Exploring Extended MOND in Galaxy Clusters. Alistair Hodson Supervisor Hongsheng Zhao
|
|
|
- Calvin Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploring Extended MOND in Galaxy Clusters Alistair Hodson Supervisor Hongsheng Zhao
2 Overview What is Extended MOND (EMOND)? What is the motivation for EMOND? What are the implications of EMOND? How successful is EMOND?
3 Some Background on Clusters in MOND Galaxy clusters cannot be explained by the current MOND formulation alone. MOND alleviates the mass discrepancy, but is not consistent with dynamical mass Central regions of clusters exhibit even larger mass discrepancies
4 3 Possible Conclusions
5 3 Possible Conclusions MOND is Falsified
6 3 Possible Conclusions MOND is Falsified Missing Mass?
7 3 Possible Conclusions MOND is Falsified Missing Mass? Missing Gravity?
8 3 Possible Conclusions MOND is Falsified Missing Mass? Missing Gravity?
9 Door 2 - Are We Just Missing Mass? Is MOND making a yet unknown mass prediction in clusters? Neutrino Mass? (Sanders 2003, Angus et al 2008, Angus 2008) Non-luminous Baryonic matter clumping on the cluster scale?
10 Door 3 Are We Just Missing Gravity? Newtonian breaks down at low accelerations. Does MOND break down in some limit? Can a generalized MOND explain Clusters and Galaxies simultaneously? Essence of Extended MOND (EMOND)
11 What is Extended MOND? Generalization of MOND EMOND assumes that acceleration scale of MOND is not constant. a0 increases in deep potential wells (Zhao, H & Famaey,B 2011)
12 What is the Motivation for EMOND? MOND works well in galaxies, but not in galaxy clusters. The effective mass of a galaxy cluster in MOND would increase if a0 were higher (Newtonian breaks down at higher accelerations). It was noted that Clusters are in much deeper potential wells than galaxies.
13 The EMOND formulation L MOND = ρφ a π G F(x M 2 ) 2 Φ N = [μ Φ M ] L EMOND = ρφ A 0 Φ 2 2 ) 8 π G F(x EM 2 Φ N = μ Φ E + T 2 x M = Φ x EM = a 0 Φ A 0 (Φ) F y α y for y 1 F y α 2 3 y3/2 for y 1 T 2 = A 0 Φ A 0 Φ F x 2 x 2 F x 2 Bekenstein, J, Milgrom, M 1984 Zhao, H & Famaey,B 2011
14 Some Immediate Implications of EMOND A 0 must be larger in galaxy clusters A 0 must be a 0 in galaxies A 0 must not tend to infinity in very deep potentials Term 2 is more complicated to calculate Even a constant gravitational potential will affect dynamics
15 Possible A 0 Interpolation Functions Exponential function A 0 exp Φ = min(a 0max, a 0 e Φ Φs ) μ function A 0 μ Φ = A 0 max μ Φ Φ s Φ s is defined such that: A 0 a 0 as Φ Φ ext
16 Solving the EMOND Equation For a single isolated and spherical body and assuming T 2 0 and simple μ function dφ N dr = μ Φ E A 0 Φ dφ E dr dφ E dr = 1 2 dφ N dr + dφ N dr 4 A 0 Φ E + dφ N dr Solved iteratively as a boundary value problem Boundary potential Constant External Potential 10-6 c 2 (m s -1 ) 2 Famaey, B et al 2007
17 Sanity Check Galaxy Model 10 7 Solar Mass Galaxy Solar Mass Galaxy ROTATION SPEED (km/s) Radius (kpc)
18 Modelling the Galaxy Clusters in EMOND
19 Initial Assumptions Spherical Symmetry EMOND s extra term T 2 is negligible Constant External Potential from nearest neighbour No neutrino mass
20 X-ray Gas Density ρ r < r out = m p n p n e 1 2 n p n e = n 0 2 ρ r > r out = 0 r r c 1 + r2 r c 2 α 3β α/ rγ r s γ 2 ε/γ + n r2 r c2 2 3β 2 X-ray Gas Temperature T/T mg r/r Vikhlinen, A 2005
21 Modelling the BCG Herniquist Profile Assume M/L= 1 Assume Scale length is 20 kpc for every BCG Φ H r = M H r = G M r + a h M r2 r + a h 2 Cluster Angus et al 2008 BCG Mass (10 11 Solar Mass) A133 8 A A A A A A RXJ MKW4 7.1
22 Calculating the Dynamical Mass Hydrostatic Equilibrium Isotropic System Solve Collisionless Boltzmann Equation M D (r) k T r r w m p G d ln ρ X d ln r + d ln T d ln r
23 Mass Results
24 A133
25 A262
26 A478
27 A1413
28 A1795
29 A1991
30 A2029
31 RXJ1159
32 MKW4
33 An Alternative Formulation?
34 EQUMOND L Q = 1 8 π G 2 Φ Φ N a 0 2 Q x Q 2 ρφ 2 Φ EQ = [ν Φ N ] L EQ = 1 8 π G 2 Φ Φ N A 0 Φ 2 2 N Q x EQ ρφ 2 Φ EQ = ν Φ + T 2 x Q = Φ N x EQ = a 0 Φ N A 0 (Φ N ) Q y α y for y 1 Q y α 4 3 y3/4 for y 1 T 2 = A 0 Φ N A 0 Φ N Q x 2 x 2 Q x 2 Milgrom, M 2010
35 EQUMOND Approach Same method and interpolation functions as in EMOND Constant External Field now Newtonian Equivalent Scale Potentials need renormalized accordingly
36 Calculating the Required Mass of the Cluster dφ N dr = G M N(r) r 2 A 0 Φ N = A 0 max μ Φ N + Φ ext Φ s M EQ r = Φ E r 2 G Φ EQ Φ N ν Φ N A 0 Φ N
37 EQUMOND Galaxy Test 10 7 Solar Mass Galaxy Solar Mass Galaxy
38 EQUMOND Masses - 1
39 EQUMOND Masses - 2
40 EQUMOND Masses - 3
41 EQUMOND Masses - 4
42 EQUMOND Masses - 5
43 The difficulty of EMOND Defining r out Calculating the External field Determining a good A 0 function Black holes experiencing deep-mond if A 0 becomes too large
44 Conclusion and Future Work EMOND can reconcile mass discrepancy in clusters But required a very large A 0 EQUMOND alternative can be constructed Need to Understand Term 2 in more detail Investigate, Develop and Test different A 0 functions Try and find a natural A 0 cut off point
Everything in baryons?
 Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant?
 Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College (moving to Penn State, Hazleton) Collaborators Duncan Farrah Chiu Man Ho Djordje Minic
Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College (moving to Penn State, Hazleton) Collaborators Duncan Farrah Chiu Man Ho Djordje Minic
The Dark Matter Problem
 The Dark Matter Problem Dr. Yves Gaspar, Ph.D. ( University of Cambridge, UK) Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Brescia Department of Mathematics and Physics. Implications of astronomical data. James
The Dark Matter Problem Dr. Yves Gaspar, Ph.D. ( University of Cambridge, UK) Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Brescia Department of Mathematics and Physics. Implications of astronomical data. James
Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College
 Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College Collaborators Duncan Farrah Chiu Man Ho Djordje Minic Y. Jack Ng Tatsu Takeuchi Outline
Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College Collaborators Duncan Farrah Chiu Man Ho Djordje Minic Y. Jack Ng Tatsu Takeuchi Outline
Miami Modified dark matter in galaxy clusters. Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College
 Miami 2015 Modified dark matter in galaxy clusters Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College Collaboration D. Edmonds Emory & Henry College D. Farrah Virginia Tech C.M. Ho Michigan State University D. Minic
Miami 2015 Modified dark matter in galaxy clusters Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College Collaboration D. Edmonds Emory & Henry College D. Farrah Virginia Tech C.M. Ho Michigan State University D. Minic
MOND and the Galaxies
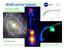 MOND and the Galaxies Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris With Olivier Tiret Angus, Famaey, Gentile, Wu, Zhao Wednesday 1st July 2009 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration
MOND and the Galaxies Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris With Olivier Tiret Angus, Famaey, Gentile, Wu, Zhao Wednesday 1st July 2009 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration
Tidal streams as gravitational experiments!
 Tidal streams as gravitational experiments! Benoit Famaey CNRS - Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg MOND paradigm MDAR: McGaugh et al. 2016 Lelli et al. 2016 Famaey & McGaugh 2012 MOND paradigm Prediction:
Tidal streams as gravitational experiments! Benoit Famaey CNRS - Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg MOND paradigm MDAR: McGaugh et al. 2016 Lelli et al. 2016 Famaey & McGaugh 2012 MOND paradigm Prediction:
The Bullet Cluster 1E evidence shows modified gravity in the absence of dark matter
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 38, 9 47 (7) doi:1.1111/j.1365-966.7.175.x The Bullet Cluster 1E657-558 evidence shows modified gravity in the absence of dark matter J. R. Brownstein 1 and J. W. Moffat 1 Perimeter
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 38, 9 47 (7) doi:1.1111/j.1365-966.7.175.x The Bullet Cluster 1E657-558 evidence shows modified gravity in the absence of dark matter J. R. Brownstein 1 and J. W. Moffat 1 Perimeter
Dark Energy vs. Dark Matter: Towards a unifying scalar field?
 Dark Energy vs. Dark Matter: Towards a unifying scalar field? Alexandre ARBEY Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, March 2nd, 2007. Introduction The Dark Stuff
Dark Energy vs. Dark Matter: Towards a unifying scalar field? Alexandre ARBEY Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, March 2nd, 2007. Introduction The Dark Stuff
Dark Matter. 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam ASTR 333/433. Today. Modified Gravity Theories MOND
 Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Today Modified Gravity Theories MOND 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam Not any theory will do - length scale based modifications can be immediately excluded as the discrepancy does
Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Today Modified Gravity Theories MOND 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam Not any theory will do - length scale based modifications can be immediately excluded as the discrepancy does
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2018](/thumbs/93/112413513.jpg) MOND in galaxy groups Mordehai Milgrom Department of Particle Physics and Astrophysics, Weizmann Institute arxiv:1810.03089v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2018 Galaxy groups, which have hardly been looked at in
MOND in galaxy groups Mordehai Milgrom Department of Particle Physics and Astrophysics, Weizmann Institute arxiv:1810.03089v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Nov 2018 Galaxy groups, which have hardly been looked at in
Dark Matter. Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses ~ 0.3 Ω M Ω b.
 Dark Matter Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses Ω M ~ 0.3 2 1 Ω b 0.04 3 Mass Density by Direct Counting Add up the mass of all the galaxies per
Dark Matter Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses Ω M ~ 0.3 2 1 Ω b 0.04 3 Mass Density by Direct Counting Add up the mass of all the galaxies per
Modifications of Gravity vs. Dark Matter/Energy
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Marie-Curie Fellowship MC-OIF 021421 Finnish-Japanese Workshop on Particle Cosmology Helsinki, March 2007 Outline 1 Gravity Problems with General Relativity 2 Galactic
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Marie-Curie Fellowship MC-OIF 021421 Finnish-Japanese Workshop on Particle Cosmology Helsinki, March 2007 Outline 1 Gravity Problems with General Relativity 2 Galactic
Collisionless Boltzmann Eq (Vlasov eq)" S+G sec 3.4! Collisionless Boltzmann Eq S&G 3.4!
 Collisionless Boltzmann Eq (Vlasov eq)" S+G sec 3.4 When considering the structure of galaxies cannot follow each individual star (10 11 of them), Consider instead stellar density and velocity distributions.
Collisionless Boltzmann Eq (Vlasov eq)" S+G sec 3.4 When considering the structure of galaxies cannot follow each individual star (10 11 of them), Consider instead stellar density and velocity distributions.
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy
 AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
General relativistic attempts to explain flat galactic rotation curves
 General relativistic attempts to explain flat galactic rotation curves based upon: H. Balasin and D. Grumiller, astro-ph/0602519 Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Leipzig DFG project GR-3157-1/1
General relativistic attempts to explain flat galactic rotation curves based upon: H. Balasin and D. Grumiller, astro-ph/0602519 Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Leipzig DFG project GR-3157-1/1
Astrophysical observations preferring Modified Gravity
 Astrophysical observations preferring Modified Gravity A natural approach to extended Newtonian gravity: tests and predictions across astrophysical scales. Mon.Not.Roy.Astron.Soc. 411 (2011) 226-234 Wide
Astrophysical observations preferring Modified Gravity A natural approach to extended Newtonian gravity: tests and predictions across astrophysical scales. Mon.Not.Roy.Astron.Soc. 411 (2011) 226-234 Wide
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Nov 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Nov 2017](/thumbs/93/111428753.jpg) Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 98 (2018), 1-4 Contributed paper arxiv:1711.06335v2 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Nov 2017 INVESTIGATING THE RADIAL ACCELERATION RELATION IN EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES USING THE JEANS ANALYSIS
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 98 (2018), 1-4 Contributed paper arxiv:1711.06335v2 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Nov 2017 INVESTIGATING THE RADIAL ACCELERATION RELATION IN EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES USING THE JEANS ANALYSIS
Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters
 Nov 11, 2015 Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters HW#9 is due; please hand in your summaries; then you get to talk (I have slides of the different facilities/telescopes. HW#10
Nov 11, 2015 Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters HW#9 is due; please hand in your summaries; then you get to talk (I have slides of the different facilities/telescopes. HW#10
GMU, April 13, The Pros and Cons of Invisible Mass and Modified Gravity. Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland
 GMU, April 13, 2007 The Pros and Cons of Invisible Mass and Modified Gravity Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland What gets us into trouble is not what we don t know. It s what we know for sure that just
GMU, April 13, 2007 The Pros and Cons of Invisible Mass and Modified Gravity Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland What gets us into trouble is not what we don t know. It s what we know for sure that just
Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E )
 Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-558) Alan G. Aversa ABSTRACT Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) is a theory that modifies Newton s force law to explain observations that
Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-558) Alan G. Aversa ABSTRACT Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) is a theory that modifies Newton s force law to explain observations that
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters
 Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa, Gianni Marconi & Roberto Gilmozzi European Southern Observatory The idea of this study sparked from the following
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa, Gianni Marconi & Roberto Gilmozzi European Southern Observatory The idea of this study sparked from the following
Dark matter and galaxy formation
 Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Astro-2: History of the Universe. Lecture 5; April
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 5; April 23 2013 Previously.. On Astro-2 Galaxies do not live in isolation but in larger structures, called groups, clusters, or superclusters This is called the
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 5; April 23 2013 Previously.. On Astro-2 Galaxies do not live in isolation but in larger structures, called groups, clusters, or superclusters This is called the
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 28 Sep 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 28 Sep 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 28 Sep 2012](/thumbs/72/67560504.jpg) Testing MOND Over a Wide Acceleration Range in X-Ray Ellipticals Mordehai Milgrom DPPA, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, Israel arxiv:1205.1308v2 [astro-ph.co] 28 Sep 2012 The gravitational
Testing MOND Over a Wide Acceleration Range in X-Ray Ellipticals Mordehai Milgrom DPPA, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, Israel arxiv:1205.1308v2 [astro-ph.co] 28 Sep 2012 The gravitational
Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect
 Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect On the Shoulders of Giants Workshop Case Western Reserve University June 7, 2017 Stephen Alexander Physics Department
Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect On the Shoulders of Giants Workshop Case Western Reserve University June 7, 2017 Stephen Alexander Physics Department
Synchronization of thermal Clocks and entropic Corrections of Gravity
 Synchronization of thermal Clocks and entropic Corrections of Gravity Andreas Schlatter Burghaldeweg 2F, 5024 Küttigen, Switzerland schlatter.a@bluewin.ch Abstract There are so called MOND corrections
Synchronization of thermal Clocks and entropic Corrections of Gravity Andreas Schlatter Burghaldeweg 2F, 5024 Küttigen, Switzerland schlatter.a@bluewin.ch Abstract There are so called MOND corrections
Tests of cosmological gravity
 Tests of cosmological gravity Jeremy Sakstein University of Pennsylvania Astrophysics Seminar UC Irvine 23 rd January 2018 Who am I? Particle-cosmology (baryogenesis, early universe) Modified gravity (dark
Tests of cosmological gravity Jeremy Sakstein University of Pennsylvania Astrophysics Seminar UC Irvine 23 rd January 2018 Who am I? Particle-cosmology (baryogenesis, early universe) Modified gravity (dark
Stellar Population Synthesis, a Discriminant Between Gravity Models
 Stellar Population Synthesis, a Discriminant Between Gravity Models Akram Hasani Zonoozi Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences, IASBS Zanjan, Iran In collaboration with: H.Haghi & Y.Sobouti
Stellar Population Synthesis, a Discriminant Between Gravity Models Akram Hasani Zonoozi Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences, IASBS Zanjan, Iran In collaboration with: H.Haghi & Y.Sobouti
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 1 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 1 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 1 Dec 2017](/thumbs/78/78460368.jpg) Can ΛCDM model reproduce MOND-like behavior? De-Chang Dai, Chunyu Lu Institute of Natural Sciences, Shanghai Key Lab for Particle Physics and Cosmology, School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong
Can ΛCDM model reproduce MOND-like behavior? De-Chang Dai, Chunyu Lu Institute of Natural Sciences, Shanghai Key Lab for Particle Physics and Cosmology, School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong
Direct empirical proof of dark matter?
 Direct empirical proof of dark matter? Masaki Mori Reference: D. Clowe et al., astro-ph/0608407 J.W. Moffat, astro-ph/0608675 ICRR CANGAROO Group Internal Seminar, 05-OCT-2006 Bergstroem and Goobar, Cosmology
Direct empirical proof of dark matter? Masaki Mori Reference: D. Clowe et al., astro-ph/0608407 J.W. Moffat, astro-ph/0608675 ICRR CANGAROO Group Internal Seminar, 05-OCT-2006 Bergstroem and Goobar, Cosmology
Galaxy Rotation Curves of a Galactic Mass Distribution. By: Camiel Pieterse Supervised by: Prof. dr. Wim Beenakker Theoretical High Energy Physics
 Galaxy Rotation Curves of a Galactic Mass Distribution By: Camiel Pieterse Supervised by: Prof. dr. Wim Beenakker Theoretical High Energy Physics 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Mass Distribution 5 2.1 The
Galaxy Rotation Curves of a Galactic Mass Distribution By: Camiel Pieterse Supervised by: Prof. dr. Wim Beenakker Theoretical High Energy Physics 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Mass Distribution 5 2.1 The
Potential energy deficit as an alternative for dark matter?
 Potential energy deficit as an alternative for dark matter? M. Kurpiewski Szczecin, Poland E-mail: marek.qrp@gmail.com This article has been published in Global Journal of Physics Vol 6, No 1. 1 Abstract
Potential energy deficit as an alternative for dark matter? M. Kurpiewski Szczecin, Poland E-mail: marek.qrp@gmail.com This article has been published in Global Journal of Physics Vol 6, No 1. 1 Abstract
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter
 Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 Apr 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 28 Apr 2012](/thumbs/81/84621898.jpg) Hubble Constant, Lensing, and Time Delay in TeVe S Yong Tian 1, Chung-Ming Ko, Mu-Chen Chiu 3 1 Department of Physics, National Central University, Jhongli, Taiwan 30, R.O.C. Institute of Astronomy, Department
Hubble Constant, Lensing, and Time Delay in TeVe S Yong Tian 1, Chung-Ming Ko, Mu-Chen Chiu 3 1 Department of Physics, National Central University, Jhongli, Taiwan 30, R.O.C. Institute of Astronomy, Department
Overview spherical accretion
 Spherical accretion - AGN generates energy by accretion, i.e., capture of ambient matter in gravitational potential of black hole -Potential energy can be released as radiation, and (some of) this can
Spherical accretion - AGN generates energy by accretion, i.e., capture of ambient matter in gravitational potential of black hole -Potential energy can be released as radiation, and (some of) this can
MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review. Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory
 MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review By Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory Everything started in 1933 with the work by Zwicky on the Coma cluster of galaxies, but were galaxy rotation
MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review By Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory Everything started in 1933 with the work by Zwicky on the Coma cluster of galaxies, but were galaxy rotation
Self similar solutions in phase space
 Self similar solutions in phase space x F (x, v,t )=F (, v, t) f (λ x, λ v, λt t )=λ f ( x, v, t ) No dependence on scale for the phase space density solution F α 3 4 Infinitesimal variations of λ implies
Self similar solutions in phase space x F (x, v,t )=F (, v, t) f (λ x, λ v, λt t )=λ f ( x, v, t ) No dependence on scale for the phase space density solution F α 3 4 Infinitesimal variations of λ implies
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies. Spherically symmetric objects Vasily Belokurov vasily@ast.cam.ac.uk Institute of Astronomy Lent Term 2016 1 / 21 Outline I 1 2 Globular of galaxies 2 / 21 Why
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies. Spherically symmetric objects Vasily Belokurov vasily@ast.cam.ac.uk Institute of Astronomy Lent Term 2016 1 / 21 Outline I 1 2 Globular of galaxies 2 / 21 Why
Tristan Clark. And. Dr. Stephen Alexander. Capstone Final Paper. Miami University of Ohio
 1 N- Body Simulations of a Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy Comparing Newtonian, Modified Newtonian, and Dark Matter Models. Tristan Clark And Dr. Stephen Alexander Capstone Final Paper Miami University of Ohio
1 N- Body Simulations of a Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy Comparing Newtonian, Modified Newtonian, and Dark Matter Models. Tristan Clark And Dr. Stephen Alexander Capstone Final Paper Miami University of Ohio
DARK MATTER IN UNIVERSE. edited by. John Bahcall Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, USA. Tsvi Piran The Hebrew University, Israel
 DARK MATTER IN UNIVERSE n d edited by John Bahcall Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, USA Tsvi Piran The Hebrew University, Israel Steven Weinberg University of Texas, Austin, USA TECHNiSCHE INFORMATIONSBIBLIOTHEK
DARK MATTER IN UNIVERSE n d edited by John Bahcall Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, USA Tsvi Piran The Hebrew University, Israel Steven Weinberg University of Texas, Austin, USA TECHNiSCHE INFORMATIONSBIBLIOTHEK
MODEL OF DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY BASED ON GRAVITATIONAL POLARIZATION. Luc Blanchet. 15 septembre 2008
 MODEL OF DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY BASED ON GRAVITATIONAL POLARIZATION Luc Blanchet Gravitation et Cosmologie (GRεCO) Institut d Astrophysique de Paris 15 septembre 2008 Luc Blanchet (GRεCO) Séminaire
MODEL OF DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY BASED ON GRAVITATIONAL POLARIZATION Luc Blanchet Gravitation et Cosmologie (GRεCO) Institut d Astrophysique de Paris 15 septembre 2008 Luc Blanchet (GRεCO) Séminaire
Gravitational Lensing of the Largest Scales
 What is dark matter? Good question. How do we answer it? Gravitational lensing! Gravitational lensing is fantastic Why Clusters of Galaxies Because they are cool!! Studying empirical properties of dark
What is dark matter? Good question. How do we answer it? Gravitational lensing! Gravitational lensing is fantastic Why Clusters of Galaxies Because they are cool!! Studying empirical properties of dark
MOND s Problem in Local Group
 MOND s Problem in Local Group Yan-Chi Shi 1 ABSTRACT I use the distances and motions of Local Group galaxies to test Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND). The old Local Group timing argument of Kahn & Woltjer,
MOND s Problem in Local Group Yan-Chi Shi 1 ABSTRACT I use the distances and motions of Local Group galaxies to test Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND). The old Local Group timing argument of Kahn & Woltjer,
A A + B. ra + A + 1. We now want to solve the Einstein equations in the following cases:
 Lecture 29: Cosmology Cosmology Reading: Weinberg, Ch A metric tensor appropriate to infalling matter In general (see, eg, Weinberg, Ch ) we may write a spherically symmetric, time-dependent metric in
Lecture 29: Cosmology Cosmology Reading: Weinberg, Ch A metric tensor appropriate to infalling matter In general (see, eg, Weinberg, Ch ) we may write a spherically symmetric, time-dependent metric in
The Need for Dark Matter in MOND on Galactic Scales
 The Need for Dark Matter in MOND on Galactic Scales Muhammad Furqaan Yusaf Kings College London, Strand Campus, Department of Physics. muhammad.yusaf@kcl.ac.uk September 28, 2007 As presented by I. Ferreras,
The Need for Dark Matter in MOND on Galactic Scales Muhammad Furqaan Yusaf Kings College London, Strand Campus, Department of Physics. muhammad.yusaf@kcl.ac.uk September 28, 2007 As presented by I. Ferreras,
OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY. Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy)
 OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy) ABSTRACT Assuming KNOWN physical laws, I first discuss OBSERVATIONAL evidence for dark matter in galaxies and
OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy) ABSTRACT Assuming KNOWN physical laws, I first discuss OBSERVATIONAL evidence for dark matter in galaxies and
The MOND Limit of the Inverse Square Law
 The MOND Limit of the Inverse Square Law Abstract Kurt L. Becker This paper attempts to give a theoretical foundation for the Modified Newtonian Dynamics equations developed by M. Milgrom Ref.1. It will
The MOND Limit of the Inverse Square Law Abstract Kurt L. Becker This paper attempts to give a theoretical foundation for the Modified Newtonian Dynamics equations developed by M. Milgrom Ref.1. It will
κ = f (r 0 ) k µ µ k ν = κk ν (5)
 1. Horizon regularity and surface gravity Consider a static, spherically symmetric metric of the form where f(r) vanishes at r = r 0 linearly, and g(r 0 ) 0. Show that near r = r 0 the metric is approximately
1. Horizon regularity and surface gravity Consider a static, spherically symmetric metric of the form where f(r) vanishes at r = r 0 linearly, and g(r 0 ) 0. Show that near r = r 0 the metric is approximately
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Gravity and the Universe
 Gravity and the Universe Test general rela7vity via: Solar System / lab tests Binary pulsars Black hole mergers (future) Cosmology evolu7on of the Universe Gravita7onal 7me dila7on observable directly
Gravity and the Universe Test general rela7vity via: Solar System / lab tests Binary pulsars Black hole mergers (future) Cosmology evolu7on of the Universe Gravita7onal 7me dila7on observable directly
Dark Matter & Dark Energy. Astronomy 1101
 Dark Matter & Dark Energy Astronomy 1101 Key Ideas: Dark Matter Matter we cannot see directly with light Detected only by its gravity (possible future direct detection in the lab) Most of the matter in
Dark Matter & Dark Energy Astronomy 1101 Key Ideas: Dark Matter Matter we cannot see directly with light Detected only by its gravity (possible future direct detection in the lab) Most of the matter in
1.1 Motivation. 1.2 The H-R diagram
 1.1 Motivation Observational: How do we explain stellar properties as demonstrated, e.g. by the H-R diagram? Theoretical: How does an isolated, self-gravitating body of gas behave? Aims: Identify and understand
1.1 Motivation Observational: How do we explain stellar properties as demonstrated, e.g. by the H-R diagram? Theoretical: How does an isolated, self-gravitating body of gas behave? Aims: Identify and understand
X-rays from Clusters of Galaxies!
 Back from Japan Clusters of Galaxies X-ray Overview Probes of the history of structure formation Dynamical timescales are not much shorter than the age of the universe Studies of their evolution, temperature
Back from Japan Clusters of Galaxies X-ray Overview Probes of the history of structure formation Dynamical timescales are not much shorter than the age of the universe Studies of their evolution, temperature
Black-Hole Solutions with Scalar Hair in Einstein-Scalar-Gauss-Bonnet Theories
 Black-Hole Solutions with Scalar Hair in Einstein-Scalar-Gauss-Bonnet Theories Athanasios Bakopoulos Physics Department University of Ioannina In collaboration with: George Antoniou and Panagiota Kanti
Black-Hole Solutions with Scalar Hair in Einstein-Scalar-Gauss-Bonnet Theories Athanasios Bakopoulos Physics Department University of Ioannina In collaboration with: George Antoniou and Panagiota Kanti
Learning from WIMPs. Manuel Drees. Bonn University. Learning from WIMPs p. 1/29
 Learning from WIMPs Manuel Drees Bonn University Learning from WIMPs p. 1/29 Contents 1 Introduction Learning from WIMPs p. 2/29 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Learning about the early Universe Learning from
Learning from WIMPs Manuel Drees Bonn University Learning from WIMPs p. 1/29 Contents 1 Introduction Learning from WIMPs p. 2/29 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Learning about the early Universe Learning from
A glimpse on Cosmology: Mathematics meets the Data
 Naples 09 Seminar A glimpse on Cosmology: Mathematics meets the Data by 10 November 2009 Monica Capone 1 Toward a unified epistemology of Sciences...As we know, There are known knowns. There are things
Naples 09 Seminar A glimpse on Cosmology: Mathematics meets the Data by 10 November 2009 Monica Capone 1 Toward a unified epistemology of Sciences...As we know, There are known knowns. There are things
The Local Group Timing Argument
 The Local Group Timing Argument Real galaxies Milky Way (MW) Andromeda (M31) Indranil Banik (ib45@st-andrews.ac.uk) Supervisor: Hongsheng Zhao University of Saint Andrews MNRAS, 467 (2), 2180 2198 Basic
The Local Group Timing Argument Real galaxies Milky Way (MW) Andromeda (M31) Indranil Banik (ib45@st-andrews.ac.uk) Supervisor: Hongsheng Zhao University of Saint Andrews MNRAS, 467 (2), 2180 2198 Basic
Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3.
 Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab
 Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Clusters: Observations
 Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Mar 2019](/thumbs/95/123586940.jpg) Author s version, Nature BCA, 12thSept.2018 Does the galaxy NGC1052-DF2 falsify Milgromian dynamics? arxiv:1903.11612v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Mar 2019 Pavel Kroupa 1,2, Hosein Haghi 1,3, Behnam Javanmardi 4,
Author s version, Nature BCA, 12thSept.2018 Does the galaxy NGC1052-DF2 falsify Milgromian dynamics? arxiv:1903.11612v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Mar 2019 Pavel Kroupa 1,2, Hosein Haghi 1,3, Behnam Javanmardi 4,
Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017
 Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Structure Formation Until now we have assumed
Physical Cosmology 12/5/2017 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2017 Structure Formation Until now we have assumed
A Scalar-Energy Field That Predicts the Mass of The Electron- Neutrino
 A Scalar-Energy Field That Predicts the Mass of The Electron- Neutrino Michael Harney mharney1268@yahoo.com Abstract: Using Wolff's model of spherical-wave centers, a scalar energy field is derived between
A Scalar-Energy Field That Predicts the Mass of The Electron- Neutrino Michael Harney mharney1268@yahoo.com Abstract: Using Wolff's model of spherical-wave centers, a scalar energy field is derived between
Atelier vide quantique et gravitation DARK MATTER AND GRAVITATIONAL THEORY. Luc Blanchet. 12 décembre 2012
 Atelier vide quantique et gravitation DARK MATTER AND GRAVITATIONAL THEORY Luc Blanchet Gravitation et Cosmologie (GRεCO) Institut d Astrophysique de Paris 12 décembre 2012 Luc Blanchet (GRεCO) Atelier
Atelier vide quantique et gravitation DARK MATTER AND GRAVITATIONAL THEORY Luc Blanchet Gravitation et Cosmologie (GRεCO) Institut d Astrophysique de Paris 12 décembre 2012 Luc Blanchet (GRεCO) Atelier
The halo is specially interesting because gravitational potential becomes dominated by the dark matter halo
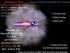 Evidence for dark matter in the Milky Way Astr 511: Galactic Astronomy Winter Quarter 2015 University of Washington Željko Ivezić The halo is specially interesting because gravitational potential becomes
Evidence for dark matter in the Milky Way Astr 511: Galactic Astronomy Winter Quarter 2015 University of Washington Željko Ivezić The halo is specially interesting because gravitational potential becomes
Introduction and Fundamental Observations
 Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Introduction and Fundamental Observations Prelude Cosmology is the study of the universe taken as a whole ruthless simplification necessary (e.g. homogeneity)! Cosmology
Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Introduction and Fundamental Observations Prelude Cosmology is the study of the universe taken as a whole ruthless simplification necessary (e.g. homogeneity)! Cosmology
CONSTRAINING MOND WITH SOLAR SYSTEM DYNAMICS LORENZO IORIO 1. Received 10 Dec.2007; Accepted 13 Feb.2008
 CONSTRAINING MOND WITH SOLAR SYSTEM DYNAMICS LORENZO IORIO 1 1 Viale Unità di Italia 68, 70125, Bari (BA), Italy. tel. 0039 328 6128815. lorenzo.iorio@libero.it. Received 10 Dec.2007; Accepted 13 Feb.2008
CONSTRAINING MOND WITH SOLAR SYSTEM DYNAMICS LORENZO IORIO 1 1 Viale Unità di Italia 68, 70125, Bari (BA), Italy. tel. 0039 328 6128815. lorenzo.iorio@libero.it. Received 10 Dec.2007; Accepted 13 Feb.2008
Estimate of the X-ray mass! in galaxy clusters! Stefano Ettori!
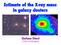 Estimate of the X-ray mass! in galaxy clusters! Stefano Ettori! (INAF-OA Bologna) X-ray total mass The ICM is a fluid because the time scale of elastic/ Coulomb collisions between ions & e - (t coulomb
Estimate of the X-ray mass! in galaxy clusters! Stefano Ettori! (INAF-OA Bologna) X-ray total mass The ICM is a fluid because the time scale of elastic/ Coulomb collisions between ions & e - (t coulomb
Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter
 Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter Jesús Zavala Franco e-mail: jzavalaf@uwaterloo.ca UW, Department of Physics and Astronomy, office: PHY 208C, ext. 38400 Perimeter Institute for
Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter Jesús Zavala Franco e-mail: jzavalaf@uwaterloo.ca UW, Department of Physics and Astronomy, office: PHY 208C, ext. 38400 Perimeter Institute for
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Jan 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Jan 2011](/thumbs/80/81776054.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Distant star clusters of the Milky Way in MOND Hossein Haghi 1,2,, Holger Baumgardt 2,3, and Pavel Kroupa 2 arxiv:111.1952v2 [astro-ph.ga]
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Distant star clusters of the Milky Way in MOND Hossein Haghi 1,2,, Holger Baumgardt 2,3, and Pavel Kroupa 2 arxiv:111.1952v2 [astro-ph.ga]
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND
 Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Brief update (3 mins/2 slides) on astrophysics behind final project
 Nov 1, 2017 Brief update (3 mins/2 slides) on astrophysics behind final project Evidence for Dark Matter Next Wed: Prelim #2, similar to last one (30 mins). Review especially lecture slides, PEs and non-project
Nov 1, 2017 Brief update (3 mins/2 slides) on astrophysics behind final project Evidence for Dark Matter Next Wed: Prelim #2, similar to last one (30 mins). Review especially lecture slides, PEs and non-project
MOND + 11eV sterile neutrinos
 MOND + 11eV sterile neutrinos PPC10 - Day 2 13 -July-2010 th Garry Angus Caustic Group @ UTorino (INFN) In collaboration with Antonaldo Diaferio & Benoit Famaey Modified Newtonian Dynamics MOND new physical
MOND + 11eV sterile neutrinos PPC10 - Day 2 13 -July-2010 th Garry Angus Caustic Group @ UTorino (INFN) In collaboration with Antonaldo Diaferio & Benoit Famaey Modified Newtonian Dynamics MOND new physical
Moment of beginning of space-time about 13.7 billion years ago. The time at which all the material and energy in the expanding Universe was coincident
 Big Bang Moment of beginning of space-time about 13.7 billion years ago The time at which all the material and energy in the expanding Universe was coincident Only moment in the history of the Universe
Big Bang Moment of beginning of space-time about 13.7 billion years ago The time at which all the material and energy in the expanding Universe was coincident Only moment in the history of the Universe
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies
 Clusters and Groups of Galaxies X-ray emission from clusters Models of the hot gas Cooling flows Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect X-ray surveys and clusters Scaling relations Evolutionary effects X-ray emitting
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies X-ray emission from clusters Models of the hot gas Cooling flows Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect X-ray surveys and clusters Scaling relations Evolutionary effects X-ray emitting
DARK MATTER IN GALAXIES. Deqian Yuan
 DARK MATTER IN GALAXIES Deqian Yuan INTRODUCTION Dark Matter(From Merriam Webster): Nonluminous matter not yet directly detected by astronomers that is hypothesized to exist to account for various observed
DARK MATTER IN GALAXIES Deqian Yuan INTRODUCTION Dark Matter(From Merriam Webster): Nonluminous matter not yet directly detected by astronomers that is hypothesized to exist to account for various observed
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 9 Jun 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 14 (006) Printed 3 February 008 (MN LATEX style file v.) Can MOND take a bullet? Analytical comparisons of three versions of MOND beyond spherical symmetry arxiv:astro-ph/060616v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 14 (006) Printed 3 February 008 (MN LATEX style file v.) Can MOND take a bullet? Analytical comparisons of three versions of MOND beyond spherical symmetry arxiv:astro-ph/060616v1
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters
 Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa Instituto de astrofisica de Canarias Gran Telescopio Canarias The idea for this study sparked from the desire of
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa Instituto de astrofisica de Canarias Gran Telescopio Canarias The idea for this study sparked from the desire of
Dark Matter and/or MOND in Giant Ellipticals
 Dark Matter and/or MOND in Giant Ellipticals NGC 4636 & NGC 1399 Ylva Schuberth Tom Richtler, Michael Hilker, Boris Dirsch 1 July 2010 / Strasbourg Y. Schuberth (AIfA) Strasbourg 1 / 16 Outline 1 Globular
Dark Matter and/or MOND in Giant Ellipticals NGC 4636 & NGC 1399 Ylva Schuberth Tom Richtler, Michael Hilker, Boris Dirsch 1 July 2010 / Strasbourg Y. Schuberth (AIfA) Strasbourg 1 / 16 Outline 1 Globular
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 13 May 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 13 May 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 13 May 2008](/thumbs/93/113494455.jpg) Draft version May 13, 28 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/6 MOND AND THE UNIVERSAL ROTATION CURVE: SIMILAR PHENOMENOLOGIES Gianfranco Gentile 1,2 Draft version May 13, 28 arxiv:85.1731v1
Draft version May 13, 28 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/6 MOND AND THE UNIVERSAL ROTATION CURVE: SIMILAR PHENOMENOLOGIES Gianfranco Gentile 1,2 Draft version May 13, 28 arxiv:85.1731v1
Presentation of Dark Matter as violation of superposition principle: is it quantum non-locality of energy? Abstract
 Presentation of Dark Matter as violation of superposition principle: is it quantum non-locality of energy? Dmitri Martila (eestidima@gmail.com) Former Tartu University Lääne 9-51, Tartu 50605, Estonia
Presentation of Dark Matter as violation of superposition principle: is it quantum non-locality of energy? Dmitri Martila (eestidima@gmail.com) Former Tartu University Lääne 9-51, Tartu 50605, Estonia
Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies
 Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies Vincent Bonnivard bonnivard@lpsc.in2p3.fr TAUP 2015 07/09/15 Collaborators: D. Maurin, C. Combet, M. G. Walker, A.
Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies Vincent Bonnivard bonnivard@lpsc.in2p3.fr TAUP 2015 07/09/15 Collaborators: D. Maurin, C. Combet, M. G. Walker, A.
Universal predictions of screened modified gravity in galaxy clusters. David F. Mota
 Universal predictions of screened modified gravity in galaxy clusters David F. Mota Universal predictions of screened modified gravity in galaxy clusters Mass of clusters inferred via lensing, kinematics
Universal predictions of screened modified gravity in galaxy clusters David F. Mota Universal predictions of screened modified gravity in galaxy clusters Mass of clusters inferred via lensing, kinematics
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.286: The Early Universe October 27, 2013 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 6
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.86: The Early Universe October 7, 013 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 6 DUE DATE: Monday, November 4, 013 READING ASSIGNMENT: Steven Weinberg,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.86: The Early Universe October 7, 013 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 6 DUE DATE: Monday, November 4, 013 READING ASSIGNMENT: Steven Weinberg,
IMPLICATIONS OF PARTICLE PHYSICS FOR COSMOLOGY
 IMPLICATIONS OF PARTICLE PHYSICS FOR COSMOLOGY Jonathan Feng University of California, Irvine 28-29 July 2005 PiTP, IAS, Princeton 28-29 July 05 Feng 1 Graphic: N. Graf OVERVIEW This Program anticipates
IMPLICATIONS OF PARTICLE PHYSICS FOR COSMOLOGY Jonathan Feng University of California, Irvine 28-29 July 2005 PiTP, IAS, Princeton 28-29 July 05 Feng 1 Graphic: N. Graf OVERVIEW This Program anticipates
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department. Final Exam
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Physics 8.282J EAPS 12.402J May 20, 2005 Final Exam Name Last First (please print) 1. Do any
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Physics 8.282J EAPS 12.402J May 20, 2005 Final Exam Name Last First (please print) 1. Do any
The structure and evolution of stars. Introduction and recap
 The structure and evolution of stars Lecture 3: The equations of stellar structure 1 Introduction and recap For our stars which are isolated, static, and spherically symmetric there are four basic equations
The structure and evolution of stars Lecture 3: The equations of stellar structure 1 Introduction and recap For our stars which are isolated, static, and spherically symmetric there are four basic equations
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Sep 2005
 Mass Profiles and Shapes of Cosmological Structures G. Mamon, F. Combes, C. Deffayet, B. Fort (eds) EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 2005 arxiv:astro-ph/0509665v1 22 Sep 2005 MONDIAN COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS
Mass Profiles and Shapes of Cosmological Structures G. Mamon, F. Combes, C. Deffayet, B. Fort (eds) EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 2005 arxiv:astro-ph/0509665v1 22 Sep 2005 MONDIAN COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS
Modified Gravity (MOG) and Dark Matter: Can Dark Matter be Detected in the Present Universe?
 Modified Gravity (MOG) and Dark Matter: Can Dark Matter be Detected in the Present Universe? John Moffat Perimeter Institute, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Talk given at the Miami 2014 topical conference on
Modified Gravity (MOG) and Dark Matter: Can Dark Matter be Detected in the Present Universe? John Moffat Perimeter Institute, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Talk given at the Miami 2014 topical conference on
modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie XENON1T Abel & Kaehler
 Dark matter or modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie Françoise Combes 11 December, 2017 XENON1T Abel & Kaehler Why modified gravity? CDM models beautifully account for LSS, CMB, galaxy formation
Dark matter or modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie Françoise Combes 11 December, 2017 XENON1T Abel & Kaehler Why modified gravity? CDM models beautifully account for LSS, CMB, galaxy formation
Large Scale Structure
 Large Scale Structure L2: Theoretical growth of structure Taking inspiration from - Ryden Introduction to Cosmology - Carroll & Ostlie Foundations of Astrophysics Where does structure come from? Initial
Large Scale Structure L2: Theoretical growth of structure Taking inspiration from - Ryden Introduction to Cosmology - Carroll & Ostlie Foundations of Astrophysics Where does structure come from? Initial
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes
 Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: Current state and future prospects
 Gravitational Waves from Core Collapse Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: Current state and future prospects Work done with E. Müller (MPA)
Gravitational Waves from Core Collapse Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: Current state and future prospects Work done with E. Müller (MPA)
with EFTCAMB: The Hořava gravity case
 Testing dark energy and modified gravity models with EFTCAMB: The Hořava gravity case Noemi Frusciante UPMC-CNRS, Institut d Astrophysique de Paris, Paris ERC-NIRG project no.307934 Based on NF, M. Raveri,
Testing dark energy and modified gravity models with EFTCAMB: The Hořava gravity case Noemi Frusciante UPMC-CNRS, Institut d Astrophysique de Paris, Paris ERC-NIRG project no.307934 Based on NF, M. Raveri,
2. Basic Assumptions for Stellar Atmospheres
 2. Basic Assumptions for Stellar Atmospheres 1. geometry, stationarity 2. conservation of momentum, mass 3. conservation of energy 4. Local Thermodynamic Equilibrium 1 1. Geometry Stars as gaseous spheres!
2. Basic Assumptions for Stellar Atmospheres 1. geometry, stationarity 2. conservation of momentum, mass 3. conservation of energy 4. Local Thermodynamic Equilibrium 1 1. Geometry Stars as gaseous spheres!
The collision velocity of the bullet cluster in conventional and modified dynamics
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 8 (2007) Printed 30 March 2007 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The collision velocity of the bullet cluster in conventional and modified dynamics G. W. Angus 1, S. S. McGaugh
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 8 (2007) Printed 30 March 2007 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The collision velocity of the bullet cluster in conventional and modified dynamics G. W. Angus 1, S. S. McGaugh
Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: What could the Signal tell us?
 Outline Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: What could the Signal tell us? Work done at the MPA in Garching Dimmelmeier, Font, Müller, Astron.
Outline Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: What could the Signal tell us? Work done at the MPA in Garching Dimmelmeier, Font, Müller, Astron.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Sep 2006
 Formation of Neutrino Stars from Cosmological Background Neutrinos M. H. Chan, M.-C. Chu Department of Physics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, New Territories, Hong Kong, China arxiv:astro-ph/0609564v1
Formation of Neutrino Stars from Cosmological Background Neutrinos M. H. Chan, M.-C. Chu Department of Physics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, New Territories, Hong Kong, China arxiv:astro-ph/0609564v1

 Circular Orbits for m
Circular Orbits for m