1 Power is transferred through a machine as shown. power input P I machine. power output P O. power loss P L. What is the efficiency of the machine?
|
|
|
- Jack Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is forced troug a valve at a constant pressure p. In one stroke of te pump te volume of air in te pump camber is reduced from V 1 to V 2. V 1 V 2 p initially to valve finally p to valve Wat is te work done on tis air in one stroke of te pump? p(v 1 + V 2 ) 2 p(v 1 + V 2 ) p(v 1 - V 2 ) pv 1 3 ar X is travelling at alf te speed of car Y. ar X as twice te mass of car Y. Wic statement is correct? ar X as alf te kinetic of car Y. ar X as one quarter of te kinetic of car Y. ar X as twice te kinetic of car Y. Te two cars ave te same kinetic.
2 4 trolley runs from P to Q along a track. t Q its potential is 5 kj less tan at P. 2 trolley P Q t P, te kinetic of te trolley is 5 kj. etween P and Q te work te trolley does against friction is 1 kj. Wat is te kinetic of te trolley at Q? 35 kj 45 kj 55 kj 65 kj 5 To travel at a constant speed, a car engine provides 24 kw of useful power. Te driving force on te car is 6 N. t wat speed does it travel? 2.5 m s 1 4. m s 1 25 m s 1 4 m s 1 6 Wic of te following expressions defines power? force x distance moved in te direction of te force force x velocity work done time taken work done x time taken
3 7 Wat is te expression used to define power? 3 output input x time taken force x velocity work done time taken 8 ball is trown vertically upwards. Neglecting air resistance, wic statement is correct? Te kinetic of te ball is greatest at te greatest eigt attained. y te principle of conservation of, te total of te ball is constant trougout its motion. y te principle of conservation of momentum, te momentum of te ball is constant trougout its motion. Te potential of te ball increases uniformly wit time during te ascent. 9 barrel of mass 5 kg is loaded onto te back of a lorry 1.6 m ig by pusing it up a smoot plank 3.4 m long. 3.4 m lorry barrel mass = 5 kg plank 1.6 m Wat is te minimum work done? 8 J 17 J 78 J 17 J 1 Wat is te internal of an object? It is te associated wit te object s movement troug space. It is te associated wit te random movement of te molecules in te object. It is te due to te attractions between te molecules witin te object. It is te sum of all te microscopic potential and kinetic energies of te molecules.
4 11 steel ball is falling at constant speed in oil. 4 Wic grap sows te variation wit time of te gravitational potential and te kinetic of te ball? time time time time 12 stone of weigt 4. N in te Eart s gravitational field is moved from P to Q and ten to R along te pat sown. Q 4 m R 3 m 5 m P Eart's surface How muc potential does te stone gain? 12 J 2 J 28 J 12 J
5 13 n electrical generator is started at time zero. Te total electrical generated during te first 5 seconds is sown in te grap. 5 5 / J time / s Wat is te maximum electrical power generated at any instant during tese first 5 seconds? 1 W 13 W 3 W 5 W 14 concrete cube of side.5 m and uniform density 2. x 1 3 kg m 3 is lifted 3. m vertically by a crane. Wat is te cange in potential of te cube?.75 kj 7.4 kj 29 kj 47 kj 15 In perfectly elastic collisions between two atoms, it is always true to say tat te initial speed of one atom will be te same as te final speed of te oter atom. te relative speed of approac between te two atoms equals teir relative speed of separation. te total momentum must be conserved, but a small amount of te total kinetic may be lost in te collision. watever teir initial states of motion, neiter atom can be stationary after te collision.
6 6 16 Te diagram sows te masses and velocities of two trolleys about to collide. 4 m s 1 2 kg 1 m s 1 4 kg fter te impact tey move off togeter. Wat is te total kinetic of te trolleys after te collision? 1.3 J 12 J 18 J 19 J 17 Wic expression defines power? force distance moved in te direction of te force force velocity work done time taken work done time taken 18 Two equal masses X and Y are moving towards eac oter on a frictionless air track as sown. Te masses make an elastic collision. air track 5 cm s 1 3 cm s 1 X Y Wic row gives possible velocities for te two masses after te collision? velocity of X velocity of Y zero 2 cm s 1 to te rigt 1 cm s 1 to te rigt 1 cm s 1 to te rigt 2 cm s 1 to te left zero 3 cm s 1 to te left 5 cm s 1 to te rigt 19 boat moving at constant speed v troug still water experiences a total frictional drag F. Wat is te power developed by te boat? 1 2Fv Fv 1 2Fv 2 Fv 2
7 7 2 steel ball is falling at constant speed in oil. Wic grap sows te variation wit time of te gravitational potential and te kinetic of te ball? time time time time 21 Te total input E in in a process is partly transferred to useful output U, and partly to tat is wasted W. Wat is te efficiency of te process? U 1 % W W 1 % E in U 1 % E in U + W E in 1 %
8 Two speres and approac eac oter along te same straigt line wit speeds u and u. Te speres collide and move off wit speeds v and v, bot in te same direction as te initial direction of spere, as sown below. before collision u u after collision v v Wic equation applies to an elastic collision? u + u = v v u u = v v u u = v + v u + u = v + v 23 Two balls X and Y approac eac oter along te same straigt line and collide elastically. Teir speeds are u X and u Y respectively. fter te collision tey move apart wit speeds v X and v Y respectively. Teir directions are sown on te diagram. before X u X u Y Y after v X X Y v Y Wic of te following equations is correct? u X + u Y = v X + v Y u X + u Y = v X v Y u X u Y = v X + v Y u X u Y = v X v Y 24 Wic of te following is an expression for power? x time force x displacement force x velocity mass x velocity
9 car driver adjusts te pressure on a car s brakes so tat te car travels at constant speed down a ill from P to Q. P Q Te magnitude of te cange in te car s kinetic is. Te magnitude of te cange in its gravitational potential is. Wic statement is correct? > = > > = 26 n area of land is an average of 2. m below sea level. To prevent flooding, pumps are used to lift rainwater up to sea level. Wat is te minimum pump output power required to deal wit kg of rain per day? 15 kw 3 kw 15 kw 3 kw 27 twig from a tree drops from a 2 m ig cliff on to a beac below. uring its fall, 4% of te twig s is converted into termal. Wat is te speed wit wic te twig its te beac? 35 m s 1 4 m s 1 49 m s 1 63 m s 1 28 mass is raised vertically. In time t, te increase in its gravitational potential is and te increase in its kinetic is. Wat is te average power input to te mass? ( )t ( + )t t + t
10 29 Te kinetic of a particle is increased by a factor of 4. 1 y wat factor does its speed increase? orizontal force of 9 N is used to pus a box across a orizontal floor. Te frictional force on te box is 5 N. Wat is te gain in kinetic of te box wen it is moved troug a distance of 6. m? 24 J 3 J 54 J 84 J 31 cyclist is capable of generating an average power of 3. kw during a 4. km speed trial. His aerodynamic suit and position on te cycle reduce resistive forces to 18 N. Wat is te approximate time acieved in te speed trial? 14 s 24 s 13 s 22 s 32 constant force of 9. kn, parallel to an inclined plane, moves a body of weigt 2 kn troug a distance of 4 m along te plane at constant speed. Te body gains 12 m in eigt, as sown. 4 m 9. kn 12 m 2 kn How muc of te work done is dissipated as eat? 12 kj 24 kj 36 kj 6 kj 33 car wit a total mass of 14 kg is travelling at 3 m s 1. Wat is te kinetic of te car? 21 kj 42 kj 63 kj 126 kj
11 11 34 n object is trown into te air. Wic grap sows ow te potential of te object varies wit eigt above te ground? 35 Te diagram sows a barrel of weigt 1. x 1 3 N on a frictionless slope inclined at 3 o to te orizontal. force of slope on barrel force slope 3 o 1. x 1 3 N barrel force is applied to te barrel to move it up te slope at constant speed. Te force is parallel to te slope. Wat is te work done in moving te barrel a distance of 5. m up te slope? 1. x 1 4 J 2.5 x 1 3 J 4.3 x 1 3 J 5. x 1 3 J In many old-style filament lamps, as muc as 93 J of is emitted as termal for every 7 J of emitted as ligt. Wat is te efficiency of te lamp, as te percentage of electrical converted to ligt? 7 % 8 % 92 % 93 % To get to is office from te entrance of te building, a man as to walk up six fligts of stairs. Te eigt of eac fligt is 2.5 m and te man as a mass of 8 kg. Wat is te approximate gain in te man s gravitational potential during te climb? 12 J 2 J 48 J 12 J
12 12 38 n electric railway locomotive as a maximum mecanical output power of 4. MW. Electrical power is delivered at 25 kv from overead wires. Te overall efficiency of te locomotive in converting electrical power to mecanical power is 8 %. Wat is te current from te overead wires wen te locomotive is operating at its maximum power? car of mass 1 kg first travels forwards at 25 m s 1 and ten backwards at 5 m s 1. Wat is te cange in te kinetic of te car? 2 kj 3 kj 325 kj 45 kj 4 Wen bungee jumping, a student starts wit maximum gravitational potential (position 1), ten falls freely until te rope fully unwinds (position 2), after wic te rope starts to stretc until te lowest point of te jump is reaced (position 3). position 1 position 2 Wat are te kinetic and elastic potential energies at position 3? position 3 kinetic elastic potential maximum maximum maximum minimum minimum maximum minimum minimum
13 13 41 wooden block rests on a roug board. Te end of te board is ten raised until te block slides down te plane of te board at constant velocity v. block v board Wic row describes te forces acting on te block wen sliding wit constant velocity? frictional force on block resultant force on block down te plane down te plane down te plane zero up te plane down te plane up te plane zero 42 Two speres approac eac oter along te same straigt line. Teir speeds are u 1 and u 2 before collision, and v 1 and v 2 after collision, in te directions sown below. before collision u 1 u 2 after collision v 1 v 2 Wic equation is correct if te collision is perfectly elastic? u 1 u 2 = v 2 + v 1 u 1 u 2 = v 2 v 1 u 1 + u 2 = v 2 + v 1 u 1 + u 2 = v 2 v 1
14 43 block of weigt W is pulled up a roug slope by a force F. 14 Wen te block as moved a distance x along te slope, it as risen eigt. x F W Wic expressions give te amount of work done on te block and te amount of gravitational potential gained by te block? work done gravitational potential Fx W F Wx Wx F W Fx 44 n object is trown into te air. Wic grap sows ow te potential of te object varies wit eigt above te ground?
15 45 pendulum bob oscillates between P and R. 15 P R y Q x ssuming te gravitational potential lost in moving from P to Q is converted into kinetic, wat is te speed of te bob at Q? 2 gx 2gx 2 gy 2gy 46 Wic operation involves te greatest mean power? a car moving against a resistive force of.4 kn at a constant speed of 2 m s 1 a crane lifting a weigt of 3 kn at a speed of 2 m s 1 a crane lifting a weigt of 5 kn at a speed of 1 m s 1 a weigt being pulled across a orizontal surface at a speed of 6 m s 1 against a frictional force of 1.5 kn
Phy 231 Sp 02 Homework #6 Page 1 of 4
 Py 231 Sp 02 Homework #6 Page 1 of 4 6-1A. Te force sown in te force-time diagram at te rigt versus time acts on a 2 kg mass. Wat is te impulse of te force on te mass from 0 to 5 sec? (a) 9 N-s (b) 6 N-s
Py 231 Sp 02 Homework #6 Page 1 of 4 6-1A. Te force sown in te force-time diagram at te rigt versus time acts on a 2 kg mass. Wat is te impulse of te force on te mass from 0 to 5 sec? (a) 9 N-s (b) 6 N-s
Problem Set 7: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy AP Physics C Supplementary Problems
 Proble Set 7: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy AP Pysics C Suppleentary Probles 1. Approxiately 5.5 x 10 6 kg of water drops 50 over Niagara Falls every second. (a) Calculate te aount of potential
Proble Set 7: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy AP Pysics C Suppleentary Probles 1. Approxiately 5.5 x 10 6 kg of water drops 50 over Niagara Falls every second. (a) Calculate te aount of potential
E p = mgh (if h i=0) E k = ½ mv 2 Ek is measured in Joules (J); m is measured in kg; v is measured in m/s. Energy Continued (E)
 nergy Continued () Gravitational Potential nergy: - e energy stored in an object due to its distance above te surface of te art. - e energy stored depends on te mass of te object, te eigt above te surface,
nergy Continued () Gravitational Potential nergy: - e energy stored in an object due to its distance above te surface of te art. - e energy stored depends on te mass of te object, te eigt above te surface,
Work and Energy. Introduction. Work. PHY energy - J. Hedberg
 Work and Energy PHY 207 - energy - J. Hedberg - 2017 1. Introduction 2. Work 3. Kinetic Energy 4. Potential Energy 5. Conservation of Mecanical Energy 6. Ex: Te Loop te Loop 7. Conservative and Non-conservative
Work and Energy PHY 207 - energy - J. Hedberg - 2017 1. Introduction 2. Work 3. Kinetic Energy 4. Potential Energy 5. Conservation of Mecanical Energy 6. Ex: Te Loop te Loop 7. Conservative and Non-conservative
M12/4/PHYSI/HPM/ENG/TZ1/XX. Physics Higher level Paper 1. Thursday 10 May 2012 (afternoon) 1 hour INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M12/4/PHYSI/HPM/ENG/TZ1/XX 22126507 Pysics Higer level Paper 1 Tursday 10 May 2012 (afternoon) 1 our INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open tis examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all te
M12/4/PHYSI/HPM/ENG/TZ1/XX 22126507 Pysics Higer level Paper 1 Tursday 10 May 2012 (afternoon) 1 our INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open tis examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all te
106 PHYS - CH6 - Part2
 106 PHYS - CH6 - Part Conservative Forces (a) A force is conservative if work one by tat force acting on a particle moving between points is inepenent of te pat te particle takes between te two points
106 PHYS - CH6 - Part Conservative Forces (a) A force is conservative if work one by tat force acting on a particle moving between points is inepenent of te pat te particle takes between te two points
Section 3: The Derivative Definition of the Derivative
 Capter 2 Te Derivative Business Calculus 85 Section 3: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Returning to te tangent slope problem from te first section, let's look at te problem of finding te slope
Capter 2 Te Derivative Business Calculus 85 Section 3: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Returning to te tangent slope problem from te first section, let's look at te problem of finding te slope
Grade: 11 International Physics Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2
 Grade: 11 International Pysics Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Max Marks: 60 Test ID: 12111 Time
Grade: 11 International Pysics Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Max Marks: 60 Test ID: 12111 Time
MAT 145. Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points
 MAT 15 Test #2 Name Solution Guide Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points Use te grap of a function sown ere as you respond to questions 1 to 8. 1. lim f (x) 0 2. lim
MAT 15 Test #2 Name Solution Guide Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points Use te grap of a function sown ere as you respond to questions 1 to 8. 1. lim f (x) 0 2. lim
PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 15 February 2005
 Name: (4 points) PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 15 February 2005 Tis test is open-note and open-book. Tis means tat any reference material is permitted during te test. Calculators also
Name: (4 points) PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 15 February 2005 Tis test is open-note and open-book. Tis means tat any reference material is permitted during te test. Calculators also
Chapters 19 & 20 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
1 Limits and Continuity
 1 Limits and Continuity 1.0 Tangent Lines, Velocities, Growt In tion 0.2, we estimated te slope of a line tangent to te grap of a function at a point. At te end of tion 0.3, we constructed a new function
1 Limits and Continuity 1.0 Tangent Lines, Velocities, Growt In tion 0.2, we estimated te slope of a line tangent to te grap of a function at a point. At te end of tion 0.3, we constructed a new function
1. Consider the trigonometric function f(t) whose graph is shown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t).
 . Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd, periodic function tat as been sifted upwards, so we will use
. Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd, periodic function tat as been sifted upwards, so we will use
f a h f a h h lim lim
 Te Derivative Te derivative of a function f at a (denoted f a) is f a if tis it exists. An alternative way of defining f a is f a x a fa fa fx fa x a Note tat te tangent line to te grap of f at te point
Te Derivative Te derivative of a function f at a (denoted f a) is f a if tis it exists. An alternative way of defining f a is f a x a fa fa fx fa x a Note tat te tangent line to te grap of f at te point
Introduction to Derivatives
 Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
2.3. Applying Newton s Laws of Motion. Objects in Equilibrium
 Appling Newton s Laws of Motion As ou read in Section 2.2, Newton s laws of motion describe ow objects move as a result of different forces. In tis section, ou will appl Newton s laws to objects subjected
Appling Newton s Laws of Motion As ou read in Section 2.2, Newton s laws of motion describe ow objects move as a result of different forces. In tis section, ou will appl Newton s laws to objects subjected
Outline. MS121: IT Mathematics. Limits & Continuity Rates of Change & Tangents. Is there a limit to how fast a man can run?
 Outline MS11: IT Matematics Limits & Continuity & 1 Limits: Atletics Perspective Jon Carroll Scool of Matematical Sciences Dublin City University 3 Atletics Atletics Outline Is tere a limit to ow fast
Outline MS11: IT Matematics Limits & Continuity & 1 Limits: Atletics Perspective Jon Carroll Scool of Matematical Sciences Dublin City University 3 Atletics Atletics Outline Is tere a limit to ow fast
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
MVT and Rolle s Theorem
 AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS
 INTODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PEVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips of sine,
INTODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PEVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips of sine,
INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS
 Capter 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PREVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips
Capter 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PREVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips
Click here to see an animation of the derivative
 Differentiation Massoud Malek Derivative Te concept of derivative is at te core of Calculus; It is a very powerful tool for understanding te beavior of matematical functions. It allows us to optimize functions,
Differentiation Massoud Malek Derivative Te concept of derivative is at te core of Calculus; It is a very powerful tool for understanding te beavior of matematical functions. It allows us to optimize functions,
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 101 LeClair Summer Exam 1 Solutions
 University of Alabama Department of Pysics and Astronomy PH 101 LeClair Summer 2011 Exam 1 Solutions 1. A motorcycle is following a car tat is traveling at constant speed on a straigt igway. Initially,
University of Alabama Department of Pysics and Astronomy PH 101 LeClair Summer 2011 Exam 1 Solutions 1. A motorcycle is following a car tat is traveling at constant speed on a straigt igway. Initially,
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY O SASKATCHEWAN Department of Pysics and Engineering Pysics Pysics 117.3 MIDTERM EXAM Regular Sitting NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 90 minutes STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please ceck):
UNIVERSITY O SASKATCHEWAN Department of Pysics and Engineering Pysics Pysics 117.3 MIDTERM EXAM Regular Sitting NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 90 minutes STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please ceck):
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Some Review Problems for First Midterm Mathematics 1300, Calculus 1
 Some Review Problems for First Midterm Matematics 00, Calculus. Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd,
Some Review Problems for First Midterm Matematics 00, Calculus. Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd,
Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions
 Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions David Lippman, Melonie Rasmussen 1 st Edition Solutions created at Te Evergreen State College and Soreline Community College 1.1 Solutions
Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions David Lippman, Melonie Rasmussen 1 st Edition Solutions created at Te Evergreen State College and Soreline Community College 1.1 Solutions
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. Section 1.5 = = = 4. Check Point Exercises The slope of the line y = 3x+ 1 is 3.
 Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
1. Questions (a) through (e) refer to the graph of the function f given below. (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) does not exist
 Mat 1120 Calculus Test 2. October 18, 2001 Your name Te multiple coice problems count 4 points eac. In te multiple coice section, circle te correct coice (or coices). You must sow your work on te oter
Mat 1120 Calculus Test 2. October 18, 2001 Your name Te multiple coice problems count 4 points eac. In te multiple coice section, circle te correct coice (or coices). You must sow your work on te oter
Excerpt from "Calculus" 2013 AoPS Inc.
 Excerpt from "Calculus" 03 AoPS Inc. Te term related rates refers to two quantities tat are dependent on eac oter and tat are canging over time. We can use te dependent relationsip between te quantities
Excerpt from "Calculus" 03 AoPS Inc. Te term related rates refers to two quantities tat are dependent on eac oter and tat are canging over time. We can use te dependent relationsip between te quantities
Section 2: The Derivative Definition of the Derivative
 Capter 2 Te Derivative Applied Calculus 80 Section 2: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Suppose we drop a tomato from te top of a 00 foot building and time its fall. Time (sec) Heigt (ft) 0.0 00
Capter 2 Te Derivative Applied Calculus 80 Section 2: Te Derivative Definition of te Derivative Suppose we drop a tomato from te top of a 00 foot building and time its fall. Time (sec) Heigt (ft) 0.0 00
Bob Brown Math 251 Calculus 1 Chapter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 CCBC Dundalk
 Bob Brown Mat 251 Calculus 1 Capter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 Te Tangent Line Problem Te idea of a tangent line first arises in geometry in te context of a circle. But before we jump into a discussion of
Bob Brown Mat 251 Calculus 1 Capter 3, Section 1 Completed 1 Te Tangent Line Problem Te idea of a tangent line first arises in geometry in te context of a circle. But before we jump into a discussion of
Tangent Lines-1. Tangent Lines
 Tangent Lines- Tangent Lines In geometry, te tangent line to a circle wit centre O at a point A on te circle is defined to be te perpendicular line at A to te line OA. Te tangent lines ave te special property
Tangent Lines- Tangent Lines In geometry, te tangent line to a circle wit centre O at a point A on te circle is defined to be te perpendicular line at A to te line OA. Te tangent lines ave te special property
2.8 The Derivative as a Function
 .8 Te Derivative as a Function Typically, we can find te derivative of a function f at many points of its domain: Definition. Suppose tat f is a function wic is differentiable at every point of an open
.8 Te Derivative as a Function Typically, we can find te derivative of a function f at many points of its domain: Definition. Suppose tat f is a function wic is differentiable at every point of an open
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
A = h w (1) Error Analysis Physics 141
 Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Math 102 TEST CHAPTERS 3 & 4 Solutions & Comments Fall 2006
 Mat 102 TEST CHAPTERS 3 & 4 Solutions & Comments Fall 2006 f(x+) f(x) 10 1. For f(x) = x 2 + 2x 5, find ))))))))) and simplify completely. NOTE: **f(x+) is NOT f(x)+! f(x+) f(x) (x+) 2 + 2(x+) 5 ( x 2
Mat 102 TEST CHAPTERS 3 & 4 Solutions & Comments Fall 2006 f(x+) f(x) 10 1. For f(x) = x 2 + 2x 5, find ))))))))) and simplify completely. NOTE: **f(x+) is NOT f(x)+! f(x+) f(x) (x+) 2 + 2(x+) 5 ( x 2
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): iel/uric PHYSICS DEPARTENT PHY 2053 Exam 1 October 3, 2012 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my onor, I ave neiter given nor receive unautorize ai on tis examination. YOUR TEST NUBER
Instructor(s): iel/uric PHYSICS DEPARTENT PHY 2053 Exam 1 October 3, 2012 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my onor, I ave neiter given nor receive unautorize ai on tis examination. YOUR TEST NUBER
Derivatives. By: OpenStaxCollege
 By: OpenStaxCollege Te average teen in te United States opens a refrigerator door an estimated 25 times per day. Supposedly, tis average is up from 10 years ago wen te average teenager opened a refrigerator
By: OpenStaxCollege Te average teen in te United States opens a refrigerator door an estimated 25 times per day. Supposedly, tis average is up from 10 years ago wen te average teenager opened a refrigerator
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Page 1. Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is A) 34 m B) 30.
 Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
 1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
11.6 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES AND THE GRADIENT VECTOR
 SECTION 11.6 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES AND THE GRADIENT VECTOR 633 wit speed v o along te same line from te opposite direction toward te source, ten te frequenc of te sound eard b te observer is were c is
SECTION 11.6 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES AND THE GRADIENT VECTOR 633 wit speed v o along te same line from te opposite direction toward te source, ten te frequenc of te sound eard b te observer is were c is
MATH Fall 08. y f(x) Review Problems for the Midterm Examination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart
![MATH Fall 08. y f(x) Review Problems for the Midterm Examination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart MATH Fall 08. y f(x) Review Problems for the Midterm Examination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart](/thumbs/87/95118706.jpg) MATH 121 - Fall 08 Review Problems for te Midterm Eamination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart 1. (a) Use te definition of te derivative to find f (3) wen f() = π 1 2. (b) Find an equation of te tangent line
MATH 121 - Fall 08 Review Problems for te Midterm Eamination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart 1. (a) Use te definition of te derivative to find f (3) wen f() = π 1 2. (b) Find an equation of te tangent line
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
5.1 We will begin this section with the definition of a rational expression. We
 Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
(1) (3)
 1. This question is about momentum, energy and power. (a) In his Principia Mathematica Newton expressed his third law of motion as to every action there is always opposed an equal reaction. State what
1. This question is about momentum, energy and power. (a) In his Principia Mathematica Newton expressed his third law of motion as to every action there is always opposed an equal reaction. State what
The Derivative The rate of change
 Calculus Lia Vas Te Derivative Te rate of cange Knowing and understanding te concept of derivative will enable you to answer te following questions. Let us consider a quantity wose size is described by
Calculus Lia Vas Te Derivative Te rate of cange Knowing and understanding te concept of derivative will enable you to answer te following questions. Let us consider a quantity wose size is described by
Name 09-MAR-04. Work Power and Energy
 Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
1 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?
 Page of 3 Work Power And Energy TEACHER ANSWER KEY March 09, 200. A spring has a spring constant of 20 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?. 2.
Page of 3 Work Power And Energy TEACHER ANSWER KEY March 09, 200. A spring has a spring constant of 20 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?. 2.
W = mgh joule and mass (m) = volume density =
 1. A rain drop of radius 2 mm falls from a height of 500 m above the ground. It falls with decreasing acceleration due to viscous resistance of the air until at half its original height, it attains its
1. A rain drop of radius 2 mm falls from a height of 500 m above the ground. It falls with decreasing acceleration due to viscous resistance of the air until at half its original height, it attains its
1.5 Functions and Their Rates of Change
 66_cpp-75.qd /6/8 4:8 PM Page 56 56 CHAPTER Introduction to Functions and Graps.5 Functions and Teir Rates of Cange Identif were a function is increasing or decreasing Use interval notation Use and interpret
66_cpp-75.qd /6/8 4:8 PM Page 56 56 CHAPTER Introduction to Functions and Graps.5 Functions and Teir Rates of Cange Identif were a function is increasing or decreasing Use interval notation Use and interpret
Section 2.7 Derivatives and Rates of Change Part II Section 2.8 The Derivative as a Function. at the point a, to be. = at time t = a is
 Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Lecture XVII. Abstract We introduce the concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation with the gradient operator.
 Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Time (hours) Morphine sulfate (mg)
 Mat Xa Fall 2002 Review Notes Limits and Definition of Derivative Important Information: 1 According to te most recent information from te Registrar, te Xa final exam will be eld from 9:15 am to 12:15
Mat Xa Fall 2002 Review Notes Limits and Definition of Derivative Important Information: 1 According to te most recent information from te Registrar, te Xa final exam will be eld from 9:15 am to 12:15
(35+70) 35 g (m 1+m 2)a=m1g a = 35 a= =3.27 g 105
 Coordinator: Dr. W. L-Basheer Monday, March 16, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. 70 N block and a 35 N block are connected by a massless inextendable string which is wrapped over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure
Coordinator: Dr. W. L-Basheer Monday, March 16, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. 70 N block and a 35 N block are connected by a massless inextendable string which is wrapped over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure
Finding and Using Derivative The shortcuts
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Finding and Using Derivative Te sortcuts We ave seen tat te formula f f(x+) f(x) (x) = lim 0 is manageable for relatively simple functions like a linear or quadratic. For more complex
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Finding and Using Derivative Te sortcuts We ave seen tat te formula f f(x+) f(x) (x) = lim 0 is manageable for relatively simple functions like a linear or quadratic. For more complex
Average Rate of Change
 Te Derivative Tis can be tougt of as an attempt to draw a parallel (pysically and metaporically) between a line and a curve, applying te concept of slope to someting tat isn't actually straigt. Te slope
Te Derivative Tis can be tougt of as an attempt to draw a parallel (pysically and metaporically) between a line and a curve, applying te concept of slope to someting tat isn't actually straigt. Te slope
CHAPTER (A) When x = 2, y = 6, so f( 2) = 6. (B) When y = 4, x can equal 6, 2, or 4.
 SECTION 3-1 101 CHAPTER 3 Section 3-1 1. No. A correspondence between two sets is a function only if eactly one element of te second set corresponds to eac element of te first set. 3. Te domain of a function
SECTION 3-1 101 CHAPTER 3 Section 3-1 1. No. A correspondence between two sets is a function only if eactly one element of te second set corresponds to eac element of te first set. 3. Te domain of a function
Continuity and Differentiability Worksheet
 Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Homework Assignment on Fluid Statics
 AMEE 0 Introduction to Fluid Mecanics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: m.fyrillas@fit.ac.cy Homework Assignment on Fluid Statics --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AMEE 0 Introduction to Fluid Mecanics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: m.fyrillas@fit.ac.cy Homework Assignment on Fluid Statics --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lim 1 lim 4 Precalculus Notes: Unit 10 Concepts of Calculus
 Syllabus Objectives: 1.1 Te student will understand and apply te concept of te limit of a function at given values of te domain. 1. Te student will find te limit of a function at given values of te domain.
Syllabus Objectives: 1.1 Te student will understand and apply te concept of te limit of a function at given values of te domain. 1. Te student will find te limit of a function at given values of te domain.
Test on Nuclear Physics
 Test on Nuclear Pysics Examination Time - 40 minutes Answer all questions in te spaces provided Tis wole test involves an imaginary element called Bedlum wic as te isotope notation sown below: 47 11 Bd
Test on Nuclear Pysics Examination Time - 40 minutes Answer all questions in te spaces provided Tis wole test involves an imaginary element called Bedlum wic as te isotope notation sown below: 47 11 Bd
(a) At what number x = a does f have a removable discontinuity? What value f(a) should be assigned to f at x = a in order to make f continuous at a?
 Solutions to Test 1 Fall 016 1pt 1. Te grap of a function f(x) is sown at rigt below. Part I. State te value of eac limit. If a limit is infinite, state weter it is or. If a limit does not exist (but is
Solutions to Test 1 Fall 016 1pt 1. Te grap of a function f(x) is sown at rigt below. Part I. State te value of eac limit. If a limit is infinite, state weter it is or. If a limit does not exist (but is
MA119-A Applied Calculus for Business Fall Homework 4 Solutions Due 9/29/ :30AM
 MA9-A Applied Calculus for Business 006 Fall Homework Solutions Due 9/9/006 0:0AM. #0 Find te it 5 0 + +.. #8 Find te it. #6 Find te it 5 0 + + = (0) 5 0 (0) + (0) + =.!! r + +. r s r + + = () + 0 () +
MA9-A Applied Calculus for Business 006 Fall Homework Solutions Due 9/9/006 0:0AM. #0 Find te it 5 0 + +.. #8 Find te it. #6 Find te it 5 0 + + = (0) 5 0 (0) + (0) + =.!! r + +. r s r + + = () + 0 () +
RELEASED FORM RELEASED. North Carolina Test of Physics
 Name Physics Form North arolina Test of Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina www.ncpublicschools.org State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction ivision of ccountability Services/North
Name Physics Form North arolina Test of Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina www.ncpublicschools.org State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction ivision of ccountability Services/North
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
LESSON 2.10 Understanding work, energy, power and efficiency.
 LESSON 2.10 Understanding work, energy, power and efficiency. Work(W),Enegy(E) and Power (P) and Effiecency Example 2 Figure shows an ice cube is pulled by a force 20N At an angle of 60 o to the surface
LESSON 2.10 Understanding work, energy, power and efficiency. Work(W),Enegy(E) and Power (P) and Effiecency Example 2 Figure shows an ice cube is pulled by a force 20N At an angle of 60 o to the surface
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
Math 34A Practice Final Solutions Fall 2007
 Mat 34A Practice Final Solutions Fall 007 Problem Find te derivatives of te following functions:. f(x) = 3x + e 3x. f(x) = x + x 3. f(x) = (x + a) 4. Is te function 3t 4t t 3 increasing or decreasing wen
Mat 34A Practice Final Solutions Fall 007 Problem Find te derivatives of te following functions:. f(x) = 3x + e 3x. f(x) = x + x 3. f(x) = (x + a) 4. Is te function 3t 4t t 3 increasing or decreasing wen
HOMEWORK HELP 2 FOR MATH 151
 HOMEWORK HELP 2 FOR MATH 151 Here we go; te second round of omework elp. If tere are oters you would like to see, let me know! 2.4, 43 and 44 At wat points are te functions f(x) and g(x) = xf(x)continuous,
HOMEWORK HELP 2 FOR MATH 151 Here we go; te second round of omework elp. If tere are oters you would like to see, let me know! 2.4, 43 and 44 At wat points are te functions f(x) and g(x) = xf(x)continuous,
Pressure & Buoyancy Worksheet : Solid & Liquid Pressure
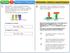 ysics 1. Tree identical cubes are arranged as in tree different (I, II and II) positions on a orizontal surface. Te pressure applied on te orizontal surface by te cubes in arrangement I is.. Solid objects
ysics 1. Tree identical cubes are arranged as in tree different (I, II and II) positions on a orizontal surface. Te pressure applied on te orizontal surface by te cubes in arrangement I is.. Solid objects
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
2.11 That s So Derivative
 2.11 Tat s So Derivative Introduction to Differential Calculus Just as one defines instantaneous velocity in terms of average velocity, we now define te instantaneous rate of cange of a function at a point
2.11 Tat s So Derivative Introduction to Differential Calculus Just as one defines instantaneous velocity in terms of average velocity, we now define te instantaneous rate of cange of a function at a point
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
 DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Important Points: 1. J.J. Tomson and Sir William Crookes studied te discarge of electricity troug gases. At about.1 mm of Hg and at ig voltage invisible streams called
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Important Points: 1. J.J. Tomson and Sir William Crookes studied te discarge of electricity troug gases. At about.1 mm of Hg and at ig voltage invisible streams called
1. Which one of the following expressions is not equal to all the others? 1 C. 1 D. 25x. 2. Simplify this expression as much as possible.
 004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
1. State whether the function is an exponential growth or exponential decay, and describe its end behaviour using limits.
 Questions 1. State weter te function is an exponential growt or exponential decay, and describe its end beaviour using its. (a) f(x) = 3 2x (b) f(x) = 0.5 x (c) f(x) = e (d) f(x) = ( ) x 1 4 2. Matc te
Questions 1. State weter te function is an exponential growt or exponential decay, and describe its end beaviour using its. (a) f(x) = 3 2x (b) f(x) = 0.5 x (c) f(x) = e (d) f(x) = ( ) x 1 4 2. Matc te
Name: Class: 903 Active Physics Winter Break Regents Prep December 2014
 In this section use the following equations for velocity and displacement to solve: 1. In a drill during basketball practice, a player runs the length of the 30.meter court and back. The player does this
In this section use the following equations for velocity and displacement to solve: 1. In a drill during basketball practice, a player runs the length of the 30.meter court and back. The player does this
Physics: Momentum, Work, Energy, Power
 Name: ate: 1. The momentum of a 5-kilogram object moving at 6 meters per second is. 1 kg m/sec. 5 kg m/sec. 11 kg m/sec. 30 kg m/sec 2. 60-kilogram student running at 3.0 meters per second has a kinetic
Name: ate: 1. The momentum of a 5-kilogram object moving at 6 meters per second is. 1 kg m/sec. 5 kg m/sec. 11 kg m/sec. 30 kg m/sec 2. 60-kilogram student running at 3.0 meters per second has a kinetic
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Class XI Exercise 6 Work, Energy And Power Physics
 Question 6.1: The sign of work done by a force on a body is important to understand. State carefully if the following quantities are positive or negative: (a) work done by a man in lifting a bucket out
Question 6.1: The sign of work done by a force on a body is important to understand. State carefully if the following quantities are positive or negative: (a) work done by a man in lifting a bucket out
June : 2016 (CBCS) Body. Load
 Engineering Mecanics st Semester : Common to all rances Note : Max. marks : 6 (i) ttempt an five questions (ii) ll questions carr equal marks. (iii) nswer sould be precise and to te point onl (iv) ssume
Engineering Mecanics st Semester : Common to all rances Note : Max. marks : 6 (i) ttempt an five questions (ii) ll questions carr equal marks. (iii) nswer sould be precise and to te point onl (iv) ssume
Notes: DERIVATIVES. Velocity and Other Rates of Change
 Notes: DERIVATIVES Velocity and Oter Rates of Cange I. Average Rate of Cange A.) Def.- Te average rate of cange of f(x) on te interval [a, b] is f( b) f( a) b a secant ( ) ( ) m troug a, f ( a ) and b,
Notes: DERIVATIVES Velocity and Oter Rates of Cange I. Average Rate of Cange A.) Def.- Te average rate of cange of f(x) on te interval [a, b] is f( b) f( a) b a secant ( ) ( ) m troug a, f ( a ) and b,
Exam 1 Review Solutions
 Exam Review Solutions Please also review te old quizzes, and be sure tat you understand te omework problems. General notes: () Always give an algebraic reason for your answer (graps are not sufficient),
Exam Review Solutions Please also review te old quizzes, and be sure tat you understand te omework problems. General notes: () Always give an algebraic reason for your answer (graps are not sufficient),
Physics 121, April 1, Equilibrium. Physics 121. April 1, Physics 121. April 1, Course Information. Discussion of Exam # 2
 Pysics 121, April 1, 2008. Pysics 121. April 1, 2008. Course Information Discussion of Exam # 2 Topics to be discussed today: Requirements for Equilibrium Gravitational Equilibrium Sample problems Pysics
Pysics 121, April 1, 2008. Pysics 121. April 1, 2008. Course Information Discussion of Exam # 2 Topics to be discussed today: Requirements for Equilibrium Gravitational Equilibrium Sample problems Pysics
Combining functions: algebraic methods
 Combining functions: algebraic metods Functions can be added, subtracted, multiplied, divided, and raised to a power, just like numbers or algebra expressions. If f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x + 2, clearly f(x)
Combining functions: algebraic metods Functions can be added, subtracted, multiplied, divided, and raised to a power, just like numbers or algebra expressions. If f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x + 2, clearly f(x)
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq
 qwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwerty uiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasd fgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzx cbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmq Projectile Motion Quick concepts regarding Projectile Motion wertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyui
qwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwerty uiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasd fgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzx cbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmq Projectile Motion Quick concepts regarding Projectile Motion wertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyui
Q2. Two forces of 6 N and 10 N act at a point. Which of the following could not be the magnitude of the result?
 Q1. Two ice skaters, initially at rest and in contact, push apart from each other. Which line, to, in the table states correctly the change in the total momentum and the total kinetic energy of the two
Q1. Two ice skaters, initially at rest and in contact, push apart from each other. Which line, to, in the table states correctly the change in the total momentum and the total kinetic energy of the two
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER P.1
 WORK, ENERGY AND OWER.1 HKCEE AER I 11 11 Figure 6 shows an experimental setup, which is used to find the friction between a block and a table. A weight is connected to the block through a frictionless
WORK, ENERGY AND OWER.1 HKCEE AER I 11 11 Figure 6 shows an experimental setup, which is used to find the friction between a block and a table. A weight is connected to the block through a frictionless
KEY CONCEPT: THE DERIVATIVE
 Capter Two KEY CONCEPT: THE DERIVATIVE We begin tis capter by investigating te problem of speed: How can we measure te speed of a moving object at a given instant in time? Or, more fundamentally, wat do
Capter Two KEY CONCEPT: THE DERIVATIVE We begin tis capter by investigating te problem of speed: How can we measure te speed of a moving object at a given instant in time? Or, more fundamentally, wat do
Derivative as Instantaneous Rate of Change
 43 Derivative as Instantaneous Rate of Cange Consider a function tat describes te position of a racecar moving in a straigt line away from some starting point Let y s t suc tat t represents te time in
43 Derivative as Instantaneous Rate of Cange Consider a function tat describes te position of a racecar moving in a straigt line away from some starting point Let y s t suc tat t represents te time in
7.1 Using Antiderivatives to find Area
 7.1 Using Antiderivatives to find Area Introduction finding te area under te grap of a nonnegative, continuous function f In tis section a formula is obtained for finding te area of te region bounded between
7.1 Using Antiderivatives to find Area Introduction finding te area under te grap of a nonnegative, continuous function f In tis section a formula is obtained for finding te area of te region bounded between
Which row, A to D, in the table correctly shows the quantities conserved in an inelastic collision? mass momentum kinetic energy total energy
 1 Water of density 1000 kg m 3 flows out of a garden hose of cross-sectional area 7.2 10 4 m 2 at a rate of 2.0 10 4 m 3 per second. How much momentum is carried by the water leaving the hose per second?
1 Water of density 1000 kg m 3 flows out of a garden hose of cross-sectional area 7.2 10 4 m 2 at a rate of 2.0 10 4 m 3 per second. How much momentum is carried by the water leaving the hose per second?
Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 12.
 Capter 6. Fluid Mecanics Notes: Most of te material in tis capter is taken from Young and Freedman, Cap. 12. 6.1 Fluid Statics Fluids, i.e., substances tat can flow, are te subjects of tis capter. But
Capter 6. Fluid Mecanics Notes: Most of te material in tis capter is taken from Young and Freedman, Cap. 12. 6.1 Fluid Statics Fluids, i.e., substances tat can flow, are te subjects of tis capter. But
Mechanics & Properties of Matter 5: Energy and Power
 Mechanics & Properties of Matter 5: Energy and Power Energy and Power AIM This unit re-introduces the formulae for calculating work done, potential energy, kinetic energy and power. The principle that
Mechanics & Properties of Matter 5: Energy and Power Energy and Power AIM This unit re-introduces the formulae for calculating work done, potential energy, kinetic energy and power. The principle that
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics. Student name:
 Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
