QOD: Suggest why placing wheels under a heavy box reduces the necessary force required to push it along at a constant speed.
|
|
|
- Isabel Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QOD: 2 22 Suggest why placing wheels under a heavy box reduces the necessary force required to push it along at a constant speed. Feb 21 3:05 PM 1
2 force: any action that can affect the motion of an object. Make a chart comparing the four fundamental forces. Include in your chart the relative strength of each and the effects of each. The four fundamental forces are gravity, the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. Feb 21 2:52 PM 2
3 The strong and weak nuclear forces act over only short distances. These are the forces that hold atoms together. The strong and weak nuclear forces are important, but you do not experience them directly in your everyday life. The force of gravity and electromagnetic forces are forces you feel every day. Gravity acts over long distances and pulls objects toward each other. Electromagnetic forces produce friction, magnetism, and static electricity. Feb 21 2:56 PM 3
4 The strong nuclear force is the strongest of all the forces. The strong nuclear force holds together the protons and neutrons in the nuclei of atoms. However, it only acts over short distances. The maximum range of the strong nuclear force is about the size of an atomic nucleus. Feb 21 2:57 PM 4
5 The weak nuclear force is about ten trillion times weaker than the strong nuclear force. The weak nuclear force affects some kinds of radioactive decay. Feb 21 2:58 PM 5
6 Electromagnetic forces can act over longer distances and are about 1% of the strength of the strong nuclear force. Electromagnetic forces hold electrons near the nucleus of an atom and hold molecules together. Feb 21 2:58 PM 6
7 Gravity is the weakest of the fundamental forces. It is about 1040 times weaker than the strong nuclear force. It also works over longer distances than any of the other fundamental forces. Gravity is an important force in shaping the structure of our galaxy and the universe. Feb 21 2:59 PM 7
8 Forces can act through contact or at a distance. If you push a cart, the cart moves. When you catch a ball, it stops moving. These pushes and pulls are examples of contact forces. There is another class of forces called field forces that do not require that the objects touch each other. The attraction of gravity or the repulsion between two north poles of a magnet are examples of field forces. Both contact and field forces can cause an object to move or to stop moving. Feb 22 7:18 AM 8
9 How Can Forces Affect Motion? Forces act to change the motion of an object. In most situations, several forces act on an object at once. The net force is the combination of all the forces acting on an object. An object will accelerate in the direction of the net force. An object will not accelerate if the net force is zero. Feb 21 3:00 PM 9
10 Balanced forces produce a net force of zero. Therefore, an object experiencing balanced forces will not change its motion. Feb 21 3:02 PM 10
11 Unbalanced Force: When the net force acting on an object is greater than zero, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force. Feb 21 3:03 PM 11
12 1. Make a holder for 50 marbles with a plastic cup and string. Tie the string around the wood block. 2.Put a 20g weight on the block and place the wood on top of a sheet the different sheets lying on a table. Hook the string to the cup and hang it over the edge 3. Add marbles to the cup until the block of wood begins to move. 4. Repeat the process using different surfaces, such as sandpaper, notebook paper, and the bare table. Feb 22 7:07 AM 12
13 Cork Rubber Sand Paper Table Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 Post Lab 1.Is the number of marbles needed to start moving the block the same for each type of surface? 2.Relate the number of marbles used in each trial to the roughness of the surface. Feb 22 7:09 AM 13
14 Feb 21 3:04 PM 14
Name Class Date. What are the four fundamental forces in nature? How can forces affect the motion of an object? Why is friction sometime necessary?
 CHAPTER 11 SECTION Motion 3 Motion and Force KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the four fundamental forces in nature? How can forces affect the motion of an object?
CHAPTER 11 SECTION Motion 3 Motion and Force KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the four fundamental forces in nature? How can forces affect the motion of an object?
Preview of Period 5: Forces and Newton s Laws
 Preview of Period 5: Forces and Newton s Laws 5.1 The Fundamental Forces of Nature What are the four fundamental forces of nature? How do we see their effects? 5.2 Forces and Newton s Laws What causes
Preview of Period 5: Forces and Newton s Laws 5.1 The Fundamental Forces of Nature What are the four fundamental forces of nature? How do we see their effects? 5.2 Forces and Newton s Laws What causes
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 7
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 7 Chapter 2 28Tension 2.8 2.9 Fundamental Forces Chapter 3 3.1 Position and Displacement Lecture 7 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ 1 Which statement about frictional forces is
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 7 Chapter 2 28Tension 2.8 2.9 Fundamental Forces Chapter 3 3.1 Position and Displacement Lecture 7 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ 1 Which statement about frictional forces is
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS FORCES L (P.121) Forces are all around us, acting on every object we see. Engineers must consider forces carefully when designing bridges and buildings. Forces are involved in
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS FORCES L (P.121) Forces are all around us, acting on every object we see. Engineers must consider forces carefully when designing bridges and buildings. Forces are involved in
Topic #7: Forces and Free Body Diagrams (Teacher) Defined as: any influence which tends to change the motion of an object.
 1.7.1 The Concept of Force Defined as: any influence which tends to change the motion of an object. 1.7.1a The Fundamental Forces The four fundamental forces, arranged in increasing order of strength,
1.7.1 The Concept of Force Defined as: any influence which tends to change the motion of an object. 1.7.1a The Fundamental Forces The four fundamental forces, arranged in increasing order of strength,
4.4. Friction and Inclines
 4.4. Friction and Inclines Frictional Forces Friction has its basis in surfaces that are not completely smooth. This roughness causes resistance to horizontal motion. Even smooth surfaces have a certain
4.4. Friction and Inclines Frictional Forces Friction has its basis in surfaces that are not completely smooth. This roughness causes resistance to horizontal motion. Even smooth surfaces have a certain
Chapter 3: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 3: Newton s Laws of Motion Mini Investigation: Predicting Forces, page 113 Answers may vary. Sample answers: A. I predicted the reading in question 3 would be the sum of the readings from questions
Chapter 3: Newton s Laws of Motion Mini Investigation: Predicting Forces, page 113 Answers may vary. Sample answers: A. I predicted the reading in question 3 would be the sum of the readings from questions
Wiley Plus Reminder! Assignment 1
 Wiley Plus Reminder! Assignment 1 6 problems from chapters and 3 Kinematics Due Monday October 5 Before 11 pm! Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws Force, mass and Newton s three laws of motion Newton s
Wiley Plus Reminder! Assignment 1 6 problems from chapters and 3 Kinematics Due Monday October 5 Before 11 pm! Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws Force, mass and Newton s three laws of motion Newton s
Ch Forces & Motion. Forces can: 1. Cause a resting object to move 2. Accelerate a moving object (by changing speed or direction)
 Ch. 12 - Forces & Motion Force --> a push or a pull that acts on an object Forces can: 1. Cause a resting object to move 2. Accelerate a moving object (by changing speed or direction) Force is measured
Ch. 12 - Forces & Motion Force --> a push or a pull that acts on an object Forces can: 1. Cause a resting object to move 2. Accelerate a moving object (by changing speed or direction) Force is measured
FORCES. Force. Combining Forces
 FORCES Force A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. The unit of force is the newton (N) 1 newton is the force required to accelerate a mass
FORCES Force A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. The unit of force is the newton (N) 1 newton is the force required to accelerate a mass
Lab Friction Cube. Esperanza Academy
 / 50 Lab Cube Names of Team Purpose Students will explore static and kinetic frictional forces by studying different types of surfaces and how they perform under constant force. Students will also learn
/ 50 Lab Cube Names of Team Purpose Students will explore static and kinetic frictional forces by studying different types of surfaces and how they perform under constant force. Students will also learn
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
12.4 Universal Forces. An artist s depiction of a planet s surface shows a world very different from Earth. Certain universal forces are present.
 An artist s depiction of a planet s surface shows a world very different from Earth. Certain universal forces are present. Observations of planets, stars, and galaxies strongly suggest four universal forces
An artist s depiction of a planet s surface shows a world very different from Earth. Certain universal forces are present. Observations of planets, stars, and galaxies strongly suggest four universal forces
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
Section 3: Motion and Force. Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Fundamental Forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces The Force of Friction Friction and Motion
 : Motion and Force Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Fundamental Forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces The Force of Friction Friction and Motion Key Ideas What do scientists identify as the fundamental forces
: Motion and Force Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Fundamental Forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces The Force of Friction Friction and Motion Key Ideas What do scientists identify as the fundamental forces
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion
 Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
 Chapter 12 Forces and Motion GOAL: Students will be able to interpret and apply Newton s three laws of motion and analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. Standard:
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion GOAL: Students will be able to interpret and apply Newton s three laws of motion and analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. Standard:
A N D. c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N F O R C E S
 F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
Fundamental Forces of the Universe
 Fundamental Forces of the Universe There are four fundamental forces, or interactions in nature. Strong nuclear Electromagnetic Weak nuclear Gravitational Strongest Weakest Strong nuclear force Holds the
Fundamental Forces of the Universe There are four fundamental forces, or interactions in nature. Strong nuclear Electromagnetic Weak nuclear Gravitational Strongest Weakest Strong nuclear force Holds the
Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
 1 Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics In this unit you will extend your study of forces. In particular, we will examine force as a vector quantity; this will involve solving problems where forces must be
1 Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics In this unit you will extend your study of forces. In particular, we will examine force as a vector quantity; this will involve solving problems where forces must be
FORCES AND INTERACTIONS (3.PS.NGSS)
 TM FORCES AND INTERACTIONS (3.PS.NGSS) UNIT AT A GLANCE ACTIVITY 1 - Observations of Motion: Toy Vehicle QUESTIONS: How can we describe motion? How can we determine if there are patterns in observed motion?
TM FORCES AND INTERACTIONS (3.PS.NGSS) UNIT AT A GLANCE ACTIVITY 1 - Observations of Motion: Toy Vehicle QUESTIONS: How can we describe motion? How can we determine if there are patterns in observed motion?
S3P-3-11: Define F net as the vector sum of all forces acting on a body.
 TOPIC 3.2: DYNAMICS The student will be able to: S3P-3-08: Identify the four fundamental forces of nature. S3P-3-09: Perform an experiment to demonstrate Newton s Second Law ( F = ma). net S3P-3-10: Define
TOPIC 3.2: DYNAMICS The student will be able to: S3P-3-08: Identify the four fundamental forces of nature. S3P-3-09: Perform an experiment to demonstrate Newton s Second Law ( F = ma). net S3P-3-10: Define
Tue Sept 15. Dynamics - Newton s Laws of Motion. Forces: Identifying Forces Free-body diagram Affect on Motion
 Tue Sept 15 Assignment 4 Friday Pre-class Thursday Lab - Print, do pre-lab Closed toed shoes Exam Monday Oct 5 7:15-9:15 PM email me if class conflict or extended time Dynamics - Newton s Laws of Motion
Tue Sept 15 Assignment 4 Friday Pre-class Thursday Lab - Print, do pre-lab Closed toed shoes Exam Monday Oct 5 7:15-9:15 PM email me if class conflict or extended time Dynamics - Newton s Laws of Motion
Forces and Newton s Laws
 chapter 3 section 1 Forces Forces and Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how force and motion are related what friction is between objects the difference between mass and weight Before You Read When you hit
chapter 3 section 1 Forces Forces and Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how force and motion are related what friction is between objects the difference between mass and weight Before You Read When you hit
Motion *All matter in the universe is constantly at motion Motion an object is in motion if its position is changing
 Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
History. The word electricity comes from the Greek elektron which means amber. The amber effect is what we call static electricity.
 Electrostatics 1 History The word electricity comes from the Greek elektron which means amber. The amber effect is what we call static electricity. 2 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces
Electrostatics 1 History The word electricity comes from the Greek elektron which means amber. The amber effect is what we call static electricity. 2 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces
Pushes and Pulls. Example- an apple falling on a tree exerts a downward force with a magnitude of about 1 newton.
 What are Forces? Pushes and Pulls Force- a push or pull that acts on an object. Forces make a moving object speed up, slow down, or change direction. Forces have both magnitude and direction. Magnitude
What are Forces? Pushes and Pulls Force- a push or pull that acts on an object. Forces make a moving object speed up, slow down, or change direction. Forces have both magnitude and direction. Magnitude
Force in Nature. <
 Force in Nature www.flickr.com/photos/nrbelex/383393596/ What is a Force? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=seblt6kd9ey&feature=youtube_gdata_player A force
Force in Nature www.flickr.com/photos/nrbelex/383393596/ What is a Force? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=seblt6kd9ey&feature=youtube_gdata_player A force
Measuring Force You may have measured forces using a spring scale. The of the spring in the scale depends on the amount of (a type of ) acting on it.
 Forces 12.1 Name 1 A is a push or a pull that on an. How do forces affect the motion of an object? Measuring Force You may have measured forces using a spring scale. The of the spring in the scale depends
Forces 12.1 Name 1 A is a push or a pull that on an. How do forces affect the motion of an object? Measuring Force You may have measured forces using a spring scale. The of the spring in the scale depends
Motion and Forces. Forces
 CHAPTER 8 Motion and LESSON 3 What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D
CHAPTER 8 Motion and LESSON 3 What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D
Unit 2 Forces. Fundamental Forces
 Lesson14.notebook July 10, 2013 Unit 2 Forces Fundamental Forces Today's goal: I can identify/name applied forces and draw appropriate free body diagrams (FBD's). There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Lesson14.notebook July 10, 2013 Unit 2 Forces Fundamental Forces Today's goal: I can identify/name applied forces and draw appropriate free body diagrams (FBD's). There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
UNIT 4: FORCES IN NATURE Test review: 4_1_ Forces in nature. Fundamentals
 UNIT 4: FORCES IN NATURE Test review: 4_1_ Forces in nature. Fundamentals 1. Contact forces are examples of which of the fundamental forces? a. Strong c. Weak b. Electromagnetic d. Gravitational 2. The
UNIT 4: FORCES IN NATURE Test review: 4_1_ Forces in nature. Fundamentals 1. Contact forces are examples of which of the fundamental forces? a. Strong c. Weak b. Electromagnetic d. Gravitational 2. The
L03 The Coefficient of Static Friction 1. Pre-Lab Exercises
 L03 The Coefficient of Static Friction 1 Full Name: Lab Section: Pre-Lab Exercises Hand this in at the beginning of the lab period. The grade for these exercises will be included in your lab grade this
L03 The Coefficient of Static Friction 1 Full Name: Lab Section: Pre-Lab Exercises Hand this in at the beginning of the lab period. The grade for these exercises will be included in your lab grade this
FORCE & MOTION Instructional Module 6
 FORCE & MOTION Instructional Module 6 Dr. Alok K. Verma Lean Institute - ODU 1 Description of Module Study of different types of forces like Friction force, Weight force, Tension force and Gravity. This
FORCE & MOTION Instructional Module 6 Dr. Alok K. Verma Lean Institute - ODU 1 Description of Module Study of different types of forces like Friction force, Weight force, Tension force and Gravity. This
FORCE. The 4 Fundamental Forces of Nature
 FORCE - Force a push or pull. Results only from interaction with another object. Without interaction, forces cannot be present. - Measured in Newtons (N) 1 Newton is the amount of force required to give
FORCE - Force a push or pull. Results only from interaction with another object. Without interaction, forces cannot be present. - Measured in Newtons (N) 1 Newton is the amount of force required to give
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
 Title: Introduction to Newton s second law Synopsis: Students will use Newton s second law (F=m*a), along with previous knowledge of kinematic equations, to explore the acceleration of a constant-mass
Title: Introduction to Newton s second law Synopsis: Students will use Newton s second law (F=m*a), along with previous knowledge of kinematic equations, to explore the acceleration of a constant-mass
1103 Period 5: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Name Section 1103 Period 5: Newton s Laws of Motion 5.1 What Are the Four Fundamental Forces? 1) Defining the fundamental forces: Based on your class activities and your instructor s explanation, give
Name Section 1103 Period 5: Newton s Laws of Motion 5.1 What Are the Four Fundamental Forces? 1) Defining the fundamental forces: Based on your class activities and your instructor s explanation, give
Trimester Two Study Guide Period 3 Science
 Trimester Two Study Guide Period 3 Science Important vocabulary: * Free fall: when gravity is the only force acting upon an object * Air resistance: objects flying through air experience this type of fluid
Trimester Two Study Guide Period 3 Science Important vocabulary: * Free fall: when gravity is the only force acting upon an object * Air resistance: objects flying through air experience this type of fluid
ELECTRIC CHARGE. 3. Is there any evidence of interaction between the can and the balloon?
 ELECTRIC CHARGE Name Partners' Names Part 1 The Existence of Charge A) 1. Place an empty soda pop can on its side on a flat table. 2. Fully inflate a balloon. Hold the balloon next to the side of the can,
ELECTRIC CHARGE Name Partners' Names Part 1 The Existence of Charge A) 1. Place an empty soda pop can on its side on a flat table. 2. Fully inflate a balloon. Hold the balloon next to the side of the can,
10th week Lectures March Chapter 12
 Electric charge. 10th week Lectures March 20. 2017. Chapter 12 Conductors and Insulators Coulomb law Electric field Electric Potential 3/20/2017 Physics 214 Spring 2017 1 Electric charge an atom has a
Electric charge. 10th week Lectures March 20. 2017. Chapter 12 Conductors and Insulators Coulomb law Electric field Electric Potential 3/20/2017 Physics 214 Spring 2017 1 Electric charge an atom has a
Force. The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object.
 Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
A Very Brief History of Statics and Dynamics
 UNIVERSAL GRAVITION A Very Brief History of Statics and Dynamics The idea that a force causes motion goes back to the 4 th century B.C., when the Greeks were developing ideas about science. Aristotle (384-33
UNIVERSAL GRAVITION A Very Brief History of Statics and Dynamics The idea that a force causes motion goes back to the 4 th century B.C., when the Greeks were developing ideas about science. Aristotle (384-33
I. What are forces? A. Characteristics:
 Chapter 5: forces I. What are forces? A. Characteristics: 1. Forces result from the interaction of objects. A FORCE is a push or a pull that one object exerts on another. 2. How are forces measured: a.
Chapter 5: forces I. What are forces? A. Characteristics: 1. Forces result from the interaction of objects. A FORCE is a push or a pull that one object exerts on another. 2. How are forces measured: a.
Review of Static Electricity
 Name: Block: Date: IP 614 Review of Static Electricity Central Concept: Stationary and moving charged particles result in the phenomena known as electricity and magnetism. 5.1 Recognize that an electric
Name: Block: Date: IP 614 Review of Static Electricity Central Concept: Stationary and moving charged particles result in the phenomena known as electricity and magnetism. 5.1 Recognize that an electric
SPH 4C Unit 2 Mechanical Systems
 SPH 4C Unit 2 Mechanical Systems Forces and Free Body Diagrams Learning Goal: I can consistently identify and draw Free Body Diagrams for given real world situations. There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
SPH 4C Unit 2 Mechanical Systems Forces and Free Body Diagrams Learning Goal: I can consistently identify and draw Free Body Diagrams for given real world situations. There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Unit 15 LESSON 1 WHAT ARE FORCES?
 Unit 15 LESSON 1 WHAT ARE FORCES? Pushing and Pulling A force is a push or pull. Forces can cause an object at rest to move, speed up, slow down, change direction, or stop. Forces can change the shape
Unit 15 LESSON 1 WHAT ARE FORCES? Pushing and Pulling A force is a push or pull. Forces can cause an object at rest to move, speed up, slow down, change direction, or stop. Forces can change the shape
Chapter 3, Section 3
 Chapter 3, Section 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
Chapter 3, Section 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
INTEGRATED SCIENCE I
 (Effective and Alternative Secondary Education) INTEGRATED SCIENCE I MODULE 7 BUREAU OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Department of Education DepED Complex, Meralco Avenue Pasig City 1 Module 7 The Nature of Forces
(Effective and Alternative Secondary Education) INTEGRATED SCIENCE I MODULE 7 BUREAU OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Department of Education DepED Complex, Meralco Avenue Pasig City 1 Module 7 The Nature of Forces
Q2. A book whose mass is 2 kg rests on a table. Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the table on the book.
 AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
ELECTROSTATICS. the study of electric charges, forces and fields Static Electricity is Stationary Electricity or Accumulation of charge
 Electrostatics 1 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces and fields Static Electricity is Stationary Electricity or Accumulation of charge Fundamental Rule Opposites attract, Likes Repel Things
Electrostatics 1 ELECTROSTATICS the study of electric charges, forces and fields Static Electricity is Stationary Electricity or Accumulation of charge Fundamental Rule Opposites attract, Likes Repel Things
Forces. Unit 2. Why are forces important? In this Unit, you will learn: Key words. Previously PHYSICS 219
 Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Force, Friction, Gravity and Newton s Laws. Chapter 3 Lessons 4-6
 Force, Friction, Gravity and Newton s Laws Chapter 3 Lessons 4-6 I can... identify when forces add or subtract. calculate the Net Force. explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. force:
Force, Friction, Gravity and Newton s Laws Chapter 3 Lessons 4-6 I can... identify when forces add or subtract. calculate the Net Force. explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. force:
Chapter Four Holt Physics. Forces and the Laws of Motion
 Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
ESSENTIAL PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY
 ESSENTIAL PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY I. MATTER: ANYTHING THAT HAS MASS AND VOLUME A. mass 1. amount of matter in an object 2. measured in grams B. volume 1. amount of space 2. measured in Liters for liquid
ESSENTIAL PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY I. MATTER: ANYTHING THAT HAS MASS AND VOLUME A. mass 1. amount of matter in an object 2. measured in grams B. volume 1. amount of space 2. measured in Liters for liquid
Chapter 4. Forces and Mass. Classical Mechanics. Forces. Newton s First Law. Fundamental (Field) Forces. Contact and Field Forces
 Chapter 4 Classical Mechanics Forces and Mass does not apply for very tiny objects (< atomic sizes) objects moving near the speed of light Newton s First Law Forces If the net force!f exerted on an object
Chapter 4 Classical Mechanics Forces and Mass does not apply for very tiny objects (< atomic sizes) objects moving near the speed of light Newton s First Law Forces If the net force!f exerted on an object
TODAY S OUTCOMES: FORCE, MOTION AND ENERGY - Review the Law of Interaction and balanced forces within bodies with constant motion
 TODAY S OUTCOMES: FORCE, MOTION AND ENERGY - Review the Law of Interaction and balanced forces within bodies with constant motion - Observe and plot an example of acceleration of an object - Study the
TODAY S OUTCOMES: FORCE, MOTION AND ENERGY - Review the Law of Interaction and balanced forces within bodies with constant motion - Observe and plot an example of acceleration of an object - Study the
Transfer of Forces Classwork
 Transfer of Forces Classwork 1. Describe what a force is. 2. List at least four forces that are observed in nature. 3. How are forces transferred between two objects if they are not in contact? 4. Describe
Transfer of Forces Classwork 1. Describe what a force is. 2. List at least four forces that are observed in nature. 3. How are forces transferred between two objects if they are not in contact? 4. Describe
Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion
 3 What You Will Learn The magnitude of the force of can vary. Kinetic is a force that, when unbalanced, can change the velocity of a moving object. Static balances an applied force and can prevent motion.
3 What You Will Learn The magnitude of the force of can vary. Kinetic is a force that, when unbalanced, can change the velocity of a moving object. Static balances an applied force and can prevent motion.
Unit 3 Lesson 1 Electric Charge and Static Electricity. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Opposites Attract What is electric charge? Electric charge is a property that leads to electromagnetic interactions between the particles that make up matter. An object can have a positive (+) charge,
Opposites Attract What is electric charge? Electric charge is a property that leads to electromagnetic interactions between the particles that make up matter. An object can have a positive (+) charge,
Force & Motion Task Cards
 Force & Motion Task Cards By: Plan Teach Grade Repeat 5.NBT.5 Plan, Teach, Grade, Repeat Differentiated Versions North Carolina Essential Standards 5.P.1 Understand force, motion and the relationship between
Force & Motion Task Cards By: Plan Teach Grade Repeat 5.NBT.5 Plan, Teach, Grade, Repeat Differentiated Versions North Carolina Essential Standards 5.P.1 Understand force, motion and the relationship between
RELEASED. Spring 2013 North Carolina Measures of Student Learning: NC s Common Exams. Physical Science
 Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Physical Science RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction Raleigh,
Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Physical Science RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction Raleigh,
Newton s First Law and IRFs
 Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
4. The Fundamental Interactions
 4. The Fundamental Interactions So far in our study of motion, we have learned that forces occur in interactions and cause accelerations. By itself, this information is of limited use until we learn how
4. The Fundamental Interactions So far in our study of motion, we have learned that forces occur in interactions and cause accelerations. By itself, this information is of limited use until we learn how
Physics Unit: Force & Motion
 Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Activity One Force, Mass, and Acceleration
 Steps Activity One Force, Mass, and Acceleration This activity may be done alone or with a partner. FOR THIS ACTIVITY, you will need: Rocks of different sizes. (Use rocks that are all the same kind of
Steps Activity One Force, Mass, and Acceleration This activity may be done alone or with a partner. FOR THIS ACTIVITY, you will need: Rocks of different sizes. (Use rocks that are all the same kind of
PH 202-1E Fall Electric Forces and Electric Fields. Lectures 1-4. Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition)
 PH 202-1E Fall 2006 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Lectures 1-4 Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition) 1 Electric Force and Electric Charge Qualitatively, a force is any push or pull
PH 202-1E Fall 2006 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Lectures 1-4 Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition) 1 Electric Force and Electric Charge Qualitatively, a force is any push or pull
Chapter 3 The Laws of motion. The Laws of motion
 Chapter 3 The Laws of motion The Laws of motion The Concept of Force. Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law. Newton s Third Law. Some Applications of Newton s Laws. 1 5.1 The Concept of Force Force:
Chapter 3 The Laws of motion The Laws of motion The Concept of Force. Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law. Newton s Third Law. Some Applications of Newton s Laws. 1 5.1 The Concept of Force Force:
The diagram below shows a radioactive isotope going through several half-lives as it decays.
 By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic induction resulting from strong magnetic fields B. Radioactivity in the interior of the star C. Nuclear fusion in the interior of the star
By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic induction resulting from strong magnetic fields B. Radioactivity in the interior of the star C. Nuclear fusion in the interior of the star
This Week. 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall 2018 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall 2018 1 Momentum What
What two factors affect the force of Gravity? Gravity It s Universal it s everywhere!
 What two factors affect the force of Gravity? Gravity It s Universal it s everywhere! Force The Standard Theory Boson (composite particle) Function Gravity Graviton Gravity curves space. And it always
What two factors affect the force of Gravity? Gravity It s Universal it s everywhere! Force The Standard Theory Boson (composite particle) Function Gravity Graviton Gravity curves space. And it always
Physics 2111 Unit 7. Today s Concepts: Work & Kinetic Energy Power. Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1
 Physics 2111 Unit 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kinetic Energy Power Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem The work done by force F as it acts on an object that moves between positions
Physics 2111 Unit 7 Today s Concepts: Work & Kinetic Energy Power Mechanics Lecture 7, Slide 1 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem The work done by force F as it acts on an object that moves between positions
Topic: Force PHYSICS 231
 Topic: Force PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Homework Set 2 due this Thursday, Jan 27, 11 pm Reading for next week: Chapters 10.1-6,10.10,8.3 2/1/11 Physics 231 Spring 2011 2 Key Concepts: Force Free body
Topic: Force PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Homework Set 2 due this Thursday, Jan 27, 11 pm Reading for next week: Chapters 10.1-6,10.10,8.3 2/1/11 Physics 231 Spring 2011 2 Key Concepts: Force Free body
Force and Motion 20 N. Force: Net Force on 2 kg mass = N. Net Force on 3 kg mass = = N. Motion: Mass Accel. of 2 kg mass = = kg m/s 2.
 Force and Motion Team In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
Force and Motion Team In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
This Week. 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
9.2.E - Particle Physics. Year 12 Physics 9.8 Quanta to Quarks
 + 9.2.E - Particle Physics Year 12 Physics 9.8 Quanta to Quarks + Atomic Size n While an atom is tiny, the nucleus is ten thousand times smaller than the atom and the quarks and electrons are at least
+ 9.2.E - Particle Physics Year 12 Physics 9.8 Quanta to Quarks + Atomic Size n While an atom is tiny, the nucleus is ten thousand times smaller than the atom and the quarks and electrons are at least
3 Types of Nuclear Decay Processes
 3 Types of Nuclear Decay Processes Radioactivity is the spontaneous decay of an unstable nucleus The radioactive decay of a nucleus may result from the emission of some particle from the nucleus. The emitted
3 Types of Nuclear Decay Processes Radioactivity is the spontaneous decay of an unstable nucleus The radioactive decay of a nucleus may result from the emission of some particle from the nucleus. The emitted
Review of Static Electricity
 Name: KEY lock: Date: IP 670 Match each of the following terms with the appropriate description. Write the letter of the best answer to the left. Terms Description C 1. atom a. a small, negatively charged
Name: KEY lock: Date: IP 670 Match each of the following terms with the appropriate description. Write the letter of the best answer to the left. Terms Description C 1. atom a. a small, negatively charged
Intro Video: n What is charge? n v=dvlpasdwxpy
 Electrostatics Intro Video: n What is charge? n https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=dvlpasdwxpy What is electrostatics? n Electrostatics or electricity at rest n Involves electric charges, the forces between
Electrostatics Intro Video: n What is charge? n https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=dvlpasdwxpy What is electrostatics? n Electrostatics or electricity at rest n Involves electric charges, the forces between
What is force? A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable.
 Chapter 3, Sec-on 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
Chapter 3, Sec-on 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
Chemistry Terms. atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom.
 Chemistry Terms atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. chemical reaction A process in which atoms and molecules interact, resulting in the alteration
Chemistry Terms atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. chemical reaction A process in which atoms and molecules interact, resulting in the alteration
A. true. 6. An object is in motion when
 1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
Tetraneutron? Can a four-neutron, no-proton particle exist? Published Feb. 3, 2016 in Physical Review Letters
 Tetraneutron? Can a four-neutron, no-proton particle exist? Published Feb. 3, 2016 in Physical Review Letters A 186 MeV/u beam of radioactive 8 He (doublycharged) collides with normal 4 He Experiments
Tetraneutron? Can a four-neutron, no-proton particle exist? Published Feb. 3, 2016 in Physical Review Letters A 186 MeV/u beam of radioactive 8 He (doublycharged) collides with normal 4 He Experiments
Chapter 6 The Atom Study Guide
 Chapter 6 The Atom Study Guide Read pages 118-125 Look at all words in bold or colored print Look at the paragraph summaries on the sides Section 6.1 Fundamental Particles and Forces Vocabulary Definition
Chapter 6 The Atom Study Guide Read pages 118-125 Look at all words in bold or colored print Look at the paragraph summaries on the sides Section 6.1 Fundamental Particles and Forces Vocabulary Definition
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD COMPETITION 2010
 SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD COMPETITION 2010 Time Allocated : 02 Hours Calculators are not allowed to use. Date of Examination : 10 07 2010 Index No. :. Time : 9.00 a.m. - 11.00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS Answer
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD COMPETITION 2010 Time Allocated : 02 Hours Calculators are not allowed to use. Date of Examination : 10 07 2010 Index No. :. Time : 9.00 a.m. - 11.00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS Answer
A negatively charged object has more electrons than protons. A negatively charged object has more electrons than protons
 Electricity Electricity Describes all phenomena caused by positive and negative charges Electrical charge is caused by protons and electrons Electrons and protons are subatomic particles found in the atom
Electricity Electricity Describes all phenomena caused by positive and negative charges Electrical charge is caused by protons and electrons Electrons and protons are subatomic particles found in the atom
Friction. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Physics terms. Equations 5/20/14. Models for friction
 Objectives Friction Calculate friction forces from equation models for static, kinetic, and rolling friction. Solve one-dimensional force problems that include friction. 1. A box with a mass of 10 kg is
Objectives Friction Calculate friction forces from equation models for static, kinetic, and rolling friction. Solve one-dimensional force problems that include friction. 1. A box with a mass of 10 kg is
Conceptual Questions. Fig.8.51 EXERCISES. 8. Why can t electric field lines cross? 9. In which direction do charges always move in an electric field?
 EXERCISES Conceptual Questions 1. Explain why a neutral object can be attracted to a charged object. Why can this neutral object not be repelled by a charged object? 2. What is the function of an electroscope?
EXERCISES Conceptual Questions 1. Explain why a neutral object can be attracted to a charged object. Why can this neutral object not be repelled by a charged object? 2. What is the function of an electroscope?
5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide
 Name: Date of Test: Vocabulary 5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide Motion- a change in position relative to a point of reference, a change in speed, or a change in distance. Point of Reference (Reference
Name: Date of Test: Vocabulary 5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide Motion- a change in position relative to a point of reference, a change in speed, or a change in distance. Point of Reference (Reference
reflector screen 10 g masses
 LAB SECTION: NAME: EXPERIMENT : NEWTON S SECOND LAW Introduction: In this lab, we will minimize friction on a moving cart by using carts having small wheels with nearly frictionless bearings. You will
LAB SECTION: NAME: EXPERIMENT : NEWTON S SECOND LAW Introduction: In this lab, we will minimize friction on a moving cart by using carts having small wheels with nearly frictionless bearings. You will
gear gravity heat inclined plane
 Equal and opposite forces which occur in pairs Upward force acting on objects when they are placed in water Substance which allows electric current to pass through it Force applied at one point of a machine
Equal and opposite forces which occur in pairs Upward force acting on objects when they are placed in water Substance which allows electric current to pass through it Force applied at one point of a machine
Newton Car Lab. Newton s 1 st Law - Every object in a state of uniform motion
 Newton Car Lab Physics Concepts: Newton s 1 st Law - Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. This we recognize as Galileo
Newton Car Lab Physics Concepts: Newton s 1 st Law - Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. This we recognize as Galileo
Contents. Objectives Newton s Laws preliminaries 1 st Law pushing things 2 nd Law 3 rd Law A Problem Fundamental Forces Fundamental Particles Recap
 Physics 121 for Majors Class 9 Newton s Laws Standard Model Last Class Matrices Classical boosts Lorentz boosts Space-time four-vectors Space and time problems in relativity Today s Class Newton s Laws
Physics 121 for Majors Class 9 Newton s Laws Standard Model Last Class Matrices Classical boosts Lorentz boosts Space-time four-vectors Space and time problems in relativity Today s Class Newton s Laws
Basic Nuclear Theory. Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability
 Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
Forces. A Force is a push or a pull on an object. Forces can cause a resting object to move
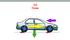 13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
6 th week Lectures Feb. 12. Feb
 Momentum Rockets and guns 6 th week Lectures Feb. 12. Feb. 16. 2018. How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 2/11/2018 Physics 214 Spring 2018 1 Announcements
Momentum Rockets and guns 6 th week Lectures Feb. 12. Feb. 16. 2018. How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 2/11/2018 Physics 214 Spring 2018 1 Announcements
STATIC ELECTRICITY. II. Directions:Answer the following questions with short answers. Use the back of this sheet to write your answers.
 1 Pre-Test I. Directions: Circle the word that completes the sentence. 1. The "building blocks of matter" are called neutrons atoms electrons. 2. When charged objects jump apart we say they each other.
1 Pre-Test I. Directions: Circle the word that completes the sentence. 1. The "building blocks of matter" are called neutrons atoms electrons. 2. When charged objects jump apart we say they each other.
Electrostatics. Physics 10. Atomic Structure
 Slide 1 Slide 6 Slide 2 Slide 7 Slide 3 Slide 8 Slide 4 Slide 9 Slide 5 Slide 10 Physics 10 Electrostatics Slide 11 Slide 12 Slide 13 Slide 14 Slide 15 Slide 16 Slide 17 Slide 18 Slide 19 Slide 20 Slide
Slide 1 Slide 6 Slide 2 Slide 7 Slide 3 Slide 8 Slide 4 Slide 9 Slide 5 Slide 10 Physics 10 Electrostatics Slide 11 Slide 12 Slide 13 Slide 14 Slide 15 Slide 16 Slide 17 Slide 18 Slide 19 Slide 20 Slide
Force and Motion. Thought Experiment
 Team Force and Motion In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
Team Force and Motion In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
Forces and Motion Forces Gravity Net Forces Free Body Diagrams
 Forces and Motion Forces Gravity Net Forces Free Body Diagrams Misc. 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 FINAL JEOPARDY Go To Score
Forces and Motion Forces Gravity Net Forces Free Body Diagrams Misc. 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 FINAL JEOPARDY Go To Score
