Assessment of Organotin Compounds in Coastal Sediments of Kuwait
|
|
|
- Evangeline Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol. 2 (2): , 2018 Assessment of Organotin Compounds in Coastal Sediments of Kuwait Amal J. Alkandari 1*, Thamer S. Ali 2 & Talat Saeed 3 1 Ministry of Public Health, Kuwait 2 Department of Natural Resources and Environment, College of Graduate Studies, Arabian Gulf University, Bahrain 3 Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait *Corresponding author: shams_aldeen2003@yahoo.com Abstract: The present study provides a baseline on organotin levels in sediments throughout the Kuwaiti marine environment. The study was designed to detect the organotin compounds including butyltin represented by mono (MBT), di (DBT), tri (TBT), tetra (TeBT) and total tin in surface and core sediments. A total of 76 grab and 19 core sediment samples were collected from 19 locations in the northern coast, Kuwait bay and around islands. The results revealed that only TBT compound has been detected in surface sediment samples at four locations; Rumaila shipwreck, Mubarak port, Failaka island and Shuwaikh port with an average of 0.991, 0.622, and µg/g, respectively. All levels were found to be exceeding the standards adopted by both EAC and EQS. However, no levels were detected in core samples neither for TBT nor for other organotin compounds. There are many sunken vessels in the NW Arabian Gulf just close to the borders with adjacent countries since the Iraq-Iran war during in additions to others sunk during the Gulf war in 1991 and Iraq invasion in These vessels represent a potential source of TBT leakage from their paints driven by current regime in the area toward the Kuwaiti waters, in addition to dry-docks activities in the ports at neighbour countries. It is of great importance to initiate the salvage for the sunken vessels and to cooperate on transboundary effect of overall marine pollutants. Introduction Kuwaiti territorial waters are characterized as well-mixed year around with a maximum depth of 30 m (Al-Yamani et al., 2004). Tidal cycle and winds are the main factors controlling the water mass movement in the NW Arabian Gulf. The water circulation in the Arabian Gulf is known as a counter clock where the water mass enters the Arabian Gulf through Strait of Hormuz aligned the Iranian side on the east turning to the Arabian side on the west in the southward path as indicated by Reynolds (1993). Received Dec. 10, 2017, accepted Feb. 12, 2018
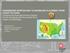
2 131 Alkandari et al. Shatt Al-Arab river which is formed by the confluence of the Euphrates- Tigris rivers is considered as the major source of freshwater influx into the Arabian Gulf. The extent of the discharge is mostly within the northwest Arabian Gulf where the Kuwaiti territorial waters located and with lesser extent to the Saudi Arabian coast. The flow rate of the discharge was estimated by 1,456 m 3 /s (Reynolds, 1993). Although the annual discharge is in a decrease trend along the last three decades as a result of constructions of dams at the upper reaches of Tigris and Euphrates basin and the diversion of Karun river, there is no recent estimation available indicating to which limit the discharge has been decreased. The previous estimation of the average of annual discharge was varied between 35 km 3 /year (Saad, 1978) and 45 km 3 /year (Reynolds, 1993). A large sediments load is transported by the river discharge of Shatt Al-Arab river and the Third river as well through Khor Al- Zubair and Khor Abdullah. According to Alkuwairan (2013), Kuwait s coastal topography is characterized by high sediment load in the northern areas and Kuwait bay. On chemical basis, the northern Arabian Gulf and Kuwait bay exhibited a mix of dolomite [CaMg (CO 3 ) 2 ], carbonate and siliciclastic sediment and dolomitic cement was a major component due to the predominance of fine silt and mud silt. Organotin compounds were widely used as antifouling substances. During 1950 s and 1960 s, the quantity was increased from 5000 tons to 60,000 tons (Ritsema et al., 1998). In 1970 s, the toxicity of organotin compounds was reported as a result of marine mollucs populations decline in the coast of Plymouth sound, United Kingdom. Consequently, several regulations were developed and implemented to reduce the use of highly toxicity organotin compounds (Okoro et al., 2011). After recognition of the complexity, regulations concerning the use of TBT on a global scale were initiated in the 1980 s, including a ban on its use since 1 st January 2008 (Maguire, 2000). Kuwait as a member of ROPME (The Regional Organization for the Protection of the Marine Environment) effectively implemented the protocol that controlled and managed the ship biofouling. The only study dealing with organotin compounds in the marine environment of the Arabian Gulf was carried by ROPME after IMO (International Maritime Organization) banned the use of TBT in antifouling paints in 2008 (ROPME, 2011). The present study aims to estimate the concentration of organotin compounds by different fraction of butyltin represented by MBT, DBT, TBT, TeBT and total tin in sediments throughout Kuwaiti marine environment. Materials and Methods Samples were collected from 19 locations, as shown in Figure (1), including ports, marinas and islands. At each site, three replicates of four
3 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 132 surface sediment samples by Van Veen grab sampler and one core sample from the center by the Kajak core were collected between March and June In the laboratory, surface sediment samples were air-dried in a hood. The same procedure was applied to the core samples after cutting it in sections of 2.5 cm, 3 cm and 5 cm interval to the end of the core. Grab and core samples were grounded and stored in clean glass containers in dark. Organotin compounds were extracted from sediment by acetate buffer to methanol (CH 3 OH) and 5% sodium tetraethyl borate (NaBEt 4 ), and partitioned into n-hexane (David et al., 2003). To 1 gram of air dried samples, blank, or CRM in a centrifuge tube, 10 ml of acetate buffer, 7 ml of methanol, 4 ml of 5% NaBEt 4, 10 ml of hexane and 250 µl of 10 ppm internal standard were added. The mix was shaken for 20 minutes, then it was centrifuged for 10 minutes. The clear upper layer was used for TBT analysis. Figure 1: Location map of sediment samples. Results and Discussion The result indicates a presence of TBT in surface sediment samples at four locations (stations 3, 4, 5 and 9), i.e. 20% of the monitoring stations, three in the northern coast and one in Kuwait bay. The highest TBT concentration
4 133 Alkandari et al. detected was µg/g dw at station 9 (Al-Shuwaikh port) and the lowest was µg/g dw at station 5 (Failaka island) as presented in Table (1). The concentrations found to be variable within the subsamples of the four locations. However, no levels neither of TBT nor of other organotin compounds have been detected in core sediment samples throughout all sections examined down to depth of 50 cm. Station 3: Rumaila Shipwreck Rumaila is an Iraqi oil tanker which sunk in the north of Khor Abdullah in 1991 and settled horizontally (Figure 2) forming a barrier against the currents movements. The oil is still continuously leaking from the shipwreck as illustrated in Figure (3). Two of the four surface sediment subsamples were collected from the southern side (subsamples 1 and 2 representing the face side of the ship) and the other two subsamples were collected from the northern side (subsamples 3 and 4 representing bottom side of the ship). TBT was detected only in subsamples 1 and 2. The concentrations of TBT triplicates in subsample 1 were 1.118, and µg/g dw, with an average of µg/g dw and in subsample 2, the concentrations were relatively lower estimated to be 0.805, and µg/g dw with an average of µg/g dw (Figure 4). The levels detected in both subsamples 1 and 2 could be attributed to the ship s paint leaking into the sediment. The no TBT detection in the subsamples 3 and 4 could be due to the huge sedimentation accumulated on the bottom side where the shipwreck acts as a barrier against the current flow. Table 1: TBT concentrations in surface sediment subsamples at the four polluted locations. Stations St. 3 St. 4 St. 5 St. 9 Location Rumaila: Iraqi wrecked ship Mubarak port, Bobyan island Failaka island Al-Shuwaikh port Sample No. Subsample 1 Subsample 2 Subsample 3 Average
5 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 134 Figure 2: TBT concentrations in sediment samples at Rumaila shipwreck location. Figure 3: Oil spill from the Rumaila shipwreck.
6 135 Alkandari et al. Figure 4: Average of TBT in sediment subsamples at Rumaila shipwreck location. Station 4: Mubarak Port Mubarak port is newly established on the east coast of Bobyan island (Figure 5). Out of the four surface subsamples collected from the port area, TBT was detected at three locations. The concentrations of TBT in subsample 1 were 0.678, and µg/g dw with an average of µg/g dw representing the highest level in this location. In subsample 2, the TBT concentrations were 0.591, and µg/g dw with an average of µg/g dw, which seem to be more or less similar to the TBT concentrations in subsample 3 those estimated to be 0.562, and µg/g dw with an average of µg/g dw (Figure 6). The highest levels of TBT observed at subsample 1 indicates trapping of pollutants potentially transported by the currents inside the port. The TBT detected could be sourced as a result of maintenance activity in the dry dock at ports in adjacent countries. Moreover, the paint leaked from the sunken vessels along Khor Abdullah since the Gulf war in 1991 probably represents a further source drifted by the currents. Station 5: Failaka Island Marina Failaka marina is characterised by a rocky shore with approximately 250 m intertidal zone. Of the four surface sediment samples collected, TBT was found in two samples those located at the marina s west side (Figure 7). TBT concentrations in these two sediment samples were 0.815, and µg/g dw in subsamples 1, with an average of µg/g dw. In subsamples 2,
7 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 136 the TBT concentrations were relatively lower represented by 0.609, and µg/g dw, with an average of µg/g dw (Figure 8). The high levels of TBT observed at the west side of the marina, particularly in the inner sample, could be attributed to trapping of pollutants transported by currents inside the marina. However, samples 3 and 4 were collected from the east side with no TBT levels. The samples were associated with new sedimentation noticeably accumulated on the east, thus no TBT were detected in the surface. Kuwait s Ministry of Communication and Touristic Enterprising Company maintained the marina by regular dredging to secure the navigation for passenger boats. The source of TBT in Failaka marina could be attributed to the sunken boats in the lower reaches of Shatt Al-Arab river and many others scattered within the Iraqi territorial waters since the Iraq-Iran war ( ) and as a result of the Gulf war (1991) as illustrated in Figure (9). Moreover, other sunken vessels at the entrance of Khor Bobyan (Figure 10) may also provide further source for TBT observed in this location where the water mass is drifting westerly toward the Kuwaiti territorial waters as a result of anticlockwise current pattern in the Arabian Gulf (Figure 11). Figure 5: TBT concentrations in sediment samples at Mubarak port location.
8 137 Alkandari et al. Figure 6: Average of TBT in sediment subsamples at Mubarak port location. Figure 7: TBT concentrations in sediment samples at Failaka marina location.
9 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 138 Figure 8: Average of TBT in sediment subsamples at Failaka marina location. Figure 9: Locations of sunken vessels in the northwest Arabian Gulf (Qasim & Ali, Unpublished).
10 139 Alkandari et al. Figure 10: Locations of sunken vessels in the Kuwaiti territorial waters (Al Turkeit & El Kandary, 2003). Figure 11: Currents regime along the Kuwait coast (Al-Ghadban, 2004).
11 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 140 Station 9: Shuwaikh Port Shuwaikh port is the largest commercial port located in the eastern part of Kuwait bay. Out of the four sediment surface samples taken from this location, only sample 1 at the dry dock was found to be contaminated by TBT (Figure 12). The TBT concentrations in the subsamples of this site were 1.149, and µg/g dw, with an average of µg/g dw (Figure 13) indicating the highest levels throughout the stations surveyed. The dry dock at Shuwaikh port was constructed in 1974 for both large and small ship maintenance. Accordingly, the main source of TBT at this site could be the result of antifouling paints escaping during the maintenance activity in the dry dock. TBT Levels in Comparison with Regional and Global Scales Compared to TBT concentrations in other Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, the concentrations found in the present study are less than those reported by Hasan & Juma (1992) in Bahrain in early 1990 (128-1,930 µg/g dw) and in 1992 ( µg/g dw). However, the TBT concentrations determined by de Mora et al. (2003) during , indicated that the levels in the United Arab Emirates were < µg/g dw, which are less than those obtained in the present study while the range of levels in Qatar (< µg/g dw), Bahrain (< µg/g dw) and Oman ( µg/g dw) were higher than the range of the present study. The recent assessment carried out by ROPME (2011) indicated that TBT concentrations in the GCC countries including Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar and Oman were < 0.3 µg/g dw during 2011 and in the United Arab Emirates was µg/g dw, confirming substantial elevation in comparison with the levels found in the present study. Recently, the study conducted by Al-Shatri et al. (2014) revealed a noticeable decrease of TBT in Saudi Arabia where the levels were ranged between µg/g and µg/g. Based on the TBT standard adopted by the OSPAR ( µg/g) and the EU Environmental Quality Standards EQS ( µg/g) as reported by Nyberg et al. (2013), all TBT concentrations determined in the Arabian Gulf are substantially beyond these two standards. The results obtained at the four contaminated locations in the present study are extremely higher than the standards of TBT levels in sediment adopted by EAC and EQS as illustrated in Figure (14). The temporal satellite image showed many shipwrecks in the Shatt Al- Arab river as a result of the Iraq-Iran war ( ) and Khor Abdullah and Khor Al-Zubair as a result of both the Gulf war (1991) and the US invasion of Iraq (2003). At least 80 ships remained as wrecks in and on the sides of the main navigation channel, which potentially threatened the marine environment due to the spills of petroleum products, unexploded ordnance
12 141 Alkandari et al. Figure 12: TBT concentrations in sediment samples at Shuwaikh port location. Figure 13: Average of TBT in sediment subsamples at Al-Shuwaikh port location.
13 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 142 Figure 14: TBT concentrations in the study area in comparison to international standards. and possibly rocket fuel, propellants and toxic chemicals (UNEP, 2003). A report published by the UN Development Programme identified 280 shipwrecks weighing more than 34 million tons, 260 of which are commercial and 40 of these shipwrecks need immediate removal (Valerie, 2005). A total of 61 sunken vessels of different sizes were located at the northwest Arabian Gulf, mostly at the entrance of Khor Abdullah as presented in Figure (9). According to Kuwaiti Ministry of Communication, further 34 sunken vessels of different sizes, most of them are a barge, were located within the Kuwaiti territorial waters along off the Kuwaiti coast as a result of the Gulf war (1991) as illustrated in Figure (10). These sunken vessels are considered as potential sources of different pollutants including TBT that might be drifted by the current regime towards the Kuwaiti territorial waters particularly during ebb cycle. Both petroleum and antifouling substances are the two critical problems posed by shipwrecks (UNEP, 2003; Valerie, 2005). TBT sorption in the natural sediment depends on ph, salinity and biotic and abiotic degradation and increase at ph 6 particularly in muddy and clay sediment (Adelman et al., 1990; Meador, 2000; Landmeyer et al., 2004; Kirli, 2005). Degradation of organotin compounds might be accelerated by UV radiation, increasing temperature and biological activity. The shallow depths throughout the Kuwaiti coasts (<10 m during high tide) provide an opportunity for irradiation by ultraviolet sunlight to degrade the TBT concentrations adsorbed onto surface sediments despite the complexity of the bottom texture.
14 143 Alkandari et al. Banning TBT as a component of antifouling paints in Kuwait since 2008 was obviously reflected on the marine environment, where the levels observed are mostly resulted due to transboundary effect that need to be regionally focus on to identify potential preventive and remedial actions to promote long-term sustainable development in the region. Conclusions The transboundary effect of maintenance activities practiced in the dry docks in adjacent countries formed potential source of antifouling compounds transported by freshwater discharge. The banning of TBT as a component of antifouling paint in Kuwait since 2008 obviously reflected on the quality of marine sediments, where the levels observed were very likely to be of transboundary sources, beyond the territorial waters. The anti- clockwise currents system at the northern Arabian Gulf is the most factor controlling the movement of the water mass discharged from the Shatt Al-Arab river and Khor Abdullah to drift westerly toward the Kuwaiti territorial waters with sediment loads associated with anticipated pollutants. On the other hand, the shallow depths throughout the Kuwait s coasts (< 10 m during high tide), provide an opportunity for irradiation by ultraviolet sunlight to degrade the TBT concentrations adsorbed onto surface sediments by photoreaction despite the complexity of the bottom texture. The northwest Arabian Gulf, where the sunken vessels are scattered, plays an important biological role as spawning, feeding and nursery grounds for broad scale of fishery species. Consequently, it is of great importance to initiate a regional survey to assess the levels and types of pollutants in this area and to take a cooperation action on the salvage of the sunken vessels. References Adelman, D.; Hinga, K.R. & Pilson, M.E.Q. (1990). Biogeochemistry of butyltins in an enclosed marine ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett., 24 (7): Al-Ghadban, A.N. (2004). Assessment of suspended sediment in Kuwait bay using landsat and spot image. Kuwait J. Sci. Eng., 31 (2): Alkuwairan, M.Y. (2013). Polygenetic dolomite in subtidal sediments of northern Kuwait bay, Kuwait. Ph. D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, 154 pp. Al-Shatri, M.A.; Nuhu, A.A.; Basheer, C.; Al-Arfaj, A. & Al-Tawabini, B. (2014). Determination of organotin compounds in coastal sediments by propylation and GC-MS analysis. Res. J. Pharmaceut., Biol. Chem. Sci., 5 (5): Al Turkeit, N.M.H. & El-Kandary, G. (2003). Final inspection report for territorial water. Ministry of Communication: Final report: Vols. I & II.
15 Assessment of organotin compounds in coastal sediments of Kuwait 144 Al-Yamani, F.Y.; Bishop, J.; Ramadhan, E.; Al-Husaini, M. & Al-Ghadban, A. (2004). Oceanographic atlas of Kuwait s water. KISR, Kuwait, 203 pp. David, F.; Sandra, P. & Wylie, P.L. (2003). Improving the analysis of organotin compounds using retention time locked methods and retention time database application. Agilent Technol., 10 pp. de Mora, S.J.; Fowler, S.W.; Cassi, R. & Tolosa, I. (2003). Assessment of organotin contamination in marine sediments and biota from the Gulf and adjacent region. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 46 (4): Hasan, M.A. & Juma, H.A. (1992). Assessment of tributyltin in the marine environment of Bahrain. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 24 (8): Kirli, L. (2005). Organotin pollution in the marine environment (review). G. U. J. Sci., 18 (3): Landmeyer, J.E.; Tanner, T.L. & Watt, B.E. (2004). Biotransformation of tributyltin to tin in freshwater river-bed sediments contaminated by an organotin release. Environ. Sci. Technol., 38 (15): Maguire, R.J. (2000). Review of the persistence, bioaccumulation and toxicity of tributyltin (TBT) in aquatic environments in relation to Canada s toxic substances management policy. Water Qual. Res. J. Can., 35 (4): Meador, J.P. (2000). Predicting the fate and effects of tributyltin in marine systems. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 166: Nyberg, E.; Poikane, R.; Strand, J.; Larsen, M.M.; Danielsson, S. & Bignert, A. (2013). Tributyltin (TBT) and imposex. HELCOM (Core Indicator Report), 17 pp. Okoro, H.K.; Fatoki, O.S.; Adekola, F.A.; Ximba, B.J. & Snyman, R.G. (2011). Sources, environmental levels and toxicity of organotin in marine environment- A review. Asian J. Chem., 23 (2): Qasim, A.M.H. & Ali, T.S. (Unpublished). Impact assessment of the sunken vessels in the northwest Arabian Gulf on the socioeconomic aspects of Iraqi fishermen. Mar. Sci., Cent., Univ. Basrah (in Arabic). Reynolds, R.M. (1993). Physical oceanography of the Gulf, Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman: Results from the Mt. Mitchell Expedition. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 27: Ritsema, R.; de Smaele, T.; Moens, L.; de Jong, A.S. & Donard, O.F.X. (1998). Determination of butyltins in harbour sediment and water by aqueous phase ethylation GC-ICP-MS and hydride generation GC- AAS. Environ. Pollut., 99 (2): ROPME (2011). ROPME Mussel watch programme, organotin compounds screening. Mission reported by MESL/IAEA. ROPME/GC- 15/3, Tech. Rep., 3: Kuwait: 26 pp.
16 145 Alkandari et al. Saad, M.A.H. (1978). Seasonal variations of some physiochemical conditions of Shatt Al-Arab estuary, Iraq. Est. Coast. Mar. Sci., 6 (5): UNEP (2003). Environment in Iraq: UNEP Progress Report, 44 pp. (Last visit 23 Aug. 2014). Valerie, J.B. (2005). Warfare: Iraq s toxic shipwrecks. Environ. Health Perspect., 113 (4): A230.
Environmental impact assessment study of the new offshore dumping sites for Šventoji port in Lithuania
 Environmental impact assessment study of the new offshore dumping sites for Šventoji port in Lithuania Introduction Summary In 2003 Lithuanian Ministry of Transport initiated the preparation of feasibility
Environmental impact assessment study of the new offshore dumping sites for Šventoji port in Lithuania Introduction Summary In 2003 Lithuanian Ministry of Transport initiated the preparation of feasibility
Beaches Carrying Capacity Assessment in Kuwait Based on Photointerpretation and Ground Survey
 Technical Session: TS 07B - GIS Applications (Number # 5463) Beaches Carrying Capacity Assessment in Kuwait Based on Photointerpretation and Ground Survey Prof. Mohamed AIT BELAID Shaikh Hamad Bin Khalifa
Technical Session: TS 07B - GIS Applications (Number # 5463) Beaches Carrying Capacity Assessment in Kuwait Based on Photointerpretation and Ground Survey Prof. Mohamed AIT BELAID Shaikh Hamad Bin Khalifa
SEDIMINTATION CHALLENGES IN UMM QASR PORT, IRAQ
 Paper No: P021 SEDIMINTATION CHALLENGES IN UMM QASR PORT, IRAQ by C. Jürgensen 1, A.A. Samir 2, S. Salim 3, J.B. Abild 4, M. Hassan 5, H.J. Vested 6, L. Dall 7 and N. Arndal 8 ABSTRACT The paper describes
Paper No: P021 SEDIMINTATION CHALLENGES IN UMM QASR PORT, IRAQ by C. Jürgensen 1, A.A. Samir 2, S. Salim 3, J.B. Abild 4, M. Hassan 5, H.J. Vested 6, L. Dall 7 and N. Arndal 8 ABSTRACT The paper describes
Butyltins in Sediments of the St. Lawrence River
 Butyltins in Sediments of the St. Lawrence River Background Butyltins are organometallic compounds that have been used as biocides in antifouling paints for ship hulls; as fungicides, insecticides and
Butyltins in Sediments of the St. Lawrence River Background Butyltins are organometallic compounds that have been used as biocides in antifouling paints for ship hulls; as fungicides, insecticides and
June 2018 Sediments and Dredging at GBR Ports
 June 2018 Sediments and Dredging at GBR Ports Reef 2050 Long Term Sustainability Plan The Great Barrier Reef is over 2000 km long and covers an area of approximately 350,000 square kilometres. It is a
June 2018 Sediments and Dredging at GBR Ports Reef 2050 Long Term Sustainability Plan The Great Barrier Reef is over 2000 km long and covers an area of approximately 350,000 square kilometres. It is a
Boil Model. Back Tracking of Oil Slick Movements in Offshore of Arabian Gulf Marine Waters. Developed By. Khaled Al-Salem April 2013
 Boil Model Back Tracking of Oil Slick Movements in Offshore of Arabian Gulf Marine Waters Developed By Khaled Al-Salem April 2013 COASTAL AND AIR POLLUTION DEPARTMENT KUWAIT INSTITUTE FOR SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
Boil Model Back Tracking of Oil Slick Movements in Offshore of Arabian Gulf Marine Waters Developed By Khaled Al-Salem April 2013 COASTAL AND AIR POLLUTION DEPARTMENT KUWAIT INSTITUTE FOR SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility
 Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
VOL. 3, NO. 4, April 2013 ISSN ARPN Journal of Science and Technology All rights reserved.
 Geomorphologic Study Of Umm Al Raşāş Island and Its Surrounding Channels, Shatt Al-Arab River, Southern Iraq 1 Usama.Q. Alwhaely, 2 Badir N. Albadran, 3 Saher T. Al-Mulla 1 Department of Marine Geology,
Geomorphologic Study Of Umm Al Raşāş Island and Its Surrounding Channels, Shatt Al-Arab River, Southern Iraq 1 Usama.Q. Alwhaely, 2 Badir N. Albadran, 3 Saher T. Al-Mulla 1 Department of Marine Geology,
WIND EFFECTS ON CHEMICAL SPILL IN ST ANDREW BAY SYSTEM
 WIND EFFECTS ON CHEMICAL SPILL IN ST ANDREW BAY SYSTEM PETER C. CHU, PATRICE PAULY Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA93943 STEVEN D. HAEGER Naval Oceanographic Office, Stennis Space Center MATHEW
WIND EFFECTS ON CHEMICAL SPILL IN ST ANDREW BAY SYSTEM PETER C. CHU, PATRICE PAULY Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA93943 STEVEN D. HAEGER Naval Oceanographic Office, Stennis Space Center MATHEW
Contamination by Butyltins in Sediment from Songkhla Old-Town Coast
 International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 101 (2017) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2017. V101. 7 Contamination by Butyltins in Sediment from Songkhla Old-Town Coast Sutisa
International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 101 (2017) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2017. V101. 7 Contamination by Butyltins in Sediment from Songkhla Old-Town Coast Sutisa
Relatively little hard substrate occurs naturally in the
 CHAPTER FIVE Rock Habitats Relatively little hard substrate occurs naturally in the estuary, owing mainly to the vast quantities of fine sediment that have been deposited by the rivers. Rock habitat is
CHAPTER FIVE Rock Habitats Relatively little hard substrate occurs naturally in the estuary, owing mainly to the vast quantities of fine sediment that have been deposited by the rivers. Rock habitat is
THREE-DIMENSIONAL HYDRO-ENVIRONMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION AND MODELING OF THE NORTHERN ARABIAN GULF
 THREE-DIMENSIONAL HYDRO-ENVIRONMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION AND MODELING OF THE NORTHERN ARABIAN GULF Tanuspong Pokavanich 1, Yousef Alosairi 1, Reimer de Graaff 2, Robin Morelissen 2, Wilbert Verbruggen 2,
THREE-DIMENSIONAL HYDRO-ENVIRONMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION AND MODELING OF THE NORTHERN ARABIAN GULF Tanuspong Pokavanich 1, Yousef Alosairi 1, Reimer de Graaff 2, Robin Morelissen 2, Wilbert Verbruggen 2,
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation
 Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
Ocean circulation, sedimentation in the San Juans - compilation of mainstream scientific literature by Dave Hyde -
 Ocean circulation, sedimentation in the San Juans - compilation of mainstream scientific literature by Dave Hyde - Salish Sea has 3 principal estuaries SG, JDF,PS San Juan Islands ocean setting uniquely
Ocean circulation, sedimentation in the San Juans - compilation of mainstream scientific literature by Dave Hyde - Salish Sea has 3 principal estuaries SG, JDF,PS San Juan Islands ocean setting uniquely
Salinity Gradients in the Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve. Kimberly Bittler GIS and Water Resources Fall 2011
 Salinity Gradients in the Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve Kimberly Bittler GIS and Water Resources Fall 2011 INTRODUCTION Freshwater inflow has a widely recognized influence on estuary
Salinity Gradients in the Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve Kimberly Bittler GIS and Water Resources Fall 2011 INTRODUCTION Freshwater inflow has a widely recognized influence on estuary
xxv PART I THE DIVIDED OCEANS: INTERNATIONAL LAW GOVERNING JURISDICTIONAL ZONES 1
 Contents Preface page xv List of Figures xvii List of Tables xviii List of Abbreviations xix Table of Cases xxi Table of Treaties and Instruments xxv PART I THE DIVIDED OCEANS: INTERNATIONAL LAW GOVERNING
Contents Preface page xv List of Figures xvii List of Tables xviii List of Abbreviations xix Table of Cases xxi Table of Treaties and Instruments xxv PART I THE DIVIDED OCEANS: INTERNATIONAL LAW GOVERNING
Tidal Constituents in the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea: a Numerical Study
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 45(8), August 2016, pp. 1010-1016 Tidal Constituents in the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea: a Numerical Study P. Akbari 1 *, M. Sadrinasab 2, V. Chegini
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 45(8), August 2016, pp. 1010-1016 Tidal Constituents in the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea: a Numerical Study P. Akbari 1 *, M. Sadrinasab 2, V. Chegini
REVIEW OF ALTERNATE BALLAST WATER EXCHANGE ZONES FOR VESSEL TRAFFIC TO NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR AND THE CANADIAN ARCTIC
 Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Science Advisory Report 2010/026 REVIEW OF ALTERNATE BALLAST WATER EXCHANGE ZONES FOR VESSEL TRAFFIC TO NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR AND THE CANADIAN ARCTIC Figure 1:
Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Science Advisory Report 2010/026 REVIEW OF ALTERNATE BALLAST WATER EXCHANGE ZONES FOR VESSEL TRAFFIC TO NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR AND THE CANADIAN ARCTIC Figure 1:
Sedimentation in the Nile River
 Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Sedimentation in the Nile River Prof. Dr. Abdalla Abdelsalam Ahmed 10-16 Oct. 2007, IRTCES, Beijing, China CWR,Sudan 1 Water is essential for mankind
Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Sedimentation in the Nile River Prof. Dr. Abdalla Abdelsalam Ahmed 10-16 Oct. 2007, IRTCES, Beijing, China CWR,Sudan 1 Water is essential for mankind
Tide and Sea Level Characteristics at Juaymah, West Coast of the Arabian Gulf
 JKAU: Mar. Sci., Vol. 21, No. 1, pp: 133-149 (2010 A. D. / 1431 A. H.) DOI: 10. 4197/Mar. 21-1.8 Tide and Sea Level Characteristics at Juaymah, West Coast of the Arabian Gulf Faculty of Marine Science
JKAU: Mar. Sci., Vol. 21, No. 1, pp: 133-149 (2010 A. D. / 1431 A. H.) DOI: 10. 4197/Mar. 21-1.8 Tide and Sea Level Characteristics at Juaymah, West Coast of the Arabian Gulf Faculty of Marine Science
PCB Aroclor Concentrations in Puget Sound Sediments
 PCB Aroclor Concentrations in Puget Sound Sediments Margaret Dutch, Sandra Aasen and Edward R. Long Washington State Department of Ecology Environmental Assessment Program [Editor s note: Tables and Figures
PCB Aroclor Concentrations in Puget Sound Sediments Margaret Dutch, Sandra Aasen and Edward R. Long Washington State Department of Ecology Environmental Assessment Program [Editor s note: Tables and Figures
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN RIVER MOUTH ESTUARY
 SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN RIVER MOUTH ESTUARY Katsuhide YOKOYAMA, Dr.Eng. dredge Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering Tokyo Metropolitan University 1-1 Minami-Osawa Osawa, Hachioji,, Tokyo,
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN RIVER MOUTH ESTUARY Katsuhide YOKOYAMA, Dr.Eng. dredge Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering Tokyo Metropolitan University 1-1 Minami-Osawa Osawa, Hachioji,, Tokyo,
GNOME Oil Spill Modeling Lab
 GNOME Oil Spill Modeling Lab Name: Goal: After simulating an actual oil spill event, you will understand how oceanographers help to protect marine resources from pollution such as oil spills. You will
GNOME Oil Spill Modeling Lab Name: Goal: After simulating an actual oil spill event, you will understand how oceanographers help to protect marine resources from pollution such as oil spills. You will
Environmental Implications A Case Study
 Grain Size Variations and Its Environmental Implications A Case Study DR PURANDARA BEKAL SCIENTIST, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY HARD ROCK REGIONAL CENTER HANUMAN NAGAR BELGAUM, KARNATAKA Particle Transport
Grain Size Variations and Its Environmental Implications A Case Study DR PURANDARA BEKAL SCIENTIST, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY HARD ROCK REGIONAL CENTER HANUMAN NAGAR BELGAUM, KARNATAKA Particle Transport
Polar complications in the law of the sea: A case study of the regime for research and survey activities in the Arctic Ocean
 2010 ABLOS Conference: Contentious Issues in UNCLOS Surely Not? International Hydrographic Bureau, 25-27 October 2010 Polar complications in the law of the sea: A case study of the regime for research
2010 ABLOS Conference: Contentious Issues in UNCLOS Surely Not? International Hydrographic Bureau, 25-27 October 2010 Polar complications in the law of the sea: A case study of the regime for research
Assessment of Sediment Quality South of Ras Al-Ardh and Northern Territorial Waters, Kuwait, Northern Arabian Gulf
 Journal of Coastal Research SI 39 44-445 ICS 24 (Proceedings) Brazil ISSN 749-28 Assessment of Sediment Quality South of Ras Al-Ardh and Northern Territorial Waters, Kuwait, Northern Arabian Gulf A.A.
Journal of Coastal Research SI 39 44-445 ICS 24 (Proceedings) Brazil ISSN 749-28 Assessment of Sediment Quality South of Ras Al-Ardh and Northern Territorial Waters, Kuwait, Northern Arabian Gulf A.A.
Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation
 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation Naser Ebadati
2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation Naser Ebadati
Modeling the Transport and Fate of Sediments Released from Dredging Projects in the Coastal Waters of British Columbia, Canada
 WEDA Dredging Summit & Expo 18 Modeling the Transport and Fate of Sediments Released from Dredging Projects in the Coastal Waters of British Columbia, Canada David B. Fissel, Yuehua (Andy) Lin and Todd
WEDA Dredging Summit & Expo 18 Modeling the Transport and Fate of Sediments Released from Dredging Projects in the Coastal Waters of British Columbia, Canada David B. Fissel, Yuehua (Andy) Lin and Todd
Determination of 17 Organotin Compounds in Beverages Using Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS System
 Determination of 17 Organotin Compounds in Beverages Using Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS System Application Note Authors Wenwen Wang, Zhe Cao Agilent Technologies, Inc. No.3, Wang Jing Bei Lu, Chao Yang District,
Determination of 17 Organotin Compounds in Beverages Using Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS System Application Note Authors Wenwen Wang, Zhe Cao Agilent Technologies, Inc. No.3, Wang Jing Bei Lu, Chao Yang District,
Influence of the Major Drainages to the Mississippi River and Implications for System Level Management
 Influence of the Major Drainages to the Mississippi River and Implications for System Level Management Brian M. Vosburg Geologist Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority brian.vosburg@la.gov
Influence of the Major Drainages to the Mississippi River and Implications for System Level Management Brian M. Vosburg Geologist Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority brian.vosburg@la.gov
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port
 Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
Organisms in the Ocean
 Oceans Objective 8.E.1.2 Summarize evidence that Earth's oceans are a reservoir of nutrients, minerals, dissolved gases, and life forms: estuaries, marine ecosystems, upwelling, and behavior of gases in
Oceans Objective 8.E.1.2 Summarize evidence that Earth's oceans are a reservoir of nutrients, minerals, dissolved gases, and life forms: estuaries, marine ecosystems, upwelling, and behavior of gases in
DISTRIBUTION OF VANADIUM IN BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM THE MARINE COASTAL AREA OF THE EGYPTIAN SEAS
 EGYPTIAN JOURNAL OF AQUATIC RESEARCH 1687-4285 VOL. 32 NO. 1, 2006: 12-21 DISTRIBUTION OF VANADIUM IN BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM THE MARINE COASTAL AREA OF THE EGYPTIAN SEAS KH. M. EL-MOSELHY National Institute
EGYPTIAN JOURNAL OF AQUATIC RESEARCH 1687-4285 VOL. 32 NO. 1, 2006: 12-21 DISTRIBUTION OF VANADIUM IN BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM THE MARINE COASTAL AREA OF THE EGYPTIAN SEAS KH. M. EL-MOSELHY National Institute
A Study on Residual Flow in the Gulf of Tongking
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 59 to 68. 2000 A Study on Residual Flow in the Gulf of Tongking DINH-VAN MANH 1 and TETSUO YANAGI 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ehime University,
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 59 to 68. 2000 A Study on Residual Flow in the Gulf of Tongking DINH-VAN MANH 1 and TETSUO YANAGI 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ehime University,
Aquaculture Spatial Planning: The case of Greece
 Aquaculture Spatial Planning: The case of Greece Nikos Anagnopoulos Panhellenic Association for Small-Medium sized Aquaculture Enterprises Panhellenic Association for Small-Medium sized Aquaculture Enterprises
Aquaculture Spatial Planning: The case of Greece Nikos Anagnopoulos Panhellenic Association for Small-Medium sized Aquaculture Enterprises Panhellenic Association for Small-Medium sized Aquaculture Enterprises
Coastal Oceanography. Coastal Oceanography. Coastal Waters
 Coastal Oceanography Coastal Oceanography 95% of ocean life is in coastal waters (320 km from shore) Estuaries and wetlands are among most productive ecosystems on Earth Major shipping routes, oil and
Coastal Oceanography Coastal Oceanography 95% of ocean life is in coastal waters (320 km from shore) Estuaries and wetlands are among most productive ecosystems on Earth Major shipping routes, oil and
Dynamics of the Ems Estuary
 Dynamics of the Ems Estuary Physics of coastal systems Jerker Menninga 0439738 Utrecht University Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht Lecturer: Prof. dr. H.E. de Swart Abstract During
Dynamics of the Ems Estuary Physics of coastal systems Jerker Menninga 0439738 Utrecht University Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht Lecturer: Prof. dr. H.E. de Swart Abstract During
HIGH RESOLUTION SEDIMENT DYNAMICS IN SALT-WEDGE ESTUARIES
 HIGH RESOLUTION SEDIMENT DYNAMICS IN SALT-WEDGE ESTUARIES Philip Orton, Dept. of Environmental Science and Engineering, Oregon Graduate Institute Douglas Wilson, Dept. of Environmental Science and Engineering,
HIGH RESOLUTION SEDIMENT DYNAMICS IN SALT-WEDGE ESTUARIES Philip Orton, Dept. of Environmental Science and Engineering, Oregon Graduate Institute Douglas Wilson, Dept. of Environmental Science and Engineering,
THERMOHALINE OCEAN CIRCULATION IN MAKRAN COASTS-IRAN by
 THERMOHALINE OCEAN CIRCULATION IN MAKRAN COASTS-IRAN by Mohammad Bagheri 1, M. Reza Allahyar 1, Mehdi Shafieefar 2, M. Hosein Nemati 1, Ali Ghasemi 2, Ahmad Rezaei 2 ABSTRACT Ocean currents are generated
THERMOHALINE OCEAN CIRCULATION IN MAKRAN COASTS-IRAN by Mohammad Bagheri 1, M. Reza Allahyar 1, Mehdi Shafieefar 2, M. Hosein Nemati 1, Ali Ghasemi 2, Ahmad Rezaei 2 ABSTRACT Ocean currents are generated
Long-term Change of Ocean Productivity: A case study in the Bay of Bengal
 Long-term Change of Ocean Productivity: A case study in the Bay of Bengal The 3 rd Asian /12 th Korean-Japan Workshop on Ocean Color Dr.Md.Latifur Rahman Sarker, UTM, Malaysia & RU, Bangladesh & Noor Saadah
Long-term Change of Ocean Productivity: A case study in the Bay of Bengal The 3 rd Asian /12 th Korean-Japan Workshop on Ocean Color Dr.Md.Latifur Rahman Sarker, UTM, Malaysia & RU, Bangladesh & Noor Saadah
FAO DESERT LOCUST BULLETIN No. 139 GENERAL SITUATION DURING MARCH 1990 FORECAST UNTIL MID MAY 1990
 1 FAO DESERT LOCUST BULLETIN No. 139 GENERAL SITUATION DURING MARCH 1990 FORECAST UNTIL MID MAY 1990 The current recession continues with very few reports of Desert Locusts received during March and no
1 FAO DESERT LOCUST BULLETIN No. 139 GENERAL SITUATION DURING MARCH 1990 FORECAST UNTIL MID MAY 1990 The current recession continues with very few reports of Desert Locusts received during March and no
Name Period Part I: INVESTIGATING OCEAN CURRENTS: PLOTTING BUOY DATA
 Name Period Part I: INVESTIGATING OCEAN CURRENTS: PLOTTING BUOY DATA INTRODUCTION: Ocean currents are like huge rivers in the sea. They carry drifting organisms, vital dissolved chemical nutrients and
Name Period Part I: INVESTIGATING OCEAN CURRENTS: PLOTTING BUOY DATA INTRODUCTION: Ocean currents are like huge rivers in the sea. They carry drifting organisms, vital dissolved chemical nutrients and
FINMARINET: Inventories and Planning for the Marine Natura 2000 Network in Finland. A.2 Geological inventories of the seafloor Final Report
 LIFE07 NAT/FIN/000151 FINMARINET: Inventories and Planning for the Marine Natura 2000 Network in Finland A.2 Geological inventories of the seafloor Final Report Geological Survey of Finland, GTK 1. Introduction
LIFE07 NAT/FIN/000151 FINMARINET: Inventories and Planning for the Marine Natura 2000 Network in Finland A.2 Geological inventories of the seafloor Final Report Geological Survey of Finland, GTK 1. Introduction
SPATIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SURFACE CIRCULATION AND WAVE CLIMATE USING HIGH-FREQUENCY RADAR
 SPATIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SURFACE CIRCULATION AND WAVE CLIMATE USING HIGH-FREQUENCY RADAR Apisit Kongprom,Siriluk Prukpitikul, Varatip Buakaew, Watchara Kesdech, and Teerawat Suwanlertcharoen Geo-Informatics
SPATIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SURFACE CIRCULATION AND WAVE CLIMATE USING HIGH-FREQUENCY RADAR Apisit Kongprom,Siriluk Prukpitikul, Varatip Buakaew, Watchara Kesdech, and Teerawat Suwanlertcharoen Geo-Informatics
Egypt-NOAA Cooperation: Advancing our Environmental Science, Technology, and Education
 Egypt-NOAA Cooperation: Advancing our Environmental Science, Technology, and Education T. G. Onsager NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center and NWS International Activities Office (one-year detail) Terry.Onsager@noaa.gov
Egypt-NOAA Cooperation: Advancing our Environmental Science, Technology, and Education T. G. Onsager NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center and NWS International Activities Office (one-year detail) Terry.Onsager@noaa.gov
Inter State Large Navigable Rivers of the United States
 Inter State Large Navigable Rivers of the United States REVIEW OF NORTH AMERICAN BASINS: GREAT LAKES AND MISSISSIPPI RIVER HELEN A. BROHL, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR US COMMITTEE ON THE MARINE TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM
Inter State Large Navigable Rivers of the United States REVIEW OF NORTH AMERICAN BASINS: GREAT LAKES AND MISSISSIPPI RIVER HELEN A. BROHL, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR US COMMITTEE ON THE MARINE TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM
Effects of possible land reclamation projects on siltation in the Rotterdam harbour area. A model study.
 Effects of possible land reclamation projects on siltation in the Rotterdam harbour area. A model study. J.M. de Kok
Effects of possible land reclamation projects on siltation in the Rotterdam harbour area. A model study. J.M. de Kok
CHAPTER 126 ^^^C^SR, SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA
 CHAPTER 126 SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA Ramiro Mayor-Mora, D. Eng. (1) Preben Mortensen, M.Sc. (2) Jorgen Fredsoe, M.Sc. (2) 1. Introduction An area of the Niger River Delta was studied
CHAPTER 126 SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA Ramiro Mayor-Mora, D. Eng. (1) Preben Mortensen, M.Sc. (2) Jorgen Fredsoe, M.Sc. (2) 1. Introduction An area of the Niger River Delta was studied
EUSAIR on sea topics from Slovenian perspective
 MINISTRY OF FOREIGN AFFAIRS REPUBLIC OF SLOVENIA EUSAIR on sea topics from Slovenian perspective Mag. Andreja Jerina National Coordinator 4 EU MRS: 270 millions of population 19 MS 12 non MS Sea basin
MINISTRY OF FOREIGN AFFAIRS REPUBLIC OF SLOVENIA EUSAIR on sea topics from Slovenian perspective Mag. Andreja Jerina National Coordinator 4 EU MRS: 270 millions of population 19 MS 12 non MS Sea basin
Significant Ecological Marine Area Assessment Sheet
 Significant Ecological arine Area Assessment Sheet Name: Eastern Bay of Island Biogenic Soft Sediment Complex Summary: The semi-sheltered areas between the central islands of the Eastern Bay of Islands
Significant Ecological arine Area Assessment Sheet Name: Eastern Bay of Island Biogenic Soft Sediment Complex Summary: The semi-sheltered areas between the central islands of the Eastern Bay of Islands
Ocean Governance and the Japanese Basic Act on Ocean Policy
 Ocean Governance and the Japanese Basic Act on Ocean Policy Hiroshi Terashima Executive Director Ocean Policy Research Foundation 14 April 2009 The United Nations Nippon Foundation Fellowship Programme
Ocean Governance and the Japanese Basic Act on Ocean Policy Hiroshi Terashima Executive Director Ocean Policy Research Foundation 14 April 2009 The United Nations Nippon Foundation Fellowship Programme
CANADIAN HYDROGRAPHIC SERVICE & OCEANOGRAPHIC SERVICES
 CANADIAN HYDROGRAPHIC SERVICE & OCEANOGRAPHIC SERVICES Presentation to Warming of the North Conference Ottawa, March 2 nd, 2015 Denis Hains, Director General & Hydrographer General of Canada TIP OF THE
CANADIAN HYDROGRAPHIC SERVICE & OCEANOGRAPHIC SERVICES Presentation to Warming of the North Conference Ottawa, March 2 nd, 2015 Denis Hains, Director General & Hydrographer General of Canada TIP OF THE
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST
 ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
Country reports. Israel did not establish an Exclusive Economic Zone. Consequently, its jurisdiction is restricted to the Israeli territorial waters.
 Country reports I. ISRAEL Disclaimer This document has not been adopted by the European Commission and should therefore not be relied upon as a statement of the European Commission. The purpose of this
Country reports I. ISRAEL Disclaimer This document has not been adopted by the European Commission and should therefore not be relied upon as a statement of the European Commission. The purpose of this
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ISTHMU S tombolo For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ISTHMU S tombolo For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
APPENDIX O. Sediment Modeling of Dredging off Lelu Island, Prince Rupert, BC Canada, and Disposal of Dredgate at Brown Passage
 APPENDIX O Sediment Modeling of Dredging off Lelu Island, Prince Rupert, BC Canada, and Disposal of Dredgate at Brown Passage Sediment Modeling of Dredging off Lelu Island, Prince Rupert, BC Canada, and
APPENDIX O Sediment Modeling of Dredging off Lelu Island, Prince Rupert, BC Canada, and Disposal of Dredgate at Brown Passage Sediment Modeling of Dredging off Lelu Island, Prince Rupert, BC Canada, and
Beaches Carrying Capacity Assessment in Kuwait Based on Photointerpretation and Ground Survey
 Beaches Carrying Capacity Assessment in Kuwait Based on Photointerpretation and Ground Survey Adel ALDOUKHI, Kuwait, Mohamed AIT BELAID*, Bahrain and Lulwa ALI, Kuwait Key Words: Carrying Capacity, Beach,
Beaches Carrying Capacity Assessment in Kuwait Based on Photointerpretation and Ground Survey Adel ALDOUKHI, Kuwait, Mohamed AIT BELAID*, Bahrain and Lulwa ALI, Kuwait Key Words: Carrying Capacity, Beach,
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT AND GO-CONG MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGE MODELING BY TELEMAC MODEL SUITE
 SEDIMENT TRANSPORT AND GO-CONG MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGE MODELING BY TELEMAC MODEL SUITE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. OBJECTIVES... 2 3. METHOLOGY... 2 4. MODEL CALIBRATION, VALIDATION OF SEDIMENT
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT AND GO-CONG MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGE MODELING BY TELEMAC MODEL SUITE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. OBJECTIVES... 2 3. METHOLOGY... 2 4. MODEL CALIBRATION, VALIDATION OF SEDIMENT
Developing Coastal Ocean Forecasting Systems and Their Applications
 Developing Coastal Ocean Forecasting Systems and Their Applications Xiaochun Wang a,b LASG/IAP, CAS, July 23, 2010 Contributions from: JPL Yi Chao, John Farrara, Peggy Li, Zhijin Li, Quoc Vu, Hongchun
Developing Coastal Ocean Forecasting Systems and Their Applications Xiaochun Wang a,b LASG/IAP, CAS, July 23, 2010 Contributions from: JPL Yi Chao, John Farrara, Peggy Li, Zhijin Li, Quoc Vu, Hongchun
HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission
 HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission HELCOM RECOMMENDATION 24/10 Adopted 25 June 2003, having regard to Article 20, Paragraph 1 b) of the 1992 Helsinki Convention IMPLEMENTATION
HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission HELCOM RECOMMENDATION 24/10 Adopted 25 June 2003, having regard to Article 20, Paragraph 1 b) of the 1992 Helsinki Convention IMPLEMENTATION
Annual transport rates at two locations on the fore-slope.
 Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Physical Processes: What have we learned about Florida Bay in the past five years, and how is that useful to CERP planning and SFER management?
 Physical Processes: What have we learned about Florida Bay in the past five years, and how is that useful to CERP planning and SFER management? Peter B. Ortner, UM/RSMAS/CIMAS Modeling Progress Statistical
Physical Processes: What have we learned about Florida Bay in the past five years, and how is that useful to CERP planning and SFER management? Peter B. Ortner, UM/RSMAS/CIMAS Modeling Progress Statistical
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
NOAA S Arctic Program in 2017
 NOAA S Arctic Program in 2017 NOAA s Arctic Mission To determine how the Arctic system is changing on time scales of weeks to decades, particularly with respect to the consequences that the loss of sea
NOAA S Arctic Program in 2017 NOAA s Arctic Mission To determine how the Arctic system is changing on time scales of weeks to decades, particularly with respect to the consequences that the loss of sea
NOAA Nautical Charts and Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning. Meredith Westington Chief Geographer NOAA/NOS/Office of Coast Survey
 NOAA Nautical Charts and Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning Meredith Westington Chief Geographer NOAA/NOS/Office of Coast Survey Ocean Policy Task Force What is CMSP? A comprehensive, adaptive, integrated,
NOAA Nautical Charts and Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning Meredith Westington Chief Geographer NOAA/NOS/Office of Coast Survey Ocean Policy Task Force What is CMSP? A comprehensive, adaptive, integrated,
Item #9: Amphipod Tox Proposal Modification Page 1 of 9
 Item #9: Amphipod Tox Proposal Modification Page 1 of 9 The effects of particle size and shape and animal health on toxicity test results using the amphipod Eohaustorius estuarius. Estimated Cost: $30,000
Item #9: Amphipod Tox Proposal Modification Page 1 of 9 The effects of particle size and shape and animal health on toxicity test results using the amphipod Eohaustorius estuarius. Estimated Cost: $30,000
Indonesian seas Numerical Assessment of the Coastal Environment (IndoNACE) Executive Summary
 Indonesian seas Numerical Assessment of the Coastal Environment (IndoNACE) Executive Summary Study team members: Dr. Martin Gade, PD Dr. Thomas Pohlmann, Dr. Mutiara Putri Research Centres: Universität
Indonesian seas Numerical Assessment of the Coastal Environment (IndoNACE) Executive Summary Study team members: Dr. Martin Gade, PD Dr. Thomas Pohlmann, Dr. Mutiara Putri Research Centres: Universität
SUBJECT INDEX. ~ ~5 physico-chemical properties 254,255 Redox potential 254,255
 Aggregates: beds formed by deposition 81,82 breakup by fluid shear, introduction 85,86 deposition from flowing water 80 implications in cohesive sediment transport 102-105 needs for further research 83
Aggregates: beds formed by deposition 81,82 breakup by fluid shear, introduction 85,86 deposition from flowing water 80 implications in cohesive sediment transport 102-105 needs for further research 83
Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science
 S 93104R Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 1 December 2015 RESOURCE BOOKLET Refer to this booklet to answer the questions for Scholarship Earth and Space Science 93104. Check that
S 93104R Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 1 December 2015 RESOURCE BOOKLET Refer to this booklet to answer the questions for Scholarship Earth and Space Science 93104. Check that
Marine Spatial Planning: A Tool for Implementing Ecosystem-Based Management
 Marine Spatial Planning: A Tool for Implementing Ecosystem-Based Management Steven Murawski, Ph.D., Ecosystem Goal Team Lead National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration NOAA November 16, 2009 1 To
Marine Spatial Planning: A Tool for Implementing Ecosystem-Based Management Steven Murawski, Ph.D., Ecosystem Goal Team Lead National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration NOAA November 16, 2009 1 To
3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL FLAT MORPHOLOGY
 Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound
 8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
Precipitation processes in the Middle East
 Precipitation processes in the Middle East J. Evans a, R. Smith a and R.Oglesby b a Dept. Geology & Geophysics, Yale University, Connecticut, USA. b Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA, Alabama,
Precipitation processes in the Middle East J. Evans a, R. Smith a and R.Oglesby b a Dept. Geology & Geophysics, Yale University, Connecticut, USA. b Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA, Alabama,
SW Florida Escarpment Mapping Area
 Overview NOAA s Okeanos Explorer (EX) Program plans to conduct systematic mapping and telepresence-enabled ROV explorations in the Gulf of Mexico during Spring 2014. In 2011, the EX conducted mapping operations
Overview NOAA s Okeanos Explorer (EX) Program plans to conduct systematic mapping and telepresence-enabled ROV explorations in the Gulf of Mexico during Spring 2014. In 2011, the EX conducted mapping operations
BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
 Studies to support the development of sea basin cooperation in the Mediterranean, Adriatic and Ionian, and Black Sea CONTRACT NUMBER MARE/2012/07 - REF. NO 2 REPORT 1 - ANNEX 2.2 COUNTRY FICHE - ANNEX
Studies to support the development of sea basin cooperation in the Mediterranean, Adriatic and Ionian, and Black Sea CONTRACT NUMBER MARE/2012/07 - REF. NO 2 REPORT 1 - ANNEX 2.2 COUNTRY FICHE - ANNEX
HYDROPEDOLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT: CASE STUDY OF AL-KHOUD RECHARGE DAM- OMAN
 HYDROPEDOLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT: CASE STUDY OF AL-KHOUD RECHARGE DAM- OMAN Dr. Ali Al-Maktoumi Sultan Qaboos University, Oman Gulf Water Conference 11 th 20-22 October 2014 Co-authors: Al-Saqri,
HYDROPEDOLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT: CASE STUDY OF AL-KHOUD RECHARGE DAM- OMAN Dr. Ali Al-Maktoumi Sultan Qaboos University, Oman Gulf Water Conference 11 th 20-22 October 2014 Co-authors: Al-Saqri,
Optimal Design of Sediment Diversions for Delta Restoration: lessons learned from examples
 Optimal Design of Sediment Diversions for Delta Restoration: lessons learned from examples Samuel Bentley 1, Angelina Freeman 2, Clinton S. Willson 1, Liviu Giosan 3, Jaye Cable 4 1 LSU 2 EDF 3 WHOI 4
Optimal Design of Sediment Diversions for Delta Restoration: lessons learned from examples Samuel Bentley 1, Angelina Freeman 2, Clinton S. Willson 1, Liviu Giosan 3, Jaye Cable 4 1 LSU 2 EDF 3 WHOI 4
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION AND WIND
 ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION AND WIND The source of water for precipitation is the moisture laden air masses that circulate through the atmosphere. Atmospheric circulation is affected by the location on the
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION AND WIND The source of water for precipitation is the moisture laden air masses that circulate through the atmosphere. Atmospheric circulation is affected by the location on the
Sediment Traps. CAG Meeting May 21, 2012
 Sediment Traps CAG Meeting May 21, 2012 Agenda Background Fundamentals of Sediment Transport Sediment Trap Existing Information Next Steps 2 The Site Saginaw River 22 mile river beginning at confluence
Sediment Traps CAG Meeting May 21, 2012 Agenda Background Fundamentals of Sediment Transport Sediment Trap Existing Information Next Steps 2 The Site Saginaw River 22 mile river beginning at confluence
The Indian Ocean. Copyright 2010 LessonSnips
 The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
Journal of Asian Scientific Research STUDYING OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN MARSH AREA USING LANDSAT SATELLITE IMAGES
 Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 STUDYING OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN MARSH AREA USING LANDSAT SATELLITE IMAGES Salah A. H. Saleh
Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 STUDYING OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES IN MARSH AREA USING LANDSAT SATELLITE IMAGES Salah A. H. Saleh
Assessment of the Hood River Delta Hood River, Oregon
 Assessment of the Hood River Delta Hood River, Oregon Pacific Northwest Waterways Association Annual Meeting October 13, 2010 Michael McElwee, Executive Director Port of Hood River Overview U.S. Army Corps
Assessment of the Hood River Delta Hood River, Oregon Pacific Northwest Waterways Association Annual Meeting October 13, 2010 Michael McElwee, Executive Director Port of Hood River Overview U.S. Army Corps
Intertidal sedimentology along Ambalappuzha coast, Kerala
 116 J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India, 53 (1) : 116-120, January K. S. - Anila June Kumary 2011 and K. R. Rajimole Intertidal sedimentology along Ambalappuzha coast, Kerala *K. S. Anila Kumary and K. R. Rajimole
116 J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India, 53 (1) : 116-120, January K. S. - Anila June Kumary 2011 and K. R. Rajimole Intertidal sedimentology along Ambalappuzha coast, Kerala *K. S. Anila Kumary and K. R. Rajimole
PTM: A Lagrangian Particle Tracking Model. Joseph Gailani
 PTM: A Lagrangian Particle Tracking Model Joseph Gailani Joe.Z.Gailani@usace.army.mil OUTLINE Motivation for sediment/constituent modeling system Objectives of modeling system Description of PTM PTM Example
PTM: A Lagrangian Particle Tracking Model Joseph Gailani Joe.Z.Gailani@usace.army.mil OUTLINE Motivation for sediment/constituent modeling system Objectives of modeling system Description of PTM PTM Example
Marine Spatial Data for Marine Spatial Planning. Ocean Leadership 2010 Public Policy Forum
 Marine Spatial Data for Marine Spatial Planning Ocean Leadership 2010 Public Policy Forum March 10, 2010 Edward Saade President, Fugro EarthData, Inc 1 Marine Spatial Data What is Marine Spatial Data?
Marine Spatial Data for Marine Spatial Planning Ocean Leadership 2010 Public Policy Forum March 10, 2010 Edward Saade President, Fugro EarthData, Inc 1 Marine Spatial Data What is Marine Spatial Data?
Maritime Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region
 Maritime Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region Talis Linkaits Head of VASAB Secretariat 20 May 2015 Helsinki A cooperation of ministers of the 11 Baltic Sea Region countries responsible for spatial
Maritime Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region Talis Linkaits Head of VASAB Secretariat 20 May 2015 Helsinki A cooperation of ministers of the 11 Baltic Sea Region countries responsible for spatial
Canadian Ice Service
 Canadian Ice Service Key Points and Details concerning the 2009 Arctic Minimum Summer Sea Ice Extent October 1 st, 2009 http://ice-glaces.ec.gc.ca 1 Key Points of Interest Arctic-wide The Arctic-wide minimum
Canadian Ice Service Key Points and Details concerning the 2009 Arctic Minimum Summer Sea Ice Extent October 1 st, 2009 http://ice-glaces.ec.gc.ca 1 Key Points of Interest Arctic-wide The Arctic-wide minimum
Sediment management in the Danube River Basin. Igor Liška ICPDR
 Sediment management in the Danube River Basin Igor Liška ICPDR Danube River Protection Convention 29 June 1994, Sofia (Bulgaria) Protection of water & ecological resources Sustainable use of water Reduce
Sediment management in the Danube River Basin Igor Liška ICPDR Danube River Protection Convention 29 June 1994, Sofia (Bulgaria) Protection of water & ecological resources Sustainable use of water Reduce
3-D Comprehensive Hydrodynamic Modelling in the Arabian Gulf
 Author(s): Zhong Peng and Jill Bradon Source: Journal of Coastal Research, 75(sp1):547-551. Published By: Coastal Education and Research Foundation https://doi.org/10.2112/si75-110.1 URL: http://www.bioone.org/doi/full/10.2112/si75-110.1
Author(s): Zhong Peng and Jill Bradon Source: Journal of Coastal Research, 75(sp1):547-551. Published By: Coastal Education and Research Foundation https://doi.org/10.2112/si75-110.1 URL: http://www.bioone.org/doi/full/10.2112/si75-110.1
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6
 Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Intertidal shellfish monitoring in the northern North Island region,
 Intertidal shellfish monitoring in the northern North Island region, 2014 15 New Zealand Fisheries Assessment Report 2015/59 K. Berkenbusch P. Neubauer ISSN 1179-6480 (online) ISBN 978-1-77665-063-7 (online)
Intertidal shellfish monitoring in the northern North Island region, 2014 15 New Zealand Fisheries Assessment Report 2015/59 K. Berkenbusch P. Neubauer ISSN 1179-6480 (online) ISBN 978-1-77665-063-7 (online)
Curriculum Vitae. 1. Personal Data: 2. Academic Qualification:
 Curriculum Vitae 1. Personal Data: 1.1. Full Name: Badir Naama Akash Albadran 1.2. Date of Birth: 1 / 7 / 1957. 1.3. Country: Iraq. 1.4. Nationality: Iraqi. 1.5. Sex: Male. 1.6. Present Address: Al-Kharbatlya,
Curriculum Vitae 1. Personal Data: 1.1. Full Name: Badir Naama Akash Albadran 1.2. Date of Birth: 1 / 7 / 1957. 1.3. Country: Iraq. 1.4. Nationality: Iraqi. 1.5. Sex: Male. 1.6. Present Address: Al-Kharbatlya,
Evaluating the results of Hormuz strait wave simulations using WAVEWATCH-III and MIKE21-SW
 Int. J. Mar. Sci. Eng., 2 (2), 163-170, Spring 2012 ISSN 2251-6743 IAU Evaluating the results of Hormuz strait wave simulations using WAVEWATCH-III and MIKE21-SW *F. S. Sharifi; M. Ezam; A. Karami Khaniki
Int. J. Mar. Sci. Eng., 2 (2), 163-170, Spring 2012 ISSN 2251-6743 IAU Evaluating the results of Hormuz strait wave simulations using WAVEWATCH-III and MIKE21-SW *F. S. Sharifi; M. Ezam; A. Karami Khaniki
Sediments: a source of chemicals for the marine environment, in more than one way. Jos van Gils 1, Remi Laane 1, Kees van de Ven 2
 Sediments: a source of chemicals for the marine environment, in more than one way Jos van Gils 1, Remi Laane 1, Kees van de Ven 2 1 DELTARES, The Netherlands 2 RIJKSWATERSTAAT Water Service, The Netherlands
Sediments: a source of chemicals for the marine environment, in more than one way Jos van Gils 1, Remi Laane 1, Kees van de Ven 2 1 DELTARES, The Netherlands 2 RIJKSWATERSTAAT Water Service, The Netherlands
Estimation of Bed Load Transport in River Omi, South Western Nigeria using Grain Size Distribution Data
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 2 No. 9, September, 2012 Estimation of Bed Load Transport in River Omi, South Western Nigeria using Grain Size Distribution Data A.A. Adegbola
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 2 No. 9, September, 2012 Estimation of Bed Load Transport in River Omi, South Western Nigeria using Grain Size Distribution Data A.A. Adegbola
Shallow Water Dynamics in the Arabian Gulf and Gulf of Oman
 Shallow Water Dynamics in the Arabian Gulf and Gulf of Oman Dr. Cheryl Ann Blain Naval Research Laboratory, Ocean Dynamics and Prediction Branch Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 phone: (228) 688-5450; fax:
Shallow Water Dynamics in the Arabian Gulf and Gulf of Oman Dr. Cheryl Ann Blain Naval Research Laboratory, Ocean Dynamics and Prediction Branch Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 phone: (228) 688-5450; fax:
A WEATHER SUMMARY FOR THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST, JULY 6 - SEPTEMBER 6, 1990
 CHAPTER 5 A WEATHER SUMMARY FOR THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST, JULY 6 - SEPTEMBER 6, 1990 5.1 THE CLIMATE Puget Sound and the Straits of Georgia together comprise a 200 mile deep-water fjord connected at right
CHAPTER 5 A WEATHER SUMMARY FOR THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST, JULY 6 - SEPTEMBER 6, 1990 5.1 THE CLIMATE Puget Sound and the Straits of Georgia together comprise a 200 mile deep-water fjord connected at right
SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL MEETING JUNE B. Petrie, R. G. Pettipas, W. M. Petrie and V. V. Soukhovtsev
 NOT TO BE CITED WITHOUT PRIOR REFERENCE TO THE AUTHOR(S) Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization Serial No. N5361 NAFO SCR Doc. 07/14 SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL MEETING JUNE 2007 Physical Oceanographic Conditions
NOT TO BE CITED WITHOUT PRIOR REFERENCE TO THE AUTHOR(S) Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization Serial No. N5361 NAFO SCR Doc. 07/14 SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL MEETING JUNE 2007 Physical Oceanographic Conditions
CONFERENCE STATEMENT
 Final draft CONFERENCE STATEMENT We, the elected representatives of Canada, Denmark/Greenland, the European Parliament, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America; In collaboration
Final draft CONFERENCE STATEMENT We, the elected representatives of Canada, Denmark/Greenland, the European Parliament, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America; In collaboration
