Lab 6: Linear Algebra
|
|
|
- Myrtle Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6.1 Introduction Lab 6: Linear Algebra This lab is aimed at demonstrating Python s ability to solve linear algebra problems. At the end of the assignment, you should be able to write code that sets up and solves linear algebra problems for both a single set of coefficients and solutions as well as an array of situations. You should also be able to determine the condition of the linear system and understand how that relates to the accuracy of the results. 6.2 Resources The additional resources required for this assignment include: 0 Books: Chapra 0 Pratt Pundit Pages: Python:Linear Algebra 6.3 Getting Started 1. Log into one of the PCs in the lab using your NetId. Be sure it is set to log on to WIN. 2. In Windows: (a) Mount your CIFS drive. For instructions, start a browser and point it to: To Get Work Done Then click the link for File Access under Your Own Windows Computer. Note the comments on Pundit modifying what the OIT page instructions say. (b) Start a terminal with graphics. For instructions, point a browser to Check out the Using the PCs to Run Unix Programs Remotely section for how to get connected and make sure the connection is working. (c) Start Spyder. In the Windows menu, there is a group for Anaconda3; Spyder is in that group. If the PC asks for network permissions, click cancel. If the PC asks about updating, do not update. 3. In the terminal window (i.e. in UNIX; note the represents a space): (a) Change into your folder for EGR 103L, create a lab6 folder inside it, then switch into that folder: cd /EGR103 mkdir lab6 cd lab6 (b) Copy the tar file from Dr. G s space into your lab6 folder and expand the tar file: wget people.duke.edu/ mrg/egr103public/lab6files.tar tar -kxvf Lab6Files.tar (c) Make a personal copy of the lab report skeleton: cp -i Lab6Sample S19.tex lab6.tex 6 1
2 6.4 Ungraded 0 Chapra Chapter 8 problems 2, 3, 4 0 Chapra Chapter 11 problems 1, Assignment Based on Chapra Problem 8.3, p. 244 First, re-cast the problem as a matrix equation: A x = b??? x 1???? x 2 =????? then write a Python script to solve for the unknowns. Compute both the transpose and inverse of the [A] matrix. Also, calculate the condition number of the system using the 1-norm, the 2-norm, the Frobenius norm, and the -norm - read Sections through in Chapra for information on norms and condition numbers. Typeset the matrix equation, the transpose, and the inverse in your lab report. Also report the values of the unknowns and the condition numbers in some professional-looking way. State what the values of the condition numbers mean with respect to the accuracy of your answer relative to the accuracy of the coefficients in the matrix (Hint: Seriously - read of Chapra ). For all non-integer values, use four significant figures (scientific notation preferred but not required). Note that L A TEX with the amsmath package gives you some excellent tools for typesetting matrix equations. The equations above, for example, were typeset with: \ begin { align *} \ begin { bmatrix }{\ mathbf A}\ end { bmatrix } \ begin { bmatrix }{\ mathbf x}\ end { bmatrix }&= \ begin { bmatrix }{\ mathbf b}\ end { bmatrix }\\ \ begin { bmatrix }? &? &? \\? &? &? \\? &? &? \ end { bmatrix } \ begin { bmatrix } ~ x_1 ~ \\ x_2 \\ x_3 \ end { bmatrix }&= \ begin { bmatrix }? \\? \\? \ end { bmatrix } \ end { align *} x 3 6 2
3 6.5.2 Chapra 8.10, pp Typo notification: Figure P8.10 incorrectly has the force at node 1 as 1000 N down; it should be 2000 N down. Be sure to use N for F 1 v when solving. Rewrite the equations symbolically in matrix form as: cos(30 o ) 0 cos(60 o ) F 1 F 1 h F 2? F 3? = H 2? V 2?? Typeset these symbolic equations in your lab report, leaving the six external forces F 1 h through F 3 v as symbols rather than the specific values in the program. Note: in your lab report you can have italicized subscripts like F 1 h and F 3 v. The first equation has been done for you. Next write a Python script that will solve for the six unknowns in this problem. Your program should print the results to the screen with the format below (these numbers come from the same truss but using different external force values and thus are not what your program will get): F1: e +02 N F2: e +03 N F3: e +03 N H2: e +03 N V2: e +03 N V3: e +02 N Note that the format command is not especially fond of 2-D arrays. Somewhere in your code you will likely have a line like: s o l n v e c = s o l n [ :, 0 ] to copy your 2-D solution array into a 1-D array and then will use soln_vec in your format() commands. If you get an error unsupported format string passed to numpy. ndarray. format you are trying to give an array, rather than a value, to the string. See if you can figure out how to print these six items in a loop rather than with six different print commands. Look at the following code to see how it works: names = [ alpha, beta, gamma, d e l t a ] v a l s = [ 3, 1, 4, 2 ] for k in range ( l e n ( names ) ) : print ( { : 5 s } : { : 2 d}. format ( names [ k ], v a l s [ k ] ) ) and adapt it as needed. Finally, add code to your script that uses open, write, and close to write a table like the one above into a text file called truss_data.txt. If you are printing in a loop, you should only need to open the file before the loop, close the file after the loop, and write to the file with one command in the loop. The L A TEX code to bring the text from that file into your lab report is in the skeleton (but commented out). The matrix equations and the table should be in the body of the lab report while the code will be in the appendix. V 3 6 3
4 6.5.3 Based Loosely on Chapra 8.16, pp Important Note: Your Python function will not be doing the plotting - your function will instead just be returning a set of rotated coordinates. The main part of your script will be doing the plotting To rotate a set of coordinates, you will pre-multiply a block matrix with the coordinates by the rotation matrix. Imagine you have some original point at (x y). That point will be at some distance r from the origin and will make some angle φ from the x axis such that: x = r cos(φ) y = r sin(φ) Now imagine you rotate the point some positive angle θ along the circle described by r from the original coordinates to some new set of coordinates (x r y r ). Figure 6.1 on page 6 6 shows both the original and rotated points. The new coordinates are at an angle φ + θ from the x axis. The coordinates for the new point can be calculated as: x r = r cos(φ + θ) y r = r sin(φ + θ) x r = r(cos(φ) cos(θ) sin(φ) sin(θ)) x r = x cos(θ) y sin(θ) y r = r(cos(φ) sin(θ) + sin(φ) cos(θ)) y r = x sin(θ) + y cos(θ) This can be written in matrix form as: x r = cos(θ) sin(θ) y r sin(θ) x = R cos(θ) y x y where the rotation matrix R is given by: cos(θ) sin(θ) sin(θ) cos(θ) To expand this to rotating multiple points simultaneously, imagine you have 1-D arrays of x and y coordinates: x = [x 1 x 2 x 3...] y = [y 1 y 2 y 3...] If you build a block matrix (i.e. a 2-D array) from them: Coords = x = x 1 x 2 x 3... y y 1 y 2 y 3... you can rotate the entire set of coordinates by pre-multiplying the coordinates matrix by a rotation matrix: New Coords = R Coords New Coords = cos(θ) sin(θ) x 1 x 2 x 3... sin(θ) cos(θ) y 1 y 2 y 3... You will then just need to extract each row from the new coordinates into an array. 0 In a script called chapra_08_16.py, define a function called rotate_2d that takes three arguments - an angle (in degrees), a 1-D array of x coordinates, and a 1-D array of y coordinates, and returns two 1-D arrays: a 1-D array of rotated x coordinates and a 1-D array of rotated y coordinates. Test your program with some easily-calculated rotations. For instance, if you rotate a point by 0 or 360 or 360*n degrees where n is an integer, you should end up at the same location. You should also be able to figure out what happens when you rotate (x 0) or (0 y) by 90*n degrees so test with those. You can put your tests in the main if tree in your script. 0 Run the test_chapra_08_16.py file to make sure your function is correctly rotating the coordinates defining the square in the problem. The tester code will rotate the square by integer multiples of 30 o. It will make a plot with all the rotated squares shown. Note that the color kwarg takes a list of three numbers between 0 and 1; these numbers represent how much red, green and blue to put in the plot. 6 4
5 0 Make art by coming up with the coordinates for some shape then using code similar to the test_chapra_08_16.py code (call the script creative_chapra_08_16.py) to draw several copies of your shape rotated around a full circle in some number of steps. Get creative You can even change the colors of each copy if you would like The example in Fig. 6.2 is a skewed octagon copied 12 times with the colors determined by the angle. Include your chapra_08_16.py and creative_chapra_08_16.py files in the lab report along with the art you made Parameter Sweep 1: Changing...Constant For this problem, you will be taking the code from Case Study 8.3 in Chapra and writing a script that graphs how current flowing from node 5 to node 2 changes as the voltage drop between nodes 1 and 6 changes. Your program will sweep through 101 linearly spaced voltages between 0 V and 400 V, solving for all the currents each time and storing the solution for i 52 in either an array or a list. After performing all the calculations, you will produce a graph of the current as a function of the voltage. Use a solid purple line for the voltage (I use purple for voltages in my classes). Add a grid and proper axis labels, including units. See Chapra Figure 1.2 on page 8 for how to label a graph with a variable name and units. You do not need a title or a legend. As a quick check, the current in index 50 of your list or array should match the i 53 current in the case study since the 50th voltage value in the linearly spaced array is 200 V; that current is as given in the second entry of the current array on p In the body of the lab report you will describe generally how the voltage value impacts the current Parameter Sweep 2: Changing Coefficient For this problem, you will be taking the code from Case Study 8.3 in Chapra and writing a script that graphs how current flowing from node 5 to node 2 changes as the resistance between nodes 5 and 2 changes. You will use an applied voltage of 200 V for this as given in the original problem. Your program will sweep through 201 (i.e. 100 more than 101) linearly spaced resistances between 0 Ω and 100 Ω, solving for all the currents each time and storing the solution for i 52 in either an array or a list. You will also be calculating the 2-norm based condition number of the coefficient matrix and storing that in an array or a list. After performing all the calculations, you will produce a graph of the current as a function of the resistance and another graph of the base-10 logarithm of the condition number as a function of the resistance. Use a solid orange line for the current (I use orange for current in my classes) and a solid black line for the condition numbers. For each graph, add a grid and proper axis labels, including units. You can get the symbol for Ω in your axis labels by putting the L A TEX command for capital omega between dollar signs in the label command; for instance, p l t. x l a b e l ( 1\Omega1 ) will put the Ω all by itself. See Chapra Figure 1.2 on page 8 for how to label a graph with a variable name and units. Note that the condition number is dimensionless. You do not need a title or a legend. As a quick check, the current in index 20 of your list or array should match the current in the case study since the 20th resistance value in the linearly spaced array is 10 Ω. In the body of the lab report you will describe generally how the resistance value impacts the current and the condition number. 6 5
6 Figure 6.1: A point and a rotated point Figure 6.2: Something creative 6 6
LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
Coulomb s Law Mini-Lab
 Setup Name Per Date Coulomb s Law Mini-Lab On a fresh piece of notebook paper, write the above title, name, date, and period. Be sure to put all headings, Roman numerals and regular numbers on your paper.
Setup Name Per Date Coulomb s Law Mini-Lab On a fresh piece of notebook paper, write the above title, name, date, and period. Be sure to put all headings, Roman numerals and regular numbers on your paper.
Remember that C is a constant and ë and n are variables. This equation now fits the template of a straight line:
 CONVERTING NON-LINEAR GRAPHS INTO LINEAR GRAPHS Linear graphs have several important attributes. First, it is easy to recognize a graph that is linear. It is much more difficult to identify if a curved
CONVERTING NON-LINEAR GRAPHS INTO LINEAR GRAPHS Linear graphs have several important attributes. First, it is easy to recognize a graph that is linear. It is much more difficult to identify if a curved
You will return this handout to the instructor at the end of the lab period. Experimental verification of Ampere s Law.
 PHY222 LAB 6 AMPERE S LAW Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names Instructions Read section A prior to attending your lab section. You will return this handout to the instructor at the end of the lab
PHY222 LAB 6 AMPERE S LAW Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names Instructions Read section A prior to attending your lab section. You will return this handout to the instructor at the end of the lab
LAB 1: MATLAB - Introduction to Programming. Objective:
 LAB 1: MATLAB - Introduction to Programming Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to review how to use MATLAB as a programming tool and to review a classic analytical solution to a steady-state
LAB 1: MATLAB - Introduction to Programming Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to review how to use MATLAB as a programming tool and to review a classic analytical solution to a steady-state
PHYSICS 211 LAB #3: Frictional Forces
 PHYSICS 211 LAB #3: Frictional Forces A Lab Consisting of 4 Activities Name: Section: TA: Date: Lab Partners: Circle the name of the person to whose report your group printouts will be attached. Individual
PHYSICS 211 LAB #3: Frictional Forces A Lab Consisting of 4 Activities Name: Section: TA: Date: Lab Partners: Circle the name of the person to whose report your group printouts will be attached. Individual
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ. EGR 103L Fall Test 2. Michael R. Gustafson II
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 103L Fall 2017 Test 2 Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) NET ID (please print): In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 103L Fall 2017 Test 2 Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) NET ID (please print): In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided
Lab 13: Ordinary Differential Equations
 EGR 53L - Fall 2009 Lab 13: Ordinary Differential Equations 13.1 Introduction This lab is aimed at introducing techniques for solving initial-value problems involving ordinary differential equations using
EGR 53L - Fall 2009 Lab 13: Ordinary Differential Equations 13.1 Introduction This lab is aimed at introducing techniques for solving initial-value problems involving ordinary differential equations using
ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK
 ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK What is SIMULINK? SIMULINK is a software package for modeling, simulating, and analyzing
ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK What is SIMULINK? SIMULINK is a software package for modeling, simulating, and analyzing
Zeeman Effect Physics 481
 Zeeman Effect Introduction You are familiar with Atomic Spectra, especially the H- atom energy spectrum. Atoms emit or absorb energies in packets, or quanta which are photons. The orbital motion of electrons
Zeeman Effect Introduction You are familiar with Atomic Spectra, especially the H- atom energy spectrum. Atoms emit or absorb energies in packets, or quanta which are photons. The orbital motion of electrons
Calculating Bond Enthalpies of the Hydrides
 Proposed Exercise for the General Chemistry Section of the Teaching with Cache Workbook: Calculating Bond Enthalpies of the Hydrides Contributed by James Foresman, Rachel Fogle, and Jeremy Beck, York College
Proposed Exercise for the General Chemistry Section of the Teaching with Cache Workbook: Calculating Bond Enthalpies of the Hydrides Contributed by James Foresman, Rachel Fogle, and Jeremy Beck, York College
Capacitors GOAL. EQUIPMENT. CapacitorDecay.cmbl 1. Building a Capacitor
 PHYSICS EXPERIMENTS 133 Capacitor 1 Capacitors GOAL. To measure capacitance with a digital multimeter. To make a simple capacitor. To determine and/or apply the rules for finding the equivalent capacitance
PHYSICS EXPERIMENTS 133 Capacitor 1 Capacitors GOAL. To measure capacitance with a digital multimeter. To make a simple capacitor. To determine and/or apply the rules for finding the equivalent capacitance
1-D Convection-Diffusion Lab
 Computational Fluid Dynamics -D Convection-Diffusion Lab The lab. uses scientificworkplace symbolic calculus and maths editor software (SWP) This file Concevtion-Diffusion-Lab is available from Blackboard
Computational Fluid Dynamics -D Convection-Diffusion Lab The lab. uses scientificworkplace symbolic calculus and maths editor software (SWP) This file Concevtion-Diffusion-Lab is available from Blackboard
Figure 1: Capacitor circuit
 Capacitors INTRODUCTION The basic function of a capacitor 1 is to store charge and thereby electrical energy. This energy can be retrieved at a later time for a variety of uses. Often, multiple capacitors
Capacitors INTRODUCTION The basic function of a capacitor 1 is to store charge and thereby electrical energy. This energy can be retrieved at a later time for a variety of uses. Often, multiple capacitors
CS1110 Lab 3 (Feb 10-11, 2015)
 CS1110 Lab 3 (Feb 10-11, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: The lab assignments are very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness does not matter.)
CS1110 Lab 3 (Feb 10-11, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: The lab assignments are very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness does not matter.)
Lab 1 Uniform Motion - Graphing and Analyzing Motion
 Lab 1 Uniform Motion - Graphing and Analyzing Motion Objectives: < To observe the distance-time relation for motion at constant velocity. < To make a straight line fit to the distance-time data. < To interpret
Lab 1 Uniform Motion - Graphing and Analyzing Motion Objectives: < To observe the distance-time relation for motion at constant velocity. < To make a straight line fit to the distance-time data. < To interpret
Assignment 5 Bounding Complexities KEY
 Assignment 5 Bounding Complexities KEY Print this sheet and fill in your answers. Please staple the sheets together. Turn in at the beginning of class on Friday, September 16. There are links in the examples
Assignment 5 Bounding Complexities KEY Print this sheet and fill in your answers. Please staple the sheets together. Turn in at the beginning of class on Friday, September 16. There are links in the examples
Lab 2 Worksheet. Problems. Problem 1: Geometry and Linear Equations
 Lab 2 Worksheet Problems Problem : Geometry and Linear Equations Linear algebra is, first and foremost, the study of systems of linear equations. You are going to encounter linear systems frequently in
Lab 2 Worksheet Problems Problem : Geometry and Linear Equations Linear algebra is, first and foremost, the study of systems of linear equations. You are going to encounter linear systems frequently in
Getting to the Roots of Quadratics
 NAME BACKGROUND Graphically: The real roots of a function are the x-coordinates of the points at which the graph of the function intercepts/crosses the x-axis. For a quadratic function, whose graph is
NAME BACKGROUND Graphically: The real roots of a function are the x-coordinates of the points at which the graph of the function intercepts/crosses the x-axis. For a quadratic function, whose graph is
ISIS/Draw "Quick Start"
 ISIS/Draw "Quick Start" Click to print, or click Drawing Molecules * Basic Strategy 5.1 * Drawing Structures with Template tools and template pages 5.2 * Drawing bonds and chains 5.3 * Drawing atoms 5.4
ISIS/Draw "Quick Start" Click to print, or click Drawing Molecules * Basic Strategy 5.1 * Drawing Structures with Template tools and template pages 5.2 * Drawing bonds and chains 5.3 * Drawing atoms 5.4
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 CSE2330 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Basic computational tools and concepts Tutorial 1 Duration: two weeks 1.1 About this tutorial The objective of this tutorial is to introduce you to: the
CSE2330 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Basic computational tools and concepts Tutorial 1 Duration: two weeks 1.1 About this tutorial The objective of this tutorial is to introduce you to: the
M E R C E R W I N WA L K T H R O U G H
 H E A L T H W E A L T H C A R E E R WA L K T H R O U G H C L I E N T S O L U T I O N S T E A M T A B L E O F C O N T E N T 1. Login to the Tool 2 2. Published reports... 7 3. Select Results Criteria...
H E A L T H W E A L T H C A R E E R WA L K T H R O U G H C L I E N T S O L U T I O N S T E A M T A B L E O F C O N T E N T 1. Login to the Tool 2 2. Published reports... 7 3. Select Results Criteria...
Experiment A11 Chaotic Double Pendulum Procedure
 AME 21216: Lab I Fall 2017 Experiment A11 Chaotic Double Pendulum Procedure Deliverables: Checked lab notebook, plots with captions Background Measuring and controlling the angular position and velocity
AME 21216: Lab I Fall 2017 Experiment A11 Chaotic Double Pendulum Procedure Deliverables: Checked lab notebook, plots with captions Background Measuring and controlling the angular position and velocity
Trigonometry LESSON SIX - Trigonometric Identities I Lesson Notes
 LESSON SIX - Trigonometric Identities I Example Understanding Trigonometric Identities. a) Why are trigonometric identities considered to be a special type of trigonometric equation? Trigonometric Identities
LESSON SIX - Trigonometric Identities I Example Understanding Trigonometric Identities. a) Why are trigonometric identities considered to be a special type of trigonometric equation? Trigonometric Identities
University of TN Chattanooga Physics 1040L 8/18/2012 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 4: R.C. TIME CONSTANT LAB
 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 4: R.C. TIME CONSTANT LAB OBJECT: To study the discharging of a capacitor and determine the time constant for a simple circuit. APPARATUS: Capacitor (about 24 μf), two resistors (about
PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 4: R.C. TIME CONSTANT LAB OBJECT: To study the discharging of a capacitor and determine the time constant for a simple circuit. APPARATUS: Capacitor (about 24 μf), two resistors (about
On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work
 Lab 5 : Linking Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of this lab is to experiment
Lab 5 : Linking Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of this lab is to experiment
Project 2: Using linear systems for numerical solution of boundary value problems
 LINEAR ALGEBRA, MATH 124 Instructor: Dr. T.I. Lakoba Project 2: Using linear systems for numerical solution of boundary value problems Goal Introduce one of the most important applications of Linear Algebra
LINEAR ALGEBRA, MATH 124 Instructor: Dr. T.I. Lakoba Project 2: Using linear systems for numerical solution of boundary value problems Goal Introduce one of the most important applications of Linear Algebra
Linear Motion with Constant Acceleration
 Linear Motion 1 Linear Motion with Constant Acceleration Overview: First you will attempt to walk backward with a constant acceleration, monitoring your motion with the ultrasonic motion detector. Then
Linear Motion 1 Linear Motion with Constant Acceleration Overview: First you will attempt to walk backward with a constant acceleration, monitoring your motion with the ultrasonic motion detector. Then
Using Microsoft Excel
 Using Microsoft Excel Objective: Students will gain familiarity with using Excel to record data, display data properly, use built-in formulae to do calculations, and plot and fit data with linear functions.
Using Microsoft Excel Objective: Students will gain familiarity with using Excel to record data, display data properly, use built-in formulae to do calculations, and plot and fit data with linear functions.
Modeling the Motion of a Projectile in Air
 In this lab, you will do the following: Modeling the Motion of a Projectile in Air analyze the motion of an object fired from a cannon using two different fundamental physics principles: the momentum principle
In this lab, you will do the following: Modeling the Motion of a Projectile in Air analyze the motion of an object fired from a cannon using two different fundamental physics principles: the momentum principle
PHYSICS LAB FREE FALL. Date: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY
 PHYSICS LAB FREE FALL Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Free Fall FREE FALL Part A Error Analysis of Reaction
PHYSICS LAB FREE FALL Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Free Fall FREE FALL Part A Error Analysis of Reaction
Matrices and Vectors
 Matrices and Vectors James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 11, 2013 Outline 1 Matrices and Vectors 2 Vector Details 3 Matrix
Matrices and Vectors James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 11, 2013 Outline 1 Matrices and Vectors 2 Vector Details 3 Matrix
CHEMICAL INVENTORY ENTRY GUIDE
 CHEMICAL INVENTORY ENTRY GUIDE Version Date Comments 1 October 2013 Initial A. SUMMARY All chemicals located in research and instructional laboratories at George Mason University are required to be input
CHEMICAL INVENTORY ENTRY GUIDE Version Date Comments 1 October 2013 Initial A. SUMMARY All chemicals located in research and instructional laboratories at George Mason University are required to be input
Purpose: This lab is an experiment to verify Malus Law for polarized light in both a two and three polarizer system.
 Purpose: This lab is an experiment to verify Malus Law for polarized light in both a two and three polarizer system. The basic description of Malus law is given as I = I 0 (cos 2 θ ) Where I is the transmitted
Purpose: This lab is an experiment to verify Malus Law for polarized light in both a two and three polarizer system. The basic description of Malus law is given as I = I 0 (cos 2 θ ) Where I is the transmitted
first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date)
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 1 Capacitance In this Experiment you will learn the relationship between the voltage and charge stored on a capacitor;
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 1 Capacitance In this Experiment you will learn the relationship between the voltage and charge stored on a capacitor;
Solving Differential Equations on 2-D Geometries with Matlab
 Solving Differential Equations on 2-D Geometries with Matlab Joshua Wall Drexel University Philadelphia, PA 19104 (Dated: April 28, 2014) I. INTRODUCTION Here we introduce the reader to solving partial
Solving Differential Equations on 2-D Geometries with Matlab Joshua Wall Drexel University Philadelphia, PA 19104 (Dated: April 28, 2014) I. INTRODUCTION Here we introduce the reader to solving partial
LAST TIME..THE COMMAND LINE
 LAST TIME..THE COMMAND LINE Maybe slightly to fast.. Finder Applications Utilities Terminal The color can be adjusted and is simply a matter of taste. Per default it is black! Dr. Robert Kofler Introduction
LAST TIME..THE COMMAND LINE Maybe slightly to fast.. Finder Applications Utilities Terminal The color can be adjusted and is simply a matter of taste. Per default it is black! Dr. Robert Kofler Introduction
Computer simulation of radioactive decay
 Computer simulation of radioactive decay y now you should have worked your way through the introduction to Maple, as well as the introduction to data analysis using Excel Now we will explore radioactive
Computer simulation of radioactive decay y now you should have worked your way through the introduction to Maple, as well as the introduction to data analysis using Excel Now we will explore radioactive
Matrix-Vector Operations
 Week3 Matrix-Vector Operations 31 Opening Remarks 311 Timmy Two Space View at edx Homework 3111 Click on the below link to open a browser window with the Timmy Two Space exercise This exercise was suggested
Week3 Matrix-Vector Operations 31 Opening Remarks 311 Timmy Two Space View at edx Homework 3111 Click on the below link to open a browser window with the Timmy Two Space exercise This exercise was suggested
Date: Summer Stem Section:
 Page 1 of 7 Name: Date: Summer Stem Section: Summer assignment: Build a Molecule Computer Simulation Learning Goals: 1. Students can describe the difference between a molecule name and chemical formula.
Page 1 of 7 Name: Date: Summer Stem Section: Summer assignment: Build a Molecule Computer Simulation Learning Goals: 1. Students can describe the difference between a molecule name and chemical formula.
Lab 2: Static Response, Cantilevered Beam
 Contents 1 Lab 2: Static Response, Cantilevered Beam 3 1.1 Objectives.......................................... 3 1.2 Scalars, Vectors and Matrices (Allen Downey)...................... 3 1.2.1 Attribution.....................................
Contents 1 Lab 2: Static Response, Cantilevered Beam 3 1.1 Objectives.......................................... 3 1.2 Scalars, Vectors and Matrices (Allen Downey)...................... 3 1.2.1 Attribution.....................................
Temperature measurement
 Luleå University of Technology Johan Carlson Last revision: July 22, 2009 Measurement Technology and Uncertainty Analysis - E7021E Lab 3 Temperature measurement Introduction In this lab you are given a
Luleå University of Technology Johan Carlson Last revision: July 22, 2009 Measurement Technology and Uncertainty Analysis - E7021E Lab 3 Temperature measurement Introduction In this lab you are given a
Lab Objective: Introduce some of the basic optimization functions available in the CVXOPT package
 Lab 14 CVXOPT Lab Objective: Introduce some of the basic optimization functions available in the CVXOPT package Notebox: CVXOPT is not part of the standard library, nor is it included in the Anaconda distribution.
Lab 14 CVXOPT Lab Objective: Introduce some of the basic optimization functions available in the CVXOPT package Notebox: CVXOPT is not part of the standard library, nor is it included in the Anaconda distribution.
LAB Exercise #4 - Answers The Traction Vector and Stress Tensor. Introduction. Format of lab. Preparation reading
 LAB Exercise #4 - Answers The Traction Vector and Stress Tensor Due: Thursday, 26 February 2009 (Special Thanks to D.D. Pollard who pioneered this exercise in 1991) Introduction Stress concentrations in
LAB Exercise #4 - Answers The Traction Vector and Stress Tensor Due: Thursday, 26 February 2009 (Special Thanks to D.D. Pollard who pioneered this exercise in 1991) Introduction Stress concentrations in
EEE161 Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory 1
 Dr. Milica Marković Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory page 1 EEE161 Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory 1 Instructor: Dr. Milica Marković Office: Riverside Hall 3028 Email: milica@csus.edu Web:http://gaia.ecs.csus.edu/
Dr. Milica Marković Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory page 1 EEE161 Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory 1 Instructor: Dr. Milica Marković Office: Riverside Hall 3028 Email: milica@csus.edu Web:http://gaia.ecs.csus.edu/
Determination of Density 1
 Introduction Determination of Density 1 Authors: B. D. Lamp, D. L. McCurdy, V. M. Pultz and J. M. McCormick* Last Update: February 1, 2013 Not so long ago a statistical data analysis of any data set larger
Introduction Determination of Density 1 Authors: B. D. Lamp, D. L. McCurdy, V. M. Pultz and J. M. McCormick* Last Update: February 1, 2013 Not so long ago a statistical data analysis of any data set larger
Math Refresher Answer Sheet (NOTE: Only this answer sheet and the following graph will be evaluated)
 Name: Score: / 50 Math Refresher Answer Sheet (NOTE: Only this answer sheet and the following graph will be evaluated) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. MAKE SURE CALCULATOR
Name: Score: / 50 Math Refresher Answer Sheet (NOTE: Only this answer sheet and the following graph will be evaluated) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. MAKE SURE CALCULATOR
Richter Scale and Logarithms
 activity 7.1 Richter Scale and Logarithms In this activity, you will investigate earthquake data and explore the Richter scale as a measure of the intensity of an earthquake. You will consider how numbers
activity 7.1 Richter Scale and Logarithms In this activity, you will investigate earthquake data and explore the Richter scale as a measure of the intensity of an earthquake. You will consider how numbers
Electric Field. Lab 4: Part 1: Electric Field from One Point Charge. Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name:
 Lab 4: Electric Field Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Simulation link: http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/charges-and-fields/charges-and-fields_en.html Type Charges and Fields PHET in Google and click
Lab 4: Electric Field Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Simulation link: http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/charges-and-fields/charges-and-fields_en.html Type Charges and Fields PHET in Google and click
HW5 computer problem: modelling a dye molecule Objectives By the end of this lab you should: Know how to manipulate complex numbers and matrices. Prog
 HW5 computer problem: modelling a dye molecule Objectives By the end of this lab you should: Know how to manipulate complex numbers and matrices. Programming environment: Spyder. To implement this, do
HW5 computer problem: modelling a dye molecule Objectives By the end of this lab you should: Know how to manipulate complex numbers and matrices. Programming environment: Spyder. To implement this, do
Using SkyTools to log Texas 45 list objects
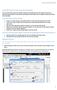 Houston Astronomical Society Using SkyTools to log Texas 45 list objects You can use SkyTools to keep track of objects observed in Columbus and copy the output into the Texas 45 observation log. Preliminary
Houston Astronomical Society Using SkyTools to log Texas 45 list objects You can use SkyTools to keep track of objects observed in Columbus and copy the output into the Texas 45 observation log. Preliminary
Driven Harmonic Oscillator
 Driven Harmonic Oscillator Physics 6B Lab Experiment 1 APPARATUS Computer and interface Mechanical vibrator and spring holder Stands, etc. to hold vibrator Motion sensor C-209 spring Weight holder and
Driven Harmonic Oscillator Physics 6B Lab Experiment 1 APPARATUS Computer and interface Mechanical vibrator and spring holder Stands, etc. to hold vibrator Motion sensor C-209 spring Weight holder and
Lecture 5b: Starting Matlab
 Lecture 5b: Starting Matlab James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University August 7, 2013 Outline 1 Resources 2 Starting Matlab 3 Homework
Lecture 5b: Starting Matlab James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University August 7, 2013 Outline 1 Resources 2 Starting Matlab 3 Homework
Describing the Relationship between Two Variables
 1 Describing the Relationship between Two Variables Key Definitions Scatter : A graph made to show the relationship between two different variables (each pair of x s and y s) measured from the same equation.
1 Describing the Relationship between Two Variables Key Definitions Scatter : A graph made to show the relationship between two different variables (each pair of x s and y s) measured from the same equation.
Lab 1: Dynamic Simulation Using Simulink and Matlab
 Lab 1: Dynamic Simulation Using Simulink and Matlab Objectives In this lab you will learn how to use a program called Simulink to simulate dynamic systems. Simulink runs under Matlab and uses block diagrams
Lab 1: Dynamic Simulation Using Simulink and Matlab Objectives In this lab you will learn how to use a program called Simulink to simulate dynamic systems. Simulink runs under Matlab and uses block diagrams
Lectures about Python, useful both for beginners and experts, can be found at (http://scipy-lectures.github.io).
 Random Matrix Theory (Sethna, "Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity", ex. 1.6, developed with Piet Brouwer) 2016, James Sethna, all rights reserved. This is an ipython notebook. This hints file is
Random Matrix Theory (Sethna, "Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity", ex. 1.6, developed with Piet Brouwer) 2016, James Sethna, all rights reserved. This is an ipython notebook. This hints file is
Lab 10: DC RC circuits
 Name: Lab 10: DC RC circuits Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Objectives: 1. To understand current and voltage characteristics of a DC RC circuit 2. To understand the effect of the RC time constant Apparatus:
Name: Lab 10: DC RC circuits Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Objectives: 1. To understand current and voltage characteristics of a DC RC circuit 2. To understand the effect of the RC time constant Apparatus:
Matlab Instruction Primer; Chem 691, Spring 2016
 1 Matlab Instruction Primer; Chem 691, Spring 2016 This version dated February 10, 2017 CONTENTS I. Help: To obtain information about any instruction in Matlab 1 II. Scripting 1 III. Loops, determine an
1 Matlab Instruction Primer; Chem 691, Spring 2016 This version dated February 10, 2017 CONTENTS I. Help: To obtain information about any instruction in Matlab 1 II. Scripting 1 III. Loops, determine an
MATH EVALUATION. What will you learn in this Lab?
 MATH EVALUATION What will you learn in this Lab? This exercise is designed to assess whether you have been exposed to the mathematical methods and skills necessary to complete the lab exercises you will
MATH EVALUATION What will you learn in this Lab? This exercise is designed to assess whether you have been exposed to the mathematical methods and skills necessary to complete the lab exercises you will
Electric Fields and Equipotentials
 OBJECTIVE Electric Fields and Equipotentials To study and describe the two-dimensional electric field. To map the location of the equipotential surfaces around charged electrodes. To study the relationship
OBJECTIVE Electric Fields and Equipotentials To study and describe the two-dimensional electric field. To map the location of the equipotential surfaces around charged electrodes. To study the relationship
Winter 2014 Practice Final 3/21/14 Student ID
 Math 4C Winter 2014 Practice Final 3/21/14 Name (Print): Student ID This exam contains 5 pages (including this cover page) and 20 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter all requested information
Math 4C Winter 2014 Practice Final 3/21/14 Name (Print): Student ID This exam contains 5 pages (including this cover page) and 20 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter all requested information
Matrix-Vector Operations
 Week3 Matrix-Vector Operations 31 Opening Remarks 311 Timmy Two Space View at edx Homework 3111 Click on the below link to open a browser window with the Timmy Two Space exercise This exercise was suggested
Week3 Matrix-Vector Operations 31 Opening Remarks 311 Timmy Two Space View at edx Homework 3111 Click on the below link to open a browser window with the Timmy Two Space exercise This exercise was suggested
PreLab 2 - Simple Harmonic Motion: Pendulum (adapted from PASCO- PS-2826 Manual)
 Musical Acoustics Lab, C. Bertulani, 2012 PreLab 2 - Simple Harmonic Motion: Pendulum (adapted from PASCO- PS-2826 Manual) A body is said to be in a position of stable equilibrium if, after displacement
Musical Acoustics Lab, C. Bertulani, 2012 PreLab 2 - Simple Harmonic Motion: Pendulum (adapted from PASCO- PS-2826 Manual) A body is said to be in a position of stable equilibrium if, after displacement
Experiment 14 It s Snow Big Deal
 Experiment 14 It s Snow Big Deal OUTCOMES After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: use computer-based data acquisition techniques to measure temperatures. draw appropriate conclusions
Experiment 14 It s Snow Big Deal OUTCOMES After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: use computer-based data acquisition techniques to measure temperatures. draw appropriate conclusions
Lab 5 - Capacitors and RC Circuits
 Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits L51 Name Date Partners Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits OBJECTIVES To define capacitance and to learn to measure it with a digital multimeter. To explore how the capacitance
Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits L51 Name Date Partners Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits OBJECTIVES To define capacitance and to learn to measure it with a digital multimeter. To explore how the capacitance
2. In words, what is electrical current? 3. Try measuring the current at various points of the circuit using an ammeter.
 PS 12b Lab 1a Fun with Circuits Lab 1a Learning Goal: familiarize students with the concepts of current, voltage, and their measurement. Warm Up: A.) Given a light bulb, a battery, and single copper wire,
PS 12b Lab 1a Fun with Circuits Lab 1a Learning Goal: familiarize students with the concepts of current, voltage, and their measurement. Warm Up: A.) Given a light bulb, a battery, and single copper wire,
Experiment 1: Linear Regression
 Experiment 1: Linear Regression August 27, 2018 1 Description This first exercise will give you practice with linear regression. These exercises have been extensively tested with Matlab, but they should
Experiment 1: Linear Regression August 27, 2018 1 Description This first exercise will give you practice with linear regression. These exercises have been extensively tested with Matlab, but they should
Test 2 Solutions - Python Edition
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 103L Fall 2017 Test 2 Solutions - Python Edition Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) NET ID (please print): In keeping with the Community Standard,
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ EGR 103L Fall 2017 Test 2 Solutions - Python Edition Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) NET ID (please print): In keeping with the Community Standard,
Joy Allen. March 12, 2015
 LATEX Newcastle University March 12, 2015 Why use L A TEX? Extremely useful tool for writing scientific papers, presentations and PhD Thesis which are heavily laden with mathematics You get lovely pretty
LATEX Newcastle University March 12, 2015 Why use L A TEX? Extremely useful tool for writing scientific papers, presentations and PhD Thesis which are heavily laden with mathematics You get lovely pretty
Supplemental Activity: Vectors and Forces
 Supplemental Activity: Vectors and Forces Objective: To use a force table to test equilibrium conditions. Required Equipment: Force Table, Pasco Mass and Hanger Set, String, Ruler, Polar Graph Paper, Protractor,
Supplemental Activity: Vectors and Forces Objective: To use a force table to test equilibrium conditions. Required Equipment: Force Table, Pasco Mass and Hanger Set, String, Ruler, Polar Graph Paper, Protractor,
5-Sep-15 PHYS101-2 GRAPHING
 GRAPHING Objectives 1- To plot and analyze a graph manually and using Microsoft Excel. 2- To find constants from a nonlinear relation. Exercise 1 - Using Excel to plot a graph Suppose you have measured
GRAPHING Objectives 1- To plot and analyze a graph manually and using Microsoft Excel. 2- To find constants from a nonlinear relation. Exercise 1 - Using Excel to plot a graph Suppose you have measured
Companion. Jeffrey E. Jones
 MATLAB7 Companion 1O11OO1O1O1OOOO1O1OO1111O1O1OO 1O1O1OO1OO1O11OOO1O111O1O1O1O1 O11O1O1O11O1O1O1O1OO1O11O1O1O1 O1O1O1111O11O1O1OO1O1O1O1OOOOO O1111O1O1O1O1O1O1OO1OO1OO1OOO1 O1O11111O1O1O1O1O Jeffrey E.
MATLAB7 Companion 1O11OO1O1O1OOOO1O1OO1111O1O1OO 1O1O1OO1OO1O11OOO1O111O1O1O1O1 O11O1O1O11O1O1O1O1OO1O11O1O1O1 O1O1O1111O11O1O1OO1O1O1O1OOOOO O1111O1O1O1O1O1O1OO1OO1OO1OOO1 O1O11111O1O1O1O1O Jeffrey E.
August 7, 2007 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF LAPLACE'S EQUATION
 August 7, 007 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF LAPLACE'S EQUATION PURPOSE: This experiment illustrates the numerical solution of Laplace's Equation using a relaxation method. The results of the relaxation method
August 7, 007 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF LAPLACE'S EQUATION PURPOSE: This experiment illustrates the numerical solution of Laplace's Equation using a relaxation method. The results of the relaxation method
Lab #10 Atomic Radius Rubric o Missing 1 out of 4 o Missing 2 out of 4 o Missing 3 out of 4
 Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations 4.7 Relationships Among Elements Lab #10 Background Information The periodic table is a wonderful source of information about all of the elements
Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations 4.7 Relationships Among Elements Lab #10 Background Information The periodic table is a wonderful source of information about all of the elements
Lecture 3: Vectors. In Song Kim. September 1, 2011
 Lecture 3: Vectors In Song Kim September 1, 211 1 Solving Equations Up until this point we have been looking at different types of functions, often times graphing them. Each point on a graph is a solution
Lecture 3: Vectors In Song Kim September 1, 211 1 Solving Equations Up until this point we have been looking at different types of functions, often times graphing them. Each point on a graph is a solution
Experiment 10. Zeeman Effect. Introduction. Zeeman Effect Physics 244
 Experiment 10 Zeeman Effect Introduction You are familiar with Atomic Spectra, especially the H-atom energy spectrum. Atoms emit or absorb energies in packets, or quanta which are photons. The orbital
Experiment 10 Zeeman Effect Introduction You are familiar with Atomic Spectra, especially the H-atom energy spectrum. Atoms emit or absorb energies in packets, or quanta which are photons. The orbital
Geology Geomath Computer Lab Quadratics and Settling Velocities
 Geology 351 - Geomath Computer Lab Quadratics and Settling Velocities In Chapter 3 of Mathematics: A simple tool for geologists, Waltham takes us through a brief review of quadratic equations and their
Geology 351 - Geomath Computer Lab Quadratics and Settling Velocities In Chapter 3 of Mathematics: A simple tool for geologists, Waltham takes us through a brief review of quadratic equations and their
Problem 1 (10 points)
 y x CHEN 1703 - HOMEWORK 4 Submit your MATLAB solutions via the course web site. Be sure to include your name and UNID in your m-file. Submit each solution seperately. Also be sure to document your solutions
y x CHEN 1703 - HOMEWORK 4 Submit your MATLAB solutions via the course web site. Be sure to include your name and UNID in your m-file. Submit each solution seperately. Also be sure to document your solutions
MATH REFRESHER ANSWER SHEET (Note: Only this answer sheet and the following graph page will be evaluated)
 NAME: SCORE: /50 MATH REFRESHER ANSWER SHEET (Note: Only this answer sheet and the following graph page will be evaluated) 1. 23. 2. 24. 3. 25. 4. 26. 5. 27. 6. 28. 7. 29. 8. 30. 9. 31. 10. 32. 11. 33.
NAME: SCORE: /50 MATH REFRESHER ANSWER SHEET (Note: Only this answer sheet and the following graph page will be evaluated) 1. 23. 2. 24. 3. 25. 4. 26. 5. 27. 6. 28. 7. 29. 8. 30. 9. 31. 10. 32. 11. 33.
MAT 343 Laboratory 6 The SVD decomposition and Image Compression
 MA 4 Laboratory 6 he SVD decomposition and Image Compression In this laboratory session we will learn how to Find the SVD decomposition of a matrix using MALAB Use the SVD to perform Image Compression
MA 4 Laboratory 6 he SVD decomposition and Image Compression In this laboratory session we will learn how to Find the SVD decomposition of a matrix using MALAB Use the SVD to perform Image Compression
LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I. Objectives
 LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I Objectives to be able to discuss potential difference and current in a circuit in terms of electric field, work per unit charge and motion of charges to understand that
LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I Objectives to be able to discuss potential difference and current in a circuit in terms of electric field, work per unit charge and motion of charges to understand that
EXPERIMENT 2 Reaction Time Objectives Theory
 EXPERIMENT Reaction Time Objectives to make a series of measurements of your reaction time to make a histogram, or distribution curve, of your measured reaction times to calculate the "average" or mean
EXPERIMENT Reaction Time Objectives to make a series of measurements of your reaction time to make a histogram, or distribution curve, of your measured reaction times to calculate the "average" or mean
Analytic Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
Experiment 7 : Newton's Third Law
 Experiment 7 : Newton's Third Law To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction, or the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary parts. If you
Experiment 7 : Newton's Third Law To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction, or the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary parts. If you
Assignment 2. Signal Processing and Speech Communication Lab. Graz University of Technology
 Signal Processing and Speech Communication Lab. Graz University of Technology Assignment 2 This homework has to be submitted via e-mail to the address hw1.spsc@tugraz.at not later than 25.5.2016. Let the
Signal Processing and Speech Communication Lab. Graz University of Technology Assignment 2 This homework has to be submitted via e-mail to the address hw1.spsc@tugraz.at not later than 25.5.2016. Let the
1 Matrices and matrix algebra
 1 Matrices and matrix algebra 1.1 Examples of matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and/or variables. For instance 4 2 0 3 1 A = 5 1.2 0.7 x 3 π 3 4 6 27 is a matrix with 3 rows and 5 columns
1 Matrices and matrix algebra 1.1 Examples of matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and/or variables. For instance 4 2 0 3 1 A = 5 1.2 0.7 x 3 π 3 4 6 27 is a matrix with 3 rows and 5 columns
17-Nov-2015 PHYS MAXWELL WHEEL. To test the conservation of energy in a system with gravitational, translational and rotational energies.
 Objective MAXWELL WHEEL To test the conservation of energy in a system with gravitational, translational and rotational energies. Introduction A wheel is suspended by two cords wrapped on its axis. After
Objective MAXWELL WHEEL To test the conservation of energy in a system with gravitational, translational and rotational energies. Introduction A wheel is suspended by two cords wrapped on its axis. After
BASIC TECHNOLOGY Pre K starts and shuts down computer, monitor, and printer E E D D P P P P P P P P P P
 BASIC TECHNOLOGY Pre K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 starts and shuts down computer, monitor, and printer P P P P P P practices responsible use and care of technology devices P P P P P P opens and quits an
BASIC TECHNOLOGY Pre K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 starts and shuts down computer, monitor, and printer P P P P P P practices responsible use and care of technology devices P P P P P P opens and quits an
Complete all the identification fields below or 10% of the lab value will be deduced from your final mark for this lab.
 Simple circuits 3 hr Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you
Simple circuits 3 hr Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you
Introduction to ArcMap
 Introduction to ArcMap ArcMap ArcMap is a Map-centric GUI tool used to perform map-based tasks Mapping Create maps by working geographically and interactively Display and present Export or print Publish
Introduction to ArcMap ArcMap ArcMap is a Map-centric GUI tool used to perform map-based tasks Mapping Create maps by working geographically and interactively Display and present Export or print Publish
MATH0328: Numerical Linear Algebra Homework 3 SOLUTIONS
 MATH038: Numerical Linear Algebra Homework 3 SOLUTIONS Due Wednesday, March 8 Instructions Complete the following problems. Show all work. Only use Matlab on problems that are marked with (MATLAB). Include
MATH038: Numerical Linear Algebra Homework 3 SOLUTIONS Due Wednesday, March 8 Instructions Complete the following problems. Show all work. Only use Matlab on problems that are marked with (MATLAB). Include
Lab 5 CAPACITORS & RC CIRCUITS
 L051 Name Date Partners Lab 5 CAPACITORS & RC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To define capacitance and to learn to measure it with a digital multimeter. To explore how the capacitance of conducting parallel
L051 Name Date Partners Lab 5 CAPACITORS & RC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To define capacitance and to learn to measure it with a digital multimeter. To explore how the capacitance of conducting parallel
Physics 201 Lab 2 Air Drag Simulation
 Physics 201 Lab 2 Air Drag Simulation Jan 28, 2013 Equipment Initial Set Up Type the data from Table 1 into the appropriate cells. By preceding the content of the cell with an equal sign (as in cell A6)
Physics 201 Lab 2 Air Drag Simulation Jan 28, 2013 Equipment Initial Set Up Type the data from Table 1 into the appropriate cells. By preceding the content of the cell with an equal sign (as in cell A6)
Introduction. How to use this book. Linear algebra. Mathematica. Mathematica cells
 Introduction How to use this book This guide is meant as a standard reference to definitions, examples, and Mathematica techniques for linear algebra. Complementary material can be found in the Help sections
Introduction How to use this book This guide is meant as a standard reference to definitions, examples, and Mathematica techniques for linear algebra. Complementary material can be found in the Help sections
CHEM 498Q / CHEM 630Q: Molecular Modeling of Proteins TUTORIAL #3a: Empirical force fields
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University! page 1 of 6 CHEM 498Q / CHEM 630Q: Molecular Modeling of Proteins TUTORIAL #3a: Empirical force fields INTRODUCTION The goal of this tutorial
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University! page 1 of 6 CHEM 498Q / CHEM 630Q: Molecular Modeling of Proteins TUTORIAL #3a: Empirical force fields INTRODUCTION The goal of this tutorial
Introduction to Computer Tools and Uncertainties
 Experiment 1 Introduction to Computer Tools and Uncertainties 1.1 Objectives To become familiar with the computer programs and utilities that will be used throughout the semester. To become familiar with
Experiment 1 Introduction to Computer Tools and Uncertainties 1.1 Objectives To become familiar with the computer programs and utilities that will be used throughout the semester. To become familiar with
LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION
 Lab 2 - Introduction to Motion 3 Name Date Partners LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise Objectives To explore how various motions are represented
Lab 2 - Introduction to Motion 3 Name Date Partners LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise Objectives To explore how various motions are represented
Programming Assignment 4: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis
 Programming Assignment 4: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis Deadline: Tuesday, April 4, at 11:59pm TA: Renie Liao (csc321ta@cs.toronto.edu) Submission: You must submit two files through MarkUs
Programming Assignment 4: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis Deadline: Tuesday, April 4, at 11:59pm TA: Renie Liao (csc321ta@cs.toronto.edu) Submission: You must submit two files through MarkUs
Sample Alignment Part
 Sample Alignment Part Contents Contents 1. How to set Part conditions...1 1.1 Setting conditions... 1 1.2 Customizing scan conditions and slit conditions... 6 2. Sample alignment sequence...13 2.1 Direct
Sample Alignment Part Contents Contents 1. How to set Part conditions...1 1.1 Setting conditions... 1 1.2 Customizing scan conditions and slit conditions... 6 2. Sample alignment sequence...13 2.1 Direct
Lab 5 - Capacitors and RC Circuits
 Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits L51 Name Date Partners Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits OBJECTIVES To define capacitance and to learn to measure it with a digital multimeter. To explore how the capacitance
Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits L51 Name Date Partners Lab 5 Capacitors and RC Circuits OBJECTIVES To define capacitance and to learn to measure it with a digital multimeter. To explore how the capacitance
