Trees. (in computer science)
|
|
|
- Nicholas Wood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Trees (in computer science)
2 Tree in Computer Science } A tree is a widely used data structure that simulates a hierarchical tree structure with a set of linked nodes 2
3 Tree in Computer Science } Fundamental data storage structures used in programming } Nonlinear structure } Represents a hierarchy } Items in a tree do not form a simple sequence } Quite efficient for retrieving items (as arrays) } Quite efficient for inserting/deleting items (as lists) 3
4 JavaFX 2.0 Layout Classes 4
5 Ordinamento dello Stato Italiano 5
6 Tree basics } Consists of nodes connected by edges } Nodes often represent entities (complex objects) } Edges between the nodes represent the way the nodes are related } The only way to get from node to node is to follow a path along the edges 6
7 Tree Basics } Node } Root (radice) } Leaf (foglia) } Interior node/branch (nodo interno) } Links } Edge (arco) } Path (cammino) 7
8 Tree Basics } Relationship } Parent (padre) } Child nodes (nodi figli) } Sibling (fratelli) } Descendant (discendente, successore) } Ancestor (antenato, predecessore) 8
9 Terminology } Visiting } A node is visited when program control arrives at the node, usually for processing } Traversing } To traverse a tree means to visit all the nodes in some specified order 9
10 Terminology } Levels } The level of a particular node refers to how many generations the node is from the root } Root is assumed to be level 0 10
11 Terminology } Height } The height of a node is the length of the path to its farthest descendant (i.e. farthest leaf node) } The height of a tree is the height of the root } A tree with only root node has height 0 11
12 Test! D B E G A F C } Number of nodes } Height } Root Node } Leaves } Levels } Interior nodes } Ancestors of H } Descendants of B } Siblings of E H I 12
13 Tree representation Store the list of children in each node 13
14 Tree representation (alt) For each node store its first-born and its brother 14
15 Tree representation (alt) } 1 } 1( ) } } 1(2(6 7 8) 3 4(9(12)) 5(10 11)) Store each sub-tree as a separate object in a list 15
16 An oversimplified tree public class Tree<T> { public Node<T> root; public Tree() { root = new Node<T>(); } } public Tree(T r) { root = new Node<T>(r); } 16
17 An oversimplified tree public class Node<T> { T data; Node<T> parent; List<Node<T>> children; [ ] public Node() { data = null; children = new ArrayList<Node<T>>(); } public Node(T d) { this(); data = d; } 17
18 An oversimplified tree [ ] [ ] public void addchild(node<t> n) { n.parent = this; children.add(n); } public void removechild(node<t> n) { children.remove(n); } 18
19 Terminology } Visiting } A node is visited when program control arrives at the node, usually for processing } Traversing } To traverse a tree means to visit all the nodes in some specified order 19
20 An oversimplified tree public class Tree<T> { [ ] } public void Visit() { root.visit(); } 20
21 An oversimplified tree public class Node<T> { [ ] void Visit() { // Do something on the node for(node<t> n : children) { n.visit(); } } } 21
22 An oversimplified tree void Visit() { if(children.size()>0) System.out.print("("); System.out.print(data); for(node<t> n : children) { System.out.print(" "); n.visit(); } if(children.size()>0) System.out.print(")"); } 22
23 An oversimplified tree public class Node<T> { [ ] void Visit() { for(node<t> n : children) { n.visit(); } // Do something on the node } } 23
24 Binary Trees
25 Binary Tree } A binary tree is a tree where each node has at most two children } The two children are ordered ( left, right ) } Right sub-tree vs. Left sub-tree 25
26 Balanced trees } (Height-)balanced trees } The left and right sub-trees heights differ by at most one } The two sub-trees are (height-)balanced } Perfectly balanced } 2 " 1 nodes } Several alternative definitions 26
27 Complete trees } Complete binary tree } Every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible 27
28 Tree representation A complete tree can be efficently stored in an array 28
29 Degenerate trees 29
30 Traversal in binary trees } Pre-order } process root node, then its left/right sub-trees } In-order } process left sub-tree, then root node, then right } Post-order } process left/right sub-trees, then root node 30
31 Traversal in binary trees Root } pre-order: } in-order: } post-order:
32 Traversal trick } To quickly generate a traversal: } Trace a path around the tree } As you pass a node on the proper side, process it } pre-order: left side } in-order: bottom } post-order: right side Root pre-order: in-order: post-order:
33 Exercise } Give pre-, in-, and post-order traversals for the following tree: Root 42 pre: in: post:
34 Polish prefix notation } Akas: Polish notation, prefix notation } Created in 1924 by the Polish logician Jan Łukasiewicz } Operators are on the left of their operands } If the arity of the operators is fixed no need for parentheses or other brackets } E.g.: } 3 * ( ) * } ( x + y ) / ( 2 - z ) / + x y - 2 z 34
35 Reverse Polish notation } } } } (Re-)Invented by Bauer and Dijkstra in early 1960s to exploit stack for evaluating expressions Operator follows all of its operands If the arity of the operators is fixed no need for parentheses or other brackets E.g.: } } 35 3*(2+7) 327+* (x+y)/(2-z) xy+2z-/
36 Traversals and notations } In-order: ( ) * 2 + ( 6-3 ) } Pre-order: + * } Post-order: *
37 BST Binary Search Tree
38 Binary search trees } A binary tree where each non-empty node R has the following properties: } Elements of R s left sub-tree contain data less than R s data } Elements of R s right sub-tree contain data greater than R s } R s left and right sub-trees are also binary search trees root
39 Binary search trees } BSTs store their elements in sorted order, which is helpful for searching/sorting tasks 39
40 Exercise } Is it a legal binary search tree?
41 Exercise } Is it a legal binary search tree? 42 41
42 Exercise } Is it a legal binary search tree?
43 Excercise } Is it a legal binary search tree? m g q b k x e 43
44 Exercise } Is it a legal binary search tree?
45 Searching in a BST } Describe an algorithm for searching a binary search tree (try searching for 31, then 6) root
46 Searching in a BST } Searching in a BST is O(h) If the tree is balanced, then h log. N Searching for an element is O(ln N) 46
47 Showdown Array List Hash BST add(element) O(1) O(1) O(1) O(ln n) remove(object) O(n) + O(n) O(n) + O(1) O(1) O(ln n) get(index) O(1) O(n) n.a. n.a. set(index, element) O(1) O(n) + O(1) n.a. n.a. add(index, element) O(1) + O(n) O(n) + O(1) n.a. n.a. remove(index) O(n) O(n) + O(1) n.a. n.a. contains(object) O(n) O(n) O(1) O(ln n) indexof(object) O(n) O(n) n.a. n.a. 47
48 Licenza d uso } Queste diapositive sono distribuite con licenza Creative Commons Attribuzione - Non commerciale - Condividi allo stesso modo (CC BY-NC-SA) } Sei libero: } di riprodurre, distribuire, comunicare al pubblico, esporre in pubblico, rappresentare, eseguire e recitare quest'opera } di modificare quest'opera } Alle seguenti condizioni: } Attribuzione Devi attribuire la paternità dell'opera agli autori originali e in modo tale da non suggerire che essi avallino te o il modo in cui tu usi l'opera. } Non commerciale Non puoi usare quest'opera per fini commerciali. } Condividi allo stesso modo Se alteri o trasformi quest'opera, o se la usi per crearne un'altra, puoi distribuire l'opera risultante solo con una licenza identica o equivalente a questa. } 48
Computational complexity. How to measure the difficulty of a problem
 Computational complexity How to measure the difficulty of a problem How to Measure Efficiency? Critical resources programmer s effort time, space (disk, RAM) Analysis empirical (run programs) analytical
Computational complexity How to measure the difficulty of a problem How to Measure Efficiency? Critical resources programmer s effort time, space (disk, RAM) Analysis empirical (run programs) analytical
Collection Family Tree
 Collection Family Tree 1 ArrayList vs. LinkedList ArrayList LinkedList add(element) IMMEDIATE IMMEDIATE remove(object) SLUGGISH IMMEDIATE get(index) IMMEDIATE SLUGGISH set(index, element) IMMEDIATE SLUGGISH
Collection Family Tree 1 ArrayList vs. LinkedList ArrayList LinkedList add(element) IMMEDIATE IMMEDIATE remove(object) SLUGGISH IMMEDIATE get(index) IMMEDIATE SLUGGISH set(index, element) IMMEDIATE SLUGGISH
Assignment 5: Solutions
 Comp 21: Algorithms and Data Structures Assignment : Solutions 1. Heaps. (a) First we remove the minimum key 1 (which we know is located at the root of the heap). We then replace it by the key in the position
Comp 21: Algorithms and Data Structures Assignment : Solutions 1. Heaps. (a) First we remove the minimum key 1 (which we know is located at the root of the heap). We then replace it by the key in the position
Discrete Mathematics
 Discrete Mathematics Trees H. Turgut Uyar Ayşegül Gençata Yayımlı Emre Harmancı 2001-2016 License You are free to: c 2001-2016 T. Uyar, A. Yayımlı, E. Harmancı Share copy and redistribute the material
Discrete Mathematics Trees H. Turgut Uyar Ayşegül Gençata Yayımlı Emre Harmancı 2001-2016 License You are free to: c 2001-2016 T. Uyar, A. Yayımlı, E. Harmancı Share copy and redistribute the material
Programming Binary Search Tree. Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 12
 SE-286: Data Structures and Programming g Binary Search Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 12 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Binary Search Trees Dictionary Operations: get(key)
SE-286: Data Structures and Programming g Binary Search Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 12 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Binary Search Trees Dictionary Operations: get(key)
Data Structures and Algorithms " Search Trees!!
 Data Structures and Algorithms " Search Trees!! Outline" Binary Search Trees! AVL Trees! (2,4) Trees! 2 Binary Search Trees! "! < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9 Ordered Dictionaries" Keys are assumed to come from a total
Data Structures and Algorithms " Search Trees!! Outline" Binary Search Trees! AVL Trees! (2,4) Trees! 2 Binary Search Trees! "! < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9 Ordered Dictionaries" Keys are assumed to come from a total
Advanced Implementations of Tables: Balanced Search Trees and Hashing
 Advanced Implementations of Tables: Balanced Search Trees and Hashing Balanced Search Trees Binary search tree operations such as insert, delete, retrieve, etc. depend on the length of the path to the
Advanced Implementations of Tables: Balanced Search Trees and Hashing Balanced Search Trees Binary search tree operations such as insert, delete, retrieve, etc. depend on the length of the path to the
Priority queues implemented via heaps
 Priority queues implemented via heaps Comp Sci 1575 Data s Outline 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 Priority queue: most important first Recall: queue is FIFO A normal queue data structure will not implement a priority
Priority queues implemented via heaps Comp Sci 1575 Data s Outline 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 Priority queue: most important first Recall: queue is FIFO A normal queue data structure will not implement a priority
Search Trees. Chapter 10. CSE 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: :52 AM
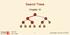 Search Trees Chapter 1 < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 3 - Binary Search Trees Ø A binary search
Search Trees Chapter 1 < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 3 - Binary Search Trees Ø A binary search
Search Trees. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: 24 March 2015
 Search Trees < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Learning Outcomes Ø From this lecture, you should be able to: q Define the properties of a binary search
Search Trees < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Learning Outcomes Ø From this lecture, you should be able to: q Define the properties of a binary search
Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis
 Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis Tsan-sheng Hsu tshsu@iis.sinica.edu.tw http://www.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~tshsu 1 Introduction Alpha-beta pruning is the standard searching procedure used for solving
Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis Tsan-sheng Hsu tshsu@iis.sinica.edu.tw http://www.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~tshsu 1 Introduction Alpha-beta pruning is the standard searching procedure used for solving
16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]
![16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ] 16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]](/thumbs/72/67371940.jpg) 418 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] 419 Dictionary implementation Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
418 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] 419 Dictionary implementation Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
1 Trees. Listing 1: Node with two child reference. public class ptwochildnode { protected Object data ; protected ptwochildnode l e f t, r i g h t ;
 1 Trees The next major set of data structures belongs to what s called Trees. They are called that, because if you try to visualize the structure, it kind of looks like a tree (root, branches, and leafs).
1 Trees The next major set of data structures belongs to what s called Trees. They are called that, because if you try to visualize the structure, it kind of looks like a tree (root, branches, and leafs).
16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]
![16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ] 16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]](/thumbs/81/84624162.jpg) 423 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] Dictionary implementation 424 Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
423 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] Dictionary implementation 424 Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
Binary Search Trees. Motivation
 Binary Search Trees Motivation Searching for a particular record in an unordered list takes O(n), too slow for large lists (databases) If the list is ordered, can use an array implementation and use binary
Binary Search Trees Motivation Searching for a particular record in an unordered list takes O(n), too slow for large lists (databases) If the list is ordered, can use an array implementation and use binary
Binary Search Trees. Lecture 29 Section Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Fri, Apr 8, 2016
 Binary Search Trees Lecture 29 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 8, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Search Trees Fri, Apr 8, 2016 1 / 40 1 Binary Search
Binary Search Trees Lecture 29 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 8, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Search Trees Fri, Apr 8, 2016 1 / 40 1 Binary Search
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk I. Yu, D. Karabeg INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Function growth & estimation of running time, trees (Exercises with hints for solution)
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk I. Yu, D. Karabeg INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Function growth & estimation of running time, trees (Exercises with hints for solution)
8 Priority Queues. 8 Priority Queues. Prim s Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm. Dijkstra s Shortest Path Algorithm
 8 Priority Queues 8 Priority Queues A Priority Queue S is a dynamic set data structure that supports the following operations: S. build(x 1,..., x n ): Creates a data-structure that contains just the elements
8 Priority Queues 8 Priority Queues A Priority Queue S is a dynamic set data structure that supports the following operations: S. build(x 1,..., x n ): Creates a data-structure that contains just the elements
Chapter 5 Data Structures Algorithm Theory WS 2017/18 Fabian Kuhn
 Chapter 5 Data Structures Algorithm Theory WS 2017/18 Fabian Kuhn Priority Queue / Heap Stores (key,data) pairs (like dictionary) But, different set of operations: Initialize-Heap: creates new empty heap
Chapter 5 Data Structures Algorithm Theory WS 2017/18 Fabian Kuhn Priority Queue / Heap Stores (key,data) pairs (like dictionary) But, different set of operations: Initialize-Heap: creates new empty heap
Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis
 Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis Tsan-sheng Hsu tshsu@iis.sinica.edu.tw http://www.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~tshsu 1 Introduction Alpha-beta pruning is the standard searching procedure used for 2-person
Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis Tsan-sheng Hsu tshsu@iis.sinica.edu.tw http://www.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~tshsu 1 Introduction Alpha-beta pruning is the standard searching procedure used for 2-person
Lecture 18 April 26, 2012
 6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Demaine Lecture 18 April 26, 2012 1 Overview In the last lecture we introduced the concept of implicit, succinct, and compact data structures, and
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Demaine Lecture 18 April 26, 2012 1 Overview In the last lecture we introduced the concept of implicit, succinct, and compact data structures, and
Lecture 17: Trees and Merge Sort 10:00 AM, Oct 15, 2018
 CS17 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Klein Contents Lecture 17: Trees and Merge Sort 10:00 AM, Oct 15, 2018 1 Tree definitions 1 2 Analysis of mergesort using a binary tree 1 3 Analysis of
CS17 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Klein Contents Lecture 17: Trees and Merge Sort 10:00 AM, Oct 15, 2018 1 Tree definitions 1 2 Analysis of mergesort using a binary tree 1 3 Analysis of
Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis
 Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis Tsan-sheng Hsu tshsu@iis.sinica.edu.tw http://www.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~tshsu 1 Introduction Alpha-beta pruning is the standard searching procedure used for 2-person
Alpha-Beta Pruning: Algorithm and Analysis Tsan-sheng Hsu tshsu@iis.sinica.edu.tw http://www.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~tshsu 1 Introduction Alpha-beta pruning is the standard searching procedure used for 2-person
Dictionary: an abstract data type
 2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
ENS Lyon Camp. Day 2. Basic group. Cartesian Tree. 26 October
 ENS Lyon Camp. Day 2. Basic group. Cartesian Tree. 26 October Contents 1 Cartesian Tree. Definition. 1 2 Cartesian Tree. Construction 1 3 Cartesian Tree. Operations. 2 3.1 Split............................................
ENS Lyon Camp. Day 2. Basic group. Cartesian Tree. 26 October Contents 1 Cartesian Tree. Definition. 1 2 Cartesian Tree. Construction 1 3 Cartesian Tree. Operations. 2 3.1 Split............................................
Dictionary: an abstract data type
 2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
Ordered Dictionary & Binary Search Tree
 Ordered Dictionary & Binary Search Tree Finite map from keys to values, assuming keys are comparable (). insert(k, v) lookup(k) aka find: the associated value if any delete(k) (Ordered set: No values;
Ordered Dictionary & Binary Search Tree Finite map from keys to values, assuming keys are comparable (). insert(k, v) lookup(k) aka find: the associated value if any delete(k) (Ordered set: No values;
Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms Part Two
 Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms Part Two Recap from Last Time Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms A divide-and-conquer algorithm is one that works as follows: (Divide) Split the input apart into multiple smaller
Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms Part Two Recap from Last Time Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms A divide-and-conquer algorithm is one that works as follows: (Divide) Split the input apart into multiple smaller
AVL Trees. Manolis Koubarakis. Data Structures and Programming Techniques
 AVL Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 AVL Trees We will now introduce AVL trees that have the property that they are kept almost balanced but not completely balanced. In this way we have O(log n) search time
AVL Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 AVL Trees We will now introduce AVL trees that have the property that they are kept almost balanced but not completely balanced. In this way we have O(log n) search time
Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms
 Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms dataminingbook.info Mohammed J. Zaki 1 Wagner Meira Jr. 2 1 Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA
Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms dataminingbook.info Mohammed J. Zaki 1 Wagner Meira Jr. 2 1 Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA
1. Prove: A full m- ary tree with i internal vertices contains n = mi + 1 vertices.
 1. Prove: A full m- ary tree with i internal vertices contains n = mi + 1 vertices. Proof: Every vertex, except the root, is the child of an internal vertex. Since there are i internal vertices, each of
1. Prove: A full m- ary tree with i internal vertices contains n = mi + 1 vertices. Proof: Every vertex, except the root, is the child of an internal vertex. Since there are i internal vertices, each of
Digital search trees JASS
 Digital search trees Analysis of different digital trees with Rice s integrals. JASS Nicolai v. Hoyningen-Huene 28.3.2004 28.3.2004 JASS 04 - Digital search trees 1 content Tree Digital search tree: Definition
Digital search trees Analysis of different digital trees with Rice s integrals. JASS Nicolai v. Hoyningen-Huene 28.3.2004 28.3.2004 JASS 04 - Digital search trees 1 content Tree Digital search tree: Definition
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 3 We are given a set of training examples, consisting of input-output pairs (x,y), where: 1. x is an item of the type we want to evaluate. 2. y is the value of some
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 3 We are given a set of training examples, consisting of input-output pairs (x,y), where: 1. x is an item of the type we want to evaluate. 2. y is the value of some
Problem: Data base too big to fit memory Disk reads are slow. Example: 1,000,000 records on disk Binary search might take 20 disk reads
 B Trees Problem: Data base too big to fit memory Disk reads are slow Example: 1,000,000 records on disk Binary search might take 20 disk reads Disk reads are done in blocks Example: One block read can
B Trees Problem: Data base too big to fit memory Disk reads are slow Example: 1,000,000 records on disk Binary search might take 20 disk reads Disk reads are done in blocks Example: One block read can
CS361 Homework #3 Solutions
 CS6 Homework # Solutions. Suppose I have a hash table with 5 locations. I would like to know how many items I can store in it before it becomes fairly likely that I have a collision, i.e., that two items
CS6 Homework # Solutions. Suppose I have a hash table with 5 locations. I would like to know how many items I can store in it before it becomes fairly likely that I have a collision, i.e., that two items
Binary Search Trees. Dictionary Operations: Additional operations: find(key) insert(key, value) erase(key)
 Binary Search Trees Dictionary Operations: find(key) insert(key, value) erase(key) Additional operations: ascend() get(index) (indexed binary search tree) delete(index) (indexed binary search tree) Complexity
Binary Search Trees Dictionary Operations: find(key) insert(key, value) erase(key) Additional operations: ascend() get(index) (indexed binary search tree) delete(index) (indexed binary search tree) Complexity
Tutorial 4. Dynamic Set: Amortized Analysis
 Tutorial 4 Dynamic Set: Amortized Analysis Review Binary tree Complete binary tree Full binary tree 2-tree P115 Unlike common binary tree, the base case is not an empty tree, but a external node Heap Binary
Tutorial 4 Dynamic Set: Amortized Analysis Review Binary tree Complete binary tree Full binary tree 2-tree P115 Unlike common binary tree, the base case is not an empty tree, but a external node Heap Binary
Lecture 7: Trees and Structural Induction
 Lecture 7: Trees Structural Induction Natural numbers, positive numbers, rational numbers, pairs, tuples etc. are the objects that we usually study in discrete math. But when we consider discrete math
Lecture 7: Trees Structural Induction Natural numbers, positive numbers, rational numbers, pairs, tuples etc. are the objects that we usually study in discrete math. But when we consider discrete math
Binary Decision Diagrams
 Binary Decision Diagrams Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are a class of graphs that can be used as data structure for compactly representing boolean functions. BDDs were introduced by R. Bryant in 1986.
Binary Decision Diagrams Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are a class of graphs that can be used as data structure for compactly representing boolean functions. BDDs were introduced by R. Bryant in 1986.
Algorithm for exact evaluation of bivariate two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistics in O(nlogn) time.
 Algorithm for exact evaluation of bivariate two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistics in O(nlogn) time. Krystian Zawistowski January 3, 2019 Abstract We propose an O(nlogn) algorithm for evaluation of bivariate
Algorithm for exact evaluation of bivariate two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistics in O(nlogn) time. Krystian Zawistowski January 3, 2019 Abstract We propose an O(nlogn) algorithm for evaluation of bivariate
Binary Decision Diagrams. Graphs. Boolean Functions
 Binary Decision Diagrams Graphs Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are a class of graphs that can be used as data structure for compactly representing boolean functions. BDDs were introduced by R. Bryant
Binary Decision Diagrams Graphs Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are a class of graphs that can be used as data structure for compactly representing boolean functions. BDDs were introduced by R. Bryant
CS 161: Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CS 161: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Greedy Algorithms 3: Minimum Spanning Trees/Scheduling Disjoint Sets, continued Analysis of Kruskal s Algorithm Interval Scheduling Disjoint Sets, Continued Each
CS 161: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Greedy Algorithms 3: Minimum Spanning Trees/Scheduling Disjoint Sets, continued Analysis of Kruskal s Algorithm Interval Scheduling Disjoint Sets, Continued Each
Splay Trees. CMSC 420: Lecture 8
 Splay Trees CMSC 420: Lecture 8 AVL Trees Nice Features: - Worst case O(log n) performance guarantee - Fairly simple to implement Problem though: - Have to maintain etra balance factor storage at each
Splay Trees CMSC 420: Lecture 8 AVL Trees Nice Features: - Worst case O(log n) performance guarantee - Fairly simple to implement Problem though: - Have to maintain etra balance factor storage at each
CS Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis
 CS 483 - Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lecture VII: Chapter 6, part 2 R. Paul Wiegand George Mason University, Department of Computer Science March 22, 2006 Outline 1 Balanced Trees 2 Heaps &
CS 483 - Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lecture VII: Chapter 6, part 2 R. Paul Wiegand George Mason University, Department of Computer Science March 22, 2006 Outline 1 Balanced Trees 2 Heaps &
Compact Representation for Answer Sets of n-ary Regular Queries
 Compact Representation for Answer Sets of n-ary Regular Queries by Kazuhiro Inaba (National Institute of Informatics, Japan) and Hauro Hosoya (The University of Tokyo) CIAA 2009, Sydney BACKGROUND N-ary
Compact Representation for Answer Sets of n-ary Regular Queries by Kazuhiro Inaba (National Institute of Informatics, Japan) and Hauro Hosoya (The University of Tokyo) CIAA 2009, Sydney BACKGROUND N-ary
HW #4. (mostly by) Salim Sarımurat. 1) Insert 6 2) Insert 8 3) Insert 30. 4) Insert S a.
 HW #4 (mostly by) Salim Sarımurat 04.12.2009 S. 1. 1. a. 1) Insert 6 2) Insert 8 3) Insert 30 4) Insert 40 2 5) Insert 50 6) Insert 61 7) Insert 70 1. b. 1) Insert 12 2) Insert 29 3) Insert 30 4) Insert
HW #4 (mostly by) Salim Sarımurat 04.12.2009 S. 1. 1. a. 1) Insert 6 2) Insert 8 3) Insert 30 4) Insert 40 2 5) Insert 50 6) Insert 61 7) Insert 70 1. b. 1) Insert 12 2) Insert 29 3) Insert 30 4) Insert
Transformational programming and forests
 Transformational programming and forests AB18 1 A. Bijlsma Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mathematics and Computing Science P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands Introduction
Transformational programming and forests AB18 1 A. Bijlsma Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mathematics and Computing Science P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands Introduction
Outline Resource Introduction Usage Testing Exercises. Linked Lists COMP SCI / SFWR ENG 2S03. Department of Computing and Software McMaster University
 COMP SCI / SFWR ENG 2S03 Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Week 10: November 7 - November 11 Outline 1 Resource 2 Introduction Nodes Illustration 3 Usage Accessing and Modifying
COMP SCI / SFWR ENG 2S03 Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Week 10: November 7 - November 11 Outline 1 Resource 2 Introduction Nodes Illustration 3 Usage Accessing and Modifying
Tutorial Session 5. Discussion of Exercise 4, Preview on Exercise 5, Preparation for Midterm 1. Running Time Analysis, Asymptotic Complexity
 Tutorial Session 5 Tuesday, 19 th of March 2019 Discussion of Exercise 4, Preview on Exercise 5, Preparation for Midterm 1 Running Time Analysis, Asymptotic Complexity 16.15 17.45 / 18.15 19.45 BIN 0.B.06
Tutorial Session 5 Tuesday, 19 th of March 2019 Discussion of Exercise 4, Preview on Exercise 5, Preparation for Midterm 1 Running Time Analysis, Asymptotic Complexity 16.15 17.45 / 18.15 19.45 BIN 0.B.06
Association Rules. Fundamentals
 Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino 1 Association rules Objective extraction of frequent correlations or pattern from a transactional database Tickets at a supermarket counter Association rule
Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino 1 Association rules Objective extraction of frequent correlations or pattern from a transactional database Tickets at a supermarket counter Association rule
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 5 Optimizing Fixed Size Samples Sampling as
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 5 Optimizing Fixed Size Samples Sampling as
3. Problem definition
 3. Problem definition In this section, we first define a multi-dimension transaction database MD, to differentiate it between the transaction databases D in traditional association rules. Then, we discuss
3. Problem definition In this section, we first define a multi-dimension transaction database MD, to differentiate it between the transaction databases D in traditional association rules. Then, we discuss
CS 240 Data Structures and Data Management. Module 4: Dictionaries
 CS 24 Data Structures and Data Management Module 4: Dictionaries A. Biniaz A. Jamshidpey É. Schost Based on lecture notes by many previous cs24 instructors David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science,
CS 24 Data Structures and Data Management Module 4: Dictionaries A. Biniaz A. Jamshidpey É. Schost Based on lecture notes by many previous cs24 instructors David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science,
Advanced Data Structures
 Simon Gog gog@kit.edu - Simon Gog: KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of the Helmholtz Association www.kit.edu Predecessor data structures We want to support
Simon Gog gog@kit.edu - Simon Gog: KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of the Helmholtz Association www.kit.edu Predecessor data structures We want to support
Part IA Algorithms Notes
 Part IA Algorithms Notes 1 Sorting 1.1 Insertion Sort 1 d e f i n s e r t i o n S o r t ( a ) : 2 f o r i from 1 i n c l u d e d to l e n ( a ) excluded : 3 4 j = i 1 5 w h i l e j >= 0 and a [ i ] > a
Part IA Algorithms Notes 1 Sorting 1.1 Insertion Sort 1 d e f i n s e r t i o n S o r t ( a ) : 2 f o r i from 1 i n c l u d e d to l e n ( a ) excluded : 3 4 j = i 1 5 w h i l e j >= 0 and a [ i ] > a
META: An Efficient Matching-Based Method for Error-Tolerant Autocompletion
 : An Efficient Matching-Based Method for Error-Tolerant Autocompletion Dong Deng Guoliang Li He Wen H. V. Jagadish Jianhua Feng Department of Computer Science, Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information
: An Efficient Matching-Based Method for Error-Tolerant Autocompletion Dong Deng Guoliang Li He Wen H. V. Jagadish Jianhua Feng Department of Computer Science, Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information
Formal Languages, Automata and Compilers
 Formal Languages, Automata and Compilers Lecure 4 2017-18 LFAC (2017-18) Lecture 4 1 / 31 Curs 4 1 Grammars of type 3 and finite automata 2 Closure properties for type 3 languages 3 Regular Expressions
Formal Languages, Automata and Compilers Lecure 4 2017-18 LFAC (2017-18) Lecture 4 1 / 31 Curs 4 1 Grammars of type 3 and finite automata 2 Closure properties for type 3 languages 3 Regular Expressions
Space-Efficient Construction Algorithm for Circular Suffix Tree
 Space-Efficient Construction Algorithm for Circular Suffix Tree Wing-Kai Hon, Tsung-Han Ku, Rahul Shah and Sharma Thankachan CPM2013 1 Outline Preliminaries and Motivation Circular Suffix Tree Our Indexes
Space-Efficient Construction Algorithm for Circular Suffix Tree Wing-Kai Hon, Tsung-Han Ku, Rahul Shah and Sharma Thankachan CPM2013 1 Outline Preliminaries and Motivation Circular Suffix Tree Our Indexes
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 5: Searching Michael Bader Winter 2014/15 Chapter 5: Searching, Winter 2014/15 1 Searching Definition (Search Problem) Input: a sequence or set A of n elements (objects)
Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 5: Searching Michael Bader Winter 2014/15 Chapter 5: Searching, Winter 2014/15 1 Searching Definition (Search Problem) Input: a sequence or set A of n elements (objects)
Advanced Data Structures
 Simon Gog gog@kit.edu - Simon Gog: KIT The Research University in the Helmholtz Association www.kit.edu Predecessor data structures We want to support the following operations on a set of integers from
Simon Gog gog@kit.edu - Simon Gog: KIT The Research University in the Helmholtz Association www.kit.edu Predecessor data structures We want to support the following operations on a set of integers from
Optimal Color Range Reporting in One Dimension
 Optimal Color Range Reporting in One Dimension Yakov Nekrich 1 and Jeffrey Scott Vitter 1 The University of Kansas. yakov.nekrich@googlemail.com, jsv@ku.edu Abstract. Color (or categorical) range reporting
Optimal Color Range Reporting in One Dimension Yakov Nekrich 1 and Jeffrey Scott Vitter 1 The University of Kansas. yakov.nekrich@googlemail.com, jsv@ku.edu Abstract. Color (or categorical) range reporting
A set theoretic view of the ISA hierarchy
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository A set theoretic view of the ISA hierarchy This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: CHEUNG,
Loughborough University Institutional Repository A set theoretic view of the ISA hierarchy This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: CHEUNG,
: Advanced Compiler Design Compu=ng DF(X) 3.4 Algorithm for inser=on of φ func=ons 3.5 Algorithm for variable renaming
 263-2810: Advanced Compiler Design 3.3.2 Compu=ng DF(X) 3.4 Algorithm for inser=on of φ func=ons 3.5 Algorithm for variable renaming Thomas R. Gross Computer Science Department ETH Zurich, Switzerland
263-2810: Advanced Compiler Design 3.3.2 Compu=ng DF(X) 3.4 Algorithm for inser=on of φ func=ons 3.5 Algorithm for variable renaming Thomas R. Gross Computer Science Department ETH Zurich, Switzerland
4.8 Huffman Codes. These lecture slides are supplied by Mathijs de Weerd
 4.8 Huffman Codes These lecture slides are supplied by Mathijs de Weerd Data Compression Q. Given a text that uses 32 symbols (26 different letters, space, and some punctuation characters), how can we
4.8 Huffman Codes These lecture slides are supplied by Mathijs de Weerd Data Compression Q. Given a text that uses 32 symbols (26 different letters, space, and some punctuation characters), how can we
Notes on Logarithmic Lower Bounds in the Cell Probe Model
 Notes on Logarithmic Lower Bounds in the Cell Probe Model Kevin Zatloukal November 10, 2010 1 Overview Paper is by Mihai Pâtraşcu and Erik Demaine. Both were at MIT at the time. (Mihai is now at AT&T Labs.)
Notes on Logarithmic Lower Bounds in the Cell Probe Model Kevin Zatloukal November 10, 2010 1 Overview Paper is by Mihai Pâtraşcu and Erik Demaine. Both were at MIT at the time. (Mihai is now at AT&T Labs.)
CMSC 132, Object-Oriented Programming II Summer Lecture 12
 CMSC 132, Object-Oriented Programming II Summer 2016 Lecturer: Anwar Mamat Lecture 12 Disclaimer: These notes may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor. 12.1 Trees
CMSC 132, Object-Oriented Programming II Summer 2016 Lecturer: Anwar Mamat Lecture 12 Disclaimer: These notes may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor. 12.1 Trees
Logic and Automata I. Wolfgang Thomas. EATCS School, Telc, July 2014
 Logic and Automata I EATCS School, Telc, July 2014 The Plan We present automata theory as a tool to make logic effective. Four parts: 1. Some history 2. Automata on infinite words First step: MSO-logic
Logic and Automata I EATCS School, Telc, July 2014 The Plan We present automata theory as a tool to make logic effective. Four parts: 1. Some history 2. Automata on infinite words First step: MSO-logic
 The Algorithm (DSC): Mark all nodes as unscheduled WHILE there are unscheduled nodes DO In descending order of priority, sort list of free nodes In descending order of priority, sort list of partial free
The Algorithm (DSC): Mark all nodes as unscheduled WHILE there are unscheduled nodes DO In descending order of priority, sort list of free nodes In descending order of priority, sort list of partial free
Height, Size Performance of Complete and Nearly Complete Binary Search Trees in Dictionary Applications
 Height, Size Performance of Complete and Nearly Complete Binary Search Trees in Dictionary Applications AHMED TAREK Department of Math and Computer Science California University of Pennsylvania Eberly
Height, Size Performance of Complete and Nearly Complete Binary Search Trees in Dictionary Applications AHMED TAREK Department of Math and Computer Science California University of Pennsylvania Eberly
5 Spatial Access Methods
 5 Spatial Access Methods 5.1 Quadtree 5.2 R-tree 5.3 K-d tree 5.4 BSP tree 3 27 A 17 5 G E 4 7 13 28 B 26 11 J 29 18 K 5.5 Grid file 9 31 8 17 24 28 5.6 Summary D C 21 22 F 15 23 H Spatial Databases and
5 Spatial Access Methods 5.1 Quadtree 5.2 R-tree 5.3 K-d tree 5.4 BSP tree 3 27 A 17 5 G E 4 7 13 28 B 26 11 J 29 18 K 5.5 Grid file 9 31 8 17 24 28 5.6 Summary D C 21 22 F 15 23 H Spatial Databases and
α-acyclic Joins Jef Wijsen May 4, 2017
 α-acyclic Joins Jef Wijsen May 4, 2017 1 Motivation Joins in a Distributed Environment Assume the following relations. 1 M[NN, Field of Study, Year] stores data about students of UMONS. For example, (19950423158,
α-acyclic Joins Jef Wijsen May 4, 2017 1 Motivation Joins in a Distributed Environment Assume the following relations. 1 M[NN, Field of Study, Year] stores data about students of UMONS. For example, (19950423158,
D B M G Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino
 Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino Association rules Objective extraction of frequent correlations or pattern from a transactional database Tickets at a supermarket
Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino Association rules Objective extraction of frequent correlations or pattern from a transactional database Tickets at a supermarket
Wolf-Tilo Balke Silviu Homoceanu Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig
 Multimedia Databases Wolf-Tilo Balke Silviu Homoceanu Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig http://www.ifis.cs.tu-bs.de 13 Indexes for Multimedia Data 13 Indexes for Multimedia
Multimedia Databases Wolf-Tilo Balke Silviu Homoceanu Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig http://www.ifis.cs.tu-bs.de 13 Indexes for Multimedia Data 13 Indexes for Multimedia
COMP 250. Lecture 24. heaps 2. Nov. 3, 2017
 COMP 250 Lecture 24 heaps 2 Nov. 3, 207 RECALL: min Heap (definition) a e b f l u k m Complete binary tree with (unique) comparable elements, such that each node s element is less than its children s element(s).
COMP 250 Lecture 24 heaps 2 Nov. 3, 207 RECALL: min Heap (definition) a e b f l u k m Complete binary tree with (unique) comparable elements, such that each node s element is less than its children s element(s).
Inge Li Gørtz. Thank you to Kevin Wayne for inspiration to slides
 02110 Inge Li Gørtz Thank you to Kevin Wayne for inspiration to slides Welcome Inge Li Gørtz. Reverse teaching and discussion of exercises: 3 teaching assistants 8.00-9.15 Group work 9.15-9.45 Discussions
02110 Inge Li Gørtz Thank you to Kevin Wayne for inspiration to slides Welcome Inge Li Gørtz. Reverse teaching and discussion of exercises: 3 teaching assistants 8.00-9.15 Group work 9.15-9.45 Discussions
Models of Computation. by Costas Busch, LSU
 Models of Computation by Costas Busch, LSU 1 Computation CPU memory 2 temporary memory input memory CPU output memory Program memory 3 Example: f ( x) x 3 temporary memory input memory Program memory compute
Models of Computation by Costas Busch, LSU 1 Computation CPU memory 2 temporary memory input memory CPU output memory Program memory 3 Example: f ( x) x 3 temporary memory input memory Program memory compute
Lower Bounds for Dynamic Connectivity (2004; Pǎtraşcu, Demaine)
 Lower Bounds for Dynamic Connectivity (2004; Pǎtraşcu, Demaine) Mihai Pǎtraşcu, MIT, web.mit.edu/ mip/www/ Index terms: partial-sums problem, prefix sums, dynamic lower bounds Synonyms: dynamic trees 1
Lower Bounds for Dynamic Connectivity (2004; Pǎtraşcu, Demaine) Mihai Pǎtraşcu, MIT, web.mit.edu/ mip/www/ Index terms: partial-sums problem, prefix sums, dynamic lower bounds Synonyms: dynamic trees 1
Greedy. Outline CS141. Stefano Lonardi, UCR 1. Activity selection Fractional knapsack Huffman encoding Later:
 October 5, 017 Greedy Chapters 5 of Dasgupta et al. 1 Activity selection Fractional knapsack Huffman encoding Later: Outline Dijkstra (single source shortest path) Prim and Kruskal (minimum spanning tree)
October 5, 017 Greedy Chapters 5 of Dasgupta et al. 1 Activity selection Fractional knapsack Huffman encoding Later: Outline Dijkstra (single source shortest path) Prim and Kruskal (minimum spanning tree)
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman
 CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 22: Greedy Algorithms: Huffman Codes Data Compression and Entropy Apr 5, 2018 Data Compression How do we store strings of text compactly? A (binary) code
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 22: Greedy Algorithms: Huffman Codes Data Compression and Entropy Apr 5, 2018 Data Compression How do we store strings of text compactly? A (binary) code
Control Dependence. Stanford University CS243 Winter 2006 Wei Li 1
 Control Dependence Wei Li 1 Control Dependence Introduction Formal Definition Optimal Control Dependence Computation 2 xample START a b c d CFG ND b is control dependent on a c is control dependent on
Control Dependence Wei Li 1 Control Dependence Introduction Formal Definition Optimal Control Dependence Computation 2 xample START a b c d CFG ND b is control dependent on a c is control dependent on
D B M G. Association Rules. Fundamentals. Fundamentals. Elena Baralis, Silvia Chiusano. Politecnico di Torino 1. Definitions.
 Definitions Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino Itemset is a set including one or more items Example: {Beer, Diapers} k-itemset is an itemset that contains k
Definitions Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino Itemset is a set including one or more items Example: {Beer, Diapers} k-itemset is an itemset that contains k
D B M G. Association Rules. Fundamentals. Fundamentals. Association rules. Association rule mining. Definitions. Rule quality metrics: example
 Association rules Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino Objective extraction of frequent correlations or pattern from a transactional database Tickets at a supermarket
Association rules Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Politecnico di Torino Objective extraction of frequent correlations or pattern from a transactional database Tickets at a supermarket
Optimal Tree-decomposition Balancing and Reachability on Low Treewidth Graphs
 Optimal Tree-decomposition Balancing and Reachability on Low Treewidth Graphs Krishnendu Chatterjee Rasmus Ibsen-Jensen Andreas Pavlogiannis IST Austria Abstract. We consider graphs with n nodes together
Optimal Tree-decomposition Balancing and Reachability on Low Treewidth Graphs Krishnendu Chatterjee Rasmus Ibsen-Jensen Andreas Pavlogiannis IST Austria Abstract. We consider graphs with n nodes together
Heaps and Priority Queues
 Heaps and Priority Queues Motivation Situations where one has to choose the next most important from a collection. Examples: patients in an emergency room, scheduling programs in a multi-tasking OS. Need
Heaps and Priority Queues Motivation Situations where one has to choose the next most important from a collection. Examples: patients in an emergency room, scheduling programs in a multi-tasking OS. Need
Solution suggestions for examination of Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures,
 Department of VT12 Software Engineering and Managment DIT725 (TIG023) Göteborg University, Chalmers 24/5-12 Solution suggestions for examination of Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures, Date : April 26,
Department of VT12 Software Engineering and Managment DIT725 (TIG023) Göteborg University, Chalmers 24/5-12 Solution suggestions for examination of Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures, Date : April 26,
Dynamic Ordered Sets with Exponential Search Trees
 Dynamic Ordered Sets with Exponential Search Trees Arne Andersson Computing Science Department Information Technology, Uppsala University Box 311, SE - 751 05 Uppsala, Sweden arnea@csd.uu.se http://www.csd.uu.se/
Dynamic Ordered Sets with Exponential Search Trees Arne Andersson Computing Science Department Information Technology, Uppsala University Box 311, SE - 751 05 Uppsala, Sweden arnea@csd.uu.se http://www.csd.uu.se/
Multimedia Databases 1/29/ Indexes for Multimedia Data Indexes for Multimedia Data Indexes for Multimedia Data
 1/29/2010 13 Indexes for Multimedia Data 13 Indexes for Multimedia Data 13.1 R-Trees Multimedia Databases Wolf-Tilo Balke Silviu Homoceanu Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig
1/29/2010 13 Indexes for Multimedia Data 13 Indexes for Multimedia Data 13.1 R-Trees Multimedia Databases Wolf-Tilo Balke Silviu Homoceanu Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig
Each internal node v with d(v) children stores d 1 keys. k i 1 < key in i-th sub-tree k i, where we use k 0 = and k d =.
 7.5 (a, b)-trees 7.5 (a, b)-trees Definition For b a an (a, b)-tree is a search tree with the following properties. all leaves have the same distance to the root. every internal non-root vertex v has at
7.5 (a, b)-trees 7.5 (a, b)-trees Definition For b a an (a, b)-tree is a search tree with the following properties. all leaves have the same distance to the root. every internal non-root vertex v has at
Improved Submatrix Maximum Queries in Monge Matrices
 Improved Submatrix Maximum Queries in Monge Matrices Pawe l Gawrychowski 1, Shay Mozes 2, and Oren Weimann 3 1 MPII, gawry@mpi-inf.mpg.de 2 IDC Herzliya, smozes@idc.ac.il 3 University of Haifa, oren@cs.haifa.ac.il
Improved Submatrix Maximum Queries in Monge Matrices Pawe l Gawrychowski 1, Shay Mozes 2, and Oren Weimann 3 1 MPII, gawry@mpi-inf.mpg.de 2 IDC Herzliya, smozes@idc.ac.il 3 University of Haifa, oren@cs.haifa.ac.il
Quiz 1 Solutions. (a) f 1 (n) = 8 n, f 2 (n) = , f 3 (n) = ( 3) lg n. f 2 (n), f 1 (n), f 3 (n) Solution: (b)
 Introduction to Algorithms October 14, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Srini Devadas and Constantinos (Costis) Daskalakis Quiz 1 Solutions Quiz 1 Solutions Problem
Introduction to Algorithms October 14, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Srini Devadas and Constantinos (Costis) Daskalakis Quiz 1 Solutions Quiz 1 Solutions Problem
Solutions to EoPL3 Exercises
 Solutions to EoPL3 Exercises Release 0.1.0 Cheng Lian May 16, 2017 Contents 1 Contents 3 2 Overview 29 i ii Author Cheng Lian Contents 1 2 Contents CHAPTER 1 Contents Chapter 1.
Solutions to EoPL3 Exercises Release 0.1.0 Cheng Lian May 16, 2017 Contents 1 Contents 3 2 Overview 29 i ii Author Cheng Lian Contents 1 2 Contents CHAPTER 1 Contents Chapter 1.
CS213d Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS21d Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and their Applications Milind Sohoni IIT Bombay and IIT Dharwad March 22, 2017 1 / 18 What did I see today? March 22, 2017 2 / 18 Heap-Trees A tree T of height
CS21d Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and their Applications Milind Sohoni IIT Bombay and IIT Dharwad March 22, 2017 1 / 18 What did I see today? March 22, 2017 2 / 18 Heap-Trees A tree T of height
COL 730: Parallel Programming
 COL 730: Parallel Programming PARALLEL SORTING Bitonic Merge and Sort Bitonic sequence: {a 0, a 1,, a n-1 }: A sequence with a monotonically increasing part and a monotonically decreasing part For some
COL 730: Parallel Programming PARALLEL SORTING Bitonic Merge and Sort Bitonic sequence: {a 0, a 1,, a n-1 }: A sequence with a monotonically increasing part and a monotonically decreasing part For some
Lecture 1 : Data Compression and Entropy
 CPS290: Algorithmic Foundations of Data Science January 8, 207 Lecture : Data Compression and Entropy Lecturer: Kamesh Munagala Scribe: Kamesh Munagala In this lecture, we will study a simple model for
CPS290: Algorithmic Foundations of Data Science January 8, 207 Lecture : Data Compression and Entropy Lecturer: Kamesh Munagala Scribe: Kamesh Munagala In this lecture, we will study a simple model for
Computing Static Single Assignment (SSA) Form
 Computing Static Single Assignment (SSA) Form Overview What is SSA? Advantages of SSA over use-def chains Flavors of SSA Dominance frontiers revisited Inserting φ-nodes Renaming the variables Translating
Computing Static Single Assignment (SSA) Form Overview What is SSA? Advantages of SSA over use-def chains Flavors of SSA Dominance frontiers revisited Inserting φ-nodes Renaming the variables Translating
Premaster Course Algorithms 1 Chapter 3: Elementary Data Structures
 Premaster Course Algorithms 1 Chapter 3: Elementary Data Structures Christian Scheideler SS 2018 23.04.2018 Chapter 3 1 Overview Basic data structures Search structures (successor searching) Dictionaries
Premaster Course Algorithms 1 Chapter 3: Elementary Data Structures Christian Scheideler SS 2018 23.04.2018 Chapter 3 1 Overview Basic data structures Search structures (successor searching) Dictionaries
1.5 F15 O Brien. 1.5: Linear Equations and Inequalities
 1.5: Linear Equations and Inequalities I. Basic Terminology A. An equation is a statement that two expressions are equal. B. To solve an equation means to find all of the values of the variable that make
1.5: Linear Equations and Inequalities I. Basic Terminology A. An equation is a statement that two expressions are equal. B. To solve an equation means to find all of the values of the variable that make
Integer Sorting on the word-ram
 Integer Sorting on the word-rm Uri Zwick Tel viv University May 2015 Last updated: June 30, 2015 Integer sorting Memory is composed of w-bit words. rithmetical, logical and shift operations on w-bit words
Integer Sorting on the word-rm Uri Zwick Tel viv University May 2015 Last updated: June 30, 2015 Integer sorting Memory is composed of w-bit words. rithmetical, logical and shift operations on w-bit words
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fundamental Algithms Chapter 4: AVL Trees Jan Křetínský Winter 2016/17 Chapter 4: AVL Trees, Winter 2016/17 1 Part I AVL Trees (Adelson-Velsky and Landis, 1962) Chapter 4: AVL Trees, Winter 2016/17 2 Binary
Fundamental Algithms Chapter 4: AVL Trees Jan Křetínský Winter 2016/17 Chapter 4: AVL Trees, Winter 2016/17 1 Part I AVL Trees (Adelson-Velsky and Landis, 1962) Chapter 4: AVL Trees, Winter 2016/17 2 Binary
CS60007 Algorithm Design and Analysis 2018 Assignment 1
 CS60007 Algorithm Design and Analysis 2018 Assignment 1 Palash Dey and Swagato Sanyal Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Please submit the solutions of the problems 6, 11, 12 and 13 (written in
CS60007 Algorithm Design and Analysis 2018 Assignment 1 Palash Dey and Swagato Sanyal Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Please submit the solutions of the problems 6, 11, 12 and 13 (written in
