INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Section A
|
|
|
- Lionel Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section A Q1 The formula CH3 can represent an anion, a cation or a free radical. Species with the molecular formula CH3 can act as an electrophile, a free radical or a nucleophile depending on the number of outer shell electrons on the central carbon atom. How many outer shell electrons must be present for CH3 to act in these different ways? Q2 Pentanol, C5H11OH, has four structural isomers that are primary alcohols. How many of these primary alcohols contain a chiral carbon atom? A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3 Q3 The diagram shows the structure of the naturally-occurring molecule cholesterol. Student X claimed that the seventeen carbon atoms in the four rings all lie in the same plane. Student Y claimed that this molecule displays cis-trans isomerism at the C=C double bond. Which of the students are correct? A both X and Y B neither X nor Y C X only D Y only Q4 Which compound does not show cis-trans isomerism? A 2-methylpent-2-ene B 3-methylpent-2-ene C 3,4-dimethylhex-3-ene D pent-2-ene Q5 Which formulae show propanone and propanal as different compounds? A empirical, molecular, structural and displayed formulae B molecular, structural and displayed formulae only C structural and displayed formulae only D displayed formulae only Q6 How many isomers with the formula C5H10 have structures that involve π bonding? A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6 Q7 How many isomeric esters have the molecular formula C4H8O2? A 2 B 3 C 4 D 5 ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
2 Q8 Which diagram gives the skeletal formula of 2-chloropentan-3-ol? Q9 Isomers X and Y both react with HBr. A mixture of X and Y is reacted with HBr. Which three structures represent three different possible products of this reaction? Q10 The following compounds are found in the seaweed Asparagopsis taxiformis. Which compound could show both cis-trans isomerism and optical isomerism? Q11 Pentane, C5H12, is reacted with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light. A compound R is found in the products. R has molecular formula C5H10Cl 2. Each molecule of R contains one chiral carbon atom. Which two atoms of the pentane chain could be bonded to chlorine atoms in this isomer? A 1 and 3 B 1 and 5 C 2 and 3 D 2 and 4 Q12 How many isomers, including structural and stereoisomers, with the formula C4H8 have structures that involve π bonding? Q13 In the general formula of which class of compound, is the ratio of hydrogen atoms to carbon atoms the highest? A alcohols B aldehydes C carboxylic acids D halogenoalkanes ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
3 Q14 The molecule shown is optically active. How many chiral carbon atoms are present in this molecule? Q15 Carvone is found in spearmint. Q16 An alkene has the formula CH3CH=CR CH2CH3 and does not possess cis-trans isomers. What is R? A H B Cl C CH3 D C2H5 Q17 Menthol is an important compound extracted from the peppermint plant. ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
4 How many chiral centres are there in one molecule of menthol? Q18 What is the skeletal formula of 2-methylpentan-1-ol? Section B Q19 What is always involved in a carbon-carbon π bond? 1 a shared pair of electrons 2 a sideways overlap of p orbitals 3 delocalised electrons Q20 What are the same for a pair of optical isomers? 1 their empirical formula 2 their functional groups 3 their structural formula Q21 Disaccharides, C12H22O11, are important in the human diet. For example, sucrose is found in pastries and lactose occurs in milk products. Both of these compounds can be hydrolysed. Which statements about these hydrolysis products are correct? 1 Glucose and fructose have structural isomers. 2 Glucose and galactose are optical isomers. 3 Glucose and galactose are ketones. ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
5 MCQ Solution 1. A 2. B 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. D 7. C 8. A 9. B 10. B 11. A 12. D 13. A 14. A 15. D 16. D 17. C 18. C 19. B 20. A 21. B ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
HYDROXY COMPOUNDS. Section A. Q1 In the reaction pathway below, an alkane is converted into a carboxylic acid through several stages.
 MCQs Section A Q1 In the reaction pathway below, an alkane is converted into a carboxylic acid through several stages. Which processes occur at stage 1 and at stage 3? Q2 Which isomer of C6H13OH gives
MCQs Section A Q1 In the reaction pathway below, an alkane is converted into a carboxylic acid through several stages. Which processes occur at stage 1 and at stage 3? Q2 Which isomer of C6H13OH gives
HYDROCARBONS. Section A
 MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
Chemistry 102 Organic Chemistry: Introduction to Isomers Workshop
 Chemistry 102 Organic Chemistry: Introduction to Isomers Workshop What are isomers? Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but different arrangements of atoms. There are different types
Chemistry 102 Organic Chemistry: Introduction to Isomers Workshop What are isomers? Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but different arrangements of atoms. There are different types
Class Revision on Intro to Organic, Alkanes and Alkenes
 Class Revision on Intro to Organic, Alkanes and Alkenes 2015 Term 1 Week 1 169 min 110 marks ~ Section A: Multiple Choice Questions Circle the best answer 1. What is the correct name of this compound?
Class Revision on Intro to Organic, Alkanes and Alkenes 2015 Term 1 Week 1 169 min 110 marks ~ Section A: Multiple Choice Questions Circle the best answer 1. What is the correct name of this compound?
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice
 IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
Name: Unit 11 Organic Chemistry
 1. Which compound is a member of the same homologous series as C3H8? A) CH4 B) C4H8 C) C5H8 D) C5H10 2. Which formula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon? 5. Which structural formula represents 2-pentyne?
1. Which compound is a member of the same homologous series as C3H8? A) CH4 B) C4H8 C) C5H8 D) C5H10 2. Which formula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon? 5. Which structural formula represents 2-pentyne?
Name: Unit 11 Organic Chemistry
 1. Which compound is a member of the same homologous series as C3H8? A) CH4 B) C4H8 C) C5H8 D) C5H10 2. Which formula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon? 5. Which structural formula represents 2-pentyne?
1. Which compound is a member of the same homologous series as C3H8? A) CH4 B) C4H8 C) C5H8 D) C5H10 2. Which formula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon? 5. Which structural formula represents 2-pentyne?
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS. Section A. Q1 Acrylic acid is produced from propene, a gaseous product of oil refineries.
 MCQs Section A Q1 Acrylic acid is produced from propene, a gaseous product of oil refineries. Which statement about acrylic acid is not correct? A Both bond angles x and y are approximately 120. B It decolourises
MCQs Section A Q1 Acrylic acid is produced from propene, a gaseous product of oil refineries. Which statement about acrylic acid is not correct? A Both bond angles x and y are approximately 120. B It decolourises
4. A sample of 0.200g of an organic compound was subjected to combustion analysis and
 1. A sample of 0.205g of an organic compound was subjected to combustion analysis and produced 0.660g of carbon dioxide, 0.225g of water and nothing else. Its RMM is 82. 2. A sample of 0.400g of an organic
1. A sample of 0.205g of an organic compound was subjected to combustion analysis and produced 0.660g of carbon dioxide, 0.225g of water and nothing else. Its RMM is 82. 2. A sample of 0.400g of an organic
Page 2. Q1.Consider the five cyclic compounds, A, B, C, D and E. The infrared spectra of compounds A, B, C and D are shown below.
 Q1.Consider the five cyclic compounds, A, B, C, D and E. (a) The infrared spectra of compounds A, B, C and D are shown below. Write the correct letter, A, B, C or D, in the box next to each spectrum. You
Q1.Consider the five cyclic compounds, A, B, C, D and E. (a) The infrared spectra of compounds A, B, C and D are shown below. Write the correct letter, A, B, C or D, in the box next to each spectrum. You
Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism
 Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism Learning Outcomes: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to : Define isomerism. Explain constitutional isomerism. chain isomers positional isomers functional group
Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism Learning Outcomes: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to : Define isomerism. Explain constitutional isomerism. chain isomers positional isomers functional group
A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows some precise relative atomic mass values.
 Butane and propanal are compounds with M r = 58.0, calculated using data from your Periodic Table. (a) A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows
Butane and propanal are compounds with M r = 58.0, calculated using data from your Periodic Table. (a) A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows
It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures
 Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
C. CH CH COH CH CCH. 6. Which substance(s) could be formed during the incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
 1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O O A. CH 3CH 2 CH B. CH 3CCH3 C. CH 3CH 2 COH D. CH COCH 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B. CH 2 CHBr C.
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O O A. CH 3CH 2 CH B. CH 3CCH3 C. CH 3CH 2 COH D. CH COCH 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B. CH 2 CHBr C.
3.1 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
Reactions of Chapter 10 Worksheet and Key
 1) Alcohol Fermentation Reactions of Chapter 10 Worksheet and Key Alcohol fermentation is a series of chemical reaction that convert sugar molecules, such a glucose, into ethanol and C 2. The overall reaction
1) Alcohol Fermentation Reactions of Chapter 10 Worksheet and Key Alcohol fermentation is a series of chemical reaction that convert sugar molecules, such a glucose, into ethanol and C 2. The overall reaction
Organic Chemistry. Unit 10
 Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
10 Introduction to organic chemistry
 Page 195 Questions 1 a) CH 3 CH(OH)CH 2 Br is called 1-bromopropan-2-ol. b) CH 2 ClCH 2 COOH is called 3-chloropropanoic acid. [e] There are three carbon atoms in the chain, so the stem name is prop-.
Page 195 Questions 1 a) CH 3 CH(OH)CH 2 Br is called 1-bromopropan-2-ol. b) CH 2 ClCH 2 COOH is called 3-chloropropanoic acid. [e] There are three carbon atoms in the chain, so the stem name is prop-.
Page (Extra space) (4) Benzene can be converted into amine U by the two-step synthesis shown below.
 Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1
 AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1 2.2 Nomenclature and isomerism in organic compounds 2.2.1 understand the terms empirical, molecular and structural formulae, homologous series and functional groups;
AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1 2.2 Nomenclature and isomerism in organic compounds 2.2.1 understand the terms empirical, molecular and structural formulae, homologous series and functional groups;
CHEM 3.2 (AS91388) 3 credits. Demonstrate understanding of spectroscopic data in chemistry
 CHEM 3.2 (AS91388) 3 credits Demonstrate understanding of spectroscopic data in chemistry Spectroscopic data is limited to mass, infrared (IR) and 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Organic
CHEM 3.2 (AS91388) 3 credits Demonstrate understanding of spectroscopic data in chemistry Spectroscopic data is limited to mass, infrared (IR) and 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Organic
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Halogenoalkanes
 F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Halogenoalkanes 56 Marks 1. Chlorofluoroalkanes, CFCs, were developed from fluoroalkanes and were used in aerosols and as refrigerants. Under the Montreal Protocol, CFCs
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Halogenoalkanes 56 Marks 1. Chlorofluoroalkanes, CFCs, were developed from fluoroalkanes and were used in aerosols and as refrigerants. Under the Montreal Protocol, CFCs
GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4
 Surname ther Names Centre 2 Candidate GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4 P.M. MNDAY, 14 January 2013 1¾ hours ADDITINAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need: Data Sheet Periodic
Surname ther Names Centre 2 Candidate GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4 P.M. MNDAY, 14 January 2013 1¾ hours ADDITINAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need: Data Sheet Periodic
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
INTRODUCTORY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 INTRODUCTORY ORGANIC CEMISTRY Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds excluding carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and carbonates. Carbon atoms usually form four bonds. They have the
INTRODUCTORY ORGANIC CEMISTRY Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds excluding carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and carbonates. Carbon atoms usually form four bonds. They have the
Full file at
 Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
CHAPTER 24 Organic Chemistry
 CHAPTER 24 rganic Chemistry 1. The general formula for alkenes is A. C n H 2n+2 B. C 2n H 2n C. C n H n+2 D. C n H 2n E. C n H 2n 2 2. The general formula of an alkane is A. C n H 2n B. C n H 2n+2 C. C
CHAPTER 24 rganic Chemistry 1. The general formula for alkenes is A. C n H 2n+2 B. C 2n H 2n C. C n H n+2 D. C n H 2n E. C n H 2n 2 2. The general formula of an alkane is A. C n H 2n B. C n H 2n+2 C. C
Unit 9. Organic compounds
 Unit 9. Organic compounds Index 1.- How to Name Organic Compounds...2 2.- Types of Compounds...3 Exercises...6 Practice exam...9 Page 1 of 11 The IUPAC Naming (nomenclature) System 1.- How to Name Organic
Unit 9. Organic compounds Index 1.- How to Name Organic Compounds...2 2.- Types of Compounds...3 Exercises...6 Practice exam...9 Page 1 of 11 The IUPAC Naming (nomenclature) System 1.- How to Name Organic
3.8 Aldehydes and ketones
 3.8 Aldehydes and ketones Introduction: p's to p's Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen: Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon meaning
3.8 Aldehydes and ketones Introduction: p's to p's Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen: Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon meaning
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Analyse this information to suggest possible structures for compounds F, G and H.
 1 In this question, you are asked to suggest structures for several organic compounds. (a) ompounds F, G and are unbranched alkenes that are isomers, each with a relative molecular mass of 70.0. ompounds
1 In this question, you are asked to suggest structures for several organic compounds. (a) ompounds F, G and are unbranched alkenes that are isomers, each with a relative molecular mass of 70.0. ompounds
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL
 Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
CHEMISTRY FOR THE IB DIPLOMA CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 10 rganic chemistry Revision checklist I am able to: explain, using an example, what is meant by the term homologous series sketch a graph of boiling point against number of carbons for the straight-chain
10 rganic chemistry Revision checklist I am able to: explain, using an example, what is meant by the term homologous series sketch a graph of boiling point against number of carbons for the straight-chain
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Classification of organic compounds
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Elimination. 148 minutes. 145 marks. Page 1 of 22
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
Answer Marks Guidance
 Question number (a) molecular formula: C 4 H 8 Answer Marks Guidance empirical formula: CH 2 This is a revision of earlier chapters. (b) (i) name of mechanism: electrophilic addition Remember that reactions
Question number (a) molecular formula: C 4 H 8 Answer Marks Guidance empirical formula: CH 2 This is a revision of earlier chapters. (b) (i) name of mechanism: electrophilic addition Remember that reactions
Unit 5: Organic Chemistry
 Unit 5: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry: discipline in chemistry focussing strictly on the study of hydrocarbons compounds made up of carbon & hydrogen Organic compounds can contain other elements
Unit 5: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry: discipline in chemistry focussing strictly on the study of hydrocarbons compounds made up of carbon & hydrogen Organic compounds can contain other elements
H 8. ) is a member of the homologous series of alkenes. But-1-ene has structural isomers (2)... (1)...
 Q1. (a) The hydrocarbon but-1-ene (C 4 H 8 ) is a member of the homologous series of alkenes. But-1-ene has structural isomers. (i) State the meaning of the term structural isomers. (ii) Give the IUPAC
Q1. (a) The hydrocarbon but-1-ene (C 4 H 8 ) is a member of the homologous series of alkenes. But-1-ene has structural isomers. (i) State the meaning of the term structural isomers. (ii) Give the IUPAC
10.2 ALCOHOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS. Reaction excess conc, H SO 180 C
 10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
18.1 Arenes benzene compounds Answers to Exam practice questions
 Pages 230 232 1 a) Benzene has a planar molecule ; with six carbon atoms in a regular hexagon. Each carbon atom forms a normal covalent ( ) bond with its two adjacent carbons atoms and a hydrogen atom.
Pages 230 232 1 a) Benzene has a planar molecule ; with six carbon atoms in a regular hexagon. Each carbon atom forms a normal covalent ( ) bond with its two adjacent carbons atoms and a hydrogen atom.
Chapter Organic Chemistry Basics
 29 Chapter Organic Chemistry Basics 2. A similarity between optical and geometrical isomerism is that [2002] (a) each forms equal number of isomers for a given compound (b) if in a compound one is present
29 Chapter Organic Chemistry Basics 2. A similarity between optical and geometrical isomerism is that [2002] (a) each forms equal number of isomers for a given compound (b) if in a compound one is present
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. Consider the following reaction sequence. CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Step 1
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. Consider the following reaction sequence. CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Step 1
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises Topic 8 Unit 30
 Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises In-text activities Checkpoint (page 60) 1 Any two of the following: 2 a) A 2-bromo-2-methylpropane B 1-bromobutane b) 3 4 a) position isomers
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises In-text activities Checkpoint (page 60) 1 Any two of the following: 2 a) A 2-bromo-2-methylpropane B 1-bromobutane b) 3 4 a) position isomers
HONORS: Naming Organic Compounds
 HONORS: Naming Organic Compounds Organic chemistry centers around the element carbon. Hydrocarbons (compounds made of the elements hydrogen and carbon are the basic building foundation of organic chemistry.
HONORS: Naming Organic Compounds Organic chemistry centers around the element carbon. Hydrocarbons (compounds made of the elements hydrogen and carbon are the basic building foundation of organic chemistry.
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
Candidate number. Centre number
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA A Level Chemistry A H432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques Practice paper Set 2 Time allowed: 2 hours 15 minutes *PRACTICE2016* You must have: the Data Sheet for Chemistry
Oxford Cambridge and RSA A Level Chemistry A H432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques Practice paper Set 2 Time allowed: 2 hours 15 minutes *PRACTICE2016* You must have: the Data Sheet for Chemistry
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
 1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade
 Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
 Q1 (a) State the reagents and conditions needed to convert benzene into (i) chlorobenzene, (ii) bromobenzene, (iii) nitrobenzene....[4] (b) The nitration of benzene is a two-step reaction that can be represented
Q1 (a) State the reagents and conditions needed to convert benzene into (i) chlorobenzene, (ii) bromobenzene, (iii) nitrobenzene....[4] (b) The nitration of benzene is a two-step reaction that can be represented
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O A. CH CH CH O B. CH CCH O C. CH CH COH O D. CH COCH
 1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O A. CH CH CH 3 2 O B. CH CCH 3 3 O C. CH CH COH 3 2 O D. CH COCH 3 3 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B.
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O A. CH CH CH 3 2 O B. CH CCH 3 3 O C. CH CH COH 3 2 O D. CH COCH 3 3 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B.
It belongs to a homologous series with general formula C n H 2n+1 O
 1 Propene can be made by the dehydration of propan-2-ol. What is the percentage yield when 30 g of propene (M r = 42.0) are formed from 50 g of propan-2-ol (M r = 60.0)? 60% 67% 81% 86% 2 Which statement
1 Propene can be made by the dehydration of propan-2-ol. What is the percentage yield when 30 g of propene (M r = 42.0) are formed from 50 g of propan-2-ol (M r = 60.0)? 60% 67% 81% 86% 2 Which statement
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Sample Assessment Materials for first
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Sample Assessment Materials for first
Complete the mechanism for the reaction, using curly arrows where appropriate. Show clearly the structure of the intermediate carbocation formed.
 1 (a) Propene, C 3 H 6, reacts with hydrogen bromide, HBr, in an electrophilic addition reaction. 2-bromopropane is formed as the major product. H 3 CCH=CH 2 + HBr H 3 CCH(Br)CH 3 Complete the mechanism
1 (a) Propene, C 3 H 6, reacts with hydrogen bromide, HBr, in an electrophilic addition reaction. 2-bromopropane is formed as the major product. H 3 CCH=CH 2 + HBr H 3 CCH(Br)CH 3 Complete the mechanism
Revision Guide Unit 2. Module 1 Organic Chemistry
 Revision Guide Unit 2 Module 1 Organic Chemistry Types of formulae Types of formula you need to know 1. Empirical 2. Molecular 3. Displayed 4. Structural 5. Skeletal 6. General DefiniJons empirical formula
Revision Guide Unit 2 Module 1 Organic Chemistry Types of formulae Types of formula you need to know 1. Empirical 2. Molecular 3. Displayed 4. Structural 5. Skeletal 6. General DefiniJons empirical formula
CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A Level 2410U20-1 NEW AS S16-2410U20-1 CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds P.M. FRIDAY, 10 June 2016 1 hour 30 minutes
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A Level 2410U20-1 NEW AS S16-2410U20-1 CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds P.M. FRIDAY, 10 June 2016 1 hour 30 minutes
1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? A) ketone B) aldehyde C) amine D) ester E) carboxylic acid
 1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone aldehyde amine ester carboxylic acid 2) Which functional group contains a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group bonded to the same carbon
1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone aldehyde amine ester carboxylic acid 2) Which functional group contains a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group bonded to the same carbon
Two stereoisomers of but-2-ene are formed when 2-bromobutane reacts with ethanolic potassium hydroxide
 Q1. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH 3) 2C=CH 2 Name of mechanism... Mechanism (4)
Q1. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH 3) 2C=CH 2 Name of mechanism... Mechanism (4)
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Basic Organic Nomenclature Packet Chemistry Level II
 Basic Organic Nomenclature Packet Chemistry Level II Name: Period: Use this packet and your book to answer the questions throughout this packet. Organic Nomenclature - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes Naming
Basic Organic Nomenclature Packet Chemistry Level II Name: Period: Use this packet and your book to answer the questions throughout this packet. Organic Nomenclature - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes Naming
2 Answer all the questions. OH(g) ΔH = 91 kj mol 1 equation 1.1. (a) A pressure of between 50 and 100 atmospheres is used for this reaction.
 2 Answer all the questions. 1 Methanol is added to ethanol to make the ethanol unfit to drink. Methanol can be made by the following reaction. CO(g) + 2H 2 (g) CH 3 OH(g) ΔH = 91 kj mol 1 equation 1.1
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Methanol is added to ethanol to make the ethanol unfit to drink. Methanol can be made by the following reaction. CO(g) + 2H 2 (g) CH 3 OH(g) ΔH = 91 kj mol 1 equation 1.1
10/6/2010. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions Organic chemical reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions Organic chemical reactions
... [1] Draw another structural isomer of these two alcohols.
![... [1] Draw another structural isomer of these two alcohols. ... [1] Draw another structural isomer of these two alcohols.](/thumbs/75/72508533.jpg) 1 This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol (a) Which alcohol is an example of a tertiary alcohol?... [1]
1 This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol (a) Which alcohol is an example of a tertiary alcohol?... [1]
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
Assessment Schedule 2016 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391)
 NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
4.1.1 Organic: Basic Concepts
 .. rganic: Basic oncepts ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds only Unsaturated : ontains a = double bond
.. rganic: Basic oncepts ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds only Unsaturated : ontains a = double bond
National 5 Chemistry. Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes
 National 5 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
National 5 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
2/28/2011. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS. Chapterwise Previous year Qs. (a) Na (b) HCl in H2O (c) KOH in C2H5OH (d) Zn in alcohol. Ans: (c)
 122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
Worksheet Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning
 Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning AS GCE CEMISTRY A F322/01 Chains, Energy and Resources *F314440113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted)
Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning AS GCE CEMISTRY A F322/01 Chains, Energy and Resources *F314440113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted)
flowers, leaves and roots of roses rose oil heat
 1 Rose oil can be extracted from the flowers, leaves and roots of roses using the apparatus below. coolant flowers, leaves and roots of roses rose oil heat (a) The rose oil contains a mixture of compounds,
1 Rose oil can be extracted from the flowers, leaves and roots of roses using the apparatus below. coolant flowers, leaves and roots of roses rose oil heat (a) The rose oil contains a mixture of compounds,
(a) Which test always gives a positive result with carbonyl compounds? (b) Which test would give a positive result with ethane-1,2-diol?
 1 Some chemical tests are described below. Warm with Fehling s (or enedict s) solution Warm with acidified potassium dichromate(vi) solution dd sodium carbonate solution dd 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine solution
1 Some chemical tests are described below. Warm with Fehling s (or enedict s) solution Warm with acidified potassium dichromate(vi) solution dd sodium carbonate solution dd 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine solution
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
CHAPTER 12 (MOORE) FUELS, ORGANIC CHEMICALS AND POLYMEYS
 CHAPTER 12 (MOORE) FUELS, ORGANIC CHEMICALS AND POLYMEYS This chapter deals organic compounds. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of hydrocarbons, which have the general chemical formula, C X H Y, and
CHAPTER 12 (MOORE) FUELS, ORGANIC CHEMICALS AND POLYMEYS This chapter deals organic compounds. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of hydrocarbons, which have the general chemical formula, C X H Y, and
CHAPTER 14: An Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 CHAPTER 14: An Introduction to rganic Chemistry 14.1 rganic Compounds 14.2 rganic Reactions 14.3 Isomerism Learning outcomes: (a) interpret, and use the general, structural, displayed and skeletal formulae
CHAPTER 14: An Introduction to rganic Chemistry 14.1 rganic Compounds 14.2 rganic Reactions 14.3 Isomerism Learning outcomes: (a) interpret, and use the general, structural, displayed and skeletal formulae
Explain what is meant by the term fraction as applied to fractional distillation. The fractions from petroleum contain alkane hydrocarbons.
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY AS REVISION QUESTIONS Q1. Petroleum is separated into fractions by fractional distillation.the petrol fraction (C 4 to C 12 ) is burned in internal combustion engines and the naphthafraction
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY AS REVISION QUESTIONS Q1. Petroleum is separated into fractions by fractional distillation.the petrol fraction (C 4 to C 12 ) is burned in internal combustion engines and the naphthafraction
GRADE 11F: Chemistry 6. UNIT 11FC.6 10 hours. Some functional groups. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 11F: Chemistry 6 Some functional groups UNIT 11FC.6 10 hours About this unit This unit is the sixth of six units on for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching
GRADE 11F: Chemistry 6 Some functional groups UNIT 11FC.6 10 hours About this unit This unit is the sixth of six units on for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching
Topic 10.1: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Notes
 Topic 10.1: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Notes Terminology Hydrocarbon: compounds that contain mostly hydrogen and carbon Homologous Series: compounds with the same general formula Molecular Formula:
Topic 10.1: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Notes Terminology Hydrocarbon: compounds that contain mostly hydrogen and carbon Homologous Series: compounds with the same general formula Molecular Formula:
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Basic Concepts
 F322: hains, Energy and Resources Basic oncepts 1. Some of the hydrocarbons in kerosene have the formula 10 22. (i) What is the name of the straight chain hydrocarbon with the formula 10 22? (ii) Draw
F322: hains, Energy and Resources Basic oncepts 1. Some of the hydrocarbons in kerosene have the formula 10 22. (i) What is the name of the straight chain hydrocarbon with the formula 10 22? (ii) Draw
Chapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals
 hapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals 24.1 Petroleum Refining and the ydrocarbons 24.2 Functional Groups and Organic Synthesis 24.3 Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals IR Tutor and Infrared Spectroscopy
hapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals 24.1 Petroleum Refining and the ydrocarbons 24.2 Functional Groups and Organic Synthesis 24.3 Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals IR Tutor and Infrared Spectroscopy
Molecular Models and Isomerism
 Name Lab Day Molecular Models and Isomerism Introduction: When two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of their atoms, the various individual compounds
Name Lab Day Molecular Models and Isomerism Introduction: When two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of their atoms, the various individual compounds
GRADE 11A: Chemistry 5. UNIT 11AC.5 15 hours. Organic chemistry. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 11A: Chemistry 5 Organic chemistry UNIT 11AC.5 15 hours About this unit This unit is the fifth of six units on chemistry for Grade 11 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching
GRADE 11A: Chemistry 5 Organic chemistry UNIT 11AC.5 15 hours About this unit This unit is the fifth of six units on chemistry for Grade 11 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch16_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone B) aldehyde C) amine D)
Ch16_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone B) aldehyde C) amine D)
Isomerism and Carbonyl Compounds
 Isomerism and Carbonyl Compounds 18 Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 7 Esters have many important commercial uses such as solvents and artificial flavourings in foods. Esters can
Isomerism and Carbonyl Compounds 18 Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 7 Esters have many important commercial uses such as solvents and artificial flavourings in foods. Esters can
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
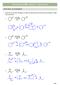 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval.
 CH 334 Form B First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, 2017 Name KEY You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval. Please do not use any electronic devices
CH 334 Form B First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, 2017 Name KEY You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval. Please do not use any electronic devices
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
(a) (i) Give the equation representing the overall reaction. (1) Give the equation representing the formation of the electrophile.
 1. Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid at about 50 º in an electrophilic substitution reaction to give nitrobenzene. (a) Give the equation representing
1. Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid at about 50 º in an electrophilic substitution reaction to give nitrobenzene. (a) Give the equation representing
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 1 answer key September 29, 2005
 CEMISTRY 313-01 MIDTERM # 1 answer key September 29, 2005 Statistics: Average: 75 pts (75%); ighest: 99 pts (99%); Lowest: 31 pts (31%) Number of students performing at or above average: 28 (57%) Number
CEMISTRY 313-01 MIDTERM # 1 answer key September 29, 2005 Statistics: Average: 75 pts (75%); ighest: 99 pts (99%); Lowest: 31 pts (31%) Number of students performing at or above average: 28 (57%) Number
