An Analysis of Tourism Competitiveness Index of Europe and Caucasus: A Study on the Regional Rank of the Tourism Competitiveness Index
|
|
|
- Dorcas Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Invention Journal of Research Technology in Engineering & Management (IJRTEM) ISSN: Volume 2 Issue 7 ǁ July 2018 ǁ PP An Analysis of Tourism Competitiveness Index of Europe and Caucasus: A Study on the Regional Rank of the Tourism Competitiveness Index 1 S. Nisthar, 2 AMM. Mustafa, 3 MBM. Ismail 1 Visiting Academic, South Eastern University of Sri Lanka, Oluvil, Sri Lanka 2 Senior Lecturer in Business Economics, Faculty of Management and Commerce, South Eastern University of Sri Lanka, Oluvil, Sri Lanka 3 Senior Lecturer in Management, Faculty of Management and Commerce, South Eastern University of Sri Lanka, Oluvil, Sri Lanka ABSTRACT: This study aims to find the association-ship between the Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index and its Indicators in 37 European countries. The cross-sectional data of the 37 European countries are collected from the World Economic Forum report The statistical software package, SPSS v is used to analyze the data. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), Multi-co-linearity, Multiple Regression, and Residual Analysis are the tools used to analyze to achieve out the objective of the study. RR: Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index is used as the dependent variable and TI: Tourism Services Infrastructure, GP: Ground & Port Infrastructure, BE: Business Environment, PT: Prioritization of Travel and Tourism, and CR: Cultural resources & business travel are used as the independent variables. It is found that there is an inverse relationship between the dependent variable and all the independent variables along with the statistical significance. It is recommended that the governments of the European countries and the respective agents of these countries should be made aware of learning the findings of this study to promote their countries which can be victorious in lowering their Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index. KEY WORDS: TTCI, Multiple Regression, Regional Rank, Europe, Business Environment I. INTRODUCTION On the basis of a methodological point of view, the objective of Tourism Competitiveness Index is to evaluate the essentials that make sure the development of the tourism sector in different countries through three categories of the factors that affect global tourism competitiveness. These categories are evaluated through three sub-indices subsidiary to TCI: 1) policy rules and regulations that are influencing on the tourism sector. The fundamentals assessed in this sub-index refer to those features that are dependent directly or indirectly on the political ambiance and the country-specific institutional environment; 2) business environment and infrastructure; 3) natural, cultural and human resources involved in tourism activities. Volume 2 Issue
2 Figure 1: T&TCI Components Source: Roberto Crotti, Tiffany Misrahi Th. (eds.), The travel and tourism competitiveness report 2015, World Economic Forum, 2015, p. 4. Each of these sub-indices consists of a number of pillars or supports that delineate the instrumental elements in the analysis of tourism competitiveness. These elements are: policy rules and regulations, environmental sustainability, safety and security, health and hygiene, prioritization of travel and tourism, air transport infrastructure, ground transport infrastructure, tourism infrastructure, ICT infrastructure; price competitiveness in the T&T industry, human resources, affinity for travel and tourism, natural and cultural resources. To these a final component, which became increasingly important in recent years, is added - climate change. Each of these pillars in turn consists of a number of individual variables. The data set that are used to calculate approximately these pillars take account of the data from annual surveys conducted by the World Economic Forum. Those are the quantitative data obtained from publicly available sources, from international organizations and institutions and experts in tourism. And also, a statistical survey has been carried out among the senior executives and the business leaders who are responsible to make decisions in this area. Further, the TCI methodology is not limited to awarding scores and points to the tourism sector in various countries, but its objective is to construct a common framework to allow comparison between performances in this field (Mihai, 2011). Europe are deliberately attracting a large number of tourists every year because of the most striking cultural resources, highest openness in the international integration, and the infrastructures of tourism services with highest class found thorough the region. In particular, the Scheme area is found with the hygiene and health which attract the international tourism in the higher degree of arrivals into the area. In ranking, Spain is the third country mostly visited by the international tourists in the world, with the arrivals of 60.6 million of tourists. The country of France is ranking in its arrivals of tourists in the second place and persists so as to attract the most number of tourists amounting to more than 84 million of arrivals due to the second rank in cultural resources and the eighth rank in the natural resources. Switzerland is ranked in 6 th place due to the recording in the rank of 4 th and 5 th places in ground infrastructure and the improvement of infrastructure in the tourist services respectively. Due to the monuments, the remarkable towns, the scenic beauty, and the sites found as World Heritage, the country of Italy is ranked in 6 th place in Europe (Roberto, 2015). Volume 2 Issue
3 The European countries which are considered in this study and their regional rank and global rank are as follows: Table 1: European countries and their TTCI Index No. Country/Economy TTCI Index Regional Rank Global Rank Value Southern & Western Europe 01 Spain France Germany Switzerland Italy Austria Netherlands Portugal Belgium Luxembourg Greece Croatia Cyprus Slovenia Malta Montenegro Macedonia, FYR Serbia Albania Northern & Eastern Europe 20 United Kingdom Iceland Ireland Norway Finland Sweden Denmark Czech Republic Estonia Hungary Russian Federation Poland Bulgaria Latvia Lithuania Slovak Republic Romania Moldova Source: Roberto Crotti, Tiffany Misrahi Th. (eds.), The travel and tourism competitiveness report 2015, World Economic Forum, 2015, p. 10. II. PROBLEM OF THE STUDY All over the world, all the countries have been trying to achieve the considerable growth and development in whatever ways likely to finding the sources and potentiality of the growth and development of the economies. One of the ways in this connection is to improve the tourism industrial development through the resources which are endemic in the countries. Accordingly, the basic criterion to cope up with the development through Volume 2 Issue
4 attracting a large number of tourists to the host countries from the guest countries in the tourism industry in the world arena is Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index T& TCI. The T&TCI is composed of the various aspects of elements. By promoting these elements, the economies are able to achieve the targets of attracting the tourists to their exclusive destinations within the domestic landscape. By this study, the problem of attracting a large number of tourists can be settled down by finding the contribution of the elements which represent the criterion of the TTCI. Objective of the Study: To find out the association-ship between the Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index and its Indicators in European countries Questions of the Study: Are there any association-ships between the Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index and its Indicators in European countries? III. METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY The quantitative data are used in this study. The data used in this study have been collected from the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2015 of World Economic Forum. The data of the 37 countries from European countries have been collected. So the data are the cross sectional in their nature. RR (Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index) is the dependent variable and TI: Tourism Services Infrastructure, GP: Ground & Port Infrastructure, BE: Business Environment, PT: Prioritization of Travel and Tourism and CR: Cultural resources & business travel are the independent variables used in this study. In this study, the regression model is run using all the independent variables and the dependent variable. The correlation between all the variables is tested to find the direction, strength and significance between the variables. The statistical package used for the data analysis in this study is SPSS v.20.0 (Statistical Package for Social Science). In this study, multiple regression, ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), Multi-co-linearity, and Residual Analysis are analyzed statistically to achieve the objective of the study using the statistical package, SPSS v Accordingly, the following model is tested in this study: Where: RR = f (TI, GP, BE, PT, CR) ( ) RR = + TI + GP + BE + PT + CR + ( ) RR: Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index TI: Tourism Services Infrastructure GP: Ground & Port Infrastructure BE: Business Environment PT: Prioritization of Travel and Tourism CR: Cultural Resources & Business Travel : Coefficients Error term Literature Review of the Study: Mihai Croitoru (2011) aimed to analyze the underlying determinants of TCI from the perspective of two directly competing states, Romania and Bulgaria in order to highlight the effects of communication on the competitiveness of the tourism sector using case study methodology. His analysis provided some answers, especially in terms of communication strategies, which might explain the completely different performances of the two national economies in the tourism sector. He concluded that while making serious efforts to improve the institutional environment to encourage investment in tourism, Romania did not Volume 2 Issue
5 have a well put together strategy for reporting these opportunities. Romania could not effectively take advantage of the favorable geographical position, of the natural and cultural resources and of the high quality human capital. Secondly, although tourism development strategies took into account, at least at declaratory level, the fundamental principles of sustainable growth, these principles are not only implemented, but they were not even transmitted to the target audience by diverse communication methods and techniques. For this reason, the Romanian audience, both as provider and beneficiary of tourism services was not educated in terms of environmental protection and sustainable development. Thirdly, the economic crisis had given a new impetus to Bulgaria which proved, once again, to be more determined to capitalize on its competitive advantages available to the international tourism market. In this connection, Bulgaria was an exemplary country unlike Romania for the good practice in the adoption of sustainable strategies and their efficient communication strategy. Bineswaree Bolaky (2011) aimed to analyze the key determinant factors of competitiveness in the Caribbean tourism industrial sector using panel data for the time period from year 1995 to year 2006, on the basis of Augmented Version of a model designed by Craigwell (2007). He found that the evidence that Caribbean tourism competitiveness could be improved through policy measures that favour, among others, increases in investment, private sector development, better infrastructure, lower government consumption, a more flexible labour market, reduced susceptibility to natural disasters, higher human development and slow rises in oil prices. Bojan Krsticet al (2015) analyzed the achieved level of tourism competitiveness in the European Union (EU) and certain Western Balkan countries by using the correlation analysis. And also, they analyzed the capacity of accommodation as an instrumental tourism resource along with the number of overnight stays of tourists. In order to assess the significance of accommodation and tourism traffic, their study examines the interdependence between the tourism competitiveness, capacities and overnight stays. The results of the correlation analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between the observed variables. Shenol Chavuset al (2012) aimed to examine by comparing TCI of the Central Asian Turkish Republics and to develop the recommendations for the improvement of competitiveness based on the descriptive analysis. Results of the study are intended to provide important information for institutions and organizations regulating market in those countries. They found that the mentioned countries were in progress on tourism regulations range, but according to business environment and infrastructure, human, natural and cultural resources criteria the situation was not good. They recommended that to obtain the expected results in tourism sector, it was necessary to increase and speed up competitiveness studies. Maharaj. S, and Balkaran. R (2014) aimed to improve on the South African tourism competitiveness with the expressed intention of enhancing growth and sustainability using descriptive analysis based on the secondary sources of data collection. They concluded that South African tourism policy makers and tourism stakeholders can use the World Economic Forum for Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2013 as a tool to benchmark against other countries used in the research to adopt best practice and adapt national tourism policies and the national development plan. Gap of the Study: This is the pioneer study based on the econometric basis using the statistical software, SPSS, v.20.0 on this particular title of the study. IV. DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION Multiple Regression: The table - 02 shows the model summary of the multiple regression, R (r) (Pearson product moment correlation) is 0.959; R square (r 2 ), the percentage variance that the five variables share (out of possible maximum of 100 percent if the same variable in effect was correlated with itself), is calculated by squaring the r figure. This figure is 0.907, representing percent of shared variance. Thus, 90.7 percent of the variance in the entire effect of tourism can be explained by the independent variables such as TI: Tourism Services Infrastructure, GP: Ground & Port Infrastructure, BE: Business Environment, PT: Prioritization of Travel and Tourism and CR: Cultural resources & business travel. The r 2 figure may not always be reliable, and instead the adjusted r 2 figure is used. Here, at 0.920, it is around close to the unadjusted r 2 in the model summary. Volume 2 Issue
6 Table - 02: Multiple Regression Model Summary Model 1 R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate R Square Change F Change Change Statistics df1 df2 Sig. F Change Durbin- Watson.959 a a. Predictors: (Constant), Cultural Resources & Business Travel, Business Environment, Ground & Port Infrastructure, Prioritization of Travel and Tourism, Tourism Services Infrastructure b. Dependent Variable: Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index Source: Survey data 2015 The value of Durbin-Watson statistics is which is higher than the value of R square (r 2 ) or Adjusted R Square (r 2 ). And also, this value is more than 1. The value of R Square is more than 60% (i.e., 92.0%). All these are the good signs of this model. Due to the presence of these good signs, this model does not suffer from the problem of spuriousness in this model. Thus, meaningless results are avoided from this model of regression because of the absence of this problem. Regression Model ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): The Table - 03 shows the results of ANOVA test. The ANOVA test is used to establish whether the findings of the study might have arisen from a sampling error. Here, it is established whether the regression line of the study is different from zero. If it is, then it is claimed that the findings have not arisen simply from a sampling error. In the table (Table 03 ANOVA), the F and Sig. columns are studied. Here the F value is and the confidence value is equal to (highly significant, p <0.0005). The result is not due to sampling error. That is, the regression statistic is significantly different from zero. It is confident that the results of the regression do not occur by chance. Table 03: Regression Model ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) Model Sum of Mean df Squares Square F Sig. Regression b 1 Residual Total a. Dependent Variable: Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index b. Predictors: (Constant), Cultural Resources & Business Travel, Business Environment, Ground & Port Infrastructure, Prioritization of Travel and Tourism, Tourism Services Infrastructure Source: Data Survey 2015 Further, the Analysis of Variance shows that the regression results are significantly different from zero (F = , p< ). The results of this regression did not occur by chance and are consistent with our research hypothesis the amount of the independent variables such as TI: Tourism Services Infrastructure, GP: Ground & Port Infrastructure, BE: Business Environment, PT: Prioritization of Travel and Tourism and CR: Cultural resources & business travel significantly raises the Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index. That is, the independent variables play significant roles on the dependent variable the Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index. Multiple Regression: The table 04 shows that all the values of coefficients of the multivariate analysis. The regression coefficient is a measure of how strongly each independent variable (also known as predictor variable) predicts the dependent variable. There are two types of regression coefficients - un-standardized coefficients and standardized coefficient, also known as beta value. The un-standardized coefficients can be used in the equation as coefficients of different independent variables along with the constant term to predict the value of dependent variable. The standardized coefficient (beta) is, however, measured in standard deviations. A beta value of 2 associated with a particular independent variable indicates that a change of 1 standard deviation in that particular independent variable will result in a change of 2 standard deviations in the dependent variable (Ajai and Sanjaya, 2008). The dependent variable of this multiple regression model is RR: Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index, and the independent variables are indicators or pillars such as Volume 2 Issue
7 TI: Tourism Services Infrastructure, GP: Ground & Port Infrastructure, BE: Business Environment, PT: Prioritization of Travel and Tourism and CR: Cultural resources & business travel. This multiple regression is subject to the linear model. As shown in table 04, B is the slope of the regression line. The slope of this multiple regression linear line is constant. Therefore, it has the constant value estimated. The coefficient of the slope means that every rise of one unit for the independent variable predicts a rise on the dependent variable. Table - 04: Multiple Regression Model Coefficients Model Un-standardized Coefficients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. B Std. Error Beta (Constant) Tourism Services Infrastructure Ground & Port Infrastructure 1 Business Environment Prioritization of Travel and Tourism Cultural Resources & Business Travel a. Dependent Variable: Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index Source: Data Survey 2015 This multiple regression is subject to the linear model. As shown in table 04, B is the slope of the regression line. The slope of this multiple regression linear line is constant. Therefore, it has the constant value estimated. The coefficient of the slope means that every rise of one unit for the independent variable predicts a fall on the dependent variable. Accordingly, the estimated model of the study is as follows: RR = TI 3.384GP 4.677BE 0.239PT CR According to the above multiple regression function, for each increase of one unit on Business Environment, the regression predicts that the Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index will decrease by around 5 units (4.677). Thus, these two variables are inversely related to each other, that is, the increase in Business Environment will decrease the Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index. For each increase of one unit on Tourism Services Infrastructure, the equation predicts that the Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index will be lower by almost 3 units (3.162). Further, for each increase of one unit on Prioritization of Travel and Tourism and Cultural resources & business travel, the regression predicts that Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index will decrease by units, around 3units (2.922) respectively. And also, all the independent variables are inversely or negatively related to the dependent variable. The most instrumental independent variable in this model is Business Environment as the increase of one unit on Business Environment leads to decrease the Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index by around 5 units (4.677). Further, all the independent variables are having statistically significant relationship between the dependent variable. That is, there is a significant effect of Business Environment (Sig. p < ) on the Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index. The value of probability on this coefficient of independent variable is less than 0.05 (5%). Moreover, all the independent variables are statistically significant to explain the relationship between the dependent variables and the independent variables in this multiple regression model as all the probability value of the independent variables are less than 0.05 (i.e. p = 0.000). This is one of the good sings of this model. Thus, all the independent variables such as Tourism Services Infrastructure, Ground & Port Infrastructure, Business Environment, Prioritization of Travel and Tourism, and Cultural resources & business travel, account for unique variance in the dependent variable Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index. None of the independent variables identified in this study are statistically significant effect on the Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index. In other worlds, there is a zero percent of chance that any effect is spurious in this model. Volume 2 Issue
8 Testing for Multi co linearity : As a rule of thumb, if VIF is greater than VIF is less than 10, there is no problem of multi-co-linearity, that is, it is on the safe grounds free from the multi-co-linearity (Ciaran, et. al, 2009). The unique part of the variance in dependent variable that is explained by each of the independent variables is very less if there is a problem of multi co linearity among the independent variables used in models. Table 05: Testing for Multi co linearity Model Co-linearity Statistics VIF Tourism Services Infrastructure Ground & Port Infrastructure Business Environment Prioritization of Travel and Tourism Cultural Resources & Business Travel a. Dependent Variable: Regional Rank of Tourism Competitiveness Index Source: Data Survey 2015 Table 05 shows the results of the test of the multi-co-linearity problems in the multiple regression model used in this study between the individual independent variables identified from the negative economic impacts of tourism. The value of VIF (Variance inflation Factor) is around 3 which is less than 10. Thus, the overlap between the independent variables is very small. In other words, there is no highly correlated independent variable in this model. Accordingly, there is no any alarm of multi co linearity problem in the whole model. Residual Analysis: The predicted values of the dependent variable are estimated of the most likely average figure the actual cases in the data will not all correspond exactly to what the equation predicts. The predicted values are the fit to the data that the regression has produced. The difference between the values of the dependent variable that are predicted that fit and the actual observed values are the residual, that which is not fit. Figure 01: Histogram of residuals Source: Survey data 2015 In a good fit to the data, the residual differences between the actual, observed values and the predicted values will be homoscedastic (that is, if the intersection point between variables are plotted around the correlation line, they will be normally distributed around the line some will be above the line, some will be below it and more points will be close to the line than far away), normally distributed above and below the predicted value with most differences being fairly small and only a few, if any, being outliers that are far from their predicted values. Volume 2 Issue
9 Figure 01 shows the visual plots of residuals appeared. Accordingly, the residuals are normally distributed around a central point of zero. Figure 02: Normal P-P Plot of Regression Standardized Source: Survey data 2015 The scatter plot of standardized residuals against standardized predicated value takes the form of a straight line running at a 45degree angle from (0, 0) on the lower left to (1.0, 1.0) on the upper right. As observed in Figure 01, the actual plot conforms very closely to this. Therefore, in this model, the residual differences between the actual, observed values and the predicted values are homoscedastic, but not heteroscedastic, normally distributed above and below the predicted value with most differences being fairly small and only a few, if any, being outliers that are far from their predicted values. So that is a good fit to the data. Accordantly, the expected cumulative probability and observed cumulative probability are very closer in the above figure 02. V. FINDINGS AND CONCLUSION There is a negative relationship between the dependent variable and all the independent variables. Business environment vitally plays major roles to influence on the dependent variable. Thus, one unit of increase in the business environment will decrease the regional competitiveness index. It is the most instrumental variable which is contributing to the determination of the regional competitiveness index of the European countries. The Prioritization of Travel and Tourism records the least contribution to the determination of the regional completeness index. All the independent variables other than Prioritization of Travel and Tourism are vital and instrumental together in influencing the dependent variable. But Prioritization of Travel and Tourism is not statistically significant to explain the relationship between the dependent variable and the independent variables. On the regional competitiveness index of the European countries, the common significant contribution of the independent variables is identified on the dependent variable. As a result, all the independent variables are inversely related with the dependent variable. Accordingly, almost 33% of Business Environment has contributed on the regional competitiveness index of the European countries. It is the highest record of the particular independent variable on the European countries so as to lower their competitiveness index in ordering the rank on the regional arena. Around 24% of the Ground & Port Infrastructure which has affected in lowering the ranking position of the countries has contributed secondly on the regional competitiveness index of the countries. Virtually 22% of the contribution of the Tourism Services Infrastructure so as to lower the competitiveness index of the countries has made significant impacts on the ranking position of the countries. Practically and statistically 21% of effects due to the presence of the cultural resources & business travel have contributed to the lowering position in the regional rank of the countries. The promotional strategies implemented by the countries targeting towards the Prioritization of Travel and Tourism has contributed considerably only to 2% in lowering the regional rank of the competitiveness index. It can be concluded from this study that any promotional strategies or policy decisional making in terms of developing business environment which is friendly to the attraction of international tourists to their home countries play Volume 2 Issue
10 the major roles on lowering the regional rank of the countries. The second significant effect on lowering the regional rank of the countries is caused by promoting the Ground & Port Infrastructure. So that any structural changes in terms of targeting the promotion of the ground and port infrastructure with the intention of coming up in the regional rank of these countries can pave the ways to lower the rank in the regional arena. The third is likely from the promotional activities of the Tourism Services Infrastructure which leads to lower the regional rank. The more the presence of services infrastructure as well in this region, the more the regional rank can be lowered down. VI. RECOMMENDATION From this study, it can be persistently recommended that the economies of the guest countries and also the policy makers of the guest countries can be aware of the making strategic planning to promote their countries which can be victorious in lowering their Regional Rank of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index. Accordingly, the researchers of this study persevere on the recommendation to apply the results of this study in their countries. REFERENCE [1] Ajai and Sanjaya (2008), Statistical Method for Practice and Research, Response books, A Division of Sage Publications India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, p [2] Bineswaree Bolaky (2011), Tourism competitiveness in the Caribbean, C E P A L R E V I E W 1 0 4, Available at: http-repositorio.cepal.org-bitstream-handle i_en.pdf-sequence=1 [3] Bojan Krstic, Tanja Stanisic, and Jelena Petrovic (2015),THE ANALYSIS OF TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND SOME WESTERN BALKAN COUNTRIES, SYNTHESIS 2015, Tourism and hospitality, Available at: [4] Ciaran and Robert Miller (2009), SPSS for Social Scientist, Palgrave Macmillan, New Delhi, p. 212 [5] Maharaj. S, Balkaran. R (2014), A comparative analysis of the South African and Global Tourism Competitiveness models with the aim of enhancing a sustainable model for South Africa, Journal of Economics and Behavioral Studies, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp , Apr 2014 (ISSN: ), Available at: [6] Mihai Croitoru (2011), Tourism Competitiveness Index An Empirical Analysis Romania vs. Bulgaria, Theoretical and Applied Economics, Volume XVIII (2011), No. 9(562), pp , Available at: [7] Roberto Crotti and Tiffany Misrahi (2015), The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2015, World Economic Forum, Available at: [8] Shenol Chavus, Azamat Maksudunov and Muratali Abdyldaev, (2012), Tourism Competitiveness in Central Asian Turkish Republics: An Assessment in Terms of Entrepreneurship, International Journal of Business and Social Science, Vol. 3 No. 23; December 2012, Available at: Volume 2 Issue
PLUTO The Transport Response to the National Planning Framework. Dr. Aoife O Grady Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport
 PLUTO 2040 The Transport Response to the National Planning Framework Dr. Aoife O Grady Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport Dublin Economics Workshop 15 th September 2018 The Story of Pluto National
PLUTO 2040 The Transport Response to the National Planning Framework Dr. Aoife O Grady Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport Dublin Economics Workshop 15 th September 2018 The Story of Pluto National
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 30 August 2012 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee Working Party on Rail Transport Sixty-sixth session
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 30 August 2012 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee Working Party on Rail Transport Sixty-sixth session
Trends in Human Development Index of European Union
 Trends in Human Development Index of European Union Department of Statistics, Hacettepe University, Beytepe, Ankara, Turkey spxl@hacettepe.edu.tr, deryacal@hacettepe.edu.tr Abstract: The Human Development
Trends in Human Development Index of European Union Department of Statistics, Hacettepe University, Beytepe, Ankara, Turkey spxl@hacettepe.edu.tr, deryacal@hacettepe.edu.tr Abstract: The Human Development
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the WHO European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the WHO European Region Table 1: Reported cases for the period January December 2018 (data as of 01 February 2019)
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the WHO European Region Table 1: Reported cases for the period January December 2018 (data as of 01 February 2019)
Gravity Analysis of Regional Economic Interdependence: In case of Japan
 Prepared for the 21 st INFORUM World Conference 26-31 August 2013, Listvyanka, Russia Gravity Analysis of Regional Economic Interdependence: In case of Japan Toshiaki Hasegawa Chuo University Tokyo, JAPAN
Prepared for the 21 st INFORUM World Conference 26-31 August 2013, Listvyanka, Russia Gravity Analysis of Regional Economic Interdependence: In case of Japan Toshiaki Hasegawa Chuo University Tokyo, JAPAN
AD HOC DRAFTING GROUP ON TRANSNATIONAL ORGANISED CRIME (PC-GR-COT) STATUS OF RATIFICATIONS BY COUNCIL OF EUROPE MEMBER STATES
 Strasbourg, 29 May 2015 PC-GR-COT (2013) 2 EN_Rev AD HOC DRAFTING GROUP ON TRANSNATIONAL ORGANISED CRIME (PC-GR-COT) STATUS OF RATIFICATIONS BY COUNCIL OF EUROPE MEMBER STATES TO THE UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION
Strasbourg, 29 May 2015 PC-GR-COT (2013) 2 EN_Rev AD HOC DRAFTING GROUP ON TRANSNATIONAL ORGANISED CRIME (PC-GR-COT) STATUS OF RATIFICATIONS BY COUNCIL OF EUROPE MEMBER STATES TO THE UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION
A Markov system analysis application on labour market dynamics: The case of Greece
 + A Markov system analysis application on labour market dynamics: The case of Greece Maria Symeonaki Glykeria Stamatopoulou This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research
+ A Markov system analysis application on labour market dynamics: The case of Greece Maria Symeonaki Glykeria Stamatopoulou This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported cases for the period June 207 May 208 (data as of 0 July 208) Population in
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported cases for the period June 207 May 208 (data as of 0 July 208) Population in
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported measles cases for the period January December 207 (data as of 02 February
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported measles cases for the period January December 207 (data as of 02 February
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the WHO European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the WHO European Region Table : Reported cases for the period November 207 October 208 (data as of 30 November
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the WHO European Region Table : Reported cases for the period November 207 October 208 (data as of 30 November
Publication Date: 15 Jan 2015 Effective Date: 12 Jan 2015 Addendum 6 to the CRI Technical Report (Version: 2014, Update 1)
 Publication Date: 15 Jan 2015 Effective Date: 12 Jan 2015 This document updates the Technical Report (Version: 2014, Update 1) and details (1) Replacement of interest rates, (2) CRI coverage expansion,
Publication Date: 15 Jan 2015 Effective Date: 12 Jan 2015 This document updates the Technical Report (Version: 2014, Update 1) and details (1) Replacement of interest rates, (2) CRI coverage expansion,
Modelling structural change using broken sticks
 Modelling structural change using broken sticks Paul White, Don J. Webber and Angela Helvin Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of the West of England, Bristol, UK Department of Economics,
Modelling structural change using broken sticks Paul White, Don J. Webber and Angela Helvin Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of the West of England, Bristol, UK Department of Economics,
40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth
 EuroGeoSurveys The role of EuroGeoSurveys in Europe-Africa geoscientific cooperation 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth EuroGeoSurveys 32 Albania Lithuania Austria Luxembourg Belgium The Netherlands
EuroGeoSurveys The role of EuroGeoSurveys in Europe-Africa geoscientific cooperation 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth EuroGeoSurveys 32 Albania Lithuania Austria Luxembourg Belgium The Netherlands
EuroGeoSurveys & ASGMI The Geological Surveys of Europe and IberoAmerica
 EuroGeoSurveys & ASGMI The Geological Surveys of Europe and IberoAmerica Geological Surveys, what role? Legal mandate for data & information: Research Collection Management Interpretation/transformation
EuroGeoSurveys & ASGMI The Geological Surveys of Europe and IberoAmerica Geological Surveys, what role? Legal mandate for data & information: Research Collection Management Interpretation/transformation
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported measles cases for the period July 207 June 208 (data as of August 208) Population
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported measles cases for the period July 207 June 208 (data as of August 208) Population
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported cases for the period September 207 August 208 (data as of 0 October 208) Population
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected Vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table : Reported cases for the period September 207 August 208 (data as of 0 October 208) Population
WHO EpiData. A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region
 A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table 1: Reported measles cases for the 12-month period February 2016 January 2017 (data as
A monthly summary of the epidemiological data on selected vaccine preventable diseases in the European Region Table 1: Reported measles cases for the 12-month period February 2016 January 2017 (data as
Structural equation modeling in evaluation of technological potential of European Union countries in the years
 Structural equation modeling in evaluation of technological potential of European Union countries in the years 2008-2012 Adam P. Balcerzak 1, Michał Bernard Pietrzak 2 Abstract The abilities of countries
Structural equation modeling in evaluation of technological potential of European Union countries in the years 2008-2012 Adam P. Balcerzak 1, Michał Bernard Pietrzak 2 Abstract The abilities of countries
EUMETSAT. A global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe. Presentation for the Spanish Industry Day Madrid, 15 March 2012
 EUMETSAT A global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe Presentation for the Spanish Industry Day Madrid, Angiolo Rolli EUMETSAT Director of Administration EUMETSAT objectives The primary
EUMETSAT A global operational satellite agency at the heart of Europe Presentation for the Spanish Industry Day Madrid, Angiolo Rolli EUMETSAT Director of Administration EUMETSAT objectives The primary
How Well Are Recessions and Recoveries Forecast? Prakash Loungani, Herman Stekler and Natalia Tamirisa
 How Well Are Recessions and Recoveries Forecast? Prakash Loungani, Herman Stekler and Natalia Tamirisa 1 Outline Focus of the study Data Dispersion and forecast errors during turning points Testing efficiency
How Well Are Recessions and Recoveries Forecast? Prakash Loungani, Herman Stekler and Natalia Tamirisa 1 Outline Focus of the study Data Dispersion and forecast errors during turning points Testing efficiency
APPLYING BORDA COUNT METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE BEST WEEE MANAGEMENT IN EUROPE. Maria-Loredana POPESCU 1
 APPLYING BORDA COUNT METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE BEST MANAGEMENT IN EUROPE Maria-Loredana POPESCU 1 ABSTRACT This article presents the Borda Count method and its application for ranking the regarding the
APPLYING BORDA COUNT METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE BEST MANAGEMENT IN EUROPE Maria-Loredana POPESCU 1 ABSTRACT This article presents the Borda Count method and its application for ranking the regarding the
Navigable maritime and river waterways in the seaside - Danube Delta area and the connected rural development
 SUMMARY OF Ph-D Thesis, with title RESEARCH STUDIES ON MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT OF MARITIME AND RIVER TRANSPORT ACTIVITY IN THE COASTAL AND DANUBE DELTA AREA FROM AN ENVIROMENTAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL PERSPECTIVE
SUMMARY OF Ph-D Thesis, with title RESEARCH STUDIES ON MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT OF MARITIME AND RIVER TRANSPORT ACTIVITY IN THE COASTAL AND DANUBE DELTA AREA FROM AN ENVIROMENTAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL PERSPECTIVE
EuroGeoSurveys An Introduction
 EGS -ASGMI Workshop, Madrid, 2015 EuroGeoSurveys An Introduction 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth Click to edit Master title Albania style EuroGeoSurveys Austria Lithuania Luxembourg Belgium
EGS -ASGMI Workshop, Madrid, 2015 EuroGeoSurveys An Introduction 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth Click to edit Master title Albania style EuroGeoSurveys Austria Lithuania Luxembourg Belgium
The School Geography Curriculum in European Geography Education. Similarities and differences in the United Europe.
 The School Geography Curriculum in European Geography Education. Similarities and differences in the United Europe. Maria Rellou and Nikos Lambrinos Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Dept.of Primary
The School Geography Curriculum in European Geography Education. Similarities and differences in the United Europe. Maria Rellou and Nikos Lambrinos Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Dept.of Primary
Regional economy upgrading triple helix at work? Some selected cases from the Czech republic (and Central Eastern Europe) Pavel Ptáček
 Regional economy upgrading triple helix at work? Some selected cases from the Czech republic (and Central Eastern Europe) Pavel Ptáček Department of Geography Palacký University in Olomouc, Czech republic
Regional economy upgrading triple helix at work? Some selected cases from the Czech republic (and Central Eastern Europe) Pavel Ptáček Department of Geography Palacký University in Olomouc, Czech republic
Testing the Validity of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index in the World Economic Forum with Classical and Fuzzy Data Envelopment Analyses
 PTiR 2013;4;121-128 121 Hatice Ozkoc, Hakan Bakan, Ercan Baldemi r Muğla Sitki Koçman Üniversitesi, Turkey Testing the Validity of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index in the World Economic Forum
PTiR 2013;4;121-128 121 Hatice Ozkoc, Hakan Bakan, Ercan Baldemi r Muğla Sitki Koçman Üniversitesi, Turkey Testing the Validity of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index in the World Economic Forum
ACCESSIBILITY TO SERVICES IN REGIONS AND CITIES: MEASURES AND POLICIES NOTE FOR THE WPTI WORKSHOP, 18 JUNE 2013
 ACCESSIBILITY TO SERVICES IN REGIONS AND CITIES: MEASURES AND POLICIES NOTE FOR THE WPTI WORKSHOP, 18 JUNE 2013 1. Significant differences in the access to basic and advanced services, such as transport,
ACCESSIBILITY TO SERVICES IN REGIONS AND CITIES: MEASURES AND POLICIES NOTE FOR THE WPTI WORKSHOP, 18 JUNE 2013 1. Significant differences in the access to basic and advanced services, such as transport,
The ESPON Programme. Goals Main Results Future
 The ESPON Programme Goals Main Results Future Structure 1. Goals Objectives and expectations Participation, organisation and networking Themes addressed in the applied research undertaken in ESPON projects
The ESPON Programme Goals Main Results Future Structure 1. Goals Objectives and expectations Participation, organisation and networking Themes addressed in the applied research undertaken in ESPON projects
Annotated Exam of Statistics 6C - Prof. M. Romanazzi
 1 Università di Venezia - Corso di Laurea Economics & Management Annotated Exam of Statistics 6C - Prof. M. Romanazzi March 17th, 2015 Full Name Matricola Total (nominal) score: 30/30 (2/30 for each question).
1 Università di Venezia - Corso di Laurea Economics & Management Annotated Exam of Statistics 6C - Prof. M. Romanazzi March 17th, 2015 Full Name Matricola Total (nominal) score: 30/30 (2/30 for each question).
The trade dispute between the US and China Who wins? Who loses?
 1 Munich, Jan 10 th, 2019 The trade dispute between the US and China Who wins? Who loses? by Gabriel Felbermayr and Marina Steininger This report offers a brief, quantitative analysis of the potential
1 Munich, Jan 10 th, 2019 The trade dispute between the US and China Who wins? Who loses? by Gabriel Felbermayr and Marina Steininger This report offers a brief, quantitative analysis of the potential
Variance estimation on SILC based indicators
 Variance estimation on SILC based indicators Emilio Di Meglio Eurostat emilio.di-meglio@ec.europa.eu Guillaume Osier STATEC guillaume.osier@statec.etat.lu 3rd EU-LFS/EU-SILC European User Conference 1
Variance estimation on SILC based indicators Emilio Di Meglio Eurostat emilio.di-meglio@ec.europa.eu Guillaume Osier STATEC guillaume.osier@statec.etat.lu 3rd EU-LFS/EU-SILC European User Conference 1
Methodological Notes research objectives research hypotheses observation units
 A ASSESSMET OF THE RELATIOSHIPS BETWEE THE CULTURAL HERITAGE, TRAVEL AD TOURISM, AD SUSTAIABLE DEVELOPMET I THE CETRAL AD EASTER EUROPEA COUTRIES Dugulan Diana Academy of Economic Studies in Bucharest
A ASSESSMET OF THE RELATIOSHIPS BETWEE THE CULTURAL HERITAGE, TRAVEL AD TOURISM, AD SUSTAIABLE DEVELOPMET I THE CETRAL AD EASTER EUROPEA COUTRIES Dugulan Diana Academy of Economic Studies in Bucharest
ESPON evidence on European cities and metropolitan areas
 BEST METROPOLISES Final Conference 18 April 2013, Warsaw ESPON evidence on European cities and metropolitan areas Michaela Gensheimer Structure of Intervention Content Part I: What is the ESPON 2013 Programme?
BEST METROPOLISES Final Conference 18 April 2013, Warsaw ESPON evidence on European cities and metropolitan areas Michaela Gensheimer Structure of Intervention Content Part I: What is the ESPON 2013 Programme?
Drawing the European map
 Welcome in Europe Objectif: mieux connaitre l'espace géographique et civilisationnel européen Opérer la distinction entre pays d'europe et pays de l'union Européenne Tâche intermédiaire: restitution de
Welcome in Europe Objectif: mieux connaitre l'espace géographique et civilisationnel européen Opérer la distinction entre pays d'europe et pays de l'union Européenne Tâche intermédiaire: restitution de
Weekly price report on Pig carcass (Class S, E and R) and Piglet prices in the EU. Carcass Class S % + 0.3% % 98.
 Weekly price report on Pig carcass (Class S, E and R) and Piglet prices in the EU Disclaimer Please note that EU prices for pig meat, are averages of the national prices communicated by Member States weighted
Weekly price report on Pig carcass (Class S, E and R) and Piglet prices in the EU Disclaimer Please note that EU prices for pig meat, are averages of the national prices communicated by Member States weighted
Part A: Salmonella prevalence estimates. (Question N EFSA-Q ) Adopted by The Task Force on 28 March 2007
 The EFSA Journal (2007) 98, 1-85 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in broiler flocks of Gallus gallus, in the EU,
The EFSA Journal (2007) 98, 1-85 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in broiler flocks of Gallus gallus, in the EU,
Discussion Papers on Entrepreneurship, Growth and Public Policy
 Discussion Papers on Entrepreneurship, Growth and Public Policy # 2706 An Empirical Relationship between Entrepreneurship and FDI. A Note. by Miltiades N. Georgiou University of Thessaly Number of Pages:
Discussion Papers on Entrepreneurship, Growth and Public Policy # 2706 An Empirical Relationship between Entrepreneurship and FDI. A Note. by Miltiades N. Georgiou University of Thessaly Number of Pages:
The Joint Programming Initiative on Cultural Heritage (JPICH): European perspective
 COPERNICUS FOR CULTURAL HERITAGE Copernicus User Forum Industry Workshop Brussels, 24 April 2017 The Joint Programming Initiative on Cultural Heritage (JPICH): European perspective Cristina Sabbioni CNR,
COPERNICUS FOR CULTURAL HERITAGE Copernicus User Forum Industry Workshop Brussels, 24 April 2017 The Joint Programming Initiative on Cultural Heritage (JPICH): European perspective Cristina Sabbioni CNR,
The EuCheMS Division Chemistry and the Environment EuCheMS/DCE
 The EuCheMS Division Chemistry and the Environment EuCheMS/DCE EuCheMS Division on Chemistry and the Environment was formed as a FECS Working Party in 1977. Membership: 37 members from 34 countries. Countries
The EuCheMS Division Chemistry and the Environment EuCheMS/DCE EuCheMS Division on Chemistry and the Environment was formed as a FECS Working Party in 1977. Membership: 37 members from 34 countries. Countries
Weighted Voting Games
 Weighted Voting Games Gregor Schwarz Computational Social Choice Seminar WS 2015/2016 Technische Universität München 01.12.2015 Agenda 1 Motivation 2 Basic Definitions 3 Solution Concepts Core Shapley
Weighted Voting Games Gregor Schwarz Computational Social Choice Seminar WS 2015/2016 Technische Universität München 01.12.2015 Agenda 1 Motivation 2 Basic Definitions 3 Solution Concepts Core Shapley
EuroGeoSurveys. Minerals, metals and mining statistics: The role of Geological Surveys in building continental-scale official data sets
 EuroGeoSurveys Minerals, metals and mining statistics: The role of Geological Surveys in building continental-scale official data sets 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth 1 EuroGeoSurveys 37 Geological
EuroGeoSurveys Minerals, metals and mining statistics: The role of Geological Surveys in building continental-scale official data sets 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth 1 EuroGeoSurveys 37 Geological
Briefing Notes for World Hydrography Day
 Briefing Notes for World Hydrography Day - 2017 Mapping our seas, oceans and waterways - more important than ever Purpose of World Hydrography Day In 2005, the General Assembly of the United Nations (UN)
Briefing Notes for World Hydrography Day - 2017 Mapping our seas, oceans and waterways - more important than ever Purpose of World Hydrography Day In 2005, the General Assembly of the United Nations (UN)
Community Engagement in Cultural Routes SiTI Higher Institute on Territorial Systems for Innovation Sara Levi Sacerdotti
 Transnational Workshop Wroclaw, 7th-8th December 2016 Community Engagement in Cultural Routes SiTI Higher Institute on Territorial Systems for Innovation Sara Levi Sacerdotti levi@siti.polito.it TAKING
Transnational Workshop Wroclaw, 7th-8th December 2016 Community Engagement in Cultural Routes SiTI Higher Institute on Territorial Systems for Innovation Sara Levi Sacerdotti levi@siti.polito.it TAKING
Figure 1. Time Series Plot of arrivals from Western Europe
 FORECASTING TOURIST ARRIVALS TO SRI LANKA FROM WESTERN EUROPE K. M. U. B. Konarasinghe 1 * 1 Institute of Mathematics & Management, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka INTRODUCTION Sri Lanka was re-emerging after defeating
FORECASTING TOURIST ARRIVALS TO SRI LANKA FROM WESTERN EUROPE K. M. U. B. Konarasinghe 1 * 1 Institute of Mathematics & Management, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka INTRODUCTION Sri Lanka was re-emerging after defeating
The National Spatial Strategy
 Purpose of this Consultation Paper This paper seeks the views of a wide range of bodies, interests and members of the public on the issues which the National Spatial Strategy should address. These views
Purpose of this Consultation Paper This paper seeks the views of a wide range of bodies, interests and members of the public on the issues which the National Spatial Strategy should address. These views
Part 2. Cost-effective Control of Acidification and Ground-level Ozone
 8 th INTERIM REPORT Part 2 Cost-effective Control of Acidification and Ground-level Ozone Markus Amann, Imrich Bertok, Janusz Cofala, Frantisek Gyarfas, Chris Heyes, Zbigniew Klimont, Wolfgang Schöpp March
8 th INTERIM REPORT Part 2 Cost-effective Control of Acidification and Ground-level Ozone Markus Amann, Imrich Bertok, Janusz Cofala, Frantisek Gyarfas, Chris Heyes, Zbigniew Klimont, Wolfgang Schöpp March
DEPENDENCE OF THE LOCATION OF THE EUROPEAN CAPITALS AND COMPETITIVENESS OF THE REGIONS
 DEPENDENCE OF THE LOCATION OF THE EUROPEAN CAPITALS AND COMPETITIVENESS OF THE REGIONS Pawel Dobrzanski Abstract Competitiveness is one of the most important topics of modern economics. Current research
DEPENDENCE OF THE LOCATION OF THE EUROPEAN CAPITALS AND COMPETITIVENESS OF THE REGIONS Pawel Dobrzanski Abstract Competitiveness is one of the most important topics of modern economics. Current research
ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT
 ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Pursuant to Article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation
ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Pursuant to Article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation
Final report for the Expert Group on the Integration of Statistical and Geospatial Information, May 2015
 Final report for the Expert Group on the Integration of Statistical and Geospatial Information, May 2015 Global geographic classification and geocoding practices Executive summary This final report was
Final report for the Expert Group on the Integration of Statistical and Geospatial Information, May 2015 Global geographic classification and geocoding practices Executive summary This final report was
Bilateral Labour Agreements, 2004
 Guest Austria Canada Turkey ( 64) Canada, Czech Republic, Hungary ( 98), Belgium Italy ( 46, 54), Turkey ( 64) Bulgaria ( 99), Pol (02) Germany ( 91) Bulgaria ( 99), Mongolia ( 99), Pol ( 92), Russia (
Guest Austria Canada Turkey ( 64) Canada, Czech Republic, Hungary ( 98), Belgium Italy ( 46, 54), Turkey ( 64) Bulgaria ( 99), Pol (02) Germany ( 91) Bulgaria ( 99), Mongolia ( 99), Pol ( 92), Russia (
Securing EUMETSAT s Mission from an Evolving Space Environment
 Securing EUMETSAT s Mission from an Evolving Space Environment ESPI 12 th Autumn Conference Andrew Monham 1 EUMETSAT: Intergovernmental Organisation of 30 Member States Presentation Contents AUSTRIA BELGIU
Securing EUMETSAT s Mission from an Evolving Space Environment ESPI 12 th Autumn Conference Andrew Monham 1 EUMETSAT: Intergovernmental Organisation of 30 Member States Presentation Contents AUSTRIA BELGIU
About the Authors Geography and Tourism: The Attraction of Place p. 1 The Elements of Geography p. 2 Themes of Geography p. 4 Location: The Where of
 Preface p. ix About the Authors p. xi Geography and Tourism: The Attraction of Place p. 1 The Elements of Geography p. 2 Themes of Geography p. 4 Location: The Where of Geography p. 4 Place and Space:
Preface p. ix About the Authors p. xi Geography and Tourism: The Attraction of Place p. 1 The Elements of Geography p. 2 Themes of Geography p. 4 Location: The Where of Geography p. 4 Place and Space:
Does socio-economic indicator influent ICT variable? II. Method of data collection, Objective and data gathered
 Does socio-economic indicator influent ICT variable? I. Introduction This paper obtains a model of relationship between ICT indicator and macroeconomic indicator in a country. Modern economy paradigm assumes
Does socio-economic indicator influent ICT variable? I. Introduction This paper obtains a model of relationship between ICT indicator and macroeconomic indicator in a country. Modern economy paradigm assumes
Composition of capital NO051
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital ES060 ES060 POWSZECHNAES060 BANCO BILBAO VIZCAYA ARGENTARIA S.A. (BBVA)
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital CY007 CY007 POWSZECHNACY007 BANK OF CYPRUS PUBLIC CO LTD
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital DE025
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital LU045 LU045 POWSZECHNALU045 BANQUE ET CAISSE D'EPARGNE DE L'ETAT
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital CY006 CY006 POWSZECHNACY006 CYPRUS POPULAR BANK PUBLIC CO LTD
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital DE028 DE028 POWSZECHNADE028 DekaBank Deutsche Girozentrale, Frankfurt
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital FR013
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital FR015
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital DE017 DE017 POWSZECHNADE017 DEUTSCHE BANK AG
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital ES059
 Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
Composition of capital POWSZECHNA (in million Euro) Capital position CRD3 rules A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds without hybrid instruments and government support measures other than
04 June Dim A W V Total. Total Laser Met
 4 June 218 Member State State as on 4 June 218 Acronyms are listed in the last page of this document. AUV Mass and Related Quantities Length PR T TF EM Mass Dens Pres F Torq Visc H Grav FF Dim A W V Total
4 June 218 Member State State as on 4 June 218 Acronyms are listed in the last page of this document. AUV Mass and Related Quantities Length PR T TF EM Mass Dens Pres F Torq Visc H Grav FF Dim A W V Total
CropCast Europe Weekly Report
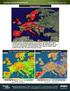 CropCast Europe Weekly Report Kenny Miller Monday, June 05, 2017 Europe Hot Spots Abundant showers should ease dryness across northern and central UK as well as across western Norway and Sweden. Improvements
CropCast Europe Weekly Report Kenny Miller Monday, June 05, 2017 Europe Hot Spots Abundant showers should ease dryness across northern and central UK as well as across western Norway and Sweden. Improvements
NASDAQ OMX Copenhagen A/S. 3 October Jyske Bank meets 9% Core Tier 1 ratio in EU capital exercise
 NASDAQ OMX Copenhagen A/S JYSKE BANK Vestergade 8-16 DK-8600 Silkeborg Tel. +45 89 89 89 89 Fax +45 89 89 19 99 A/S www. jyskebank.dk E-mail: jyskebank@jyskebank.dk Business Reg. No. 17616617 - meets 9%
NASDAQ OMX Copenhagen A/S JYSKE BANK Vestergade 8-16 DK-8600 Silkeborg Tel. +45 89 89 89 89 Fax +45 89 89 19 99 A/S www. jyskebank.dk E-mail: jyskebank@jyskebank.dk Business Reg. No. 17616617 - meets 9%
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules)
 Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules)
 Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules)
 Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules)
 Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules)
 Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules)
 Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Composition of capital as of 30 September 2011 (CRD3 rules) Capital position CRD3 rules September 2011 Million EUR % RWA References to COREP reporting A) Common equity before deductions (Original own funds
Third Annual Climate Science and Policy Conference, UC Santa Cruz: Earth s Climate Future: Unchartered Territory
 Third Annual Climate Science and Policy Conference, UC Santa Cruz: Earth s Climate Future: Unchartered Territory Geopolitics of Climate Change: The Arctic Case Steven L. Lamy, PhD Vice Dean for Academic
Third Annual Climate Science and Policy Conference, UC Santa Cruz: Earth s Climate Future: Unchartered Territory Geopolitics of Climate Change: The Arctic Case Steven L. Lamy, PhD Vice Dean for Academic
EUROCONTROL. Short-Term Forecast. May Flight Movements EUROCONTROL
 EUROCONTROL Short-Term Forecast May 2010 Flight Movements 2010-2011 EUROCONTROL v1.0 31/5/10 EUROCONTROL Short-Term Forecast, May 2010. Summary: Growth, Ash and Sovereign Debt: a fragile recovery. The
EUROCONTROL Short-Term Forecast May 2010 Flight Movements 2010-2011 EUROCONTROL v1.0 31/5/10 EUROCONTROL Short-Term Forecast, May 2010. Summary: Growth, Ash and Sovereign Debt: a fragile recovery. The
International Economic Geography- Introduction
 International Economic Geography- Introduction dr hab. Bart Rokicki Chair of Macroeconomics and Foreign Trade Theory Faculty of Economic Sciences, University of Warsaw Course structure Introduction LocationtheoryI
International Economic Geography- Introduction dr hab. Bart Rokicki Chair of Macroeconomics and Foreign Trade Theory Faculty of Economic Sciences, University of Warsaw Course structure Introduction LocationtheoryI
SUSTAINABLE TOURISM ASSESSMENT INDICATORS THE CASE OF ARMENIA. Hasmik Amiryan Polytechnic Institute of Viana do Castelo
 SUSTAINABLE TOURISM ASSESSMENT INDICATORS THE CASE OF ARMENIA Hasmik Amiryan Polytechnic Institute of Viana do Castelo Introduction to the Research 1. Research Problem 2. Conceptual Framework 3. Background
SUSTAINABLE TOURISM ASSESSMENT INDICATORS THE CASE OF ARMENIA Hasmik Amiryan Polytechnic Institute of Viana do Castelo Introduction to the Research 1. Research Problem 2. Conceptual Framework 3. Background
Strengthening the cooperation in the region: Carpathian, Tisa,, Danube and Black Sea areas
 Strengthening the cooperation in the region: Carpathian, Tisa,, Danube and Black Sea areas 14th October 2009 SEE Annual Conference Advancing development through transnational cooperation in South East
Strengthening the cooperation in the region: Carpathian, Tisa,, Danube and Black Sea areas 14th October 2009 SEE Annual Conference Advancing development through transnational cooperation in South East
RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES FOR LANDSLIDES
 RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES FOR LANDSLIDES Jean-Philippe MALET Olivier MAQUAIRE CNRS & CERG. Welcome to Paris! 1 Landslide RAMs Landslide RAM A method based on the use of available information to estimate
RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES FOR LANDSLIDES Jean-Philippe MALET Olivier MAQUAIRE CNRS & CERG. Welcome to Paris! 1 Landslide RAMs Landslide RAM A method based on the use of available information to estimate
1. Demand for property on the coast
 1. Demand for property on the coast Key message Irrespective of density and location, population in Europe in general tends to concentrate in coastal areas. Detailed spatial elaboration of processes shows
1. Demand for property on the coast Key message Irrespective of density and location, population in Europe in general tends to concentrate in coastal areas. Detailed spatial elaboration of processes shows
UNCTAD Single-year Expert Meeting on Tourism s Contribution to Sustainable Development
 UNCTAD Single-year Expert Meeting on Tourism s Contribution to Sustainable Development Geneva, Palais des Nations, Salle XXVI, 14-15 March 2013 Zoritsa Urosevic Head, Institutional & Corporate Relations,
UNCTAD Single-year Expert Meeting on Tourism s Contribution to Sustainable Development Geneva, Palais des Nations, Salle XXVI, 14-15 March 2013 Zoritsa Urosevic Head, Institutional & Corporate Relations,
Canadian Imports of Honey
 of 0409000029 - Honey, natural, in containers of a weight > 5 kg, nes (Kilogram) Argentina 236,716 663,087 2,160,216 761,990 35.27% 202.09% /0 76,819 212,038 717,834 257,569 35.88% 205.69% /0 United States
of 0409000029 - Honey, natural, in containers of a weight > 5 kg, nes (Kilogram) Argentina 236,716 663,087 2,160,216 761,990 35.27% 202.09% /0 76,819 212,038 717,834 257,569 35.88% 205.69% /0 United States
United Nations Environment Programme
 UNITED NATIONS United Nations Environment Programme Distr. GENERAL 13 April 2016 EP ORIGINAL: ENGLISH EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE OF THE MULTILATERAL FUND FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL Seventy-sixth
UNITED NATIONS United Nations Environment Programme Distr. GENERAL 13 April 2016 EP ORIGINAL: ENGLISH EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE OF THE MULTILATERAL FUND FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL Seventy-sixth
Lecture 9: Location Effects, Economic Geography and Regional Policy
 Lecture 9: Location Effects, Economic Geography and Regional Policy G. Di Bartolomeo Index, EU-25 = 100 < 30 30-50 50-75 75-100 100-125 >= 125 Canarias (E) Guadeloupe Martinique RÈunion (F) (F) (F) Guyane
Lecture 9: Location Effects, Economic Geography and Regional Policy G. Di Bartolomeo Index, EU-25 = 100 < 30 30-50 50-75 75-100 100-125 >= 125 Canarias (E) Guadeloupe Martinique RÈunion (F) (F) (F) Guyane
CLUSTERS INFLUENCE ON COMPETITIVENESS. EVIDENCES FROM EUROPEAN UNION COUNTRIES
 CLUSTERS INFLUENCE ON COMPETITIVENESS. EVIDENCES FROM EUROPEAN UNION COUNTRIES Diana Claudia SALA 1 Mădălina Dumitrița MATICIUC 2 Valentin Partenie MUNTEANU 3 ABSTRACT Lately, The European Union has established
CLUSTERS INFLUENCE ON COMPETITIVENESS. EVIDENCES FROM EUROPEAN UNION COUNTRIES Diana Claudia SALA 1 Mădălina Dumitrița MATICIUC 2 Valentin Partenie MUNTEANU 3 ABSTRACT Lately, The European Union has established
Assessment and Improvement of Methodologies used for GHG Projections
 Assessment and Improvement of Methodologies used for GHG Projections Jan Duerinck Etsap workshop 3 July 2008 Paris Who is using Markal and how Jan Duerinck Etsap workshop 3 July 2008 Paris 1 Outline of
Assessment and Improvement of Methodologies used for GHG Projections Jan Duerinck Etsap workshop 3 July 2008 Paris Who is using Markal and how Jan Duerinck Etsap workshop 3 July 2008 Paris 1 Outline of
OPINION. Results of EU Structural Policy in NSPA
 OPINION on the future European Cohesion Policy of the Northern Sparsely Populated Areas (NSPA) of Finland and Sweden with the contribution of North Norway The remote Northern Sparsely Populated Areas (NSPA)
OPINION on the future European Cohesion Policy of the Northern Sparsely Populated Areas (NSPA) of Finland and Sweden with the contribution of North Norway The remote Northern Sparsely Populated Areas (NSPA)
Sustainability of balancing item of balance of payment for OECD countries: evidence from Fourier Unit Root Tests
 Theoretical and Applied Economics FFet al Volume XXII (2015), No. 3(604), Autumn, pp. 93-100 Sustainability of balancing item of balance of payment for OECD countries: evidence from Fourier Unit Root Tests
Theoretical and Applied Economics FFet al Volume XXII (2015), No. 3(604), Autumn, pp. 93-100 Sustainability of balancing item of balance of payment for OECD countries: evidence from Fourier Unit Root Tests
Entrepreneurship on islands and other peripheral regions. Specific Contract No 6511 implementing Framework contract No CDR/DE/16/2015/
 Entrepreneurship on islands and other peripheral regions Specific Contract No 6511 implementing Framework contract No CDR/DE/16/2015/ Aims of this study: To analyse the particular challenges and obstacles
Entrepreneurship on islands and other peripheral regions Specific Contract No 6511 implementing Framework contract No CDR/DE/16/2015/ Aims of this study: To analyse the particular challenges and obstacles
The view of Europaforum Northern Sweden concerning the future of EU cohesion policy
 Northern Sweden 2008-01-31 The view of Europaforum Northern Sweden concerning the future of EU cohesion policy Europaforum Northern Sweden Europaforum Northern Sweden is a partnership and network for councillors
Northern Sweden 2008-01-31 The view of Europaforum Northern Sweden concerning the future of EU cohesion policy Europaforum Northern Sweden Europaforum Northern Sweden is a partnership and network for councillors
International Student Achievement in Mathematics
 Chapter 1 International Student Achievement in Mathematics Chapter 1 contains the TIMSS 2007 achievement results for fourth and eighth grade students in mathematics for each of the participating countries
Chapter 1 International Student Achievement in Mathematics Chapter 1 contains the TIMSS 2007 achievement results for fourth and eighth grade students in mathematics for each of the participating countries
THE EFFECTS OF WEATHER CHANGES ON NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION
 Geosciences and Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 2 (2012), pp. 303 314. THE EFFECTS OF WEATHER CHANGES ON NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION LÁSZLÓ TIHANYI 1 ISTVÁN SZUNYOG 2 Petroleum and Natural Gas Institute, University
Geosciences and Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 2 (2012), pp. 303 314. THE EFFECTS OF WEATHER CHANGES ON NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION LÁSZLÓ TIHANYI 1 ISTVÁN SZUNYOG 2 Petroleum and Natural Gas Institute, University
C o p e r n i c u s M a r i n e S e r v i c e i n s u p p o r t t o s u s t a i n a b l e B l u e G r o w t h
 Implemented by C o p e r n i c u s M a r i n e S e r v i c e i n s u p p o r t t o s u s t a i n a b l e B l u e G r o w t h European Commission, DG MARE 19 Januray 2018 C O P E R N I C U S I N B R I E
Implemented by C o p e r n i c u s M a r i n e S e r v i c e i n s u p p o r t t o s u s t a i n a b l e B l u e G r o w t h European Commission, DG MARE 19 Januray 2018 C O P E R N I C U S I N B R I E
Governments that have requested pre-export notifications pursuant to article 12, paragraph 10 (a), of the 1988 Convention
 Annex X Governments that have requested pre-export notifications pursuant to article 12, paragraph 10 (a), of the 1988 Convention 1. Governments of all exporting countries and territories are reminded
Annex X Governments that have requested pre-export notifications pursuant to article 12, paragraph 10 (a), of the 1988 Convention 1. Governments of all exporting countries and territories are reminded
BOOK REVIEWS. ESPON Atlas: Territorial Dimensions of the Europe 2020 Strategy. ESPON 2013 Programme, Luxembourg, 2013, 66 p. ISBN
 BOOK REVIEWS Journal of Urban and Regional Analysis, vol. VII, 1, 2015, p. 101-107 ESPON Atlas: Territorial Dimensions of the Europe 2020 Strategy ESPON 2013 Programme, Luxembourg, 2013, 66 p. ISBN 978-2-919777-36-5
BOOK REVIEWS Journal of Urban and Regional Analysis, vol. VII, 1, 2015, p. 101-107 ESPON Atlas: Territorial Dimensions of the Europe 2020 Strategy ESPON 2013 Programme, Luxembourg, 2013, 66 p. ISBN 978-2-919777-36-5
Bathing water results 2011 Slovakia
 Bathing water results Slovakia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Slovakia for the season. Slovakia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008. When
Bathing water results Slovakia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Slovakia for the season. Slovakia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008. When
CONFERENCE STATEMENT
 Final draft CONFERENCE STATEMENT We, the elected representatives of Canada, Denmark/Greenland, the European Parliament, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America; In collaboration
Final draft CONFERENCE STATEMENT We, the elected representatives of Canada, Denmark/Greenland, the European Parliament, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America; In collaboration
Bathing water results 2011 Latvia
 Bathing water results 2011 Latvia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Latvia for the 2011 season. Latvia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008.
Bathing water results 2011 Latvia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Latvia for the 2011 season. Latvia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008.
PIRLS 2011 The PIRLS 2011 Safe and Orderly School Scale
 PIRLS 2011 The PIRLS 2011 Safe and Orderly School Scale The Safe and Orderly School (SOS) scale was created based on teachers degree of agreement with the five statements described below. See Creating
PIRLS 2011 The PIRLS 2011 Safe and Orderly School Scale The Safe and Orderly School (SOS) scale was created based on teachers degree of agreement with the five statements described below. See Creating
CONFERENCE STATEMENT
 CONFERENCE STATEMENT We, the elected representatives from Canada, Denmark/Greenland, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America; In collaboration with the indigenous peoples
CONFERENCE STATEMENT We, the elected representatives from Canada, Denmark/Greenland, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America; In collaboration with the indigenous peoples
