9/6. Grades. Exam. Card Game. Homework/quizzes: 15% (two lowest scores dropped) Midterms: 25% each Final Exam: 35%
|
|
|
- Brendan Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
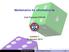
1 9/6 Wednesday, September 06, 2017 Grades Homework/quizzes: 15% (two lowest scores dropped) Midterms: 25% each Final Exam: 35% Exam Midterm exam 1 Wednesday, October 18 8:50AM - 9:40AM Midterm exam 2 Final exam No Calculator Card Game Wednesday, November 29 8:50AM - 9:40AM Friday, December 15 2:45PM - 4:45PM Simplified Version 1st 2nd 3rd Probability Never Change Cutoff 2 or /6 W W /6 W W /6 L W /6 W W /6 L L /6 L L Probability: 1/2 Probability: 2/3
2 9/8 Friday, September 08, 2017 Probability Space A probability model has three ingredients Sample space The sample space is the set of all possible outcomes Set of all events A subset of We let Probability measure is calle event be the set of all events A probability measure is a function from to that satisfies, for any event Note: and being pairwise disjoint is denonted Equally Likely Outcome Definition When all outcomes are equally likely Example: 431 card game (with full standard deck) Example: 431 card game (with 3 deck) Winning event for the never-change strategy
3 9/11 Monday, September 11, 2017 Probability Space sample space (list of all outcomes) : collection of events (subsets of ) probability measure Equally Likely Outcome Example: 431 game with full deck Example: 431 game with replacement Different Types of Random Experiments Sampling with replacement where order matters Sampling without replacement where order matters
4 Sampling without replacement where order is irrelevant
5 9/13 Wednesday, September 13, 2017 Probability Space Sample Space Collection of events Equally Likely Outcome For finite set with Sampling with replacement where order matters Sampling without replacement where order matters Sampling without replacement where order is irrelevant Note: is called choose Example 1.15
6 Number the shirts Striped: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Plaid: 6, 7, 8 Solid: 9, 10 Infinite Sample Spaces Example 1.16
7 Example 1.18
8 9/15 Friday, September 15, 2017 Rule 1 Theorem If are pairwise disjoint Example 1.20
9 Rule 2 Theorem Proof Example 1.21 are disjoint Rule 3 Theorem
10 Rule 3 Theorem Proof Example 1.25 General Inclusion-Exclusion Formula
11
12 9/18 Monday, September 18, 2017 Random Variable Definition A random variable is a function from to the real numbers The probability distribution of For all subsets Discrete Random Variable in the collection of probability A discrete random variable takes values in some countable set Probability Mass Function (PMF) Probability mass function is a function Example 1.30 Setup Random Variable Probability mass function of
13 Calculate Let Conditional Probability and Independence Definition be events and assume that Then the conditional probability of given is As a function of, Special case: equally like outcome satisfies the axioms of probability measure Example: 431 game with full deck (without replacement, order matters)
14 9/20 Wednesday, September 20, 2017 Conditional Probability Definition Special case: equally likely Example 2.5 Multiplication Rule Illumination Fact 2.6 If Example 2.7 are events and all the conditional probabilities below make sense, then
15 Partition Definition A partition of is a collection of events that are pairwise disjoint and such that their union is Theorem Let be a partition of Proof For pairwise disjoint evens By multiplication rule Example: 431 game with 4 distinct cards Setup
16 For Therefore when, choose a new card
17 9/22 Friday, September 22, 2017 Conditional Probability Definition More generally For partition of : Example: 431 game with 4 cards Setup For For For For The overall probability of winning
18 Bayes' Rule Definition Let be an event of positive probability Proof Bayes' Rule and Law of Total Probability Example 2.14
19 Independent of Events and are independent if
20 9/25 Monday, September 25, 2017 Independence Definition We says that events and are independent if In particular, if Similarly, if Example 2.19 Independence and Complement Fact 2.20
21 Suppose that and are independent. Then the same is true for each of these pairs Proof Independence of Random Variables Definition Let be random variables defined on the same probability space. Then are independent if For all choices of subsets Discrete Case Discrete random variables of the real line. are independent if and only if For all choices Proof of possible values of the random variables
22 Bernoulli Distribution Binomial Distribution
23 9/27 Wednesday, September 27, :00 AM Independence Independence of Events Events where RVs are independent if for every collection and Independence of Random Variables b Bernoulli Distribution Bernoulli Random Variables Example 4 independent random variables More Generally Binomial Distribution Success in Definition independent trials b Binomial distribution with success probability and trials is denoted as
24 Geometric Distribution Motivation Definition RV Definition number of trials needed to see first success has the geometric distribution with success parameter if the possible values of are {1, 2, 3,... } and fi for positive integers Abbreviate this by Conditional independent Example 2.39 Let be events with. We say and are conditionally independent given B if
25 9/29 Friday, September 29, 2017 Birthday Paradox Assume birthday are equally likely among 365 days, and also independent Suppose people in a room How large does need to be for probability that 2 people have the same birthday Let be the probiability of at least one repeatition among people Let b Discrete Random Variables Recall Definition A random variable is a function from sample space into the real numbers. A random variable fi b fi Probability Mass Function so that b Continuous Random Variables Definition A random variable is continuous if there exists a function Probability Density Function The function For any is called the probability density function of
26 Note could be greater than 1, but it cannot be less than b ε ε ε Example: Uniform Density over Example 3.6 Example
MATH 556: PROBABILITY PRIMER
 MATH 6: PROBABILITY PRIMER 1 DEFINITIONS, TERMINOLOGY, NOTATION 1.1 EVENTS AND THE SAMPLE SPACE Definition 1.1 An experiment is a one-off or repeatable process or procedure for which (a there is a well-defined
MATH 6: PROBABILITY PRIMER 1 DEFINITIONS, TERMINOLOGY, NOTATION 1.1 EVENTS AND THE SAMPLE SPACE Definition 1.1 An experiment is a one-off or repeatable process or procedure for which (a there is a well-defined
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS June 15, 2011 MIDTERM EXAM
 MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS June 15, 2011 MIDTERM EXAM YOUR NAME: KEY: Answers in Blue Show all your work. Answers out of the blue and without any supporting work may receive no credit even if they
MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS June 15, 2011 MIDTERM EXAM YOUR NAME: KEY: Answers in Blue Show all your work. Answers out of the blue and without any supporting work may receive no credit even if they
Why study probability? Set theory. ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables
 ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I
 STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Week 3 Luke Tierney University of Iowa Fall 2015 Luke Tierney (U Iowa) STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Fall 2015 1 Recap Matching problem Generalized
STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Week 3 Luke Tierney University of Iowa Fall 2015 Luke Tierney (U Iowa) STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Fall 2015 1 Recap Matching problem Generalized
Probability, Random Processes and Inference
 INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION EN COMPUTACION Laboratorio de Ciberseguridad Probability, Random Processes and Inference Dr. Ponciano Jorge Escamilla Ambrosio pescamilla@cic.ipn.mx
INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION EN COMPUTACION Laboratorio de Ciberseguridad Probability, Random Processes and Inference Dr. Ponciano Jorge Escamilla Ambrosio pescamilla@cic.ipn.mx
Lecture 8: Probability
 Lecture 8: Probability The idea of probability is well-known The flipping of a balanced coin can produce one of two outcomes: T (tail) and H (head) and the symmetry between the two outcomes means, of course,
Lecture 8: Probability The idea of probability is well-known The flipping of a balanced coin can produce one of two outcomes: T (tail) and H (head) and the symmetry between the two outcomes means, of course,
Chapter 2 Class Notes
 Chapter 2 Class Notes Probability can be thought of in many ways, for example as a relative frequency of a long series of trials (e.g. flips of a coin or die) Another approach is to let an expert (such
Chapter 2 Class Notes Probability can be thought of in many ways, for example as a relative frequency of a long series of trials (e.g. flips of a coin or die) Another approach is to let an expert (such
Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
 Probability Theory Foundations Thursday, September 03, 2015 1:57 PM Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
Probability Theory Foundations Thursday, September 03, 2015 1:57 PM Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
6 CARDINALITY OF SETS
 6 CARDINALITY OF SETS MATH10111 - Foundations of Pure Mathematics We all have an idea of what it means to count a finite collection of objects, but we must be careful to define rigorously what it means
6 CARDINALITY OF SETS MATH10111 - Foundations of Pure Mathematics We all have an idea of what it means to count a finite collection of objects, but we must be careful to define rigorously what it means
P (A B) P ((B C) A) P (B A) = P (B A) + P (C A) P (A) = P (B A) + P (C A) = Q(A) + Q(B).
 Lectures 7-8 jacques@ucsdedu 41 Conditional Probability Let (Ω, F, P ) be a probability space Suppose that we have prior information which leads us to conclude that an event A F occurs Based on this information,
Lectures 7-8 jacques@ucsdedu 41 Conditional Probability Let (Ω, F, P ) be a probability space Suppose that we have prior information which leads us to conclude that an event A F occurs Based on this information,
Randomized Algorithms
 Randomized Algorithms Prof. Tapio Elomaa tapio.elomaa@tut.fi Course Basics A new 4 credit unit course Part of Theoretical Computer Science courses at the Department of Mathematics There will be 4 hours
Randomized Algorithms Prof. Tapio Elomaa tapio.elomaa@tut.fi Course Basics A new 4 credit unit course Part of Theoretical Computer Science courses at the Department of Mathematics There will be 4 hours
Review: Probability. BM1: Advanced Natural Language Processing. University of Potsdam. Tatjana Scheffler
 Review: Probability BM1: Advanced Natural Language Processing University of Potsdam Tatjana Scheffler tatjana.scheffler@uni-potsdam.de October 21, 2016 Today probability random variables Bayes rule expectation
Review: Probability BM1: Advanced Natural Language Processing University of Potsdam Tatjana Scheffler tatjana.scheffler@uni-potsdam.de October 21, 2016 Today probability random variables Bayes rule expectation
Problem #1 #2 #3 #4 Extra Total Points /3 /13 /7 /10 /4 /33
 STAT/MATH 394 A - Autumn Quarter 206 - Midterm - October 2, 206 Name: Student ID Number: Problem # #2 #3 #4 Extra Total Points /3 /3 /7 /0 /4 /33 Read directions carefully and show all your work. Particularly,
STAT/MATH 394 A - Autumn Quarter 206 - Midterm - October 2, 206 Name: Student ID Number: Problem # #2 #3 #4 Extra Total Points /3 /3 /7 /0 /4 /33 Read directions carefully and show all your work. Particularly,
Recitation 6. Randomization. 6.1 Announcements. RandomLab has been released, and is due Monday, October 2. It s worth 100 points.
 Recitation 6 Randomization 6.1 Announcements RandomLab has been released, and is due Monday, October 2. It s worth 100 points. FingerLab will be released after Exam I, which is going to be on Wednesday,
Recitation 6 Randomization 6.1 Announcements RandomLab has been released, and is due Monday, October 2. It s worth 100 points. FingerLab will be released after Exam I, which is going to be on Wednesday,
4. Suppose that we roll two die and let X be equal to the maximum of the two rolls. Find P (X {1, 3, 5}) and draw the PMF for X.
 Math 10B with Professor Stankova Worksheet, Midterm #2; Wednesday, 3/21/2018 GSI name: Roy Zhao 1 Problems 1.1 Bayes Theorem 1. Suppose a test is 99% accurate and 1% of people have a disease. What is the
Math 10B with Professor Stankova Worksheet, Midterm #2; Wednesday, 3/21/2018 GSI name: Roy Zhao 1 Problems 1.1 Bayes Theorem 1. Suppose a test is 99% accurate and 1% of people have a disease. What is the
ECE 313: Hour Exam I
 University of Illinois Fall 07 ECE 3: Hour Exam I Wednesday, October, 07 8:45 p.m. 0:00 p.m.. [6 points] Suppose that a fair coin is independently tossed twice. Define the events: A = { The first toss
University of Illinois Fall 07 ECE 3: Hour Exam I Wednesday, October, 07 8:45 p.m. 0:00 p.m.. [6 points] Suppose that a fair coin is independently tossed twice. Define the events: A = { The first toss
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness
 Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Axiomatic Foundations of Probability. Definition: Probability Function
 Chapter 1 sections We will SKIP a number of sections Set theory SKIP Real number uncountability Definition of probability Finite sample spaces Counting methods Combinatorial methods SKIP tennis tournament
Chapter 1 sections We will SKIP a number of sections Set theory SKIP Real number uncountability Definition of probability Finite sample spaces Counting methods Combinatorial methods SKIP tennis tournament
Dynamic Programming Lecture #4
 Dynamic Programming Lecture #4 Outline: Probability Review Probability space Conditional probability Total probability Bayes rule Independent events Conditional independence Mutual independence Probability
Dynamic Programming Lecture #4 Outline: Probability Review Probability space Conditional probability Total probability Bayes rule Independent events Conditional independence Mutual independence Probability
Properties of Probability
 Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Probability Theory for Machine Learning. Chris Cremer September 2015
 Probability Theory for Machine Learning Chris Cremer September 2015 Outline Motivation Probability Definitions and Rules Probability Distributions MLE for Gaussian Parameter Estimation MLE and Least Squares
Probability Theory for Machine Learning Chris Cremer September 2015 Outline Motivation Probability Definitions and Rules Probability Distributions MLE for Gaussian Parameter Estimation MLE and Least Squares
STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes. Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed.
 STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed. Chapter 1: Combinatorial Analysis Demonstrate the ability to solve combinatorial
STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed. Chapter 1: Combinatorial Analysis Demonstrate the ability to solve combinatorial
Probabilistic models
 Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
Random Variables. Definition: A random variable (r.v.) X on the probability space (Ω, F, P) is a mapping
 Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Probability Experiments, Trials, Outcomes, Sample Spaces Example 1 Example 2
 Probability Probability is the study of uncertain events or outcomes. Games of chance that involve rolling dice or dealing cards are one obvious area of application. However, probability models underlie
Probability Probability is the study of uncertain events or outcomes. Games of chance that involve rolling dice or dealing cards are one obvious area of application. However, probability models underlie
2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY
 IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
Midterm 2 Review. CS70 Summer Lecture 6D. David Dinh 28 July UC Berkeley
 Midterm 2 Review CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6D David Dinh 28 July 2016 UC Berkeley Midterm 2: Format 8 questions, 190 points, 110 minutes (same as MT1). Two pages (one double-sided sheet) of handwritten
Midterm 2 Review CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6D David Dinh 28 July 2016 UC Berkeley Midterm 2: Format 8 questions, 190 points, 110 minutes (same as MT1). Two pages (one double-sided sheet) of handwritten
1. Discrete Distributions
 Virtual Laboratories > 2. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. Discrete Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an underlying sample space Ω.
Virtual Laboratories > 2. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. Discrete Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an underlying sample space Ω.
Lecture 16. Lectures 1-15 Review
 18.440: Lecture 16 Lectures 1-15 Review Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Counting tricks and basic principles of probability Discrete random variables 2 Outline Counting tricks and basic principles of probability
18.440: Lecture 16 Lectures 1-15 Review Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Counting tricks and basic principles of probability Discrete random variables 2 Outline Counting tricks and basic principles of probability
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Disjointness and Additivity
 Midterm 2: Format Midterm 2 Review CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6D David Dinh 28 July 2016 UC Berkeley 8 questions, 190 points, 110 minutes (same as MT1). Two pages (one double-sided sheet) of handwritten
Midterm 2: Format Midterm 2 Review CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6D David Dinh 28 July 2016 UC Berkeley 8 questions, 190 points, 110 minutes (same as MT1). Two pages (one double-sided sheet) of handwritten
Module 1. Probability
 Module 1 Probability 1. Introduction In our daily life we come across many processes whose nature cannot be predicted in advance. Such processes are referred to as random processes. The only way to derive
Module 1 Probability 1. Introduction In our daily life we come across many processes whose nature cannot be predicted in advance. Such processes are referred to as random processes. The only way to derive
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 5 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 7, 2012 Reminders Pick up a copy of B&T Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 5 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 7, 2012 Reminders Pick up a copy of B&T Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
Stat 451: Solutions to Assignment #1
 Stat 451: Solutions to Assignment #1 2.1) By definition, 2 Ω is the set of all subsets of Ω. Therefore, to show that 2 Ω is a σ-algebra we must show that the conditions of the definition σ-algebra are
Stat 451: Solutions to Assignment #1 2.1) By definition, 2 Ω is the set of all subsets of Ω. Therefore, to show that 2 Ω is a σ-algebra we must show that the conditions of the definition σ-algebra are
MATH 450: Mathematical statistics
 Departments of Mathematical Sciences University of Delaware August 28th, 2018 General information Classes: Tuesday & Thursday 9:30-10:45 am, Gore Hall 115 Office hours: Tuesday Wednesday 1-2:30 pm, Ewing
Departments of Mathematical Sciences University of Delaware August 28th, 2018 General information Classes: Tuesday & Thursday 9:30-10:45 am, Gore Hall 115 Office hours: Tuesday Wednesday 1-2:30 pm, Ewing
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]
![Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]](/thumbs/93/111285649.jpg) Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
= 2 5 Note how we need to be somewhat careful with how we define the total number of outcomes in b) and d). We will return to this later.
 PROBABILITY MATH CIRCLE (ADVANCED /27/203 The likelyhood of something (usually called an event happening is called the probability. Probability (informal: We can calculate probability using a ratio: want
PROBABILITY MATH CIRCLE (ADVANCED /27/203 The likelyhood of something (usually called an event happening is called the probability. Probability (informal: We can calculate probability using a ratio: want
UC Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. EE 126: Probablity and Random Processes. Solutions 5 Spring 2006
 Review problems UC Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EE 6: Probablity and Random Processes Solutions 5 Spring 006 Problem 5. On any given day your golf score is any integer
Review problems UC Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EE 6: Probablity and Random Processes Solutions 5 Spring 006 Problem 5. On any given day your golf score is any integer
Chapter 3 : Conditional Probability and Independence
 STAT/MATH 394 A - PROBABILITY I UW Autumn Quarter 2016 Néhémy Lim Chapter 3 : Conditional Probability and Independence 1 Conditional Probabilities How should we modify the probability of an event when
STAT/MATH 394 A - PROBABILITY I UW Autumn Quarter 2016 Néhémy Lim Chapter 3 : Conditional Probability and Independence 1 Conditional Probabilities How should we modify the probability of an event when
ORF 245 Fundamentals of Statistics Chapter 1 Probability
 ORF 245 Fundamentals of Statistics Chapter 1 Probability Robert Vanderbei Sept 2014 Slides last edited on September 19, 2014 http://www.princeton.edu/ rvdb Course Info Prereqs: Textbook: Three semesters
ORF 245 Fundamentals of Statistics Chapter 1 Probability Robert Vanderbei Sept 2014 Slides last edited on September 19, 2014 http://www.princeton.edu/ rvdb Course Info Prereqs: Textbook: Three semesters
Sample Spaces, Random Variables
 Sample Spaces, Random Variables Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan August 3, 22 Probabilities In talking about probabilities, the fundamental object is Ω, the sample space. (elements) in Ω are denoted
Sample Spaces, Random Variables Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan August 3, 22 Probabilities In talking about probabilities, the fundamental object is Ω, the sample space. (elements) in Ω are denoted
Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation. Lectures Definition 6.1. Two random variables defined on a probability space are said to be
 Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation Lectures 24-30 In this chapter, we introduce expected value or the mean of a random variable. First we define expectation for discrete random variables
Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation Lectures 24-30 In this chapter, we introduce expected value or the mean of a random variable. First we define expectation for discrete random variables
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability. Elements of Probability. Conditional probability. Sequential Calculation of Probability
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Lecture 6. Probability events. Definition 1. The sample space, S, of a. probability experiment is the collection of all
 Lecture 6 1 Lecture 6 Probability events Definition 1. The sample space, S, of a probability experiment is the collection of all possible outcomes of an experiment. One such outcome is called a simple
Lecture 6 1 Lecture 6 Probability events Definition 1. The sample space, S, of a probability experiment is the collection of all possible outcomes of an experiment. One such outcome is called a simple
Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
 Review of Probability Theory Tuesday, September 06, 2011 2:05 PM Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
Review of Probability Theory Tuesday, September 06, 2011 2:05 PM Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
Homework 1 Solutions ECEn 670, Fall 2013
 Homework Solutions ECEn 670, Fall 03 A.. Use the rst seven relations to prove relations (A.0, (A.3, and (A.6. Prove (F G c F c G c (A.0. (F G c ((F c G c c c by A.6. (F G c F c G c by A.4 Prove F (F G
Homework Solutions ECEn 670, Fall 03 A.. Use the rst seven relations to prove relations (A.0, (A.3, and (A.6. Prove (F G c F c G c (A.0. (F G c ((F c G c c c by A.6. (F G c F c G c by A.4 Prove F (F G
Mathematics for Informatics 4a
 Mathematics for Informatics 4a José Figueroa-O Farrill Lecture 1 18 January 2012 José Figueroa-O Farrill mi4a (Probability) Lecture 1 1 / 23 Introduction Topic: Probability and random processes Lectures:
Mathematics for Informatics 4a José Figueroa-O Farrill Lecture 1 18 January 2012 José Figueroa-O Farrill mi4a (Probability) Lecture 1 1 / 23 Introduction Topic: Probability and random processes Lectures:
ABOUT THE CLASS AND NOTES ON SET THEORY
 ABOUT THE CLASS AND NOTES ON SET THEORY About the Class Evaluation. Final grade will be based 25%, 25%, 25%, 25%, on homework, midterm 1, midterm 2, final exam. Exam dates. Midterm 1: Oct 4. Midterm 2:
ABOUT THE CLASS AND NOTES ON SET THEORY About the Class Evaluation. Final grade will be based 25%, 25%, 25%, 25%, on homework, midterm 1, midterm 2, final exam. Exam dates. Midterm 1: Oct 4. Midterm 2:
Probability 1 (MATH 11300) lecture slides
 Probability 1 (MATH 11300) lecture slides Márton Balázs School of Mathematics University of Bristol Autumn, 2015 December 16, 2015 To know... http://www.maths.bris.ac.uk/ mb13434/prob1/ m.balazs@bristol.ac.uk
Probability 1 (MATH 11300) lecture slides Márton Balázs School of Mathematics University of Bristol Autumn, 2015 December 16, 2015 To know... http://www.maths.bris.ac.uk/ mb13434/prob1/ m.balazs@bristol.ac.uk
Review of Basic Probability Theory
 Review of Basic Probability Theory James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 35 Review of Basic Probability Theory
Review of Basic Probability Theory James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 35 Review of Basic Probability Theory
CSE 21 Practice Exam for Midterm 2 Fall 2017
 CSE 1 Practice Exam for Midterm Fall 017 These practice problems should help prepare you for the second midterm, which is on monday, November 11 This is longer than the actual exam will be, but good practice
CSE 1 Practice Exam for Midterm Fall 017 These practice problems should help prepare you for the second midterm, which is on monday, November 11 This is longer than the actual exam will be, but good practice
Math , Fall 2012: HW 5 Solutions
 Math 230.0, Fall 202: HW 5 Solutions Due Thursday, October 4th, 202. Problem (p.58 #2). Let X and Y be the numbers obtained in two draws at random from a box containing four tickets labeled, 2, 3, 4. Display
Math 230.0, Fall 202: HW 5 Solutions Due Thursday, October 4th, 202. Problem (p.58 #2). Let X and Y be the numbers obtained in two draws at random from a box containing four tickets labeled, 2, 3, 4. Display
ECE 450 Lecture 2. Recall: Pr(A B) = Pr(A) + Pr(B) Pr(A B) in general = Pr(A) + Pr(B) if A and B are m.e. Lecture Overview
 ECE 450 Lecture 2 Recall: Pr(A B) = Pr(A) + Pr(B) Pr(A B) in general = Pr(A) + Pr(B) if A and B are m.e. Lecture Overview Conditional Probability, Pr(A B) Total Probability Bayes Theorem Independent Events
ECE 450 Lecture 2 Recall: Pr(A B) = Pr(A) + Pr(B) Pr(A B) in general = Pr(A) + Pr(B) if A and B are m.e. Lecture Overview Conditional Probability, Pr(A B) Total Probability Bayes Theorem Independent Events
Sample Space: Specify all possible outcomes from an experiment. Event: Specify a particular outcome or combination of outcomes.
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Probability 2.1 Probability Model Probability concerns about the chance of observing certain outcome resulting from an experiment. However, since chance is an abstraction of something
Chapter 2 Introduction to Probability 2.1 Probability Model Probability concerns about the chance of observing certain outcome resulting from an experiment. However, since chance is an abstraction of something
Discrete Random Variables
 Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan 2014 Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random
Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan 2014 Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random
ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model
 ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model Fall 2018 Prof Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 35 1. Probability Model 2 / 35 What is Probability? It is a number.
ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model Fall 2018 Prof Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 35 1. Probability Model 2 / 35 What is Probability? It is a number.
Week 6, 9/24/12-9/28/12, Notes: Bernoulli, Binomial, Hypergeometric, and Poisson Random Variables
 Week 6, 9/24/12-9/28/12, Notes: Bernoulli, Binomial, Hypergeometric, and Poisson Random Variables 1 Monday 9/24/12 on Bernoulli and Binomial R.V.s We are now discussing discrete random variables that have
Week 6, 9/24/12-9/28/12, Notes: Bernoulli, Binomial, Hypergeometric, and Poisson Random Variables 1 Monday 9/24/12 on Bernoulli and Binomial R.V.s We are now discussing discrete random variables that have
Notes slides from before lecture. CSE 21, Winter 2017, Section A00. Lecture 16 Notes. Class URL:
 Notes slides from before lecture CSE 21, Winter 2017, Section A00 Lecture 16 Notes Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17/ Notes slides from before lecture Notes March 8 (1) This week: Days
Notes slides from before lecture CSE 21, Winter 2017, Section A00 Lecture 16 Notes Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17/ Notes slides from before lecture Notes March 8 (1) This week: Days
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes. Markov Processes Markov Chains. Random Processes
 Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Tutorial 3: Random Processes
 August 18 Semester 2018-II Tutorial 3: Random Processes Lecturer: Utpal Mukherji/ Parimal Parag Prepared by: Prathamesh Mayekar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. 3.1 Conditional Probability
August 18 Semester 2018-II Tutorial 3: Random Processes Lecturer: Utpal Mukherji/ Parimal Parag Prepared by: Prathamesh Mayekar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. 3.1 Conditional Probability
Random variables. Lecture 5 - Discrete Distributions. Discrete Probability distributions. Example - Discrete probability model
 Random Variables Random variables Lecture 5 - Discrete Distributions Sta02 / BME02 Colin Rundel Setember 8, 204 A random variable is a numeric uantity whose value deends on the outcome of a random event
Random Variables Random variables Lecture 5 - Discrete Distributions Sta02 / BME02 Colin Rundel Setember 8, 204 A random variable is a numeric uantity whose value deends on the outcome of a random event
Class 26: review for final exam 18.05, Spring 2014
 Probability Class 26: review for final eam 8.05, Spring 204 Counting Sets Inclusion-eclusion principle Rule of product (multiplication rule) Permutation and combinations Basics Outcome, sample space, event
Probability Class 26: review for final eam 8.05, Spring 204 Counting Sets Inclusion-eclusion principle Rule of product (multiplication rule) Permutation and combinations Basics Outcome, sample space, event
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 2 Discrete Random Variables
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 2 Discrete Random Variables Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Random Variable Discrete Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 2 Discrete Random Variables Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Random Variable Discrete Random
EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction. About EE178. About Probability. Course Goals. Course Topics. Lecture Notes EE 178
 EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction About EE178 About Probability Course Goals Course Topics Lecture Notes EE 178: Course Introduction Page 0 1 EE 178 EE 178 provides an introduction to probabilistic
EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction About EE178 About Probability Course Goals Course Topics Lecture Notes EE 178: Course Introduction Page 0 1 EE 178 EE 178 provides an introduction to probabilistic
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio
 4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
Random variables. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
Conditional Probability
 Conditional Probability Idea have performed a chance experiment but don t know the outcome (ω), but have some partial information (event A) about ω. Question: given this partial information what s the
Conditional Probability Idea have performed a chance experiment but don t know the outcome (ω), but have some partial information (event A) about ω. Question: given this partial information what s the
Random Signals and Systems. Chapter 1. Jitendra K Tugnait. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering. James B Davis Professor.
 Random Signals and Systems Chapter 1 Jitendra K Tugnait James B Davis Professor Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University 2 3 Descriptions of Probability Relative frequency approach»
Random Signals and Systems Chapter 1 Jitendra K Tugnait James B Davis Professor Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University 2 3 Descriptions of Probability Relative frequency approach»
HW2 Solutions, for MATH441, STAT461, STAT561, due September 9th
 HW2 Solutions, for MATH44, STAT46, STAT56, due September 9th. You flip a coin until you get tails. Describe the sample space. How many points are in the sample space? The sample space consists of sequences
HW2 Solutions, for MATH44, STAT46, STAT56, due September 9th. You flip a coin until you get tails. Describe the sample space. How many points are in the sample space? The sample space consists of sequences
Lecture 4: Probability and Discrete Random Variables
 Error Correcting Codes: Combinatorics, Algorithms and Applications (Fall 2007) Lecture 4: Probability and Discrete Random Variables Wednesday, January 21, 2009 Lecturer: Atri Rudra Scribe: Anonymous 1
Error Correcting Codes: Combinatorics, Algorithms and Applications (Fall 2007) Lecture 4: Probability and Discrete Random Variables Wednesday, January 21, 2009 Lecturer: Atri Rudra Scribe: Anonymous 1
With Question/Answer Animations. Chapter 7
 With Question/Answer Animations Chapter 7 Chapter Summary Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability Theory Bayes Theorem Section 7.1 Section Summary Finite Probability Probabilities of Complements
With Question/Answer Animations Chapter 7 Chapter Summary Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability Theory Bayes Theorem Section 7.1 Section Summary Finite Probability Probabilities of Complements
Probability. 25 th September lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.)
 Probability 25 th September 2017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Properties of Probability Methods of Enumeration Conditional Probability Independent
Probability 25 th September 2017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Properties of Probability Methods of Enumeration Conditional Probability Independent
Probabilistic models
 Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 1.4 Give an example of a non-regular language Outline two strategies for proving
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 1.4 Give an example of a non-regular language Outline two strategies for proving
RVs and their probability distributions
 RVs and their probability distributions RVs and their probability distributions In these notes, I will use the following notation: The probability distribution (function) on a sample space will be denoted
RVs and their probability distributions RVs and their probability distributions In these notes, I will use the following notation: The probability distribution (function) on a sample space will be denoted
5. Conditional Distributions
 1 of 12 7/16/2009 5:36 AM Virtual Laboratories > 3. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5. Conditional Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an
1 of 12 7/16/2009 5:36 AM Virtual Laboratories > 3. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5. Conditional Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an
Chapter 2. Conditional Probability and Independence. 2.1 Conditional Probability
 Chapter 2 Conditional Probability and Independence 2.1 Conditional Probability Probability assigns a likelihood to results of experiments that have not yet been conducted. Suppose that the experiment has
Chapter 2 Conditional Probability and Independence 2.1 Conditional Probability Probability assigns a likelihood to results of experiments that have not yet been conducted. Suppose that the experiment has
p. 4-1 Random Variables
 Random Variables A Motivating Example Experiment: Sample k students without replacement from the population of all n students (labeled as 1, 2,, n, respectively) in our class. = {all combinations} = {{i
Random Variables A Motivating Example Experiment: Sample k students without replacement from the population of all n students (labeled as 1, 2,, n, respectively) in our class. = {all combinations} = {{i
Conditional Probability
 Conditional Probability Conditional Probability The Law of Total Probability Let A 1, A 2,..., A k be mutually exclusive and exhaustive events. Then for any other event B, P(B) = P(B A 1 ) P(A 1 ) + P(B
Conditional Probability Conditional Probability The Law of Total Probability Let A 1, A 2,..., A k be mutually exclusive and exhaustive events. Then for any other event B, P(B) = P(B A 1 ) P(A 1 ) + P(B
Rules of Probability
 Rules of Probability The additive rule P[A B] = P[A] + P[B] P[A B] and P[A B] = P[A] + P[B] if P[A B] = f The additive rule for more than two events n n P A i P Ai P Ai A j i1 i1 i j P A A A i j k i j
Rules of Probability The additive rule P[A B] = P[A] + P[B] P[A B] and P[A B] = P[A] + P[B] if P[A B] = f The additive rule for more than two events n n P A i P Ai P Ai A j i1 i1 i j P A A A i j k i j
18440: Probability and Random variables Quiz 1 Friday, October 17th, 2014
 18440: Probability and Random variables Quiz 1 Friday, October 17th, 014 You will have 55 minutes to complete this test. Each of the problems is worth 5 % of your exam grade. No calculators, notes, or
18440: Probability and Random variables Quiz 1 Friday, October 17th, 014 You will have 55 minutes to complete this test. Each of the problems is worth 5 % of your exam grade. No calculators, notes, or
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/86/94002861.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 8 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 8 Notes Goals for Today Counting Partitions
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 8 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 8 Notes Goals for Today Counting Partitions
A random variable is a quantity whose value is determined by the outcome of an experiment.
 Random Variables A random variable is a quantity whose value is determined by the outcome of an experiment. Before the experiment is carried out, all we know is the range of possible values. Birthday example
Random Variables A random variable is a quantity whose value is determined by the outcome of an experiment. Before the experiment is carried out, all we know is the range of possible values. Birthday example
Introduction to Probability Theory, Algebra, and Set Theory
 Summer School on Mathematical Philosophy for Female Students Introduction to Probability Theory, Algebra, and Set Theory Catrin Campbell-Moore and Sebastian Lutz July 28, 2014 Question 1. Draw Venn diagrams
Summer School on Mathematical Philosophy for Female Students Introduction to Probability Theory, Algebra, and Set Theory Catrin Campbell-Moore and Sebastian Lutz July 28, 2014 Question 1. Draw Venn diagrams
Introduction to Probability 2017/18 Supplementary Problems
 Introduction to Probability 2017/18 Supplementary Problems Problem 1: Let A and B denote two events with P(A B) 0. Show that P(A) 0 and P(B) 0. A A B implies P(A) P(A B) 0, hence P(A) 0. Similarly B A
Introduction to Probability 2017/18 Supplementary Problems Problem 1: Let A and B denote two events with P(A B) 0. Show that P(A) 0 and P(B) 0. A A B implies P(A) P(A B) 0, hence P(A) 0. Similarly B A
Math 200D - Linear Algebra Fall Term 2017 Course Description
 Math 200D - Linear Algebra Fall Term 2017 Course Description September 6, 2017 Instructor: John Schmitt Office: Warner 311, Tel: Ext. 5952 E-mail: jschmitt@middlebury.edu Office Hours: Monday 1:30pm-2:30pm,
Math 200D - Linear Algebra Fall Term 2017 Course Description September 6, 2017 Instructor: John Schmitt Office: Warner 311, Tel: Ext. 5952 E-mail: jschmitt@middlebury.edu Office Hours: Monday 1:30pm-2:30pm,
Discrete Random Variables
 Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random processes,
Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random processes,
General Info. Grading
 Syllabus & Policies General Info Lecture 1: Introduction, Set Theory, and Boolean Algebra Classroom: Perkins 2-072 Time: Mon - Fri, 2:00-3:15 pm Wed, 3:30-4:30 pm Sta 111 Colin Rundel May 13, 2014 Professor:
Syllabus & Policies General Info Lecture 1: Introduction, Set Theory, and Boolean Algebra Classroom: Perkins 2-072 Time: Mon - Fri, 2:00-3:15 pm Wed, 3:30-4:30 pm Sta 111 Colin Rundel May 13, 2014 Professor:
Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
 Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS. Dr N A Heard. 1 Sample Spaces and Events Sample Spaces Events Combinations of Events...
 Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
MATH MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting
 MATH 2030 3.00MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting Tom Salisbury salt@yorku.ca York University Winter 2010 Introduction [Jan 5] Probability: the mathematics used for Statistics
MATH 2030 3.00MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting Tom Salisbury salt@yorku.ca York University Winter 2010 Introduction [Jan 5] Probability: the mathematics used for Statistics
Probability Theory and Simulation Methods
 Feb 28th, 2018 Lecture 10: Random variables Countdown to midterm (March 21st): 28 days Week 1 Chapter 1: Axioms of probability Week 2 Chapter 3: Conditional probability and independence Week 4 Chapters
Feb 28th, 2018 Lecture 10: Random variables Countdown to midterm (March 21st): 28 days Week 1 Chapter 1: Axioms of probability Week 2 Chapter 3: Conditional probability and independence Week 4 Chapters
Origins of Probability Theory
 1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
Theorem 1.7 [Bayes' Law]: Assume that,,, are mutually disjoint events in the sample space s.t.. Then Pr( )
![Theorem 1.7 [Bayes' Law]: Assume that,,, are mutually disjoint events in the sample space s.t.. Then Pr( ) Theorem 1.7 [Bayes' Law]: Assume that,,, are mutually disjoint events in the sample space s.t.. Then Pr( )](/thumbs/95/125074181.jpg) Theorem 1.7 [Bayes' Law]: Assume that,,, are mutually disjoint events in the sample space s.t.. Then Pr Pr = Pr Pr Pr() Pr Pr. We are given three coins and are told that two of the coins are fair and the
Theorem 1.7 [Bayes' Law]: Assume that,,, are mutually disjoint events in the sample space s.t.. Then Pr Pr = Pr Pr Pr() Pr Pr. We are given three coins and are told that two of the coins are fair and the
Conditional Probability and Independence
 Conditional Probability and Independence September 3, 2009 1 Restricting the Sample Space - Conditional Probability How do we modify the probability of an event in light of the fact that something is known?
Conditional Probability and Independence September 3, 2009 1 Restricting the Sample Space - Conditional Probability How do we modify the probability of an event in light of the fact that something is known?
2.1 Elementary probability; random sampling
 Chapter 2 Probability Theory Chapter 2 outlines the probability theory necessary to understand this text. It is meant as a refresher for students who need review and as a reference for concepts and theorems
Chapter 2 Probability Theory Chapter 2 outlines the probability theory necessary to understand this text. It is meant as a refresher for students who need review and as a reference for concepts and theorems
