EVAPORATION. Robert evaporator. Balance equations Material balance (total) Component balance. Heat balance
|
|
|
- Leslie Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EAPORATION Roert eorator Balance equation Material alance (total) S S=Solution =aor =Steam K=Steam condenate S Comonent alance S S Heat alance S S v Merkel lot can e ued for otaining entaly data Heat ower conumtion Cae of large eorator (eat lo in te or ace) S S v Cae of mall eorator (eat lo in te team ace) Heat tranort S U v v S A T corr T corr T T T Tcorr T TS U A Falling film eorator work a a eat excanger and logaritmic aroac temerature i ued.
2 Prolem / oiling aquou NaOH olution of 3% i eorated to 4% at.5 ar wit 43 C team. Heat lo i 5 /. Wat i te team conumtion? Solution Notation S = / =.3 =.5 ar T = 43 C =.4 v = 5 / =? Outut tream S S S S S S S S 75 Entaly value,3 Merkel lot.5ar.4 Merkel lot.5ar Heat ower S S v aor entaly Inerolation i alied ecaue no.5 ar data i own in te. 4, 4.93 Pa , 5.33 Pa
3 3 (i mean ),,,,,, Pa 4.93 Pa 5.33 Pa 4.93 Pa Heat ower conumtion S S v 6585 Steam orization eat 36.5 C 43 T Steam flow rate
4 Prolem An atmoeric eorator a 5 m eating area, and i eated wit 65 C aturated team. Te eat lo i 4 %, and te corrected overall eat tranfer coefficient i U corr =. kw/m K. C NaOH i eorated from a) 37% ) 4% to 55% concentration. c) Wat i te team conumtion if te eoration eat of te team i 65.7 /? Solution Notation A = 5 m = ar T = C =.55 T = 65 C a) =.37 v =.4 U corr =. kw/m K = 65.7 / S =? =? Heat ower Dene olution temerature.55 Merkel lot T 55C ar Corrected aroac temerature Tcorr T T 65C 55C C Heat ower U corr AT corr kw. 5m m K C 6kW Entaly value.37 Merkel lot 7 T C.55 Merkel lot 8 ar ar
5 Stream flow rate (alance) rearranged (S in te rigt and ide) S S S S S S S S S S S Heat alance S S v S S S.96 S S S ) = Only te canged value ave to e re-calculated. Entaly.4 Merkel lot T C 7.966kW From te eat alance S S kW c) Wat i te team conumtion if te eoration eat of te team i 65.7 /? 6kW
6 Prolem 3 t/ 5% NaOH olution i to e concentrated to 5% under ar reure. Calculate team conumtion and eat tranfer area if te dilute feed i fed to a Roert eorator in a tate a a) C, ) ule oint, c) uereated to ar Te eating team i at 33 C and containing 5% wetne. Heat lo i 3 kw. irtual overall eat tranfer coefficient i U = kw/m K. Solution Notation a) T = C S = t/ =.5 = ar =.5 T = 33 C x =.95 v = 3 kw U = kw/m K =? A =? Outlet tream flow rate S S S S t.5.5 S S t t S S Entaly value.5 Merkel lot T C.5 Merkel lot 3 ar teamtale ar t t 6
7 Heat ower S S v Steam orization eat T 33C kW 36 Steam conumtion Net team conumtion net net Wet team conumtion 94.6 net t x.95 Heat tranfer area aor temerature ar T C irtual aroac temerature T Area U A U T T A T T 33C C 33C 7.58 kw 33C 36 m K 7m 7
8 ) Boiling feed Entaly.5 Merkel lot ar Heat ower S S v kW 36 Steam conumtion Net team conumtion net Wet team conumtion 8959 net t x.95 Heat tranfer area U A U A T T 7.94 kw 33C 36 m K 63.5m 8
9 c) = ar Entaly.5 Merkel lot ar Heat ower S 3 S v kW 36 Steam conumtion Net team conumtion net Wet team conumtion 8 net t x.95 Heat tranfer area U A U A T T 7.78 kw 33C 36 m K 49.8m 9
10 Prolem 4 One a falling film eorator i ued to concentrate 5 t/ % C NaOH olution to 35%, under.5 ar. Heat lo i 3%. Determine: a) Heat conumtion ) Saturation temerature of te team to e alied if minimum aroac temerature i 6 C c) Required eat tranfer area if average overall eat tranfer coefficient i.5 kw/m K Solution Notation S = 5 t/ =. =.35 =.5 ar T = C lo a) Heat conumtion Outut tream S S S S =.3 t S S t t S S 5.86 t.86 t.4 Entaly value. Merkel lot 4 T C.35 Merkel lot 35.5ar.5ar Heat ower S S
11 ) Saturation temerature of te team to e alied if minimum aroac temerature i 6 C Maximum temerature amongt te roce tream elong to te dene olution..35 Merkel lot T 5C.5ar Steam temerature: T T T 5C 6C C Steam min c) Required eat tranfer area if average overall eat tranfer coefficient i.5 kw/m K Altoug te feed i of C, te dilute olution reace it ule oint in te eorator almot at once. Terefore te oiling oint i to e alied at calculating te logaritmic mean aroac temerature., Merkel lot T.5ar, 88C Aroac temerature at te two endoint T T T C 88C 3C a Steam, T TSteam T C 5C 6C Logaritmic aroac temerature Ta T 3C 6C Tav.65C Ta 3C ln ln T 6C Heat tranfer area UA A U T av T av kw.5.65c 36 m K.7m
12 Prolem 5 C NaOH olution i concentrated to 4 % under. ar reure, reulting in.6 t dene olution and.5 t or in eac our.. ar aturated team, otained y mixing.48 ar live team wit a art of te or. Te oter art of te or i condened in a mixing arometric condener uing 8 m 3 / C cooling water. Calculate: a) Live team conumtion ) Fraction of te or ued in te team c) Temerature of te arometric condener outlet tream d) Flow rate of te fla team otained from te team condenate Solution Notation H: cooling water K: or condenate É: live team : team K: team condenate S: fla team F: exaut =.4 =. ar T = C S =.6 t/ =.5 t/ =. ar É =.48 ar H = 8 m 3 / T H = C
13 a) Live team conumtion Fead tream flow rate t t S S.6.5 Feed tream concentration S S t. t.6 S.4. S t. Entaly value. Merkel lot T C.4 Merkel lot.ar.ar Heat ower S S Steam conumtion Steam orization eat.ar Steam ma flow rate 6 4,
14 ) Fraction of te or utilized in te team Material alance around te comreor É Heat alance around te comreor É É (Te or looe it uereated value a it leave te eorator; it aturated tate i taken into account) Entaly value.ar ar É É Ma flow rate of live team and of utilized or (from alance) É É É É É É É É É É É É É c) Temerature of te arometric condener outlet tream Remaining or Cooling water ma flow rate 3 m H HH 8 3 m 8 aor mixed condenate ma flow rate K H Cooling water entaly value TH C H
15 Heat alance of te arometric mixing condener H K H K Mixed or condenate entaly H H K K Mixed or condenate temerature K 4 TK 5C d) Flow rate of te fla team otained from te team condenate Ma alance K S F Entaly value K.ar K 44. S ar S F ar F (Exaut i conidered a liquid) Steam condenate ma flow rate K Fla team ma flow rate Heat alance K S K K K S F K S S K S F S K K K S S F F F S F F
1 = The rate at which the entropy of the high temperature reservoir changes, according to the definition of the entropy, is
 8-7 8-9 A reverible eat um wit eciied reervoir temerature i conidered. e entroy cange o two reervoir i to be calculated and it i to be determed i ti eat um atiie te creae entroy rcile. Aumtion e eat um
8-7 8-9 A reverible eat um wit eciied reervoir temerature i conidered. e entroy cange o two reervoir i to be calculated and it i to be determed i ti eat um atiie te creae entroy rcile. Aumtion e eat um
v v = = Mixing chamber: = 30 or, = s6 Then, and = 52.4% Turbine Boiler process heater Condenser 7 MPa Q in 0.6 MPa Q proces 10 kpa Q out
 0-0- A cogeneration plant i to generate poer and proce eat. art o te team extracted rom te turbe at a relatively ig preure i ued or proce eatg. e poer produced and te utilization actor o te plant are to
0-0- A cogeneration plant i to generate poer and proce eat. art o te team extracted rom te turbe at a relatively ig preure i ued or proce eatg. e poer produced and te utilization actor o te plant are to
(b) The heat transfer can be determined from an energy balance on the system
 8-5 Heat is transferred to a iston-cylinder device wit a set of stos. e work done, te eat transfer, te exergy destroyed, and te second-law efficiency are to be deterined. Assutions e device is stationary
8-5 Heat is transferred to a iston-cylinder device wit a set of stos. e work done, te eat transfer, te exergy destroyed, and te second-law efficiency are to be deterined. Assutions e device is stationary
This appendix derives Equations (16) and (17) from Equations (12) and (13).
 Capital growt pat of te neoclaical growt model Online Supporting Information Ti appendix derive Equation (6) and (7) from Equation () and (3). Equation () and (3) owed te evolution of pyical and uman capital
Capital growt pat of te neoclaical growt model Online Supporting Information Ti appendix derive Equation (6) and (7) from Equation () and (3). Equation () and (3) owed te evolution of pyical and uman capital
KNOWN: Air undergoes a polytropic process in a piston-cylinder assembly. The work is known.
 PROBLEM.7 A hown in Fig. P.7, 0 ft of air at T = 00 o R, 00 lbf/in. undergoe a polytropic expanion to a final preure of 5.4 lbf/in. The proce follow pv. = contant. The work i W = 94.4 Btu. Auming ideal
PROBLEM.7 A hown in Fig. P.7, 0 ft of air at T = 00 o R, 00 lbf/in. undergoe a polytropic expanion to a final preure of 5.4 lbf/in. The proce follow pv. = contant. The work i W = 94.4 Btu. Auming ideal
Notes on the function gsw_enthalpy_first_derivatives_ct_exact(sa,ct,p)
 Notes on gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact 1 Notes on te function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) is function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) evaluates two of te first order artial derivatives
Notes on gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact 1 Notes on te function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) is function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) evaluates two of te first order artial derivatives
Psychrometrics. PV = N R u T (9.01) PV = N M R T (9.02) Pv = R T (9.03) PV = m R T (9.04)
 Pycrometric Abtract. Ti capter include baic coverage of pycrometric propertie and pycrometric procee. Empai i upon propertie and procee relative to te environment and to proceing of biological material.
Pycrometric Abtract. Ti capter include baic coverage of pycrometric propertie and pycrometric procee. Empai i upon propertie and procee relative to te environment and to proceing of biological material.
2b m 1b: Sat liq C, h = kj/kg tot 3a: 1 MPa, s = s 3 -> h 3a = kj/kg, T 3b
 .6 A upercritical team power plant ha a high preure of 0 Ma and an exit condener temperature of 50 C. he maximum temperature in the boiler i 000 C and the turbine exhaut i aturated vapor here i one open
.6 A upercritical team power plant ha a high preure of 0 Ma and an exit condener temperature of 50 C. he maximum temperature in the boiler i 000 C and the turbine exhaut i aturated vapor here i one open
Continuity and Differentiability Worksheet
 Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Section A 01. (12 M) (s 2 s 3 ) = 313 s 2 = s 1, h 3 = h 4 (s 1 s 3 ) = kj/kgk. = kj/kgk. 313 (s 3 s 4f ) = ln
 0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
8-4 P 2. = 12 kw. AIR T = const. Therefore, Q &
 8-4 8-4 Air i compreed teadily by a compreor. e air temperature i mataed contant by eat rejection to te urroundg. e rate o entropy cange o air i to be determed. Aumption i i a teady-low proce ce tere i
8-4 8-4 Air i compreed teadily by a compreor. e air temperature i mataed contant by eat rejection to te urroundg. e rate o entropy cange o air i to be determed. Aumption i i a teady-low proce ce tere i
Logarithmic functions
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter 5: Derivatives of transcendental functions Section Derivatives of Logaritmic functions Wat ou need to know alread: Definition of derivative and all basic
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter 5: Derivatives of transcendental functions Section Derivatives of Logaritmic functions Wat ou need to know alread: Definition of derivative and all basic
SIMPLE RANKINE CYCLE. 3 expander. boiler. pump. condenser 1 W Q. cycle cycle. net. shaft
 SIMPLE RANKINE CYCLE um boiler exander condener Steady Flow, Oen Sytem - region ace Steady Flow Energy Equation for Procee m (u Pum Proce,, Boiler Proce,, V ρg) 0, 0, Exanion Proce,, 0, Condener Proce,,
SIMPLE RANKINE CYCLE um boiler exander condener Steady Flow, Oen Sytem - region ace Steady Flow Energy Equation for Procee m (u Pum Proce,, Boiler Proce,, V ρg) 0, 0, Exanion Proce,, 0, Condener Proce,,
Kelvin Planck Statement of the Second Law. Clausius Statement of the Second Law
 Kelv Planck Statement of te Second aw It is imossible to construct an enge wic, oeratg a cycle, will roduce no oter effect tan te extraction of eat from a sgle reservoir and te erformance of an equivalent
Kelv Planck Statement of te Second aw It is imossible to construct an enge wic, oeratg a cycle, will roduce no oter effect tan te extraction of eat from a sgle reservoir and te erformance of an equivalent
Compressor 1. Evaporator. Condenser. Expansion valve. CHE 323, October 8, Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Tutorial problem 5.
 CHE 33, October 8, 014. Cemical Engineering Termodynamics. Tutorial problem 5. In a simple compression refrigeration process, an adiabatic reversible compressor is used to compress propane, used as a refrigerant.
CHE 33, October 8, 014. Cemical Engineering Termodynamics. Tutorial problem 5. In a simple compression refrigeration process, an adiabatic reversible compressor is used to compress propane, used as a refrigerant.
Chapters 19 & 20 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Developing Transfer Functions from Heat & Material Balances
 Colorado Sool of Mine CHEN43 Stirred ank Heater Develoing ranfer untion from Heat & Material Balane Examle ranfer untion Stirred ank Heater,,, A,,,,, We will develo te tranfer funtion for a tirred tank
Colorado Sool of Mine CHEN43 Stirred ank Heater Develoing ranfer untion from Heat & Material Balane Examle ranfer untion Stirred ank Heater,,, A,,,,, We will develo te tranfer funtion for a tirred tank
Special Topic: Binary Vapor Cycles
 0- Special opic: Bary Vapor ycle 0- Bary poer cycle i a cycle ic i actually a combation o to cycle; one te ig temperature region, and te oter te lo temperature region. It purpoe i to creae termal eiciency.
0- Special opic: Bary Vapor ycle 0- Bary poer cycle i a cycle ic i actually a combation o to cycle; one te ig temperature region, and te oter te lo temperature region. It purpoe i to creae termal eiciency.
T Turbine 8. Boiler fwh fwh I Condenser 4 3 P II P I P III. (a) From the steam tables (Tables A-4, A-5, and A-6), = = 10 MPa. = 0.
 - - A team poer plant operate on an ideal regenerative anke cycle it to open feedater eater. e poer put of te poer plant and te termal efficiency of te cycle are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
- - A team poer plant operate on an ideal regenerative anke cycle it to open feedater eater. e poer put of te poer plant and te termal efficiency of te cycle are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
( )( ) 7 MPa q in = = 10 kpa q out. 1 h. = s. Thus, and = 38.9% (b) (c) The rate of heat rejection to the cooling water and its temperature rise are
 . A team poer plant operate on a imple ideal Ranke cycle beteen te peciied preure limit. e termal eiciency o te cycle, te ma lo rate o te team, and te temperature rie o te coolg ater are to be determed.
. A team poer plant operate on a imple ideal Ranke cycle beteen te peciied preure limit. e termal eiciency o te cycle, te ma lo rate o te team, and te temperature rie o te coolg ater are to be determed.
CANKAYA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ME 212 THERMODYNAMICS II CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES SOLUTION
 CANKAYA UNIVESIY FACULY OF ENGINEEING AND ACHIECUE MECHANICAL ENGINEEING DEPAMEN ME HEMODYNAMICS II CHAPE EXAMPLES SOLUION ) he reure wthn a. m tank hould not exeed 0 ar. Chek the reure wthn the tank f
CANKAYA UNIVESIY FACULY OF ENGINEEING AND ACHIECUE MECHANICAL ENGINEEING DEPAMEN ME HEMODYNAMICS II CHAPE EXAMPLES SOLUION ) he reure wthn a. m tank hould not exeed 0 ar. Chek the reure wthn the tank f
Lecture 3 Heat Exchangers
 L3 Leture 3 Heat Exangers Heat Exangers. Heat Exangers Transfer eat from one fluid to anoter. Want to imise neessary ardware. Examples: boilers, ondensors, ar radiator, air-onditioning oils, uman body.
L3 Leture 3 Heat Exangers Heat Exangers. Heat Exangers Transfer eat from one fluid to anoter. Want to imise neessary ardware. Examples: boilers, ondensors, ar radiator, air-onditioning oils, uman body.
FOCUS ON THEORY. We recall that a function g(x) is differentiable at the point a if the limit
 FOCUS ON THEORY 653 DIFFERENTIABILITY Notes on Differentiabilit In Section 13.3 we gave an informal introduction to te concet of differentiabilit. We called a function f (; ) differentiable at a oint (a;
FOCUS ON THEORY 653 DIFFERENTIABILITY Notes on Differentiabilit In Section 13.3 we gave an informal introduction to te concet of differentiabilit. We called a function f (; ) differentiable at a oint (a;
5.1 We will begin this section with the definition of a rational expression. We
 Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Hilbert-Space Integration
 Hilbert-Space Integration. Introduction. We often tink of a PDE, like te eat equation u t u xx =, a an evolution equation a itorically wa done for ODE. In te eat equation example two pace derivative are
Hilbert-Space Integration. Introduction. We often tink of a PDE, like te eat equation u t u xx =, a an evolution equation a itorically wa done for ODE. In te eat equation example two pace derivative are
Heat Transfer/Heat Exchanger
 Heat ransfer/heat Excanger How is te eat transfer? Mecanism of Convection Applications. Mean fluid Velocity and Boundary and teir effect on te rate of eat transfer. Fundamental equation of eat transfer
Heat ransfer/heat Excanger How is te eat transfer? Mecanism of Convection Applications. Mean fluid Velocity and Boundary and teir effect on te rate of eat transfer. Fundamental equation of eat transfer
å Q d = 0 T dq =0 ò T reversible processes 1
 δ reeribe ree d Caiu Inequaity fr an Irreeribe Cye eeribe Cye fr a CaiuInequaity fr a yemed f a reeribe andan irreeribe re irre re Entry Definitin and Cange DEFINE A POPEY S S re irre S S S ENOPY reeribe
δ reeribe ree d Caiu Inequaity fr an Irreeribe Cye eeribe Cye fr a CaiuInequaity fr a yemed f a reeribe andan irreeribe re irre re Entry Definitin and Cange DEFINE A POPEY S S re irre S S S ENOPY reeribe
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Evaporation
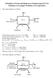 Princiles of Food and Biorocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Examle Problems on Eaoration 1. The system diagram is as follows: Solids balance equation: 0.1 (m f) = 0.5 (1,000) Thus, m f = 5,000 kg/hr
Princiles of Food and Biorocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Examle Problems on Eaoration 1. The system diagram is as follows: Solids balance equation: 0.1 (m f) = 0.5 (1,000) Thus, m f = 5,000 kg/hr
Physics 207 Lecture 23
 ysics 07 Lecture ysics 07, Lecture 8, Dec. Agenda:. Finis, Start. Ideal gas at te molecular level, Internal Energy Molar Specific Heat ( = m c = n ) Ideal Molar Heat apacity (and U int = + W) onstant :
ysics 07 Lecture ysics 07, Lecture 8, Dec. Agenda:. Finis, Start. Ideal gas at te molecular level, Internal Energy Molar Specific Heat ( = m c = n ) Ideal Molar Heat apacity (and U int = + W) onstant :
Chapter 20: Exercises: 3, 7, 11, 22, 28, 34 EOC: 40, 43, 46, 58
 Chater 0: Exercises:, 7,,, 8, 4 EOC: 40, 4, 46, 8 E: A gasoline engine takes in.80 0 4 and delivers 800 of work er cycle. The heat is obtained by burning gasoline with a heat of combustion of 4.60 0 4.
Chater 0: Exercises:, 7,,, 8, 4 EOC: 40, 4, 46, 8 E: A gasoline engine takes in.80 0 4 and delivers 800 of work er cycle. The heat is obtained by burning gasoline with a heat of combustion of 4.60 0 4.
Maths for Computer Graphics
 Trigonometry Is concerned wit te analysis of triangles. Degrees and radians Te degree (or sexagesimal unit of measure derives from defining one complete rotation as 360. Eac degree divides into 60 minutes,
Trigonometry Is concerned wit te analysis of triangles. Degrees and radians Te degree (or sexagesimal unit of measure derives from defining one complete rotation as 360. Eac degree divides into 60 minutes,
NEWCOMEN ATMOSPHERIC ENGINE
 NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m F 7 stroke 5 sia steam 8 50 F water NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m 5 sia steam 8 F 50 F water 7
NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m F 7 stroke 5 sia steam 8 50 F water NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m 5 sia steam 8 F 50 F water 7
The Second Law implies:
 e Send Law ilie: ) Heat Engine η W in H H L H L H, H H ) Ablute eerature H H L L Sale, L L W ) Fr a yle H H L L H 4) Fr an Ideal Ga Cyle H H L L L δ reerible ree d Claiu Inequality δ eerible Cyle fr a
e Send Law ilie: ) Heat Engine η W in H H L H L H, H H ) Ablute eerature H H L L Sale, L L W ) Fr a yle H H L L H 4) Fr an Ideal Ga Cyle H H L L L δ reerible ree d Claiu Inequality δ eerible Cyle fr a
Lecture 10: Carnot theorem
 ecture 0: Carnot teorem Feb 7, 005 Equivalence of Kelvin and Clausius formulations ast time we learned tat te Second aw can be formulated in two ways. e Kelvin formulation: No process is possible wose
ecture 0: Carnot teorem Feb 7, 005 Equivalence of Kelvin and Clausius formulations ast time we learned tat te Second aw can be formulated in two ways. e Kelvin formulation: No process is possible wose
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Earth s Magnetic Field. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 4 Eart s Magnetic Field Your name Lab section 1. Wat do you investigate in tis lab?. For a pair of Helmoltz coils described in tis manual and sown in Figure, r=.15 m, N=13, I =.4 A, wat
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 4 Eart s Magnetic Field Your name Lab section 1. Wat do you investigate in tis lab?. For a pair of Helmoltz coils described in tis manual and sown in Figure, r=.15 m, N=13, I =.4 A, wat
Test 2 Review. 1. Find the determinant of the matrix below using (a) cofactor expansion and (b) row reduction. A = 3 2 =
 Test Review Find te determinant of te matrix below using (a cofactor expansion and (b row reduction Answer: (a det + = (b Observe R R R R R R R R R Ten det B = (((det Hence det Use Cramer s rule to solve:
Test Review Find te determinant of te matrix below using (a cofactor expansion and (b row reduction Answer: (a det + = (b Observe R R R R R R R R R Ten det B = (((det Hence det Use Cramer s rule to solve:
A High Throughput String Matching Architecture for Intrusion Detection and Prevention
 A Hig Trougput tring Matcing Arcitecture for Intruion Detection and Prevention Lin Tan, Timoty erwood Appeared in ICA 25 Preented by: aile Kumar Dicuion Leader: Max Podleny Overview Overview of ID/IP ytem»
A Hig Trougput tring Matcing Arcitecture for Intruion Detection and Prevention Lin Tan, Timoty erwood Appeared in ICA 25 Preented by: aile Kumar Dicuion Leader: Max Podleny Overview Overview of ID/IP ytem»
NONISOTHERMAL OPERATION OF IDEAL REACTORS Plug Flow Reactor
 NONISOTHERMAL OPERATION OF IDEAL REACTORS Plug Flow Reactor T o T T o T F o, Q o F T m,q m T m T m T mo Aumption: 1. Homogeneou Sytem 2. Single Reaction 3. Steady State Two type of problem: 1. Given deired
NONISOTHERMAL OPERATION OF IDEAL REACTORS Plug Flow Reactor T o T T o T F o, Q o F T m,q m T m T m T mo Aumption: 1. Homogeneou Sytem 2. Single Reaction 3. Steady State Two type of problem: 1. Given deired
CFD calculation of convective heat transfer coefficients and validation Part I: Laminar flow. Annex 41 Kyoto, April 3 rd to 5 th, 2006
 CFD calculation of convective eat transfer coefficients and validation Part I: Laminar flow Annex 41 Kyoto, April 3 rd to 5 t, 2006 Adam Neale 1, Dominique Derome 1, Bert Blocken 2 and Jan Carmeliet 2,3
CFD calculation of convective eat transfer coefficients and validation Part I: Laminar flow Annex 41 Kyoto, April 3 rd to 5 t, 2006 Adam Neale 1, Dominique Derome 1, Bert Blocken 2 and Jan Carmeliet 2,3
( ) Given: In a constant pressure combustor. C4H10 and theoretical air burns at P1 = 0.2 MPa, T1 = 600K. Products exit at P2 = 0.
 (SP 9) N-butane (C4H1) i burned with 85 percent theoretical air, and the product of combution, an equilibrium mixture containing only O, CO, CO, H, HO, N, and NO, exit from a combution chamber at K,. MPa.
(SP 9) N-butane (C4H1) i burned with 85 percent theoretical air, and the product of combution, an equilibrium mixture containing only O, CO, CO, H, HO, N, and NO, exit from a combution chamber at K,. MPa.
The average velocity of water in the tube and the Reynolds number are Hot R-134a
 hater 0:, 8, 4, 47, 50, 5, 55, 7, 75, 77, 8 and 85. 0- Refrigerant-4a is cooled by water a double-ie heat exchanger. he overall heat transfer coefficient is to be determed. Assumtions he thermal resistance
hater 0:, 8, 4, 47, 50, 5, 55, 7, 75, 77, 8 and 85. 0- Refrigerant-4a is cooled by water a double-ie heat exchanger. he overall heat transfer coefficient is to be determed. Assumtions he thermal resistance
LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION
 LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION LAURA EVANS.. Introduction Not all differential equations can be explicitly solved for y. Tis can be problematic if we need to know te value of y
LIMITATIONS OF EULER S METHOD FOR NUMERICAL INTEGRATION LAURA EVANS.. Introduction Not all differential equations can be explicitly solved for y. Tis can be problematic if we need to know te value of y
m 5 ME-200 Fall 2017 HW-19 1/2 Given Diffuser and two-stage compressor with intercooling in a turbojet engine
 ME-00 Fall 07 HW-9 / Gven Dffuer and two-tage compreor wth ntercoolng n a turbojet engne Fnd (a) Temperature (K) of ar at the dffuer ext (b) Ma flow rate (/) of ar through the engne (c) Total power nput
ME-00 Fall 07 HW-9 / Gven Dffuer and two-tage compreor wth ntercoolng n a turbojet engne Fnd (a) Temperature (K) of ar at the dffuer ext (b) Ma flow rate (/) of ar through the engne (c) Total power nput
MTH-112 Quiz 1 Name: # :
 MTH- Quiz Name: # : Please write our name in te provided space. Simplif our answers. Sow our work.. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation.. Does te equation
MTH- Quiz Name: # : Please write our name in te provided space. Simplif our answers. Sow our work.. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation.. Does te equation
General Physics I. New Lecture 27: Carnot Cycle, The 2nd Law, Entropy and Information. Prof. WAN, Xin
 General Pysics I New Lecture 27: Carnot Cycle, e 2nd Law, Entropy and Information Prof. AN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn ttp://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Carnot s Engine Efficiency of a Carnot Engine isotermal
General Pysics I New Lecture 27: Carnot Cycle, e 2nd Law, Entropy and Information Prof. AN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn ttp://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Carnot s Engine Efficiency of a Carnot Engine isotermal
ECH 4224L Unit Operations Lab I Thin Film Evaporator. Introduction. Objective
 Introduction In this experiment, you will use thin-film evaporator (TFE) to separate a mixture of water and ethylene glycol (EG). In a TFE a mixture of two fluids runs down a heated inner wall of a cylindrical
Introduction In this experiment, you will use thin-film evaporator (TFE) to separate a mixture of water and ethylene glycol (EG). In a TFE a mixture of two fluids runs down a heated inner wall of a cylindrical
Chapter 3- Answers to selected exercises
 Chater 3- Anwer to elected exercie. he chemical otential of a imle uid of a ingle comonent i gien by the exreion o ( ) + k B ln o ( ) ; where i the temerature, i the reure, k B i the Boltzmann contant,
Chater 3- Anwer to elected exercie. he chemical otential of a imle uid of a ingle comonent i gien by the exreion o ( ) + k B ln o ( ) ; where i the temerature, i the reure, k B i the Boltzmann contant,
3.1 Extreme Values of a Function
 .1 Etreme Values of a Function Section.1 Notes Page 1 One application of te derivative is finding minimum and maimum values off a grap. In precalculus we were only able to do tis wit quadratics by find
.1 Etreme Values of a Function Section.1 Notes Page 1 One application of te derivative is finding minimum and maimum values off a grap. In precalculus we were only able to do tis wit quadratics by find
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR COUNTER FLOW COOLING TOWER- PART I, EXIT COLD WATER TEMPERATURE
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR COUNTER FLOW COOLING TOWER- PART I, EXIT COLD WATER TEMPERATURE *Citranjan Agaral Department of Mecanical Engineering, College of Tecnology and Engineering, Maarana Pratap Univerity
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR COUNTER FLOW COOLING TOWER- PART I, EXIT COLD WATER TEMPERATURE *Citranjan Agaral Department of Mecanical Engineering, College of Tecnology and Engineering, Maarana Pratap Univerity
Figure 1 Siemens PSSE Web Site
 Stability Analyi of Dynamic Sytem. In the lat few lecture we have een how mall ignal Lalace domain model may be contructed of the dynamic erformance of ower ytem. The tability of uch ytem i a matter of
Stability Analyi of Dynamic Sytem. In the lat few lecture we have een how mall ignal Lalace domain model may be contructed of the dynamic erformance of ower ytem. The tability of uch ytem i a matter of
Introduction to Derivatives
 Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation
 Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation Compensation Feedforward Control Feedforward Control of a Heat Exchanger Implementation Issues Comments Nomenclature The inherent limitation of feedback control
Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation Compensation Feedforward Control Feedforward Control of a Heat Exchanger Implementation Issues Comments Nomenclature The inherent limitation of feedback control
Bob Brown Math 251 Calculus 1 Chapter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 CCBC Dundalk
 Bob Brown Mat 251 Calculus 1 Capter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 Te Tangent Line Problem Te idea of a tangent line first arises in geometry in te context of a circle. But before we jump into a discussion of
Bob Brown Mat 251 Calculus 1 Capter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 Te Tangent Line Problem Te idea of a tangent line first arises in geometry in te context of a circle. But before we jump into a discussion of
1 Power is transferred through a machine as shown. power input P I machine. power output P O. power loss P L. What is the efficiency of the machine?
 1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is
1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muhammad Rashid Usman
 Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muammad Rasid Usman Institute of Cemical Engineering and Tecnology University of te Punjab, Laore. Figure taken from: ttp://eatexcanger-design.com/20/0/06/eat-excangers-6/
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Muammad Rasid Usman Institute of Cemical Engineering and Tecnology University of te Punjab, Laore. Figure taken from: ttp://eatexcanger-design.com/20/0/06/eat-excangers-6/
RP 2.4. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1513
 P 2.4 Measurement of sear ave velocity of eavy oil De-ua Han, Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Micael Batzle, Colorado Scool of Mines Introduction It is ell knon tat te fluids ave no sear modulus and
P 2.4 Measurement of sear ave velocity of eavy oil De-ua Han, Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Micael Batzle, Colorado Scool of Mines Introduction It is ell knon tat te fluids ave no sear modulus and
The Art Exhibition Catalog
 The 2013 Illinois River Salon Art Exhibition Catalog Featuring over 50 carefully selected artworks by 40 artists celebrating and promoting the beautiful Illinois River Watershed of Northwest Arkansas and
The 2013 Illinois River Salon Art Exhibition Catalog Featuring over 50 carefully selected artworks by 40 artists celebrating and promoting the beautiful Illinois River Watershed of Northwest Arkansas and
Conductance from Transmission Probability
 Conductance rom Transmission Probability Kelly Ceung Department o Pysics & Astronomy University o Britis Columbia Vancouver, BC. Canada, V6T1Z1 (Dated: November 5, 005). ntroduction For large conductors,
Conductance rom Transmission Probability Kelly Ceung Department o Pysics & Astronomy University o Britis Columbia Vancouver, BC. Canada, V6T1Z1 (Dated: November 5, 005). ntroduction For large conductors,
Solutions to Homework #10
 Solution to Homeork #0 0-6 A teady-lo Carnot enge it ater a te orkg luid operate at peciied condition. e termal eiciency, te preure at te turbe let, and te ork put are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
Solution to Homeork #0 0-6 A teady-lo Carnot enge it ater a te orkg luid operate at peciied condition. e termal eiciency, te preure at te turbe let, and te ork put are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
2.3 Product and Quotient Rules
 .3. PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 75.3 Product and Quotient Rules.3.1 Product rule Suppose tat f and g are two di erentiable functions. Ten ( g (x)) 0 = f 0 (x) g (x) + g 0 (x) See.3.5 on page 77 for a proof.
.3. PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 75.3 Product and Quotient Rules.3.1 Product rule Suppose tat f and g are two di erentiable functions. Ten ( g (x)) 0 = f 0 (x) g (x) + g 0 (x) See.3.5 on page 77 for a proof.
MAT 1800 FINAL EXAM HOMEWORK
 MAT 800 FINAL EXAM HOMEWORK Read te directions to eac problem careully ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR Problems come rom old inal eams (SS4, W4, F, SS, W) Solving Equations: Let 5 Find all
MAT 800 FINAL EXAM HOMEWORK Read te directions to eac problem careully ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR Problems come rom old inal eams (SS4, W4, F, SS, W) Solving Equations: Let 5 Find all
Given: Hot fluid oil, Cold fluid - water (T 1, T 2 ) (t 1, t 2 ) Water
 . In a counter flow double pipe eat excanger, oil is cooled fro 85 to 55 by water entering at 5. Te ass flow rate of oil is 9,800 kg/ and specific eat f oil is 000 J/kg K. Te ass flow rate of water is
. In a counter flow double pipe eat excanger, oil is cooled fro 85 to 55 by water entering at 5. Te ass flow rate of oil is 9,800 kg/ and specific eat f oil is 000 J/kg K. Te ass flow rate of water is
Polynomial Functions. Linear Functions. Precalculus: Linear and Quadratic Functions
 Concepts: definition of polynomial functions, linear functions tree representations), transformation of y = x to get y = mx + b, quadratic functions axis of symmetry, vertex, x-intercepts), transformations
Concepts: definition of polynomial functions, linear functions tree representations), transformation of y = x to get y = mx + b, quadratic functions axis of symmetry, vertex, x-intercepts), transformations
Math 102 TEST CHAPTERS 3 & 4 Solutions & Comments Fall 2006
 Mat 102 TEST CHAPTERS 3 & 4 Solutions & Comments Fall 2006 f(x+) f(x) 10 1. For f(x) = x 2 + 2x 5, find ))))))))) and simplify completely. NOTE: **f(x+) is NOT f(x)+! f(x+) f(x) (x+) 2 + 2(x+) 5 ( x 2
Mat 102 TEST CHAPTERS 3 & 4 Solutions & Comments Fall 2006 f(x+) f(x) 10 1. For f(x) = x 2 + 2x 5, find ))))))))) and simplify completely. NOTE: **f(x+) is NOT f(x)+! f(x+) f(x) (x+) 2 + 2(x+) 5 ( x 2
Section 2.7 Derivatives and Rates of Change Part II Section 2.8 The Derivative as a Function. at the point a, to be. = at time t = a is
 Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
CHAPTER 5: Derivatives of Exponential and Trigonometric Functions
 CHAPTER : Derivatives of Eonential and Trigonometric Functions Review of Prerequisite Skills,.. a. c. d. a b a b. a. 9 Q" R 7 Q" 7R 9 9 log 6 log 6 c. log d. log 0 0 w e. log z 8 f. log a T b. a. 0 Te
CHAPTER : Derivatives of Eonential and Trigonometric Functions Review of Prerequisite Skills,.. a. c. d. a b a b. a. 9 Q" R 7 Q" 7R 9 9 log 6 log 6 c. log d. log 0 0 w e. log z 8 f. log a T b. a. 0 Te
P E R E N C O - C H R I S T M A S P A R T Y
 L E T T I C E L E T T I C E I S A F A M I L Y R U N C O M P A N Y S P A N N I N G T W O G E N E R A T I O N S A N D T H R E E D E C A D E S. B A S E D I N L O N D O N, W E H A V E T H E P E R F E C T R
L E T T I C E L E T T I C E I S A F A M I L Y R U N C O M P A N Y S P A N N I N G T W O G E N E R A T I O N S A N D T H R E E D E C A D E S. B A S E D I N L O N D O N, W E H A V E T H E P E R F E C T R
CHAPTER 6 : LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER 6 : LITERATURE REVIEW Chapter : LITERATURE REVIEW 77 M E A S U R I N G T H E E F F I C I E N C Y O F D E C I S I O N M A K I N G U N I T S A B S T R A C T A n o n l i n e a r ( n o n c o n v e
CHAPTER 6 : LITERATURE REVIEW Chapter : LITERATURE REVIEW 77 M E A S U R I N G T H E E F F I C I E N C Y O F D E C I S I O N M A K I N G U N I T S A B S T R A C T A n o n l i n e a r ( n o n c o n v e
Types of Heat Transfer
 ype of Heat ranfer * Dvz Dt x k d dx v S * * v Gr z HH vap lat uject in the coure conduction (Fourier Law) forced convection (due to flow) ource term free convection (fluid motion due to denity variation
ype of Heat ranfer * Dvz Dt x k d dx v S * * v Gr z HH vap lat uject in the coure conduction (Fourier Law) forced convection (due to flow) ource term free convection (fluid motion due to denity variation
Lecture XVII. Abstract We introduce the concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation with the gradient operator.
 Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Given A gas turbine power plant operating with air-standard Brayton cycle
 ME-200 Fall 2017 HW-38 1/4 Given A ga turbine power plant operating with air-tandard Brayton cycle Find For ientropic compreion and expanion: (a) Net power (kw) produced by the power plant (b) Thermal
ME-200 Fall 2017 HW-38 1/4 Given A ga turbine power plant operating with air-tandard Brayton cycle Find For ientropic compreion and expanion: (a) Net power (kw) produced by the power plant (b) Thermal
SFU UBC UNBC Uvic Calculus Challenge Examination June 5, 2008, 12:00 15:00
 SFU UBC UNBC Uvic Calculus Callenge Eamination June 5, 008, :00 5:00 Host: SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY First Name: Last Name: Scool: Student signature INSTRUCTIONS Sow all your work Full marks are given only
SFU UBC UNBC Uvic Calculus Callenge Eamination June 5, 008, :00 5:00 Host: SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY First Name: Last Name: Scool: Student signature INSTRUCTIONS Sow all your work Full marks are given only
MANUFACTURING TOLERANCES AS A CAUSE FOR AUDIBLE NOISE OF INDUCTION MOTORS
 MANUFACTURING TOLERANCES AS A CAUSE FOR AUDIBLE NOISE OF INDUCTION MOTORS Delaere K., Franen J., Hameyer K., Belman R. Katholieke Univeriteit Leuven, De. EE (ESAT) Div. ELEN, Kardinaal Mercierlaan 94,
MANUFACTURING TOLERANCES AS A CAUSE FOR AUDIBLE NOISE OF INDUCTION MOTORS Delaere K., Franen J., Hameyer K., Belman R. Katholieke Univeriteit Leuven, De. EE (ESAT) Div. ELEN, Kardinaal Mercierlaan 94,
. h I B. Average velocity can be interpreted as the slope of a tangent line. I C. The difference quotient program finds the exact value of f ( a)
 Capter Review Packet (questions - ) KEY. In eac case determine if te information or statement is correct (C) or incorrect (I). If it is incorrect, include te correction. f ( a ) f ( a) I A. represents
Capter Review Packet (questions - ) KEY. In eac case determine if te information or statement is correct (C) or incorrect (I). If it is incorrect, include te correction. f ( a ) f ( a) I A. represents
Physics 41 Chapter 22 HW
 Pysis 41 apter 22 H 1. eat ine performs 200 J of work in ea yle and as an effiieny of 30.0%. For ea yle, ow mu energy is (a) taken in and (b) expelled as eat? = = 200 J (1) e = 1 0.300 = = (2) From (2),
Pysis 41 apter 22 H 1. eat ine performs 200 J of work in ea yle and as an effiieny of 30.0%. For ea yle, ow mu energy is (a) taken in and (b) expelled as eat? = = 200 J (1) e = 1 0.300 = = (2) From (2),
Simulation and verification of a plate heat exchanger with a built-in tap water accumulator
 Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Exponential and logarithmic functions (pp ) () Supplement October 14, / 1. a and b positive real numbers and x and y real numbers.
 MA123, Supplement Exponential and logaritmic functions pp. 315-319) Capter s Goal: Review te properties of exponential and logaritmic functions. Learn ow to differentiate exponential and logaritmic functions.
MA123, Supplement Exponential and logaritmic functions pp. 315-319) Capter s Goal: Review te properties of exponential and logaritmic functions. Learn ow to differentiate exponential and logaritmic functions.
Theory of turbomachinery. Chapter 1
 Theory of turbomachinery Chater Introduction: Basic Princiles Take your choice of those that can best aid your action. (Shakeseare, Coriolanus) Introduction Definition Turbomachinery describes machines
Theory of turbomachinery Chater Introduction: Basic Princiles Take your choice of those that can best aid your action. (Shakeseare, Coriolanus) Introduction Definition Turbomachinery describes machines
Basic Models of Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer
 20 Basic Models of Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer Keywords: Unit Models, Evaporator, Vaporizer A chemical process invariably involves energy transfer simultaneously with mass transfer. So in this
20 Basic Models of Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer Keywords: Unit Models, Evaporator, Vaporizer A chemical process invariably involves energy transfer simultaneously with mass transfer. So in this
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. Section 1.5 = = = 4. Check Point Exercises The slope of the line y = 3x+ 1 is 3.
 Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
The total error in numerical differentiation
 AMS 147 Computational Metods and Applications Lecture 08 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Loss of accuracy due to numerical cancellation A B 3, 3 ~10 16 In calculating te difference between A and
AMS 147 Computational Metods and Applications Lecture 08 Copyrigt by Hongyun Wang, UCSC Recap: Loss of accuracy due to numerical cancellation A B 3, 3 ~10 16 In calculating te difference between A and
Key Concepts. Important Techniques. 1. Average rate of change slope of a secant line. You will need two points ( a, the formula: to find value
 AB Calculus Unit Review Key Concepts Average and Instantaneous Speed Definition of Limit Properties of Limits One-sided and Two-sided Limits Sandwic Teorem Limits as x ± End Beaviour Models Continuity
AB Calculus Unit Review Key Concepts Average and Instantaneous Speed Definition of Limit Properties of Limits One-sided and Two-sided Limits Sandwic Teorem Limits as x ± End Beaviour Models Continuity
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES CONDITIONS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF A LIMIT
 LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Te limit of a function is defined as te value of y tat te curve approaces, as x approaces a particular value. Te limit of f (x) as x approaces a is written as f (x) approaces, as
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Te limit of a function is defined as te value of y tat te curve approaces, as x approaces a particular value. Te limit of f (x) as x approaces a is written as f (x) approaces, as
Exercises for lectures 20 Digital Control
 Exercie for lecture 0 Digital Control Micael Šebek Automatic control 06-4- Sampling: and z relationip for complex pole Continuou ignal Laplace tranform wit pole Dicrete ignal z-tranform, t y( t) e in t,
Exercie for lecture 0 Digital Control Micael Šebek Automatic control 06-4- Sampling: and z relationip for complex pole Continuou ignal Laplace tranform wit pole Dicrete ignal z-tranform, t y( t) e in t,
Lecture Notes Di erentiating Trigonometric Functions page 1
 Lecture Notes Di erentiating Trigonometric Functions age (sin ) 7 sin () sin 8 cos 3 (tan ) sec tan + 9 tan + 4 (cot ) csc cot 0 cot + 5 sin (sec ) cos sec tan sec jj 6 (csc ) sin csc cot csc jj c Hiegkuti,
Lecture Notes Di erentiating Trigonometric Functions age (sin ) 7 sin () sin 8 cos 3 (tan ) sec tan + 9 tan + 4 (cot ) csc cot 0 cot + 5 sin (sec ) cos sec tan sec jj 6 (csc ) sin csc cot csc jj c Hiegkuti,
The derivative function
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter : Definition of derivative Section Te derivative function Wat you need to know already: f is at a point on its grap and ow to compute it. Wat te derivative
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Capter : Definition of derivative Section Te derivative function Wat you need to know already: f is at a point on its grap and ow to compute it. Wat te derivative
Name: Sept 21, 2017 Page 1 of 1
 MATH 111 07 (Kunkle), Eam 1 100 pts, 75 minutes No notes, books, electronic devices, or outside materials of an kind. Read eac problem carefull and simplif our answers. Name: Sept 21, 2017 Page 1 of 1
MATH 111 07 (Kunkle), Eam 1 100 pts, 75 minutes No notes, books, electronic devices, or outside materials of an kind. Read eac problem carefull and simplif our answers. Name: Sept 21, 2017 Page 1 of 1
Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in the Corrugated Packing of the Counter Flow Cooling Tower
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 59-577 (2008) Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in the Corrugated Packing of the Counter Flow Cooling Tower Montri Pirunkaset* and Santi Laksitanonta BSTRCT This paper
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 59-577 (2008) Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in the Corrugated Packing of the Counter Flow Cooling Tower Montri Pirunkaset* and Santi Laksitanonta BSTRCT This paper
Heat Integration - Introduction
 Heat Integration - Introduction Sub-Topics Design of Heat Exchanger Networks Selection of Utilities Ø Consumption and Production Correct Integration Ø Distillation and Evaporation Ø Heat Pumps Ø Turbines
Heat Integration - Introduction Sub-Topics Design of Heat Exchanger Networks Selection of Utilities Ø Consumption and Production Correct Integration Ø Distillation and Evaporation Ø Heat Pumps Ø Turbines
The Basics of Vacuum Technology
 Te Basics of Vacuum Tecnology Grolik Benno, Kopp Joacim January 2, 2003 Basics Many scientific and industrial processes are so sensitive tat is is necessary to omit te disturbing influence of air. For
Te Basics of Vacuum Tecnology Grolik Benno, Kopp Joacim January 2, 2003 Basics Many scientific and industrial processes are so sensitive tat is is necessary to omit te disturbing influence of air. For
USE OF INTERNET TO DO EXPERIMENTS IN DYNAMICS AND CONTROL FROM ZACATECAS MEXICO IN THE LABORATORY OF THE UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT CHATANOOGAA.
 USE OF INTERNET TO DO EXPERIMENTS IN DYNAMICS AND CONTROL FROM ZACATECAS MEXICO IN TE LABORATORY OF TE UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT CATANOOGAA. Jim enry *, Joé Alberto González Guerrero, Benito Serrano Roale..
USE OF INTERNET TO DO EXPERIMENTS IN DYNAMICS AND CONTROL FROM ZACATECAS MEXICO IN TE LABORATORY OF TE UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT CATANOOGAA. Jim enry *, Joé Alberto González Guerrero, Benito Serrano Roale..
Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems
 ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
Intermediate Math Circles November 5, 2008 Geometry II
 1 Univerity of Waterloo Faculty of Matematic Centre for Education in Matematic and Computing Intermediate Mat Circle November 5, 2008 Geometry II Geometry 2-D Figure Two-dimenional ape ave a perimeter
1 Univerity of Waterloo Faculty of Matematic Centre for Education in Matematic and Computing Intermediate Mat Circle November 5, 2008 Geometry II Geometry 2-D Figure Two-dimenional ape ave a perimeter
Design of Robust PI Controller for Counter-Current Tubular Heat Exchangers
 Deign of Robut PI Controller for Counter-Current Tubular Heat Excanger Jana Závacká Monika Bakošová Intitute of Information Engineering Automation Matematic Faculty of Cemical Food Tecnology STU in Bratilava
Deign of Robut PI Controller for Counter-Current Tubular Heat Excanger Jana Závacká Monika Bakošová Intitute of Information Engineering Automation Matematic Faculty of Cemical Food Tecnology STU in Bratilava
Announcements. Exam 4 - Review of important concepts
 Announcements 1. Exam 4 starts Friday! a. Available in esting Center from Friday, Dec 7 (opening time), up to Monday, Dec 10 at 4:00 pm. i. Late fee if you start your exam after 4 pm b. Covers C. 9-1 (up
Announcements 1. Exam 4 starts Friday! a. Available in esting Center from Friday, Dec 7 (opening time), up to Monday, Dec 10 at 4:00 pm. i. Late fee if you start your exam after 4 pm b. Covers C. 9-1 (up
ME 315 Exam 3 8:00-9:00 PM Thursday, April 16, 2009 CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION
 ME 315 Exam 3 8:00-9:00 PM Thurday, Aril 16, 009 Thi i a cloed-book, cloed-note examination. There i a formula heet at the back. You mut turn off all communication device before tarting thi exam, and leave
ME 315 Exam 3 8:00-9:00 PM Thurday, Aril 16, 009 Thi i a cloed-book, cloed-note examination. There i a formula heet at the back. You mut turn off all communication device before tarting thi exam, and leave
The isentropic exponent in plasmas
 Te isentroic exonent in lasmas Burm K.T.A.L.; Goedeer W.J.; cram D.C. Publised in: Pysics of Plasmas DOI: 10.1063/1.873535 Publised: 01/01/1999 Document Version Publiser s PDF also known as Version of
Te isentroic exonent in lasmas Burm K.T.A.L.; Goedeer W.J.; cram D.C. Publised in: Pysics of Plasmas DOI: 10.1063/1.873535 Publised: 01/01/1999 Document Version Publiser s PDF also known as Version of
0 o C. H vap. H evap
 Solution. Energy P (00 ) Pν x 0 5 ρ 850,4 J kg - J kg Power kg s 000,4 600 70 W Solution. 00 o C H evap H vap 0 o C H liq 00 t H liq (4. x0 t ) dt 4.t x0 0 40 0 40 kj kg - H evap 40,68 J mol - (From Appendix
Solution. Energy P (00 ) Pν x 0 5 ρ 850,4 J kg - J kg Power kg s 000,4 600 70 W Solution. 00 o C H evap H vap 0 o C H liq 00 t H liq (4. x0 t ) dt 4.t x0 0 40 0 40 kj kg - H evap 40,68 J mol - (From Appendix
Solved problems 4 th exercise
 Soled roblem th exercie Soled roblem.. On a circular conduit there are different diameter: diameter D = m change into D = m. The elocity in the entrance rofile wa meaured: = m -. Calculate the dicharge
Soled roblem th exercie Soled roblem.. On a circular conduit there are different diameter: diameter D = m change into D = m. The elocity in the entrance rofile wa meaured: = m -. Calculate the dicharge
Differential Calculus: Differentiation (First Principles, Rules) and Sketching Graphs (Grade 12) *
 OpenStax-CNX moule: m39313 1 Differential Calculus: Differentiation (First Principles, Rules) an Sketcing Graps (Grae 12) * Free Hig Scool Science Texts Project Tis work is prouce by OpenStax-CNX an license
OpenStax-CNX moule: m39313 1 Differential Calculus: Differentiation (First Principles, Rules) an Sketcing Graps (Grae 12) * Free Hig Scool Science Texts Project Tis work is prouce by OpenStax-CNX an license
