Electric Flux and Gauss Law
|
|
|
- Howard Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Electric Flux and Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used to find the electric field of complex charge distribution. Easier than treating it as a collection of point charge and using superposition To use Gauss Law, a quantity called electric flux is needed The electric flux is equal the product of the electric field that passes through a particular surface and the area of the surface The electric flux is denoted by ϕ E
3 Electric Flux Examples Fig. A The electric field is perpendicular to the surface of area A ϕ E = E A Fig. B The electric field is parallel to the surface of area A ϕ E = 0 No field lines pass through the area
4 Electric Flux Examples, cont. Fig. C The electric field makes an angle with the surface ϕ E = E A cos θ Flux is a scalar quantity
5 Electric Flux Examples, Closed The flux is positive if the field is directed out of the region surrounded by the surface and negative if going into the region Fig. D and E The total flux is the sum of the contributions of the fields going in and coming out ϕ E = 0 Surface
6 Gauss Law Gauss Law says that the electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the charge q inside the surface E o The constant ε o is the emissitivity of free space This was encountered in one form of Coulomb s Law Since the flux depends on the electric field, Gauss Law can be used to find the field q
7 Gauss Law: Point Charge Choose a Gaussian surface Want a surface that will make the calculation as easy as possible Choose a surface that matches the symmetry of the problem For a point charge, the field lines have a spherical symmetry
8 Gauss Law: Point Charge, final Since the field is perpendicular to the area, the flux is the product of the field and the area: ϕ E = E A sphere A sphere is the area of the Gaussian sphere With a radius of r, A sphere = 4 π r 2 Therefore, ϕ E = 4 π r 2 E From Gauss Law, 2 q q E 4 r E and E 2 o 4 or This agrees with the result from Coulomb s Law
9 Problem Solving Strategy Solve Calculate the total electric flux through the entire Gaussian surface Find the total electric charge inside the surface Apply Gauss Law to solve for the electric field Check Consider what your answer means Check that your answer makes sense
10 Electric Field from Spherical Charge Given a uniform spherical ball of charge Choose a sphere as a Gaussian surface Q kq E r r o The electric field from any spherical distribution of charge is the same as the field from a point charge with the same total charge This applies only outside the ball of charge
11 Electric Field from Line of Charge The line of charge has a total length L and a total charge Q The electric field is perpendicular to the line Choose a cylinder of radius r for the Gaussian surface E Q 4 Lr o
12 Electric Field: Flat Sheet of Charge The large, flat sheet of charge has a charge per unit area of σ Choose a cylinder as the Gaussian surface The field through the sides of the surface is zero Through each end of the surface, ϕ E = EA Since there are two ends, ϕ E = 2EA
13 Flat Sheet of Charge, cont. The total charge is equal to the charge / area multiplied by the cross-sectional area of the cylinder q= σ A Therefore, the electric field is: A 2EA The electric field is constant and independent of the distance from the sheet of charge E 2 o o
14 Conductors Each atom by itself is electrically neutral Equal numbers of protons and electrons This example is copper When these atoms come together to form the piece of metal electrons are freed Section 17.4
15 Conductors, cont. These electrons move freely through the entire piece of metal These electrons are called conduction electrons The electrons leave behind positively charged ion cores that are bound and not mobile A piece of metal can also accept extra electrons or release some of its conduction electrons so the entire object can acquire a net positive or negative charge Section 17.4
16 Insulators In insulators the electrons are not able to move freely through the material Examples include quartz, plastic and amber This example is quartz (SiO 2 ) Section 17.4
17 Insulators, cont. Electrons cannot escape from these ions There are no conduction electrons available to carry charge through the solid If extra electrons are placed on an insulator, they tend to stay in the place where initially placed Section 17.4
18 Liquids and Gases The total charge is zero and the sample is neutral A few molecules always dissociate into free ions These ions can carry charge from place to place similarly to the conduction electrons This example is water, but gases are similar Section 17.4
19 DEMONSTRATIONS: 5A 12, 5A 13 GAUSS S LAW
20 Capacitor Concept A capacitor consists of two parallel metal plates that carry charges of +Q and Q The excess charge on the two plates will attract each other and draw all the excess charge to the inner sides of the two plates
21 Capacitor, cont. Each plate has an area A and charge densities of +σ = +Q/A and -σ = -Q/A The total field is the vector sum of the fields from the individual plates From superposition The field between the plates is E o Q A o
22 Notes on Gaussian Surfaces To make analysis easier, some simplifications have been made in the examples Highly symmetric charge distributions Gaussian surfaces on which the electric field was either constant or zero Gauss Law applies to any surface and any charge distribution Even with little or no symmetry The total electric flux through a closed surface depends only on the total charge enclosed
23 How Are Protons Held Together? Experiments have shown that the proton is an assembly of three particles called quarks The large repulsive electric forces are overcome by an attractive force called the strong force The strong force is a fundamental force of nature Section 17.7
24 Electrons Are Point Charges The electron is truly a point particle The mass and charge of an electron are located at an infinitesimal point in space There is no internal structure to the electron Section 17.7
25 Conservation of Charge Electric charge is conserved The total charge of the universe is a constant This does not mean the total number of protons or electrons is constant The net charge remains the same even when the number of charged particles changes The principle of conservation of charge is believed to be an exact law of nature No violations of the principle have ever been observed Section 17.7
Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
 Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Overview of Chapter 19 Electric Charge! Insulators and Conductors! Coulomb s Law! The Electric Field! Electric Field Lines! Shielding and Charging by Induction
Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Overview of Chapter 19 Electric Charge! Insulators and Conductors! Coulomb s Law! The Electric Field! Electric Field Lines! Shielding and Charging by Induction
Chapter 15. Electric Forces and Electric Fields
 Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields First Observations Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified and attracted pieces
Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields First Observations Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified and attracted pieces
PHYS102 - Gauss s Law.
 PHYS102 - Gauss s Law. Dr. Suess February 2, 2007 PRS Questions 2 Question #1.............................................................................. 2 Answer to Question #1......................................................................
PHYS102 - Gauss s Law. Dr. Suess February 2, 2007 PRS Questions 2 Question #1.............................................................................. 2 Answer to Question #1......................................................................
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Electric Flux Gauss s Law Units of Chapter 22 Applications of Gauss s Law Experimental Basis of Gauss s and Coulomb s Laws 22-1 Electric Flux Electric flux: Electric flux through
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Electric Flux Gauss s Law Units of Chapter 22 Applications of Gauss s Law Experimental Basis of Gauss s and Coulomb s Laws 22-1 Electric Flux Electric flux: Electric flux through
Lecture Outline Chapter 19. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 19 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields Units of Chapter 19 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric
Lecture Outline Chapter 19 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields Units of Chapter 19 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric
Chapter 15. Electric Forces and Electric Fields
 Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields First Studies Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified and attracted pieces of
Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields First Studies Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified and attracted pieces of
Chapter 21. Electric Fields
 Chapter 21 Electric Fields The Origin of Electricity The electrical nature of matter is inherent in the atoms of all substances. An atom consists of a small relatively massive nucleus that contains particles
Chapter 21 Electric Fields The Origin of Electricity The electrical nature of matter is inherent in the atoms of all substances. An atom consists of a small relatively massive nucleus that contains particles
Chapter 23: Gauss Law. PHY2049: Chapter 23 1
 Chapter 23: Gauss Law PHY2049: Chapter 23 1 Two Equivalent Laws for Electricity Coulomb s Law equivalent Gauss Law Derivation given in Sec. 23-5 (Read!) Not derived in this book (Requires vector calculus)
Chapter 23: Gauss Law PHY2049: Chapter 23 1 Two Equivalent Laws for Electricity Coulomb s Law equivalent Gauss Law Derivation given in Sec. 23-5 (Read!) Not derived in this book (Requires vector calculus)
Chapter 2 Gauss Law 1
 Chapter 2 Gauss Law 1 . Gauss Law Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface Consider the flux passing through a closed surface
Chapter 2 Gauss Law 1 . Gauss Law Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface Consider the flux passing through a closed surface
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_24 Sunday, February 03, 2008 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_4 Sunday, February 03, 008 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. A point charged particle is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The net electric flux Φ net
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_4 Sunday, February 03, 008 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. A point charged particle is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The net electric flux Φ net
Gauss s Law. Chapter 22. Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition. Applications of Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Uniform Charged Sphere Infinite Line of Charge Infinite Sheet of Charge Two infinite sheets of charge Phys 2435:
Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Uniform Charged Sphere Infinite Line of Charge Infinite Sheet of Charge Two infinite sheets of charge Phys 2435:
Phys 2102 Spring 2002 Exam 1
 Phys 2102 Spring 2002 Exam 1 February 19, 2002 1. When a positively charged conductor touches a neutral conductor, the neutral conductor will: (a) Lose protons (b) Gain electrons (c) Stay neutral (d) Lose
Phys 2102 Spring 2002 Exam 1 February 19, 2002 1. When a positively charged conductor touches a neutral conductor, the neutral conductor will: (a) Lose protons (b) Gain electrons (c) Stay neutral (d) Lose
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 22 Gauss s Law 22-1 Electric Flux Electric flux: Electric flux through an area is proportional to the total number of field lines crossing the area. 22-1 Electric Flux Example 22-1: Electric flux.
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law 22-1 Electric Flux Electric flux: Electric flux through an area is proportional to the total number of field lines crossing the area. 22-1 Electric Flux Example 22-1: Electric flux.
Electric Flux. If we know the electric field on a Gaussian surface, we can find the net charge enclosed by the surface.
 Chapter 23 Gauss' Law Instead of considering the electric fields of charge elements in a given charge distribution, Gauss' law considers a hypothetical closed surface enclosing the charge distribution.
Chapter 23 Gauss' Law Instead of considering the electric fields of charge elements in a given charge distribution, Gauss' law considers a hypothetical closed surface enclosing the charge distribution.
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section
 Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 9: 21 Oct. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Last time: Gauss's Law To formulate Gauss's law, introduced a few new
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 9: 21 Oct. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Last time: Gauss's Law To formulate Gauss's law, introduced a few new
Chapter 21. Electric Charge
 Chapter 21 Electric Charge Electric Charge When an amber rod is rubbed with fur, some of the electrons on the atoms in the fur are transferred to the amber: Electric Charge: Water (H2O) molecule can be
Chapter 21 Electric Charge Electric Charge When an amber rod is rubbed with fur, some of the electrons on the atoms in the fur are transferred to the amber: Electric Charge: Water (H2O) molecule can be
Electrostatics. Electrical properties generated by static charges. Introduction
 Electrostatics Electrical properties generated by static charges Introduction First Greek discovery Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified and attracted pieces of straw or feathers Introduction
Electrostatics Electrical properties generated by static charges Introduction First Greek discovery Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified and attracted pieces of straw or feathers Introduction
Chapter 23. Gauss Law. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
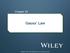 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 Electric Flux Electric field vectors and field lines pierce an imaginary, spherical Gaussian surface that encloses a particle with charge +Q. Now the enclosed particle
Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 Electric Flux Electric field vectors and field lines pierce an imaginary, spherical Gaussian surface that encloses a particle with charge +Q. Now the enclosed particle
Flux. Flux = = va. This is the same as asking What is the flux of water through the rectangle? The answer depends on:
 Ch. 22: Gauss s Law Gauss s law is an alternative description of Coulomb s law that allows for an easier method of determining the electric field for situations where the charge distribution contains symmetry.
Ch. 22: Gauss s Law Gauss s law is an alternative description of Coulomb s law that allows for an easier method of determining the electric field for situations where the charge distribution contains symmetry.
CH 23. Gauss Law. A. Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface.
 CH 23 Gauss Law [SHIVOK SP212] January 4, 2016 I. Introduction to Gauss Law A. Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface.
CH 23 Gauss Law [SHIVOK SP212] January 4, 2016 I. Introduction to Gauss Law A. Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface.
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 22: ELECTRIC FORCE & FIELD; GAUSS' LAW
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRIC CHARGE e Atoms are built up of protons, neutrons and electrons p, n e ELECTRIC CHARGE is a property of matter, similar to MASS: MASS (m) ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) - Mass
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRIC CHARGE e Atoms are built up of protons, neutrons and electrons p, n e ELECTRIC CHARGE is a property of matter, similar to MASS: MASS (m) ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) - Mass
Chapters 21 and 22: Giancoli, 4 th Edition Electrostatics
 Chapters 21 and 22: Giancoli, 4 th Edition Electrostatics Electric Charges Coulomb s Law and Electric force The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric flux Gauss Law and applications of Gauss Law
Chapters 21 and 22: Giancoli, 4 th Edition Electrostatics Electric Charges Coulomb s Law and Electric force The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric flux Gauss Law and applications of Gauss Law
Look over. Examples 11, 12, 2/3/2008. Read over Chapter 23 sections 1-9 Examples 1, 2, 3, 6. 1) What a Gaussian surface is.
 PHYS 2212 Read over Chapter 23 sections 1-9 Examples 1, 2, 3, 6 PHYS 1112 Look over Chapter 16 Section 10 Examples 11, 12, Good Things To Know 1) What a Gaussian surface is. 2) How to calculate the Electric
PHYS 2212 Read over Chapter 23 sections 1-9 Examples 1, 2, 3, 6 PHYS 1112 Look over Chapter 16 Section 10 Examples 11, 12, Good Things To Know 1) What a Gaussian surface is. 2) How to calculate the Electric
Chapter Electric Forces and Electric Fields. Prof. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 25-26 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Prof. Armen Kocharian First Observations Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified
Chapter 25-26 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Prof. Armen Kocharian First Observations Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC Found that amber, when rubbed, became electrified
Quiz. Chapter 15. Electrical Field. Quiz. Electric Field. Electric Field, cont. 8/29/2011. q r. Electric Forces and Electric Fields
 Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields uiz Four point charges, each of the same magnitude, with varying signs as specified, are arranged at the corners of a square as shown. Which of the arrows
Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields uiz Four point charges, each of the same magnitude, with varying signs as specified, are arranged at the corners of a square as shown. Which of the arrows
Gauss s Law. Lecture 3. Chapter Course website:
 Lecture 3 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 24: Section 24.2 Idea of Flux Section 24.3 Electric
Lecture 3 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 24: Section 24.2 Idea of Flux Section 24.3 Electric
AP Physics C. Gauss s Law. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics Gauss s Law Free Response Problems 1. A flat sheet of glass of area 0.4 m 2 is placed in a uniform electric field E = 500 N/. The normal line to the sheet makes an angle θ = 60 ẘith the electric
AP Physics Gauss s Law Free Response Problems 1. A flat sheet of glass of area 0.4 m 2 is placed in a uniform electric field E = 500 N/. The normal line to the sheet makes an angle θ = 60 ẘith the electric
Fall Lee - Midterm 2 solutions
 Fall 2009 - Lee - Midterm 2 solutions Problem 1 Solutions Part A Because the middle slab is a conductor, the electric field inside of the slab must be 0. Parts B and C Recall that to find the electric
Fall 2009 - Lee - Midterm 2 solutions Problem 1 Solutions Part A Because the middle slab is a conductor, the electric field inside of the slab must be 0. Parts B and C Recall that to find the electric
Lecture 4-1 Physics 219 Question 1 Aug Where (if any) is the net electric field due to the following two charges equal to zero?
 Lecture 4-1 Physics 219 Question 1 Aug.31.2016. Where (if any) is the net electric field due to the following two charges equal to zero? y Q Q a x a) at (-a,0) b) at (2a,0) c) at (a/2,0) d) at (0,a) and
Lecture 4-1 Physics 219 Question 1 Aug.31.2016. Where (if any) is the net electric field due to the following two charges equal to zero? y Q Q a x a) at (-a,0) b) at (2a,0) c) at (a/2,0) d) at (0,a) and
Taller de Electróstatica
 Taller de Electróstatica TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A neutron carries a negative charge. 1) 2) The coulomb, which is the unit of charge, is the
Taller de Electróstatica TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A neutron carries a negative charge. 1) 2) The coulomb, which is the unit of charge, is the
Questions Chapter 23 Gauss' Law
 Questions Chapter 23 Gauss' Law 23-1 What is Physics? 23-2 Flux 23-3 Flux of an Electric Field 23-4 Gauss' Law 23-5 Gauss' Law and Coulomb's Law 23-6 A Charged Isolated Conductor 23-7 Applying Gauss' Law:
Questions Chapter 23 Gauss' Law 23-1 What is Physics? 23-2 Flux 23-3 Flux of an Electric Field 23-4 Gauss' Law 23-5 Gauss' Law and Coulomb's Law 23-6 A Charged Isolated Conductor 23-7 Applying Gauss' Law:
Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field
 Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field Units of Chapter 16 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Electric Charge in the Atom Insulators and Conductors Induced Charge; the Electroscope
Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field Units of Chapter 16 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Electric Charge in the Atom Insulators and Conductors Induced Charge; the Electroscope
Welcome. to Electrostatics
 Welcome to Electrostatics Outline 1. Coulomb s Law 2. The Electric Field - Examples 3. Gauss Law - Examples 4. Conductors in Electric Field Coulomb s Law Coulomb s law quantifies the magnitude of the electrostatic
Welcome to Electrostatics Outline 1. Coulomb s Law 2. The Electric Field - Examples 3. Gauss Law - Examples 4. Conductors in Electric Field Coulomb s Law Coulomb s law quantifies the magnitude of the electrostatic
HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 18 3. REASONING AND SOLUTION The total charge to be removed is 5.0 µc. The number of electrons corresponding to this charge is N = ( 5.0 10 6 C)/( 1.60 10 19 C) = 3.1 10 13
HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 18 3. REASONING AND SOLUTION The total charge to be removed is 5.0 µc. The number of electrons corresponding to this charge is N = ( 5.0 10 6 C)/( 1.60 10 19 C) = 3.1 10 13
Chapter 28. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 28. Gauss s Law Using Gauss s law, we can deduce electric fields, particularly those with a high degree of symmetry, simply from the shape of the charge distribution. The nearly spherical shape
Chapter 28. Gauss s Law Using Gauss s law, we can deduce electric fields, particularly those with a high degree of symmetry, simply from the shape of the charge distribution. The nearly spherical shape
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law
 Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
PHY102 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law
 PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
Phys102 General Physics II. Chapter 24: Gauss s Law
 Phys102 General Physics II Gauss Law Chapter 24: Gauss s Law Flux Electric Flux Gauss Law Coulombs Law from Gauss Law Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor Application of Gauss Law Charged
Phys102 General Physics II Gauss Law Chapter 24: Gauss s Law Flux Electric Flux Gauss Law Coulombs Law from Gauss Law Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor Application of Gauss Law Charged
Chapter 21 Chapter 23 Gauss Law. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 21 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 What is Physics? Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers
Chapter 21 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 What is Physics? Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers
Gauss s Law. Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss
 Gauss s Law Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss 1777-1855 Mathematics and physics: including number theory, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, electricity, magnetism, astronomy and optics. y = Be cx 2 First,
Gauss s Law Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss 1777-1855 Mathematics and physics: including number theory, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, electricity, magnetism, astronomy and optics. y = Be cx 2 First,
PH 222-2C Fall Gauss Law. Lectures 3-4. Chapter 23 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 212 Gauss Law Lectures 3-4 Chapter 23 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 23 Gauss Law In this chapter we will introduce the following new concepts:
PH 222-2C Fall 212 Gauss Law Lectures 3-4 Chapter 23 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 23 Gauss Law In this chapter we will introduce the following new concepts:
Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux
 Lecture 3 Chapter 23 Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter
Lecture 3 Chapter 23 Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter
(a) This cannot be determined since the dimensions of the square are unknown. (b) 10 7 N/C (c) 10 6 N/C (d) 10 5 N/C (e) 10 4 N/C
 1. 4 point charges (1 C, 3 C, 4 C and 5 C) are fixed at the vertices of a square. When a charge of 10 C is placed at the center of the square, it experiences a force of 10 7 N. What is the magnitude of
1. 4 point charges (1 C, 3 C, 4 C and 5 C) are fixed at the vertices of a square. When a charge of 10 C is placed at the center of the square, it experiences a force of 10 7 N. What is the magnitude of
ELECTROSTATICS 3. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 15 January 2013: Electrostatics 3
 ELECTROSTATICS 3 q 0 Electro negativity ti it Rl Relative electro negativity ranking for some common materials from electron donating materials (+, glass) to electron accepting materials (, teflon) + +
ELECTROSTATICS 3 q 0 Electro negativity ti it Rl Relative electro negativity ranking for some common materials from electron donating materials (+, glass) to electron accepting materials (, teflon) + +
3/22/2016. Chapter 27 Gauss s Law. Chapter 27 Preview. Chapter 27 Preview. Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2.
 Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-3 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-4 1 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-5 Chapter 27 Preview Slide
Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-3 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-4 1 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-5 Chapter 27 Preview Slide
CHAPTER 15 PRE-TEST: ELECTRIC FORCE AND FIELDS
 Class: Date: CHAPTER 5 PRE-TEST: ELECTRIC FORCE AND FIELDS Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with
Class: Date: CHAPTER 5 PRE-TEST: ELECTRIC FORCE AND FIELDS Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with
How to define the direction of A??
 Chapter Gauss Law.1 Electric Flu. Gauss Law. A charged Isolated Conductor.4 Applying Gauss Law: Cylindrical Symmetry.5 Applying Gauss Law: Planar Symmetry.6 Applying Gauss Law: Spherical Symmetry You will
Chapter Gauss Law.1 Electric Flu. Gauss Law. A charged Isolated Conductor.4 Applying Gauss Law: Cylindrical Symmetry.5 Applying Gauss Law: Planar Symmetry.6 Applying Gauss Law: Spherical Symmetry You will
1. ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
 1. ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS 1. What are point charges? One mark questions with answers A: Charges whose sizes are very small compared to the distance between them are called point charges 2. The net
1. ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS 1. What are point charges? One mark questions with answers A: Charges whose sizes are very small compared to the distance between them are called point charges 2. The net
Chapter (2) Gauss s Law
 Chapter (2) Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface! What is meant by electric flux and how you can calculate it. How
Chapter (2) Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface! What is meant by electric flux and how you can calculate it. How
E. not enough information given to decide
 Q22.1 A spherical Gaussian surface (#1) encloses and is centered on a point charge +q. A second spherical Gaussian surface (#2) of the same size also encloses the charge but is not centered on it. Compared
Q22.1 A spherical Gaussian surface (#1) encloses and is centered on a point charge +q. A second spherical Gaussian surface (#2) of the same size also encloses the charge but is not centered on it. Compared
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law
 Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 22 To use the electric field at a surface to determine the charge within the surface To learn the meaning of electric flux and how to calculate
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 22 To use the electric field at a surface to determine the charge within the surface To learn the meaning of electric flux and how to calculate
PHYSICS. Chapter 24 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
Chapter 23. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 23 Gauss s Law 23.1 What is Physics?: Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers a hypothetical
Chapter 23 Gauss s Law 23.1 What is Physics?: Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers a hypothetical
Ch 16 practice. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 16 practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge?
Ch 16 practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge?
Chapter 22: Gauss s Law
 Chapter 22: Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface. What is meant by electric flux, and how to calculate it. How Gauss
Chapter 22: Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface. What is meant by electric flux, and how to calculate it. How Gauss
Physics 6C Review 1. Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz. July 16, Figure 1: Coulombs Law
 Physics 6C Review 1 Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz July 16, 2012 1 Review 1.1 Coulombs Law Figure 1: Coulombs Law The steps for solving any problem of this type
Physics 6C Review 1 Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz July 16, 2012 1 Review 1.1 Coulombs Law Figure 1: Coulombs Law The steps for solving any problem of this type
Chapter 24 Gauss Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss Law A charge inside a box can be probed with a test charge q o to measure E field outside the box. The volume (V) flow rate (dv/dt) of fluid through the wire rectangle (a) is va when the
Chapter 24 Gauss Law A charge inside a box can be probed with a test charge q o to measure E field outside the box. The volume (V) flow rate (dv/dt) of fluid through the wire rectangle (a) is va when the
Physics 202, Lecture 3. The Electric Field
 Physics 202, Lecture 3 Today s Topics Electric Field (Review) Motion of charged particles in external E field Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium (Ch. 21.9) Gauss s Law (Ch. 22) Reminder: HW #1 due
Physics 202, Lecture 3 Today s Topics Electric Field (Review) Motion of charged particles in external E field Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium (Ch. 21.9) Gauss s Law (Ch. 22) Reminder: HW #1 due
The Basic Definition of Flux
 The Basic Definition of Flux Imagine holding a rectangular wire loop of area A in front of a fan. The volume of air flowing through the loop each second depends on the angle between the loop and the direction
The Basic Definition of Flux Imagine holding a rectangular wire loop of area A in front of a fan. The volume of air flowing through the loop each second depends on the angle between the loop and the direction
- Like charges repel Induced Charge. or by induction. Electric charge is conserved
 Course website: http://course.physastro.iastate.edu/phys112/ Here you will find the syllabus, lecture notes and other course information Links to the website are also on Blackboard: Phys 112 (Spring 2017)
Course website: http://course.physastro.iastate.edu/phys112/ Here you will find the syllabus, lecture notes and other course information Links to the website are also on Blackboard: Phys 112 (Spring 2017)
Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter
 Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter 4.1. Polarization 4.2. The Field of a Polarized Object 4.3. The Electric Displacement 4.4. Linear Dielectrics 4.5. Energy in dielectric systems 4.6. Forces on
Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter 4.1. Polarization 4.2. The Field of a Polarized Object 4.3. The Electric Displacement 4.4. Linear Dielectrics 4.5. Energy in dielectric systems 4.6. Forces on
Chapter 25. Capacitance
 Chapter 25 Capacitance 25.2: Capacitance: 25.2: Capacitance: When a capacitor is charged, its plates have charges of equal magnitudes but opposite signs: q+ and q-. However, we refer to the charge of a
Chapter 25 Capacitance 25.2: Capacitance: 25.2: Capacitance: When a capacitor is charged, its plates have charges of equal magnitudes but opposite signs: q+ and q-. However, we refer to the charge of a
Chapter 1 The Electric Force
 Chapter 1 The Electric Force 1. Properties of the Electric Charges 1- There are two kinds of the electric charges in the nature, which are positive and negative charges. - The charges of opposite sign
Chapter 1 The Electric Force 1. Properties of the Electric Charges 1- There are two kinds of the electric charges in the nature, which are positive and negative charges. - The charges of opposite sign
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2015
 Physics 2212 GH uiz #2 Solutions Spring 2015 Fundamental Charge e = 1.602 10 19 C Mass of an Electron m e = 9.109 10 31 kg Coulomb constant K = 8.988 10 9 N m 2 /C 2 Vacuum Permittivity ϵ 0 = 8.854 10
Physics 2212 GH uiz #2 Solutions Spring 2015 Fundamental Charge e = 1.602 10 19 C Mass of an Electron m e = 9.109 10 31 kg Coulomb constant K = 8.988 10 9 N m 2 /C 2 Vacuum Permittivity ϵ 0 = 8.854 10
Ampere s Law. Outline. Objectives. BEE-Lecture Notes Anurag Srivastava 1
 Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
ConcepTest: Electric Potential
 ConcepTest: Electric Potential Which point has the largest potential when Q > 0? E Which two points have the same potential? (a) A and C (b) B and E (c) B and D (d) C and D (e) no pair C A Smallest radius
ConcepTest: Electric Potential Which point has the largest potential when Q > 0? E Which two points have the same potential? (a) A and C (b) B and E (c) B and D (d) C and D (e) no pair C A Smallest radius
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 ELECTRIC CHARGE. Lecture 1. Chapter 21 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 ELECTRIC CHARGE Lecture 1 Chapter 21 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 21 Electric Charge In this chapter we will introduce a new property of
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 ELECTRIC CHARGE Lecture 1 Chapter 21 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 21 Electric Charge In this chapter we will introduce a new property of
Chapter 17 & 18. Electric Field and Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
Chapter 24. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Let s return to the field lines and consider the flux through a surface. The number of lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field. This means that
Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Let s return to the field lines and consider the flux through a surface. The number of lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field. This means that
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
 Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Physics 2049 Exam 1 Solutions Fall 2002
 Physics 2049 xam 1 Solutions Fall 2002 1. A metal ball is suspended by a string. A positively charged plastic ruler is placed near the ball, which is observed to be attracted to the ruler. What can we
Physics 2049 xam 1 Solutions Fall 2002 1. A metal ball is suspended by a string. A positively charged plastic ruler is placed near the ball, which is observed to be attracted to the ruler. What can we
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
Gauss s Law. Phys102 Lecture 4. Key Points. Electric Flux Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law. References. SFU Ed: 22-1,2,3. 6 th Ed: 16-10,+.
 Phys102 Lecture 4 Phys102 Lecture 4-1 Gauss s Law Key Points Electric Flux Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law References SFU Ed: 22-1,2,3. 6 th Ed: 16-10,+. Electric Flux Electric flux: The direction
Phys102 Lecture 4 Phys102 Lecture 4-1 Gauss s Law Key Points Electric Flux Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law References SFU Ed: 22-1,2,3. 6 th Ed: 16-10,+. Electric Flux Electric flux: The direction
Chapter 22 Gauss s law. Electric charge and flux (sec &.3) Gauss s Law (sec &.5) Charges on conductors (sec. 22.6)
 Chapter 22 Gauss s law Electric charge and flux (sec. 22.2 &.3) Gauss s Law (sec. 22.4 &.5) Charges on conductors (sec. 22.6) 1 Learning Goals for CH 22 Determine the amount of charge within a closed surface
Chapter 22 Gauss s law Electric charge and flux (sec. 22.2 &.3) Gauss s Law (sec. 22.4 &.5) Charges on conductors (sec. 22.6) 1 Learning Goals for CH 22 Determine the amount of charge within a closed surface
2014 F 2014 AI. 1. Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason.
 2014 F 1. Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason. 2. Figure shows the field lines on a positive charge. Is the work done
2014 F 1. Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason. 2. Figure shows the field lines on a positive charge. Is the work done
A) 1, 2, 3, 4 B) 4, 3, 2, 1 C) 2, 3, 1, 4 D) 2, 4, 1, 3 E) 3, 2, 4, 1. Page 2
 1. Two parallel-plate capacitors with different plate separation but the same capacitance are connected in series to a battery. Both capacitors are filled with air. The quantity that is NOT the same for
1. Two parallel-plate capacitors with different plate separation but the same capacitance are connected in series to a battery. Both capacitors are filled with air. The quantity that is NOT the same for
Chapter 23 Term083 Term082
 Chapter 23 Term083 Q6. Consider two large oppositely charged parallel metal plates, placed close to each other. The plates are square with sides L and carry charges Q and Q. The magnitude of the electric
Chapter 23 Term083 Q6. Consider two large oppositely charged parallel metal plates, placed close to each other. The plates are square with sides L and carry charges Q and Q. The magnitude of the electric
Chapter 23. Electric Fields
 Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electricity and Magnetism The laws of electricity and magnetism play a central role in the operation of many modern devices. The interatomic and intermolecular forces responsible
Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electricity and Magnetism The laws of electricity and magnetism play a central role in the operation of many modern devices. The interatomic and intermolecular forces responsible
Chapter 22. Dr. Armen Kocharian. Gauss s Law Lecture 4
 Chapter 22 Dr. Armen Kocharian Gauss s Law Lecture 4 Field Due to a Plane of Charge E must be perpendicular to the plane and must have the same magnitude at all points equidistant from the plane Choose
Chapter 22 Dr. Armen Kocharian Gauss s Law Lecture 4 Field Due to a Plane of Charge E must be perpendicular to the plane and must have the same magnitude at all points equidistant from the plane Choose
Electric Field Lines. lecture 4.1.1
 Electric Field Lines Two protons, A and B, are in an electric field. Which proton has the larger acceleration? A. Proton A B. Proton B C. Both have the same acceleration. lecture 4.1.1 Electric Field Lines
Electric Field Lines Two protons, A and B, are in an electric field. Which proton has the larger acceleration? A. Proton A B. Proton B C. Both have the same acceleration. lecture 4.1.1 Electric Field Lines
Physics 420 Fall 2004 Quiz 1 Wednesday This quiz is worth 6 points. Be sure to show your work and label your final answers.
 Quiz 1 Wednesday This quiz is worth 6 points. Be sure to show your work and label your final answers. 1. A charge q 1 = +5.0 nc is located on the y-axis, 15 µm above the origin, while another charge q
Quiz 1 Wednesday This quiz is worth 6 points. Be sure to show your work and label your final answers. 1. A charge q 1 = +5.0 nc is located on the y-axis, 15 µm above the origin, while another charge q
Physics 114 Exam 1 Fall 2015
 Physics 114 Exam 1 Fall 015 Name: For grading purposes (do not write here): Question 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the following questions and each of the problems. Points for each question and
Physics 114 Exam 1 Fall 015 Name: For grading purposes (do not write here): Question 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the following questions and each of the problems. Points for each question and
Physics 114 Exam 1 Spring 2013
 Physics 114 Exam 1 Spring 2013 Name: For grading purposes (do not write here): Question 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the following questions and each of the problems. Points for each question
Physics 114 Exam 1 Spring 2013 Name: For grading purposes (do not write here): Question 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the following questions and each of the problems. Points for each question
More Gauss, Less Potential
 More Gauss, Less Potential Today: Gauss Law examples Monday: Electrical Potential Energy (Guest Lecturer) new SmartPhysics material Wednesday: Electric Potential new SmartPhysics material Thursday: Midterm
More Gauss, Less Potential Today: Gauss Law examples Monday: Electrical Potential Energy (Guest Lecturer) new SmartPhysics material Wednesday: Electric Potential new SmartPhysics material Thursday: Midterm
Ch 24 Electric Flux, & Gauss s Law
 Ch 24 Electric Flux, & Gauss s Law Electric Flux...is related to the number of field lines penetrating a given surface area. Φ e = E A Φ = phi = electric flux Φ units are N m 2 /C Electric Flux Φ = E A
Ch 24 Electric Flux, & Gauss s Law Electric Flux...is related to the number of field lines penetrating a given surface area. Φ e = E A Φ = phi = electric flux Φ units are N m 2 /C Electric Flux Φ = E A
Physics Lecture 13
 Physics 113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 113 Lecture 13 EXAM I: REVIEW A few concepts: electric force, field and potential Gravitational Force What is the force on a mass produced by other masses? Kepler s
Physics 113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 113 Lecture 13 EXAM I: REVIEW A few concepts: electric force, field and potential Gravitational Force What is the force on a mass produced by other masses? Kepler s
Review. Spring Semester /21/14. Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 1
 Review Spring Semester 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 1 Notes! Homework set 13 extended to Tuesday, 4/22! Remember to fill out SIRS form: https://sirsonline.msu.edu Physics for Scientists &
Review Spring Semester 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 1 Notes! Homework set 13 extended to Tuesday, 4/22! Remember to fill out SIRS form: https://sirsonline.msu.edu Physics for Scientists &
HW Chapter 16 Q 6,8,10,18,19,21 P 1,2,3,4. Chapter 16. Part 1: Electric Forces and Electric Fields. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 16 Q 6,8,10,18,19,21 P 1,2,3,4 Chapter 16 Part 1: Electric Forces and Electric Fields Dr. Armen Kocharian First Observations Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC
HW Chapter 16 Q 6,8,10,18,19,21 P 1,2,3,4 Chapter 16 Part 1: Electric Forces and Electric Fields Dr. Armen Kocharian First Observations Greeks Observed electric and magnetic phenomena as early as 700 BC
Physics 212 Exam I Sample Question Bank 2008 Multiple Choice: choose the best answer "none of the above" may can be a valid answer
 Multiple Choice: choose the best answer "none of the above" may can be a valid answer The (attempted) demonstration in class with the pith balls and a variety of materials indicated that () there are two
Multiple Choice: choose the best answer "none of the above" may can be a valid answer The (attempted) demonstration in class with the pith balls and a variety of materials indicated that () there are two
Chapter 24. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Cutnell/Johnson Physics
 Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 18 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Interactive Lecture Questions 18.1.1. A brass key has a net positive charge of +1.92 10 16 C.
Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 18 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Interactive Lecture Questions 18.1.1. A brass key has a net positive charge of +1.92 10 16 C.
AP Physics C. Electricity - Term 3
 AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
24 Gauss s Law. Gauss s Law 87:
 Green Items that must be covered for the national test Blue Items from educator.com Red Items from the 8 th edition of Serway 24 Gauss s Law 24.1 Electric Flux 24.2 Gauss s Law 24.3 Application of Gauss
Green Items that must be covered for the national test Blue Items from educator.com Red Items from the 8 th edition of Serway 24 Gauss s Law 24.1 Electric Flux 24.2 Gauss s Law 24.3 Application of Gauss
CHAPTER 15 ELECTRIC FORCE & FIELDS
 CHAPTER 15 ELECTRIC FORCE & FIELDS We will look at the basic properties of electric charge. Electric charge comes in discrete units The total charge in the universe remains constant The force law that
CHAPTER 15 ELECTRIC FORCE & FIELDS We will look at the basic properties of electric charge. Electric charge comes in discrete units The total charge in the universe remains constant The force law that
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Conductors and Insulators
 Conductors and Insulators Lecture 11: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Self Energy of a Charge Distribution : In Lecture 1 we briefly discussed what we called
Conductors and Insulators Lecture 11: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Self Energy of a Charge Distribution : In Lecture 1 we briefly discussed what we called
Physics 1214 Chapter 17: Electric Charge and Electric Field
 Physics 1214 Chapter 17: Electric Charge and Electric Field Introduction electrostatic interactions interactions between electric charges at rest in our frame of reference modeled by Coulomb s equation
Physics 1214 Chapter 17: Electric Charge and Electric Field Introduction electrostatic interactions interactions between electric charges at rest in our frame of reference modeled by Coulomb s equation
( E ) = Lecture 1 Electric Charges & Coulomb s Law. Electric & Magnetic Fields. Electric Charge. Electric Charge
 Electric & Magnetic Fields Lecture 1 Electric Charges & Coulomb s Law Electric and magnetic fields manifest their existence through interactions with matter. Differential Form div E E = ( ) = div( B )
Electric & Magnetic Fields Lecture 1 Electric Charges & Coulomb s Law Electric and magnetic fields manifest their existence through interactions with matter. Differential Form div E E = ( ) = div( B )
MTE1 results. Mean 75% = 90/120
 MTE1 results Mean 75% = 90/120 Scores available at Learn@UW, your TAs have exams If your score is an F or a D, talk to us and your TAs for suggestions on how to improve From last times Electric charges
MTE1 results Mean 75% = 90/120 Scores available at Learn@UW, your TAs have exams If your score is an F or a D, talk to us and your TAs for suggestions on how to improve From last times Electric charges
Physics Lecture: 09
 Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 2113 Lecture: 09 Flux Capacitor (Schematic) Gauss Law II Carl Friedrich Gauss 1777 1855 Gauss Law: General Case Consider any ARBITRARY CLOSED surface S -- NOTE: this
Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 2113 Lecture: 09 Flux Capacitor (Schematic) Gauss Law II Carl Friedrich Gauss 1777 1855 Gauss Law: General Case Consider any ARBITRARY CLOSED surface S -- NOTE: this
