Supplementary Materials for
|
|
|
- Meryl Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 advances.scienceag.org/cgi/conen/full/3/9/e /dc1 Suppleenary Maerials for Bioinspired brigh noniridescen phoonic elanin supraballs Ming Xiao, Ziying Hu, Zhao Wang, Yiwen Li, Aleandro Diaz Toro, Nicolas Le Thoas, Boxiang Wang, Nahan C. Gianneschi, Mahew D. Shawkey, Ali Dhinowala The PDF file includes: Published 15 Sepeber 2017, Sci. Adv. 3, e (2017 DOI: /sciadv Opical Model able S1. Condiions used for synhesizing differen sizes of CS-SMNPs. fig. S1. UV-vis absorpion specra of pure SMNPs, CS-SMNPs, and pure silica nanoparicles in aqueous soluion (20 g/lier. fig. S2. Represenaive TEM iage of a sall supraball ade of 160/0-n CS- SMNPs. fig. S3. FDTD siulaions of reflecance specra a noral incidence using he diensions of he core-shell paricles in supraballs. fig. S4. Coparisons of reflecance specra colleced for single supraballs ade of elanin, core-shell nanoparicles, and ixures of elanin and core-shell nanoparicles. fig. S5. TEM iages of he inner srucure of supraballs of binary CS-SMNPs. fig. S6. Noral reflecance specra of supraballs ade fro 160/66- and 160/36- n CS-SMNPs, and supraballs ade by ixing differen raios of 160/66- and 160/36-n CS-SMNPs. fig. S7. Calculaions of inverse of noralized ranspor ean free pah as a funcion of differen ixing raios of 160/36- and 160/66-n CS-SMNPs using he scaering heory oulined in SI. fig. S8. Iage of a drop of waer on an OTS-coaed glass. References (33 44 Oher Suppleenary Maerial for his anuscrip includes he following: (available a advances.scienceag.org/cgi/conen/full/3/9/e /dc1
2 ovie S1 (.p4 fora. Supraball-pained flowers do no change colors when he saple is roaing a differen angles.
3 Opical Model FDTD siulaion We used Luerical FDTD soluions 8.15 o run he opical odeling. In he siulaion, we creaed an FCC colloidal laice wih is plane (111 as X-Y plane and a plane wave ligh was ineced down fro Z direcion, perpendicular o plane (111. For he siulaion in Fig. 1B, we copared heoreical reflecance specra fro core-shell and hoogenous nanoparicles. The hoogenous nanoparicles is he sae size as core-shell nanoparicles wih a RI of averaged RI value of core-shell nanoparicles based on he equaion n ( hoo V + V = n V + n V core shell core core shell shell (1 We se he RI value of 1.74 for high RI aerial (idenical o synheic elanin, bu wihou any absorpion and 1.45 for he low RI aerial (sae wih fused silica in our calculaions. The laice has 30 periods along he X and Y direcions and 12 periods along Z direcions. We chose auo non-unifor esh ype wih accuracy of 6 and a ligh source range of n (esh size is around 8 n. Boh core and shell aerials conained no absorpion so ha we could decouple opical response fro he core-shell srucures and absorpion. When coparing siulaion resuls wih experienal reflecance of supraballs (Fig. 3D, we considered absorpion fro SMNPs core (19. In his calculaion, he Luerical sofware used RI values fro fiing of boh he real par and iaginary par of RI values based on experienal daa (fig. S3A. Based on our observaion
4 ha only he op 5~10 layers of supraball conribues o he colors, we calculaed only 6 layers along z direcions. We chose auo non-unifor esh ype wih accuracy of 5 and a ligh source of n (esh size is around 5 n. Scaering heory Because he supraballs ade of ixed ype 1 (160/36 n and ype 2 (160/66 n CS-SMNPs are far fro he ordered FCC packing (Fig. 5C, we can no siply regard he as phoonic crysals. To consider he disorder effec, we used he uliple scaering heory o explain he color shifing fro blending wo sizes of CS-SMNPs wih differen ass raio (27, 28. The uliple scaering heory of ligh can provide basic analyical ehods o address ligh scaering proble in disordered phoonic edia. To predic he reflecance specra profile analyically wihou resoring o ie-consuing nuerical siulaions, here we define he paraeer A ( k l 1 = o presen he diffuse reflecance of he supraballs, where k0l = 2 πl / λ Firs, l direcly deerines he diffuse reflecance of supraballs, which plays a key role in he producion of srucural colors. For 0 he diffusive ligh ranspor wihou absorpion, ransission is proporional o l as T ~ l and hus reflecance increases when l is reduced (27, 28. When he opical absorpion of CS-SMNPs is considered, he reflecance is sill negaively relaed o l, because saller l leads o a sronger uliple scaering effec (noe l doesn rely on absorpion, which is he only source of backscaering and hus diffuse reflecance (27, 28. Secondly, here are significan inerference effecs when l is coparable wih he wavelengh λ ( A ~ 1, which are also observed in he scenarios such as coheren backscaering (33 and Anderson localizaion (34.
5 Consrucive inerference effecs lead o a reducion in diffusion consan D (i.e. coheren 2 backscaering gives rise o a correcion as D / D ~ A (35 and hus an increase in reflecance, which can be also quanified by he paraeer A. Therefore, we can use he paraeer A o esiae specral profile of diffuse reflecance. This paraeer has also been used by F. Scheffold e al in predicing opical specra of densely packed TiO 2 nanoparicles (36. Since CS-SMNPs are densely packed in supraballs, he shor-range order induced inerference echanis aong binary CS-SMNPs in uliple scaering of ligh likely plays a key role in l as well as he observed reflecance specra ( To suppor his arguen, here we consider he shor-range order induced inerference effec in he uliple scaering using a heoreical odel where wo-paricle correlaion is aken ino accoun (known as Born s approxiaion (39. Then we copare his resul wih ha fro he independen scaering approxiaion (ISA wihou consideraion of he shor-range order (27, 28, 35. The heoreical odel predics he ranspor ean free pah of ligh in supraballs as l ( ρσ 1 σ is calculaed in he following expression (39 = where ρ is he nuber densiy of paricles. π π σ = B( θ sin θ (1 cos θ dθ 2 k 0 (2 where k = 2 πn eff / λ and B( θ = αf11 ( θ S11( θ + (1 α F22 ( θ S22( θ + 2 α(1 α F12 ( θ S12 ( θ. We calculae effecive refracive index n eff = ε using he Maxwell-Garne forula for eff hree-coponen ediu (core, shell, and air as (40
6 ε eff 1 core 1 shell 1 f ε core f ε = + shell ε + 2 ε + 2 ε + 2 (3 eff core shell where r r f = f + f and core 3 3 1,core 2,core r1,oal r2,oal 3 3 r 1,core r 2,core fshell = f1 1 + f r 1,oal r 2,oal. f and 1 f 2 are he volue fracion of ype 1 and ype 2 CS-SMNPs. ε core and ε shell are periiviy of core (synheic elanin and shell (silica. r and 1,core r are he core radius and oal radius of ype 1 1,oal CS-SMNPs, while r and 2,core r are he core radius and oal radius of ype 2 CS-SMNPs. 2,oal α = N / ( N + N is he nuber fracion of ype-1 CS-SMNPs. S ( θ, S ( θ, and S ( θ are parial srucure facors of he binary-paricle syse calculaed based on Percus-Yevick hard sphere odel (41. The Percus-Yevick odel is a sufficien approxiaion for calculaing pair correlaion funcion characerizing shor-range order in packing hard-sphere syses. F ( θ, 11 F ( θ, and 12 F ( 22 θ are for facors derived fro he Mie heory for core-shell paricles. They are calculaed as follows F ( θ = fs fs + f p f p * * (4 F ( θ = fs fs + f p f p * * (5 * * F12 ( θ = Re fs1 fs2 + f p1 f p2 (6
7 where fs ( θ = (2 + 1 a, τ(cos θ + b, π(cos θ and fp ( θ = (2 + 1 a, π(cos θ + b, τ(cos θ wih = 1 = 1,2 denoing differen paricle species. Here τ and π are funcions defined as = 1 P 1 (cos θ π(cos θ = and sinθ dp 1 (cos θ τ (cos θ =, where dθ P 1 (cos θ is he associaed Legendre funcion. a, and b, are Mie coefficiens calculaed as (42, 43 a, = ( ɶ ( D, / nshell + / y ψ ( y ψ 1( y Dɶ / n + / y ξ ( y ξ ( y (7, shell 1 b, = ( ɶ ( nshellg, + / y ψ ( y ψ 1( y n Gɶ + / y ξ ( y ξ ( y (8 shell, 1 where y = kr is he size paraeer for he oal radius of ype- paricle and k = 2 πn eff / λ is,oal he wavenuber in he surrounding ediu wih effecive refracive index n eff as calculaed previously. We defined n = nshell / ncore, where n shell = ε shell and ncore = ε core are coplex refracive indices of shell and core aerials. The paraeers, D ɶ,, G ɶ, are calculaed as Dɶ, = D ( n y A χ ( n y / ψ ( n y shell, shell shell 1 A χ ( n y / ψ ( n y, shell shell (9 Gɶ, = D ( n y B χ ( n y / ψ ( n y shell, shell shell 1 B χ ( n y / ψ ( n y, shell shell (10
8 And, A, B, are nd ( ncore x D ( nshell x A, = ψ ( nshell x nd ( n x χ ( n x χ ( n x (11 core shell shell D ( ncore x / n D ( nshell x B, = ψ ( nshell x D ( n x χ ( n x χ ( n x (12 core shell shell where x = kr is he size paraeer for he core radius of ype- paricle. In above equaions,,core ψ ( α, ξ( α and D ( α are special funcions defined using arguen α as ψ ( α = α ( α, χ ( α = α y ( α, ξ α = α α and D ( α = ψ ( α / ψ ( α. Here ( α, y ( α and (1 ( h ( h (1 ( α are spherical Bessel funcions of he firs kind and second kind, and spherical Hankel funcion of he firs kind, in he order of n respecively (42. ψ ( α and χ ( α denoe he firs-order derivaive respec o arguen α. Equaions (7-12 are also applicable for hoogeneous spheres by seing r,oal = r,core. We calculaed he A paraeer for supraballs consising of binary CS-SMNPs wih differen ass raios. fig. S7A showed he noralized A for differen ass raios for 160/36 n and 160/66 n CS-SMNPs. A clear rend of blue-shif was observed when increasing he aoun of 160/36 n CS-SMNPs, which is consisen wih he experienal observaion. As a coparison, we also calculaed A wihou consideraion of shor-range order and inerference effecs (fig. S7B, where we se he parial srucure facors S11( θ = S22( θ = 1,
9 S ( θ = 0 and wavenuber 12 k = k0 = 2 π / λ, unlike using k = 2 πn eff / λ in he shor-range-order case because using he effecive index also akes parial inerference effecs ino accoun (44. This approxiaion for calculaing ranspor ean free pah is called independen scaering approxiaion (ISA (44. No significan shif of peaks was observed by changing he coposiion of binary CS-SMNPs, which was invalid according o experienal resuls. This finding suppors our conclusion ha shor-range order plays he crucial role in producing he blended colors of supraballs when ixing binary sizes of CS-SMNPs.
10 Supporing Table and Figures able S1. Condiions used for synhesizing differen sizes of CS-SMNPs. Supraball Colors Core diaeer (n Shell hickness (n TEOS (μl Reacion Tie Red 160 ± 7 66 ± h Orange 160 ± 7 50 ± h Olive 160 ± 7 36 ± in Blue-green 123 ± ± h Navy 123 ± ± in fig. S1. UV-vis absorpion specra of pure SMNPs, CS-SMNPs, and pure silica nanoparicles in aqueous soluion (20 g/lier.
11 fig. S2. Represenaive TEM iage of a sall supraball ade of 160/0-n CS-SMNPs. fig. S3. FDTD siulaions of reflecance specra a noral incidence using he diensions of he core-shell paricles in supraballs. (A The real and iaginary refracive indices for synheic elanin paricles used in he FDTD calculaions (hese values were calculaed based on our previous published resuls (19. (B Coparisons of heoreical noral reflecance specra (FDTD for supraballs coposed of hree differen sizes of CS-SMNPs wih (solid lines and wihou (dash lines considering absorpion of elanin.
12 fig. S4. Coparisons of reflecance specra colleced for single supraballs ade of elanin, core-shell nanoparicles, and ixures of elanin and core-shell nanoparicles. (A Reflecance of single supraballs ade of pure 160/0-n, ixed 160/0-n & 160/36-n CS-SMNPs, and ixed 160/0-n & 160/66-n CS-SMNPs. (B Reflecance of single supraballs ade of pure 160/36-n CS-SMNPs, pure 160/66-n CS-SMNPs, and ixed 160/36-n & 160/66-n CS-SMNPs. fig. S5. TEM iages of he inner srucure of supraballs of binary CS-SMNPs. (A 160/0-n & 160/36-n CS-SMNPs, (B 160/0-n & 160/66-n CS-SMNPs, and (C 160/36-n & 160/66-n CS-SMNPs. Scale, 500 n
13 fig. S6. Noral reflecance specra of supraballs ade fro 160/66- and 160/36-n CS-SMNPs, and supraballs ade by ixing differen raios of 160/66- and 160/36-n CS-SMNPs.
14 fig. S7. Calculaions of inverse of noralized ranspor ean free pah as a funcion of differen ixing raios of 160/36- and 160/66-n CS-SMNPs using he scaering heory oulined in SI. (A Shor-range order was aken ino accoun. (B We used independen scaering approxiaion wihou including he odel for shor-range order. The legend represens he ixing ass raios of wo sizes of CS-SMNPs. fig. S8. Iage of a drop of waer on an OTS-coaed glass.
Introduction to Numerical Analysis. In this lesson you will be taken through a pair of techniques that will be used to solve the equations of.
 Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Chapter 9 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Chaper 9 Sinusoidal Seady Sae Analysis 9.-9. The Sinusoidal Source and Response 9.3 The Phasor 9.4 pedances of Passive Eleens 9.5-9.9 Circui Analysis Techniques in he Frequency Doain 9.0-9. The Transforer
Chaper 9 Sinusoidal Seady Sae Analysis 9.-9. The Sinusoidal Source and Response 9.3 The Phasor 9.4 pedances of Passive Eleens 9.5-9.9 Circui Analysis Techniques in he Frequency Doain 9.0-9. The Transforer
1. Calibration factor
 Annex_C_MUBDandP_eng_.doc, p. of pages Annex C: Measureen uncerainy of he oal heigh of profile of a deph-seing sandard ih he sandard deviaion of he groove deph as opography er In his exaple, he uncerainy
Annex_C_MUBDandP_eng_.doc, p. of pages Annex C: Measureen uncerainy of he oal heigh of profile of a deph-seing sandard ih he sandard deviaion of he groove deph as opography er In his exaple, he uncerainy
Thus the force is proportional but opposite to the displacement away from equilibrium.
 Chaper 3 : Siple Haronic Moion Hooe s law saes ha he force (F) eered by an ideal spring is proporional o is elongaion l F= l where is he spring consan. Consider a ass hanging on a he spring. In equilibriu
Chaper 3 : Siple Haronic Moion Hooe s law saes ha he force (F) eered by an ideal spring is proporional o is elongaion l F= l where is he spring consan. Consider a ass hanging on a he spring. In equilibriu
TP A.14 The effects of cut angle, speed, and spin on object ball throw
 echnical proof echnical proof TP A.14 The effecs of cu angle, speed, and spin on objec ball hrow supporing: The Illusraed Principles of Pool and illiards hp://billiards.colosae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore,
echnical proof echnical proof TP A.14 The effecs of cu angle, speed, and spin on objec ball hrow supporing: The Illusraed Principles of Pool and illiards hp://billiards.colosae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore,
CHAPTER 16 KINETICS: RATES AND MECHANISMS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 CHAPTER 6 KINETICS: RATES AND MECHANISMS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS FOLLOW UP PROBLEMS 6.A Plan: Balance he equaion. The rae in ers of he change in concenraion wih ie for each subsance is [ A] expressed as,
CHAPTER 6 KINETICS: RATES AND MECHANISMS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS FOLLOW UP PROBLEMS 6.A Plan: Balance he equaion. The rae in ers of he change in concenraion wih ie for each subsance is [ A] expressed as,
Application of Homotopy Analysis Method for Solving various types of Problems of Partial Differential Equations
 Applicaion of Hooopy Analysis Mehod for olving various ypes of Probles of Parial Differenial Equaions V.P.Gohil, Dr. G. A. anabha,assisan Professor, Deparen of Maheaics, Governen Engineering College, Bhavnagar,
Applicaion of Hooopy Analysis Mehod for olving various ypes of Probles of Parial Differenial Equaions V.P.Gohil, Dr. G. A. anabha,assisan Professor, Deparen of Maheaics, Governen Engineering College, Bhavnagar,
ψ(t) = V x (0)V x (t)
 .93 Home Work Se No. (Professor Sow-Hsin Chen Spring Term 5. Due March 7, 5. This problem concerns calculaions of analyical expressions for he self-inermediae scaering funcion (ISF of he es paricle in
.93 Home Work Se No. (Professor Sow-Hsin Chen Spring Term 5. Due March 7, 5. This problem concerns calculaions of analyical expressions for he self-inermediae scaering funcion (ISF of he es paricle in
Fourier Series & The Fourier Transform. Joseph Fourier, our hero. Lord Kelvin on Fourier s theorem. What do we want from the Fourier Transform?
 ourier Series & The ourier Transfor Wha is he ourier Transfor? Wha do we wan fro he ourier Transfor? We desire a easure of he frequencies presen in a wave. This will lead o a definiion of he er, he specru.
ourier Series & The ourier Transfor Wha is he ourier Transfor? Wha do we wan fro he ourier Transfor? We desire a easure of he frequencies presen in a wave. This will lead o a definiion of he er, he specru.
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Spike-count autocorrelations in time.
 Supplemenary Figure 1 Spike-coun auocorrelaions in ime. Normalized auocorrelaion marices are shown for each area in a daase. The marix shows he mean correlaion of he spike coun in each ime bin wih he spike
Supplemenary Figure 1 Spike-coun auocorrelaions in ime. Normalized auocorrelaion marices are shown for each area in a daase. The marix shows he mean correlaion of he spike coun in each ime bin wih he spike
TIME DELAY BASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OBSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM
 TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Lecture 23 Damped Motion
 Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
On the approximation of particular solution of nonhomogeneous linear differential equation with Legendre series
 The Journal of Applied Science Vol. 5 No. : -9 [6] วารสารว ทยาศาสตร ประย กต doi:.446/j.appsci.6.8. ISSN 53-785 Prined in Thailand Research Aricle On he approxiaion of paricular soluion of nonhoogeneous
The Journal of Applied Science Vol. 5 No. : -9 [6] วารสารว ทยาศาสตร ประย กต doi:.446/j.appsci.6.8. ISSN 53-785 Prined in Thailand Research Aricle On he approxiaion of paricular soluion of nonhoogeneous
Multivariate Auto-Regressive Model for Groundwater Flow Around Dam Site
 Mulivariae uo-regressive Model for Groundwaer Flow round Da Sie Yoshiada Mio ), Shinya Yaaoo ), akashi Kodaa ) and oshifui Masuoka ) ) Dep. of Earh Resources Engineering, Kyoo Universiy, Kyoo, 66-85, Japan.
Mulivariae uo-regressive Model for Groundwaer Flow round Da Sie Yoshiada Mio ), Shinya Yaaoo ), akashi Kodaa ) and oshifui Masuoka ) ) Dep. of Earh Resources Engineering, Kyoo Universiy, Kyoo, 66-85, Japan.
Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations and Structural Dynamics
 Inroducion o Mechanical Viraions and Srucural Dynaics The one seeser schedule :. Viraion - classificaion. ree undaped single DO iraion, equaion of oion, soluion, inegraional consans, iniial condiions..
Inroducion o Mechanical Viraions and Srucural Dynaics The one seeser schedule :. Viraion - classificaion. ree undaped single DO iraion, equaion of oion, soluion, inegraional consans, iniial condiions..
Navneet Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (2013); Term Project AML310; Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
 Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Final Spring 2007
 .615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
.615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
M x t = K x F t x t = A x M 1 F t. M x t = K x cos t G 0. x t = A x cos t F 0
 Forced oscillaions (sill undaped): If he forcing is sinusoidal, M = K F = A M F M = K cos G wih F = M G = A cos F Fro he fundaenal heore for linear ransforaions we now ha he general soluion o his inhoogeneous
Forced oscillaions (sill undaped): If he forcing is sinusoidal, M = K F = A M F M = K cos G wih F = M G = A cos F Fro he fundaenal heore for linear ransforaions we now ha he general soluion o his inhoogeneous
What is Elliptic Flow?
 Wha is Ellipic Flow? To Trainor (for he STAR collaboraion) Monreal July, 7 Agenda Aziuh auocorrelaions Nonflow and inijes Quadrupole (flow) syseaics A-A eccenriciy odels Universal quadrupole rends Flow
Wha is Ellipic Flow? To Trainor (for he STAR collaboraion) Monreal July, 7 Agenda Aziuh auocorrelaions Nonflow and inijes Quadrupole (flow) syseaics A-A eccenriciy odels Universal quadrupole rends Flow
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
1. Define the following: molecular cloud, molecular core, protostar. Include typical properties when necessary.
 1 Soluions o PH6820 Miderm 1. Define he following: molecular cloud, molecular core, proosar. Include ypical properies when necessary. A molecular cloud is a disinc, self-graviaing cloud comprised primarily
1 Soluions o PH6820 Miderm 1. Define he following: molecular cloud, molecular core, proosar. Include ypical properies when necessary. A molecular cloud is a disinc, self-graviaing cloud comprised primarily
Macroeconomic Theory Ph.D. Qualifying Examination Fall 2005 ANSWER EACH PART IN A SEPARATE BLUE BOOK. PART ONE: ANSWER IN BOOK 1 WEIGHT 1/3
 Macroeconomic Theory Ph.D. Qualifying Examinaion Fall 2005 Comprehensive Examinaion UCLA Dep. of Economics You have 4 hours o complee he exam. There are hree pars o he exam. Answer all pars. Each par has
Macroeconomic Theory Ph.D. Qualifying Examinaion Fall 2005 Comprehensive Examinaion UCLA Dep. of Economics You have 4 hours o complee he exam. There are hree pars o he exam. Answer all pars. Each par has
Diebold, Chapter 7. Francis X. Diebold, Elements of Forecasting, 4th Edition (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 2006). Chapter 7. Characterizing Cycles
 Diebold, Chaper 7 Francis X. Diebold, Elemens of Forecasing, 4h Ediion (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 006). Chaper 7. Characerizing Cycles Afer compleing his reading you should be able o: Define covariance
Diebold, Chaper 7 Francis X. Diebold, Elemens of Forecasing, 4h Ediion (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 006). Chaper 7. Characerizing Cycles Afer compleing his reading you should be able o: Define covariance
Summary of shear rate kinematics (part 1)
 InroToMaFuncions.pdf 4 CM465 To proceed o beer-designed consiuive equaions, we need o know more abou maerial behavior, i.e. we need more maerial funcions o predic, and we need measuremens of hese maerial
InroToMaFuncions.pdf 4 CM465 To proceed o beer-designed consiuive equaions, we need o know more abou maerial behavior, i.e. we need more maerial funcions o predic, and we need measuremens of hese maerial
EE650R: Reliability Physics of Nanoelectronic Devices Lecture 9:
 EE65R: Reliabiliy Physics of anoelecronic Devices Lecure 9: Feaures of Time-Dependen BTI Degradaion Dae: Sep. 9, 6 Classnoe Lufe Siddique Review Animesh Daa 9. Background/Review: BTI is observed when he
EE65R: Reliabiliy Physics of anoelecronic Devices Lecure 9: Feaures of Time-Dependen BTI Degradaion Dae: Sep. 9, 6 Classnoe Lufe Siddique Review Animesh Daa 9. Background/Review: BTI is observed when he
Conservation of Momentum. The purpose of this experiment is to verify the conservation of momentum in two dimensions.
 Conseraion of Moenu Purose The urose of his exerien is o erify he conseraion of oenu in wo diensions. Inroducion and Theory The oenu of a body ( ) is defined as he roduc of is ass () and elociy ( ): When
Conseraion of Moenu Purose The urose of his exerien is o erify he conseraion of oenu in wo diensions. Inroducion and Theory The oenu of a body ( ) is defined as he roduc of is ass () and elociy ( ): When
Chapter 15: Phenomena. Chapter 15 Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Rates. Reaction Rates R P. Reaction Rates. Rate Laws
 Chaper 5: Phenomena Phenomena: The reacion (aq) + B(aq) C(aq) was sudied a wo differen emperaures (98 K and 35 K). For each emperaure he reacion was sared by puing differen concenraions of he 3 species
Chaper 5: Phenomena Phenomena: The reacion (aq) + B(aq) C(aq) was sudied a wo differen emperaures (98 K and 35 K). For each emperaure he reacion was sared by puing differen concenraions of he 3 species
22. Inbreeding. related measures: = coefficient of kinship, a measure of relatedness of individuals of a population; panmictic index, P = 1 F;
 . Inbreeding Inbreeding: maing beween relaives. has predicable consequences for gene and genoype frequencies; increases he frequency of homozygous genoypes a he expense of heerozygous genoypes; hus decreases
. Inbreeding Inbreeding: maing beween relaives. has predicable consequences for gene and genoype frequencies; increases he frequency of homozygous genoypes a he expense of heerozygous genoypes; hus decreases
Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway
 Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Errata (1 st Edition)
 P Sandborn, os Analysis of Elecronic Sysems, s Ediion, orld Scienific, Singapore, 03 Erraa ( s Ediion) S K 05D Page 8 Equaion (7) should be, E 05D E Nu e S K he L appearing in he equaion in he book does
P Sandborn, os Analysis of Elecronic Sysems, s Ediion, orld Scienific, Singapore, 03 Erraa ( s Ediion) S K 05D Page 8 Equaion (7) should be, E 05D E Nu e S K he L appearing in he equaion in he book does
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Localized Photon States
 Localized Phoon Saes Here be dragons Margare Hawon Lakehead Universiy Thunder Bay, Canada Inroducion In sandard quanum mechanics a measuremen is associaed wih an operaor and collapse o one of is eigenvecors.
Localized Phoon Saes Here be dragons Margare Hawon Lakehead Universiy Thunder Bay, Canada Inroducion In sandard quanum mechanics a measuremen is associaed wih an operaor and collapse o one of is eigenvecors.
CHAPTER 2 Signals And Spectra
 CHAPER Signals And Specra Properies of Signals and Noise In communicaion sysems he received waveform is usually caegorized ino he desired par conaining he informaion, and he undesired par. he desired par
CHAPER Signals And Specra Properies of Signals and Noise In communicaion sysems he received waveform is usually caegorized ino he desired par conaining he informaion, and he undesired par. he desired par
Homework 2 Solutions
 Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
Innova Junior College H2 Mathematics JC2 Preliminary Examinations Paper 2 Solutions 0 (*)
 Soluion 3 x 4x3 x 3 x 0 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x x 3x 3 4x3 x Innova Junior College H Mahemaics JC Preliminary Examinaions Paper Soluions 3x 3 4x 3x 0 4x 3 4x 3 0 (*) 0 0 + + + - 3 3 4 3 3 3 3 Hence x or
Soluion 3 x 4x3 x 3 x 0 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x x 3x 3 4x3 x Innova Junior College H Mahemaics JC Preliminary Examinaions Paper Soluions 3x 3 4x 3x 0 4x 3 4x 3 0 (*) 0 0 + + + - 3 3 4 3 3 3 3 Hence x or
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
14 Autoregressive Moving Average Models
 14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
Stable block Toeplitz matrix for the processing of multichannel seismic data
 Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 33(3), Sepember 2004, pp. 215-219 Sable block Toepliz marix for he processing of mulichannel seismic daa Kiri Srivasava* & V P Dimri Naional Geophysical Research
Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 33(3), Sepember 2004, pp. 215-219 Sable block Toepliz marix for he processing of mulichannel seismic daa Kiri Srivasava* & V P Dimri Naional Geophysical Research
Unsteady Mass- Transfer Models
 See T&K Chaper 9 Unseady Mass- Transfer Models ChEn 6603 Wednesday, April 4, Ouline Conex for he discussion Soluion for ransien binary diffusion wih consan c, N. Soluion for mulicomponen diffusion wih
See T&K Chaper 9 Unseady Mass- Transfer Models ChEn 6603 Wednesday, April 4, Ouline Conex for he discussion Soluion for ransien binary diffusion wih consan c, N. Soluion for mulicomponen diffusion wih
Chapter 2. Experimental Methods
 Chaper Experienal Mehods This chaper presens a brief inroducion o he experienal echniques which are eployed in he presen work..1. Inroducion There are a several characerizaion echniques available for easuring
Chaper Experienal Mehods This chaper presens a brief inroducion o he experienal echniques which are eployed in he presen work..1. Inroducion There are a several characerizaion echniques available for easuring
Problem Set 5. Graduate Macro II, Spring 2017 The University of Notre Dame Professor Sims
 Problem Se 5 Graduae Macro II, Spring 2017 The Universiy of Nore Dame Professor Sims Insrucions: You may consul wih oher members of he class, bu please make sure o urn in your own work. Where applicable,
Problem Se 5 Graduae Macro II, Spring 2017 The Universiy of Nore Dame Professor Sims Insrucions: You may consul wih oher members of he class, bu please make sure o urn in your own work. Where applicable,
Practice Problems - Week #4 Higher-Order DEs, Applications Solutions
 Pracice Probles - Wee #4 Higher-Orer DEs, Applicaions Soluions 1. Solve he iniial value proble where y y = 0, y0 = 0, y 0 = 1, an y 0 =. r r = rr 1 = rr 1r + 1, so he general soluion is C 1 + C e x + C
Pracice Probles - Wee #4 Higher-Orer DEs, Applicaions Soluions 1. Solve he iniial value proble where y y = 0, y0 = 0, y 0 = 1, an y 0 =. r r = rr 1 = rr 1r + 1, so he general soluion is C 1 + C e x + C
Solutions to Odd Number Exercises in Chapter 6
 1 Soluions o Odd Number Exercises in 6.1 R y eˆ 1.7151 y 6.3 From eˆ ( T K) ˆ R 1 1 SST SST SST (1 R ) 55.36(1.7911) we have, ˆ 6.414 T K ( ) 6.5 y ye ye y e 1 1 Consider he erms e and xe b b x e y e b
1 Soluions o Odd Number Exercises in 6.1 R y eˆ 1.7151 y 6.3 From eˆ ( T K) ˆ R 1 1 SST SST SST (1 R ) 55.36(1.7911) we have, ˆ 6.414 T K ( ) 6.5 y ye ye y e 1 1 Consider he erms e and xe b b x e y e b
Module 2 F c i k c s la l w a s o s f dif di fusi s o i n
 Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Viscous Damping Summary Sheet No Damping Case: Damped behaviour depends on the relative size of ω o and b/2m 3 Cases: 1.
 Viscous Daping: && + & + ω Viscous Daping Suary Shee No Daping Case: & + ω solve A ( ω + α ) Daped ehaviour depends on he relaive size of ω o and / 3 Cases:. Criical Daping Wee 5 Lecure solve sae BC s
Viscous Daping: && + & + ω Viscous Daping Suary Shee No Daping Case: & + ω solve A ( ω + α ) Daped ehaviour depends on he relaive size of ω o and / 3 Cases:. Criical Daping Wee 5 Lecure solve sae BC s
On Measuring Pro-Poor Growth. 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growth: A Short Review of the Literature
 On Measuring Pro-Poor Growh 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growh: A Shor eview of he Lieraure During he pas en years or so here have been various suggesions concerning he way one should check
On Measuring Pro-Poor Growh 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growh: A Shor eview of he Lieraure During he pas en years or so here have been various suggesions concerning he way one should check
b denotes trend at time point t and it is sum of two
 Inernaional Conference on Innovaive Applicaions in Engineering and Inforaion echnology(iciaei207) Inernaional Journal of Advanced Scienific echnologies,engineering and Manageen Sciences (IJASEMSISSN: 2454356X)
Inernaional Conference on Innovaive Applicaions in Engineering and Inforaion echnology(iciaei207) Inernaional Journal of Advanced Scienific echnologies,engineering and Manageen Sciences (IJASEMSISSN: 2454356X)
Wave Particle Duality & Interference Explained
 Journal of Modern Physics, 016, 7, 67-76 Published Online February 016 in SciRes. hp://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp hp://dx.doi.org/10.436/jmp.016.7306 Wave Paricle Dualiy & Inerference Explained Narendra
Journal of Modern Physics, 016, 7, 67-76 Published Online February 016 in SciRes. hp://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp hp://dx.doi.org/10.436/jmp.016.7306 Wave Paricle Dualiy & Inerference Explained Narendra
CHAPTER 2: Mathematics for Microeconomics
 CHAPTER : Mahemaics for Microeconomics The problems in his chaper are primarily mahemaical. They are inended o give sudens some pracice wih he conceps inroduced in Chaper, bu he problems in hemselves offer
CHAPTER : Mahemaics for Microeconomics The problems in his chaper are primarily mahemaical. They are inended o give sudens some pracice wih he conceps inroduced in Chaper, bu he problems in hemselves offer
A Study of Design Method of Process and Layout of Parts and Facilities for Cell Production
 A Sudy of Design Mehod of Process and Layou of Pars and Faciliies for Cell Producion Mizuki Ohashi Graduae School of Engineering, Maser Degree Progra Nagoya Insiue of Technology, Nagoya, Japan Tel: (+81)52-7355-7408,
A Sudy of Design Mehod of Process and Layou of Pars and Faciliies for Cell Producion Mizuki Ohashi Graduae School of Engineering, Maser Degree Progra Nagoya Insiue of Technology, Nagoya, Japan Tel: (+81)52-7355-7408,
Kriging Models Predicting Atrazine Concentrations in Surface Water Draining Agricultural Watersheds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Kriging Models Predicing Arazine Concenraions in Surface Waer Draining Agriculural Waersheds Paul L. Mosquin, Jeremy Aldworh, Wenlin Chen Supplemenal Maerial Number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Kriging Models Predicing Arazine Concenraions in Surface Waer Draining Agriculural Waersheds Paul L. Mosquin, Jeremy Aldworh, Wenlin Chen Supplemenal Maerial Number
Higher Order Difference Schemes for Heat Equation
 Available a p://pvau.edu/aa Appl. Appl. Ma. ISSN: 9-966 Vol., Issue (Deceber 009), pp. 6 7 (Previously, Vol., No. ) Applicaions and Applied Maeaics: An Inernaional Journal (AAM) Higer Order Difference
Available a p://pvau.edu/aa Appl. Appl. Ma. ISSN: 9-966 Vol., Issue (Deceber 009), pp. 6 7 (Previously, Vol., No. ) Applicaions and Applied Maeaics: An Inernaional Journal (AAM) Higer Order Difference
Activity 4 Solutions: Transfer of Thermal Energy
 Aciviy 4 Soluions: Transfer of Thermal nergy 4.1 How Does Temperaure Differ from Thermal nergy? a) Temperaure Your insrucor will demonsrae molecular moion a differen emperaures. 1) Wha happens o molecular
Aciviy 4 Soluions: Transfer of Thermal nergy 4.1 How Does Temperaure Differ from Thermal nergy? a) Temperaure Your insrucor will demonsrae molecular moion a differen emperaures. 1) Wha happens o molecular
Expert Advice for Amateurs
 Exper Advice for Amaeurs Ernes K. Lai Online Appendix - Exisence of Equilibria The analysis in his secion is performed under more general payoff funcions. Wihou aking an explici form, he payoffs of he
Exper Advice for Amaeurs Ernes K. Lai Online Appendix - Exisence of Equilibria The analysis in his secion is performed under more general payoff funcions. Wihou aking an explici form, he payoffs of he
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Final Exam Advanced Macroeconomics I
 Advanced Macroeconomics I WS 00/ Final Exam Advanced Macroeconomics I February 8, 0 Quesion (5%) An economy produces oupu according o α α Y = K (AL) of which a fracion s is invesed. echnology A is exogenous
Advanced Macroeconomics I WS 00/ Final Exam Advanced Macroeconomics I February 8, 0 Quesion (5%) An economy produces oupu according o α α Y = K (AL) of which a fracion s is invesed. echnology A is exogenous
T L. t=1. Proof of Lemma 1. Using the marginal cost accounting in Equation(4) and standard arguments. t )+Π RB. t )+K 1(Q RB
 Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
Time series Decomposition method
 Time series Decomposiion mehod A ime series is described using a mulifacor model such as = f (rend, cyclical, seasonal, error) = f (T, C, S, e) Long- Iner-mediaed Seasonal Irregular erm erm effec, effec,
Time series Decomposiion mehod A ime series is described using a mulifacor model such as = f (rend, cyclical, seasonal, error) = f (T, C, S, e) Long- Iner-mediaed Seasonal Irregular erm erm effec, effec,
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
Moment Analysis of Hadronic Vacuum Polarization Proposal for a lattice QCD evaluation of g µ 2
 Moen Analysis of Hadronic Vacuu Polarizaion Proposal for a laice QCD evaluaion of g Eduardo de Rafael Cenre de Physique Théorique CNRS-Luiny, Marseille 7h June 04 NAPLES Seinar Moivaion a (E8 BNL) = 6
Moen Analysis of Hadronic Vacuu Polarizaion Proposal for a laice QCD evaluaion of g Eduardo de Rafael Cenre de Physique Théorique CNRS-Luiny, Marseille 7h June 04 NAPLES Seinar Moivaion a (E8 BNL) = 6
Underwater Target Tracking Based on Gaussian Particle Filter in Looking Forward Sonar Images
 Journal of Copuaional Inforaion Syses 6:4 (00) 480-4809 Available a hp://www.jofcis.co Underwaer Targe Tracing Based on Gaussian Paricle Filer in Looing Forward Sonar Iages Tiedong ZHANG, Wenjing ZENG,
Journal of Copuaional Inforaion Syses 6:4 (00) 480-4809 Available a hp://www.jofcis.co Underwaer Targe Tracing Based on Gaussian Paricle Filer in Looing Forward Sonar Iages Tiedong ZHANG, Wenjing ZENG,
E β t log (C t ) + M t M t 1. = Y t + B t 1 P t. B t 0 (3) v t = P tc t M t Question 1. Find the FOC s for an optimum in the agent s problem.
 Noes, M. Krause.. Problem Se 9: Exercise on FTPL Same model as in paper and lecure, only ha one-period govenmen bonds are replaced by consols, which are bonds ha pay one dollar forever. I has curren marke
Noes, M. Krause.. Problem Se 9: Exercise on FTPL Same model as in paper and lecure, only ha one-period govenmen bonds are replaced by consols, which are bonds ha pay one dollar forever. I has curren marke
Symmetry and Numerical Solutions for Systems of Non-linear Reaction Diffusion Equations
 Symmery and Numerical Soluions for Sysems of Non-linear Reacion Diffusion Equaions Sanjeev Kumar* and Ravendra Singh Deparmen of Mahemaics, (Dr. B. R. Ambedkar niversiy, Agra), I. B. S. Khandari, Agra-8
Symmery and Numerical Soluions for Sysems of Non-linear Reacion Diffusion Equaions Sanjeev Kumar* and Ravendra Singh Deparmen of Mahemaics, (Dr. B. R. Ambedkar niversiy, Agra), I. B. S. Khandari, Agra-8
1 Widrow-Hoff Algorithm
 COS 511: heoreical Machine Learning Lecurer: Rob Schapire Lecure # 18 Scribe: Shaoqing Yang April 10, 014 1 Widrow-Hoff Algorih Firs le s review he Widrow-Hoff algorih ha was covered fro las lecure: Algorih
COS 511: heoreical Machine Learning Lecurer: Rob Schapire Lecure # 18 Scribe: Shaoqing Yang April 10, 014 1 Widrow-Hoff Algorih Firs le s review he Widrow-Hoff algorih ha was covered fro las lecure: Algorih
Diffusion & Viscosity: Navier-Stokes Equation
 4/5/018 Diffusion & Viscosiy: Navier-Sokes Equaion 1 4/5/018 Diffusion Equaion Imagine a quaniy C(x,) represening a local propery in a fluid, eg. - hermal energy densiy - concenraion of a polluan - densiy
4/5/018 Diffusion & Viscosiy: Navier-Sokes Equaion 1 4/5/018 Diffusion Equaion Imagine a quaniy C(x,) represening a local propery in a fluid, eg. - hermal energy densiy - concenraion of a polluan - densiy
The general Solow model
 The general Solow model Back o a closed economy In he basic Solow model: no growh in GDP per worker in seady sae This conradics he empirics for he Wesern world (sylized fac #5) In he general Solow model:
The general Solow model Back o a closed economy In he basic Solow model: no growh in GDP per worker in seady sae This conradics he empirics for he Wesern world (sylized fac #5) In he general Solow model:
Chapter Q1. We need to understand Classical wave first. 3/28/2004 H133 Spring
 Chaper Q1 Inroducion o Quanum Mechanics End of 19 h Cenury only a few loose ends o wrap up. Led o Relaiviy which you learned abou las quarer Led o Quanum Mechanics (1920 s-30 s and beyond) Behavior of
Chaper Q1 Inroducion o Quanum Mechanics End of 19 h Cenury only a few loose ends o wrap up. Led o Relaiviy which you learned abou las quarer Led o Quanum Mechanics (1920 s-30 s and beyond) Behavior of
Heat Transfer. Revision Examples
 Hea Transfer Revision Examples Hea ransfer: energy ranspor because of a emperaure difference. Thermal energy is ransferred from one region o anoher. Hea ranspor is he same phenomena lie mass ransfer, momenum
Hea Transfer Revision Examples Hea ransfer: energy ranspor because of a emperaure difference. Thermal energy is ransferred from one region o anoher. Hea ranspor is he same phenomena lie mass ransfer, momenum
Riemann Hypothesis and Primorial Number. Choe Ryong Gil
 Rieann Hyohesis Priorial Nuber Choe Ryong Gil Dearen of Maheaics Universiy of Sciences Gwahak- dong Unjong Disric Pyongyang DPRKorea Eail; ryonggilchoe@sar-conek Augus 8 5 Absrac; In his aer we consider
Rieann Hyohesis Priorial Nuber Choe Ryong Gil Dearen of Maheaics Universiy of Sciences Gwahak- dong Unjong Disric Pyongyang DPRKorea Eail; ryonggilchoe@sar-conek Augus 8 5 Absrac; In his aer we consider
Solutions Problem Set 3 Macro II (14.452)
 Soluions Problem Se 3 Macro II (14.452) Francisco A. Gallego 04/27/2005 1 Q heory of invesmen in coninuous ime and no uncerainy Consider he in nie horizon model of a rm facing adjusmen coss o invesmen.
Soluions Problem Se 3 Macro II (14.452) Francisco A. Gallego 04/27/2005 1 Q heory of invesmen in coninuous ime and no uncerainy Consider he in nie horizon model of a rm facing adjusmen coss o invesmen.
KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Winter 2008 section 002 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
Chapter 14 Homework Answers
 4. Suden responses will vary. (a) combusion of gasoline (b) cooking an egg in boiling waer (c) curing of cemen Chaper 4 Homework Answers 4. A collision beween only wo molecules is much more probable han
4. Suden responses will vary. (a) combusion of gasoline (b) cooking an egg in boiling waer (c) curing of cemen Chaper 4 Homework Answers 4. A collision beween only wo molecules is much more probable han
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume 13, Number 1/2012, pp
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue, Nuber /0, pp 4 SOLITON PERTURBATION THEORY FOR THE GENERALIZED KLEIN-GORDON EQUATION WITH FULL NONLINEARITY
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue, Nuber /0, pp 4 SOLITON PERTURBATION THEORY FOR THE GENERALIZED KLEIN-GORDON EQUATION WITH FULL NONLINEARITY
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
First-Order Temperature-Compensated Total-Current Reference
 2h WSEAS Inernaional Conference on CIRCUITS, Heraklion, Greece, July 22-24, 2008 Firs-Order Teperaure-Copensaed Toal-Curren Reference RADU DAN MIHAESCU Alcael-Lucen Sr.Gheorghe Lazar, nr.9, Tiisoara ROMANIA
2h WSEAS Inernaional Conference on CIRCUITS, Heraklion, Greece, July 22-24, 2008 Firs-Order Teperaure-Copensaed Toal-Curren Reference RADU DAN MIHAESCU Alcael-Lucen Sr.Gheorghe Lazar, nr.9, Tiisoara ROMANIA
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Testing the Random Walk Model. i.i.d. ( ) r
 he random walk heory saes: esing he Random Walk Model µ ε () np = + np + Momen Condiions where where ε ~ i.i.d he idea here is o es direcly he resricions imposed by momen condiions. lnp lnp µ ( lnp lnp
he random walk heory saes: esing he Random Walk Model µ ε () np = + np + Momen Condiions where where ε ~ i.i.d he idea here is o es direcly he resricions imposed by momen condiions. lnp lnp µ ( lnp lnp
I-Optimal designs for third degree kronecker model mixture experiments
 Inernaional Journal of Saisics and Applied Maheaics 207 2(2): 5-40 ISSN: 2456-452 Mahs 207 2(2): 5-40 207 Sas & Mahs www.ahsjournal.co Received: 9-0-207 Acceped: 20-02-207 Cheruiyo Kipkoech Deparen of
Inernaional Journal of Saisics and Applied Maheaics 207 2(2): 5-40 ISSN: 2456-452 Mahs 207 2(2): 5-40 207 Sas & Mahs www.ahsjournal.co Received: 9-0-207 Acceped: 20-02-207 Cheruiyo Kipkoech Deparen of
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Poisson s Raio For a slender bar subjeced o axial loading: ε x x y 0 The elongaion in he x-direcion i is accompanied by a conracion in he oher direcions. Assuming ha he maerial is isoropic (no direcional
Poisson s Raio For a slender bar subjeced o axial loading: ε x x y 0 The elongaion in he x-direcion i is accompanied by a conracion in he oher direcions. Assuming ha he maerial is isoropic (no direcional
Traveling Waves. Chapter Introduction
 Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
On a Discrete-In-Time Order Level Inventory Model for Items with Random Deterioration
 Journal of Agriculure and Life Sciences Vol., No. ; June 4 On a Discree-In-Time Order Level Invenory Model for Iems wih Random Deerioraion Dr Biswaranjan Mandal Associae Professor of Mahemaics Acharya
Journal of Agriculure and Life Sciences Vol., No. ; June 4 On a Discree-In-Time Order Level Invenory Model for Iems wih Random Deerioraion Dr Biswaranjan Mandal Associae Professor of Mahemaics Acharya
Thermal Forces and Brownian Motion
 Theral Forces and Brownian Moion Ju Li GEM4 Suer School 006 Cell and Molecular Mechanics in BioMedicine Augus 7 18, 006, MIT, Cabridge, MA, USA Ouline Meaning of he Cenral Lii Theore Diffusion vs Langevin
Theral Forces and Brownian Moion Ju Li GEM4 Suer School 006 Cell and Molecular Mechanics in BioMedicine Augus 7 18, 006, MIT, Cabridge, MA, USA Ouline Meaning of he Cenral Lii Theore Diffusion vs Langevin
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
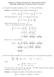 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Some Ramsey results for the n-cube
 Some Ramsey resuls for he n-cube Ron Graham Universiy of California, San Diego Jozsef Solymosi Universiy of Briish Columbia, Vancouver, Canada Absrac In his noe we esablish a Ramsey-ype resul for cerain
Some Ramsey resuls for he n-cube Ron Graham Universiy of California, San Diego Jozsef Solymosi Universiy of Briish Columbia, Vancouver, Canada Absrac In his noe we esablish a Ramsey-ype resul for cerain
Bias in Conditional and Unconditional Fixed Effects Logit Estimation: a Correction * Tom Coupé
 Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
Economics 8105 Macroeconomic Theory Recitation 6
 Economics 8105 Macroeconomic Theory Reciaion 6 Conor Ryan Ocober 11h, 2016 Ouline: Opimal Taxaion wih Governmen Invesmen 1 Governmen Expendiure in Producion In hese noes we will examine a model in which
Economics 8105 Macroeconomic Theory Reciaion 6 Conor Ryan Ocober 11h, 2016 Ouline: Opimal Taxaion wih Governmen Invesmen 1 Governmen Expendiure in Producion In hese noes we will examine a model in which
SPH3U: Projectiles. Recorder: Manager: Speaker:
 SPH3U: Projeciles Now i s ime o use our new skills o analyze he moion of a golf ball ha was ossed hrough he air. Le s find ou wha is special abou he moion of a projecile. Recorder: Manager: Speaker: 0
SPH3U: Projeciles Now i s ime o use our new skills o analyze he moion of a golf ball ha was ossed hrough he air. Le s find ou wha is special abou he moion of a projecile. Recorder: Manager: Speaker: 0
NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION
 Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
Q.1 Define work and its unit?
 CHP # 6 ORK AND ENERGY Q.1 Define work and is uni? A. ORK I can be define as when we applied a force on a body and he body covers a disance in he direcion of force, hen we say ha work is done. I is a scalar
CHP # 6 ORK AND ENERGY Q.1 Define work and is uni? A. ORK I can be define as when we applied a force on a body and he body covers a disance in he direcion of force, hen we say ha work is done. I is a scalar
EFFECT OF OPERATING PARAMETERS ON FORMATION PROCESS OF DEFECTS IN MODERATOR BLOCK IN GRAPHITE REACTORS
 Jr of Indusrial Polluion Conrol 32(2)(2016) pp 437-441 wwwiconrolpolluioncom Research EFFECT OF OPERATING PARAMETERS ON FORMATION PROCESS OF A MOCHALOV, A NAYMUSHIN *, V NESTEROV, S SAVANYUK AND I SHAMANIN
Jr of Indusrial Polluion Conrol 32(2)(2016) pp 437-441 wwwiconrolpolluioncom Research EFFECT OF OPERATING PARAMETERS ON FORMATION PROCESS OF A MOCHALOV, A NAYMUSHIN *, V NESTEROV, S SAVANYUK AND I SHAMANIN
Real Part of the Impedance for a Smooth Taper*
 SLAC-PUB-95-739 Ocober 995 Real Par of he Ipedance for a Sooh Taper* G. V. Supakov Sanford Linear Acceleraor Cener Sanford Universiy, P.O. Box 4349, Sanford, CA 9439 Absrac Real par of he ransverse and
SLAC-PUB-95-739 Ocober 995 Real Par of he Ipedance for a Sooh Taper* G. V. Supakov Sanford Linear Acceleraor Cener Sanford Universiy, P.O. Box 4349, Sanford, CA 9439 Absrac Real par of he ransverse and
arxiv:cond-mat/ May 2002
 -- uadrupolar Glass Sae in para-hydrogen and orho-deuerium under pressure. T.I.Schelkacheva. arxiv:cond-ma/5538 6 May Insiue for High Pressure Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Troisk 49, Moscow Region,
-- uadrupolar Glass Sae in para-hydrogen and orho-deuerium under pressure. T.I.Schelkacheva. arxiv:cond-ma/5538 6 May Insiue for High Pressure Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Troisk 49, Moscow Region,
a. Show that these lines intersect by finding the point of intersection. b. Find an equation for the plane containing these lines.
 Mah A Final Eam Problems for onsideraion. Show all work for credi. Be sure o show wha you know. Given poins A(,,, B(,,, (,, 4 and (,,, find he volume of he parallelepiped wih adjacen edges AB, A, and A.
Mah A Final Eam Problems for onsideraion. Show all work for credi. Be sure o show wha you know. Given poins A(,,, B(,,, (,, 4 and (,,, find he volume of he parallelepiped wih adjacen edges AB, A, and A.
MATHEMATICAL DESCRIPTION OF THEORETICAL METHODS OF RESERVE ECONOMY OF CONSIGNMENT STORES
 MAHEMAICAL DESCIPION OF HEOEICAL MEHODS OF ESEVE ECONOMY OF CONSIGNMEN SOES Péer elek, József Cselényi, György Demeer Universiy of Miskolc, Deparmen of Maerials Handling and Logisics Absrac: Opimizaion
MAHEMAICAL DESCIPION OF HEOEICAL MEHODS OF ESEVE ECONOMY OF CONSIGNMEN SOES Péer elek, József Cselényi, György Demeer Universiy of Miskolc, Deparmen of Maerials Handling and Logisics Absrac: Opimizaion
Wavelet Methods for Time Series Analysis. What is a Wavelet? Part I: Introduction to Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms. sines & cosines are big waves
 Wavele Mehods for Time Series Analysis Par I: Inroducion o Waveles and Wavele Transforms waveles are analysis ools for ime series and images as a subjec, waveles are relaively new (983 o presen) a synhesis
Wavele Mehods for Time Series Analysis Par I: Inroducion o Waveles and Wavele Transforms waveles are analysis ools for ime series and images as a subjec, waveles are relaively new (983 o presen) a synhesis
Waves are naturally found in plasmas and have to be dealt with. This includes instabilities, fluctuations, waveinduced
 Lecure 1 Inroducion Why is i imporan o sudy waves in plasma? Waves are naurally found in plasmas and have o be deal wih. This includes insabiliies, flucuaions, waveinduced ranspor... Waves can deliver
Lecure 1 Inroducion Why is i imporan o sudy waves in plasma? Waves are naurally found in plasmas and have o be deal wih. This includes insabiliies, flucuaions, waveinduced ranspor... Waves can deliver
