Nanoscience, MCC026 2nd quarter, fall Quantum Transport, Lecture 1/2. Tomas Löfwander Applied Quantum Physics Lab
|
|
|
- Johnathan Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nanoscience, MCC026 2nd quarter, fall 2012 Quantum Transport, Lecture 1/2 Tomas Löfwander Applied Quantum Physics Lab
2 Quantum Transport Nanoscience: Quantum transport: control and making of useful things at the atomic scale; goal/dream: build devices atom by atom interdisciplinary: Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Materials Science, Engineering technology working on small spatial scales (the nano 10-9 m) properties and behavior of nanostructures that 1) cannot be understood starting from classical (non-quantum) physics 2) does not depend on materials or atomic structure per se, rather, on a set of principles that holds in certain regimes Example: contuctance G of the order GQ=2e2/h the quantum of conductance
3 Energy scales Temperature k B T, note k B ~0.087 mev/k Voltage applied to the device Level spacing δ, ~0.038 ev nm 2 Charging energy E ch =e 2 /C, ~0.1 mev (for C=10-15 F) Fermi energy E F, ~ several ev for 3D metals ~14 mev (GaAs 2DEG), ~ mev (Si 2DEG)
4 System size L Length scales Fermi wave length λ F, ~20 nm (GaAs), ~100 nm (Si) L < λ F, wave character pronounced L > λ F, electron billiards + interference Elastic scattering length l imp, ~100 nm - 10 µm (GaAs), ~100 nm (Si) L < l imp, ballistic motion L > l imp, diffusive motion Phase coherence length l φ, ~100 nm (GaAs, Si) at 1K (scales as 1/ T) L < l φ, mesoscopic regime L > l φ, macroscopic regime
5 Outline of Quantum Transport Lectures Examples of nanostructures: 2DEG, graphene, nanotubes, molecules Transport of electrons: key concepts Size quantization, energy levels Density of states Semiclassical transport: Boltzmann approach Scattering approach to electron transport in nanostructures Sharvin resistance Conductance quantization and the Landauer formula Tunneling, resonant tunneling Master equation approach to electron transport in nanostructures single-level quantum dot without Coulomb interactions Coulomb interaction and the multi-electron picture single-level quantum dot with Coulomb interactions Coulomb blockade
6 Basic concepts in these lectures size quantization matters in nanoscale devices Schrödinger equation the concept of the scattering (Landauer) approach to coherent quantum transport in nanoscale devices reservoir (= lead, contact) scattering region how to sum over scattering states (quantum numbers) the role of Coulomb interaction in ultra small devices (simplest case: incoherent transport regime) Coulomb blockade
7 Literature Electron Transport in Mesoscopic Systems S. Datta Cambridge University Press 1995 Quantum Transport: Atom to Transistor S. Datta Cambridge University Press 2005 Quantum Transport: Introduction to Nanoscience Y.V. Nazarov and Y.M. Blanter Cambridge University Press 2009
8 Low-dimensional structures - examples 2D quantum contacts (B. van Wees et al PRL 60, 848, 1988) 1D quantum contacts 0D quantum contacts (C. Dekker et al, Nature 386, 474, 2003) (S. Kubatkin et al, Nature 425, 698, 2003) 2DEG= 2 Dimensional Electron Gas single-walled carbon nanotubes extended molecular electron orbits conductance quantization quantum wires quantum dots
9 The 2DEG Quantum point contact Quantum dot
10 Low-dimensional materials 2D graphene K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim et al, Science 306, 666 (2004) 1D Carbon Nanotubes S. Iijima, Nature 354, 56 (1991)
11 Carbon LEGO The Rise of Graphene, A.K. Geim and K.S. Novoselov, Nature Materials 6, 183 (2007)
12 Transport: key concepts electronics cooling, heating, thermoelectricity Measurements of charge, heat, and spin currents How do we compute charge currents? spintronics
13 Transport: key concepts electronics cooling, heating, thermoelectricity Measurements of charge, heat, and spin currents How do we compute charge currents? spintronics distribution function = probability of state p being occupied sum over states (quantum numbers) current carried by state p
14 Transport: key concepts How do we compute charge currents? When we know the energy dispersion, e.g. integral over energies density of states spectral current distribution function density of states = # of states per energy interval & unit volume
15 Size quantization Textbook examples of size quantization: (a) particle in a box in one dimension energy levels: follows from Schrödinger s eq. with hard wall boundary conditions discrete wave numbers: (a) particle in a harmonic potential energy levels:
16 Density of states The previous considerations of energy levels can be extended to more complicated structures and to 2D and 3D. But the energy levels become more dense and degenerate. More useful concept: local density of states Examples: (a) Free electrons (3D) with dispersion (b) compare with 2D (quantization in one of three dimensions) (c) compare with 1D (quantization in two of three dimensions)
17 Density of states The previous considerations of energy levels can be extended to more complicated structures and to 2D and 3D. But the energy levels become more dense and degenerate. More useful concept: local density of states Examples: (a) Free electrons (3D) with dispersion (b) compare with 2D (quantization in one of three dimensions) (c) compare with 1D (quantization in two of three dimensions) blackboard
18 Density of states Collection of results: 0D: discrete spectrum
19 Density of states examples Graphene Linear DOS near the Fermi level Carbon nanotubes Semiconducting or metallic (zero or finite DOS near the Fermi level)
20 Semiclassical transport: Boltzmann approach Macroscopic regime: L Conductance σ = conductivity (material specific) recall Ohm s law j = σe What determines the current? V j =? group velocity current density: Boltzmann s eq:
21 Semiclassical transport: Boltzmann approach Linear response: local equilibrium (symmetric) small correction (antisymmetric) => => =>
22 Semiclassical transport: Boltzmann approach Ohm s law: with diffusion constant (material parameter): Einstein relation
23 The Fermi-Dirac distribution function determines the occupation of the energy levels: The Fermi energy of metals are typically ~5 ev to 10 ev. Room temperature (300 K) corresponds to ~0.026 ev.
24 The Fermi-Dirac distribution function determines the occupation of the energy levels: The Fermi energy of metals are typically ~5 ev to 10 ev. Room temperature (300 K) corresponds to ~0.026 ev.
25 Size quantization: the 2DEG z-direction confinement Method of separation of variables: 3 f 1 2 2DEG
26 Sharvin resistance Consider a pinhole - e.g. a 2DEG with a constriction (here viewed from above): (ballistic regime) Under applied voltage: local equilibrium deep in the reservoar, d w
27 Sharvin resistance The current can be computed within frame work of the scattering approach: net current = difference between right and left going currents
28 Sharvin resistance quantum of conductance # of conducting channels
29 Sharvin resistance quantum of conductance # of conducting channels Sharvin
30 Conductance of one channel y x Separation of variables for one transverse mode in the channel: assume reflectionless contacts wavefunction: E k -E 0 µ L energy: µ R net current = difference between right and left going currents k x
31 Conductance of one channel y E k -E 0 x µ R µ L k x remember: peculiar cancellation in 1D
32 Conductance of one channel y E k -E 0 x µ R µ L k x Thus: = the quantum of conductance note:
33 1D conductance: many channels y (wider contact) x Separation of variables for many transverse modes in the channel: wavefunction: E k energy: µ L consider M open channels: µ R conductance: k x
34 1D conductance: many channels y (wider contact) x M open channels conductance: E k Note: finite resistance in a perfect sample. Why? µ L Note: where is the energy dissipated? µ R k x
35 1D conductance: many channels y (wider contact) x conductance: Sharvin s resistance! =contact resistance E k Note: finite resistance in a perfect sample. Why? µ L Note: where is the energy dissipated? µ R k x
36 1D conductance: many channels y (wider contact) x conductance: Sharvin s resistance! =contact resistance E k Note: finite resistance in a perfect sample. Why? µ L Note: where is the energy dissipated? µ R in the reservoirs! k x
37 Observation of opening of modes
Nanoscience quantum transport
 Nanoscience quantum transport Janine Splettstößer Applied Quantum Physics, MC2, Chalmers University of Technology Chalmers, November 2 10 Plan/Outline 4 Lectures (1) Introduction to quantum transport (2)
Nanoscience quantum transport Janine Splettstößer Applied Quantum Physics, MC2, Chalmers University of Technology Chalmers, November 2 10 Plan/Outline 4 Lectures (1) Introduction to quantum transport (2)
The Physics of Nanoelectronics
 The Physics of Nanoelectronics Transport and Fluctuation Phenomena at Low Temperatures Tero T. Heikkilä Low Temperature Laboratory, Aalto University, Finland OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols
The Physics of Nanoelectronics Transport and Fluctuation Phenomena at Low Temperatures Tero T. Heikkilä Low Temperature Laboratory, Aalto University, Finland OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols
Quantum transport in nanoscale solids
 Quantum transport in nanoscale solids The Landauer approach Dietmar Weinmann Institut de Physique et Chimie des Matériaux de Strasbourg Strasbourg, ESC 2012 p. 1 Quantum effects in electron transport R.
Quantum transport in nanoscale solids The Landauer approach Dietmar Weinmann Institut de Physique et Chimie des Matériaux de Strasbourg Strasbourg, ESC 2012 p. 1 Quantum effects in electron transport R.
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures
 Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics
 Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
wire z axis Under these assumptions, if we model the electrons by plane waves in the z direction we get n E, n, 1,2,
 Part 4. Two Terminal Quantum Wire Devices Part 4. Two Terminal Quantum Wire Devices Let s consider a quantum wire between two contacts. As we saw in Part, a quantum wire is a one-dimensional conductor.
Part 4. Two Terminal Quantum Wire Devices Part 4. Two Terminal Quantum Wire Devices Let s consider a quantum wire between two contacts. As we saw in Part, a quantum wire is a one-dimensional conductor.
Three-terminal quantum-dot thermoelectrics
 Three-terminal quantum-dot thermoelectrics Björn Sothmann Université de Genève Collaborators: R. Sánchez, A. N. Jordan, M. Büttiker 5.11.2013 Outline Introduction Quantum dots and Coulomb blockade Quantum
Three-terminal quantum-dot thermoelectrics Björn Sothmann Université de Genève Collaborators: R. Sánchez, A. N. Jordan, M. Büttiker 5.11.2013 Outline Introduction Quantum dots and Coulomb blockade Quantum
GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice
 GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice dimensionality of carbon diamond, graphite GRAPHENE realized in 2004 (Novoselov, Science 306, 2004) carbon nanotubes fullerenes, buckyballs what s so special about
GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice dimensionality of carbon diamond, graphite GRAPHENE realized in 2004 (Novoselov, Science 306, 2004) carbon nanotubes fullerenes, buckyballs what s so special about
Coulomb blockade in metallic islands and quantum dots
 Coulomb blockade in metallic islands and quantum dots Charging energy and chemical potential of a metallic island Coulomb blockade and single-electron transistors Quantum dots and the constant interaction
Coulomb blockade in metallic islands and quantum dots Charging energy and chemical potential of a metallic island Coulomb blockade and single-electron transistors Quantum dots and the constant interaction
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Coulomb Blockade and Kondo Effect in Nanostructures
 Coulomb Blockade and Kondo Effect in Nanostructures Marcin M. Wysokioski 1,2 1 Institute of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg 2 Institute of Physics Jagiellonian University, Cracow, Poland 2.VI.2010
Coulomb Blockade and Kondo Effect in Nanostructures Marcin M. Wysokioski 1,2 1 Institute of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg 2 Institute of Physics Jagiellonian University, Cracow, Poland 2.VI.2010
Nanoscale Energy Transport and Conversion A Parallel Treatment of Electrons, Molecules, Phonons, and Photons
 Nanoscale Energy Transport and Conversion A Parallel Treatment of Electrons, Molecules, Phonons, and Photons Gang Chen Massachusetts Institute of Technology OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2005 Contents Foreword,
Nanoscale Energy Transport and Conversion A Parallel Treatment of Electrons, Molecules, Phonons, and Photons Gang Chen Massachusetts Institute of Technology OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2005 Contents Foreword,
Lectures: Condensed Matter II 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum dots 2 Kondo effect: Intro/theory. 3 Kondo effect in nanostructures
 Lectures: Condensed Matter II 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum dots 2 Kondo effect: Intro/theory. 3 Kondo effect in nanostructures Luis Dias UT/ORNL Lectures: Condensed Matter II 1 Electronic Transport
Lectures: Condensed Matter II 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum dots 2 Kondo effect: Intro/theory. 3 Kondo effect in nanostructures Luis Dias UT/ORNL Lectures: Condensed Matter II 1 Electronic Transport
single-electron electron tunneling (SET)
 single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
Introduction to Molecular Electronics. Lecture 1: Basic concepts
 Introduction to Molecular Electronics Lecture 1: Basic concepts Conductive organic molecules Plastic can indeed, under certain circumstances, be made to behave very like a metal - a discovery for which
Introduction to Molecular Electronics Lecture 1: Basic concepts Conductive organic molecules Plastic can indeed, under certain circumstances, be made to behave very like a metal - a discovery for which
Electronic Quantum Transport in Mesoscopic Semiconductor Structures
 Thomas Ihn Electronic Quantum Transport in Mesoscopic Semiconductor Structures With 90 Illustrations, S in Full Color Springer Contents Part I Introduction to Electron Transport l Electrical conductance
Thomas Ihn Electronic Quantum Transport in Mesoscopic Semiconductor Structures With 90 Illustrations, S in Full Color Springer Contents Part I Introduction to Electron Transport l Electrical conductance
Transport through Andreev Bound States in a Superconductor-Quantum Dot-Graphene System
 Transport through Andreev Bound States in a Superconductor-Quantum Dot-Graphene System Nadya Mason Travis Dirk, Yung-Fu Chen, Cesar Chialvo Taylor Hughes, Siddhartha Lal, Bruno Uchoa Paul Goldbart University
Transport through Andreev Bound States in a Superconductor-Quantum Dot-Graphene System Nadya Mason Travis Dirk, Yung-Fu Chen, Cesar Chialvo Taylor Hughes, Siddhartha Lal, Bruno Uchoa Paul Goldbart University
Quantum Confinement in Graphene
 Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Intrinsic Charge Fluctuations and Nuclear Spin Order in GaAs Nanostructures
 Physics Department, University of Basel Intrinsic Charge Fluctuations and Nuclear Spin Order in GaAs Nanostructures Dominik Zumbühl Department of Physics, University of Basel Basel QC2 Center and Swiss
Physics Department, University of Basel Intrinsic Charge Fluctuations and Nuclear Spin Order in GaAs Nanostructures Dominik Zumbühl Department of Physics, University of Basel Basel QC2 Center and Swiss
What is Quantum Transport?
 What is Quantum Transport? Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic Semiclassical Transport (is boring!) Bloch-Boltzmann
What is Quantum Transport? Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic Semiclassical Transport (is boring!) Bloch-Boltzmann
ELECTRONIC ENERGY DISPERSION AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND CARBON NANOTUBES
 ELECTRONIC ENERGY DISPERSION AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND CARBON NANOTUBES D. RACOLTA, C. ANDRONACHE, D. TODORAN, R. TODORAN Technical University of Cluj Napoca, North University Center of
ELECTRONIC ENERGY DISPERSION AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND CARBON NANOTUBES D. RACOLTA, C. ANDRONACHE, D. TODORAN, R. TODORAN Technical University of Cluj Napoca, North University Center of
Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems
 Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems Description This book provides an in-depth description of transport phenomena relevant to systems of nanoscale dimensions. The different viewpoints and theoretical
Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems Description This book provides an in-depth description of transport phenomena relevant to systems of nanoscale dimensions. The different viewpoints and theoretical
Charges and Spins in Quantum Dots
 Charges and Spins in Quantum Dots L.I. Glazman Yale University Chernogolovka 2007 Outline Confined (0D) Fermi liquid: Electron-electron interaction and ground state properties of a quantum dot Confined
Charges and Spins in Quantum Dots L.I. Glazman Yale University Chernogolovka 2007 Outline Confined (0D) Fermi liquid: Electron-electron interaction and ground state properties of a quantum dot Confined
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Büttiker s probe in molecular electronics: Applications to charge and heat transport
 Büttiker s probe in molecular electronics: Applications to charge and heat transport Dvira Segal Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Michael Kilgour (poster) Büttiker s probe in molecular electronics:
Büttiker s probe in molecular electronics: Applications to charge and heat transport Dvira Segal Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Michael Kilgour (poster) Büttiker s probe in molecular electronics:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.138 Graphene Nanoribbons with Smooth Edges as Quantum Wires Xinran Wang, Yijian Ouyang, Liying Jiao, Hailiang Wang, Liming Xie, Justin Wu, Jing Guo, and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.138 Graphene Nanoribbons with Smooth Edges as Quantum Wires Xinran Wang, Yijian Ouyang, Liying Jiao, Hailiang Wang, Liming Xie, Justin Wu, Jing Guo, and
Low Bias Transport in Graphene: An Introduction
 Lecture Notes on Low Bias Transport in Graphene: An Introduction Dionisis Berdebes, Tony Low, and Mark Lundstrom Network for Computational Nanotechnology Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University West
Lecture Notes on Low Bias Transport in Graphene: An Introduction Dionisis Berdebes, Tony Low, and Mark Lundstrom Network for Computational Nanotechnology Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University West
A. F. J. Levi 1 EE539: Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017.
 A. F. J. Levi 1 Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017. TTh 9.00 a.m. 10.50 a.m., VHE 210. Web site: http://alevi.usc.edu Web site: http://classes.usc.edu/term-20173/classes/ee EE539: Abstract and Prerequisites
A. F. J. Levi 1 Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017. TTh 9.00 a.m. 10.50 a.m., VHE 210. Web site: http://alevi.usc.edu Web site: http://classes.usc.edu/term-20173/classes/ee EE539: Abstract and Prerequisites
Conductance quantization and quantum Hall effect
 UNIVERSITY OF LJUBLJANA FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS DEPARTMENT FOR PHYSICS Miha Nemevšek Conductance quantization and quantum Hall effect Seminar ADVISER: Professor Anton Ramšak Ljubljana, 2004
UNIVERSITY OF LJUBLJANA FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS DEPARTMENT FOR PHYSICS Miha Nemevšek Conductance quantization and quantum Hall effect Seminar ADVISER: Professor Anton Ramšak Ljubljana, 2004
Lecture 8, April 12, 2017
 Lecture 8, April 12, 2017 This week (part 2): Semiconductor quantum dots for QIP Introduction to QDs Single spins for qubits Initialization Read-Out Single qubit gates Book on basics: Thomas Ihn, Semiconductor
Lecture 8, April 12, 2017 This week (part 2): Semiconductor quantum dots for QIP Introduction to QDs Single spins for qubits Initialization Read-Out Single qubit gates Book on basics: Thomas Ihn, Semiconductor
Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid
 Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid Contents Density of states. DOS in a 3D uniform solid.................... 3.2 DOS for a 2D solid........................ 4.3 DOS for a D solid........................
Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid Contents Density of states. DOS in a 3D uniform solid.................... 3.2 DOS for a 2D solid........................ 4.3 DOS for a D solid........................
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems
 Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
Scattering theory of thermoelectric transport. Markus Büttiker University of Geneva
 Scattering theory of thermoelectric transport Markus Büttiker University of Geneva Summer School "Energy harvesting at micro and nanoscales, Workshop "Energy harvesting: models and applications, Erice,
Scattering theory of thermoelectric transport Markus Büttiker University of Geneva Summer School "Energy harvesting at micro and nanoscales, Workshop "Energy harvesting: models and applications, Erice,
Computational Nanoscience
 Computational Nanoscience Applications for Molecules, Clusters, and Solids KALMÄN VARGA AND JOSEPH A. DRISCOLL Vanderbilt University, Tennessee Щ CAMBRIDGE HP UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Part I One-dimensional
Computational Nanoscience Applications for Molecules, Clusters, and Solids KALMÄN VARGA AND JOSEPH A. DRISCOLL Vanderbilt University, Tennessee Щ CAMBRIDGE HP UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Part I One-dimensional
Branislav K. Nikolić
 First-principles quantum transport modeling of thermoelectricity in nanowires and single-molecule nanojunctions Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark,
First-principles quantum transport modeling of thermoelectricity in nanowires and single-molecule nanojunctions Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark,
Spin electronics at the nanoscale. Michel Viret Service de Physique de l Etat Condensé CEA Saclay France
 Spin electronics at the nanoscale Michel Viret Service de Physique de l Etat Condensé CEA Saclay France Principles of spin electronics: ferromagnetic metals spin accumulation Resistivity of homogeneous
Spin electronics at the nanoscale Michel Viret Service de Physique de l Etat Condensé CEA Saclay France Principles of spin electronics: ferromagnetic metals spin accumulation Resistivity of homogeneous
MCC026:Nanoscience. at the border between chemistry and physics. Samuel Lara-Avila
 MCC026:Nanoscience at the border between chemistry and physics Samuel Lara-Avila Quantum Device Physics Lab Department of Microtechnology and Nanoscience (MC2) November, 2016 Nanoscience Femto 10-15 Nano:
MCC026:Nanoscience at the border between chemistry and physics Samuel Lara-Avila Quantum Device Physics Lab Department of Microtechnology and Nanoscience (MC2) November, 2016 Nanoscience Femto 10-15 Nano:
Subbands and quantum confinement
 Ballistic nanotransistors Modeled on analysis by Mark Lundstrom C, Purdue. Unless otherwise indicated, all images are his. nteresting hybrid of classical transistor behavior, quantum confinement effects,
Ballistic nanotransistors Modeled on analysis by Mark Lundstrom C, Purdue. Unless otherwise indicated, all images are his. nteresting hybrid of classical transistor behavior, quantum confinement effects,
INTRODUCTION À LA PHYSIQUE MÉSOSCOPIQUE: ÉLECTRONS ET PHOTONS INTRODUCTION TO MESOSCOPIC PHYSICS: ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS
 Chaire de Physique Mésoscopique Michel Devoret Année 2007, Cours des 7 et 14 juin INTRODUCTION À LA PHYSIQUE MÉSOSCOPIQUE: ÉLECTRONS ET PHOTONS INTRODUCTION TO MESOSCOPIC PHYSICS: ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS
Chaire de Physique Mésoscopique Michel Devoret Année 2007, Cours des 7 et 14 juin INTRODUCTION À LA PHYSIQUE MÉSOSCOPIQUE: ÉLECTRONS ET PHOTONS INTRODUCTION TO MESOSCOPIC PHYSICS: ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS
Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots. Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan
 Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan Outline 1. Introduction: next three slides for quantum dots 2. Kondo effect
Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan Outline 1. Introduction: next three slides for quantum dots 2. Kondo effect
tunneling theory of few interacting atoms in a trap
 tunneling theory of few interacting atoms in a trap Massimo Rontani CNR-NANO Research Center S3, Modena, Italy www.nano.cnr.it Pino D Amico, Andrea Secchi, Elisa Molinari G. Maruccio, M. Janson, C. Meyer,
tunneling theory of few interacting atoms in a trap Massimo Rontani CNR-NANO Research Center S3, Modena, Italy www.nano.cnr.it Pino D Amico, Andrea Secchi, Elisa Molinari G. Maruccio, M. Janson, C. Meyer,
Recent developments in spintronic
 Recent developments in spintronic Tomas Jungwirth nstitute of Physics ASCR, Prague University of Nottingham in collaboration with Hitachi Cambridge, University of Texas, Texas A&M University - Spintronics
Recent developments in spintronic Tomas Jungwirth nstitute of Physics ASCR, Prague University of Nottingham in collaboration with Hitachi Cambridge, University of Texas, Texas A&M University - Spintronics
No reason one cannot have double-well structures: With MBE growth, can control well thicknesses and spacings at atomic scale.
 The story so far: Can use semiconductor structures to confine free carriers electrons and holes. Can get away with writing Schroedinger-like equation for Bloch envelope function to understand, e.g., -confinement
The story so far: Can use semiconductor structures to confine free carriers electrons and holes. Can get away with writing Schroedinger-like equation for Bloch envelope function to understand, e.g., -confinement
Quantum transport through graphene nanostructures
 Quantum transport through graphene nanostructures S. Rotter, F. Libisch, L. Wirtz, C. Stampfer, F. Aigner, I. Březinová, and J. Burgdörfer Institute for Theoretical Physics/E136 December 9, 2009 Graphene
Quantum transport through graphene nanostructures S. Rotter, F. Libisch, L. Wirtz, C. Stampfer, F. Aigner, I. Březinová, and J. Burgdörfer Institute for Theoretical Physics/E136 December 9, 2009 Graphene
Kondo Physics in Nanostructures. A.Abdelrahman Department of Physics University of Basel Date: 27th Nov. 2006/Monday meeting
 Kondo Physics in Nanostructures A.Abdelrahman Department of Physics University of Basel Date: 27th Nov. 2006/Monday meeting Kondo Physics in Nanostructures Kondo Effects in Metals: magnetic impurities
Kondo Physics in Nanostructures A.Abdelrahman Department of Physics University of Basel Date: 27th Nov. 2006/Monday meeting Kondo Physics in Nanostructures Kondo Effects in Metals: magnetic impurities
Electrical and Optical Properties. H.Hofmann
 Introduction to Nanomaterials Electrical and Optical Properties H.Hofmann Electrical Properties Ohm: G= σw/l where is the length of the conductor, measured in meters [m], A is the cross-section area of
Introduction to Nanomaterials Electrical and Optical Properties H.Hofmann Electrical Properties Ohm: G= σw/l where is the length of the conductor, measured in meters [m], A is the cross-section area of
Surfaces, Interfaces, and Layered Devices
 Surfaces, Interfaces, and Layered Devices Building blocks for nanodevices! W. Pauli: God made solids, but surfaces were the work of Devil. Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Interface between a crystal and vacuum
Surfaces, Interfaces, and Layered Devices Building blocks for nanodevices! W. Pauli: God made solids, but surfaces were the work of Devil. Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Interface between a crystal and vacuum
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Nov 2001
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Nov 2001 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Nov 2001](/thumbs/72/66784898.jpg) Published in: Single-Electron Tunneling and Mesoscopic Devices, edited by H. Koch and H. Lübbig (Springer, Berlin, 1992): pp. 175 179. arxiv:cond-mat/0111505v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Nov 2001 Resonant
Published in: Single-Electron Tunneling and Mesoscopic Devices, edited by H. Koch and H. Lübbig (Springer, Berlin, 1992): pp. 175 179. arxiv:cond-mat/0111505v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Nov 2001 Resonant
Master thesis. Thermoelectric effects in quantum dots with interaction
 Master thesis Thermoelectric effects in quantum dots with interaction Miguel Ambrosio Sierra Seco de Herrera Master in Physics of Complex Systems July 17, 2014 Abstract Thermoelectric effects of small
Master thesis Thermoelectric effects in quantum dots with interaction Miguel Ambrosio Sierra Seco de Herrera Master in Physics of Complex Systems July 17, 2014 Abstract Thermoelectric effects of small
Commensurability-dependent transport of a Wigner crystal in a nanoconstriction
 NPCQS2012, OIST Commensurability-dependent transport of a Wigner crystal in a nanoconstriction David Rees, RIKEN, Japan Kimitoshi Kono (RIKEN) Paul Leiderer (University of Konstanz) Hiroo Totsuji (Okayama
NPCQS2012, OIST Commensurability-dependent transport of a Wigner crystal in a nanoconstriction David Rees, RIKEN, Japan Kimitoshi Kono (RIKEN) Paul Leiderer (University of Konstanz) Hiroo Totsuji (Okayama
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures
 Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
are microscopically large but macroscopically small contacts which may be connected to a battery to provide the bias voltage across the junction.
 At present, we observe a long-lasting process of miniaturization of electronic devices. The ultimate limit for the miniaturization of electronic components is set by the atomic scale. However, in the case
At present, we observe a long-lasting process of miniaturization of electronic devices. The ultimate limit for the miniaturization of electronic components is set by the atomic scale. However, in the case
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Charging and Kondo Effects in an Antidot in the Quantum Hall Regime
 Semiconductor Physics Group Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge Charging and Kondo Effects in an Antidot in the Quantum Hall Regime M. Kataoka C. J. B. Ford M. Y. Simmons D. A. Ritchie University
Semiconductor Physics Group Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge Charging and Kondo Effects in an Antidot in the Quantum Hall Regime M. Kataoka C. J. B. Ford M. Y. Simmons D. A. Ritchie University
Lecture 11 - Phonons II - Thermal Prop. Continued
 Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Lessons from Nanoscience: A Lecture Note Series
 Lessons from Nanoscience: A Lecture Note Series http://nanohub.org/topics/lessonsfromnanoscience Volume 1: Lessons from Nanoelectronics: A New Perspective on Transport Supriyo Datta Purdue University datta@purdue.edu
Lessons from Nanoscience: A Lecture Note Series http://nanohub.org/topics/lessonsfromnanoscience Volume 1: Lessons from Nanoelectronics: A New Perspective on Transport Supriyo Datta Purdue University datta@purdue.edu
From nanophysics research labs to cell phones. Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor
 From nanophysics research labs to cell phones Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor Curriculum Vitae Birth: 1976. High-school graduation: 1994. Master degree: 1999. PhD: 2003.
From nanophysics research labs to cell phones Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor Curriculum Vitae Birth: 1976. High-school graduation: 1994. Master degree: 1999. PhD: 2003.
Index. Index. More information. in this web service Cambridge University Press
 absorption edge, 290 absorption of one photon, 285 acceptors, 118 active medium, 287 active region, 293 alkanethiol endgroups, 150 alligator clips, 147 alloy, 68 amino acids, 145 amorphous, 68 amphoteric,
absorption edge, 290 absorption of one photon, 285 acceptors, 118 active medium, 287 active region, 293 alkanethiol endgroups, 150 alligator clips, 147 alloy, 68 amino acids, 145 amorphous, 68 amphoteric,
Single Electron Tunneling Examples
 Single Electron Tunneling Examples Danny Porath 2002 (Schönenberger et. al.) It has long been an axiom of mine that the little things are infinitely the most important Sir Arthur Conan Doyle Books and
Single Electron Tunneling Examples Danny Porath 2002 (Schönenberger et. al.) It has long been an axiom of mine that the little things are infinitely the most important Sir Arthur Conan Doyle Books and
Semiclassical formulation
 The story so far: Transport coefficients relate current densities and electric fields (currents and voltages). Can define differential transport coefficients + mobility. Drude picture: treat electrons
The story so far: Transport coefficients relate current densities and electric fields (currents and voltages). Can define differential transport coefficients + mobility. Drude picture: treat electrons
Effect of Spin-Orbit Interaction and In-Plane Magnetic Field on the Conductance of a Quasi-One-Dimensional System
 ArXiv : cond-mat/0311143 6 November 003 Effect of Spin-Orbit Interaction and In-Plane Magnetic Field on the Conductance of a Quasi-One-Dimensional System Yuriy V. Pershin, James A. Nesteroff, and Vladimir
ArXiv : cond-mat/0311143 6 November 003 Effect of Spin-Orbit Interaction and In-Plane Magnetic Field on the Conductance of a Quasi-One-Dimensional System Yuriy V. Pershin, James A. Nesteroff, and Vladimir
Final exam. Introduction to Nanotechnology. Name: Student number:
 1 Final exam. Introduction to Nanotechnology Name: Student number: 1. (a) What is the definition for a cluster size-wise? (3%) (b) Calculate the energy separation near the Fermi surface of a metallic cluster
1 Final exam. Introduction to Nanotechnology Name: Student number: 1. (a) What is the definition for a cluster size-wise? (3%) (b) Calculate the energy separation near the Fermi surface of a metallic cluster
IH2654 Nanoelectronics, 9hp autumn 2012, period 1 and ****** Nanoelectronics, PhD course
 IH2654 Nanoelectronics, 9hp autumn 2012, period 1 and ****** Nanoelectronics, PhD course For Master programs in Nanotechnology and E, F, ME and PhD students (Previously: 2B1234, 6p and 4H1716, 4p) https://www.kth.se/social/course/ih2654/
IH2654 Nanoelectronics, 9hp autumn 2012, period 1 and ****** Nanoelectronics, PhD course For Master programs in Nanotechnology and E, F, ME and PhD students (Previously: 2B1234, 6p and 4H1716, 4p) https://www.kth.se/social/course/ih2654/
Quantum physics in quantum dots
 Quantum physics in quantum dots Klaus Ensslin Solid State Physics Zürich AFM nanolithography Multi-terminal tunneling Rings and dots Time-resolved charge detection Moore s Law Transistors per chip 10 9
Quantum physics in quantum dots Klaus Ensslin Solid State Physics Zürich AFM nanolithography Multi-terminal tunneling Rings and dots Time-resolved charge detection Moore s Law Transistors per chip 10 9
Lecture 20: Semiconductor Structures Kittel Ch 17, p , extra material in the class notes
 Lecture 20: Semiconductor Structures Kittel Ch 17, p 494-503, 507-511 + extra material in the class notes MOS Structure Layer Structure metal Oxide insulator Semiconductor Semiconductor Large-gap Semiconductor
Lecture 20: Semiconductor Structures Kittel Ch 17, p 494-503, 507-511 + extra material in the class notes MOS Structure Layer Structure metal Oxide insulator Semiconductor Semiconductor Large-gap Semiconductor
Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts)
 Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts) By Boxiao Chen PH 464: Applied Optics Instructor: Andres L arosa Abstract One of the main factors that impacts the efficiency of solar cells is
Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts) By Boxiao Chen PH 464: Applied Optics Instructor: Andres L arosa Abstract One of the main factors that impacts the efficiency of solar cells is
Heterostructures and sub-bands
 Heterostructures and sub-bands (Read Datta 6.1, 6.2; Davies 4.1-4.5) Quantum Wells In a quantum well, electrons are confined in one of three dimensions to exist within a region of length L z. If the barriers
Heterostructures and sub-bands (Read Datta 6.1, 6.2; Davies 4.1-4.5) Quantum Wells In a quantum well, electrons are confined in one of three dimensions to exist within a region of length L z. If the barriers
Spin-Polarized Current in Coulomb Blockade and Kondo Regime
 Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the XXXVI International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2007 Spin-Polarized Current in Coulomb Blockade and Kondo Regime P. Ogrodnik
Vol. 112 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the XXXVI International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2007 Spin-Polarized Current in Coulomb Blockade and Kondo Regime P. Ogrodnik
2. TranSIESTA 1. SIESTA. DFT In a Nutshell. Introduction to SIESTA. Boundary Conditions: Open systems. Greens functions and charge density
 1. SIESTA DFT In a Nutshell Introduction to SIESTA Atomic Orbitals Capabilities Resources 2. TranSIESTA Transport in the Nanoscale - motivation Boundary Conditions: Open systems Greens functions and charge
1. SIESTA DFT In a Nutshell Introduction to SIESTA Atomic Orbitals Capabilities Resources 2. TranSIESTA Transport in the Nanoscale - motivation Boundary Conditions: Open systems Greens functions and charge
Quantum transport in nanostructures
 Quantum transport in nanostructures About the manifestations of quantum mechanics on the electrical transport properties of conductors V At macro scale I = V/R (Ohm s law) = σv At nano scale I? V Moore
Quantum transport in nanostructures About the manifestations of quantum mechanics on the electrical transport properties of conductors V At macro scale I = V/R (Ohm s law) = σv At nano scale I? V Moore
Observation of neutral modes in the fractional quantum hall effect regime. Aveek Bid
 Observation of neutral modes in the fractional quantum hall effect regime Aveek Bid Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Nature 585 466 (2010) Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field
Observation of neutral modes in the fractional quantum hall effect regime Aveek Bid Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Nature 585 466 (2010) Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field
Olivier Bourgeois Institut Néel
 Olivier Bourgeois Institut Néel Outline Introduction: necessary concepts: phonons in low dimension, characteristic length Part 1: Transport and heat storage via phonons Specific heat and kinetic equation
Olivier Bourgeois Institut Néel Outline Introduction: necessary concepts: phonons in low dimension, characteristic length Part 1: Transport and heat storage via phonons Specific heat and kinetic equation
PH575 Spring Lecture #28 Nanoscience: the case study of graphene and carbon nanotubes.
 PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #28 Nanoscience: the case study of graphene and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscience scale 1-100 nm "Artificial atoms" Small size => discrete states Large surface to volume ratio Bottom-up
PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #28 Nanoscience: the case study of graphene and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscience scale 1-100 nm "Artificial atoms" Small size => discrete states Large surface to volume ratio Bottom-up
Semiconductor Physics and Devices Chapter 3.
 Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids We applied quantum mechanics and Schrödinger s equation to determine the behavior of electrons in a potential. Important findings Semiconductor Physics and
Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids We applied quantum mechanics and Schrödinger s equation to determine the behavior of electrons in a potential. Important findings Semiconductor Physics and
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013
 Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Overview. Carbon in all its forms. Background & Discovery Fabrication. Important properties. Summary & References. Overview of current research
 Graphene Prepared for Solid State Physics II Pr Dagotto Spring 2009 Laurene Tetard 03/23/09 Overview Carbon in all its forms Background & Discovery Fabrication Important properties Overview of current
Graphene Prepared for Solid State Physics II Pr Dagotto Spring 2009 Laurene Tetard 03/23/09 Overview Carbon in all its forms Background & Discovery Fabrication Important properties Overview of current
Class 24: Density of States
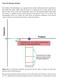 Class 24: Density of States The solution to the Schrödinger wave equation showed us that confinement leads to quantization. The smaller the region within which the electron is confined, the more widely
Class 24: Density of States The solution to the Schrödinger wave equation showed us that confinement leads to quantization. The smaller the region within which the electron is confined, the more widely
Quantum Transport and Dissipation
 Thomas Dittrich, Peter Hänggi, Gert-Ludwig Ingold, Bernhard Kramer, Gerd Schön and Wilhelm Zwerger Quantum Transport and Dissipation WILEY-VCH Weinheim Berlin New York Chichester Brisbane Singapore Toronto
Thomas Dittrich, Peter Hänggi, Gert-Ludwig Ingold, Bernhard Kramer, Gerd Schön and Wilhelm Zwerger Quantum Transport and Dissipation WILEY-VCH Weinheim Berlin New York Chichester Brisbane Singapore Toronto
Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele
 Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele Large radius theory of optical transitions in semiconducting nanotubes derived from low energy theory of graphene Phys.
Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele Large radius theory of optical transitions in semiconducting nanotubes derived from low energy theory of graphene Phys.
Transient grating measurements of spin diffusion. Joe Orenstein UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab
 Transient grating measurements of spin diffusion Joe Orenstein UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab LBNL, UC Berkeley and UCSB collaboration Chris Weber, Nuh Gedik, Joel Moore, JO UC Berkeley
Transient grating measurements of spin diffusion Joe Orenstein UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab LBNL, UC Berkeley and UCSB collaboration Chris Weber, Nuh Gedik, Joel Moore, JO UC Berkeley
3-month progress Report
 3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor
 Chapter 1 Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we apply the formalism we have developed for charge currents to understand the output characteristics of
Chapter 1 Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we apply the formalism we have developed for charge currents to understand the output characteristics of
Electrical spin-injection into semiconductors
 Electrical spin-injection into semiconductors L. W. Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut Universität Würzburg Am Hubland 97074 Würzburg Germany Contents Motivation The usual approach Theoretical treatment
Electrical spin-injection into semiconductors L. W. Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut Universität Würzburg Am Hubland 97074 Würzburg Germany Contents Motivation The usual approach Theoretical treatment
Spin Filtering: how to write and read quantum information on mobile qubits
 Spin Filtering: how to write and read quantum information on mobile qubits Amnon Aharony Physics Department and Ilse Katz Nano institute Ora Entin-Wohlman (BGU), Guy Cohen (BGU) Yasuhiro Tokura (NTT) Shingo
Spin Filtering: how to write and read quantum information on mobile qubits Amnon Aharony Physics Department and Ilse Katz Nano institute Ora Entin-Wohlman (BGU), Guy Cohen (BGU) Yasuhiro Tokura (NTT) Shingo
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER PH8252 - PHYSICS FOR INFORMATION SCIENCE (Common to CSE & IT) Regulation 2017 Academic Year
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER PH8252 - PHYSICS FOR INFORMATION SCIENCE (Common to CSE & IT) Regulation 2017 Academic Year
Coulomb blockade and single electron tunnelling
 Coulomb blockade and single electron tunnelling Andrea Donarini Institute of theoretical physics, University of Regensburg Three terminal device Source System Drain Gate Variation of the electrostatic
Coulomb blockade and single electron tunnelling Andrea Donarini Institute of theoretical physics, University of Regensburg Three terminal device Source System Drain Gate Variation of the electrostatic
Review of Semiconductor Physics
 Solid-state physics Review of Semiconductor Physics The daunting task of solid state physics Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation The equation is only analytically solvable for a handful
Solid-state physics Review of Semiconductor Physics The daunting task of solid state physics Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation The equation is only analytically solvable for a handful
Research Article Graphene Nanoribbon Conductance Model in Parabolic Band Structure
 Nanomaterials Volume 21, Article ID 753738, 4 pages doi:1.1155/21/753738 Research Article Graphene Nanoribbon Conductance Model in Parabolic Band Structure Mohammad Taghi Ahmadi, Zaharah Johari, N. Aziziah
Nanomaterials Volume 21, Article ID 753738, 4 pages doi:1.1155/21/753738 Research Article Graphene Nanoribbon Conductance Model in Parabolic Band Structure Mohammad Taghi Ahmadi, Zaharah Johari, N. Aziziah
PG5295 Muitos Corpos 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum dots 2 Kondo effect: Intro/theory. 3 Kondo effect in nanostructures
 PG5295 Muitos Corpos 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum dots 2 Kondo effect: Intro/theory. 3 Kondo effect in nanostructures Prof. Luis Gregório Dias DFMT PG5295 Muitos Corpos 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum
PG5295 Muitos Corpos 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum dots 2 Kondo effect: Intro/theory. 3 Kondo effect in nanostructures Prof. Luis Gregório Dias DFMT PG5295 Muitos Corpos 1 Electronic Transport in Quantum
Quantum Transport in One-Dimensional Systems
 Lecture 2 Quantum Transport in One-Dimensional Systems K J Thomas Department of Physics Central University of Kerala Kasaragod, Kerala Harish Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad February 23, 2016 ONE-DIMENSIONAL
Lecture 2 Quantum Transport in One-Dimensional Systems K J Thomas Department of Physics Central University of Kerala Kasaragod, Kerala Harish Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad February 23, 2016 ONE-DIMENSIONAL
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Condensed Matter Physics 2016 Lecture 13/12: Charge and heat transport.
 Condensed Matter Physics 2016 Lecture 13/12: Charge and heat transport. 1. Theoretical tool: Boltzmann equation (review). 2. Electrical and thermal conductivity in metals. 3. Ballistic transport and conductance
Condensed Matter Physics 2016 Lecture 13/12: Charge and heat transport. 1. Theoretical tool: Boltzmann equation (review). 2. Electrical and thermal conductivity in metals. 3. Ballistic transport and conductance
Quantum-Effect and Single-Electron Devices
 368 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, VOL. 2, NO. 4, DECEMBER 2003 Quantum-Effect and Single-Electron Devices Stephen M. Goodnick, Fellow, IEEE, and Jonathan Bird, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract In this
368 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, VOL. 2, NO. 4, DECEMBER 2003 Quantum-Effect and Single-Electron Devices Stephen M. Goodnick, Fellow, IEEE, and Jonathan Bird, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract In this
Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect
 Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field spectrum of the correlated 2D electron system: Electron interactions lead to a range of manifestations 10? = 4? = 2 Resistance (arb.
Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field spectrum of the correlated 2D electron system: Electron interactions lead to a range of manifestations 10? = 4? = 2 Resistance (arb.
First-Principles Modeling of Charge Transport in Molecular Junctions
 First-Principles Modeling of Charge Transport in Molecular Junctions Chao-Cheng Kaun Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica Department of Physics, National Tsing Hua University September
First-Principles Modeling of Charge Transport in Molecular Junctions Chao-Cheng Kaun Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica Department of Physics, National Tsing Hua University September
MESOSCOPIC QUANTUM OPTICS
 MESOSCOPIC QUANTUM OPTICS by Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ata Imamoglu A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Toronto Singapore Preface xi 1 Basic Concepts
MESOSCOPIC QUANTUM OPTICS by Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ata Imamoglu A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Toronto Singapore Preface xi 1 Basic Concepts
Coherent Control of a Single Electron Spin with Electric Fields
 Coherent Control of a Single Electron Spin with Electric Fields Presented by Charulata Barge Graduate student Zumbühl Group Department of Physics, University of Basel Date:- 9-11-2007 Friday Group Meeting
Coherent Control of a Single Electron Spin with Electric Fields Presented by Charulata Barge Graduate student Zumbühl Group Department of Physics, University of Basel Date:- 9-11-2007 Friday Group Meeting
Solid State Physics (Major, 8 ECTS)
 Solid State Physics (Major, 8 ECTS) 1 physicist over 3 in US declares to be a condensed matter physicist (CMP) CMP: solids, amorphous materials, liquids, soft materials 20 CMP physics Nobel prizes + 5
Solid State Physics (Major, 8 ECTS) 1 physicist over 3 in US declares to be a condensed matter physicist (CMP) CMP: solids, amorphous materials, liquids, soft materials 20 CMP physics Nobel prizes + 5
Molecular Electronics
 Molecular Electronics An Introduction to Theory and Experiment Juan Carlos Cuevas Universidad Autönoma de Madrid, Spain Elke Scheer Universität Konstanz, Germany 1>World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE
Molecular Electronics An Introduction to Theory and Experiment Juan Carlos Cuevas Universidad Autönoma de Madrid, Spain Elke Scheer Universität Konstanz, Germany 1>World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE
ECE440 Nanoelectronics. Lecture 07 Atomic Orbitals
 ECE44 Nanoelectronics Lecture 7 Atomic Orbitals Atoms and atomic orbitals It is instructive to compare the simple model of a spherically symmetrical potential for r R V ( r) for r R and the simplest hydrogen
ECE44 Nanoelectronics Lecture 7 Atomic Orbitals Atoms and atomic orbitals It is instructive to compare the simple model of a spherically symmetrical potential for r R V ( r) for r R and the simplest hydrogen
