Chapter 5 The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions
|
|
|
- Shanon Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5 The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions
2 The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist Fronterra Geosciences Denver, Colorado
3 ! What is a volcano? Volcanic Eruptions " An erupting vent through which molten rock surfaces. " A mountain built from magmatic eruptions.! Volcanoes are a clear result of tectonic activity.! Volcanoes pose a number of hazards to humans. " Mexico City " Seattle, U.S " Naples, Italy
4 Volcanic Eruptions! In 79 C.E. Mount Vesuvius erupted violently.! Pyroclastic debris destroyed Pompeii, killing 20,000.! A record of Roman life was preserved under ash. Fig. 5.1b, c
5 ! Eruptions are unpredictable, dangerous. " Build large mountains " Blow mountains to bits! Eruptions can Volcanic Eruptions " provide highly productive soils to feed a civilization. " extinguish a civilization in a matter of minutes.! Eruptions affect climate and civilizations. Fig. 5.3a
6 Volcanic Materials! The products of volcanic eruption come in three forms: " Lava flows molten rock that moves over the ground " Pyroclastic debris fragments blown out of a volcano " Volcanic gases expelled vapor and aerosols Fig. 5.6d
7 Lava Flows! Lava can be thin and runny or thick and sticky.! Flow style depends on viscosity, which depends on " composition, especially silica (SiO 2 ) content. " temperature. " gas content. " crystal content. Fig. 5.2 mass. Fig. 5.3b
8 Basaltic Lava Flows! Mafic lava very hot, low silica, and low viscosity! Basalt flows are often thin and fluid. " They can flow rapidly (up to 30 km per hour). " They can flow for long distances (up to several hundred km). #Most flows measure less than 10 km. #Long-distance flow is facilitated by lava tubes. Interlude C
9 Basaltic Lava Flows! Pahoehoe (pa-hoy-hoy) a Hawaiian word describing basalt with a glassy, ropy texture " Pahoehoe forms when extremely hot basalt forms a skin. " With flow, the skin is rolled into ropy ridges and furrows.
10 Basaltic Lava Flows! A a (ah-ah) is a Hawaiian word describing basalt that solidifies with a jagged, sharp, angular texture. " A a forms when hot flowing basalt cools and thickens. " With flow, lava crumbles into shards and fragments. " A a is what you say walking on this material barefoot.
11 Basaltic Lava Flows! Solidified flows may contract with vertical fractures, creating polygonal columns. Giant s Causway (OJ)! This feature, called columnar jointing, indicates lava. Fig. 5.3e
12 Basaltic Lava Flows! Pillow basalt round blobs of basalt cooled in water " Underwater, basalt cools instantly forming a pillow. #The pillow surface is cracked, quenched glass. #Lava pressure ruptures a pillow to form the next blob. #The process repeats to form a mound of pillow basalts. " Common on the mid-ocean ridge Fig. 5.3f
13 Andesitic Lava Flows! Higher SiO 2 content makes andesitic lavas viscous. " Unlike basalt, they do not flow rapidly. " Instead, they mound around the vent and flow slowly.! The crust fractures into rubble, called blocky lava.! Andesitic lava flows remain close to the vent. Fig. 4.12c
14 Rhyolitic Lava Flows! Rhyolite has the highest SiO 2 and the most viscous lava.! Rhyolitic lava rarely flows.! Rather, lava plugs the vent as a lava dome.! Sometimes lava domes are blown to smithereens. Fig. 5.4
15 Volcaniclastic Deposits! Volcanoes often erupt large quantities of fragments.! Volcaniclastic deposits include " pyroclastic debris lava fragments that freeze in air. " preexisting rock blasted apart by eruption. " landslide debris blocks that have rolled downslope. " lahars transported as water-rich slurries. Fig. 5.11b
16 ! Basaltic eruptions Pyroclastic Debris " Released gases eject clots and drops of molten magma. " Sometimes basaltic eruptions form dramatic fountains. #Lapilli pea-sized fragments #Pele s tears frozen droplets #Pele s hair thin glass strands #Blocks large fragments $Bombs streamlined Fig. 5.5
17 Pyroclastic Debris! Andesitic or rhyolitic eruptions " More viscous magmas; more volcanic gases " Make these volcanoes more prone to explode " Explosive eruptions generate huge volumes of debris. #Pumice frothy volcanic glass #Ash fragments less than 2 mm in diameter #Pumice lapilli angular pumice fragments #Accretion lapilli clumps formed by falling through moist air 0.01 mm Fig. 5.6 a-c
18 Again Mt. Toba (75ka)! We know of several supervolcano eruptions in recent geological time. Mt. Toba might have been the largest of them. What Would Happen if a Super Volcanic Eruption Happens Again? (video) Long Valley, CA Lake Toba, Indonesia Yellowstone hotspot! Closer to home: YELLOWSTONE SUPERVOLCANO GETTING READY TO BLOW? (video) You might look to the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory
19 Pyroclastic Debris! Pyroclastic flow (from the French nuée ardente, meaning glowing ash cloud): " Avalanches of hot ash (200 o to 450 o C) that race downslope " Move up to 300 km per hour; incinerate all in their path " Deadly; they kill everything quickly. " Several historic examples: #Mount Vesuvius #Mount Pelée #Mount Augustine Fig. 5.6e
20 Pyroclastic Deposits! Andesitic or rhyolitic eruptions " Tephra deposits of pyroclastic debris of any size. " Tuff lithified ash, may or may not contain lapilli #Air-fall tuff accumulations of ash that fall like snow #Ignimbrite tuff deposited while hot that welds together
21 Other Volcaniclastic Deposits! Volcanic debris flow wetted debris that moves downhill " Occur where volcanoes are covered with ice and snow or drenched in abundant rain " Volcanic debris flows move downslope like wet concrete. " Lahar water-rich debris flow of ash and blocks #Can move very fast (~50 km/hour) and very far (~tens of km). Fig. 5.18a
22 Volcanic Gas! Up to 9% of magma may be gas. " Water (H 2 O) the most abundant gas " Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) second in abundance " Sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) and hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) #rotten-egg smell Fig. 5.7a
23 Volcanic Gas! Gases are expelled as magma rises (P drops).! SO 2 reacts with water to form aerosol sulfuric acid.! Style of gas escape controls eruption violence. " Low viscosity (basalt) easy escape; mellow eruption " High viscosity (rhyolite) difficult escape; violent release! Gas bubbles in rock are called vesicles. Fig. 5.7b
24 Volcanic Architecture! Volcanoes have characteristic features. " Magma chamber " Fissures and vents " Craters " Calderas " Distinctive profiles #Shield volcanoes #Scoria cones (cinder cones) #Stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes) Geology at a Glance
25 Volcanic Architecture! Magma chambers are located in the upper crust. " Usually an open cavity or area of highly fractured rock " May contain a large quantity of magma! Some magma cools here to form intrusive igneous rock.! Some magma may rise to the surface to form a volcano. Geology at a Glance
26 Volcanic Architecture! Some magma rises via a conduit to the surface.! Magma may erupt along a linear tear called a fissure. " Fissure eruptions may display a curtain of fire. " Fissures evolve into discrete vents and craters. Fig. 5.8
27 Volcanic Architecture! Crater a bowl-shaped depression atop a volcano.! Craters are up to 500 m across and 200 m deep.! Form as erupted lava piles up around the vent " Summit eruptions located within the summit crater " Flank eruption located along the side of a volcano Fig. 5.9a
28 Volcanic Architecture! A caldera is a gigantic volcanic depression. " Much larger than a crater (one to tens of km across) " Usually exhibit steep sidewalls and flat floors! A magma chamber empties and the volcano collapses in. Crater Lake, OR Fig. 5.9 b-d
29 ! Shield volcanoes Volcanic Architecture " Broad, slightly dome-shaped (like an inverted shield) " Constructed by lateral flow of low-viscosity basaltic lava. " Have a low slope and cover large geographic areas " Mauna Loa on Hawaii is a perfect example. Mauna Loa, HI Fig. 5.10a
30 Volcanic Architecture! Scoria cones (also called cinder cones) " Conical piles of tephra; the smallest type of volcano " Built of ejected lapilli and blocks piled up at a vent " Often symmetrical, with a deep summit crater " Typically from a single eruption event Nazko Cone, BC Fig. 5.10b
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
A. What is a volcano?
 VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 5 9/10/2011. Introduction. Volcanoes and Volcanism. Volcanism. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Study guide chapter 9
 Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
What is Inside a Volcano?
 Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Chapter 5 Volcanoes All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some crystals and varying amounts of dissolved gases Lava is erupted magma The behavior
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Chapter 5 Volcanoes All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some crystals and varying amounts of dissolved gases Lava is erupted magma The behavior
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted.
 What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Introduction to volcanoes. Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt
 Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Vulcanicity. Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form.
 Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
3/24/2016. Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016
 Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Physical Geography. Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Volcanism. Chapter 12 GEOGRAPHY Earthquakes and Volcanoes. What are Earthquakes?
 Physical Geography GEOGRAPHY 1710 DAVID R. SALLEE Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Chapter 12 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes? The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated
Physical Geography GEOGRAPHY 1710 DAVID R. SALLEE Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Chapter 12 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes? The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated
Chapter 5 Lecture. Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology. Twelfth Edition. Volcanic Hazards. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions All eruptions involve
Chapter 5 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions All eruptions involve
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2
 FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Types of Volcanoes. Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries.
 Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
 Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980) Largest historic eruption in North America Lowered peak by more than 400 m Destroyed all trees in
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980) Largest historic eruption in North America Lowered peak by more than 400 m Destroyed all trees in
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
 Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Focus Question 7.1 How were the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and Hawaii s Kilauea volcano different? Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980)
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Focus Question 7.1 How were the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and Hawaii s Kilauea volcano different? Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980)
V o l c a n o es. Part I Composition. Types of deposits. Types of volcanoes Distribution
 V o l c a n o es Part I Composition Types of deposits Types of volcanoes Distribution Volcano: A mound of material that is extruded to the Earth s surface from a vent that is connected to a magma chamber
V o l c a n o es Part I Composition Types of deposits Types of volcanoes Distribution Volcano: A mound of material that is extruded to the Earth s surface from a vent that is connected to a magma chamber
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Erupted and killed approximately 15,000 people 200 years ago
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Chapter 8 Volcanic Activity Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic. Case History: Mt.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Chapter 8 Volcanic Activity Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic. Case History: Mt.
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES.
 Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
1/31/2013 BASALTIC BASALTIC ANDESITIC RHYOLITIC
 Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition of magma affect eruptions? What are two ways that magma can erupt from a volcano?
 CHAPTER 9 1 Volcanic Eruptions SECTION Volcanoes BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition
CHAPTER 9 1 Volcanic Eruptions SECTION Volcanoes BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Volcano Vocabulary ROCK CYCLE. Igneous REMELTED REMELTED BURIED BURIED HEAT ERODED DEPOSITED. Metamorphic Sedimentary ERODED, TRANSPORTED DEPOSITED
 Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
2/25/2013. Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic.
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Chapter 8 Volcanic Activity Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic. Lecture Presentation
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Edward A. Keller Chapter 8 Volcanic Activity Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic. Lecture Presentation
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Volcanoes What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Volcanoes What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
6/26/2018. Volcanoes & Volcanic Hazards Earth, Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Volcanoes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Volcanoes & Earth, Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Volcanoes From the VolcanoCam, 12 September 2007 All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Volcanoes & Earth, Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Volcanoes From the VolcanoCam, 12 September 2007 All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some
Critical Thinking 1. Contrast How could you tell the difference between a mafic rock and a felsic rock by looking at them?
 CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes
 The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have
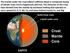 The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have derived from the mantle by fractional melting that operates
The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have derived from the mantle by fractional melting that operates
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Volcanism. Dr. Dan Britt Department of Physics
 Volcanism Dr. Dan Britt Department of Physics Pompeii and Herculaneum Buried in a AD 79 eruption of Mt. Vesuvius. Pompeii was under ~20 feet of ash and pumice Herculaneum was under ~80 feet of welded tuff.
Volcanism Dr. Dan Britt Department of Physics Pompeii and Herculaneum Buried in a AD 79 eruption of Mt. Vesuvius. Pompeii was under ~20 feet of ash and pumice Herculaneum was under ~80 feet of welded tuff.
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Volcanoes. Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman
 Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Volcano. Magma. Lava. weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up. molten mixture of rockforming
 Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening.
 Chapter 9 Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening. 3 Conditions Allow Magma to Form: Decrease in pressure
Chapter 9 Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening. 3 Conditions Allow Magma to Form: Decrease in pressure
IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 300 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 300 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore VO L CANIC CO NE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore VO L CANIC CO NE For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
OIKOS > volcano > mechanism >types of volcanoes
 Main Types of Volcanoes Volcanologists have classified volcanoes into groups based on the shape of the volcano, the materials they are built of, and the way the volcano erupts. The main one can be described
Main Types of Volcanoes Volcanologists have classified volcanoes into groups based on the shape of the volcano, the materials they are built of, and the way the volcano erupts. The main one can be described
Dynamic Planet PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. c) low temperature d) high volatile content
 School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Folding. Faulting. Volcanoes
 Folding Faulting Volcanoes Most major global mountain ranges were formed by the collision of continental (tectonic) plates Fold mountains are actually formed by crust which have been uplifted and folded
Folding Faulting Volcanoes Most major global mountain ranges were formed by the collision of continental (tectonic) plates Fold mountains are actually formed by crust which have been uplifted and folded
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann
 17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
Volcanoes. I Types of Volcanoes II Plutonic Activity III Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity IV Magma and Lava V Types of Lava Flows
 Volcanoes I Types of Volcanoes II Plutonic Activity III Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity IV Magma and Lava V Types of Lava Flows 1 Some Definitions Igneous refers to processes and rocks involving or
Volcanoes I Types of Volcanoes II Plutonic Activity III Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity IV Magma and Lava V Types of Lava Flows 1 Some Definitions Igneous refers to processes and rocks involving or
Geography. Key facts. Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions
 Geography Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions Volcanoes form when magma reaches the Earth's surface, causing eruptions of lava and ash. They occur at destructive (compressional) and constructive (tensional)
Geography Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions Volcanoes form when magma reaches the Earth's surface, causing eruptions of lava and ash. They occur at destructive (compressional) and constructive (tensional)
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Conversational volcano (less challenging) Lava. Magma. Pyroclastic Flow. Lava bomb. Acid rain. Convection. Volcanic ash.
 Conversational volcano (less challenging) Lava Magma Pyroclastic Flow Lava bomb Acid rain Convection Volcanic ash Volcanic gases The hot molten fluid rock that erupts from a volcano or volcanic fissure.
Conversational volcano (less challenging) Lava Magma Pyroclastic Flow Lava bomb Acid rain Convection Volcanic ash Volcanic gases The hot molten fluid rock that erupts from a volcano or volcanic fissure.
Volcanoes. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are the parts of a volcano? 2. What are the four types? 3. What processes form volcanoes? 4. Where are volcanoes located on earth? What is a Volcano?
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are the parts of a volcano? 2. What are the four types? 3. What processes form volcanoes? 4. Where are volcanoes located on earth? What is a Volcano?
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure. Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
S3 IHE GE 2014/Chan ML
 S3 IHE GE 2014/Chan ML Formation Types Advantages and Disadvantages of living near/in volcanic areas Introduction Volcano, mountain or hill formed by the accumulation of materials erupted through one or
S3 IHE GE 2014/Chan ML Formation Types Advantages and Disadvantages of living near/in volcanic areas Introduction Volcano, mountain or hill formed by the accumulation of materials erupted through one or
1. Volcanoes. A volcano is a landform (usually a mountain) where molten rock erupts through the surface of the planet.
 1. Volcanoes A volcano is a landform (usually a mountain) where molten rock erupts through the surface of the planet. In simple terms a volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock
1. Volcanoes A volcano is a landform (usually a mountain) where molten rock erupts through the surface of the planet. In simple terms a volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Pyroclastic Flows. Lesson 6
 Pyroclastic Flows Lesson 6 P yroclastic flows are one of the most dangerous natural events that occur on our planet. They can at hurricane speeds down the slopes of a mountain, destroying everything in
Pyroclastic Flows Lesson 6 P yroclastic flows are one of the most dangerous natural events that occur on our planet. They can at hurricane speeds down the slopes of a mountain, destroying everything in
GLG Ch 6: Volcanoes & Volcanic Hazards. 3. Name, describe (DSC) and draw the three types of volcanoes from smallest to largest.
 GLG 101 - Ch 6: Volcanoes & Volcanic Hazards Name 6.1 What Is and and Is Not a Volcano? 1. Three common characteristics of a volcano include A B C 2. How did the Hopi Buttes (figure 06 01.b1) form? 3.
GLG 101 - Ch 6: Volcanoes & Volcanic Hazards Name 6.1 What Is and and Is Not a Volcano? 1. Three common characteristics of a volcano include A B C 2. How did the Hopi Buttes (figure 06 01.b1) form? 3.
Chapter 12 Vocabulary and Study Guide Volcanoes
 Chapter 12 Vocabulary and Study Guide Volcanoes 1) acid rain Moisture with a PH below 5.6 that falls to Earth as rain or snow and can damage forests, harm organisms, and corrode structures. Sulfurous gases
Chapter 12 Vocabulary and Study Guide Volcanoes 1) acid rain Moisture with a PH below 5.6 that falls to Earth as rain or snow and can damage forests, harm organisms, and corrode structures. Sulfurous gases
VOLCANOES. Homework due Wed./Thurs. I have a few copies left, or get by moodle or webpage
 VOLCANOES Homework due Wed./Thurs. I have a few copies left, or get by moodle or webpage Bowen s Reaction Series Oceanic basin tectonics http://my.execpc.com/~acmelasr/mountains/geogramsnf.html Icelandic
VOLCANOES Homework due Wed./Thurs. I have a few copies left, or get by moodle or webpage Bowen s Reaction Series Oceanic basin tectonics http://my.execpc.com/~acmelasr/mountains/geogramsnf.html Icelandic
Science Read. 10 July. About Volcanoes
 Issue 13 Science Read 10 July Career Guidance Interesting Science Real Life Application Real Time News Upper Secondary About Volcanoes U.S. Geological survey 14 December 2017 Volcanoes are openings, or
Issue 13 Science Read 10 July Career Guidance Interesting Science Real Life Application Real Time News Upper Secondary About Volcanoes U.S. Geological survey 14 December 2017 Volcanoes are openings, or
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
1 Types of Volcanoes CHAPTER. Chapter 1. Types of Volcanoes
 CHAPTER 1 Types of Volcanoes Describe the magma compositions and characteristics of different types of volcanoes. What does an active volcano look like? Climbing up Mount St. Helens and looking into the
CHAPTER 1 Types of Volcanoes Describe the magma compositions and characteristics of different types of volcanoes. What does an active volcano look like? Climbing up Mount St. Helens and looking into the
Tectonics of Magma. From partial melting of mantle Occurs at oceanic ridges and mantle plumes More dense: makes oceanic crust
 VOLCANOES Tectonics of Magma Basaltic magma From partial melting of mantle Occurs at oceanic ridges and mantle plumes More dense: makes oceanic crust Granitic magma From melting of crust, with water as
VOLCANOES Tectonics of Magma Basaltic magma From partial melting of mantle Occurs at oceanic ridges and mantle plumes More dense: makes oceanic crust Granitic magma From melting of crust, with water as
Volcanoes. 11/25/2013. Geology 15 Lecture 27 VOLCANO!
 Hazard Update Surprise POP Review Tsunami Activity 10 B Today s Material Volcanoes Volcanic Hazards Geology 15 Lecture 27 VOLCANO! http://motherboard.vice.com/blog/watch an erupting volcano create a newisland
Hazard Update Surprise POP Review Tsunami Activity 10 B Today s Material Volcanoes Volcanic Hazards Geology 15 Lecture 27 VOLCANO! http://motherboard.vice.com/blog/watch an erupting volcano create a newisland
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
