Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere
|
|
|
- Isaac Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Climate Dynamics (Summer Semester 2017) J. Mülmenstädt Today s Lecture (Lecture 5): General circulation of the atmosphere Reference Hartmann, Global Physical Climatology (1994), Ch. 2, 3, 6 Peixoto and Oort, Ch. 4, 6, 7
2 2.3 General circulation of the atmosphere Atmospheric transport in response to radiative imbalance Mean meridional circulation and eddy circulation
3 2.3 General circulation of the atmosphere Atmospheric transport in response to radiative imbalance Mean meridional circulation and eddy circulation Energy cycle Entropy cycle
4 2.3 General circulation of the atmosphere Atmospheric transport in response to radiative imbalance Mean meridional circulation and eddy circulation Energy cycle Entropy cycle Cycles of momentum, angular momentum Hydrological cycle
5 Radiative budgets for the atmosphere and at TOA Radiative energy balance of the atmosphere (sign convention: downwelling positive) is R a = F TOA F s + R TOA R s = ( ) ( 239) ( ) W m 2 = O( 100 W m 2 ), (2.85) balanced by fluxes of sensible and latent heat into the atmosphere Figure: Wild et al., 2015
6 Zonal-mean radiative budget at TOA TOA radiative budget... The top-of-atmosphere (TOA) radiative balance measures how much energy enters or leaves the climate system In the tropics, the net energy flux is positive (into the climate system) In the extratropics, the net energy flux is negative (out of the climate system)... requires meridional energy transport To maintain a steady state (e.g., constant long-term zonal-mean temperature), energy transport from the tropics into the extratropics is required The meridional divergence of the energy transport balances the radiative energy flux Contributions to transport from ocean and atmosphere Figures: Hartmann (1994), Trenberth and Caron (2001)
7 Atmospheric energy budget requires atmospheric transport As we saw in the previous section, the net radiative energy balance of the atmosphere is R a = O( 100 W m 2 ); the balance is fairly constant in latitude The radiative energy loss is balanced by latent (LP) and sensible (SH) heat flux from land and ocean; but these are strong functions of latitude Meridional advective atmospheric energy flux is required to provide local energy balance: R a + F LH + F SH = F a (2.86) The advective energy flux is the meridional divergence of the meridional heat transport (sign convention: northward positive): dn dφ = 2π 0 dλ R 2 E Fa(φ) cos φ = 2πR2 E Fa(φ) cos φ (2.87) Figures from Hartmann (1994) unless noted
8 Atmospheric energy budget requires atmospheric transport As we saw in the previous section, the net radiative energy balance of the atmosphere is R a = O( 100 W m 2 ); the balance is fairly constant in latitude The radiative energy loss is balanced by latent (LP) and sensible (SH) heat flux from land and ocean; but these are strong functions of latitude Meridional advective atmospheric energy flux is required to provide local energy balance: R a + F LH + F SH = F a (2.86) The advective energy flux is the meridional divergence of the meridional heat transport (sign convention: northward positive): dn dφ = 2π 0 dλ R 2 E Fa(φ) cos φ = 2πR2 E Fa(φ) cos φ (2.87) Trenberth and Caron (2001)
9 Averaging operators Temporal mean and the zonal mean The instantaneous value of A is given by A = A(λ, φ, p) = 1 τ/2 A(λ, φ, p, t) dt (2.88) τ τ/2 [A] = [A](φ, p, t) = 1 2π where A is called the fluctuating component of A. Likewise where A is the departure from the zonal mean. 2π A(λ, φ, p, t) dλ (2.89) 0 A = A + A (2.90) A = [A] + A (2.91) Decomposition of a field into time-average and fluctuating, zonally symmetric and zonally asymmetric components: A = [Ā] + [A ] + Ā + A (2.92)
10 Decomposition of the flow Products of fields contain covariance terms (where fluctuations do not average to zero) AB = Ā B + A B (2.93) [AB] = [A][B] + [A B ] (2.94) [ ] AB = [ Ā ] [ B ] + [ Ā B ] ] + [A B (2.95) The terms in (2.95) are the mean circulation, stationary eddies, and transient eddies. To take a concrete example, the decomposition of northward flux of sensible heat is ] [ ] c p [vt = c p v][ T + c p [ v T ] ] + c p [v T (2.96) This week s homework will analyze the relative importance of each contribution as a function of latitude.
11 Example of meridional heat transport by a transient eddy [v][t] [v T ] in the eddy covering northern Europe
12 Mean circulation streamfunction The zonal-mean continuity equation (zonal flow is integrated out) is 1 [ ω] ([ v] cos φ) + R E cos φ φ p = 0 (2.97) For a nondivergent flow, velocity components can be written with the aid of a streamfunction: g [ v] = 2πR E cos φ [ ω] = Ψ M p g Ψ M 2πR 2 E cos φ φ (2.98) (2.99) (2.98) and (2.99) satisfy (2.97); normalization, including the minus sign, is convention but the relative minus sign is required. To calculate Ψ M, first impose boundary condition Ψ M = 0 at TOA, then integrate (2.98): Ψ M = 2πR E cos φ g p [ v] dp (2.100) 0 The normalization is chosen to give units of kg s 1 (mass streamfunction); the cos φ factor is required to ensure constant Ψ M for constant meridional flow. Mass transport is tangent to contours of the streamfunction. Mass flow between two contours is equal to Ψ M.
13 Mean meridional circulation Hadley cell with rising branch in the ITCZ and descending in the subtropics Transport is from winter hemisphere to summer hemisphere at the surface, summer hemisphere to winter hemisphere at altitude transport of potential energy, latent heat, sensible heat Mass transport by mean circulation is small outside the Hadley cell This is where (temporal and zonal) fluctuations in the circulation are important eddy transport Figure: Hartmann (1994); shaded: Ψ M < 0; units: kg s 1
14 Meridional energy transport Recall static energy (2.72): sum of potential energy (PE), sensible heat (SH) and latent heat (LH) h = gz + c pt + L lv q (2.101) The divergence of poleward transport of these energy terms balances the atmospheric energy budget. Mean transport dominates in the Hadley cell but note large terms of opposite signs Eddy transport, especially in winter (large temperature gradient), dominates in midlatitudes
7 The General Circulation
 7 The General Circulation 7.1 The axisymmetric state At the beginning of the class, we discussed the nonlinear, inviscid, axisymmetric theory of the meridional structure of the atmosphere. The important
7 The General Circulation 7.1 The axisymmetric state At the beginning of the class, we discussed the nonlinear, inviscid, axisymmetric theory of the meridional structure of the atmosphere. The important
Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations
 Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Monsoons- Past, Present and future May 20th, 2015 Caltech, Pasadena Outline Introduction Global monsoon in isentropic coordinates Dry ventilation
Isentropic flows and monsoonal circulations Olivier Pauluis (NYU) Monsoons- Past, Present and future May 20th, 2015 Caltech, Pasadena Outline Introduction Global monsoon in isentropic coordinates Dry ventilation
General Atmospheric Circulation
 General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
Tropical Meridional Circulations: The Hadley Cell
 Tropical Meridional Circulations: The Hadley Cell Introduction Throughout much of the previous sections, we have alluded to but not fully described the mean meridional overturning circulation of the tropics
Tropical Meridional Circulations: The Hadley Cell Introduction Throughout much of the previous sections, we have alluded to but not fully described the mean meridional overturning circulation of the tropics
CHAPTER 4. THE HADLEY CIRCULATION 59 smaller than that in midlatitudes. This is illustrated in Fig. 4.2 which shows the departures from zonal symmetry
 Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate
 Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
no eddies eddies Figure 3. Simulated surface winds. Surface winds no eddies u, v m/s φ0 =12 φ0 =0
 References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
The general circulation: midlatitude storms
 The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean*
 JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
Estimating the zonal wavenumber dependence of the meridional energy transport
 MO91 egree Project in Atmospheric Sciences, Oceanography and Climate, 3hp Estimating the zonal wavenumber dependence of the meridional energy transport Mattias Burtu Supervisor: Rune Grand Graversen epartment
MO91 egree Project in Atmospheric Sciences, Oceanography and Climate, 3hp Estimating the zonal wavenumber dependence of the meridional energy transport Mattias Burtu Supervisor: Rune Grand Graversen epartment
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles. Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild
 The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
Course , General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget
 Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget Water Vapor Distribution First let us look at the distribution of specific humidity, q. The
Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 4: Water Vapor Budget Water Vapor Distribution First let us look at the distribution of specific humidity, q. The
The general circulation of the atmosphere
 Lecture Summer term 2015 The general circulation of the atmosphere Prof. Dr. Volkmar Wirth, Zi. 426, Tel.: 39-22868, vwirth@uni-mainz.de Lecture: 2 Stunden pro Woche Recommended reading Hartmann, D. L.,
Lecture Summer term 2015 The general circulation of the atmosphere Prof. Dr. Volkmar Wirth, Zi. 426, Tel.: 39-22868, vwirth@uni-mainz.de Lecture: 2 Stunden pro Woche Recommended reading Hartmann, D. L.,
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport. Recall that the most primitive equilibrium climate model can be written
 2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
Angular Momentum Presentation Week 2
 Angular Momentum Presentation Week 2 from Iskenderian and Salstein, Monthly Weather Review (1998) zonally averaged zonal wind [u] (m s -1 ) 90 S 0 90 N Courtesy of David Salstein ΔM = k x Δ(L.O.D.) Courtesy
Angular Momentum Presentation Week 2 from Iskenderian and Salstein, Monthly Weather Review (1998) zonally averaged zonal wind [u] (m s -1 ) 90 S 0 90 N Courtesy of David Salstein ΔM = k x Δ(L.O.D.) Courtesy
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
On the role of planetary-scale waves in the abrupt seasonal. transition of the Northern Hemisphere general circulation. Tiffany A.
 Generated using version 3.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 On the role of planetary-scale waves in the abrupt seasonal 2 transition of the Northern Hemisphere general circulation 3 Tiffany A. Shaw
Generated using version 3.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 On the role of planetary-scale waves in the abrupt seasonal 2 transition of the Northern Hemisphere general circulation 3 Tiffany A. Shaw
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
(after Stephens et al. 2012)
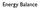 Energy Balance Incoming solar radiation 34 Reflected solar radiation Outgoing longwave radiation 1 24 TOA 75 Atmospheric absorption Atmospheric reflection 77 Atmospheric window 4 165 35 Clear Sky Cloud
Energy Balance Incoming solar radiation 34 Reflected solar radiation Outgoing longwave radiation 1 24 TOA 75 Atmospheric absorption Atmospheric reflection 77 Atmospheric window 4 165 35 Clear Sky Cloud
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/2/2015
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
The meteorology of monsoons
 978--521-84799-5 - The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects 1 The meteorology of monsoons 1.1 Introduction Monsoon circulations are major features of the tropical atmosphere, which, primarily through
978--521-84799-5 - The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects 1 The meteorology of monsoons 1.1 Introduction Monsoon circulations are major features of the tropical atmosphere, which, primarily through
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments
 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
The Energy Balance Model
 1 The Energy Balance Model 2 D.S. Battisti 3 Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle Generated using v.3.2 of the AMS LATEX template 1 ABSTRACT 5 ad 2 6 1. Zero-order climatological
1 The Energy Balance Model 2 D.S. Battisti 3 Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle Generated using v.3.2 of the AMS LATEX template 1 ABSTRACT 5 ad 2 6 1. Zero-order climatological
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Goal: Understand the dynamics and thermodynamics of the Hadley circulation
 Description of the zonal mean tropical overturning (or Hadley) circulation Some simple dynamical and thermodynamic models of the Hadley circulation* The Hadley circulation in a global circulation context
Description of the zonal mean tropical overturning (or Hadley) circulation Some simple dynamical and thermodynamic models of the Hadley circulation* The Hadley circulation in a global circulation context
ATMS 321: Sci. of Climate Final Examination Study Guide Page 1 of 4
 ATMS 321: Sci. of Climate Final Examination Study Guide Page 1 of 4 Atmospheric Sciences 321: Final Examination Study Guide The final examination will consist of similar questions Science of Climate Multiple
ATMS 321: Sci. of Climate Final Examination Study Guide Page 1 of 4 Atmospheric Sciences 321: Final Examination Study Guide The final examination will consist of similar questions Science of Climate Multiple
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Eliassen-Palm Cross Sections Edmon et al. (1980)
 Eliassen-Palm Cross Sections Edmon et al. (1980) Cecily Keppel November 14 2014 Eliassen-Palm Flux For β-plane Coordinates (y, p) in northward, vertical directions Zonal means F = v u f (y) v θ θ p F will
Eliassen-Palm Cross Sections Edmon et al. (1980) Cecily Keppel November 14 2014 Eliassen-Palm Flux For β-plane Coordinates (y, p) in northward, vertical directions Zonal means F = v u f (y) v θ θ p F will
14.1 Simple model of global radiation balance
 Chapter 1 Global Circulations 1.1 Simple model of global radiation balance The earth receives energy from the sun in the form of visible, near-infrared, and ultraviolet radiation. Most of this energy is
Chapter 1 Global Circulations 1.1 Simple model of global radiation balance The earth receives energy from the sun in the form of visible, near-infrared, and ultraviolet radiation. Most of this energy is
Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions in the Seasonal Cycle of a Hadley Circulation and Implications for Monsoon Dynamics
 Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences (to appear) Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions in the Seasonal Cycle of a Hadley Circulation and Implications for Monsoon Dynamics TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences (to appear) Eddy-Mediated Regime Transitions in the Seasonal Cycle of a Hadley Circulation and Implications for Monsoon Dynamics TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell
 1522 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 60 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell IOANA M. DIMA AND JOHN M. WALLACE Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
1522 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES VOLUME 60 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Seasonality of the Hadley Cell IOANA M. DIMA AND JOHN M. WALLACE Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8
 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8 1. Consider a zonally symmetric circulation (i.e., one with no longitudinal variations) in the atmosphere. In the inviscid upper troposphere,
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8 1. Consider a zonally symmetric circulation (i.e., one with no longitudinal variations) in the atmosphere. In the inviscid upper troposphere,
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
Tropical and Subtropical Meridional Latent Heat Transports by Disturbances to the Zonal Mean and Their Role in the General Circulation
 1872 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Tropical and Subtropical Meridional Latent Heat Transports by Disturbances to the Zonal Mean and Their Role in the General Circulation
1872 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Tropical and Subtropical Meridional Latent Heat Transports by Disturbances to the Zonal Mean and Their Role in the General Circulation
General Circulation of the Atmosphere. René Garreaud
 General Circulation of the Atmosphere René Garreaud www.dgf.uchile.cl/rene General circulation of the Atmosphere Low latitude areas receive more solar energy than high latitudes (because of earth sphericity).
General Circulation of the Atmosphere René Garreaud www.dgf.uchile.cl/rene General circulation of the Atmosphere Low latitude areas receive more solar energy than high latitudes (because of earth sphericity).
Lecture 7 Basic Principles of Climate
 Lecture 7 Basic Principles of Climate Raymond T. Pierrehumbert One-dimensional climate models Introduction In zero-dimensional models, variations of temperature with latitude cannot be taken into account.
Lecture 7 Basic Principles of Climate Raymond T. Pierrehumbert One-dimensional climate models Introduction In zero-dimensional models, variations of temperature with latitude cannot be taken into account.
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments
 Clim Dyn DOI 1.17/s382-13-1843-4 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments Aaron Donohoe Dargan M. W. Frierson David S. Battisti Received: 21 April 13 / Accepted:
Clim Dyn DOI 1.17/s382-13-1843-4 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments Aaron Donohoe Dargan M. W. Frierson David S. Battisti Received: 21 April 13 / Accepted:
Hadley Circulation as a Modulator of the Extratropical Climate
 2437 Hadley Circulation as a Modulator of the Extratropical Climate ARTHUR Y. HOU Data Assimilation Office, Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland (Manuscript
2437 Hadley Circulation as a Modulator of the Extratropical Climate ARTHUR Y. HOU Data Assimilation Office, Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland (Manuscript
Validation of parametrisations for the meridional energy and moisture transport used in simple climate models
 Climate Dynamics (2000) 16:63±77 Ó Springer-Verlag 2000 A. Schmittner C. Appenzeller T. F. Stocker Validation of parametrisations for the meridional energy and moisture transport used in simple climate
Climate Dynamics (2000) 16:63±77 Ó Springer-Verlag 2000 A. Schmittner C. Appenzeller T. F. Stocker Validation of parametrisations for the meridional energy and moisture transport used in simple climate
The relationship between the transient, meridional eddy
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. D12, PAGES 13,487-13,494, JUNE 27, 1997 The relationship between the transient, meridional eddy sensible and latent heat flux Marilyn N. Raphael Department
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. D12, PAGES 13,487-13,494, JUNE 27, 1997 The relationship between the transient, meridional eddy sensible and latent heat flux Marilyn N. Raphael Department
1 The circulation of a zonally symmetric atmosphere. 1.1 Angular momentum conservation and its implications
 1 The circulation of a zonally symmetric atmosphere We will begin our attempts to understand the big picture of the structure of the atmosphere by asking about what theory predicts if we ignore eddies
1 The circulation of a zonally symmetric atmosphere We will begin our attempts to understand the big picture of the structure of the atmosphere by asking about what theory predicts if we ignore eddies
Lecture 3. Background materials. Planetary radiative equilibrium TOA outgoing radiation = TOA incoming radiation Figure 3.1
 Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models
 Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Dynamics of the Atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere Course description: Discusses the dynamics of the atmosphere, with emphasis on the large scale. Instructor: Paul O Gorman Email: pog@mit.edu Office: 54-1712 Questions:
Dynamics of the Atmosphere. General circulation of the atmosphere
 12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
12.810 Dynamics of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere 1 Spinup of the general circulation in an idealized model Fig. 1 Schneider, General circulation of the atmosphere, 2006 2 Sigma 0.2
Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes*
 MARCH 212 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 875 Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes* FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada TIFFANY
MARCH 212 L A L I B E R T É ET AL. 875 Moist Recirculation and Water Vapor Transport on Dry Isentropes* FRÉDÉRIC LALIBERTÉ Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada TIFFANY
WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA
 WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA INTRODUCTION A good understanding of the causes of climate variability depend, to the large extend, on the precise knowledge of the functioning of the
WATER VAPOR FLUXES OVER EQUATORIAL CENTRAL AFRICA INTRODUCTION A good understanding of the causes of climate variability depend, to the large extend, on the precise knowledge of the functioning of the
1 Climatological balances of heat, mass, and angular momentum (and the role of eddies)
 1 Climatological balances of heat, mass, and angular momentum (and the role of eddies) We saw that the middle atmospheric temperature structure (which, through thermal wind balance, determines the mean
1 Climatological balances of heat, mass, and angular momentum (and the role of eddies) We saw that the middle atmospheric temperature structure (which, through thermal wind balance, determines the mean
1) The energy balance at the TOA is: 4 (1 α) = σt (1 0.3) = ( ) 4. (1 α) 4σ = ( S 0 = 255 T 1
 EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
Eliassen-Palm Theory
 Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
The General Circulation of the Atmosphere
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006. 34:655 88 The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science is online at earth.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.earth.34.031405.125144 Copyright c 2006 by Annual
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006. 34:655 88 The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science is online at earth.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.earth.34.031405.125144 Copyright c 2006 by Annual
ENERGETICS. [This article treats a technical aspect of climate and weather studies; some of it is intended for readers at an advanced level.
 ENERGETICS. [This article treats a technical aspect of climate and weather studies; some of it is intended for readers at an advanced level.] Atmospheric energetics, the study of the distribution and transformation
ENERGETICS. [This article treats a technical aspect of climate and weather studies; some of it is intended for readers at an advanced level.] Atmospheric energetics, the study of the distribution and transformation
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7 Community Business Quiz discussion Next Topic will be Chapter 8, Natural Climate variability in the instrumental record. Homework
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7 Community Business Quiz discussion Next Topic will be Chapter 8, Natural Climate variability in the instrumental record. Homework
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
An Interconnected Planet
 An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
Global Atmospheric Moisture Budget
 Global Atmospheric Moisture Budget Sinan Sahin (1), Juerg Luterbacher (2), Elena Xoplaki (2), and Murat Türkeş (3) (1) Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Çorlu Engineering, Namik Kemal University/TURKEY
Global Atmospheric Moisture Budget Sinan Sahin (1), Juerg Luterbacher (2), Elena Xoplaki (2), and Murat Türkeş (3) (1) Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Çorlu Engineering, Namik Kemal University/TURKEY
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance
 Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Surface Energy Balance 1. Factors affecting surface energy balance 2. Surface heat storage 3. Surface
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Surface Energy Balance 1. Factors affecting surface energy balance 2. Surface heat storage 3. Surface
Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell
 Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell Geoff Vallis; notes by Jim Thomas and Geoff J. Stanley June 27 In this short lecture we take a look at the general circulation of the atmosphere, and in particular the Hadley
Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell Geoff Vallis; notes by Jim Thomas and Geoff J. Stanley June 27 In this short lecture we take a look at the general circulation of the atmosphere, and in particular the Hadley
Atmospheric Angular Momentum Transport and Balance in the AGCM-SAMIL
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 27, NO. 5, 2010, 1183 1192 Atmospheric Angular Momentum Transport and Balance in the AGCM-SAMIL LI Jun 1,2,3 ( ) and WU Guoxiong 1 ( ) 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 27, NO. 5, 2010, 1183 1192 Atmospheric Angular Momentum Transport and Balance in the AGCM-SAMIL LI Jun 1,2,3 ( ) and WU Guoxiong 1 ( ) 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical
Temperature changes in the tropical tropopause layer
 Temperature changes in the tropical tropopause layer Kohei Yoshida Division of Earth System Science, Graduate School of Environmental Science, Hokkaido University February 011 Abstract ⅰ Abstract Temperature
Temperature changes in the tropical tropopause layer Kohei Yoshida Division of Earth System Science, Graduate School of Environmental Science, Hokkaido University February 011 Abstract ⅰ Abstract Temperature
4. Atmospheric transport. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
What determines meridional heat transport in climate models?
 Generated using version 3.1 of the official AMS L A TEX template What determines meridional heat transport in climate models? Aaron Donohoe and David S. Battisti Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
Generated using version 3.1 of the official AMS L A TEX template What determines meridional heat transport in climate models? Aaron Donohoe and David S. Battisti Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
The effect of varying forcing on the transport of heat by transient eddies.
 The effect of varying forcing on the transport of heat by transient eddies. LINDA MUDONI Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University May 02 20 1. Introduction The major transport of heat
The effect of varying forcing on the transport of heat by transient eddies. LINDA MUDONI Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa State University May 02 20 1. Introduction The major transport of heat
Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes
 Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman) Water vapor dynamics in warming
Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology (based on Rev. Geophys. article with Xavier Levine and Paul O Gorman) Water vapor dynamics in warming
DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere
 DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere Lodovica Illari 1 Introduction What is responsible for stormy weather? What causes relatively warm temperatures one day and
DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere Lodovica Illari 1 Introduction What is responsible for stormy weather? What causes relatively warm temperatures one day and
F = ma. ATS 150 Global Climate Change Winds and Weather. Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1. Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook
 Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Seamless Poleward Atmospheric Energy Transports and Implications for the Hadley Circulation
 3706 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Seamless Poleward Atmospheric Energy Transports and Implications for the Hadley Circulation KEVIN E. TRENBERTH AND DAVID P. STEPANIAK National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
3706 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Seamless Poleward Atmospheric Energy Transports and Implications for the Hadley Circulation KEVIN E. TRENBERTH AND DAVID P. STEPANIAK National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
Tropical Zonal Momentum Balance in the NCEP Reanalyses
 JULY 2005 D I M A E T A L. 2499 Tropical Zonal Momentum Balance in the NCEP Reanalyses IOANA M. DIMA, JOHN M. WALLACE, AND IAN KRAUCUNAS Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle,
JULY 2005 D I M A E T A L. 2499 Tropical Zonal Momentum Balance in the NCEP Reanalyses IOANA M. DIMA, JOHN M. WALLACE, AND IAN KRAUCUNAS Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle,
Midlatitude Storm Track Response to Increased Greenhouse Warming
 Midlatitude Storm Track Response to Increased Greenhouse Warming Yutian Wu Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and
Midlatitude Storm Track Response to Increased Greenhouse Warming Yutian Wu Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and
Hydrodynamic conservation laws and turbulent friction in atmospheric circulation models
 Hydrodynamic conservation laws and turbulent friction in atmospheric circulation models Erich Becker Leibniz-Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Kühlungsborn, Germany Including contributions from Ulrike
Hydrodynamic conservation laws and turbulent friction in atmospheric circulation models Erich Becker Leibniz-Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Kühlungsborn, Germany Including contributions from Ulrike
Lecture 11: Meridonal structure of the atmosphere
 Lecture 11: Meridonal structure of the atmosphere September 28, 2003 1 Meridional structure of the atmosphere In previous lectures we have focussed on the vertical structure of the atmosphere. Today, we
Lecture 11: Meridonal structure of the atmosphere September 28, 2003 1 Meridional structure of the atmosphere In previous lectures we have focussed on the vertical structure of the atmosphere. Today, we
GEO1010 tirsdag
 GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
ATS 421/521. Climate Modeling. Spring 2015
 ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2015 Lecture 9 Hadley Circulation (Held and Hou, 1980) General Circulation Models (tetbook chapter 3.2.3; course notes chapter 5.3) The Primitive Equations (tetbook
ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2015 Lecture 9 Hadley Circulation (Held and Hou, 1980) General Circulation Models (tetbook chapter 3.2.3; course notes chapter 5.3) The Primitive Equations (tetbook
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
Climate of an Earth- like Aquaplanet: the high- obliquity case and the <dally- locked case
 Climate of an Earth- like Aquaplanet: the high- obliquity case and the
Climate of an Earth- like Aquaplanet: the high- obliquity case and the
( δx ) = δ dx = δu, etc. Course , General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 2: Analysis Techniques
 Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 2: Analysis Techniques Pressure Coordinates: Most meteorological measurements are made in pressure coordinates, e.g.,
Course 12.812, General Circulation of the Earth's Atmosphere Prof. Peter Stone Section 2: Analysis Techniques Pressure Coordinates: Most meteorological measurements are made in pressure coordinates, e.g.,
Response of the North Atlantic atmospheric circulation to increasing LGM ice-sheet elevation
 Response of the North Atlantic atmospheric circulation to increasing LGM ice-sheet elevation Marcus Löfverström NCAR Rodrigo Caballero Johan Nilsson Gabriele Messori Stockholm University The Northern Hemisphere
Response of the North Atlantic atmospheric circulation to increasing LGM ice-sheet elevation Marcus Löfverström NCAR Rodrigo Caballero Johan Nilsson Gabriele Messori Stockholm University The Northern Hemisphere
General Circula,on of the Atmosphere
 General Circula,on of the Atmosphere Today: Angular momentum transport - how do eddies affect the mean flow? Eulerian view Transformed Eulerian Mean EP fluxes Momentum budget Local momentum fluxes: E vectors
General Circula,on of the Atmosphere Today: Angular momentum transport - how do eddies affect the mean flow? Eulerian view Transformed Eulerian Mean EP fluxes Momentum budget Local momentum fluxes: E vectors
arxiv: v2 [physics.ao-ph] 24 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v2 [physics.ao-ph] 24 Nov 2009 arxiv: v2 [physics.ao-ph] 24 Nov 2009](/thumbs/75/72853030.jpg) WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts,
WATER VAPOR AND THE DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE CHANGES Tapio Schneider California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA Paul A. O Gorman Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts,
The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet ABSTRACT
 Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments. 3 Aaron Donohoe Dargan Frierson 4 5 Manuscript
Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 The effect of ocean mixed layer depth on climate in slab ocean aquaplanet experiments. 3 Aaron Donohoe Dargan Frierson 4 5 Manuscript
Hemispherical Asymmetry of Tropical Precipitation in ECHAM5/MPI-OM during El Niño and under Global Warming
 15 MARCH 2008 C H O U A N D T U 1309 Hemispherical Asymmetry of Tropical Precipitation in ECHAM5/MPI-OM during El Niño and under Global Warming CHIA CHOU Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia
15 MARCH 2008 C H O U A N D T U 1309 Hemispherical Asymmetry of Tropical Precipitation in ECHAM5/MPI-OM during El Niño and under Global Warming CHIA CHOU Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation
 Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation September 30, 2003 We learnt last time that there is a planetary radiative drive net warming in the tropics, cooling over the pole which induces
Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation September 30, 2003 We learnt last time that there is a planetary radiative drive net warming in the tropics, cooling over the pole which induces
Baroclinic Adjustment in an Atmosphere Ocean Thermally Coupled Model: The Role of the Boundary Layer Processes
 2710 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 68 Baroclinic Adjustment in an Atmosphere Ocean Thermally Coupled Model: The Role of the Boundary Layer Processes YANG ZHANG School
2710 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 68 Baroclinic Adjustment in an Atmosphere Ocean Thermally Coupled Model: The Role of the Boundary Layer Processes YANG ZHANG School
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Is the Atmospheric Zonal Index Driven by an Eddy Feedback?
 1OCTOBER 1998 FELDSTEIN AND LEE 3077 Is the Atmospheric Zonal Index Driven by an Eddy Feedback? STEVEN FELDSTEIN Earth System Science Center, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania
1OCTOBER 1998 FELDSTEIN AND LEE 3077 Is the Atmospheric Zonal Index Driven by an Eddy Feedback? STEVEN FELDSTEIN Earth System Science Center, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania
Lecture 2 Global and Zonal-mean Energy Balance
 Lecture 2 Global and Zonal-mean Energy Balance A zero-dimensional view of the planet s energy balance RADIATIVE BALANCE Roughly 70% of the radiation received from the Sun at the top of Earth s atmosphere
Lecture 2 Global and Zonal-mean Energy Balance A zero-dimensional view of the planet s energy balance RADIATIVE BALANCE Roughly 70% of the radiation received from the Sun at the top of Earth s atmosphere
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
The Atmospheric Dynamics of Intraseasonal Length-of-Day Fluctuations during the Austral Winter
 1SEPTEMBER 1999 FELDSTEIN 3043 The Atmospheric Dynamics of Intraseasonal Length-of-Day Fluctuations during the Austral Winter STEVEN B. FELDSTEIN Earth System Science Center, The Pennsylvania State University,
1SEPTEMBER 1999 FELDSTEIN 3043 The Atmospheric Dynamics of Intraseasonal Length-of-Day Fluctuations during the Austral Winter STEVEN B. FELDSTEIN Earth System Science Center, The Pennsylvania State University,
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Steady Flow: rad conv. where. E c T gz L q 2. p v 2 V. Integrate from surface to top of atmosphere: rad TOA rad conv surface
 The Three-Dimensional Circulation 1 Steady Flow: F k ˆ F k ˆ VE 0, rad conv where 1 E c T gz L q 2 p v 2 V Integrate from surface to top of atmosphere: VE F FF F 0 rad TOA rad conv surface 2 What causes
The Three-Dimensional Circulation 1 Steady Flow: F k ˆ F k ˆ VE 0, rad conv where 1 E c T gz L q 2 p v 2 V Integrate from surface to top of atmosphere: VE F FF F 0 rad TOA rad conv surface 2 What causes
The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates
 1JUNE 2010 P A U L U I S E T A L. 3077 The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York New York
1JUNE 2010 P A U L U I S E T A L. 3077 The Global Atmospheric Circulation in Moist Isentropic Coordinates OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York New York
ATMO 436a. The General Circulation. Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it
 ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
ATMO 436a The General Circulation Redacted version from my NATS lectures because Wallace and Hobbs virtually ignores it Scales of Atmospheric Motion vs. Lifespan The general circulation Atmospheric oscillations
