nahville, TN, USA 2 Mechanical
Learning Multiplicative Interactions
 CSC2535 2011 Lecture 6a Learning Multiplicative Interaction Geoffrey Hinton Two different meaning of multiplicative If we take two denity model and multiply together their probability ditribution at each
CSC2535 2011 Lecture 6a Learning Multiplicative Interaction Geoffrey Hinton Two different meaning of multiplicative If we take two denity model and multiply together their probability ditribution at each
High-field behavior: the law of approach to saturation (Is there an equation for the magnetization at high fields?)
 High-field behavior: the law of approach to aturation (I there an equation for the magnetization at high field? In the high-field region the magnetization approache aturation. The firt attempt to give
High-field behavior: the law of approach to aturation (I there an equation for the magnetization at high field? In the high-field region the magnetization approache aturation. The firt attempt to give
Lab 2: Mach Zender Interferometer Overview
 Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
An Analytical Solution of the Radiative Transfer Equation for Inhomogeneous Finite Medium with Fresnel Boundary Conditions
 rab ournal of Nuclear Science pplication, 46(3), (4-5) 3 n nalytical Solution of the Radiative Tranfer Equation for Inhomogeneou Finite Medium with Frenel Boundary Condition. Elghazaly Reactor & Neutron
rab ournal of Nuclear Science pplication, 46(3), (4-5) 3 n nalytical Solution of the Radiative Tranfer Equation for Inhomogeneou Finite Medium with Frenel Boundary Condition. Elghazaly Reactor & Neutron
L. (2016) A 2016 IEEE
 Simon, G. and Andrade, M. A. B. and Roolvink, D. and Cormack, P. A. G. and Riehle, M. O. and Bernaau, A. L. (6) A determinitic method for particle orting by dynamic acoutic field. In: 6 IEEE International
Simon, G. and Andrade, M. A. B. and Roolvink, D. and Cormack, P. A. G. and Riehle, M. O. and Bernaau, A. L. (6) A determinitic method for particle orting by dynamic acoutic field. In: 6 IEEE International
Shear Stress. Horizontal Shear in Beams. Average Shear Stress Across the Width. Maximum Transverse Shear Stress. = b h
 Shear Stre Due to the preence of the hear force in beam and the fact that t xy = t yx a horizontal hear force exit in the beam that tend to force the beam fiber to lide. Horizontal Shear in Beam The horizontal
Shear Stre Due to the preence of the hear force in beam and the fact that t xy = t yx a horizontal hear force exit in the beam that tend to force the beam fiber to lide. Horizontal Shear in Beam The horizontal
Experimental study of the heat transfer for a tube bundle in a transversally flowing air
 oceeding of the th WSEAS Int. Conf. on HEAT TRASFER, THERMA EGIEERIG and EVIROMET, Elounda, Greece, Augut -, 00 (pp-8) Experimental tudy of the heat tranfer for a tube bundle in a tranverally flowing air
oceeding of the th WSEAS Int. Conf. on HEAT TRASFER, THERMA EGIEERIG and EVIROMET, Elounda, Greece, Augut -, 00 (pp-8) Experimental tudy of the heat tranfer for a tube bundle in a tranverally flowing air
Part 3 - Image Formation
 Part 3 - Image Formation Three classes of scattering outcomes Types of electron microscopes Example SEM image: fly nose Example TEM image: muscle Skeletal muscle. Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure Mercer
Part 3 - Image Formation Three classes of scattering outcomes Types of electron microscopes Example SEM image: fly nose Example TEM image: muscle Skeletal muscle. Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure Mercer
Phys102 Lecture Diffraction of Light
 Phys102 Lecture 31-33 Diffraction of Light Key Points Diffraction by a Single Slit Diffraction in the Double-Slit Experiment Limits of Resolution Diffraction Grating and Spectroscopy Polarization References
Phys102 Lecture 31-33 Diffraction of Light Key Points Diffraction by a Single Slit Diffraction in the Double-Slit Experiment Limits of Resolution Diffraction Grating and Spectroscopy Polarization References
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Quantification of predictability The main method of thi paper i quantitative etimation of the predictability of a pike train from a predictor variable, which may be any combination
Supplementary information Quantification of predictability The main method of thi paper i quantitative etimation of the predictability of a pike train from a predictor variable, which may be any combination
Chapter 6 SCALAR DIFFRACTION THEORY
 Chapter 6 SCALAR DIFFRACTION THEORY [Reading assignment: Hect 0..4-0..6,0..8,.3.3] Scalar Electromagnetic theory: monochromatic wave P : position t : time : optical frequency u(p, t) represents the E or
Chapter 6 SCALAR DIFFRACTION THEORY [Reading assignment: Hect 0..4-0..6,0..8,.3.3] Scalar Electromagnetic theory: monochromatic wave P : position t : time : optical frequency u(p, t) represents the E or
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
SIMG Optics for Imaging Solutions to Final Exam
 SIMG-733-009 Optics for Imaging Solutions to Final Exam. An imaging system consists of two identical thin lenses each with focal length f = f = +300 mm and diameter d = d =50mm. The lenses are separated
SIMG-733-009 Optics for Imaging Solutions to Final Exam. An imaging system consists of two identical thin lenses each with focal length f = f = +300 mm and diameter d = d =50mm. The lenses are separated
New bounds for Morse clusters
 New bound for More cluter Tamá Vinkó Advanced Concept Team, European Space Agency, ESTEC Keplerlaan 1, 2201 AZ Noordwijk, The Netherland Tama.Vinko@ea.int and Arnold Neumaier Fakultät für Mathematik, Univerität
New bound for More cluter Tamá Vinkó Advanced Concept Team, European Space Agency, ESTEC Keplerlaan 1, 2201 AZ Noordwijk, The Netherland Tama.Vinko@ea.int and Arnold Neumaier Fakultät für Mathematik, Univerität
Ultra-Small Coherent Thermal Conductance Using Multi-Layer Photonic Crystal
 Ultra-Small Coherent Thermal Conductance Uing Multi-Layer Photonic Crytal W. T. Lau*, J. -T. Shen, G. Veroni and S. Fan Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford Univerity, Stanford, CA 94305, USA ABSTRACT
Ultra-Small Coherent Thermal Conductance Uing Multi-Layer Photonic Crytal W. T. Lau*, J. -T. Shen, G. Veroni and S. Fan Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford Univerity, Stanford, CA 94305, USA ABSTRACT
General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18
 95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
M2 TP. Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED)
 M2 TP Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) Guide for report preparation I. Introduction: Elastic scattering or diffraction of electrons is the standard technique in surface science for obtaining structural
M2 TP Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) Guide for report preparation I. Introduction: Elastic scattering or diffraction of electrons is the standard technique in surface science for obtaining structural
Fast Convolutional Sparse Coding (FCSC)
 Fat Convolutional Spare Coding (FCSC) Bailey ong Department of Computer Science Univerity of California, Irvine bhkong@ic.uci.edu Charle C. Fowlke Department of Computer Science Univerity of California,
Fat Convolutional Spare Coding (FCSC) Bailey ong Department of Computer Science Univerity of California, Irvine bhkong@ic.uci.edu Charle C. Fowlke Department of Computer Science Univerity of California,
Lattice Design in Particle Accelerators Bernhard Holzer, CERN. 1952: Courant, Livingston, Snyder: Theory of strong focusing in particle beams
 Lattice Deign in Particle Accelerator Bernhard Holzer, CERN β, y D 95: Courant, Livington, Snyder: Theory of trong focuing in particle beam Lattice Deign: how to build a torage ring High energy accelerator
Lattice Deign in Particle Accelerator Bernhard Holzer, CERN β, y D 95: Courant, Livington, Snyder: Theory of trong focuing in particle beam Lattice Deign: how to build a torage ring High energy accelerator
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 2 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 2 Jul 2016 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 2 Jul 2016](/thumbs/73/69091835.jpg) Tranvere Target Azimuthal Single Spin Aymmetry in Elatic e N Scattering Tareq Alhalholy and Matthia Burkardt Department of Phyic, New Mexico State Univerity, La Cruce, NM 883-1, U.S.A. arxiv:167.1287v1
Tranvere Target Azimuthal Single Spin Aymmetry in Elatic e N Scattering Tareq Alhalholy and Matthia Burkardt Department of Phyic, New Mexico State Univerity, La Cruce, NM 883-1, U.S.A. arxiv:167.1287v1
