Fluctuation-induced forces near critical points
|
|
|
- Lawrence Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluctuation-induced forces near critical points From Casimir to anisotropic critical systems H. W. Diehl Fakultät für Physik, U. Duisburg-Essen October 20, 2010 Third International Conference Models in Quantum Field Theory dedicated to A. N. Vassiliev Collaborators: Matthias Burgsmüller, U. Duisburg-Essen Felix M. Schmidt, U. Duisburg-Essen Mykola A. Shpot, ICMP Lviv (Ukraine) Work supported in part by: DFG, grant # Die-378/5
2 Fluctuation-induced forces effective force F 12 induced by fluctuations in medium examples: van der Waals Casimir, Casimir-Polder, dispersion forces, (near-)critical Casimir forces critical Casimir forces in anisotropic critical systems
3 Casimir Effect in QED July 15, 1909 May 4, : vacuum fluctuations L vacuum bound. cond. 1 conducting plates bound. cond. 2 normal modes of electromagnetic field between plates: q ω q,ν = c q = c qx 2 + qy 2 + qz; 2 q = (q x,q y, q z = m π/l), m N ground-state energy: E 0(L) = 1 X ω q,ν = C Λ V + CΛ s A+ π2 2 {z } 720 q,ν=1,2 infinities {z } universal BC c L A L 2 (fluctuation induced) force: F C (L) = E0 L = π2 240 c L 4 A
4 Casimir Effect in QED July 15, 1909 May 4, : vacuum fluctuations L vacuum bound. cond. 1 conducting plates bound. cond. 2 normal modes of electromagnetic field between plates: q ω q,ν = c q = c qx 2 + qy 2 + qz; 2 q = (q x,q y, q z = m π/l), m N ground-state energy: E 0(L) = 1 X ω q,ν = C Λ V + CΛ s A+ π2 2 {z } 720 q,ν=1,2 infinities {z } universal BC (fluctuation induced) force: c L A L 2 F C (L) = E0 L = (L/µm) 4 dyn cm 2 A
5 Experimental Verification S. Lamoreaux, PRL 87, 5 (1997); U. Mohideen & A. Roy, PRL 81, 4549 (1998); plates: G. Bressi et al, PRL 99, (2002) polystyrene sphere ( 196 µm) and sapphire plate coated with Au plate-sphere separations from 0.1 to 0.9 µm
6 Experimental Verification S. Lamoreaux, PRL 87, 5 (1997); U. Mohideen & A. Roy, PRL 81, 4549 (1998); plates: G. Bressi et al, PRL 99, (2002) polystyrene sphere ( 196 µm) and sapphire plate coated with Au plate-sphere separations from 0.1 to 0.9 µm solid line: Casimir force for plate-sphere geometry including corrections due to finite conductivity surface roughness finite temperatures Proximity Force (Derjaguin) Approximation
7 Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) Attractive Casimir forces may cause STICTION. Interest in repulsive Casimir forces.
8 Signs: Gaussian Results for Parallel Plates Massless Euclidean field theory in d space dimensions H = d d x 1 2 ( φ)2 R d 1 [0,L] Symanzik 81: (D,D) = 2 d π d/2 Γ(d/2)ζ(d) < 0 Krech & Dietrich 91: (N,N) = (D,D) < 0 (PBC) = 2 d (D,D) < 0 (D,N) = (2 1 d 1) (D,D) > 0 (APB) = 2 d (D,N) > 0 Theorems for attractive CFs: Kenneth & I. Klich 2007 ( Gauss ) Bachas 2007 (beyond Gauss: reflection positivity )
9 Thermodynamic Casimir Effect pressure 0 0 K solid liquid gas critical point temperature M.E. Fisher & P.-G. de Gennes (1978): large-λ modes massless consider confined nearly critical systems B 1 : area A nearly critical fluid B 2 : area A L F L,A (T) k B T = LAf b(t) {z } bulk contribution + A[f s,1(t,...) + f s,2(t,...)] {z } surface contributions + Af res(t,l,...) {z } residual
10 Thermodynamic Casimir Effect pressure 0 0 K solid liquid gas critical point temperature M.E. Fisher & P.-G. de Gennes (1978): large-λ modes massless consider confined nearly critical systems B 1 : area A nearly critical fluid B 2 : area A L F L,A (T) k B T = LAf b(t) {z } bulk contribution + A[f s,1(t,...) + f s,2(t,...)] {z } surface contributions + Af res(t,l,...) {z } residual Casimir force per area: F(T, L,...)/A = k B T fres L finite size scaling (only short-range interactions): f res(t,l,...) 1 L d 1 Θ {z} universal (L/ξ,...) at T c, : f res 1 L d 1 {z} Casimir amplitude
11 Universality Casimir amplitudes and scaling functions Θ are universal, depend on: 1 gross features of the medium (bulk universality class) 2 gross features of boundaries (surface universality classes) 3 geometry
12 Lattice and Continuum Models free bc K K 1 X H lat = K s is j i,j / B 1 B 2 X K 1 s is j K 2 i,j B 1 X i,j B 2 s is j K 2 free bc B 1 B 2 c 1 n V n c 2 H = Z R d 1 [0,L] d d x L b {z} bulk density + 2X Z da L j j=1 B j {z } boundary planes z = 0 and z = L L b = 1 2 ( φ)2 + τ 2 φ2 + ů 4! φ4 ; L j = 1 cj φ2 2 mesoscopic BC: n φ = c j φ
13 Lattice and Continuum Models free bc K K 1 X H lat = K s is j i,j / B 1 B 2 X K 1 s is j K 2 i,j B 1 X i,j B 2 s is j K 2 free bc B 1 B 2 c 1,h 1 n V n c 2,h 2 H = Z R d 1 [0,L] d d x L b {z} bulk density + 2X Z da L j j=1 B j {z } boundary planes z = 0 and z = L L b = 1 2 ( φ)2 + τ 2 φ2 + ů 4! φ4 ; L j = 1 2 cj φ2 h jφ mesoscopic BC: n φ = c j φ h j
14 Standard φ 4 model for slab B 1 B 2 c 1 n V n c 2 H = Z R d 1 [0,L] d d x L b {z} bulk density + 2X Z da L j j=1 B j {z } boundary planes z = 0 and z = L L b = 1 2 ( φ)2 + τ 2 φ2 + ů 4! φ4 ; L j = 1 cj φ2 2 mesoscopic BC: n φ = c j φ
15 Standard φ 4 model for slab B 1 B 2 c 1 n V n c 2 H = Z R d 1 [0,L] d d x L b {z} bulk density + 2X Z da L j j=1 B j {z } boundary planes z = 0 and z = L L b = 1 2 ( φ)2 + τ 2 φ2 + ů 4! φ4 ; L j = 1 cj φ2 2 mesoscopic BC: n φ = c j φ, c j c j c sp SD/BD T SD/BD Dirichlet SO/BD c j = c j SO/BO c j = 0 c sp SO/BO enhancement c j =
16 Standard φ 4 model for slab B 1 B 2 c 1 n V n c 2 H = Z R d 1 [0,L] d d x L b {z} bulk density + 2X Z da L j j=1 B j {z } boundary planes z = 0 and z = L L b = 1 2 ( φ)2 + τ 2 φ2 + ů 4! φ4 ; L j = 1 cj φ2 2 mesoscopic BC: n φ = c j φ, c j c j c sp SD/BD T SD/BD Dirichlet Neumann c j = 0 SO/BD c j = c j SO/BO c j = 0 c sp SO/BO enhancement c j =
17 Consequences T Dirichlet Neumann c j = 0 SO/BD c j = c j SO/BO c j = 0 c sp SO/BO enhancement c j = BC = scale-dependent! assume c 1, c 2 0 (non-supercritical enhancement), then: microscopic BC: free mesoscopic BC: Robin BC nφ = c jφ large-scale asymptotic BC: D-D, D-sp, sp-sp (sp = special, critically enhanced)
18 Consequences T Dirichlet Neumann c j = 0 SO/BD c j = c j SO/BO c j = 0 c sp SO/BO enhancement c j = BC = scale-dependent! assume c 1, c 2 0 (non-supercritical enhancement), then: microscopic BC: free mesoscopic BC: Robin BC nφ = c jφ large-scale asymptotic BC: D-D, D-sp, sp-sp (sp = special, critically enhanced) f res,crit(l)/n D`c 1L Φ/ν,c 2L Φ/ν L (d 1) Φ/ν 0.8
19 Scaling Function: Critical Casimir Force F nak B T L d D ( c 1 L Φ/ν, c 2 L Φ/ν) Φ/ν 0.8 D(c1, c2) c 1 c c 2 c 2+1 D(c 1, c 2 ) = [ d 1 + (Φ/ν) ( c 1 c1 + c 2 c2 )] D(c1, c 2 )
20 Scaling Function: Critical Casimir Force F nak B T L d D ( c 1 L Φ/ν, c 2 L Φ/ν) Φ/ν c2 c c1 c1+1 D(c 1, c 2 ) = [ d 1 + (Φ/ν) ( c 1 c1 + c 2 c2 )] D(c1, c 2 )
21 Crossover repulsive attractive 0.02 D(c1L Φ/ν, c2l Φ/ν ) (c 1, c 2 ) = (0, 0.1) (c 1, c 2 ) = (10, 0.1) L Scaled Casimir force F nak B T Ld = D ( c 1 L Φ/ν, c 2 L Φ/ν) F. M. Schmidt & HWD: PRL 101, (2008); arxiv: , and to be published
22 Universality Casimir amplitudes and scaling functions Θ are universal, depend on: 1 gross features of the medium (bulk universality class) 2 gross features of boundaries (surface universality classes) surface coupling subcritically enhanced: ordinary (O) transition surface coupling critically enhanced: special (sp) transition fixed boundary magnetizations / h 1 = ±, h 2 = ± 3 geometry (O,O), (O,sp), (sp,sp), (+,+), (+, ), PBC, APB
23 Universality Casimir amplitudes and scaling functions Θ are universal, depend on: 1 gross features of the medium (bulk universality class) 2 gross features of boundaries (surface universality classes) surface coupling subcritically enhanced: ordinary (O) transition surface coupling critically enhanced: special (sp) transition fixed boundary magnetizations / h 1 = ±, h 2 = ± 3 geometry (O,O), (O,sp), (sp,sp), (+,+), (+, ), PBC, APB experimental verifications: a) indirect: thinning of 4 He films (Garcia & Chan 1999) b) direct measurements (binary fluids): Hertlein et al 2008 theoretical results: many, distinct methods Nightingale & Indekeu, Krech & Dietrich 1990,..., HWD s group,..., Hucht, Vasilyev et al, Hasenbusch,..., Abrahams, Maciolek, Dantchev, Dohm,...,Kardar et al,... reviews: M. Krech: Casimir effect in Critical Systems (World Scientific, 1994); Brankov, Tonchev, & Dantchev (World Scientific, 2000); Gabassi 2009
24 Isotropic versus strongly anisotropic critical behavior isotropic strongly anisotropic ξ = ξ (0) ± τ ν ν α ν β, θ = ν α /ν β 1 ξ α = ξ (0) α,± τ να ξ β = ξ (0) β,± τ ν β
25 Isotropic versus strongly anisotropic critical behavior isotropic strongly anisotropic ξ = ξ (0) ± τ ν ν α ν β, θ = ν α /ν β 1 ξ α = ξ (0) α,± τ να ξ β = ξ (0) β,± τ ν β
26 Isotropic versus strongly anisotropic critical behavior isotropic strongly anisotropic ξ = ξ (0) ± τ ν ν α ν β, θ = ν α /ν β 1 ξ α = ξ (0) α,± τ να ξ β = ξ (0) β,± τ ν β f res,crit BC CP L (d 1) f res,crit E }{{} nonuniversal BC L ζ
27 φ 4 model for m-axial Lifshitz point Z H b = h 1 d d x 2 dx β=m+1 ( β φ) 2 + ρ 2 mx ( αφ) 2 + σ 2 α=1 mx ( αφ) τ 2 φ2 + ů 4! φ4i α=1 LP in Landau theory at τ = ρ = 0. Full two-loop RG analysis in d = 4 + m 2 ǫ dimensions: HWD & MA Shpot 2000, MA Shpot & HWD 2001; HWD, MA Shpot & RKP Zia 2003; work on boundary critical behavior: HWD with Gerwinski, Rutkevic, Shpot, Prudnikov
28 Orientation Matters! 2 fundamentally distinct orientations ς: parallel ( ) perpendicular ( ) y 1 y 2 y 1 y 2 L n n L n n z = β-direction z = α-direction z l 1 H = V dv L b + δ BC,free z l θ da L, s B 1 B 2 1 BC 2 BC large-scale BC O φ = 0 φ = 0, n φ = 0
29 Methods of Investigation 1 parallel orientation: Gauß theory (1-loop) for general d,m RG-improved perturbation theory in d = 4 + m 2 ǫ dimensions (2-loops, O(ǫ)) PBC: modified RG-improved perturbation theory (zero-mode): e Heff[ϕ] = exp( H[ ϕ + ψ ]) {z} {z} q=0 modes q 0 modes CP case: HWD, Grüneberg &Shpot 2006, Grüneberg & HWD 2008, 2009 n limit (PBC) 2 perpendicular orientation: Gauß theory (1-loop), general d,m, for (O,O) and PBC PBC: modified RG-improved perturbation theory in d = 4 + m 2 ǫ dimensions (2-loops), failed n limit (PBC) M. Burgsmüller, HWD & MA Shpot, Jstat (to appear); arxiv:
30 General Results: Non-/Universality fres;lp BC (L; σ, µ) L nonuniv. µ m(1 2θ) 2 ( µ (d m)(2θ 1) 2θ {}}{ E σ σ) m 4 BC L ζ, ς =, ( Eσ σ) d m 4θ BC }{{} L ζ, ς =, nonuniv. ζ = d m + θ m 1 ζ = d m θ + m 1. BC, definable as universal ratios! M. Burgsmüller, HWD & MA Shpot, Jstat (to appear); arxiv:
31 Results: Orientation 1 Gauß: BC = PBC and (O, O) BC,G(d,m,n) = C m BC CP,G(d m 2,n), Cm = π(2 m)/4 2 m Γ( m+2 4 ) (1) PBC,G (d,m,n) = 2 d m/2 (O,O),G (d,m, n) = n Cm Γ( d 2 m 4 ) ζ(d m 2 ) π (d m/2)/2 2 small-ǫ expansion: (1) prevails to calculated order (O,O) /n = C m[a 0 + a 1(n)ǫ] + O(ǫ 2 ) PBC /n = C m[b 0 + b 1(n)ǫ + b 3/2 (n)ǫ 3/2 ] + o(ǫ 3/2 ) 3 large-n limit: (1) prevails lim n PBC,(O,O) /n PBC,(O,O), PBC: consistency with small-ǫ expansion! (d, m) = C }{{} m PBC,(O,O) CP, (d m 2 ) }{{} 3,1 5/2
32 Results: Orientation d = 3, m = n = 1 PBC,G = PBC, = (n ) PBC,small-ǫ = (O,O),G = (O,O),small-ǫ = Critical Casimir force is attractive!
33 Orientation, PBC,G (d, m, n)/n = Γ(d m 22d 2m+1 2 )ζ(2d m) π (d 1)/2 Γ( m d 1 PBC PBC,G (3, 1, 1) = +12ζ(5) = π PBC, (3, 1, 1) (n ) Critical Casimir force is repulsive! 2 )
34 Orientation, (O,O) BC Y Y φ = 0, n φ = 0 Tr φ e H b[φ] δ(φ)δ( nφ) δ(φ)δ( nφ) x 1 B 1 x 2 B 2 φ = 0, n φ = 0 use Fadeev-Popov trick, introduce 4 n-component auxiliary fields χ 1,..., χ 4 integrate out φ lim A F G Ak B T = n 2 Z d d 1 p ln det M(p) (2π) d 1 {z } 4 4 (O,O),G (d, 1, n)/n = K d 12 1 d dq q 2d 3 ln[2e q (coshq + cosq 2)] 0 (O,O),G (3, 1, 1) Critical Casimir force is attractive!
35 Summary & Conclusions fluctuation-induced critical forces depend on type of orientation! distinct ζ, and BC,! universal ratios BC, definable! attraction and repulsion possible! simulation results for ANNNI model desirable experiments?
36 Summary & Conclusions fluctuation-induced critical forces depend on type of orientation! distinct ζ, and BC,! universal ratios BC, definable! attraction and repulsion possible! simulation results for ANNNI model desirable experiments? Thank you for your attention!
Effective forces due to confined nearly critical fluctuations
 Effective forces due to confined nearly critical fluctuations H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, U. Duisburg-Essen June 24, 2009 Collaborators: Daniel Grüneberg, U. Duisburg-Essen F. M. Schmidt, U. Duisburg-Essen
Effective forces due to confined nearly critical fluctuations H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, U. Duisburg-Essen June 24, 2009 Collaborators: Daniel Grüneberg, U. Duisburg-Essen F. M. Schmidt, U. Duisburg-Essen
Fluctuation-induced forces in confined He and Bose gases
 Fluctuation-induced forces in confined He and Bose gases H. W. Diehl Fakultät für Physik, U. Duisburg-Essen November 24, 2016 Collaborators: S. Rutkevich, U. Duisburg-Essen M. Hasenbusch, Institut für
Fluctuation-induced forces in confined He and Bose gases H. W. Diehl Fakultät für Physik, U. Duisburg-Essen November 24, 2016 Collaborators: S. Rutkevich, U. Duisburg-Essen M. Hasenbusch, Institut für
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 31 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 31 Oct 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 31 Oct 2012](/thumbs/72/66554702.jpg) epl draft Exact thermodynamic Casimir forces for an interacting threedimensional model system in film geometry with free surfaces arxiv:125.6613v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 31 Oct 212 H. W. Diehl 1, Daniel
epl draft Exact thermodynamic Casimir forces for an interacting threedimensional model system in film geometry with free surfaces arxiv:125.6613v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 31 Oct 212 H. W. Diehl 1, Daniel
The square lattice Ising model on the rectangle
 The square lattice Ising model on the rectangle Fred Hucht, Theoretische Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, 47048 Duisburg Introduction Connection to Casimir forces Free energy contributions Analytical
The square lattice Ising model on the rectangle Fred Hucht, Theoretische Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, 47048 Duisburg Introduction Connection to Casimir forces Free energy contributions Analytical
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Feb 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Feb 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Feb 2012](/thumbs/89/100778602.jpg) arxiv:1110.141v [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 Feb 01 Critical Casimir effect in films for generic non-symmetry-breaking boundary conditions H. W. Diehl and Felix M. Schmidt Fakultät für Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen,
arxiv:1110.141v [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 Feb 01 Critical Casimir effect in films for generic non-symmetry-breaking boundary conditions H. W. Diehl and Felix M. Schmidt Fakultät für Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen,
Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians. Renormalization Group without Field Theory
 Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians Renormalization Group without Field Theory Alberto Parola Università dell Insubria (Como - Italy) Renormalization Group Universality Only dimensionality and
Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians Renormalization Group without Field Theory Alberto Parola Università dell Insubria (Como - Italy) Renormalization Group Universality Only dimensionality and
Critical Behavior II: Renormalization Group Theory
 Critical Behavior II: Renormalization Group Theor H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Phsik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 What the Theor should Accomplish Theor should ield & explain: scaling laws #
Critical Behavior II: Renormalization Group Theor H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Phsik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 What the Theor should Accomplish Theor should ield & explain: scaling laws #
Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling
 Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 Goals recall basic facts about (static equilibrium) critical behavior
Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 Goals recall basic facts about (static equilibrium) critical behavior
Critical exponents in quantum Einstein gravity
 Critical exponents in quantum Einstein gravity Sándor Nagy Department of Theoretical physics, University of Debrecen MTA-DE Particle Physics Research Group, Debrecen Leibnitz, 28 June Critical exponents
Critical exponents in quantum Einstein gravity Sándor Nagy Department of Theoretical physics, University of Debrecen MTA-DE Particle Physics Research Group, Debrecen Leibnitz, 28 June Critical exponents
New Measurements of Wetting by Helium Mixtures
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 140, Nos. 1/2, July 2005 ( 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10909-005-6010-9 New Measurements of Wetting by Helium Mixtures Ryosuke Ishiguro and Sébastien Balibar Laboratoire
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 140, Nos. 1/2, July 2005 ( 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10909-005-6010-9 New Measurements of Wetting by Helium Mixtures Ryosuke Ishiguro and Sébastien Balibar Laboratoire
Casimir energy & Casimir entropy
 Workshop HBAR-KB, Grenoble, 29/09-01/10/2014 Casimir energy & Casimir entropy Astrid Lambrecht, Serge Reynaud, Romain Guérout, Gabriel Dufour, Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Paris with M.-T. Jaekel (LPTENS
Workshop HBAR-KB, Grenoble, 29/09-01/10/2014 Casimir energy & Casimir entropy Astrid Lambrecht, Serge Reynaud, Romain Guérout, Gabriel Dufour, Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Paris with M.-T. Jaekel (LPTENS
Critical Region of the QCD Phase Transition
 Critical Region of the QCD Phase Transition Mean field vs. Renormalization group B.-J. Schaefer 1 and J. Wambach 1,2 1 Institut für Kernphysik TU Darmstadt 2 GSI Darmstadt 18th August 25 Uni. Graz B.-J.
Critical Region of the QCD Phase Transition Mean field vs. Renormalization group B.-J. Schaefer 1 and J. Wambach 1,2 1 Institut für Kernphysik TU Darmstadt 2 GSI Darmstadt 18th August 25 Uni. Graz B.-J.
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/72/67050148.jpg) Thermodynamic Casimir effects involving interacting field theories with zero modes Daniel Grüneberg H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, D-4748 Duisburg, Germany (Dated: February
Thermodynamic Casimir effects involving interacting field theories with zero modes Daniel Grüneberg H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, D-4748 Duisburg, Germany (Dated: February
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Mar 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Mar 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Mar 2016](/thumbs/76/73375034.jpg) Direct calculation of the critical Casimir force in a binary fluid arxiv:163.7891v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Mar 216 Francesco Puosi, 1 David Lopes Cardozo, 1 Sergio Ciliberto, 1 and Peter C. W. Holdsworth
Direct calculation of the critical Casimir force in a binary fluid arxiv:163.7891v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 25 Mar 216 Francesco Puosi, 1 David Lopes Cardozo, 1 Sergio Ciliberto, 1 and Peter C. W. Holdsworth
Interface Profiles in Field Theory
 Florian König Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Münster January 10, 2011 / Forschungsseminar Quantenfeldtheorie Outline φ 4 -Theory in Statistical Physics Critical Phenomena and Order Parameter
Florian König Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Münster January 10, 2011 / Forschungsseminar Quantenfeldtheorie Outline φ 4 -Theory in Statistical Physics Critical Phenomena and Order Parameter
Analysis of the susceptibility in a fluid system with Neumann plus boundary conditions
 Analysis of the susceptibility in a fluid system with Neumann plus boundary conditions Peter Djondjorov 1,, Vassil Vassilev 1,, and Daniel Dantchev 1, 1 Institute of Mechanics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
Analysis of the susceptibility in a fluid system with Neumann plus boundary conditions Peter Djondjorov 1,, Vassil Vassilev 1,, and Daniel Dantchev 1, 1 Institute of Mechanics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
ɛ(k) = h2 k 2 2m, k F = (3π 2 n) 1/3
 4D-XY Quantum Criticality in Underdoped High-T c cuprates M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca February 22, 2005 In collaboration with: A.P. Iyengar (theory) D.P. Broun, D.A. Bonn
4D-XY Quantum Criticality in Underdoped High-T c cuprates M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca February 22, 2005 In collaboration with: A.P. Iyengar (theory) D.P. Broun, D.A. Bonn
On the Casimir energy for scalar fields with bulk inhomogeneities
 On the Casimir energy for scalar fields with bulk inhomogeneities arxiv:080.3603v1 [hep-th] 22 Apr 2008 I.V. Fialkovsky a, V.N. Markov b, Yu.M. Pis mak a a) St Petersburg State University, St Petersburg,
On the Casimir energy for scalar fields with bulk inhomogeneities arxiv:080.3603v1 [hep-th] 22 Apr 2008 I.V. Fialkovsky a, V.N. Markov b, Yu.M. Pis mak a a) St Petersburg State University, St Petersburg,
Baryonic Spectral Functions at Finite Temperature
 Baryonic Spectral Functions at Finite Temperature Masayuki Asakawa Department of Physics, Osaka University July 2008 @ XQCD 2008 QCD Phase Diagram T LHC 160-190 MeV 100MeV ~ 10 12 K RHIC crossover CEP(critical
Baryonic Spectral Functions at Finite Temperature Masayuki Asakawa Department of Physics, Osaka University July 2008 @ XQCD 2008 QCD Phase Diagram T LHC 160-190 MeV 100MeV ~ 10 12 K RHIC crossover CEP(critical
Quantum phase transitions
 Quantum phase transitions Thomas Vojta Department of Physics, University of Missouri-Rolla Phase transitions and critical points Quantum phase transitions: How important is quantum mechanics? Quantum phase
Quantum phase transitions Thomas Vojta Department of Physics, University of Missouri-Rolla Phase transitions and critical points Quantum phase transitions: How important is quantum mechanics? Quantum phase
NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS. Past questions. EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL PHYSICS Minor Topics. (27 February 2010)
 NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part III Past questions EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL PHYSICS Minor Topics (27 February 21) 1 In one-dimension, the q-state Potts model is defined by the lattice Hamiltonian βh =
NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part III Past questions EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL PHYSICS Minor Topics (27 February 21) 1 In one-dimension, the q-state Potts model is defined by the lattice Hamiltonian βh =
Design and realization of exotic quantum phases in atomic gases
 Design and realization of exotic quantum phases in atomic gases H.P. Büchler and P. Zoller Theoretische Physik, Universität Innsbruck, Austria Institut für Quantenoptik und Quanteninformation der Österreichischen
Design and realization of exotic quantum phases in atomic gases H.P. Büchler and P. Zoller Theoretische Physik, Universität Innsbruck, Austria Institut für Quantenoptik und Quanteninformation der Österreichischen
VACUUM ENERGY IN QUANTUM FIELD THEORY
 VACUUM ENERGY IN QUANTUM FIELD THEORY V.V. Nesterenko BLTP JINR, Dubna Advances of Quantum Field Theory Dubna, 4 7 October 2011 INTRODUCTION Is it possible to calculate the vacuum energy in the standard
VACUUM ENERGY IN QUANTUM FIELD THEORY V.V. Nesterenko BLTP JINR, Dubna Advances of Quantum Field Theory Dubna, 4 7 October 2011 INTRODUCTION Is it possible to calculate the vacuum energy in the standard
Cri$cal Casimir forces from the equa$on of state of quantum cri$cal systems
 Cri$cal Casimir forces from the equa$on of state of quantum cri$cal systems A. Rançon D. Lopes Cardozo T. Roscilde P. Holdsworth Ecole Normale Superieure de Lyon F. Rose N. Dupuis LPTMC Paris 6 L.-P. Henry
Cri$cal Casimir forces from the equa$on of state of quantum cri$cal systems A. Rançon D. Lopes Cardozo T. Roscilde P. Holdsworth Ecole Normale Superieure de Lyon F. Rose N. Dupuis LPTMC Paris 6 L.-P. Henry
Nonlinear BEC Dynamics by Harmonic Modulation of s-wave Scattering Length
 Nonlinear BEC Dynamics by Harmonic Modulation of s-wave Scattering Length I. Vidanović, A. Balaž, H. Al-Jibbouri 2, A. Pelster 3 Scientific Computing Laboratory, Institute of Physics Belgrade, Serbia 2
Nonlinear BEC Dynamics by Harmonic Modulation of s-wave Scattering Length I. Vidanović, A. Balaž, H. Al-Jibbouri 2, A. Pelster 3 Scientific Computing Laboratory, Institute of Physics Belgrade, Serbia 2
Towards a quantitative FRG approach for the BCS-BEC crossover
 Towards a quantitative FRG approach for the BCS-BEC crossover Michael M. Scherer Theoretisch Physikalisches Institut, Jena University in collaboration with Sebastian Diehl, Stefan Flörchinger, Holger Gies,
Towards a quantitative FRG approach for the BCS-BEC crossover Michael M. Scherer Theoretisch Physikalisches Institut, Jena University in collaboration with Sebastian Diehl, Stefan Flörchinger, Holger Gies,
On the definition and interpretation of a static quark anti-quark potential in the colour-adjoint channel
 On the definition and interpretation of a static quark anti-quark potential in the colour-adjoint channel Effective Field Theory Seminar Technische Universität München, Germany Marc Wagner, Owe Philipsen
On the definition and interpretation of a static quark anti-quark potential in the colour-adjoint channel Effective Field Theory Seminar Technische Universität München, Germany Marc Wagner, Owe Philipsen
Classification theorem for the static and asymptotically flat Einstein-Maxwell-dilaton spacetimes possessing a photon sphere
 Classification theorem for the static and asymptotically flat Einstein-Maxwell-dilaton spacetimes possessing a photon sphere Boian Lazov and Stoytcho Yazadjiev Varna, 2017 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Preliminaries
Classification theorem for the static and asymptotically flat Einstein-Maxwell-dilaton spacetimes possessing a photon sphere Boian Lazov and Stoytcho Yazadjiev Varna, 2017 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Preliminaries
Continuity of the Deconfinement Transition in (Super) Yang Mills Theory
 Continuity of the Deconfinement Transition in (Super) Yang Mills Theory Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.5
Continuity of the Deconfinement Transition in (Super) Yang Mills Theory Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.5
Domains and Domain Walls in Quantum Spin Chains
 Domains and Domain Walls in Quantum Spin Chains Statistical Interaction and Thermodynamics Ping Lu, Jared Vanasse, Christopher Piecuch Michael Karbach and Gerhard Müller 6/3/04 [qpis /5] Domains and Domain
Domains and Domain Walls in Quantum Spin Chains Statistical Interaction and Thermodynamics Ping Lu, Jared Vanasse, Christopher Piecuch Michael Karbach and Gerhard Müller 6/3/04 [qpis /5] Domains and Domain
Critical Casimir effect and wetting by helium mixtures
 Critical Casimir effect and wetting by helium mixtures Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki, Frederic Caupin, Etienne Rolley To cite this version: Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki,
Critical Casimir effect and wetting by helium mixtures Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki, Frederic Caupin, Etienne Rolley To cite this version: Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki,
Hydrodynamic Modes of Incoherent Black Holes
 Hydrodynamic Modes of Incoherent Black Holes Vaios Ziogas Durham University Based on work in collaboration with A. Donos, J. Gauntlett [arxiv: 1707.xxxxx, 170x.xxxxx] 9th Crete Regional Meeting on String
Hydrodynamic Modes of Incoherent Black Holes Vaios Ziogas Durham University Based on work in collaboration with A. Donos, J. Gauntlett [arxiv: 1707.xxxxx, 170x.xxxxx] 9th Crete Regional Meeting on String
The bosonic Kondo effect:
 The bosonic Kondo effect: probing spin liquids and multicomponent cold gases Serge Florens Institut für Theorie der Kondensierten Materie (Karlsruhe) with: Lars Fritz, ITKM (Karlsruhe) Matthias Vojta,
The bosonic Kondo effect: probing spin liquids and multicomponent cold gases Serge Florens Institut für Theorie der Kondensierten Materie (Karlsruhe) with: Lars Fritz, ITKM (Karlsruhe) Matthias Vojta,
the renormalization group (RG) idea
 the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
The three-dimensional O(n) φ 4 model on a strip with free boundary conditions: exact results for a nontrivial dimensional crossover in the limit n
 arxiv:1512.05892v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Feb 2017 The three-dimensional O(n) φ 4 model on a strip with free boundary conditions: exact results for a nontrivial dimensional crossover in the limit n H.
arxiv:1512.05892v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Feb 2017 The three-dimensional O(n) φ 4 model on a strip with free boundary conditions: exact results for a nontrivial dimensional crossover in the limit n H.
Static continuum theory of nematic liquid crystals.
 Static continuum theory of nematic liquid crystals. Dmitry Golovaty The University of Akron June 11, 2015 1 Some images are from Google Earth and http://www.personal.kent.edu/ bisenyuk/liquidcrystals Dmitry
Static continuum theory of nematic liquid crystals. Dmitry Golovaty The University of Akron June 11, 2015 1 Some images are from Google Earth and http://www.personal.kent.edu/ bisenyuk/liquidcrystals Dmitry
Mean-field Gauge Interactions in Five Dimensions I (The Torus)
 Mean-field Gauge Interactions in Five Dimensions I (The Torus) Nikos Irges, Wuppertal U. Based on N.I. & F. Knechtli, arxiv:0905.2757 [hep-lat] 5th RMST, Kolymbari, June 2009 Background. J. M. Drouffe
Mean-field Gauge Interactions in Five Dimensions I (The Torus) Nikos Irges, Wuppertal U. Based on N.I. & F. Knechtli, arxiv:0905.2757 [hep-lat] 5th RMST, Kolymbari, June 2009 Background. J. M. Drouffe
Interfaces with short-range correlated disorder: what we learn from the Directed Polymer
 Interfaces with short-range correlated disorder: what we learn from the Directed Polymer Elisabeth Agoritsas (1), Thierry Giamarchi (2) Vincent Démery (3), Alberto Rosso (4) Reinaldo García-García (3),
Interfaces with short-range correlated disorder: what we learn from the Directed Polymer Elisabeth Agoritsas (1), Thierry Giamarchi (2) Vincent Démery (3), Alberto Rosso (4) Reinaldo García-García (3),
Exact and Numerical Methods in Casimir Calculations
 Exact and Numerical Methods in Casimir Calculations K. A. Milton based on collaboration with K. V. Shajesh, P. Parashar, J. Wagner supported by NSF and DOE Oklahoma Center for High Energy Physics, and
Exact and Numerical Methods in Casimir Calculations K. A. Milton based on collaboration with K. V. Shajesh, P. Parashar, J. Wagner supported by NSF and DOE Oklahoma Center for High Energy Physics, and
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas
 Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Heidelberg with S. Diehl, J. M. Pawlowski, and C. Wetterich C o ld atom s Δ13, 11. 1. 2013 tio
Equation of state of the unitary Fermi gas Igor Boettcher Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Heidelberg with S. Diehl, J. M. Pawlowski, and C. Wetterich C o ld atom s Δ13, 11. 1. 2013 tio
Entanglement in Quantum Field Theory
 Entanglement in Quantum Field Theory John Cardy University of Oxford Landau Institute, June 2008 in collaboration with P. Calabrese; O. Castro-Alvaredo and B. Doyon Outline entanglement entropy as a measure
Entanglement in Quantum Field Theory John Cardy University of Oxford Landau Institute, June 2008 in collaboration with P. Calabrese; O. Castro-Alvaredo and B. Doyon Outline entanglement entropy as a measure
Observation of the thermal Casimir force. Diego A. R. Dalvit Theoretical Division Los Alamos National Laboratory
 Observation of the thermal Casimir force Diego A. R. Dalvit Theoretical Division Los Alamos National Laboratory Collaborators Steve Lamoreaux (Yale) Alex Sushkov (Yale, now @ Harvard) Woo-Joong Kim (Seattle)
Observation of the thermal Casimir force Diego A. R. Dalvit Theoretical Division Los Alamos National Laboratory Collaborators Steve Lamoreaux (Yale) Alex Sushkov (Yale, now @ Harvard) Woo-Joong Kim (Seattle)
Where is the PdV term in the first law of black-hole thermodynamics?
 Where is the PdV term in the first law of black-hole thermodynamics? Brian P Dolan National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland and Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Ireland 9th Vienna Central
Where is the PdV term in the first law of black-hole thermodynamics? Brian P Dolan National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland and Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Ireland 9th Vienna Central
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics.
 Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
 1 CE 530 Molecular Simulation Lecture 14 Molecular Models David A. Kofke Department of Chemical Engineering SUNY Buffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu 2 Review Monte Carlo ensemble averaging, no dynamics easy
1 CE 530 Molecular Simulation Lecture 14 Molecular Models David A. Kofke Department of Chemical Engineering SUNY Buffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu 2 Review Monte Carlo ensemble averaging, no dynamics easy
Probing Universality in AdS/CFT
 1 / 24 Probing Universality in AdS/CFT Adam Ritz University of Victoria with P. Kovtun [0801.2785, 0806.0110] and J. Ward [0811.4195] Shifmania workshop Minneapolis May 2009 2 / 24 Happy Birthday Misha!
1 / 24 Probing Universality in AdS/CFT Adam Ritz University of Victoria with P. Kovtun [0801.2785, 0806.0110] and J. Ward [0811.4195] Shifmania workshop Minneapolis May 2009 2 / 24 Happy Birthday Misha!
(Super) Fluid Dynamics. Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University
 (Super) Fluid Dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics (undergraduate version): Newton s law for continuous, deformable media. Fluids: Gases, liquids, plasmas,...
(Super) Fluid Dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics (undergraduate version): Newton s law for continuous, deformable media. Fluids: Gases, liquids, plasmas,...
Tricritical Casimir Forces in 3 He - 4 He Wetting Films
 Tricritical Casimir Forces in 3 He - 4 He Wetting Films Von der Fakultät Mathematik und Physik der Universität Stuttgart zur Erlangung der Würde eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften (Dr. rer. nat.) genehmigte
Tricritical Casimir Forces in 3 He - 4 He Wetting Films Von der Fakultät Mathematik und Physik der Universität Stuttgart zur Erlangung der Würde eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften (Dr. rer. nat.) genehmigte
Mesonic and nucleon fluctuation effects in nuclear medium
 Mesonic and nucleon fluctuation effects in nuclear medium Research Center for Nuclear Physics Osaka University Workshop of Recent Developments in QCD and Quantum Field Theories National Taiwan University,
Mesonic and nucleon fluctuation effects in nuclear medium Research Center for Nuclear Physics Osaka University Workshop of Recent Developments in QCD and Quantum Field Theories National Taiwan University,
Superconducting properties of carbon nanotubes
 Superconducting properties of carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf A. De Martino, F. Siano Overview Superconductivity in ropes of nanotubes
Superconducting properties of carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf A. De Martino, F. Siano Overview Superconductivity in ropes of nanotubes
Possible string effects in 4D from a 5D anisotropic gauge theory in a mean-field background
 Possible string effects in 4D from a 5D anisotropic gauge theory in a mean-field background Nikos Irges, Wuppertal U. Based on N.I. & F. Knechtli, arxiv:0905.2757 to appear in NPB + work in progress Corfu,
Possible string effects in 4D from a 5D anisotropic gauge theory in a mean-field background Nikos Irges, Wuppertal U. Based on N.I. & F. Knechtli, arxiv:0905.2757 to appear in NPB + work in progress Corfu,
Quantum Dynamics of Supergravity
 Quantum Dynamics of Supergravity David Tong Work with Carl Turner Based on arxiv:1408.3418 Crete, September 2014 An Old Idea: Euclidean Quantum Gravity Z = Dg exp d 4 x g R topology A Preview of the Main
Quantum Dynamics of Supergravity David Tong Work with Carl Turner Based on arxiv:1408.3418 Crete, September 2014 An Old Idea: Euclidean Quantum Gravity Z = Dg exp d 4 x g R topology A Preview of the Main
arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 28 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 28 Oct 2014 arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 28 Oct 2014](/thumbs/92/108057367.jpg) Spherical Casimir effect for a massive scalar field on the three dimensional ball Andrea Erdas Department of Physics, Loyola University Maryland, 45 North Charles Street, Baltimore, Maryland, USA arxiv:4.7798v
Spherical Casimir effect for a massive scalar field on the three dimensional ball Andrea Erdas Department of Physics, Loyola University Maryland, 45 North Charles Street, Baltimore, Maryland, USA arxiv:4.7798v
Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II Lecture XI
 Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II Lecture XI The main result of the last lecture was a calculation of the averaged magnetization in mean-field theory in Fourier space when the spin at the origin is
Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II Lecture XI The main result of the last lecture was a calculation of the averaged magnetization in mean-field theory in Fourier space when the spin at the origin is
Symmetry of the Dielectric Tensor
 Symmetry of the Dielectric Tensor Curtis R. Menyuk June 11, 2010 In this note, I derive the symmetry of the dielectric tensor in two ways. The derivations are taken from Landau and Lifshitz s Statistical
Symmetry of the Dielectric Tensor Curtis R. Menyuk June 11, 2010 In this note, I derive the symmetry of the dielectric tensor in two ways. The derivations are taken from Landau and Lifshitz s Statistical
Photons in the Chiral Magnetic Effect
 Photons in the Chiral Magnetic Effect Kenji Fukushima Department of Physics, Keio University June 25, 2012 @ CPODD 1 Current from the Quantum Anomaly Anomaly Relation j = N c i=flavor Q i 2 e 2 μ 5 2π
Photons in the Chiral Magnetic Effect Kenji Fukushima Department of Physics, Keio University June 25, 2012 @ CPODD 1 Current from the Quantum Anomaly Anomaly Relation j = N c i=flavor Q i 2 e 2 μ 5 2π
Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality. Hans-Henning Klauss. Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden
 Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality Hans-Henning Klauss Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden 1 References [1] Stephen Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed
Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality Hans-Henning Klauss Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden 1 References [1] Stephen Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed
Critical Depletion Force
 XCVI CONGRESSO NAZIONALE SOCIETA ITALIANA DI FISICA BOLOGNA 20-24 settembre 2010 Critical Depletion Force Stefano BUZZACCARO Prof. Roberto PIAZZA Politecnico di Milano Prof. Alberto PAROLA Jader COLOMBO
XCVI CONGRESSO NAZIONALE SOCIETA ITALIANA DI FISICA BOLOGNA 20-24 settembre 2010 Critical Depletion Force Stefano BUZZACCARO Prof. Roberto PIAZZA Politecnico di Milano Prof. Alberto PAROLA Jader COLOMBO
Casimir Force in Anisotropic Materials with AC Kerr Effect
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 38, 165 173, 2014 Casimir Force in Anisotropic Materials with AC Kerr Effect Junlong Zhang 1, Zhixiang Huang 1, *, and Xianliang Wu 1, 2 Abstract The Casimir
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 38, 165 173, 2014 Casimir Force in Anisotropic Materials with AC Kerr Effect Junlong Zhang 1, Zhixiang Huang 1, *, and Xianliang Wu 1, 2 Abstract The Casimir
Cooperative atom-light interaction in a blockaded Rydberg ensemble
 Cooperative atom-light interaction in a blockaded Rydberg ensemble α 1 Jonathan Pritchard University of Durham, UK Overview 1. Cooperative optical non-linearity due to dipole-dipole interactions 2. Observation
Cooperative atom-light interaction in a blockaded Rydberg ensemble α 1 Jonathan Pritchard University of Durham, UK Overview 1. Cooperative optical non-linearity due to dipole-dipole interactions 2. Observation
The Chiral and Deconfinement Phase Transitions in Strongly-Interacting Matter
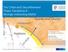 The Chiral and Deconfinement Phase Transitions in Strongly-Interacting Matter in collaboration with: B-J. Schaefer & J. Wambach Schaefer, MW: PRD 79 (1418) arxiv: 812.2855 [hep-ph] 9.3.29 Mathias Wagner
The Chiral and Deconfinement Phase Transitions in Strongly-Interacting Matter in collaboration with: B-J. Schaefer & J. Wambach Schaefer, MW: PRD 79 (1418) arxiv: 812.2855 [hep-ph] 9.3.29 Mathias Wagner
Quantum Field Theory. Kerson Huang. Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH. From Operators to Path Integrals
 Kerson Huang Quantum Field Theory From Operators to Path Integrals Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA I vh Contents Preface XIII 1 Introducing Quantum Fields
Kerson Huang Quantum Field Theory From Operators to Path Integrals Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA I vh Contents Preface XIII 1 Introducing Quantum Fields
Phase transitions and critical phenomena
 Phase transitions and critical phenomena Classification of phase transitions. Discontinous (st order) transitions Summary week -5 st derivatives of thermodynamic potentials jump discontinously, e.g. (
Phase transitions and critical phenomena Classification of phase transitions. Discontinous (st order) transitions Summary week -5 st derivatives of thermodynamic potentials jump discontinously, e.g. (
t Hooft Loops and S-Duality
 t Hooft Loops and S-Duality Jaume Gomis KITP, Dualities in Physics and Mathematics with T. Okuda and D. Trancanelli Motivation 1) Quantum Field Theory Provide the path integral definition of all operators
t Hooft Loops and S-Duality Jaume Gomis KITP, Dualities in Physics and Mathematics with T. Okuda and D. Trancanelli Motivation 1) Quantum Field Theory Provide the path integral definition of all operators
The glass transition as a spin glass problem
 The glass transition as a spin glass problem Mike Moore School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester UBC 2007 Co-Authors: Joonhyun Yeo, Konkuk University Marco Tarzia, Saclay Mike Moore (Manchester)
The glass transition as a spin glass problem Mike Moore School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester UBC 2007 Co-Authors: Joonhyun Yeo, Konkuk University Marco Tarzia, Saclay Mike Moore (Manchester)
Inverse square potential, scale anomaly, and complex extension
 Inverse square potential, scale anomaly, and complex extension Sergej Moroz Seattle, February 2010 Work in collaboration with Richard Schmidt ITP, Heidelberg Outline Introduction and motivation Functional
Inverse square potential, scale anomaly, and complex extension Sergej Moroz Seattle, February 2010 Work in collaboration with Richard Schmidt ITP, Heidelberg Outline Introduction and motivation Functional
Asymptotic Expansion of N = 4 Dyon Degeneracy
 Asymptotic Expansion of N = 4 Dyon Degeneracy Nabamita Banerjee Harish-Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad, India Collaborators: D. Jatkar, A.Sen References: (1) arxiv:0807.1314 [hep-th] (2) arxiv:0810.3472
Asymptotic Expansion of N = 4 Dyon Degeneracy Nabamita Banerjee Harish-Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad, India Collaborators: D. Jatkar, A.Sen References: (1) arxiv:0807.1314 [hep-th] (2) arxiv:0810.3472
Linear Response in Fluctuational Electrodynamics
 Max Planck Institute Stuttgart Linear Response in Fluctuational Electrodynamics Matthias Krüger Group Members: Artem Aerov Roberta Incardone Moritz Förster MIT - Student: Vladyslav Golyk Collaborators:
Max Planck Institute Stuttgart Linear Response in Fluctuational Electrodynamics Matthias Krüger Group Members: Artem Aerov Roberta Incardone Moritz Förster MIT - Student: Vladyslav Golyk Collaborators:
Bulk Thermodynamics: What do we (want to) know?
 Bulk Thermodynamics: What do we (want to) know? µ = : properties of transition in, ( + 1)-flavor QCD: crossover or phase transition, deconfinement vs. chiral symmetry restoration, universality,... T c,
Bulk Thermodynamics: What do we (want to) know? µ = : properties of transition in, ( + 1)-flavor QCD: crossover or phase transition, deconfinement vs. chiral symmetry restoration, universality,... T c,
Casimir and Casimir-Polder forces in chiral and non-reciprocal media
 Casimir and Casimir-Polder forces in chiral and non-reciprocal media Stefan Yoshi Buhmann, Stefan Scheel, David Butcher Quantum Optics and Laser Science Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College London, UK
Casimir and Casimir-Polder forces in chiral and non-reciprocal media Stefan Yoshi Buhmann, Stefan Scheel, David Butcher Quantum Optics and Laser Science Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College London, UK
Introduction. Statistical physics: microscopic foundation of thermodynamics degrees of freedom 2 3 state variables!
 Introduction Thermodynamics: phenomenological description of equilibrium bulk properties of matter in terms of only a few state variables and thermodynamical laws. Statistical physics: microscopic foundation
Introduction Thermodynamics: phenomenological description of equilibrium bulk properties of matter in terms of only a few state variables and thermodynamical laws. Statistical physics: microscopic foundation
Polymer Solution Thermodynamics:
 Polymer Solution Thermodynamics: 3. Dilute Solutions with Volume Interactions Brownian particle Polymer coil Self-Avoiding Walk Models While the Gaussian coil model is useful for describing polymer solutions
Polymer Solution Thermodynamics: 3. Dilute Solutions with Volume Interactions Brownian particle Polymer coil Self-Avoiding Walk Models While the Gaussian coil model is useful for describing polymer solutions
The Nernst effect in high-temperature superconductors
 The Nernst effect in high-temperature superconductors Iddo Ussishkin (University of Minnesota) with Shivaji Sondhi David Huse Vadim Oganesyan Outline Introduction: - High-temperature superconductors: physics
The Nernst effect in high-temperature superconductors Iddo Ussishkin (University of Minnesota) with Shivaji Sondhi David Huse Vadim Oganesyan Outline Introduction: - High-temperature superconductors: physics
The QCD phase diagram from the lattice
 The QCD phase diagram from the lattice Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR CBM Meeting VECC Kolkata July 31, 2010 Zero baryon density Background Exact SU(2) flavour symmetry Exact SU(3) flavour symmetry Broken
The QCD phase diagram from the lattice Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR CBM Meeting VECC Kolkata July 31, 2010 Zero baryon density Background Exact SU(2) flavour symmetry Exact SU(3) flavour symmetry Broken
QCD and Instantons: 12 Years Later. Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State
 QCD and Instantons: 12 Years Later Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State 1 ESQGP: A man ahead of his time 2 Instanton Liquid: Pre-History 1975 (Polyakov): The instanton solution r 2 2 E + B A a µ(x) = 2
QCD and Instantons: 12 Years Later Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State 1 ESQGP: A man ahead of his time 2 Instanton Liquid: Pre-History 1975 (Polyakov): The instanton solution r 2 2 E + B A a µ(x) = 2
An exact result for the behavior of Yang-Mills Green functions in the deep infrared region
 An exact result for the behavior of Yang-Mills Green functions in the deep infrared region MG12, Paris, 17 July 2009 Kei-Ichi Kondo* (Univ. of Tokyo/hiba Univ., Japan) Based on K.-I. Kondo, Kugo-Ojima
An exact result for the behavior of Yang-Mills Green functions in the deep infrared region MG12, Paris, 17 July 2009 Kei-Ichi Kondo* (Univ. of Tokyo/hiba Univ., Japan) Based on K.-I. Kondo, Kugo-Ojima
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 29 May 2000
 Photon-Photon Interaction in a Photon Gas Markus H. Thoma Theory Division, CERN, CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland and Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Giessen, 35392 Giessen, Germany arxiv:hep-ph/0005282v1
Photon-Photon Interaction in a Photon Gas Markus H. Thoma Theory Division, CERN, CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland and Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Giessen, 35392 Giessen, Germany arxiv:hep-ph/0005282v1
The Superfluid-Insulator transition
 The Superfluid-Insulator transition Boson Hubbard model M.P. A. Fisher, P.B. Weichmann, G. Grinstein, and D.S. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 40, 546 (1989). Superfluid-insulator transition Ultracold 87 Rb atoms
The Superfluid-Insulator transition Boson Hubbard model M.P. A. Fisher, P.B. Weichmann, G. Grinstein, and D.S. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 40, 546 (1989). Superfluid-insulator transition Ultracold 87 Rb atoms
Instanton constituents in sigma models and Yang-Mills theory at finite temperature
 Instanton constituents in sigma models and Yang-Mills theory at finite temperature Falk Bruckmann Univ. of Regensburg Extreme QCD, North Carolina State, July 8 PRL (8) 56 [77.775] EPJ Spec.Top.5 (7) 6-88
Instanton constituents in sigma models and Yang-Mills theory at finite temperature Falk Bruckmann Univ. of Regensburg Extreme QCD, North Carolina State, July 8 PRL (8) 56 [77.775] EPJ Spec.Top.5 (7) 6-88
1. (3) Write Gauss Law in differential form. Explain the physical meaning.
 Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about the physics involved,
Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about the physics involved,
Squeezing and superposing many-body states of Bose gases in confining potentials
 Squeezing and superposing many-body states of Bose gases in confining potentials K. B. Whaley Department of Chemistry, Kenneth S. Pitzer Center for Theoretical Chemistry, Berkeley Quantum Information and
Squeezing and superposing many-body states of Bose gases in confining potentials K. B. Whaley Department of Chemistry, Kenneth S. Pitzer Center for Theoretical Chemistry, Berkeley Quantum Information and
Finite Temperature Field Theory
 Finite Temperature Field Theory Dietrich Bödeker, Universität Bielefeld 1. Thermodynamics (better: thermo-statics) (a) Imaginary time formalism (b) free energy: scalar particles, resummation i. pedestrian
Finite Temperature Field Theory Dietrich Bödeker, Universität Bielefeld 1. Thermodynamics (better: thermo-statics) (a) Imaginary time formalism (b) free energy: scalar particles, resummation i. pedestrian
Linking U(2) U(2) to O(4) via decoupling
 Linking U(2) U(2) to O(4) via decoupling Norikazu Yamada (KEK, GUAS) in collaboration with Tomomi Sato (KEK, GUAS) Based on Linking U(2) U(2) to O(4) model via decoupling, PRD91(2015)034025 [arxiv:1412.8026
Linking U(2) U(2) to O(4) via decoupling Norikazu Yamada (KEK, GUAS) in collaboration with Tomomi Sato (KEK, GUAS) Based on Linking U(2) U(2) to O(4) model via decoupling, PRD91(2015)034025 [arxiv:1412.8026
Waves in plasma. Denis Gialis
 Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
QCD Phases with Functional Methods
 QCD Phases with Mario PhD-Advisors: Bernd-Jochen Schaefer Reinhard Alkofer Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz Institut für Physik Fachbereich Theoretische Physik Rab, September 2010 QCD Phases with Table of
QCD Phases with Mario PhD-Advisors: Bernd-Jochen Schaefer Reinhard Alkofer Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz Institut für Physik Fachbereich Theoretische Physik Rab, September 2010 QCD Phases with Table of
Properties of monopole operators in 3d gauge theories
 Properties of monopole operators in 3d gauge theories Silviu S. Pufu Princeton University Based on: arxiv:1303.6125 arxiv:1309.1160 (with Ethan Dyer and Mark Mezei) work in progress with Ethan Dyer, Mark
Properties of monopole operators in 3d gauge theories Silviu S. Pufu Princeton University Based on: arxiv:1303.6125 arxiv:1309.1160 (with Ethan Dyer and Mark Mezei) work in progress with Ethan Dyer, Mark
Ultraviolet divergences, repulsive forces and a spherical plasma shell
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Ultraviolet divergences, repulsive forces and a spherical plasma shell To cite this article: M Bordag 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 161 012018 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Ultraviolet divergences, repulsive forces and a spherical plasma shell To cite this article: M Bordag 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 161 012018 View the article online
Equation of state. Pasi Huovinen Uniwersytet Wroc lawski. Collective Flows and Hydrodynamics in High Energy Nuclear Collisions
 Equation of state Pasi Huovinen Uniwersytet Wroc lawski Collective Flows and Hydrodynamics in High Energy Nuclear Collisions Dec 14, 2016, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China The
Equation of state Pasi Huovinen Uniwersytet Wroc lawski Collective Flows and Hydrodynamics in High Energy Nuclear Collisions Dec 14, 2016, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China The
Asymptotically free nonabelian Higgs models. Holger Gies
 Asymptotically free nonabelian Higgs models Holger Gies Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena & Helmholtz-Institut Jena & Luca Zambelli, PRD 92, 025016 (2015) [arxiv:1502.05907], arxiv:16xx.yyyyy Prologue:
Asymptotically free nonabelian Higgs models Holger Gies Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena & Helmholtz-Institut Jena & Luca Zambelli, PRD 92, 025016 (2015) [arxiv:1502.05907], arxiv:16xx.yyyyy Prologue:
Axial symmetry in the chiral symmetric phase
 Axial symmetry in the chiral symmetric phase Swagato Mukherjee June 2014, Stoney Brook, USA Axial symmetry in QCD massless QCD Lagrangian is invariant under U A (1) : ψ (x) e i α ( x) γ 5 ψ(x) μ J 5 μ
Axial symmetry in the chiral symmetric phase Swagato Mukherjee June 2014, Stoney Brook, USA Axial symmetry in QCD massless QCD Lagrangian is invariant under U A (1) : ψ (x) e i α ( x) γ 5 ψ(x) μ J 5 μ
Applications to simulations: Monte-Carlo
 Applications to simulations: Monte-Carlo A.C. Maggs ESPCI, Paris June 2016 Summary Algorithms Faster/simpler codes Thermodynamics of Electric fields Partition function of electric field Thermal Casimir/Lifshitz
Applications to simulations: Monte-Carlo A.C. Maggs ESPCI, Paris June 2016 Summary Algorithms Faster/simpler codes Thermodynamics of Electric fields Partition function of electric field Thermal Casimir/Lifshitz
Thermal Casimir Effect for Colloids at a Fluid Interface
 Thermal Casimir Effect for Colloids at a Fluid Interface Jef Wagner Ehsan Noruzifar Roya Zandi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California, Riverside Outline 1 2 3 4 5 : Capillary Wave
Thermal Casimir Effect for Colloids at a Fluid Interface Jef Wagner Ehsan Noruzifar Roya Zandi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California, Riverside Outline 1 2 3 4 5 : Capillary Wave
Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field
 Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5,
Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5,
Kolloquium Universität Innsbruck October 13, The renormalization group: from the foundations to modern applications
 Kolloquium Universität Innsbruck October 13, 2009 The renormalization group: from the foundations to modern applications Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt 1.) Historical introduction: what is the RG?
Kolloquium Universität Innsbruck October 13, 2009 The renormalization group: from the foundations to modern applications Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt 1.) Historical introduction: what is the RG?
Casimir effect and the quark anti-quark potential. Zoltán Bajnok,
 Gauge/gravity duality, Munich, July 3, 23 Casimir effect and the quark anti-quark potential Zoltán Bajnok, MTA-Lendület Holographic QFT Group, Wigner esearch Centre for Physics, Hungary with L. Palla,
Gauge/gravity duality, Munich, July 3, 23 Casimir effect and the quark anti-quark potential Zoltán Bajnok, MTA-Lendület Holographic QFT Group, Wigner esearch Centre for Physics, Hungary with L. Palla,
lim = F F = F x x + F y y + F z
 Physics 361 Summary of Results from Lecture Physics 361 Derivatives of Scalar and Vector Fields The gradient of a scalar field f( r) is given by g = f. coordinates f g = ê x x + ê f y y + ê f z z Expressed
Physics 361 Summary of Results from Lecture Physics 361 Derivatives of Scalar and Vector Fields The gradient of a scalar field f( r) is given by g = f. coordinates f g = ê x x + ê f y y + ê f z z Expressed
8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Spring 2014 Test 2 Review Problems
 8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Spring 014 Test Review Problems The test is closed book, but if you wish you may bring a one-sided sheet of formulas. The intent of this sheet is as a reminder of important
8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Spring 014 Test Review Problems The test is closed book, but if you wish you may bring a one-sided sheet of formulas. The intent of this sheet is as a reminder of important
Mott metal-insulator transition on compressible lattices
 Mott metal-insulator transition on compressible lattices Markus Garst Universität zu Köln T p in collaboration with : Mario Zacharias (Köln) Lorenz Bartosch (Frankfurt) T c Mott insulator p c T metal pressure
Mott metal-insulator transition on compressible lattices Markus Garst Universität zu Köln T p in collaboration with : Mario Zacharias (Köln) Lorenz Bartosch (Frankfurt) T c Mott insulator p c T metal pressure
On the Dirty Boson Problem
 On the Dirty Boson Problem Axel Pelster 1. Experimental Realizations of Dirty Bosons 2. Theoretical Description of Dirty Bosons 3. Huang-Meng Theory (T=0) 4. Shift of Condensation Temperature 5. Hartree-Fock
On the Dirty Boson Problem Axel Pelster 1. Experimental Realizations of Dirty Bosons 2. Theoretical Description of Dirty Bosons 3. Huang-Meng Theory (T=0) 4. Shift of Condensation Temperature 5. Hartree-Fock
