,258 10,680
|
|
|
- Ilene Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 ASU/GRU GLAZE LIST (HOLLINGSWORTH/CERAMICS HIGHFIRE Stoneware Clay Body #1 cone New FHC 25 Hawthorn Bond 10 kaolin 10 ball clay 5 G-200 feldspar 1 00 Add 5% sand or grog if desired. A very low-iron throwing body. White in raku. Stoneware Clay Body #2 cone Goldart 30 Hawthorn Bond 20 ball clay 12 Lizella clay 10 feldspar (G-200) 122 Add sand and/or grog to taste. Stoneware for TomMac cone FHC 15 Goldart 20 Hawthorn Bond 13 Lizella 20 ball (OM4) 10 flint 7 G-200 feldspar Add sand and/or grog to taste Copper Red Glaze cone 9-10 (BF) frit custer spar 7.07 whiting 3.45 zinc oxide flint 1.55 bentonite.49 copper carbonate.29 silicon carbide 1.08 tin oxide.66 frit sodium silicate 2.88 kaolin (calcined) 2.16 borax Red Deb Glaze - cone custer feldspar 2157 flint 631 kaolin 631 talc 791 whiting 996 bone ash 913 red iron oxide 270 bentonite 11,258 Mason Red Glaze - cone G-200 feldspar 1680 bone ash 930 dolomite 750 red iron oxide 570 ball clay 750 flint 10,680 Blue Chun Glaze - cone G-200 feldspar 180 EPK 2720 flint 900 whiting 880 gerstley borate 880 dolomite 170 zinc oxide 260 tin oxide 10,200 plus: 400 rutile 50 copper carbonate Plum Chun Glaze Start with Blue Chun recipe above. Delete rutile and copper. Add 2% copper carbonate.. Woo's Blue Glaze - Reduction cone G-200 feldspar 2700 flint 1800 whiting
2 OM4 ball clay 400 red iron oxide 400 rutile bentonite 10,900 Segar Blue Glaze - cone G-200 feldspar 1440 whiting 1040 ball clay 2160 flint 240 rutile 320 red iron oxide 8560 Rutile Blue Glaze - cone dolomite 1500 G-200 feldspar 555 whiting 840 EPK 1315 flint 400 rutile 5400 Shino Glaze - Reduction cone nepheline syenite 0 OM4 ball clay 250 EPK 250 soda ash 250 spodumene 5500 Add 10% redart clay. Buckwheat Glaze - Reduction cone G-200 feldspar 2030 EPK 1370 dolomite 840 whiting 680 zircopax red iron oxide rutile 9360 Beautiful Teal Glaze- Reduction cone 9-10 (BB) 44.1 F-4 feldspar 7.7 ball clay 12.4 gerstley borate 15.1 talc 20.6 flint 99.9 Add.5% cobalt oxide Add 1% chrome oxide A semi-matte to gloss glaze. Lung Chaun Celadon Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 51 custer feldspar 29 flint 11 EPK 20 whiting 111 Add 1% black iron oxide A light greenish celadon glaze Sky Celadon Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 30 flint 20 whiting 49 potash feldspar 1 red iron oxide Wonderful White Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 27.0 K-200 feldspar 12.0 gerstley borate 8.8 dolomite 19.5 talc 7.5 ball clay 25.2 flint.0 A semi-matte white glaze Variations on Wonderful White: to the base glaze, add
3 3 Wonderful Lavender Wonderful Purple Add 1% cobalt carbonate Wonderful Green (Teal) Add 1% chrome oxide Wonderful Khaki & Cream Add 3% rutile Add 3% copper carbonate Beautiful Blue Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 44.1 F-4 feldspar 7.7 ball clay 12.4 gerstley borate 15.1 talc 20.6 flint 99.9 (To get intense blue, add 1% cobalt carbonate) A medium blue semi-matte to gloss glaze Celadon Base Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 42.2 nepheline syenite 10.0 whiting 5.4 EPK 5.0 soda ash 29.4 flint 2.0 zinc oxide 2.0 bentonite 96.0 Celadon Variations: to base glaze, add Purple/Black Celadon Add 3% manganese dioxide Green Celadon Add 6% copper carbonate Bright Blue Celadon Purple-Blue to Tan Celadon Add 6% rutile Add 3% manganese dioxide Blue to Tan Celadon Add 6% rutile Green and Blue Celadon Add 6% copper carbonate Peach Bloom Glaze cone 10 (BB) 27.1 nepheline syenite 16.8 gerstley borate 12.4 dolomite 40.9 flint.95 copper carbonate.95 rutile.95 tin.05 This glaze must go to cone 10. Lots of color variation within the glaze. Reduction must be heavy. Glaze must be applied thick but not too thick. Not for beginnersl St. John's Black Glaze cone 9 &10 (BB) 75 Alberta Slip 35 nepheline syenite 5 cobalt carbonate 115 A shiny, dark black-blue glaze.works well with peach bloom glaze. Copper Red Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 40 nepheline syenite 18 whiting 40 flint 12 borax 2 tin oxide 4 copper carbonate 3 bentonite 119 Looks better at cone 9 than cone 10. Sea Green to Tan Celadon Add 6% rutile Add 6% copper carbonate
4 4 Ox Blood Red Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 42 nepheline syenite 9 custer feldspar 2 kaolin 23 flint 13 gerstley borate 11 whiting Add 3% black copper oxide Add 1% tin oxide Add 3% bentonite Looks better at cone 9 than cone 10 Tomato Red Glaze cone 9-10 (BB) 54 F-4 feldspar 29 flint 8 EPK 8 magnesium carbonate 13 bone ash 8 red iron oxide 2 bentonite 122 Looks better at cone 9 than cone 10 David's Turquoise Glaze cone 9 (AC) 45 soda feldspar 5 EPK 15 talc 20 flint 7 dolomite 8 zircopax 6.5 gerstley borate A shiny glaze Albany Celadon Glaze cone 9 (AC) 50 Albany slip 20 whiting 10 flint 20 cornwall stone Saturated Iron Glaze cone 9 (AC) 41 feldspar 30 flint 21 whiting 8 kaolin 15 red iron oxide 115 Your basic temmoku glaze (black where thick, brown where thin) Jack's Blood Red Glaze cone 9 (AC) 72.5 potash feldspar 10.9 gerstley borate 7.2 whiting 7.2 flint (400 mesh) 1.1 tin oxide 1.1 copper carbonate.0 Apply thickly and reduce heavily. Clear cone 9 Glaze (AC) 44 soda feldspar 18 whiting 10 kaolin 28 flint 1 red iron oxide 101 This shiny clear glaze is slightly on the celadon side (gray to green). Jack's Yellow Glaze cone 9 (AC) 80 feldspar 30 kaolin 44 dolomite 8 whiting 8 rutile 170 Cool Spodumene White Glaze cone 9 (AC) 80 feldspar 30 kaolin 44 dolomite 8 whiting 40 spodumene
5 % rutile Satin Black cone custer feldspar 20 F-4 feldspar 15 dolomite 13 talc 20 flint 10 ball clay 2 whiting 1 chrome oxide 3 red iron oxide 2 manganese dioxide 3 cobalt oxide 2 bentonite Carbon Trap - cone nepheline syenite 10.8 F-4 feldspar 15.2 spodumene 15 ball 10 EPK 4 soda ash Turner Beauty - cone potash feldspar 20 EPK 22 dolomite 2 calcium carbonate 20 spodumene 4 tin oxide 1 rutile.5 copper carbonate 99.5 Limestone White - cone custer feldspar ball clay (OM4) 6.92 EPK whiting flint Yanagahara s Lavender - cone custer feldspar talc whiting 2.90 bentonite 2.90 EPK flint 4.00% cobalt carbonate Iron Blue Celadon - cone cornwall stone flint EPK dolomite 5.00 barium carbonate 5.00 zinc oxide 2.30% yellow iron oxide Sana s Green - cone custer feldspar 9.17 whiting gerstley borate 7.76 barium carbonate 2.91 magnesium 4.85 EPK flint 2.91 tin oxide % copper carbonate
6 6 This shino recipe traps carbon well. Lipstick Purple - cone custer feldspar 9.74 gerstley borate.89 EPK 8.86 whiting flint 2.21 dolomite 1.11 barium carbonate.44 zinc oxide 1.40 tin oxide.3% copper carbonate.2% iron oxide.1% rutile Very Dry Shino - cone nepheline syenite spodumene EPK 4.20 zircopax 3.50 bentonite.01 Blue Celadon - cone 9-10 (Steve Loucks) 50 custer 8 barium carbonate 6 strontium carbonate 7 whiting 5 grolleg 24 flint Add 2% Spanish red iron oxide Shino (Steve Loucks) - cone nepheline syenite 15 spodumene 10 F-4 feldspar 15 OM4 ball clay 10 EPK 5 red art 18 soda ash 118 Fake Yellow Ash - cone 9-10 (Steve Loucks) 50 Alberta slip 30 whiting 15 EPK 5 rutile This glaze runs a lot. Amber Celadon - cone Alberta slip 20 custer feldspar 13 wollastonite 7 whiting 3 gerstley borate 3 EPK 14 flint 7 yellow ochre Oribe Green - cone 9-10 (Vince Pitelka) 1.05 bone ash 7.81 talc whiting custer feldspar EPK flint 5.49% black copper oxide This is a translucent but very dark green with areas of saturated-metal black. Shiny glaze. Light Green Celadon - cone 9-10 (Vince Pitelka) 48.5 custer feldspar 28.2 flint 10.8 EPK 13.0 whiting.5
7 7 0.75% red iron oxide 0.25% chrome oxide 21.1 dolomite zircopax 4.3 OM4 ball clay Mellow Salts Glaze - cone nepheline syenite 1.0% red iron oxide 4.0% bentonite Vapor Blue - cone custer feldspar 17.0 whiting 11.0 EPK 27.0 flint.0 4.0% cobalt carbonate 4.0% bentonite
LA MERIDIANA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF CERAMIC ART IN TUSCANY
 LA MERIDIANA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF CERAMIC ART IN TUSCANY Notes on ash glazes ASH GLAZES Wood or vegetable ashes have been used as glaze materials since antiquity, and they may lend a quality to glazes
LA MERIDIANA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF CERAMIC ART IN TUSCANY Notes on ash glazes ASH GLAZES Wood or vegetable ashes have been used as glaze materials since antiquity, and they may lend a quality to glazes
CERAMIC MATERIALS I. Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe KALEMTAŞ
 CERAMIC MATERIALS I akalemtas@mu.edu.tr, akalemtas@gmail.com, Phone: 211 19 17 Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department CLASSIFICATION OF CERAMICS Ceramic Materials Advanced Ceramics Traditional
CERAMIC MATERIALS I akalemtas@mu.edu.tr, akalemtas@gmail.com, Phone: 211 19 17 Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department CLASSIFICATION OF CERAMICS Ceramic Materials Advanced Ceramics Traditional
5E Essential Lesson-SC.8.P.8.6. Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1. Number of valence electrons: 2
 Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates
 Why are some minerals harder than others? Their atomic structure and chemical formula. This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates Part #1 - Silicates: Silicon and Oxygen make up 70%
Why are some minerals harder than others? Their atomic structure and chemical formula. This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates Part #1 - Silicates: Silicon and Oxygen make up 70%
Science for Potters. Linda Bloomfield
 Science for Potters Linda Bloomfield Table of Contents Acknowledgements... v Introduction... x Chapter 1. Chemistry for Potters.... 1 Elements.... 2 Structure of the Atom.... 2 Symbols... 3 Molecules....
Science for Potters Linda Bloomfield Table of Contents Acknowledgements... v Introduction... x Chapter 1. Chemistry for Potters.... 1 Elements.... 2 Structure of the Atom.... 2 Symbols... 3 Molecules....
Minerals: Minerals: Building blocks of rocks. Atomic Structure of Matter. Building Blocks of Rocks Chapter 3 Outline
 Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Chapter 3 Outline Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Minerals: Building blocks of rocks Definition
Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Chapter 3 Outline Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Minerals: Building blocks of rocks Definition
Bridal Color Collection
 Bridal Color Collection trend wedding color stories Featuring: Luxe Fine Double Face Satin 088 Double Face Satin Double Face Satin 087 Neons & Brights Double Face Satin Wired Taffeta French Wired Taffeta
Bridal Color Collection trend wedding color stories Featuring: Luxe Fine Double Face Satin 088 Double Face Satin Double Face Satin 087 Neons & Brights Double Face Satin Wired Taffeta French Wired Taffeta
Physical Geology 101 Laboratory MINERALS II Silicate and Carbonate Rock-Forming Minerals
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory MINERALS II Silicate and Carbonate Rock-Forming Minerals I. INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lab is you will improve your mineral identification
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory MINERALS II Silicate and Carbonate Rock-Forming Minerals I. INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lab is you will improve your mineral identification
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20
 Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Matter and Minerals Earth: Chapter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Matter and Minerals Earth: Chapter 3 Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks By definition a mineral is: Naturally occurring An inorganic solid Ordered internal molecular structure Definite chemical composition
Matter and Minerals Earth: Chapter 3 Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks By definition a mineral is: Naturally occurring An inorganic solid Ordered internal molecular structure Definite chemical composition
Emily and Megan. Earth System Science. Elements of Earth by weight. Crust Elements, by weight. Minerals. Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight
 Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Crust Elements. Elements of Earth. Minerals. Crystals. Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air
 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Chapter 4. Rocks and Minerals: Documents that Record Earth's History
 Chapter 4 Rocks and Minerals: Documents that Record Earth's History What can Minerals Tell Us? 1. Minerals may contain radioactive elements that can be used for radiometric age dating. 2. Minerals that
Chapter 4 Rocks and Minerals: Documents that Record Earth's History What can Minerals Tell Us? 1. Minerals may contain radioactive elements that can be used for radiometric age dating. 2. Minerals that
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table. Quick Fire Questions
 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Quick Fire Questions This work sheet is fully supported by a video tutorial https://youtu.be/mjlipj_c018 1. What element is represented by W? 2. What element is
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Quick Fire Questions This work sheet is fully supported by a video tutorial https://youtu.be/mjlipj_c018 1. What element is represented by W? 2. What element is
Matter and Minerals. Earth 9 th edition Chapter 3 Minerals: summary in haiku form "Mineral" defined: natural, inorganic, solid (and two more).
 1 2 Matter and Minerals Earth 9 th edition Chapter 3 Minerals: summary in haiku form "Mineral" defined: natural, inorganic, solid (and two more). continued... 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Also crystalline,
1 2 Matter and Minerals Earth 9 th edition Chapter 3 Minerals: summary in haiku form "Mineral" defined: natural, inorganic, solid (and two more). continued... 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Also crystalline,
MV18. Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING
![MV18. Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING MV18. Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING](/thumbs/85/91312857.jpg) General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 2015 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier MV18 [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING TIME 1 hour, plus your additional time allowance.
General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 2015 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier MV18 [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING TIME 1 hour, plus your additional time allowance.
2.7: Chemical Symbols and Formulas
 Science 9 2.7: Chemical Symbols and Formulas Chemical Symbols On the periodic table all the elements are represented by different symbols letters which are an abbreviation of the element s name. These
Science 9 2.7: Chemical Symbols and Formulas Chemical Symbols On the periodic table all the elements are represented by different symbols letters which are an abbreviation of the element s name. These
EXPERIMENTS. Testing products of combustion: Reducing Copper(III) Oxide to Copper. Page 4
 APPARATUS Page 2 APPARATUS Page 3 Reducing Copper(III) Oxide to Copper EXPERIMENTS Page 4 Testing products of combustion: EXPERIMENTS Showing that oxygen and water is needed for rusting iron Page 5 Showing
APPARATUS Page 2 APPARATUS Page 3 Reducing Copper(III) Oxide to Copper EXPERIMENTS Page 4 Testing products of combustion: EXPERIMENTS Showing that oxygen and water is needed for rusting iron Page 5 Showing
Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Part I: The Big Picture Chemical Formulas and Equations Reminder: H is the element symbol for Hydrogen. H 2 is the chemical formula for hydrogen. The subscript 2 after the H means that two atoms of hydrogen
Part I: The Big Picture Chemical Formulas and Equations Reminder: H is the element symbol for Hydrogen. H 2 is the chemical formula for hydrogen. The subscript 2 after the H means that two atoms of hydrogen
Students will: 1. review electron configurations. 2. define valence electrons. 3. identify valence electrons within an electron configuration.
 Chemistry Objective: Students will: 1. review electron configurations. 2. define valence electrons. 3. identify valence electrons within an electron configuration. Warm-up: Remembering back to electron
Chemistry Objective: Students will: 1. review electron configurations. 2. define valence electrons. 3. identify valence electrons within an electron configuration. Warm-up: Remembering back to electron
PŘEVODNÍK ARIADNA-DMC
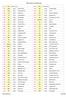 1500 3865 99,22 Winter White 1538 893 94,34 Carnation Light 1501 3823 99,61 Yelow Ultra Pale 1539 351 97,02 Coral 1502 744 98,40 Yelow Pale 1540 356 97,72 Terra Cota Medium 1503 743 97,02 Yelow Medium
1500 3865 99,22 Winter White 1538 893 94,34 Carnation Light 1501 3823 99,61 Yelow Ultra Pale 1539 351 97,02 Coral 1502 744 98,40 Yelow Pale 1540 356 97,72 Terra Cota Medium 1503 743 97,02 Yelow Medium
SURFACE TEXTURES. Sand Blasted: This surface is the result of a pressurized flow of sand water that provides a textured surface with a matte gloss.
 Natural Stone SURFACE TEXTURES There are many different types of stone available. When stone is ordered, it is fabricated with a particular type of surface. There are six main type of surfaces that are
Natural Stone SURFACE TEXTURES There are many different types of stone available. When stone is ordered, it is fabricated with a particular type of surface. There are six main type of surfaces that are
Lab 16: Metals and Oxidation
 Concepts to explore: Observe an oxidation reduction reaction Use the properties of a reaction product to verify its identity Rank the reactivity of certain metals in a weak acid, and compare it to their
Concepts to explore: Observe an oxidation reduction reaction Use the properties of a reaction product to verify its identity Rank the reactivity of certain metals in a weak acid, and compare it to their
Studying Rocks and Soil
 Studying Rocks and Soil How do rocks form? Rocks Rock is found in nature. Rock is solid. It is nonliving matter. All rocks are made of one or more minerals. A mineral is a natural material that forms from
Studying Rocks and Soil How do rocks form? Rocks Rock is found in nature. Rock is solid. It is nonliving matter. All rocks are made of one or more minerals. A mineral is a natural material that forms from
CERAMIC GLAZING as an IGNEOUS PROCESS
 GEOL 640: Geology through Global Arts and Artifacts CERAMIC GLAZING as an IGNEOUS PROCESS GLAZE COMPONENTS A glaze is a waterproof silica glass on the surface of a ceramic pot, and was first produced by
GEOL 640: Geology through Global Arts and Artifacts CERAMIC GLAZING as an IGNEOUS PROCESS GLAZE COMPONENTS A glaze is a waterproof silica glass on the surface of a ceramic pot, and was first produced by
COUNTERTOP SELECTIONS. Limestone
 NATURAL STONE COUNTERTOP SELECTIONS Nature and Types Natural stone is classified based on its origin. There are three basic types of stones: 1. Volcanic or Igneous Stone formed on solidification of lava
NATURAL STONE COUNTERTOP SELECTIONS Nature and Types Natural stone is classified based on its origin. There are three basic types of stones: 1. Volcanic or Igneous Stone formed on solidification of lava
Minerals By Patti Hutchison
 Minerals By Patti Hutchison 1 Minerals. They are all around us. We eat them, wear them, and build with them. What is a mineral? How are they identified? What can we do with them? 2 Earth's crust is made
Minerals By Patti Hutchison 1 Minerals. They are all around us. We eat them, wear them, and build with them. What is a mineral? How are they identified? What can we do with them? 2 Earth's crust is made
INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE
 CPC - C05D - 2017.08 C05D INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE Fertiliser compositions containing potassium, calcium, magnesium and others, including
CPC - C05D - 2017.08 C05D INORGANIC FERTILISERS NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C05B, C05C; FERTILISERS PRODUCING CARBON DIOXIDE Fertiliser compositions containing potassium, calcium, magnesium and others, including
1/31/2013 CHEMICAL EQUATIONS & REACTIONS NOTES. Write the formulas of the following compounds: 1. nickel (II) chloride. 2. copper (II) nitrate
 CEMICAL EQUATIONS & REACTIONS NOTES Ionic compounds can form from metals Transition metals do not always follow the patterns that we discussed Can have more than one oxidation number () To identify the
CEMICAL EQUATIONS & REACTIONS NOTES Ionic compounds can form from metals Transition metals do not always follow the patterns that we discussed Can have more than one oxidation number () To identify the
The City School PAF Chapter First Term 2 nd Comprehensive Worksheet October 2015 Subject: Science Class 7 Time: 40 minutes Total Marks [20]
![The City School PAF Chapter First Term 2 nd Comprehensive Worksheet October 2015 Subject: Science Class 7 Time: 40 minutes Total Marks [20] The City School PAF Chapter First Term 2 nd Comprehensive Worksheet October 2015 Subject: Science Class 7 Time: 40 minutes Total Marks [20]](/thumbs/89/99385122.jpg) The City School PAF Chapter First Term 2 nd Comprehensive Worksheet October 2015 Subject: Science Class 7 Time: 40 minutes Total Marks [20] TOPICS: DICHOTOMOUS KEY, ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS, MIXTURES Q-1:
The City School PAF Chapter First Term 2 nd Comprehensive Worksheet October 2015 Subject: Science Class 7 Time: 40 minutes Total Marks [20] TOPICS: DICHOTOMOUS KEY, ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS, MIXTURES Q-1:
General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy
 General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy J. Nentwig M. Kreuder K. Morgenstern VCH Contents How to use this book XIII Program 1 1 Introducüon. Chemistry as a natural science - chemical and physical processes
General and Inorganic Chemistry Made Easy J. Nentwig M. Kreuder K. Morgenstern VCH Contents How to use this book XIII Program 1 1 Introducüon. Chemistry as a natural science - chemical and physical processes
The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature.
 Chemistry Lecture #63: Changes of State The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature. For example, a solid substance can be converted into a liquid by heating
Chemistry Lecture #63: Changes of State The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature. For example, a solid substance can be converted into a liquid by heating
Current State of Extraction Don t Be Deceived! Sharon F. Webb, Ph.D. Director of Quality Program
 Current State of Extraction Don t Be Deceived! Sharon F. Webb, Ph.D. Director of Quality Program Overview Factors Purpose of Dissolution Quality Objectives of Program Effectiveness of Dissolution Technique
Current State of Extraction Don t Be Deceived! Sharon F. Webb, Ph.D. Director of Quality Program Overview Factors Purpose of Dissolution Quality Objectives of Program Effectiveness of Dissolution Technique
CHEMISTRY ELEMENTS, COMPOUNDS & MIXTURES
 CHEMISTRY ELEMENTS, COMPOUNDS & MIXTURES Lesson Intentions In this lesson we will classify substances as Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Key Words 1. Compounds 2. Mixtures 3. Elementary 4. Symbols 5. Reaction
CHEMISTRY ELEMENTS, COMPOUNDS & MIXTURES Lesson Intentions In this lesson we will classify substances as Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Key Words 1. Compounds 2. Mixtures 3. Elementary 4. Symbols 5. Reaction
Worldwide Mineral Set
 Worldwide Mineral Set These sets are put together with many different minerals from worldwide sources. You will get some of the minerals described on the attached sheets. Some of the minerals will be on
Worldwide Mineral Set These sets are put together with many different minerals from worldwide sources. You will get some of the minerals described on the attached sheets. Some of the minerals will be on
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Magnetic Flowmeter Material Selection Guide
 Magnetic Flowmeter Material Selection Guide www.sparlinginstruments.com Introduction The purpose of this guide is to provide a general resource for the selection of materials for the magnetic flowmeter.
Magnetic Flowmeter Material Selection Guide www.sparlinginstruments.com Introduction The purpose of this guide is to provide a general resource for the selection of materials for the magnetic flowmeter.
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
The Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry
 The Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry Question Paper Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Chemistry AQA C1 The Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry Silver Level Question Paper Time
The Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry Question Paper Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Chemistry AQA C1 The Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry Silver Level Question Paper Time
3.1 Classification of Matter. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements 3.1 Classification of Matter Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Matter Matter is the stuff that makes up all things. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Pure
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements 3.1 Classification of Matter Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Matter Matter is the stuff that makes up all things. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Pure
HGMS Worldwide Minerals and Descriptions
 NAME ACTINOLITE ADAMITE on brown goethite, Mapimi, Durango, Mexico. ANHYDRITE APATITE - blue APATITE, hardness of 5 ARAGONITE - amber colored crystal ARAGONITE - twinned crystal from Clarendon, Texas.
NAME ACTINOLITE ADAMITE on brown goethite, Mapimi, Durango, Mexico. ANHYDRITE APATITE - blue APATITE, hardness of 5 ARAGONITE - amber colored crystal ARAGONITE - twinned crystal from Clarendon, Texas.
Worksheet on Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
 Worksheet on Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Name : ( ) Date: 05042007 Class : Instruction: Answer all questions 1-9 below by filling the correct answer in the given bracket. 1. How many atoms are present
Worksheet on Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Name : ( ) Date: 05042007 Class : Instruction: Answer all questions 1-9 below by filling the correct answer in the given bracket. 1. How many atoms are present
Note Taking Guide: Episode 701. Lab results: 1 doz grains of rice = g (Use this fact as a conversion factor.) Avogadro s Number - the = the number
 Note Taking Guide: Episode 701 Name Lab results: 1 doz grains of rice = g (Use this fact as a conversion factor.)? grains of rice = 1.94 g Avogadro s Number - the = the number Molar Mass the of one of
Note Taking Guide: Episode 701 Name Lab results: 1 doz grains of rice = g (Use this fact as a conversion factor.)? grains of rice = 1.94 g Avogadro s Number - the = the number Molar Mass the of one of
THE APPLICATION OF BASALT IN THE MANUFACTURING OF CERAMIC GLAZES
 Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, 43 A (2007) 53-60 THE APPLICATION OF BASALT IN THE MANUFACTURING OF CERAMIC GLAZES Aurel PRSTIĆ *, Zagorka AĆIMOVIĆ-PAVLOVIĆ *, Ljubica PAVLOVIĆ **, Ljubiša ANDRIĆ #**,
Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, 43 A (2007) 53-60 THE APPLICATION OF BASALT IN THE MANUFACTURING OF CERAMIC GLAZES Aurel PRSTIĆ *, Zagorka AĆIMOVIĆ-PAVLOVIĆ *, Ljubica PAVLOVIĆ **, Ljubiša ANDRIĆ #**,
The earth is composed of various kinds
 UNIT III LANDFORMS This unit deals with Rocks and minerals major types of rocks and their characteristics Landforms and their evolution Geomorphic processes weathering, mass wasting, erosion and deposition;
UNIT III LANDFORMS This unit deals with Rocks and minerals major types of rocks and their characteristics Landforms and their evolution Geomorphic processes weathering, mass wasting, erosion and deposition;
Work hard. Be nice. Date: Hybrid Chemistry Regents Prep Ms. Hart/Mr. Kuhnau. UNIT 2: BONDING Lecture 2.4: Free- Response Bonding Practice
 Name: Period: Date: Hybrid Chemistry Regents Prep Ms. Hart/Mr. Kuhnau UNIT 2: BONDING Lecture 2.4: Free- Response Bonding Practice Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How do we solve
Name: Period: Date: Hybrid Chemistry Regents Prep Ms. Hart/Mr. Kuhnau UNIT 2: BONDING Lecture 2.4: Free- Response Bonding Practice Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How do we solve
2014 Chemistry 1 st Semester Exam Review Packet
 Name: Date: Hour: 2014 Chemistry 1 st Semester Exam Review Packet 1. What percentage of the water on Earth is salt water? (1 point) A. 97.2% B. 0.009% C. 2.11% D. 2.8 % 2. One similarity between all mixtures
Name: Date: Hour: 2014 Chemistry 1 st Semester Exam Review Packet 1. What percentage of the water on Earth is salt water? (1 point) A. 97.2% B. 0.009% C. 2.11% D. 2.8 % 2. One similarity between all mixtures
Lesson 1: What are chemical changes?
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: What are chemical changes? Vocabulary Use with pp. 375 377 physical change a change in which the material keeps its identify chemical change a change in which one substance or
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: What are chemical changes? Vocabulary Use with pp. 375 377 physical change a change in which the material keeps its identify chemical change a change in which one substance or
Chemistry at Home Summary Notes
 Neutral Yellow Green Cyan Chemistry at Home Summary Notes Section 1 - Indicators Substances can be acid, alkali or neutral. Acid and alkali are the opposite of each other and neutral is in the middle.
Neutral Yellow Green Cyan Chemistry at Home Summary Notes Section 1 - Indicators Substances can be acid, alkali or neutral. Acid and alkali are the opposite of each other and neutral is in the middle.
Class X. Exercises solution
 Exercises solution Question 1: Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect? Lead is getting reduced. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised. Carbon is getting oxidised. Lead oxide is getting
Exercises solution Question 1: Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect? Lead is getting reduced. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised. Carbon is getting oxidised. Lead oxide is getting
Chemistry Chapter 1 Test Review
 Chemistry Chapter 1 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A chemical can be defined as a. a toxic substance. b. an unnatural additive
Chemistry Chapter 1 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A chemical can be defined as a. a toxic substance. b. an unnatural additive
INTRODUCTION TO MATTER: CLASSI F ICATION OF MATTER, PHYSICAL AND C He MICAL PROPERTIES, AND PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES
 Experiment 3 Name: INTRODUCTION TO MATTER: 9 4 CLASSI F ICATION OF MATTER, PHYSICAL AND C He MICAL e PROPERTIES, AND PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES In this experiment, you will encounter various classification
Experiment 3 Name: INTRODUCTION TO MATTER: 9 4 CLASSI F ICATION OF MATTER, PHYSICAL AND C He MICAL e PROPERTIES, AND PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES In this experiment, you will encounter various classification
Physical Properties of Matter. Examples of Physical Properties. QUESTION: How could you find the volume of air in an "empty" room?
 QUESTION: How could you find the volume of air in an "empty" room? The volume of regularly shaped solids can be calculated from their dimensions. For example, the volume of a rectangular solid is the product
QUESTION: How could you find the volume of air in an "empty" room? The volume of regularly shaped solids can be calculated from their dimensions. For example, the volume of a rectangular solid is the product
It s just like finding out your test score!!!
 It s just like finding out your test score!!! 97 correct out of 100 questions = 97 x 100 = 97% 100 Total of something x 100 = % TOTAL The chemical composition can be expressed as the mass percent of each
It s just like finding out your test score!!! 97 correct out of 100 questions = 97 x 100 = 97% 100 Total of something x 100 = % TOTAL The chemical composition can be expressed as the mass percent of each
mixtures reflect What properties could you use to separate the ingredients in these mixtures?
 reflect Every day, we interact with many different kinds of matter. We look at it, feel it, taste it, and even breathe it. Sometimes different types of matter are combined. For example, a salad might have
reflect Every day, we interact with many different kinds of matter. We look at it, feel it, taste it, and even breathe it. Sometimes different types of matter are combined. For example, a salad might have
Mineral Identification
 Mineral Identification! Mineral identification is a skill. " Requires learning diagnostic properties #Some properties are easily seen. $Color $Crystal shape #Some properties require handling or testing.
Mineral Identification! Mineral identification is a skill. " Requires learning diagnostic properties #Some properties are easily seen. $Color $Crystal shape #Some properties require handling or testing.
33-40 vessels vessels
 8-32 Aluminum Alloy 10 15 20 25 15 180 0.2 grams, 5 ml HCl and 5 ml H 2 O, Add H 2 O BEFORE HCl Aluminum Oxide 15 20 270 0.25 grams, 6.5 ml H 3 PO 4 and 3.5 ml H 2 SO 4 Animal Tissue 15 15 20 25 15 200
8-32 Aluminum Alloy 10 15 20 25 15 180 0.2 grams, 5 ml HCl and 5 ml H 2 O, Add H 2 O BEFORE HCl Aluminum Oxide 15 20 270 0.25 grams, 6.5 ml H 3 PO 4 and 3.5 ml H 2 SO 4 Animal Tissue 15 15 20 25 15 200
Mixtures, Elements, and Compounds
 Mixtures, Elements, and Compounds Chapter 3 (plus K4 & K5) (Big 11 & 12) Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 3-1 Classes of Matter It is important to classify,
Mixtures, Elements, and Compounds Chapter 3 (plus K4 & K5) (Big 11 & 12) Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 3-1 Classes of Matter It is important to classify,
GCSE Additional Science
 GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
Compounds. Elements. Elements in a Compound. Matter. Pure Substances. Basic Chemistry. Chapter 3 Lecture. 3.1 Classification of Matter
 Chapter 3 Lecture Chapter 3 and Energy 3.1 Classification of Fifth Edition is the material that makes up all things is anything that has mass and occupies space Learning Goal Classify examples of matter
Chapter 3 Lecture Chapter 3 and Energy 3.1 Classification of Fifth Edition is the material that makes up all things is anything that has mass and occupies space Learning Goal Classify examples of matter
The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Hydrochloric acid is added. Solution
 1 Chemical tests can be used to identify compounds. The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Solution Flame Test Hydrochloric acid is added Sodium hydroxide
1 Chemical tests can be used to identify compounds. The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Solution Flame Test Hydrochloric acid is added Sodium hydroxide
Periodic Table of Elements
 Periodic Table of Elements The Atomic Nucleus The nucleus is a small, dense region at the center of the atom. It consists of positive protons and neutral neutrons, so it has an overall positive charge.
Periodic Table of Elements The Atomic Nucleus The nucleus is a small, dense region at the center of the atom. It consists of positive protons and neutral neutrons, so it has an overall positive charge.
CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry
 CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry Properties of Matter From Chapter 2 and 3 Textbook Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Physical States of Matter
CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry Properties of Matter From Chapter 2 and 3 Textbook Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Physical States of Matter
Website: Page 1. Page 14»Exercise» Page 15» Question 1:
 Page 14»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect? (a) Lead is getting reduced. (b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised. (c) Carbon is getting oxidised. (d) Lead
Page 14»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect? (a) Lead is getting reduced. (b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised. (c) Carbon is getting oxidised. (d) Lead
The most common elements that make up minerals are oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, potassium, and magnesium
 Mineralogy: The Study of Minerals and their Properties A Mineral! Occurs! Is a! Is a substance (element or compound)! Has atoms arrange in an orderly pattern ( )! Is (not formed by any process involving
Mineralogy: The Study of Minerals and their Properties A Mineral! Occurs! Is a! Is a substance (element or compound)! Has atoms arrange in an orderly pattern ( )! Is (not formed by any process involving
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 2 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 2 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 2 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
PHILADELPHIA UNIVERSITY
 PHILADELPHIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING. Engineering Geology Part one 1 2nd semester 2018/2019 Eng. Amany Assouli 1 INTRODUCTION: What is the engineering
PHILADELPHIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING. Engineering Geology Part one 1 2nd semester 2018/2019 Eng. Amany Assouli 1 INTRODUCTION: What is the engineering
UmllluIfiW, SfOLOGICAL SURVEY
 UmllluIfiW, SfOLOGICAL SURVEY 3 3051 00005 8770 Digitized by the Internet Archive in 2012 with funding from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign http://archive.org/details/heavymineralsini01shro s
UmllluIfiW, SfOLOGICAL SURVEY 3 3051 00005 8770 Digitized by the Internet Archive in 2012 with funding from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign http://archive.org/details/heavymineralsini01shro s
2.3 Elements and Compounds > Chapter 2 Matter and Change. 2.3 Elements and Compounds. 2.1 Properties of Matter 2.2 Mixtures. 2.4 Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 2 Matter and Change 2.1 Properties of Matter 2.2 Mixtures 2.3 Elements and Compounds 2.4 Chemical Reactions 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY
Chapter 2 Matter and Change 2.1 Properties of Matter 2.2 Mixtures 2.3 Elements and Compounds 2.4 Chemical Reactions 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY
Periods on the Periodic Table
 Minerals Chapter 2 Matter Matter includes anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). It exists in 3 main states on Earth solid, liquid, and gas. Matter can be classified based on its physical
Minerals Chapter 2 Matter Matter includes anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). It exists in 3 main states on Earth solid, liquid, and gas. Matter can be classified based on its physical
ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS
 C03 04/19/2013 13:31:38 Page 20 CHAPTER 3 ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Silicon 25:7% Hydrogen 0:9% In 100 g 25:7g Si 0:9g H ¼ 30 g Si=1 g H ð 1 sig: fig: Þ Si is 28 times heavier
C03 04/19/2013 13:31:38 Page 20 CHAPTER 3 ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Silicon 25:7% Hydrogen 0:9% In 100 g 25:7g Si 0:9g H ¼ 30 g Si=1 g H ð 1 sig: fig: Þ Si is 28 times heavier
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Weathering and Soil Physical Geology 15/e, Chapter 5 Weathering, Erosion and Transportation Rocks exposed at Earth s surface are constantly
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Weathering and Soil Physical Geology 15/e, Chapter 5 Weathering, Erosion and Transportation Rocks exposed at Earth s surface are constantly
Chemical Reactions Chapter 8 PART TWO
 NAME Hour Date Chemical Reactions Chapter 8 PART TWO Practice A Assessment 1 Objective 5: Predict the product of a combination reaction by writing a complete balanced equation. Directions: Write a complete
NAME Hour Date Chemical Reactions Chapter 8 PART TWO Practice A Assessment 1 Objective 5: Predict the product of a combination reaction by writing a complete balanced equation. Directions: Write a complete
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS. Subtitle
 THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
Section 1: Elements Pages 56-59
 Study Guide Chapter 3 Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Section 1: Elements Pages 56-59 1. Which of the following processes is NOT a physical or chemical change? a. crushing b. weighing c. melting d. passing
Study Guide Chapter 3 Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Section 1: Elements Pages 56-59 1. Which of the following processes is NOT a physical or chemical change? a. crushing b. weighing c. melting d. passing
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3
 Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3 Chemical bonds and structural formulas. ctober 1, 2017 1 Structure of molecules The concept of valence allows us to make some important conclusions about structure of molecules.
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3 Chemical bonds and structural formulas. ctober 1, 2017 1 Structure of molecules The concept of valence allows us to make some important conclusions about structure of molecules.
Unit 3: Physical Science Classifying Matter in our Daily Lives
 Science 7 Unit 3: Physical Science Classifying Matter in our Daily Lives Name Period Purpose: I understand the relationship between atoms, molecules, elements, compounds, and mixtures and can also provide
Science 7 Unit 3: Physical Science Classifying Matter in our Daily Lives Name Period Purpose: I understand the relationship between atoms, molecules, elements, compounds, and mixtures and can also provide
Name: Period: Date: Types of Bonding Lab Inquiry
 Types of Bonding Lab Inquiry One of the most important jobs of a chemist is to relate the properties of observable amounts of substance to the properties on the atomic level which are less easily observed.
Types of Bonding Lab Inquiry One of the most important jobs of a chemist is to relate the properties of observable amounts of substance to the properties on the atomic level which are less easily observed.
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chemical Reactions and Equations Question 1: Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium is very reactive metal. When stored it reacts with oxygen to form a layer magnesium
Chemical Reactions and Equations Question 1: Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium is very reactive metal. When stored it reacts with oxygen to form a layer magnesium
Chapter 8. Chemical Equations and Reactions
 Chapter 8 Chemical Equations and Reactions Chemical Equations Represents, w/ symbols & formulas, the reactants & products in a chemical reaction Requirements Must represent the known facts Must contain
Chapter 8 Chemical Equations and Reactions Chemical Equations Represents, w/ symbols & formulas, the reactants & products in a chemical reaction Requirements Must represent the known facts Must contain
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2
 1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
Chapter 2. Section 1
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Describing Matter Properties used to describe matter can be classified as extensive or intensive Extensive property - depends on the amount of matter in a sample. Ex. Mass and Volume
Chapter 2 Section 1 Describing Matter Properties used to describe matter can be classified as extensive or intensive Extensive property - depends on the amount of matter in a sample. Ex. Mass and Volume
Mineral Properties and Identification
 Mineral Properties and Identification Introductory Geology Lab GEOL 101 Ray Rector - Instructor http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/mineral_id/index.html MINERAL INQUIRY I. What are Minerals? How do minerals
Mineral Properties and Identification Introductory Geology Lab GEOL 101 Ray Rector - Instructor http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/mineral_id/index.html MINERAL INQUIRY I. What are Minerals? How do minerals
Safety Manual > Incompatible Chemicals Partial Listing
 Safety Manual > Incompatible Chemicals Partial Listing C. Incompatible Chemicals Partial Listing Chemical Incompatible Chemicals Acetic acid Chromic acid, nitric acid, permanganates, and peroxides Acetic
Safety Manual > Incompatible Chemicals Partial Listing C. Incompatible Chemicals Partial Listing Chemical Incompatible Chemicals Acetic acid Chromic acid, nitric acid, permanganates, and peroxides Acetic
Learning Target.. I Can.. Identify the differences between a mineral and a rock.
 Rocks and Minerals Learning Target.. n I Can.. Identify the differences between a mineral and a rock. What is a mineral? A mineral o Is a Inorganic solid formed in nature (Inorganic -- not living or ever
Rocks and Minerals Learning Target.. n I Can.. Identify the differences between a mineral and a rock. What is a mineral? A mineral o Is a Inorganic solid formed in nature (Inorganic -- not living or ever
Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mixtures 2 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Pure and impure substances 3 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 All materials can be classified as either a pure substance or an impure
Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mixtures 2 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Pure and impure substances 3 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 All materials can be classified as either a pure substance or an impure
EXTRA CREDIT PAGES K
 Mixtures (13K) EXTRA CREDIT PAGES 13-14 K Elements and compounds are pure substances, but most of the materials you see every day are not. Instead, they are mixtures. A mixture is made of two or more substances
Mixtures (13K) EXTRA CREDIT PAGES 13-14 K Elements and compounds are pure substances, but most of the materials you see every day are not. Instead, they are mixtures. A mixture is made of two or more substances
Chapter 1 Lecture Outline. Matter and Minerals
 Chapter 1 Lecture Outline Matter and Minerals Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Minerals are the building blocks of rocks Minerals important in human history Flint and chert for weapons and tools Gold,
Chapter 1 Lecture Outline Matter and Minerals Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Minerals are the building blocks of rocks Minerals important in human history Flint and chert for weapons and tools Gold,
Chemistry Spring Packet Study Guide for Benchmark Exam
 Chemistry Spring Packet-1 --- Study Guide for Benchmark Exam 1. Which action will result in a new product with new chemical properties? A. shredding a newspaper B. cutting wood C. breaking a mirror D.
Chemistry Spring Packet-1 --- Study Guide for Benchmark Exam 1. Which action will result in a new product with new chemical properties? A. shredding a newspaper B. cutting wood C. breaking a mirror D.
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry
 Chapter 1 INSTRUCTOR S NOTES This chapter discusses a wide range of basic subjects needed for the study of chemistry. How you use the material will depend on the preparation level of your students. Essentially
Chapter 1 INSTRUCTOR S NOTES This chapter discusses a wide range of basic subjects needed for the study of chemistry. How you use the material will depend on the preparation level of your students. Essentially
SYENITE, IJOLITE, CARBONATITE, ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS AND LAMPROPHYRE
 SYENITE, IJOLITE, CARBONATITE, ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS AND LAMPROPHYRE #13 Hornblende 20-2 -subh 2.5 6 6 mm laths 3% gray 2 6 3 mm 53-58% -subh White 2.5 6 6mm laths 2 6 7 mm 14% -euh 4 6 8.5 mm equant,, or polyhedral
SYENITE, IJOLITE, CARBONATITE, ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS AND LAMPROPHYRE #13 Hornblende 20-2 -subh 2.5 6 6 mm laths 3% gray 2 6 3 mm 53-58% -subh White 2.5 6 6mm laths 2 6 7 mm 14% -euh 4 6 8.5 mm equant,, or polyhedral
WORKING WITH MOLES LAB STATION #1: AVERAGE MASS OF PLASTIC BAGS
 WORKING WITH MOLES LAB STATION #1: AVERAGE MASS OF PLASTIC BAGS Determine and record the mass of three different plastic bags with labels. Calculate the average mass of one plastic bag. *Bag #1 grams *Bag
WORKING WITH MOLES LAB STATION #1: AVERAGE MASS OF PLASTIC BAGS Determine and record the mass of three different plastic bags with labels. Calculate the average mass of one plastic bag. *Bag #1 grams *Bag
Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind.
 Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind. 1. calcium + oxygen 2. cupric carbonate 3. aluminum + hydrochloric
Identify the reaction type, predict the products, and balance the equations. If it is a special decomposition or synthesis, identify which kind. 1. calcium + oxygen 2. cupric carbonate 3. aluminum + hydrochloric
2016 Phys PRACTICE Sci Quiz 1
 2016 Phys PRTIE Sci Quiz 1 Name: ate: 1. mixture of crystals of salt and sugar is added to water and stirred until all solids have dissolved. Which statement best describes the resulting mixture?. The
2016 Phys PRTIE Sci Quiz 1 Name: ate: 1. mixture of crystals of salt and sugar is added to water and stirred until all solids have dissolved. Which statement best describes the resulting mixture?. The
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS
 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS 1 WHAT ARE IONIC COMPOUNDS Ionic compounds are formed between elements that are in ionic form. A simpler way of determining whether a compound is ionic is to see if there are any
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS 1 WHAT ARE IONIC COMPOUNDS Ionic compounds are formed between elements that are in ionic form. A simpler way of determining whether a compound is ionic is to see if there are any
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge nternational Examinations Cambridge nternational Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level CHEMSTRY 9701/32 Paper 3 Advanced Practical Skills 2 May/June 2014 2 hours Candidates answer on the Question
Cambridge nternational Examinations Cambridge nternational Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level CHEMSTRY 9701/32 Paper 3 Advanced Practical Skills 2 May/June 2014 2 hours Candidates answer on the Question
Name Date ID. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (1) Interim Assessment Third Grading Period
 Name Date ID Integrated Physics and Chemistry (1) Interim Assessment Third Grading Period 1. The MSDS sheet for a chemical states, "use only in a well ventilated area." This caution probably indicates
Name Date ID Integrated Physics and Chemistry (1) Interim Assessment Third Grading Period 1. The MSDS sheet for a chemical states, "use only in a well ventilated area." This caution probably indicates
CLASS EXERCISE 5.1 List processes occurring in soils that cause changes in the levels of ions.
 5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
