Sec Water vapour variables each has its own usefulness 2/11 The ideal gas law inter-relates vapour pressure (e) & absolute humidity ( ρv) 1 e
|
|
|
- Oliver Willis Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ch7. Water vapour: the most variable gas & most important GHG Absolute humidity Specific humidity ρv ρv = q q= mass of water vapour volume of sample EAS270_Ch7_WaterVapour_A.odp JDW, EAS Ualberta, last mod. 17 Oct [kg m 3 ] ρ mass of water vapour = ρv total mass of sample [kg kg 1 ] or Mixing ratio r Partial pressure of water vapour e ρv mass of water vapour r= =ρ d mass of dry air in sample [g kg 1 ] [Pa ] At the same pressure and temperature, humid air weighs less (and has lower density) than dry air We shall prove this...
2 Sec Water vapour variables each has its own usefulness 2/11 The ideal gas law inter-relates vapour pressure (e) & absolute humidity ( ρv) 1 e = ρv R v T "vapour" R* 1 1 Rv= = 462 J kg K MM 2 Pd = ρd R d T 3 P = ρ Rd T v "virtual" Partial pressure of water vapour ("vapour pressure"), e = ratio of Rd to Rv q= r 1+r temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur (with no change in pressure or moisture content) Numerically, q and r are almost identical (q r ). Both remain constant so long as water vapour is not added or removed from the parcel
3 Water vapour variables each has its own utility specific humidy q (or mixing ratio r ) behaves as a tracer away from the surface and from clouds, it doesn't change as a parcel of air moves around the parcel shown has expanded, but its specific humidity and mixing ratio are unchanged q q 3/11
4 Water vapour variables each has its own usefulness During calm, cloudless weather the late afternoon dewpoint is sometimes considered as a reasonable estimate for overnight minum temperature: e.g. 08:33 MDT Wed 26 Sept a/11
5 "At the same pressure and temperature, humid air weighs less (and has lower density) than dry air" 4/11 Proof: P V = n R* T PV = n = const. R* T MM v nv +MMd nd ρ= V MM v Δ nv +MMd Δ nd Δρ = V n = nv + nd = const. Δρ = So if one adds nv moles of vapour to dry air, keeping volume, pressure and temperature unchanged, then Δρ 1 = [ MM v MM d ] Δ nv V negative, because Δn= 0 and so MM v Δ nv MM d Δ n v V Δ nd = Δ nv MM v = [kg mol 1 ] MM d = [kg mol 1 ]
6 Sec 7.3 Equilibrium vapour pressure (also termed "saturation" vapour press.) 5/11 If/when there are enough vapour molecules above the surface, the evaporation and condensation rates balance, and the air is said to be saturated The vapour pressure e* at which this occurs is a function e*=e*(t) only of the temperature T e*(t) is known as the "equilibrium vapour pressure" or "saturation vapour pressure" (and implictly carries this rider: equilib. with respect to a flat surface of pure water or ice) non-equilibrium e0 equilibrium e1 Fig 7.2 e2
7 15. Water vapour variables equilibrium vapour pressure vs. temperature Will use symbols es and e* interchangeably to denote equilibrium vapour pressure Clausius-Clapeyron eqn. gives es(t) curve. e s (T ) = 6.11 exp Fig 7.4 6/11 [ ( L Rv )] 1 1, hpa T Eq 7.1 L is latent heat (of vaporization or sublimation) and Rv=461.5 [J kg-1 K-1] is gas const for w.v. alternative formulae for es(t ) exist will expect students to be able to use Table 7.1 Fig 7.2c Fig 7.3
8 Sec 7.3 Equilibrium vapour pressure vs. temperature over ice versus over water 7/11 Tiny water droplets in the atmosphere can (and mostly do) remain unfrozen for temperatures far below 0oC, and are said to be "supercooled." Perhaps e (T ) is a strange choice of * "benchmark" for vapour pressure Fig 7.5b Fig 7.5a water ice molecules held tighter in ice lattice
9 Sec 7.3 Equilibrium vapour pressure curve: one graph, two relationships Vapour pressure e and dewpoint temperature Td are in Extracted from Table 7.1 1:1 relationship they are not independent pieces of information. If you know one, you can deduce the other. Symbolically, we write e = e * (T d ) meaning e is a function of Td (the function being the e* curve). Similarly, T d = e 1 * (e) Check: is the adjacent figure consistent with Table 7.1? equiv. to Figure 7.4 8/11
10 Sec 7.3 Four ways to use the equilibrium vapour pressure curve/table 9/11 e * = e * (T ) insert T and get out equilibrium vapour pressure e e = e * (T d ) insert Td and get out actual vapour pressure e T d = e (e) insert e (actual vapour pressure) and get out Td T = e 1 * (e* ) insert e (equilibrium vapour pressure) and get out T 1 * * * Fig 7.4
11 Sec 7.3 Equilibrium vapour pressure curve: one graph, two relationships over water (ice) If T=10, what is the equilib.v.p.? If Td=10, what is the v.p.? If T=10, what is the v.p.? If Td=10, what is the equilib.v.p.? If e=13.12 hpa, what is Td? If e*=13.12 hpa, what is Td? If e*=13.12 hpa, what is T? 10/11
12 Sec 7.4 Bringing air to saturation ie. manipulating sample to arrange that e=e*(t ) 11/11 Which statepoint on Fig 7.7 represents unsaturated air? Which represents supersaturated air? What three processes can bring air to saturation? Fig 7.7 Fig 7.9 Isobaric and adiabatic mixing: Fig 7.10 Tmix = emix = 2 mix 1
13 Topics/concepts covered humid parcels are positively buoyant (relative to dry parcels at same temperature and total pressure) common humidity variables, and their connection with one another notion of a "tracer" of parcel identity understanding definition/meaning of equilibrium vapour pressure 1:1 relationship between vapour pressure e and dewpoint Td using the e*(t ) table (or curve) to get e* given T, or, e given Td or T given e*, or, Td given e "Because the relationship between dew-point temperature and vapour pressure is the same as that between air temperature and saturation vapour pressure, we can use Table 7.1 to determine dew-point temperature given vapour pressure" (p164)
actual vapour pressure e = 100 equilib. vapour pressure
 Chapter 7 (ctd). Water vapour. over water (ice) EAS270_Ch7_WaterVapour_B.odp JDW, EAS U.Alberta, last mod. 18 Oct. 2016 If T=10, what is the equilib.v.p.? If Td=10, what is the v.p.? If T=10, what is the
Chapter 7 (ctd). Water vapour. over water (ice) EAS270_Ch7_WaterVapour_B.odp JDW, EAS U.Alberta, last mod. 18 Oct. 2016 If T=10, what is the equilib.v.p.? If Td=10, what is the v.p.? If T=10, what is the
Lecture Ch. 6. Condensed (Liquid) Water. Cloud in a Jar Demonstration. How does saturation occur? Saturation of Moist Air. Saturation of Moist Air
 Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes)
 10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
Chapter 5 - Atmospheric Moisture
 Chapter 5 - Atmospheric Moisture Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Water Water Vapor - water in a gaseous form, not droplets. Water can also achieve solid and liquid phases on Earth Temperature
Chapter 5 - Atmospheric Moisture Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Water Water Vapor - water in a gaseous form, not droplets. Water can also achieve solid and liquid phases on Earth Temperature
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
1. Water Vapor in Air
 1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.
![P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C. P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.](/thumbs/79/79184286.jpg) Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
4 WATER VAPOR. Contents 4.1. VAPOR PRESSURE AT SATURATION
 Copyright 2017 by Roland Stull. Practical Meteorology: An Algebra-based Survey of Atmospheric Science. v1.02b 4 WATER VAPOR Contents 4.1. Vapor Pressure at Saturation 87 HIGHER MATH Clausius-Clapeyron
Copyright 2017 by Roland Stull. Practical Meteorology: An Algebra-based Survey of Atmospheric Science. v1.02b 4 WATER VAPOR Contents 4.1. Vapor Pressure at Saturation 87 HIGHER MATH Clausius-Clapeyron
Atmospheric Composition הרכב האטמוספירה
 Atmospheric Composition הרכב האטמוספירה N 2 O 2 Trace Gases Water Vapor (H 2 O) Argon (Ar) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Neon (Ne) Helium (He) Methane (CH 4 ) Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Ozone (O 3 ) Nitrogen and oxygen
Atmospheric Composition הרכב האטמוספירה N 2 O 2 Trace Gases Water Vapor (H 2 O) Argon (Ar) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Neon (Ne) Helium (He) Methane (CH 4 ) Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Ozone (O 3 ) Nitrogen and oxygen
Lecture 7. Science A-30 February 21, 2008 Air may be forced to move up or down in the atmosphere by mechanical forces (wind blowing over an obstacle,
 Lecture 7. Science A-30 February 21, 2008 Air may be forced to move up or down in the atmosphere by mechanical forces (wind blowing over an obstacle, like a mountain) or by buoyancy forces. Air that is
Lecture 7. Science A-30 February 21, 2008 Air may be forced to move up or down in the atmosphere by mechanical forces (wind blowing over an obstacle, like a mountain) or by buoyancy forces. Air that is
5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER EARTH SCIENCE
 EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
EARTH SCIENCE 5.2 (HUMIDITY) WEATHER Text: The water vapor content of the air is called humidity. The amount of water vapor air can hold depends on its temperature. Warm air can hold far more moisture
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
2σ e s (r,t) = e s (T)exp( rr v ρ l T ) = exp( ) 2σ R v ρ l Tln(e/e s (T)) e s (f H2 O,r,T) = f H2 O
 Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Outline. Aim. Gas law. Pressure. Scale height Mixing Column density. Temperature Lapse rate Stability. Condensation Humidity.
 Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern Outline A planetary atmosphere consists of different gases hold to the planet by gravity The laws of thermodynamics hold structure as vertical coordinate
Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern Outline A planetary atmosphere consists of different gases hold to the planet by gravity The laws of thermodynamics hold structure as vertical coordinate
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics
 Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
14.3 Ideal Gases > Chapter 14 The Behavior of Gases Ideal Gases Properties of Gases The Gas Laws Gases: Mixtures and Movements
 Chapter 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 Properties of Gases 14.2 The Gas Laws 14.3 Ideal Gases 14.4 Gases: Mixtures and Movements 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Chapter 14 The Behavior of Gases 14.1 Properties of Gases 14.2 The Gas Laws 14.3 Ideal Gases 14.4 Gases: Mixtures and Movements 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
7. The weather instrument below can be used to determine relative humidity.
 1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
1. What is the dewpoint temperature when the dry-bulb temperature is 12 C and the wet-bulb temperature is 7 C? A) 1 C B) -2 C C) -5 C D) 4 C 2. A parcel of air has a dry-bulb temperature reading of 16
Introduction. Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere. How Much Heat Is Brought Upward By Water Vapor?
 Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Chapter 7. Water and Atmospheric Moisture. Water on Earth Unique Properties of Water Humidity Atmospheric Stability Clouds and Fog
 Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Parcel Model. Meteorology September 3, 2008
 Parcel Model Meteorology 5210 September 3, 2008 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature, θ, mixing
Parcel Model Meteorology 5210 September 3, 2008 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature, θ, mixing
12. Heat of melting and evaporation of water
 VS 12. Heat of melting and evaporation of water 12.1 Introduction The change of the physical state of a substance in general requires the absorption or release of heat. In this case, one speaks of a first
VS 12. Heat of melting and evaporation of water 12.1 Introduction The change of the physical state of a substance in general requires the absorption or release of heat. In this case, one speaks of a first
Kelvin Effect. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
Quasi-equilibrium transitions
 Quasi-equilibrium transitions We have defined a two important equilibrium conditions. he first is one in which there is no heating, or the system is adiabatic, and dh/ =0, where h is the total enthalpy
Quasi-equilibrium transitions We have defined a two important equilibrium conditions. he first is one in which there is no heating, or the system is adiabatic, and dh/ =0, where h is the total enthalpy
Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts. Whiteman (2000)
 Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts Whiteman (2000) Dalton s law of partial pressures! The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of the partial pressure of the gases! Partial
Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts Whiteman (2000) Dalton s law of partial pressures! The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of the partial pressure of the gases! Partial
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]
![Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]](/thumbs/81/83694823.jpg) Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Chapter 5. On-line resource
 Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
EAS270, The Atmosphere 2 nd Mid-term Exam 2 Nov. 2016
 EAS270, The Atmosphere 2 nd Mid-term Exam 2 Nov. 2016 Professor: J.D. Wilson Time available: 50 mins Value: 25% No formula sheets; no use of tablet computers etc. or cell phones. Formulae/data at back.
EAS270, The Atmosphere 2 nd Mid-term Exam 2 Nov. 2016 Professor: J.D. Wilson Time available: 50 mins Value: 25% No formula sheets; no use of tablet computers etc. or cell phones. Formulae/data at back.
Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties
 Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties For Further Reading Most information contained within these lecture notes is drawn from Chapters 1, 2, 4, and 6 of The Use of the Skew
Synoptic Meteorology I: Skew-T Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties For Further Reading Most information contained within these lecture notes is drawn from Chapters 1, 2, 4, and 6 of The Use of the Skew
Aorangi (Mt. Cook) we typically view the state of the troposphere on "isobaric surfaces" (surfaces of constant pressure) rather
 Ch3 (ctd.) EAS270_Ch3_BehaviourAtmos_B.odp JDW, EAS UAlberta, last mod. 19 Sept. 2016 Atmospheric "behaviour" Aorani (Mt. Cook) "ride" we typically view the state of the troposphere on "isobaric surfaces"
Ch3 (ctd.) EAS270_Ch3_BehaviourAtmos_B.odp JDW, EAS UAlberta, last mod. 19 Sept. 2016 Atmospheric "behaviour" Aorani (Mt. Cook) "ride" we typically view the state of the troposphere on "isobaric surfaces"
Chapter 5. Atmospheric Moisture
 Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
The Water Cycle. Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site:
 Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
Water in the Atmosphere AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Latent Heat Evaporation & Saturation Relative Humidity Dew Point Lecture 11 Oct 2 2018
In this chapter we explain the processes by which nonprecipitating cloud droplets and ice crystals grow large enough to fall as precipitation
 Goals for today: 19 Oct., 2011 Ch 7, Precipitation Processes In this chapter we explain the processes by which nonprecipitating cloud droplets and ice crystals grow large enough to fall as precipitation
Goals for today: 19 Oct., 2011 Ch 7, Precipitation Processes In this chapter we explain the processes by which nonprecipitating cloud droplets and ice crystals grow large enough to fall as precipitation
ATM 10. Severe and Unusual Weather. Prof. Richard Grotjahn.
 ATM 10 Severe and Unusual Weather Prof. Richard Grotjahn http://atm.ucdavis.edu/~grotjahn/course/atm10/index.html Moisture Mixing ratio Vapor pressure Relative humidity Lecture topics: Saturation vapor
ATM 10 Severe and Unusual Weather Prof. Richard Grotjahn http://atm.ucdavis.edu/~grotjahn/course/atm10/index.html Moisture Mixing ratio Vapor pressure Relative humidity Lecture topics: Saturation vapor
EAS270, The Atmosphere Mid-term Exam 28 Oct. 2011
 EAS270, The Atmosphere Mid-term Exam 28 Oct. 2011 Professor: J.D. Wilson Time available: 50 mins Value: 20% Instructions: For each of the 30 multi-choice questions, choose the most logical option. Use
EAS270, The Atmosphere Mid-term Exam 28 Oct. 2011 Professor: J.D. Wilson Time available: 50 mins Value: 20% Instructions: For each of the 30 multi-choice questions, choose the most logical option. Use
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH
 INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
Parcel Model. Atmospheric Sciences September 30, 2012
 Parcel Model Atmospheric Sciences 6150 September 30, 2012 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature,
Parcel Model Atmospheric Sciences 6150 September 30, 2012 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature,
EART 121 PROBLEM SET #5 SOLUTIONS
 ERT 121 PROLEM SET #5 SOLUTIONS 1. Condensation is not sufficient to make rain Consider 1 mg of air with T = 15 C and RH = 80%. If this small parcel of air gets lofted very high (say, in a cumulonimbus
ERT 121 PROLEM SET #5 SOLUTIONS 1. Condensation is not sufficient to make rain Consider 1 mg of air with T = 15 C and RH = 80%. If this small parcel of air gets lofted very high (say, in a cumulonimbus
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere
![Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere](/thumbs/72/66535634.jpg) Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
5 Atmospheric Stability
 5 Atmospheric Stability Introduction In Chapter 4, we examined the concept of horizontal and vertical atmospheric motion, and how pressure differences create the winds that form on a variety of different
5 Atmospheric Stability Introduction In Chapter 4, we examined the concept of horizontal and vertical atmospheric motion, and how pressure differences create the winds that form on a variety of different
Name 28-MAY-08. FA RP 1 Mr. Chase. 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of millibars?
 FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
FA RP 1 Mr. Chase Name 28-MAY-08 1. Which weather-station model shows an air pressure of 993.4 millibars? 2. Which station model shows the correct form for indicating a northwest wind at 25 knots and an
Generating cloud drops from CCN. Wallace & Hobbs (1977)
 Generating cloud drops from CCN Wallace & Hobbs (1977) Cloud Drops and Equilibrium Considera3ons: review We discussed how to compute the equilibrium vapor pressure over a pure water drop, or a solu3on
Generating cloud drops from CCN Wallace & Hobbs (1977) Cloud Drops and Equilibrium Considera3ons: review We discussed how to compute the equilibrium vapor pressure over a pure water drop, or a solu3on
1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium
 1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium The preceding section involved only single phase systems. For it to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, a homogeneous system must be in thermal equilibrium
1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium The preceding section involved only single phase systems. For it to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, a homogeneous system must be in thermal equilibrium
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
Name Class Date. 3. In what part of the water cycle do clouds form? a. precipitation b. evaporation c. condensation d. runoff
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Water in the Air 1. What do we call the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place? a. the water cycle b. weather c. climate d. precipitation THE
Melting of ice particles:
 Melting of ice particles: When ice particles fall below 0 C they begin to melt, but the process takes some time since heat transfer needs to occur (heat from ambient environment has to supply the latent
Melting of ice particles: When ice particles fall below 0 C they begin to melt, but the process takes some time since heat transfer needs to occur (heat from ambient environment has to supply the latent
Köhler Curve. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Köhler Curve Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Review of Kelvin Effect Gibbs Energy for formation of a drop G = G &'()*+, G ).'+
Köhler Curve Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Review of Kelvin Effect Gibbs Energy for formation of a drop G = G &'()*+, G ).'+
CHAPTER 1 Matter in our Surroundings CONCEPT DETAILS
 CHAPTER 1 Matter in our Surroundings CONCEPT DETAILS KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] 1. Particle nature of Matter *** 2. States of Matter **** 3. Interchange in states of Matter
CHAPTER 1 Matter in our Surroundings CONCEPT DETAILS KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] 1. Particle nature of Matter *** 2. States of Matter **** 3. Interchange in states of Matter
Precipitation. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7
 Precipitation GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7 Last lecture! Atmospheric stability! Condensation! Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)! Types of clouds Precipitation! Why clouds don t fall! Terminal
Precipitation GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7 Last lecture! Atmospheric stability! Condensation! Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)! Types of clouds Precipitation! Why clouds don t fall! Terminal
The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations
 PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to:
 Unit 9. Liquids and Solids - ANSWERS Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to: 9.1 List the various intermolecular attractions in liquids and solids (dipole-dipole, London
Unit 9. Liquids and Solids - ANSWERS Upon successful completion of this unit, the students should be able to: 9.1 List the various intermolecular attractions in liquids and solids (dipole-dipole, London
The Behaviour of the Atmosphere
 3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Describing Weather -- Lesson 1 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 Describe weather. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 List and define the variables used to describe weather.
ATMOSPHERIC THERMODYNAMICS
 ATMOSPHERIC THERMODYNAMICS 1. Introduction 1.1 The field of thermodynamics Classical thermodynamics deals with energy and the transformations of the nature of energy. To a certain extent, it classifies
ATMOSPHERIC THERMODYNAMICS 1. Introduction 1.1 The field of thermodynamics Classical thermodynamics deals with energy and the transformations of the nature of energy. To a certain extent, it classifies
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
5) The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 C is called: Page Ref: 69
 Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
Homework #2 Due 9/19/14 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, what would the daily mean temperature be? (Page Ref: 66) 2) How is the annual mean
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2015
 CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2015 Week 5: September 24, 2015 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2015 Week 5: September 24, 2015 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Psychometric Processes Good afternoon, yesterday we
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Psychometric Processes Good afternoon, yesterday we
The atmosphere s water
 The atmosphere s water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Process Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main points for
The atmosphere s water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Process Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main points for
9 Condensation. Learning Goals. After studying this chapter, students should be able to:
 9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
Simplified Microphysics. condensation evaporation. evaporation
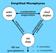 Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 1 CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The objective of atmospheric chemistry is to understand the factors that control the concentrations of chemical species in the atmosphere. In this book
1 CHAPTER 1. MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The objective of atmospheric chemistry is to understand the factors that control the concentrations of chemical species in the atmosphere. In this book
ATMO 551a Moist Adiabat Fall Change in internal energy: ΔU
 Enthalpy and the Moist Adiabat We have described the dry adiabat where an air parcel is lifted rapidly causing the air parcel to expand as the environmental pressure decreases and the air parcel does work
Enthalpy and the Moist Adiabat We have described the dry adiabat where an air parcel is lifted rapidly causing the air parcel to expand as the environmental pressure decreases and the air parcel does work
Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics
 Name: Date: Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics 1. The kelvin temperature of an object is a measure of A. the total energy of the molecules of the object. B. the total kinetic energy of the molecules of
Name: Date: Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics 1. The kelvin temperature of an object is a measure of A. the total energy of the molecules of the object. B. the total kinetic energy of the molecules of
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
EARTH SCIENCE. Prentice Hall Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere.
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
PHASE CHANGE. Freezing Sublimation
 Melting Graphic Organizer Deposition PHASE CHANGE Freezing Sublimation Boiling Evaporation Condensation PHASE CHANGE Phase change happens as the temperature changes. All matter can move from one state
Melting Graphic Organizer Deposition PHASE CHANGE Freezing Sublimation Boiling Evaporation Condensation PHASE CHANGE Phase change happens as the temperature changes. All matter can move from one state
Clouds and atmospheric convection
 Clouds and atmospheric convection Caroline Muller CNRS/Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique (LMD) Département de Géosciences ENS M2 P7/ IPGP 1 What are clouds? Clouds and atmospheric convection 3 What
Clouds and atmospheric convection Caroline Muller CNRS/Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique (LMD) Département de Géosciences ENS M2 P7/ IPGP 1 What are clouds? Clouds and atmospheric convection 3 What
CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes CHAPTER 1 Matter in our Surroundings
 CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes CHAPTER 1 Matter in our Surroundings Anything that occupies space and has mass and is felt by senses is called matter. According to indian ancient philosphor, matter
CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes CHAPTER 1 Matter in our Surroundings Anything that occupies space and has mass and is felt by senses is called matter. According to indian ancient philosphor, matter
Chapter 12. Insert picture from First page of chapter. Intermolecular Forces and the Physical Properties of Liquids and Solids
 Chapter 12 Insert picture from First page of chapter Intermolecular Forces and the Physical Properties of Liquids and Solids Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 12.1 Intermolecular Forces Intermolecular forces
Chapter 12 Insert picture from First page of chapter Intermolecular Forces and the Physical Properties of Liquids and Solids Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 12.1 Intermolecular Forces Intermolecular forces
Measuring State Parameters of the Atmosphere
 Measuring State Parameters of the Atmosphere Some Applications of Atmospheric Thermodynamics Earth Observing Laboratory, NCAR IDEAS-4 Tutorial Introduction Goals of This Presentation Present two complementary
Measuring State Parameters of the Atmosphere Some Applications of Atmospheric Thermodynamics Earth Observing Laboratory, NCAR IDEAS-4 Tutorial Introduction Goals of This Presentation Present two complementary
Worksheet 1.1. Chapter 1: Quantitative chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 1.1 Chapter 1: Quantitative chemistry glossary Amount The number of moles of a substance present in a sample. Aqueous solution A solution with water as the solvent. Atmosphere The unit atmosphere
Worksheet 1.1 Chapter 1: Quantitative chemistry glossary Amount The number of moles of a substance present in a sample. Aqueous solution A solution with water as the solvent. Atmosphere The unit atmosphere
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
latent heat/humidity
 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010. MAPH Physical Meteorology
 SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010 MAPH 40240 Physical Meteorology Extern examiner: Professor Keith Shine Head of School: Professor Micheal O Searcoid Examiner: Dr. Rodrigo Caballero Time Allowed: 2 hours
SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010 MAPH 40240 Physical Meteorology Extern examiner: Professor Keith Shine Head of School: Professor Micheal O Searcoid Examiner: Dr. Rodrigo Caballero Time Allowed: 2 hours
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper.
 Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
February 11, Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6
 Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6 What is dew point? Bell Work Response Sheet: Water In The Air Answers When we put water on our hands and waved them in the air, our skin felt cooler. That's because
Weather and Water Investigation 6 Day 6 What is dew point? Bell Work Response Sheet: Water In The Air Answers When we put water on our hands and waved them in the air, our skin felt cooler. That's because
Vantage Pro Technical Reference
 Vantage Pro Technical Reference Davis Instruments 3465 Diablo Ave. Hayward, CA 94545 Created: 9/11/01 Calculations of Derived Variables The following parameters do not have any sensors or circuitry. They
Vantage Pro Technical Reference Davis Instruments 3465 Diablo Ave. Hayward, CA 94545 Created: 9/11/01 Calculations of Derived Variables The following parameters do not have any sensors or circuitry. They
Cloud Condensation Nuclei Hygroscopic Parameter Kappa
 Cloud Condensation Nuclei Hygroscopic Parameter Kappa Covers Reading Material in Chapter 17.5 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) Form a cloud
Cloud Condensation Nuclei Hygroscopic Parameter Kappa Covers Reading Material in Chapter 17.5 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) Form a cloud
Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know
 The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2017
 CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2017 October 5, 2017 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com Twitter: @built_envi
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2017 October 5, 2017 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com Twitter: @built_envi
Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solids
 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solids Chapter 11 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. A phase is a homogeneous part of the system in contact
Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solids Chapter 11 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. A phase is a homogeneous part of the system in contact
Change in temperature of object of mass m kg. -T i. T= T f. Q mc
 PHYS1001 Physics 1 REGULAR Module 2 Thermal Physics SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY PHASE CHANGES CALORIMETRY Energy Mechanical energy: kinetic and potential Thermal energy: internal energy, Σ(KE + PE) Chemical
PHYS1001 Physics 1 REGULAR Module 2 Thermal Physics SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY PHASE CHANGES CALORIMETRY Energy Mechanical energy: kinetic and potential Thermal energy: internal energy, Σ(KE + PE) Chemical
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 2
 Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 2 Topics Some aspects of advection and the Coriolis-effect (1.7) Composition of the atmosphere (figure 1.6) Equation of state (1.8&1.9) Water vapour in the atmosphere (1.10)
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 2 Topics Some aspects of advection and the Coriolis-effect (1.7) Composition of the atmosphere (figure 1.6) Equation of state (1.8&1.9) Water vapour in the atmosphere (1.10)
Thursday, June 5, Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation
 Thursday, June 5, 2014 Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation Chapter 5: Condensation and Precipitation Formation of Condensation Saturated Air Condensation Nuclei Results of Condensation Clouds Fog Dew
Thursday, June 5, 2014 Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation Chapter 5: Condensation and Precipitation Formation of Condensation Saturated Air Condensation Nuclei Results of Condensation Clouds Fog Dew
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation
 Atmospheric Water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Processes Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main topics for today
Atmospheric Water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Processes Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main topics for today
Final Examination. Part A Answer ONLY TWELVE QUESTIONS in Part A. (Each question is 3 points)
 ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
ATS 210 Spring Term 2001 NAME: Final Examination This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. Calculators may be used. All answers should be written on the examination paper. Use the final sheet for any
A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time
 WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012
 GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012 Løsningsforslag til oppgavesett 4 WH06 3.46 (WH 2.49) The air parcel has the properties p = 1000hPa, T = 15 C and T d = 4 C. b Lifting the air parcel to p 2 = 900hPa, T 2 we
GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012 Løsningsforslag til oppgavesett 4 WH06 3.46 (WH 2.49) The air parcel has the properties p = 1000hPa, T = 15 C and T d = 4 C. b Lifting the air parcel to p 2 = 900hPa, T 2 we
LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture
 Name School LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture Our atmosphere is a very dynamic area especially when we see what type of interactions it has with the surrounding environment. This lab will begin discussing
Name School LAB 3: Atmospheric Pressure & Moisture Our atmosphere is a very dynamic area especially when we see what type of interactions it has with the surrounding environment. This lab will begin discussing
Supporting Information: On Localized Vapor Pressure Gradients Governing Condensation and Frost Phenomena
 Supporting Information: On Localized Vapor Pressure Gradients Governing Condensation and Frost Phenomena Saurabh Nath and Jonathan B. Boreyko Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, Virginia
Supporting Information: On Localized Vapor Pressure Gradients Governing Condensation and Frost Phenomena Saurabh Nath and Jonathan B. Boreyko Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, Virginia
CHAPTER ELEVEN KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
 CHAPTER ELEVEN AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Differences between condensed states and gases? KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Phase Homogeneous part
CHAPTER ELEVEN AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Differences between condensed states and gases? KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Phase Homogeneous part
The two major assumptions required to reduce VLE calculations to Raoult's law are:
 10.4 SIMPLE MODELS FOR VAPOR/LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM The preceding section has described what is observed through experimental observation. When thermodynamics is applied to vapour/liquid equilibrium, the goal
10.4 SIMPLE MODELS FOR VAPOR/LIQUID EQUILIBRIUM The preceding section has described what is observed through experimental observation. When thermodynamics is applied to vapour/liquid equilibrium, the goal
Unit 4: Gas Laws. Matter and Phase Changes
 Unit 4: Gas Laws Matter and Phase Changes ENERGY and matter What is 에너지 A fundamental property of the universe that cannot be easily defined. Energy No one knows what energy is, only what it does or has
Unit 4: Gas Laws Matter and Phase Changes ENERGY and matter What is 에너지 A fundamental property of the universe that cannot be easily defined. Energy No one knows what energy is, only what it does or has
