Heaps and Priority Queues
|
|
|
- Christiana Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heaps and Priority Queues Motivation Situations where one has to choose the next most important from a collection. Examples: patients in an emergency room, scheduling programs in a multi-tasking OS. Need to choose the task with the highest priority A priority queue orders elements by their importance. A queue is insufficient, need an efficient solution. A binary search tree is also insufficient, especially worst case. Data Structures 1 Heaps and Priority Queues
2 Complete Binary Trees(Review) Tree of d levels, in which all levels are filled, except possibly d 1. Bottom most level has nodes filled in from the left. A B C E F H I J K L Data Structures 2 Heaps and Priority Queues
3 Why a Complete Binary Tree for a Heap No Pointers! Can use an array representation for the tree. Number node positions in level order. Nodes are positioned in an array in level order. Node Determination: Parent(r) = (r 1)/2, if 0 < r < n Left child(r) = 2r + 1 if 2r + 1 < n Right child(r) = 2r + 2 if 2r + 2 < n Left sibling(r) = r 1 if r is even and 0 < r < n Right sibling(r) = r + 1 if r is odd and r + 1 < n Data Structures 3 Heaps and Priority Queues
4 Heap Data Type Complete binary tree with the Heap Property. Heap has partial ordering. Min-heap: All nodes have values less than child values. Max-heap: All nodes have values greater than child values. The root stores the smallest value in a min-heap, largest value in a max-heap No relationship between node and its sibling in heaps. Applications: Heapsort uses the max-heap, replacement selection algorithm using the min-heap. Data Structures 4 Heaps and Priority Queues
5 Heap Data Type MAX Heap MIN Heap Data Structures 5 Heaps and Priority Queues
6 Heap Operations Build the heap May insert one element at a time If all elements are available, can re-heap Insert Remove Data Structures 6 Heaps and Priority Queues
7 Heap Ops:Build Heap Use principle of induction: make subtrees to be heaps prior to tackling their root. Root may sift down. Work from the middle of the array (high end to low end) Exchanges: (5 2), (7 3), (7 1), (6 1) Data Structures 7 Heaps and Priority Queues
8 Heap Ops:Insert Insert element to last position of the array. Reheap using exchanges (move up towards root). 28 Insert Data Structures 8 Heaps and Priority Queues
9 Heap Ops:Remove (Max) Root element removed. Bring last element to the root. Reheap 28 Delete Data Structures 9 Heaps and Priority Queues
10 Heap Ops:Remove (at position p) Exchange element to be deleted with last element. Compare p to its parent and move up as needed, until the root is reached. Sift down from position p. Data Structures 10 Heaps and Priority Queues
11 Max Heap Implementation public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<? super E>> { private E [ ] Heap ; / / P o i n t e r to the heap array private i n t size ; / / Maximum size of the heap private i n t n ; / / Number of t h i n g s i n heap public MaxHeap(E [ ] h, i n t num, i n t max) { Heap = h ; n = num ; size = max ; buildheap ( ) ; / / Return c u r r e n t size of the heap public i n t heapsize ( ) { return n ; / / I s pos a l e a f p o s i t i o n? public boolean i s L e a f ( i n t pos ) { return ( pos >= n / 2 ) && ( pos < n ) ; Data Structures 11 Heaps and Priority Queues
12 Max Heap Implementation:Access Functions / / Return p o s i t i o n f o r l e f t c h i l d of pos public i n t l e f t c h i l d ( i n t pos ) { a s s e r t pos < n /2 : P o s i t i o n has no l e f t c h i l d ; return 2 pos + 1; / / Return p o s i t i o n f o r r i g h t c h i l d of pos public i n t r i g h t c h i l d ( i n t pos ) { a s s e r t pos < ( n 1)/2 : P o s i t i o n has no r i g h t c h i l d ; return 2 pos + 2; / / Return p o s i t i o n f o r parent public i n t parent ( i n t pos ) { a s s e r t pos > 0 : P o s i t i o n has no parent ; return ( pos 1)/2; / / Heapify contents of Heap / public void buildheap ( ) { for ( i n t i =n/2 1; i >=0; i ) s i f t d o w n ( i ) ; Data Structures 12 Heaps and Priority Queues
13 Max Heap Implementation:Insert / / I n s e r t i n t o heap public void i n s e r t (E v a l ) { a s s e r t n < size : Heap i s f u l l ; i n t c u r r = n++; Heap [ c u r r ] = v a l ; / / S t a r t at end of heap / / Now s i f t up u n t i l c u r r s parent s key > c u r r s key while ( ( c u r r!= 0) && ( Heap [ c u r r ]. compareto ( Heap [ parent ( c u r r ) ] ) > 0 ) ) { D S u t i l. swap ( Heap, curr, parent ( c u r r ) ) ; c u r r = parent ( c u r r ) ; Data Structures 13 Heaps and Priority Queues
14 Max Heap Implementation:siftdown / / Put element i n i t s c o r r e c t place / private void s i f t d o w n ( i n t pos ) { a s s e r t ( pos >= 0) && ( pos < n ) : I l l e g a l heap p o s i t i o n ; while (! i s L e a f ( pos ) ) { i n t j = l e f t c h i l d ( pos ) ; i f ( ( j <(n 1)) && ( Heap [ j ]. compareto ( Heap [ j + 1 ] ) < 0 ) ) j ++; / / j i s now index of c h i l d with g r e a t e r value i f ( Heap [ pos ]. compareto ( Heap [ j ] ) >= 0) return ; D S u t i l. swap ( Heap, pos, j ) ; pos = j ; / / Move down Data Structures 14 Heaps and Priority Queues
15 Max Heap Implementation:remove public E removemax ( ) { / / Remove maximum value a s s e r t n > 0 : Removing from empty heap ; D S u t i l. swap ( Heap, 0, n ) ; / / Swap maximum with l a s t va i f ( n!= 0) / / Not on l a s t element s i f t d o w n ( 0 ) ; / / Put new heap r o o t v a l i n c o r r e c t pl return Heap [ n ] ; / / Remove element at s p e c i f i e d p o s i t i o n public E remove ( i n t pos ) { a s s e r t ( pos >= 0) && ( pos < n ) : I l l e g a l heap p o s i t i o n D S u t i l. swap ( Heap, pos, n ) ; / / Swap with l a s t value / / I f we j u s t swapped i n a big value, push i t up while ( Heap [ pos ]. compareto ( Heap [ parent ( pos ) ] ) > 0) { D S u t i l. swap ( Heap, pos, parent ( pos ) ) ; pos = parent ( pos ) ; i f ( n!= 0) s i f t d o w n ( pos ) ; / / I f i t i s l i t t l e, push down return Heap [ n ] ; Data Structures 15 Heaps and Priority Queues
16 Cost of Heap Construction Level n 1 of the heap has half the number of nodes at level n. Nodes move down from each level of the tree; node at level i: (i 1) moves. log n (i 1) n 2 Θ(n) i i=1 Data Structures 16 Heaps and Priority Queues
Priority queues implemented via heaps
 Priority queues implemented via heaps Comp Sci 1575 Data s Outline 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 Priority queue: most important first Recall: queue is FIFO A normal queue data structure will not implement a priority
Priority queues implemented via heaps Comp Sci 1575 Data s Outline 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 Priority queue: most important first Recall: queue is FIFO A normal queue data structure will not implement a priority
Binary Search Trees. Motivation
 Binary Search Trees Motivation Searching for a particular record in an unordered list takes O(n), too slow for large lists (databases) If the list is ordered, can use an array implementation and use binary
Binary Search Trees Motivation Searching for a particular record in an unordered list takes O(n), too slow for large lists (databases) If the list is ordered, can use an array implementation and use binary
CS Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis
 CS 483 - Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lecture VII: Chapter 6, part 2 R. Paul Wiegand George Mason University, Department of Computer Science March 22, 2006 Outline 1 Balanced Trees 2 Heaps &
CS 483 - Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lecture VII: Chapter 6, part 2 R. Paul Wiegand George Mason University, Department of Computer Science March 22, 2006 Outline 1 Balanced Trees 2 Heaps &
ENS Lyon Camp. Day 2. Basic group. Cartesian Tree. 26 October
 ENS Lyon Camp. Day 2. Basic group. Cartesian Tree. 26 October Contents 1 Cartesian Tree. Definition. 1 2 Cartesian Tree. Construction 1 3 Cartesian Tree. Operations. 2 3.1 Split............................................
ENS Lyon Camp. Day 2. Basic group. Cartesian Tree. 26 October Contents 1 Cartesian Tree. Definition. 1 2 Cartesian Tree. Construction 1 3 Cartesian Tree. Operations. 2 3.1 Split............................................
Chapter 5 Data Structures Algorithm Theory WS 2017/18 Fabian Kuhn
 Chapter 5 Data Structures Algorithm Theory WS 2017/18 Fabian Kuhn Priority Queue / Heap Stores (key,data) pairs (like dictionary) But, different set of operations: Initialize-Heap: creates new empty heap
Chapter 5 Data Structures Algorithm Theory WS 2017/18 Fabian Kuhn Priority Queue / Heap Stores (key,data) pairs (like dictionary) But, different set of operations: Initialize-Heap: creates new empty heap
Insertion Sort. We take the first element: 34 is sorted
 Insertion Sort Idea: by Ex Given the following sequence to be sorted 34 8 64 51 32 21 When the elements 1, p are sorted, then the next element, p+1 is inserted within these to the right place after some
Insertion Sort Idea: by Ex Given the following sequence to be sorted 34 8 64 51 32 21 When the elements 1, p are sorted, then the next element, p+1 is inserted within these to the right place after some
COMP 250. Lecture 24. heaps 2. Nov. 3, 2017
 COMP 250 Lecture 24 heaps 2 Nov. 3, 207 RECALL: min Heap (definition) a e b f l u k m Complete binary tree with (unique) comparable elements, such that each node s element is less than its children s element(s).
COMP 250 Lecture 24 heaps 2 Nov. 3, 207 RECALL: min Heap (definition) a e b f l u k m Complete binary tree with (unique) comparable elements, such that each node s element is less than its children s element(s).
Objec&ves. Review. Data structure: Heaps Data structure: Graphs. What is a priority queue? What is a heap?
 Objec&ves Data structure: Heaps Data structure: Graphs Submit problem set 2 1 Review What is a priority queue? What is a heap? Ø Proper&es Ø Implementa&on What is the process for finding the smallest element
Objec&ves Data structure: Heaps Data structure: Graphs Submit problem set 2 1 Review What is a priority queue? What is a heap? Ø Proper&es Ø Implementa&on What is the process for finding the smallest element
8 Priority Queues. 8 Priority Queues. Prim s Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm. Dijkstra s Shortest Path Algorithm
 8 Priority Queues 8 Priority Queues A Priority Queue S is a dynamic set data structure that supports the following operations: S. build(x 1,..., x n ): Creates a data-structure that contains just the elements
8 Priority Queues 8 Priority Queues A Priority Queue S is a dynamic set data structure that supports the following operations: S. build(x 1,..., x n ): Creates a data-structure that contains just the elements
Review Of Topics. Review: Induction
 Review Of Topics Asymptotic notation Solving recurrences Sorting algorithms Insertion sort Merge sort Heap sort Quick sort Counting sort Radix sort Medians/order statistics Randomized algorithm Worst-case
Review Of Topics Asymptotic notation Solving recurrences Sorting algorithms Insertion sort Merge sort Heap sort Quick sort Counting sort Radix sort Medians/order statistics Randomized algorithm Worst-case
2-INF-237 Vybrané partie z dátových štruktúr 2-INF-237 Selected Topics in Data Structures
 2-INF-237 Vybrané partie z dátových štruktúr 2-INF-237 Selected Topics in Data Structures Instructor: Broňa Brejová E-mail: brejova@fmph.uniba.sk Office: M163 Course webpage: http://compbio.fmph.uniba.sk/vyuka/vpds/
2-INF-237 Vybrané partie z dátových štruktúr 2-INF-237 Selected Topics in Data Structures Instructor: Broňa Brejová E-mail: brejova@fmph.uniba.sk Office: M163 Course webpage: http://compbio.fmph.uniba.sk/vyuka/vpds/
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk I. Yu, D. Karabeg INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Function growth & estimation of running time, trees (Exercises with hints for solution)
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk I. Yu, D. Karabeg INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Function growth & estimation of running time, trees (Exercises with hints for solution)
Lecture 14: Nov. 11 & 13
 CIS 2168 Data Structures Fall 2014 Lecturer: Anwar Mamat Lecture 14: Nov. 11 & 13 Disclaimer: These notes may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor. 14.1 Sorting
CIS 2168 Data Structures Fall 2014 Lecturer: Anwar Mamat Lecture 14: Nov. 11 & 13 Disclaimer: These notes may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor. 14.1 Sorting
Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms Part Two
 Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms Part Two Recap from Last Time Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms A divide-and-conquer algorithm is one that works as follows: (Divide) Split the input apart into multiple smaller
Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms Part Two Recap from Last Time Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms A divide-and-conquer algorithm is one that works as follows: (Divide) Split the input apart into multiple smaller
Fibonacci Heaps These lecture slides are adapted from CLRS, Chapter 20.
 Fibonacci Heaps These lecture slides are adapted from CLRS, Chapter 20. Princeton University COS 4 Theory of Algorithms Spring 2002 Kevin Wayne Priority Queues Operation mae-heap insert find- delete- union
Fibonacci Heaps These lecture slides are adapted from CLRS, Chapter 20. Princeton University COS 4 Theory of Algorithms Spring 2002 Kevin Wayne Priority Queues Operation mae-heap insert find- delete- union
Tree Heap Priority Queue
 Tree Heap Priority Queue Rivers 171860553@smail.nju.edu.cn May 23, 2018 Rivers (171860553@smail.nju.end.cn) Rivers Second Open Topic May 23, 2018 1 / 33 Contents Section 1 Contents Rivers (171860553@smail.nju.end.cn)
Tree Heap Priority Queue Rivers 171860553@smail.nju.edu.cn May 23, 2018 Rivers (171860553@smail.nju.end.cn) Rivers Second Open Topic May 23, 2018 1 / 33 Contents Section 1 Contents Rivers (171860553@smail.nju.end.cn)
CSE548, AMS542: Analysis of Algorithms, Fall 2017 Date: Oct 26. Homework #2. ( Due: Nov 8 )
 CSE548, AMS542: Analysis of Algorithms, Fall 2017 Date: Oct 26 Homework #2 ( Due: Nov 8 ) Task 1. [ 80 Points ] Average Case Analysis of Median-of-3 Quicksort Consider the median-of-3 quicksort algorithm
CSE548, AMS542: Analysis of Algorithms, Fall 2017 Date: Oct 26 Homework #2 ( Due: Nov 8 ) Task 1. [ 80 Points ] Average Case Analysis of Median-of-3 Quicksort Consider the median-of-3 quicksort algorithm
CS213d Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS21d Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and their Applications Milind Sohoni IIT Bombay and IIT Dharwad March 22, 2017 1 / 18 What did I see today? March 22, 2017 2 / 18 Heap-Trees A tree T of height
CS21d Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and their Applications Milind Sohoni IIT Bombay and IIT Dharwad March 22, 2017 1 / 18 What did I see today? March 22, 2017 2 / 18 Heap-Trees A tree T of height
Fibonacci (Min-)Heap. (I draw dashed lines in place of of circular lists.) 1 / 17
 Fibonacci (Min-)Heap A forest of heap-order trees (parent priority child priority). Roots in circular doubly-linked list. Pointer to minimum-priority root. Siblings in circular doubly-linked list; parent
Fibonacci (Min-)Heap A forest of heap-order trees (parent priority child priority). Roots in circular doubly-linked list. Pointer to minimum-priority root. Siblings in circular doubly-linked list; parent
Binary Search Trees. Lecture 29 Section Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Fri, Apr 8, 2016
 Binary Search Trees Lecture 29 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 8, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Search Trees Fri, Apr 8, 2016 1 / 40 1 Binary Search
Binary Search Trees Lecture 29 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 8, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Search Trees Fri, Apr 8, 2016 1 / 40 1 Binary Search
Part IA Algorithms Notes
 Part IA Algorithms Notes 1 Sorting 1.1 Insertion Sort 1 d e f i n s e r t i o n S o r t ( a ) : 2 f o r i from 1 i n c l u d e d to l e n ( a ) excluded : 3 4 j = i 1 5 w h i l e j >= 0 and a [ i ] > a
Part IA Algorithms Notes 1 Sorting 1.1 Insertion Sort 1 d e f i n s e r t i o n S o r t ( a ) : 2 f o r i from 1 i n c l u d e d to l e n ( a ) excluded : 3 4 j = i 1 5 w h i l e j >= 0 and a [ i ] > a
Advanced Implementations of Tables: Balanced Search Trees and Hashing
 Advanced Implementations of Tables: Balanced Search Trees and Hashing Balanced Search Trees Binary search tree operations such as insert, delete, retrieve, etc. depend on the length of the path to the
Advanced Implementations of Tables: Balanced Search Trees and Hashing Balanced Search Trees Binary search tree operations such as insert, delete, retrieve, etc. depend on the length of the path to the
Mon Tue Wed Thurs Fri
 In lieu of recitations 320 Office Hours Mon Tue Wed Thurs Fri 8 Cole 9 Dr. Georg Dr. Georg 10 Dr. Georg/ Jim 11 Ali Jim 12 Cole Ali 1 Cole/ Shannon Ali 2 Shannon 3 Dr. Georg Dr. Georg Jim 4 Upcoming Check
In lieu of recitations 320 Office Hours Mon Tue Wed Thurs Fri 8 Cole 9 Dr. Georg Dr. Georg 10 Dr. Georg/ Jim 11 Ali Jim 12 Cole Ali 1 Cole/ Shannon Ali 2 Shannon 3 Dr. Georg Dr. Georg Jim 4 Upcoming Check
Solution suggestions for examination of Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures,
 Department of VT12 Software Engineering and Managment DIT725 (TIG023) Göteborg University, Chalmers 24/5-12 Solution suggestions for examination of Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures, Date : April 26,
Department of VT12 Software Engineering and Managment DIT725 (TIG023) Göteborg University, Chalmers 24/5-12 Solution suggestions for examination of Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures, Date : April 26,
Assignment 5: Solutions
 Comp 21: Algorithms and Data Structures Assignment : Solutions 1. Heaps. (a) First we remove the minimum key 1 (which we know is located at the root of the heap). We then replace it by the key in the position
Comp 21: Algorithms and Data Structures Assignment : Solutions 1. Heaps. (a) First we remove the minimum key 1 (which we know is located at the root of the heap). We then replace it by the key in the position
Quiz 1 Solutions. Problem 2. Asymptotics & Recurrences [20 points] (3 parts)
![Quiz 1 Solutions. Problem 2. Asymptotics & Recurrences [20 points] (3 parts) Quiz 1 Solutions. Problem 2. Asymptotics & Recurrences [20 points] (3 parts)](/thumbs/87/95581149.jpg) Introduction to Algorithms October 13, 2010 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Fall 2010 Professors Konstantinos Daskalakis and Patrick Jaillet Quiz 1 Solutions Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. We
Introduction to Algorithms October 13, 2010 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Fall 2010 Professors Konstantinos Daskalakis and Patrick Jaillet Quiz 1 Solutions Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. We
Algorithm runtime analysis and computational tractability
 Algorithm runtime analysis and computational tractability As soon as an Analytic Engine exists, it will necessarily guide the future course of the science. Whenever any result is sought by its aid, the
Algorithm runtime analysis and computational tractability As soon as an Analytic Engine exists, it will necessarily guide the future course of the science. Whenever any result is sought by its aid, the
University of New Mexico Department of Computer Science. Midterm Examination. CS 361 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring, 2003
 University of New Mexico Department of Computer Science Midterm Examination CS 361 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring, 2003 Name: Email: Print your name and email, neatly in the space provided above;
University of New Mexico Department of Computer Science Midterm Examination CS 361 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring, 2003 Name: Email: Print your name and email, neatly in the space provided above;
Algorithms Theory. 08 Fibonacci Heaps
 Algorithms Theory 08 Fibonacci Heaps Prof. Dr. S. Albers Priority queues: operations Priority queue Q Operations: Q.initialize(): initializes an empty queue Q Q.isEmpty(): returns true iff Q is empty Q.insert(e):
Algorithms Theory 08 Fibonacci Heaps Prof. Dr. S. Albers Priority queues: operations Priority queue Q Operations: Q.initialize(): initializes an empty queue Q Q.isEmpty(): returns true iff Q is empty Q.insert(e):
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Sorting Algorithms (contd.) Outline Sorting Algorithms (contd.) 1 Sorting Algorithms (contd.) Analysis of Quicksort Time to sort array of length
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Sorting Algorithms (contd.) Outline Sorting Algorithms (contd.) 1 Sorting Algorithms (contd.) Analysis of Quicksort Time to sort array of length
Amortized analysis. Amortized analysis
 In amortized analysis the goal is to bound the worst case time of a sequence of operations on a data-structure. If n operations take T (n) time (worst case), the amortized cost of an operation is T (n)/n.
In amortized analysis the goal is to bound the worst case time of a sequence of operations on a data-structure. If n operations take T (n) time (worst case), the amortized cost of an operation is T (n)/n.
Dijkstra s Single Source Shortest Path Algorithm. Andreas Klappenecker
 Dijkstra s Single Source Shortest Path Algorithm Andreas Klappenecker Single Source Shortest Path Given: a directed or undirected graph G = (V,E) a source node s in V a weight function w: E -> R. Goal:
Dijkstra s Single Source Shortest Path Algorithm Andreas Klappenecker Single Source Shortest Path Given: a directed or undirected graph G = (V,E) a source node s in V a weight function w: E -> R. Goal:
Slides for CIS 675. Huffman Encoding, 1. Huffman Encoding, 2. Huffman Encoding, 3. Encoding 1. DPV Chapter 5, Part 2. Encoding 2
 Huffman Encoding, 1 EECS Slides for CIS 675 DPV Chapter 5, Part 2 Jim Royer October 13, 2009 A toy example: Suppose our alphabet is { A, B, C, D }. Suppose T is a text of 130 million characters. What is
Huffman Encoding, 1 EECS Slides for CIS 675 DPV Chapter 5, Part 2 Jim Royer October 13, 2009 A toy example: Suppose our alphabet is { A, B, C, D }. Suppose T is a text of 130 million characters. What is
Dictionary: an abstract data type
 2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 5: Searching Michael Bader Winter 2014/15 Chapter 5: Searching, Winter 2014/15 1 Searching Definition (Search Problem) Input: a sequence or set A of n elements (objects)
Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 5: Searching Michael Bader Winter 2014/15 Chapter 5: Searching, Winter 2014/15 1 Searching Definition (Search Problem) Input: a sequence or set A of n elements (objects)
Algorithms. Algorithms 2.4 PRIORITY QUEUES. Pro tip: Sit somewhere where you can work in a group of 2 or 3
 Algorithms ROBRT SDGWICK KVIN WAYN 2.4 PRIORITY QUUS Algorithms F O U R T H D I T I O N Fundamentals and flipped lectures Priority queues and heaps Heapsort Deeper thinking ROBRT SDGWICK KVIN WAYN http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
Algorithms ROBRT SDGWICK KVIN WAYN 2.4 PRIORITY QUUS Algorithms F O U R T H D I T I O N Fundamentals and flipped lectures Priority queues and heaps Heapsort Deeper thinking ROBRT SDGWICK KVIN WAYN http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
Dictionary: an abstract data type
 2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
2-3 Trees 1 Dictionary: an abstract data type A container that maps keys to values Dictionary operations Insert Search Delete Several possible implementations Balanced search trees Hash tables 2 2-3 trees
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 6 Greedy Algorithms Interval Scheduling Interval Partitioning Scheduling to Minimize Lateness Sofya Raskhodnikova S. Raskhodnikova; based on slides by E. Demaine,
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 6 Greedy Algorithms Interval Scheduling Interval Partitioning Scheduling to Minimize Lateness Sofya Raskhodnikova S. Raskhodnikova; based on slides by E. Demaine,
Greedy Algorithms. CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 10
 Greedy Algorithms CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 10 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Greedy algorithms Reading: Kleinberg and Tardos, sections 4.1, 4.2, and 4.3 Homework 4
Greedy Algorithms CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 10 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Greedy algorithms Reading: Kleinberg and Tardos, sections 4.1, 4.2, and 4.3 Homework 4
CPSC 320 Sample Final Examination December 2013
 CPSC 320 Sample Final Examination December 2013 [10] 1. Answer each of the following questions with true or false. Give a short justification for each of your answers. [5] a. 6 n O(5 n ) lim n + This is
CPSC 320 Sample Final Examination December 2013 [10] 1. Answer each of the following questions with true or false. Give a short justification for each of your answers. [5] a. 6 n O(5 n ) lim n + This is
! Insert. ! Remove largest. ! Copy. ! Create. ! Destroy. ! Test if empty. ! Fraud detection: isolate $$ transactions.
 Priority Queues Priority Queues Data. Items that can be compared. Basic operations.! Insert.! Remove largest. defining ops! Copy.! Create.! Destroy.! Test if empty. generic ops Reference: Chapter 6, Algorithms
Priority Queues Priority Queues Data. Items that can be compared. Basic operations.! Insert.! Remove largest. defining ops! Copy.! Create.! Destroy.! Test if empty. generic ops Reference: Chapter 6, Algorithms
Randomized Sorting Algorithms Quick sort can be converted to a randomized algorithm by picking the pivot element randomly. In this case we can show th
 CSE 3500 Algorithms and Complexity Fall 2016 Lecture 10: September 29, 2016 Quick sort: Average Run Time In the last lecture we started analyzing the expected run time of quick sort. Let X = k 1, k 2,...,
CSE 3500 Algorithms and Complexity Fall 2016 Lecture 10: September 29, 2016 Quick sort: Average Run Time In the last lecture we started analyzing the expected run time of quick sort. Let X = k 1, k 2,...,
Analysis of Algorithms. Outline 1 Introduction Basic Definitions Ordered Trees. Fibonacci Heaps. Andres Mendez-Vazquez. October 29, Notes.
 Analysis of Algorithms Fibonacci Heaps Andres Mendez-Vazquez October 29, 2015 1 / 119 Outline 1 Introduction Basic Definitions Ordered Trees 2 Binomial Trees Example 3 Fibonacci Heap Operations Fibonacci
Analysis of Algorithms Fibonacci Heaps Andres Mendez-Vazquez October 29, 2015 1 / 119 Outline 1 Introduction Basic Definitions Ordered Trees 2 Binomial Trees Example 3 Fibonacci Heap Operations Fibonacci
CS 151. Red Black Trees & Structural Induction. Thursday, November 1, 12
 CS 151 Red Black Trees & Structural Induction 1 Announcements Majors fair tonight 4:30-6:30pm in the Root Room in Carnegie. Come and find out about the CS major, or some other major. Winter Term in CS
CS 151 Red Black Trees & Structural Induction 1 Announcements Majors fair tonight 4:30-6:30pm in the Root Room in Carnegie. Come and find out about the CS major, or some other major. Winter Term in CS
The Greedy Method. Design and analysis of algorithms Cs The Greedy Method
 Design and analysis of algorithms Cs 3400 The Greedy Method 1 Outline and Reading The Greedy Method Technique Fractional Knapsack Problem Task Scheduling 2 The Greedy Method Technique The greedy method
Design and analysis of algorithms Cs 3400 The Greedy Method 1 Outline and Reading The Greedy Method Technique Fractional Knapsack Problem Task Scheduling 2 The Greedy Method Technique The greedy method
25. Minimum Spanning Trees
 695 25. Minimum Spanning Trees Motivation, Greedy, Algorithm Kruskal, General Rules, ADT Union-Find, Algorithm Jarnik, Prim, Dijkstra, Fibonacci Heaps [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 9.6, 6.2, 6.1, Cormen et al,
695 25. Minimum Spanning Trees Motivation, Greedy, Algorithm Kruskal, General Rules, ADT Union-Find, Algorithm Jarnik, Prim, Dijkstra, Fibonacci Heaps [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 9.6, 6.2, 6.1, Cormen et al,
25. Minimum Spanning Trees
 Problem Given: Undirected, weighted, connected graph G = (V, E, c). 5. Minimum Spanning Trees Motivation, Greedy, Algorithm Kruskal, General Rules, ADT Union-Find, Algorithm Jarnik, Prim, Dijkstra, Fibonacci
Problem Given: Undirected, weighted, connected graph G = (V, E, c). 5. Minimum Spanning Trees Motivation, Greedy, Algorithm Kruskal, General Rules, ADT Union-Find, Algorithm Jarnik, Prim, Dijkstra, Fibonacci
Tutorial 4. Dynamic Set: Amortized Analysis
 Tutorial 4 Dynamic Set: Amortized Analysis Review Binary tree Complete binary tree Full binary tree 2-tree P115 Unlike common binary tree, the base case is not an empty tree, but a external node Heap Binary
Tutorial 4 Dynamic Set: Amortized Analysis Review Binary tree Complete binary tree Full binary tree 2-tree P115 Unlike common binary tree, the base case is not an empty tree, but a external node Heap Binary
Data Structures and Algorithms " Search Trees!!
 Data Structures and Algorithms " Search Trees!! Outline" Binary Search Trees! AVL Trees! (2,4) Trees! 2 Binary Search Trees! "! < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9 Ordered Dictionaries" Keys are assumed to come from a total
Data Structures and Algorithms " Search Trees!! Outline" Binary Search Trees! AVL Trees! (2,4) Trees! 2 Binary Search Trees! "! < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9 Ordered Dictionaries" Keys are assumed to come from a total
Each internal node v with d(v) children stores d 1 keys. k i 1 < key in i-th sub-tree k i, where we use k 0 = and k d =.
 7.5 (a, b)-trees 7.5 (a, b)-trees Definition For b a an (a, b)-tree is a search tree with the following properties. all leaves have the same distance to the root. every internal non-root vertex v has at
7.5 (a, b)-trees 7.5 (a, b)-trees Definition For b a an (a, b)-tree is a search tree with the following properties. all leaves have the same distance to the root. every internal non-root vertex v has at
Data Structures 1 NTIN066
 Data Structures 1 NTIN066 Jirka Fink Department of Theoretical Computer Science and Mathematical Logic Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Charles University in Prague Winter semester 2017/18 Last change
Data Structures 1 NTIN066 Jirka Fink Department of Theoretical Computer Science and Mathematical Logic Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Charles University in Prague Winter semester 2017/18 Last change
Weak Heaps and Friends: Recent Developments
 Weak Heaps and Friends: Recent Developments Stefan Edelkamp 1, Amr Elmasry 2, Jyrki Katajainen 3,4, 1) University of Bremen 2) Alexandria University 3) University of Copenhagen 4) Jyrki Katajainen and
Weak Heaps and Friends: Recent Developments Stefan Edelkamp 1, Amr Elmasry 2, Jyrki Katajainen 3,4, 1) University of Bremen 2) Alexandria University 3) University of Copenhagen 4) Jyrki Katajainen and
FIBONACCI HEAPS. preliminaries insert extract the minimum decrease key bounding the rank meld and delete. Copyright 2013 Kevin Wayne
 FIBONACCI HEAPS preliminaries insert extract the minimum decrease key bounding the rank meld and delete Copyright 2013 Kevin Wayne http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~wayne/kleinberg-tardos Last updated on Sep
FIBONACCI HEAPS preliminaries insert extract the minimum decrease key bounding the rank meld and delete Copyright 2013 Kevin Wayne http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~wayne/kleinberg-tardos Last updated on Sep
Amortized Analysis. DistributeMoney(n, k) 1 Each of n people gets $1. 2 for i = 1to k 3 do Give a dollar to a random person
 Amortized Analysis DistributeMoney(n, k) 1 Each of n people gets $1. 2 for i = 1to k 3 do Give a dollar to a random person What is the maximum amount of money I can receive? Amortized Analysis DistributeMoney(n,
Amortized Analysis DistributeMoney(n, k) 1 Each of n people gets $1. 2 for i = 1to k 3 do Give a dollar to a random person What is the maximum amount of money I can receive? Amortized Analysis DistributeMoney(n,
1. Introduction Bottom-Up-Heapsort is a variant of the classical Heapsort algorithm due to Williams ([Wi64]) and Floyd ([F64]) and was rst presented i
![1. Introduction Bottom-Up-Heapsort is a variant of the classical Heapsort algorithm due to Williams ([Wi64]) and Floyd ([F64]) and was rst presented i 1. Introduction Bottom-Up-Heapsort is a variant of the classical Heapsort algorithm due to Williams ([Wi64]) and Floyd ([F64]) and was rst presented i](/thumbs/93/112938972.jpg) A Tight Lower Bound for the Worst Case of Bottom-Up-Heapsort 1 by Rudolf Fleischer 2 Keywords : heapsort, bottom-up-heapsort, tight lower bound ABSTRACT Bottom-Up-Heapsort is a variant of Heapsort. Its
A Tight Lower Bound for the Worst Case of Bottom-Up-Heapsort 1 by Rudolf Fleischer 2 Keywords : heapsort, bottom-up-heapsort, tight lower bound ABSTRACT Bottom-Up-Heapsort is a variant of Heapsort. Its
Greedy Alg: Huffman abhi shelat
 L15 Greedy Alg: Huffman 4102 10.17.201 abhi shelat Huffman Coding image: wikimedia In testimony before the committee, Mr. Lew stressed that the Treasury Department would run out of extraordinary measures
L15 Greedy Alg: Huffman 4102 10.17.201 abhi shelat Huffman Coding image: wikimedia In testimony before the committee, Mr. Lew stressed that the Treasury Department would run out of extraordinary measures
CS 240 Data Structures and Data Management. Module 4: Dictionaries
 CS 24 Data Structures and Data Management Module 4: Dictionaries A. Biniaz A. Jamshidpey É. Schost Based on lecture notes by many previous cs24 instructors David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science,
CS 24 Data Structures and Data Management Module 4: Dictionaries A. Biniaz A. Jamshidpey É. Schost Based on lecture notes by many previous cs24 instructors David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science,
Premaster Course Algorithms 1 Chapter 3: Elementary Data Structures
 Premaster Course Algorithms 1 Chapter 3: Elementary Data Structures Christian Scheideler SS 2018 23.04.2018 Chapter 3 1 Overview Basic data structures Search structures (successor searching) Dictionaries
Premaster Course Algorithms 1 Chapter 3: Elementary Data Structures Christian Scheideler SS 2018 23.04.2018 Chapter 3 1 Overview Basic data structures Search structures (successor searching) Dictionaries
Data Structures 1 NTIN066
 Data Structures 1 NTIN066 Jiří Fink https://kam.mff.cuni.cz/ fink/ Department of Theoretical Computer Science and Mathematical Logic Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Charles University in Prague Winter
Data Structures 1 NTIN066 Jiří Fink https://kam.mff.cuni.cz/ fink/ Department of Theoretical Computer Science and Mathematical Logic Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Charles University in Prague Winter
16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]
![16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ] 16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]](/thumbs/72/67371940.jpg) 418 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] 419 Dictionary implementation Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
418 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] 419 Dictionary implementation Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
Chapter 5 Arrays and Strings 5.1 Arrays as abstract data types 5.2 Contiguous representations of arrays 5.3 Sparse arrays 5.4 Representations of
 Chapter 5 Arrays and Strings 5.1 Arrays as abstract data types 5.2 Contiguous representations of arrays 5.3 Sparse arrays 5.4 Representations of strings 5.5 String searching algorithms 0 5.1 Arrays as
Chapter 5 Arrays and Strings 5.1 Arrays as abstract data types 5.2 Contiguous representations of arrays 5.3 Sparse arrays 5.4 Representations of strings 5.5 String searching algorithms 0 5.1 Arrays as
16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]
![16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ] 16. Binary Search Trees. [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap ]](/thumbs/81/84624162.jpg) 423 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] Dictionary implementation 424 Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
423 16. Binary Search Trees [Ottman/Widmayer, Kap. 5.1, Cormen et al, Kap. 12.1-12.3] Dictionary implementation 424 Hashing: implementation of dictionaries with expected very fast access times. Disadvantages
CS361 Homework #3 Solutions
 CS6 Homework # Solutions. Suppose I have a hash table with 5 locations. I would like to know how many items I can store in it before it becomes fairly likely that I have a collision, i.e., that two items
CS6 Homework # Solutions. Suppose I have a hash table with 5 locations. I would like to know how many items I can store in it before it becomes fairly likely that I have a collision, i.e., that two items
Heaps Induction. Heaps. Heaps. Tirgul 6
 Tirgul 6 Induction A binary heap is a nearly complete binary tree stored in an array object In a max heap, the value of each node that of its children (In a min heap, the value of each node that of its
Tirgul 6 Induction A binary heap is a nearly complete binary tree stored in an array object In a max heap, the value of each node that of its children (In a min heap, the value of each node that of its
4.8 Huffman Codes. These lecture slides are supplied by Mathijs de Weerd
 4.8 Huffman Codes These lecture slides are supplied by Mathijs de Weerd Data Compression Q. Given a text that uses 32 symbols (26 different letters, space, and some punctuation characters), how can we
4.8 Huffman Codes These lecture slides are supplied by Mathijs de Weerd Data Compression Q. Given a text that uses 32 symbols (26 different letters, space, and some punctuation characters), how can we
1 ListElement l e = f i r s t ; / / s t a r t i n g p o i n t 2 while ( l e. next!= n u l l ) 3 { l e = l e. next ; / / next step 4 } Removal
 Präsenzstunden Today In the same room as in the first week Assignment 5 Felix Friedrich, Lars Widmer, Fabian Stutz TA lecture, Informatics II D-BAUG March 18, 2014 HIL E 15.2 15:00-18:00 Timon Gehr (arriving
Präsenzstunden Today In the same room as in the first week Assignment 5 Felix Friedrich, Lars Widmer, Fabian Stutz TA lecture, Informatics II D-BAUG March 18, 2014 HIL E 15.2 15:00-18:00 Timon Gehr (arriving
Shortest Path Algorithms
 Shortest Path Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Single Source Shortest Path 2 Single Source Shortest Path Given: a directed or undirected graph G = (V,E) a source node
Shortest Path Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Single Source Shortest Path 2 Single Source Shortest Path Given: a directed or undirected graph G = (V,E) a source node
Algorithms and Data Structures 2016 Week 5 solutions (Tues 9th - Fri 12th February)
 Algorithms and Data Structures 016 Week 5 solutions (Tues 9th - Fri 1th February) 1. Draw the decision tree (under the assumption of all-distinct inputs) Quicksort for n = 3. answer: (of course you should
Algorithms and Data Structures 016 Week 5 solutions (Tues 9th - Fri 1th February) 1. Draw the decision tree (under the assumption of all-distinct inputs) Quicksort for n = 3. answer: (of course you should
/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution to Assignment 4
 600.363/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution to Assignment 4 (30+20 points) I (10 points) This problem brings in an extra constraint on the optimal binary search tree - for every node v, the number of nodes
600.363/463 Algorithms - Fall 2013 Solution to Assignment 4 (30+20 points) I (10 points) This problem brings in an extra constraint on the optimal binary search tree - for every node v, the number of nodes
Outline. Computer Science 331. Cost of Binary Search Tree Operations. Bounds on Height: Worst- and Average-Case
 Outline Computer Science Average Case Analysis: Binary Search Trees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture #7 Motivation and Objective Definition 4 Mike Jacobson (University
Outline Computer Science Average Case Analysis: Binary Search Trees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture #7 Motivation and Objective Definition 4 Mike Jacobson (University
Lecture 1 : Data Compression and Entropy
 CPS290: Algorithmic Foundations of Data Science January 8, 207 Lecture : Data Compression and Entropy Lecturer: Kamesh Munagala Scribe: Kamesh Munagala In this lecture, we will study a simple model for
CPS290: Algorithmic Foundations of Data Science January 8, 207 Lecture : Data Compression and Entropy Lecturer: Kamesh Munagala Scribe: Kamesh Munagala In this lecture, we will study a simple model for
Search Trees. Chapter 10. CSE 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: :52 AM
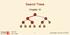 Search Trees Chapter 1 < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 3 - Binary Search Trees Ø A binary search
Search Trees Chapter 1 < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 3 - Binary Search Trees Ø A binary search
Problem 5. Use mathematical induction to show that when n is an exact power of two, the solution of the recurrence
 A. V. Gerbessiotis CS 610-102 Spring 2014 PS 1 Jan 27, 2014 No points For the remainder of the course Give an algorithm means: describe an algorithm, show that it works as claimed, analyze its worst-case
A. V. Gerbessiotis CS 610-102 Spring 2014 PS 1 Jan 27, 2014 No points For the remainder of the course Give an algorithm means: describe an algorithm, show that it works as claimed, analyze its worst-case
Data Structures and and Algorithm Xiaoqing Zheng
 Data Structures and Algorithm Xiaoqing Zheng zhengxq@fudan.edu.cn Trees (max heap) 1 16 2 3 14 10 4 5 6 7 8 7 9 3 8 9 10 2 4 1 PARENT(i) return i /2 LEFT(i) return 2i RIGHT(i) return 2i +1 16 14 10 8 7
Data Structures and Algorithm Xiaoqing Zheng zhengxq@fudan.edu.cn Trees (max heap) 1 16 2 3 14 10 4 5 6 7 8 7 9 3 8 9 10 2 4 1 PARENT(i) return i /2 LEFT(i) return 2i RIGHT(i) return 2i +1 16 14 10 8 7
CSE 4502/5717 Big Data Analytics Spring 2018; Homework 1 Solutions
 CSE 502/5717 Big Data Analytics Spring 2018; Homework 1 Solutions 1. Consider the following algorithm: for i := 1 to α n log e n do Pick a random j [1, n]; If a[j] = a[j + 1] or a[j] = a[j 1] then output:
CSE 502/5717 Big Data Analytics Spring 2018; Homework 1 Solutions 1. Consider the following algorithm: for i := 1 to α n log e n do Pick a random j [1, n]; If a[j] = a[j + 1] or a[j] = a[j 1] then output:
Functional Data Structures
 Functional Data Structures with Isabelle/HOL Tobias Nipkow Fakultät für Informatik Technische Universität München 2017-2-3 1 Part II Functional Data Structures 2 Chapter 1 Binary Trees 3 1 Binary Trees
Functional Data Structures with Isabelle/HOL Tobias Nipkow Fakultät für Informatik Technische Universität München 2017-2-3 1 Part II Functional Data Structures 2 Chapter 1 Binary Trees 3 1 Binary Trees
Search Trees. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: 24 March 2015
 Search Trees < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Learning Outcomes Ø From this lecture, you should be able to: q Define the properties of a binary search
Search Trees < 6 2 > 1 4 = 8 9-1 - Outline Ø Binary Search Trees Ø AVL Trees Ø Splay Trees - 2 - Learning Outcomes Ø From this lecture, you should be able to: q Define the properties of a binary search
Analysis of Algorithms - Midterm (Solutions)
 Analysis of Algorithms - Midterm (Solutions) K Subramani LCSEE, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV {ksmani@cseewvuedu} 1 Problems 1 Recurrences: Solve the following recurrences exactly or asymototically
Analysis of Algorithms - Midterm (Solutions) K Subramani LCSEE, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV {ksmani@cseewvuedu} 1 Problems 1 Recurrences: Solve the following recurrences exactly or asymototically
Lecture 6 September 21, 2016
 ICS 643: Advanced Parallel Algorithms Fall 2016 Lecture 6 September 21, 2016 Prof. Nodari Sitchinava Scribe: Tiffany Eulalio 1 Overview In the last lecture, we wrote a non-recursive summation program and
ICS 643: Advanced Parallel Algorithms Fall 2016 Lecture 6 September 21, 2016 Prof. Nodari Sitchinava Scribe: Tiffany Eulalio 1 Overview In the last lecture, we wrote a non-recursive summation program and
AVL trees. AVL trees
 Dnamic set DT dnamic set DT is a structure tat stores a set of elements. Eac element as a (unique) ke and satellite data. Te structure supports te following operations. Searc(S, k) Return te element wose
Dnamic set DT dnamic set DT is a structure tat stores a set of elements. Eac element as a (unique) ke and satellite data. Te structure supports te following operations. Searc(S, k) Return te element wose
Sorting. Chapter 11. CSE 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: :11 AM
 Sorting Chapter 11-1 - Sorting Ø We have seen the advantage of sorted data representations for a number of applications q Sparse vectors q Maps q Dictionaries Ø Here we consider the problem of how to efficiently
Sorting Chapter 11-1 - Sorting Ø We have seen the advantage of sorted data representations for a number of applications q Sparse vectors q Maps q Dictionaries Ø Here we consider the problem of how to efficiently
CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 3
 CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 3 Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Announcement Homework 1 out Due on Tue Jan 24 in class No late homeworks will be accepted Greedy Algorithms Direct argument
CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 3 Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Announcement Homework 1 out Due on Tue Jan 24 in class No late homeworks will be accepted Greedy Algorithms Direct argument
Chapter 4. Greedy Algorithms. Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Greedy Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 4.1 Interval Scheduling Interval Scheduling Interval scheduling. Job j starts at s j and
Chapter 4 Greedy Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 4.1 Interval Scheduling Interval Scheduling Interval scheduling. Job j starts at s j and
Week 5: Quicksort, Lower bound, Greedy
 Week 5: Quicksort, Lower bound, Greedy Agenda: Quicksort: Average case Lower bound for sorting Greedy method 1 Week 5: Quicksort Recall Quicksort: The ideas: Pick one key Compare to others: partition into
Week 5: Quicksort, Lower bound, Greedy Agenda: Quicksort: Average case Lower bound for sorting Greedy method 1 Week 5: Quicksort Recall Quicksort: The ideas: Pick one key Compare to others: partition into
Data selection. Lower complexity bound for sorting
 Data selection. Lower complexity bound for sorting Lecturer: Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 220 Algorithms and Data Structures 1 / 12 1 Data selection: Quickselect 2 Lower complexity bound for sorting 3 The
Data selection. Lower complexity bound for sorting Lecturer: Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 220 Algorithms and Data Structures 1 / 12 1 Data selection: Quickselect 2 Lower complexity bound for sorting 3 The
HW #4. (mostly by) Salim Sarımurat. 1) Insert 6 2) Insert 8 3) Insert 30. 4) Insert S a.
 HW #4 (mostly by) Salim Sarımurat 04.12.2009 S. 1. 1. a. 1) Insert 6 2) Insert 8 3) Insert 30 4) Insert 40 2 5) Insert 50 6) Insert 61 7) Insert 70 1. b. 1) Insert 12 2) Insert 29 3) Insert 30 4) Insert
HW #4 (mostly by) Salim Sarımurat 04.12.2009 S. 1. 1. a. 1) Insert 6 2) Insert 8 3) Insert 30 4) Insert 40 2 5) Insert 50 6) Insert 61 7) Insert 70 1. b. 1) Insert 12 2) Insert 29 3) Insert 30 4) Insert
Tutorial Session 5. Discussion of Exercise 4, Preview on Exercise 5, Preparation for Midterm 1. Running Time Analysis, Asymptotic Complexity
 Tutorial Session 5 Tuesday, 19 th of March 2019 Discussion of Exercise 4, Preview on Exercise 5, Preparation for Midterm 1 Running Time Analysis, Asymptotic Complexity 16.15 17.45 / 18.15 19.45 BIN 0.B.06
Tutorial Session 5 Tuesday, 19 th of March 2019 Discussion of Exercise 4, Preview on Exercise 5, Preparation for Midterm 1 Running Time Analysis, Asymptotic Complexity 16.15 17.45 / 18.15 19.45 BIN 0.B.06
1 Trees. Listing 1: Node with two child reference. public class ptwochildnode { protected Object data ; protected ptwochildnode l e f t, r i g h t ;
 1 Trees The next major set of data structures belongs to what s called Trees. They are called that, because if you try to visualize the structure, it kind of looks like a tree (root, branches, and leafs).
1 Trees The next major set of data structures belongs to what s called Trees. They are called that, because if you try to visualize the structure, it kind of looks like a tree (root, branches, and leafs).
Greedy. Outline CS141. Stefano Lonardi, UCR 1. Activity selection Fractional knapsack Huffman encoding Later:
 October 5, 017 Greedy Chapters 5 of Dasgupta et al. 1 Activity selection Fractional knapsack Huffman encoding Later: Outline Dijkstra (single source shortest path) Prim and Kruskal (minimum spanning tree)
October 5, 017 Greedy Chapters 5 of Dasgupta et al. 1 Activity selection Fractional knapsack Huffman encoding Later: Outline Dijkstra (single source shortest path) Prim and Kruskal (minimum spanning tree)
The null-pointers in a binary search tree are replaced by pointers to special null-vertices, that do not carry any object-data
 Definition 1 A red black tree is a balanced binary search tree in which each internal node has two children. Each internal node has a color, such that 1. The root is black. 2. All leaf nodes are black.
Definition 1 A red black tree is a balanced binary search tree in which each internal node has two children. Each internal node has a color, such that 1. The root is black. 2. All leaf nodes are black.
AVL Trees. Manolis Koubarakis. Data Structures and Programming Techniques
 AVL Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 AVL Trees We will now introduce AVL trees that have the property that they are kept almost balanced but not completely balanced. In this way we have O(log n) search time
AVL Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 AVL Trees We will now introduce AVL trees that have the property that they are kept almost balanced but not completely balanced. In this way we have O(log n) search time
Greedy Algorithms and Data Compression. Curs 2018
 Greedy Algorithms and Data Compression. Curs 2018 Greedy Algorithms A greedy algorithm, is a technique that always makes a locally optimal choice in the myopic hope that this choice will lead to a globally
Greedy Algorithms and Data Compression. Curs 2018 Greedy Algorithms A greedy algorithm, is a technique that always makes a locally optimal choice in the myopic hope that this choice will lead to a globally
Elementary Sorts 1 / 18
 Elementary Sorts 1 / 18 Outline 1 Rules of the Game 2 Selection Sort 3 Insertion Sort 4 Shell Sort 5 Visualizing Sorting Algorithms 6 Comparing Sorting Algorithms 2 / 18 Rules of the Game Sorting is the
Elementary Sorts 1 / 18 Outline 1 Rules of the Game 2 Selection Sort 3 Insertion Sort 4 Shell Sort 5 Visualizing Sorting Algorithms 6 Comparing Sorting Algorithms 2 / 18 Rules of the Game Sorting is the
CS60007 Algorithm Design and Analysis 2018 Assignment 1
 CS60007 Algorithm Design and Analysis 2018 Assignment 1 Palash Dey and Swagato Sanyal Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Please submit the solutions of the problems 6, 11, 12 and 13 (written in
CS60007 Algorithm Design and Analysis 2018 Assignment 1 Palash Dey and Swagato Sanyal Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Please submit the solutions of the problems 6, 11, 12 and 13 (written in
CMSC 132, Object-Oriented Programming II Summer Lecture 12
 CMSC 132, Object-Oriented Programming II Summer 2016 Lecturer: Anwar Mamat Lecture 12 Disclaimer: These notes may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor. 12.1 Trees
CMSC 132, Object-Oriented Programming II Summer 2016 Lecturer: Anwar Mamat Lecture 12 Disclaimer: These notes may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor. 12.1 Trees
CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis
 CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis Jeremiah Blocki Purdue University Spring 2018 Reminder: Homework 1 due tonight at 11:59PM! Recap: Greedy Algorithms Interval Scheduling Goal: Maximize number of meeting
CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis Jeremiah Blocki Purdue University Spring 2018 Reminder: Homework 1 due tonight at 11:59PM! Recap: Greedy Algorithms Interval Scheduling Goal: Maximize number of meeting
Outline Resource Introduction Usage Testing Exercises. Linked Lists COMP SCI / SFWR ENG 2S03. Department of Computing and Software McMaster University
 COMP SCI / SFWR ENG 2S03 Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Week 10: November 7 - November 11 Outline 1 Resource 2 Introduction Nodes Illustration 3 Usage Accessing and Modifying
COMP SCI / SFWR ENG 2S03 Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Week 10: November 7 - November 11 Outline 1 Resource 2 Introduction Nodes Illustration 3 Usage Accessing and Modifying
3 Greedy Algorithms. 3.1 An activity-selection problem
 3 Greedy Algorithms [BB chapter 6] with different examples or [Par chapter 2.3] with different examples or [CLR2 chapter 16] with different approach to greedy algorithms 3.1 An activity-selection problem
3 Greedy Algorithms [BB chapter 6] with different examples or [Par chapter 2.3] with different examples or [CLR2 chapter 16] with different approach to greedy algorithms 3.1 An activity-selection problem
Another way of saying this is that amortized analysis guarantees the average case performance of each operation in the worst case.
 Amortized Analysis: CLRS Chapter 17 Last revised: August 30, 2006 1 In amortized analysis we try to analyze the time required by a sequence of operations. There are many situations in which, even though
Amortized Analysis: CLRS Chapter 17 Last revised: August 30, 2006 1 In amortized analysis we try to analyze the time required by a sequence of operations. There are many situations in which, even though
Problem. Problem Given a dictionary and a word. Which page (if any) contains the given word? 3 / 26
 Binary Search Introduction Problem Problem Given a dictionary and a word. Which page (if any) contains the given word? 3 / 26 Strategy 1: Random Search Randomly select a page until the page containing
Binary Search Introduction Problem Problem Given a dictionary and a word. Which page (if any) contains the given word? 3 / 26 Strategy 1: Random Search Randomly select a page until the page containing
