d = +20 m symbol units direction magnitude PHYSICS Quantities that can be measured by using an instrument and have specific units of measurement.
|
|
|
- Abel McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GROUP ACTIVITY PHYSICS PERIODS 2 & 6 UNIT 1 Introduction to Physics Work with your group. Take a chart from the front table and tape it on your Physics notebook. Take 5 instruments and make measurements (your group decides what to measure). Complete the chart. Be ready to participate in class. MR. LARGO MR. Hill INSTRUMENT A Device used to measure physical quantities. Examples: Meter stick, thermometer, spring scale, graduated cylinder, stop watch, Multimeter. PHYSICAL QUANTITY Quantities that can be measured by using an instrument and have specific units of measurement. Mass EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL QUANTITY Force (weight) Clock reading (time) Distance (length) Volume 1. Symbol 2. Direction 3. Magnitude 4. Units ELEMENTS OF PHYSICAL QUANTITIES d = +20 m symbol units direction magnitude 1
2 SYMBOL DIRECTION Short representation of a The place towards which an object is directed MAGNITUDE UNITS The number of a physical quantity Standard adopted to measure a Metric System (world) English system (USA) The number of a The place towards which an object is directed. Quantities that can be measured by using an instrument and have specific units of measurement DIRECTION INSTRUMENT SYMBOL Standard adopted to measure a A Device used to measure physical quantities. Short representation of a physical quantity PHYSICAL QUANTITY MAGNITUDE UNITS 2
3 PHYSICS CLASS We work with physical quantities such as mass, distance, velocity, etc., that can be measured with an instrument such as spring scale, meter stick, speedometer. We do not deal with feelings or emotions such as love, happiness, sadness, etc. PLEASE 4 VOLUNTEERS TO THE FRONT OF THE ROOM! TAKE OUT YOUR PERSONAL TELESCOPE MOTION An object is in motion with respect to another object (reference object) if, as time progresses, its position changes relative to a reference object. REFERENCE FRAME THE ROBOT ACTIVITY Who wants to be a robot for the day? A tool used by physicists to make a specific description of an object s motion. 3
4 ELEMENTS OF A REFERENCE FRAME 1. An object of reference 2. A coordinate system with a scale for measuring distance 3. Clock readings SETTING A REFERENCE FRAME EXAMPLE: Jordan bats a baseball 20 m away from home plate and the ball lands 15 s later. What to do? Sketch the situation Identify and circle your system Set the reference frame SETTING A REFERENCE FRAME SETTING A REFERENCE FRAME EXAMPLE: Jordan bats a baseball 20 m away from home plate and the ball lands 15 s later. SKETCH: Drawing of the given situation SYSTEM: The object we choose to analyze (circle it). d x =0 m t 0 = 0 s 1. Identify the object of reference d x [m] t f = 15 s 2. A coordinate system with a scale for measuring distance 3. Clock readings WHITEBOARD WHITEBOARD MAKE UP A WORD STORY Luisa rides her bike 100 m in 20 s towards the left. Set the reference frame. d x0 =0 mi t 0 =0 hour d x [m] t F = 20 s d x =0m t 0 =0s d x =2860 mi t F =6 hours 4
5 LINEAR MOTION It is a model of motion that assumes that an object, considered as a pointlike object, moves along a straight line. Particle Dimensionless object (point-like object) The runner is the object of interest (system) moving toward a person on a bench. The runner moves in a straight line (linear motion) The runner is now represented with a particle to simplify the physics. I am Usain Bolt! PHYSICS Science that studies MODELS of real life situations. These MODELS are not perfect and are limited. EXAMPLES OF MODELS Particle model Mathematical models Linear Motion Projectile Motion Circular Motion TYPES OF PHYSICAL QUANTITIES PHYSICAL QUANTITY Vectors: Physical quantities that require of a magnitude (number) and direction. Scalar: Physical quantities that require of a magnitude (number) only. CLOCK READING (time): The reading from a stop watch when an object moves between two points. Name Symbol Units Units symbol Type of PQ Clock Reading t seconds s Scalar (doesn t need direction) 5
6 POSITION Location of an object with respect to a particular coordinate system. Name Position Symbol dx Type of PQ Vector (needs direction) d X DISPLACEMENT Vector that starts from an object initial position and ends at its final position. Also known as change in position Difference between two positions. Final position minus initial position. Math model: dx = dx f dx i Name Displacement Symbol dx d X DELTA Greek letter DELTA ( ) Physics meaning: change between two physical quantities We need to have two of the same kind: Initial & Final DISTANCE The magnitude (length) of the displacement vector (direction does not matter). Name distance Symbol d d Type of PQ scalar (doesn t need direction) DISTANCE VS. DISPLACEMENT Distance and Displacement have the same magnitude. Distance is a scalar (Only magnitude is needed) Displacement is a Vector (Magnitude and direction are needed. Distance is the magnitude of the Displacement. PATH LENGTH Length of a string laid along the path the object took. Name Path length Symbol L Type of PQ scalar L 6
7 PIKACHU BULBASAUR CHARMANDER SQUIRTLE JIGGLYPUFF MEW 7
Unit 4 Review. inertia interaction pair net force Newton s first law Newton s second law Newton s third law position-time graph
 Unit 4 Review Vocabulary Review Each term may be used once. acceleration constant acceleration constant velocity displacement force force of gravity friction force inertia interaction pair net force Newton
Unit 4 Review Vocabulary Review Each term may be used once. acceleration constant acceleration constant velocity displacement force force of gravity friction force inertia interaction pair net force Newton
We can make a motion diagram of the student walking across the room:
 Lecture 2 / Day 1 Motion and Kinematics Intro. Motion Diagrams Vector Subtraction Velocity We ve gone through the basics of measurement and using vectors now we re ready to get into Kinematics, which is
Lecture 2 / Day 1 Motion and Kinematics Intro. Motion Diagrams Vector Subtraction Velocity We ve gone through the basics of measurement and using vectors now we re ready to get into Kinematics, which is
The Language of Motion
 The Language of Motion Textbook pages 344 361 Section 8.1 Summary Before You Read What does the term uniform mean to you? If motion is uniform, how does it behave? Write your ideas in the lines below.
The Language of Motion Textbook pages 344 361 Section 8.1 Summary Before You Read What does the term uniform mean to you? If motion is uniform, how does it behave? Write your ideas in the lines below.
Chapter 2: Representing Motion. Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue.
 Chapter 2: Representing Motion Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue. Chapter 2 Representing Motion In this chapter you will: Represent motion through the use of words, motion diagrams, and
Chapter 2: Representing Motion Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue. Chapter 2 Representing Motion In this chapter you will: Represent motion through the use of words, motion diagrams, and
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving?
 Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving? 3.1 Observe and represent Decide on a starting point. You will need 2 cars (or other moving objects). For each car, you will mark its position at each second. Make sure
Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving? 3.1 Observe and represent Decide on a starting point. You will need 2 cars (or other moving objects). For each car, you will mark its position at each second. Make sure
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
SECTION 3 - VELOCITY
 UNIT 2 MOTION SECTION 3 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67
UNIT 2 MOTION SECTION 3 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67
SECTION 2 - VELOCITY
 MOTION SECTION 2 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67 mph Why
MOTION SECTION 2 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67 mph Why
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
Solving Problems In Physics
 Solving Problems In Physics 1. Read the problem carefully. 2. Identify what is given. 3. Identify the unknown. 4. Find a useable equation and solve for the unknown quantity. 5. Substitute the given quantities.
Solving Problems In Physics 1. Read the problem carefully. 2. Identify what is given. 3. Identify the unknown. 4. Find a useable equation and solve for the unknown quantity. 5. Substitute the given quantities.
Unit 7, 8, 9 Physics Review
 Unit 7, 8, 9 Physics Review 1. A 2 kg mass is held 4 m above the ground. What is the approximate potential energy due to gravity of the mass with respect to the ground? a. 20 J. b. 40 J. c. 60 J. d. 80
Unit 7, 8, 9 Physics Review 1. A 2 kg mass is held 4 m above the ground. What is the approximate potential energy due to gravity of the mass with respect to the ground? a. 20 J. b. 40 J. c. 60 J. d. 80
1. A force is a or a. 2. Forces are described by how they are and in what they are going. 3. forces on an object will change the objects motion.
 Name period date assigned date due date returned? 1. A force is a or a. 2. Forces are described by how they are and in what they are going. 3. forces on an object will change the objects motion. - - -
Name period date assigned date due date returned? 1. A force is a or a. 2. Forces are described by how they are and in what they are going. 3. forces on an object will change the objects motion. - - -
Chapter 2: Motion a Straight Line
 Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once.
 PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
Speed and Velocity. v av 5 Dd. Sample Problem 1: Determining Average Speed
 1.2 Figure 1 A laser speed device can accurately measure the speed of an oncoming vehicle. average speed (v av ) the total distance travelled divided by the total time taken to travel that distance Speed
1.2 Figure 1 A laser speed device can accurately measure the speed of an oncoming vehicle. average speed (v av ) the total distance travelled divided by the total time taken to travel that distance Speed
Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]
![Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]](/thumbs/77/76428187.jpg) Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Kinematics 7 Solutions. 7.1 Represent and Reason a) The bike is moving at a constant velocity of 4 m/s towards the east
 Kinematics 7 Solutions 7.1 Represent and Reason a) The bike is moving at a constant velocity of 4 m/s towards the east b) For the same motion, a position versus time graph would be a straight line at a
Kinematics 7 Solutions 7.1 Represent and Reason a) The bike is moving at a constant velocity of 4 m/s towards the east b) For the same motion, a position versus time graph would be a straight line at a
Four Types of Motion We ll Study
 Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
170 Test example problems CH1,2,3
 170 Test example problems CH1,2,3 WARNING: these are simply examples that showed up in previous semesters test. It does NOT mean that similar problems will be present in THIS semester s test. Hence, you
170 Test example problems CH1,2,3 WARNING: these are simply examples that showed up in previous semesters test. It does NOT mean that similar problems will be present in THIS semester s test. Hence, you
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Chapter 8 Rotational Motion In this chapter you will: Learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. Learn how torque changes rotational velocity. Explore factors that
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Chapter 8 Rotational Motion In this chapter you will: Learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. Learn how torque changes rotational velocity. Explore factors that
Physics Midterm Review Sheet
 Practice Problems Physics Midterm Review Sheet 2012 2013 Aswers 1 Speed is: a a measure of how fast something is moving b the distance covered per unit time c always measured in units of distance divided
Practice Problems Physics Midterm Review Sheet 2012 2013 Aswers 1 Speed is: a a measure of how fast something is moving b the distance covered per unit time c always measured in units of distance divided
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 12/09/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 Science -Day 1 1. A reference point is an object
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 12/09/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 Science -Day 1 1. A reference point is an object
Motion and Forces study Guide
 Motion and Forces study Guide Completion Complete each statement. 1. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different. 2. The SI unit for measuring is the meter. 3. The direction and length
Motion and Forces study Guide Completion Complete each statement. 1. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different. 2. The SI unit for measuring is the meter. 3. The direction and length
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics. Free Response Problems
 PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. What is Science? Worksheets CSS AP Physics 1 2015-16 Summer Assignment Part 1 of 3 CHAPTER 1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Scientific Inquiry 1.2 Fundamental Units
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. What is Science? Worksheets CSS AP Physics 1 2015-16 Summer Assignment Part 1 of 3 CHAPTER 1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Scientific Inquiry 1.2 Fundamental Units
Physics 218 Exam I. Spring 2017 (all sections) February 13 th, 2017
 Physics 218 Exam I Spring 2017 (all sections) February 13 th, 2017 Rules of the exam: Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to do so. 1. You
Physics 218 Exam I Spring 2017 (all sections) February 13 th, 2017 Rules of the exam: Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to do so. 1. You
Motion Section 3 Acceleration
 Section 3 Acceleration Review velocity Scan Use the checklist below to preview Section 3 of your book. Read all section titles. Read all boldfaced words. Read all graphs and equations. Look at all the
Section 3 Acceleration Review velocity Scan Use the checklist below to preview Section 3 of your book. Read all section titles. Read all boldfaced words. Read all graphs and equations. Look at all the
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Section 1: Units, Measurements and Error What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Qualitative and Quantitative Descriptions
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 3 Physical Science Motion Section 1: Units, Measurements and Error What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Qualitative and Quantitative Descriptions
Motion in 1 Dimension. By Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi, University of Miami
 Motion in 1 Dimension By Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi, University of Miami When you throw a pebble straight up, how high does it go? How fast is it when it gets back? If you are in your car at a red light
Motion in 1 Dimension By Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi, University of Miami When you throw a pebble straight up, how high does it go? How fast is it when it gets back? If you are in your car at a red light
Free-Fall Motion. All objects near the surface of the Earth experience a downward acceleration caused by gravity. The
 Author: Bob Leonard Lab partner: Rob Horne 10/6/2012 Free-Fall Motion Abstract All objects near the surface of the Earth experience a downward acceleration caused by gravity. The acceleration due to gravity
Author: Bob Leonard Lab partner: Rob Horne 10/6/2012 Free-Fall Motion Abstract All objects near the surface of the Earth experience a downward acceleration caused by gravity. The acceleration due to gravity
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style
 Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
So, whether or not something is moving depends on your frame of reference.
 When an object changes position relative to a reference point. (Frame of reference) Not from where she s sitting, but from space, the earth rotates and the wall with it. So, whether or not something is
When an object changes position relative to a reference point. (Frame of reference) Not from where she s sitting, but from space, the earth rotates and the wall with it. So, whether or not something is
3.3 Acceleration An example of acceleration Definition of acceleration Acceleration Figure 3.16: Steeper hills
 3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration.
 BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration. What does the below equation tell us? v = d t NOTES 2.1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL
BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration. What does the below equation tell us? v = d t NOTES 2.1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL
PHYSICS Principles and Problems. Chapter 2: Representing Motion
 PHYSICS Principles and Problems Chapter 2: Representing Motion CHAPTER 2 Representing Motion BIG IDEA You can use displacement and velocity to describe an object s motion. CHAPTER 2 Table Of Contents Section
PHYSICS Principles and Problems Chapter 2: Representing Motion CHAPTER 2 Representing Motion BIG IDEA You can use displacement and velocity to describe an object s motion. CHAPTER 2 Table Of Contents Section
AP Physics 1 Lesson 15.a Rotational Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use. Name. Date. Period. Engage
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 15.a Rotational Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use Name Outcomes Date Interpret graphical evidence of angular motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply
AP Physics 1 Lesson 15.a Rotational Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use Name Outcomes Date Interpret graphical evidence of angular motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion Rotation and Revolution
 Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. 10.1 Rotation and Revolution Two types of circular motion are and. An is the straight line around which rotation takes place. When an object turns
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. 10.1 Rotation and Revolution Two types of circular motion are and. An is the straight line around which rotation takes place. When an object turns
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement
 Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014)
 Name: Date: AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014) Instructions: 1. Read and study Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2. Answer the questions below. 3. Submit your answers online
Name: Date: AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014) Instructions: 1. Read and study Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2. Answer the questions below. 3. Submit your answers online
June To Advanced Placement Calculus Student,
 June 2018 To Advanced Placement Calculus Student, I congratulate you on accepting the challenge of taking the Advanced Placement Calculus course at Northwestern. I have prepared this packet to give you
June 2018 To Advanced Placement Calculus Student, I congratulate you on accepting the challenge of taking the Advanced Placement Calculus course at Northwestern. I have prepared this packet to give you
AP Physics I Summer Assignment. Mrs. Verdi
 AP Physics I Summer Assignment Mrs. Verdi 2015-2016 ALL STUDENTS ENROLLED IN AP PHYSICS: Please email me at averdi@leepublicschools.net before the start of school. Leave your first and last name so I know
AP Physics I Summer Assignment Mrs. Verdi 2015-2016 ALL STUDENTS ENROLLED IN AP PHYSICS: Please email me at averdi@leepublicschools.net before the start of school. Leave your first and last name so I know
Measurement & Lab Equipment
 Measurement & Lab Equipment Abstract This lab reviews the concept of scientific measurement, which you will employ weekly throughout this course. Specifically, we will review the metric system so that
Measurement & Lab Equipment Abstract This lab reviews the concept of scientific measurement, which you will employ weekly throughout this course. Specifically, we will review the metric system so that
Graphing and Physical Quantities
 Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 3.1 Observe and Describe Graphing and Physical Quantities Taylor recorded the position of a motorized toy car using the origin as her reference point. She wrote
Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 3.1 Observe and Describe Graphing and Physical Quantities Taylor recorded the position of a motorized toy car using the origin as her reference point. She wrote
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2)
 AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2) FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2) FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
SUMMARY. ) t, UNIT. Constant velocity represents uniform motion. Acceleration causes a change in velocity.
 UNIT A SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 1 Constant velocity represents uniform motion. Distance and Displacement Position-time graphs Average speed and average velocity Positive, negative, and zero
UNIT A SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 1 Constant velocity represents uniform motion. Distance and Displacement Position-time graphs Average speed and average velocity Positive, negative, and zero
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Web Resources for Physics 1 Physics Classroom http://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/ Quantities in Motion Any motion involves three
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Web Resources for Physics 1 Physics Classroom http://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/ Quantities in Motion Any motion involves three
Mechanics is the study of motion, and is typically subdivided into two main categories:
 Ch1 Page 1 Sunday, September 01, 2013 1:43 PM Brock University PHYS 1P21/1P91 Mechanics and Introduction to Relativity Course Overview Overview of Mechanics Core theories of mechanics: Quantum Field Theory
Ch1 Page 1 Sunday, September 01, 2013 1:43 PM Brock University PHYS 1P21/1P91 Mechanics and Introduction to Relativity Course Overview Overview of Mechanics Core theories of mechanics: Quantum Field Theory
SUBJECT: PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE: 10 CHAPTER / MODULE: MECHANICS UNIT / LESSON TOPIC: - Equations of Motion - Graphs of Motion
 SUBJECT: PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE: 10 CHAPTER / MODULE: MECHANICS UNIT / LESSON TOPIC: - Equations of Motion - Graphs of Motion By the end of this unit, you should be able to: describe motion along a straight
SUBJECT: PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE: 10 CHAPTER / MODULE: MECHANICS UNIT / LESSON TOPIC: - Equations of Motion - Graphs of Motion By the end of this unit, you should be able to: describe motion along a straight
Engage 1. Compare the total distance traveled between A and B, if both paths arrive at the factory.
 Unit 1: Phenomenon The Physics of Skydiving Lesson 2.f Displacement and Velocity Student Performance Objectives Students will define displacement. Students will define velocity. Students will differentiate
Unit 1: Phenomenon The Physics of Skydiving Lesson 2.f Displacement and Velocity Student Performance Objectives Students will define displacement. Students will define velocity. Students will differentiate
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
3 Acceleration. positive and one is negative. When a car changes direction, it is also accelerating. In the figure to the
 What You ll Learn how acceleration, time, and velocity are related the different ways an object can accelerate how to calculate acceleration the similarities and differences between straight line motion,
What You ll Learn how acceleration, time, and velocity are related the different ways an object can accelerate how to calculate acceleration the similarities and differences between straight line motion,
FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
 AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion. FACT: Displacement
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion. FACT: Displacement
Four Basic Types of Motion Pearson Education, Inc.
 Four Basic Types of Motion Making a Motion Diagram An easy way to study motion is to make a video of a moving object. A video camera takes images at a fixed rate, typically 30 every second. Each separate
Four Basic Types of Motion Making a Motion Diagram An easy way to study motion is to make a video of a moving object. A video camera takes images at a fixed rate, typically 30 every second. Each separate
Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures
 Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures Bởi: OpenStaxCollege A double-pan mechanical balance is used to compare different masses. Usually an object with unknown mass is placed in one pan and objects
Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures Bởi: OpenStaxCollege A double-pan mechanical balance is used to compare different masses. Usually an object with unknown mass is placed in one pan and objects
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review Answers
 Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review Answers 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s A truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1.
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review Answers 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s A truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1.
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
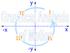 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Kinematics and Dynamics
 AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
The Laws of Motion. Before You Read. Science Journal
 The Laws of Motion Before You Read Before you read the chapter, use the What I know column to list three things you know about motion. Then list three questions you have about motion in the What I want
The Laws of Motion Before You Read Before you read the chapter, use the What I know column to list three things you know about motion. Then list three questions you have about motion in the What I want
Lec 1, , Course Intro. PHYS-1401, General Physics I Spring Physics I Lab starts next week.
 Lec 1, 2019-01-14, Course Intro Monday, January 14, 2019 10:21 AM PHYS-1401, General Physics I Spring 2019 - Physics I Lab starts next week. Science - Studying patterns in Nature Mathematics - Language
Lec 1, 2019-01-14, Course Intro Monday, January 14, 2019 10:21 AM PHYS-1401, General Physics I Spring 2019 - Physics I Lab starts next week. Science - Studying patterns in Nature Mathematics - Language
velocity = displacement time elapsed
 Section 1 Velocity and Acceleration: The Big Thrill distance time a) Measure the distance the steel ball rolls and the time it takes to reach the end of the track using a ruler and a stopwatch. Record
Section 1 Velocity and Acceleration: The Big Thrill distance time a) Measure the distance the steel ball rolls and the time it takes to reach the end of the track using a ruler and a stopwatch. Record
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name: We Love Gravity! Presenter(s) Virginia Lehr, Laura Hidrobo Grade Level 5 Standards Connection(s) Solar System and Gravity Teaser: Gravity is
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name: We Love Gravity! Presenter(s) Virginia Lehr, Laura Hidrobo Grade Level 5 Standards Connection(s) Solar System and Gravity Teaser: Gravity is
1D Motion: Review Packet Problem 1: Consider the following eight velocity vs. time graphs. Positive velocity is forward velocity.
 Name: 1D Motion: Review Packet Problem 1: Consider the following eight velocity vs. time graphs. Positive velocity is forward velocity. Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D Graph E Graph F Graph G Graph H (a)
Name: 1D Motion: Review Packet Problem 1: Consider the following eight velocity vs. time graphs. Positive velocity is forward velocity. Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D Graph E Graph F Graph G Graph H (a)
Station 1: measuring & graphing short lengths
 Station 1: measuring & graphing short lengths 1. Read the task carefully. 2. Make a TABLE to collect your data. 3. Collect your data. 4. Graph the data using a bar graph. 5. Clean up the station & put
Station 1: measuring & graphing short lengths 1. Read the task carefully. 2. Make a TABLE to collect your data. 3. Collect your data. 4. Graph the data using a bar graph. 5. Clean up the station & put
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES BEGIN
 SIGNIFICANT FIGURES BEGIN and someone hands you this. Imagine you are asked to measure the length of something... How do we use it most effectively? Rulers, thermometers, and graduated cylinders, to name
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES BEGIN and someone hands you this. Imagine you are asked to measure the length of something... How do we use it most effectively? Rulers, thermometers, and graduated cylinders, to name
AP Physics I Summer Work
 AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
Motion in One Dimension - Grade 10
 Chapter 3 Motion in One Dimension - Grade 10 3.1 Introduction This chapter is about how things move in a straight line or more scientifically how things move in one dimension. This is useful for learning
Chapter 3 Motion in One Dimension - Grade 10 3.1 Introduction This chapter is about how things move in a straight line or more scientifically how things move in one dimension. This is useful for learning
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
Lesson 3 Acceleration
 Lesson 3 Acceleration Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 45 Content Vocabulary 46 Lesson Outline 47 MiniLab 49 Content Practice A 50 Content Practice B 51 Language Arts Support 52 Math Skills
Lesson 3 Acceleration Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 45 Content Vocabulary 46 Lesson Outline 47 MiniLab 49 Content Practice A 50 Content Practice B 51 Language Arts Support 52 Math Skills
Introduction to Physics Physics 114 Eyres
 What is Physics? Introduction to Physics Collecting and analyzing experimental data Making explanations and experimentally testing them Creating different representations of physical processes Finding
What is Physics? Introduction to Physics Collecting and analyzing experimental data Making explanations and experimentally testing them Creating different representations of physical processes Finding
Measurement Stations. Length, Mass, Volume, Density, Temperature, and Time
 Measurement Stations Length, Mass, Volume, Density, Temperature, and Time Length Length measures the distance from end to end on an object; height and width are variations on length. Standard (S.I.) Unit:
Measurement Stations Length, Mass, Volume, Density, Temperature, and Time Length Length measures the distance from end to end on an object; height and width are variations on length. Standard (S.I.) Unit:
Physical Science Chapter 11. Motion
 Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Math 2 1. Lesson 4-5: Completing the Square. When a=1 in a perfect square trinomial, then. On your own: a. x 2 18x + = b.
 Math 1 Lesson 4-5: Completing the Square Targets: I can identify and complete perfect square trinomials. I can solve quadratic equations by Completing the Square. When a=1 in a perfect square trinomial,
Math 1 Lesson 4-5: Completing the Square Targets: I can identify and complete perfect square trinomials. I can solve quadratic equations by Completing the Square. When a=1 in a perfect square trinomial,
Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement
 Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Displacement and Velocity
 2.2 Displacement and Velocity In the last section, you saw how diagrams allow you to describe motion qualitatively. It is not at all difficult to determine whether an object or person is at rest, speeding
2.2 Displacement and Velocity In the last section, you saw how diagrams allow you to describe motion qualitatively. It is not at all difficult to determine whether an object or person is at rest, speeding
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a
 Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
1 Science/Physics. 2 Motion. GS 104, Exam Review
 1 Science/Physics 1. Homework #1 questions: Look over units of measure questions and solutions. 2. Name a subfield within science 3. Name a subfield within physics 4. 10 3 m = meter? (Prefix) 5. 10 9 m
1 Science/Physics 1. Homework #1 questions: Look over units of measure questions and solutions. 2. Name a subfield within science 3. Name a subfield within physics 4. 10 3 m = meter? (Prefix) 5. 10 9 m
Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 BROCK UNIVERSITY. Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 260 Examination date: 10 November 2014
 Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS P or PHYS P9 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 5: November 04 Number of pages: 5 + formula sheet Course: PHYS P/P9 Number of students: 0 Examination date: 0
Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS P or PHYS P9 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 5: November 04 Number of pages: 5 + formula sheet Course: PHYS P/P9 Number of students: 0 Examination date: 0
12/15/2015. Newton per Coulomb N/C. vector. A model of the mechanism for electrostatic interactions. The Electric Field
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Electric Field A model of the mechanism for electrostatic interactions A model for electric interactions, suggested by Michael Faraday, involves some sort of electric disturbance
Chapter 15 Lecture The Electric Field A model of the mechanism for electrostatic interactions A model for electric interactions, suggested by Michael Faraday, involves some sort of electric disturbance
Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages )
 Name Class Date Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages 328 331) This section defines distance and displacement. Methods of describing motion are presented. Vector addition and subtraction are introduced.
Name Class Date Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages 328 331) This section defines distance and displacement. Methods of describing motion are presented. Vector addition and subtraction are introduced.
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review
 Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS. Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3
 INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
Unit 2 - Motion. Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed. Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76
 Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Physics General Physics. Mostly mechanics, some fluid mechanics, wave motion and thermodynamics! Fall 2016 Semester Prof.
 Physics 22000 General Physics Mostly mechanics, some fluid mechanics, wave motion and thermodynamics! Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Physics 22000 General Physics Physics Department home page:
Physics 22000 General Physics Mostly mechanics, some fluid mechanics, wave motion and thermodynamics! Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Physics 22000 General Physics Physics Department home page:
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
Modern Physics. Light and Relativity
 Modern Physics Light and Relativity Electromagnetism In the late 1800 s, Electricity and Magnetism were united as one force: Electromagnetism Electromagnetism In the late 1800 s, Electricity and Magnetism
Modern Physics Light and Relativity Electromagnetism In the late 1800 s, Electricity and Magnetism were united as one force: Electromagnetism Electromagnetism In the late 1800 s, Electricity and Magnetism
2. a) Explain the equilibrium of i) Concurrent force system, and ii) General force system.
 Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
Honors Physics Review
 Honors Physics Review Work, Power, & Energy (Chapter 5) o Free Body [Force] Diagrams Energy Work Kinetic energy Gravitational Potential Energy (using g = 9.81 m/s 2 ) Elastic Potential Energy Hooke s Law
Honors Physics Review Work, Power, & Energy (Chapter 5) o Free Body [Force] Diagrams Energy Work Kinetic energy Gravitational Potential Energy (using g = 9.81 m/s 2 ) Elastic Potential Energy Hooke s Law
General Physics. Linear Motion. Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha
 General Physics Linear Motion Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha High Throw How high can a human throw something? Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description
General Physics Linear Motion Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha High Throw How high can a human throw something? Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description
Physics 206 Exam I. Spring 2019 (all UP sections) February 18 th, 2019
 Rules of the exam: Physics 206 Exam I Spring 2019 (all UP sections) February 18 th, 2019 Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to do so. 1.
Rules of the exam: Physics 206 Exam I Spring 2019 (all UP sections) February 18 th, 2019 Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to do so. 1.
The Nature of Science
 chapter 1 The Nature of Science section 2 Standards of Measurement Before You Read If someone asked you how wide your desk is, how would you measure it? Would you measure using inches, centimeters, feet,
chapter 1 The Nature of Science section 2 Standards of Measurement Before You Read If someone asked you how wide your desk is, how would you measure it? Would you measure using inches, centimeters, feet,
MMSTC AP PHYSICS REVEIW
 1) Which section of the following velocity vs. time graph shows the greatest displacement? 2) Which section of the Velocity vs. time graph above displays a change in direction? 3) Which section of the
1) Which section of the following velocity vs. time graph shows the greatest displacement? 2) Which section of the Velocity vs. time graph above displays a change in direction? 3) Which section of the
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension:
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension: Vector / Scaler Quantities Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Graphing Motion Distance vs Time Graphs Velocity vs Time Graphs Solving Problems Free Falling Objects
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension: Vector / Scaler Quantities Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Graphing Motion Distance vs Time Graphs Velocity vs Time Graphs Solving Problems Free Falling Objects
Activity 2 Mechanical Interactions and Motion Energy INTERACTIONS AND ENERGY. What changes in motion energy occur? The car s motion energy increases.
 Activity 2 Interactions and Motion Energy Activity 2: Interactions and Motion Energy Use How To Identify Interactions to create and complete a interactions chart for the 11 events described below. Use
Activity 2 Interactions and Motion Energy Activity 2: Interactions and Motion Energy Use How To Identify Interactions to create and complete a interactions chart for the 11 events described below. Use
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes
 Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
