CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
2 Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl alcohol allyl chloride Allylic Carbocations carbocation with a vinyl group as a substituent (next to a double bond) 2
3 Allyl carbocations are stabilized by resonance The atoms must remain fixed in all resonance forms. Resonance forms differ only by the placement of electrons No one resonance form is entirely accurate. The actual structure is a hybrid of all the resonance forms. Resonance forms do not necessarily contribute equally to the resonance hybrid. 3
4 S N 1 Reactions of Allylic Halides allylic halides and sulfonates are more reactive toward than simple alkyl halides toward nucleophilic substitution by the S N 1 mechanism over 100x more reactive than (H 3 C)C Cl Resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate 85 : 15 4
5 S N 2 Reactions of Allylic Halides allylic halides and sulfonates are more reactive toward than simple alkyl halides toward nucleophilic substitution by the S N 2 mechanism ~ 80x more reactive than Cl CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 5
6 Allylic Free Radicals Map of the electron density due to the unpaired electron (the spin ) 6
7 Free Radical Stabilities are Related to Bond Dissociation Energies CH 3 CH 3 CH H 410 kj/mol CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 + H (CH 3 ) 2 CH H 397 kj/mol (CH 3 ) 2 CH + H (CH 3 ) 3 C H 380 kj/mol (CH 3 ) 3 C + H 368 kj/mol H 2 C CHCH 2 H H 2 C CHCH 2 + H C H bond is weaker in propene because the resulting allyl radical is more stable than the alkyl radicals. 7
8 Allylic Halogenation Allylic halogenation of an alkene takes place through a free radical mechanism. 8
9 Limitation: Allylic halogenation is only useful when all of the allylic hydrogens are equivalent and the resonance forms of allylic radical are equivalent. Allylic Anions 9
10 pk a ~ 60 _ CH 3 CH 3 CH H CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 + H + _ pk a ~ 43 H 2 C CHCH 2 H H 2 C CHCH 2 + H + Classes of Dienes Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds 10
11 Relative Stabilities of Dienes Recall from Chapter 6 that heats of hydrogenation (ΔH H2 ) was used to measure the relative stability of isomeric alkenes ΔH H2-126 KJ/mol -252 KJ/mol (2 x 126 = 252) -111 KJ/mol ( = 15) -226 KJ/mol the double bonds of conjugated dienes are more stable than isolated double bonds. 11
12 Bonding in Conjugated Dienes When the carbons of a conjugate diene all lie in the same plane, the π-molecular orbitals overlap. The four π-electrons of a conjugated diene are delocalized over the four p-orbitals Bond lengths in pm
13 There are three conformations of butadiene. The (lower case) s prefix designates a conformation around single (σ) bond. 180 rotation of the central σ bond Energy 90 rotation of the central σ bond s cis The perpendicular conformation is 16 KJ/mol higher in energy than the s cis The s cis conformation is 12 KJ/mol higher in energy than the s trans s trans 13
14 β carotene alkenes conjugated to carbonyls lycopene alkenes conjugated to non-bonding pairs of electrons 14
15 Bonding in Allenes Preparation of Dienes Preparation of conjugated dienes (1,3-dienes) from alkenes: allylic bromination followed by dehydrohalogenation 15
16 Halogen Addition to Dienes Electrophilc additions of other electrophile to dienes give similar results 16
17 The π Molecular Orbitals of Ethylene and 1,3 Butadiene π MO s of ethylene ψ 2 Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO) ψ 1 Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) 17
18 π-molecular orbitals of butadiene 3 Nodes 0 bonding interactions 3 antibonding interactions ANTIBONDING MO 2 Nodes 1 bonding interactions 2 antibonding interactions ANTIBONDING MO 1 Nodes 2 bonding interactions 1 antibonding interactions BONDING MO 0 Nodes 3 bonding interactions 0 antibonding interactions BONDING MO ψ 2 is the Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) ψ 3 is the Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO) 18
19 The Diels Alder Reaction Reaction between a conjugated diene and an alkene (dienophile) to give a cyclohexene. Mechanism: concerted reaction (bond breaking and bond forming) takes place in a single step. Cycloaddition non cyclic reactant react to form a cyclic product Pericyclic cyclic aromatic like transition state 19
20 The Diels Alder reaction is favored by electron withdrawing groups on the dienophile and electron donating groups on the diene. H H O O O H H H R OR ethylene (unreactive) conjugated carbonyls (aldehydes, ketones and esters) O O C N CO 2 R O O O Good dienophiles The diene must adopt an s-cis conformation to be reactive: 20
21 Stereochemistry of the Diels Alder Reaction: The stereochemistry of the alkene reactants (dienophile) is preserved in the product. 21
22 A π Molecular Orbital Analysis of the Diels Alder Reaction ψ 2 of butadiene ψ 2 of ethylene The orbitals between the diene and dienophile involved in bond formation are in phase symmetry allowed. orbitals are out of phase Symmetry forbidden 22
23 THANK YOU
11/5/ Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Heats of Hydrogenation
 8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
Conjugated Systems. With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn
 Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): 1. Isolated: (two or more single bonds between them)
 1 Chapter 15: Conjugation and Reactions of Dienes I. Introduction to Conjugation There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): 1. Isolated: (two or more
1 Chapter 15: Conjugation and Reactions of Dienes I. Introduction to Conjugation There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): 1. Isolated: (two or more
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds
 Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds C-C single bond lkene Diene C=C double bonds Conjugate
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds C-C single bond lkene Diene C=C double bonds Conjugate
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
10.12 The Diels-Alder Reaction. Synthetic method for preparing compounds containing a cyclohexene ring
 10.12 The Diels-Alder Reaction Synthetic method for preparing compounds containing a cyclohexene ring In general... + conjugated diene alkene (dienophile) cyclohexene via transition state Mechanistic features
10.12 The Diels-Alder Reaction Synthetic method for preparing compounds containing a cyclohexene ring In general... + conjugated diene alkene (dienophile) cyclohexene via transition state Mechanistic features
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 1
 Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 1 Chemistry of polyfunction 1. Types of carbon atom Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 2 Classification of multiple bonds of polyunsaturated compounds Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 3 Organic chemistry,
Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 1 Chemistry of polyfunction 1. Types of carbon atom Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 2 Classification of multiple bonds of polyunsaturated compounds Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 3 Organic chemistry,
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy
 Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Conjugated Dienes. Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry
 Conjugated Dienes Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry 1 Dienes Propadiene (allene) is a cumulated diene 1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene. 1,4-Pentadiene is an isolated diene.
Conjugated Dienes Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry 1 Dienes Propadiene (allene) is a cumulated diene 1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene. 1,4-Pentadiene is an isolated diene.
17.1 Classes of Dienes
 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for dienes: Cumulated: pi bonds are adjacent. Conjugated: pi bonds are separated by exactly ONE single bond. Isolated: pi bonds are separated by any distance
17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for dienes: Cumulated: pi bonds are adjacent. Conjugated: pi bonds are separated by exactly ONE single bond. Isolated: pi bonds are separated by any distance
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes
 Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes Coverage: 1. Conjugated vs Nonconjugated dienes and Stability 2. MO picture of 1,3-butadiene 3. Electrophilic addition to Dienes 4. Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Control 5. Diels-Alder
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes Coverage: 1. Conjugated vs Nonconjugated dienes and Stability 2. MO picture of 1,3-butadiene 3. Electrophilic addition to Dienes 4. Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Control 5. Diels-Alder
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Dienes & Polyenes: An overview and two key reactions (Ch )
 Dienes & Polyenes: An overview and two key reactions (h. 14.1-14.5) Polyenes contain more than one double bond and are very common in natural products (ex: carotene). Diene chemistry applies to trienes,
Dienes & Polyenes: An overview and two key reactions (h. 14.1-14.5) Polyenes contain more than one double bond and are very common in natural products (ex: carotene). Diene chemistry applies to trienes,
Conjugated Dienes. Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry
 Conjugated Dienes Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry 1 Dienes Propadiene (allene) is a cumulated diene 1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene. 1,4-Pentadiene is an isolated diene.
Conjugated Dienes Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry 1 Dienes Propadiene (allene) is a cumulated diene 1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene. 1,4-Pentadiene is an isolated diene.
Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320
 Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320 I. Cumulated, isolated, and conjugated dienes Name 1. Draw structures which fit the following descriptions. Use correct geometry! a conjugated diene with the formula C
Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320 I. Cumulated, isolated, and conjugated dienes Name 1. Draw structures which fit the following descriptions. Use correct geometry! a conjugated diene with the formula C
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
Conjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions
 onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
17.1 Classes of Dienes
 W 2/1 Due: HW14, spec03 Due: n/a M 2/6 Lecture HW14 grading Lect17a Conjugated π systems Lecture quiz Lect17b Lab Lab02 Qual Analysis II (cont) 7-1 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for
W 2/1 Due: HW14, spec03 Due: n/a M 2/6 Lecture HW14 grading Lect17a Conjugated π systems Lecture quiz Lect17b Lab Lab02 Qual Analysis II (cont) 7-1 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH.8 - DELOCALIZED ELECTRONS AND THEIR EFFECT
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: RESONANCE STRUCTURES Resonance theory is used to represent all the different ways that the same molecule can distribute its electrons. Atoms move! The only thing that moves
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: RESONANCE STRUCTURES Resonance theory is used to represent all the different ways that the same molecule can distribute its electrons. Atoms move! The only thing that moves
CHEMISTRY Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay Different Kinds of Dienes When a molecule contains multiple π-bonds, their reactivity is dictated in part by
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay Different Kinds of Dienes When a molecule contains multiple π-bonds, their reactivity is dictated in part by
Lecture 22 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 22 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop April 1, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which starting material could not be used to prepare the tribromide below?
CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 22 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop April 1, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which starting material could not be used to prepare the tribromide below?
Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
3 - CONJUGATION. More than one double bond can be in a given compound: n=0
 3 - NJUGATIN 1. Terminology and Nomenclature (SF 13.1 13.6; SFS 13.1 13.6) A compound containing a double bond is called an alkene, olefin or maybe simply "ene". There are often other names associated
3 - NJUGATIN 1. Terminology and Nomenclature (SF 13.1 13.6; SFS 13.1 13.6) A compound containing a double bond is called an alkene, olefin or maybe simply "ene". There are often other names associated
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH DIENES, CONJUGATED SYSTEMS, AND PERICYCLIC REACTIONS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCTION TO CONJUGATION Conjugation exists when three or more atoms with the ability to resonate are adjacent to each other (overlapping). Conjugation provides an electron
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCTION TO CONJUGATION Conjugation exists when three or more atoms with the ability to resonate are adjacent to each other (overlapping). Conjugation provides an electron
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Pericyclic reactions
 Pericyclic reactions In pericyclic reactions the breaking and making of bonds occur simultaneously by the way of a single cyclic transition state (concerted reaction). There are no intermediates formed
Pericyclic reactions In pericyclic reactions the breaking and making of bonds occur simultaneously by the way of a single cyclic transition state (concerted reaction). There are no intermediates formed
Organic Chemistry: CHEM2322
 Conjugated Systems Organic Chemistry: We met in Chem 2321 unsaturated bonds as either a C=C bond or C C bond. If these unsaturated bonds are well separated then they react independently however if there
Conjugated Systems Organic Chemistry: We met in Chem 2321 unsaturated bonds as either a C=C bond or C C bond. If these unsaturated bonds are well separated then they react independently however if there
Exam. Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
CHEM 330. Topics Discussed on Nov. 25
 CM 330 Topics Discussed on Nov. 25 A typical cycloaddition process leading to C C bond formation: the Diels-Alder reaction between an appropriately substituted 1,3-butadiene and an alkene: R 1 R 2 heat
CM 330 Topics Discussed on Nov. 25 A typical cycloaddition process leading to C C bond formation: the Diels-Alder reaction between an appropriately substituted 1,3-butadiene and an alkene: R 1 R 2 heat
Key ideas: In EAS, pi bond is Nu and undergoes addition.
 Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Bond length (pm) Bond strength (KJ/mol)
 hapter 10: Alkyl alides = F, l,, I Alkyl halide Aryl halide Vinyl halide 10.1 Naming alkyl halides- ead 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides Table 10.1 alomethane 3 -F 3 -l 3-3 -I Bond length (pm) 139 178 193
hapter 10: Alkyl alides = F, l,, I Alkyl halide Aryl halide Vinyl halide 10.1 Naming alkyl halides- ead 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides Table 10.1 alomethane 3 -F 3 -l 3-3 -I Bond length (pm) 139 178 193
Ethers. Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, & Sulfides. General Formula: Types: a) Symmetrical: Examples: b) Unsymmetrical: Examples: Physical Properties:
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 1 Materials Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, & Sulfides Ethers General Formula: Types: a) Symmetrical: Examples: b) Unsymmetrical: Examples: Physical Properties:
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 1 Materials Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, & Sulfides Ethers General Formula: Types: a) Symmetrical: Examples: b) Unsymmetrical: Examples: Physical Properties:
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes
 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
3) The delocalized π system in benzene is formed by a cyclic overlap of 6 orbitals. A) s B) p C) sp D) sp2 E) sp3
 Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Chapter 27 Pericyclic Reactions
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 27 Pericyclic Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 27.1 (b) This is a sigmatropic reaction; two electrons are
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 27 Pericyclic Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 27.1 (b) This is a sigmatropic reaction; two electrons are
Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity
 17 17 Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity An allylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a double bond. A benzylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a benzene ring or substituted benzene ring.
17 17 Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity An allylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a double bond. A benzylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a benzene ring or substituted benzene ring.
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Diels-Alder Cycloaddition
 Diels-Alder ycloaddition A lab practice for the reaction between cyclopentadiene and maleic anhydride The Diels-Alder ycloaddition + onjugated diene Dienophile Diels-Alder reaction: * Stereospecific *
Diels-Alder ycloaddition A lab practice for the reaction between cyclopentadiene and maleic anhydride The Diels-Alder ycloaddition + onjugated diene Dienophile Diels-Alder reaction: * Stereospecific *
General Glossary. General Glossary
 General Glossary Absolute configuration The actual three-dimensional structure of a chiral molecule. Absolute configurations are specified verbally by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog R,S convention and are represented
General Glossary Absolute configuration The actual three-dimensional structure of a chiral molecule. Absolute configurations are specified verbally by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog R,S convention and are represented
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
The General Stabilization Effect of Conjugation (Section 15.1, 2, 3, 8, 9) Conjugated (more stable)
 Chem 0 Jasperse Ch Notes. Conjugation Ch. Conjugated Systems The General Stabilization Effect of Conjugation (Section.,,, 8, 9) Conjugated (more stable) Isolated (less stable) Notes: Cations Radicals Anions
Chem 0 Jasperse Ch Notes. Conjugation Ch. Conjugated Systems The General Stabilization Effect of Conjugation (Section.,,, 8, 9) Conjugated (more stable) Isolated (less stable) Notes: Cations Radicals Anions
ADDITION OF HYDROGEN HALIDES TO CONJUGATED DIENES A. 1,2- and 1,4-Additions 700 CHAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY
 700 CAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY 15.18 Give the structures of the starting materials that would yield each of the compounds below in Diels Alder reactions. Pay careful attention to stereochemistry,
700 CAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY 15.18 Give the structures of the starting materials that would yield each of the compounds below in Diels Alder reactions. Pay careful attention to stereochemistry,
Loudon Chapter 15 Review: Dienes and Aromaticity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/28/2019
 This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
Chem 263 Notes Sept. 26, 2013
 Chem 263 Notes Sept. 26, 2013 Example of Predicting Stereochemistry The following example uses 2Z, 4E-hexadiene (diene) and cyclopentene (dienophile) to produce an endo product. As shown before with the
Chem 263 Notes Sept. 26, 2013 Example of Predicting Stereochemistry The following example uses 2Z, 4E-hexadiene (diene) and cyclopentene (dienophile) to produce an endo product. As shown before with the
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Review and Preview. Coursepack: pp (14.6 is FYI only)
 Review and Preview We have studied many compounds with pi bonds. When a compound has more than one multiple bond in its structure, the relative positions of those multiple bonds with respect to one another
Review and Preview We have studied many compounds with pi bonds. When a compound has more than one multiple bond in its structure, the relative positions of those multiple bonds with respect to one another
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Aromatic Compounds. A number of these compounds had a distinct odor. Hence these compounds were called aromatic
 Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
THE DIELS-ALDER REACTION
 22.6 TE DIELS-ALDER REATIN 977 2 Both overlaps are bonding. ± 2 ± 2 2 M of the diene LUM of the alkene ( 2 ) (*) The [ + 2] cycloaddition is allowed by a thermal pathway. Both overlaps are bonding, so
22.6 TE DIELS-ALDER REATIN 977 2 Both overlaps are bonding. ± 2 ± 2 2 M of the diene LUM of the alkene ( 2 ) (*) The [ + 2] cycloaddition is allowed by a thermal pathway. Both overlaps are bonding, so
24.4: Acidity of Phenols. Phenols are more acidic than aliphatic alcohols. + Electron-withdrawing groups make an O
 Chapter 24: Phenols. Alcohols contain an group bonded to an sp 3 -hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an group bonded to an sp 2 -hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 24.1: Nomenclature (please read) 24.2:
Chapter 24: Phenols. Alcohols contain an group bonded to an sp 3 -hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an group bonded to an sp 2 -hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 24.1: Nomenclature (please read) 24.2:
Lecture 21 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 21 Organic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 30, 2010 1 Self Test Question Ethanolysis of alkyl halide 1 gives ether 2 as one product; however, several
CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 21 Organic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 30, 2010 1 Self Test Question Ethanolysis of alkyl halide 1 gives ether 2 as one product; however, several
New σ bond closes a ring. Loss of one π bond and gain of one σ bond
 CHAPTER 1 Pericyclic Reactions 1.1 INTRODUCTION Pericyclic reactions are defined as the reactions that occur by a concerted cyclic shift of electrons. This definition states two key points that characterise
CHAPTER 1 Pericyclic Reactions 1.1 INTRODUCTION Pericyclic reactions are defined as the reactions that occur by a concerted cyclic shift of electrons. This definition states two key points that characterise
Diels-Alder Reaction
 Diels-Alder Reaction Method for synthesis of 6-membered ring ne-step, concerted reaction Termed [4+2] cycloaddition reaction where 4 and 2 electrons react. + Diels-Alder Reaction Discovered by. Diels and
Diels-Alder Reaction Method for synthesis of 6-membered ring ne-step, concerted reaction Termed [4+2] cycloaddition reaction where 4 and 2 electrons react. + Diels-Alder Reaction Discovered by. Diels and
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
PAPER No. 5: REACTION MECHANISM MODULE No. 2: Types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Pericyclic Reactions: Electrocyclic Reaction
 Pericyclic Reaction Pericyclic Reactions: Electrocyclic Reaction 1. Electrocyclic ring closing 2. Electrocyclic ring opening Electrocyclic ring closing reaction is characterized by a. The formation of
Pericyclic Reaction Pericyclic Reactions: Electrocyclic Reaction 1. Electrocyclic ring closing 2. Electrocyclic ring opening Electrocyclic ring closing reaction is characterized by a. The formation of
MO THEORY FOR CONJUGATED MOLECULES
 22.2 MO TEORY FOR CONJUGATED MOLECULES 959 methyl groups have a cis orientation in the cyclobutene product. There is no obvious reason why conrotation should be preferred over disrotation in the thermal
22.2 MO TEORY FOR CONJUGATED MOLECULES 959 methyl groups have a cis orientation in the cyclobutene product. There is no obvious reason why conrotation should be preferred over disrotation in the thermal
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
11/30/ Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions. Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions
 Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
CEM 351 3rd EXAM/Version A Friday, November 21, :50 2:40 p.m. Room 138, Chemistry
 Name (print) Signature Student # Section Number CEM 351 3rd EXAM/Version A Friday, November 21, 2003 1:50 2:40 p.m. Room 138, Chemistry Key Grade? 1.(20 2.(20. 3.(20 4.(20 5.(20 6.(20 TTAL 100 Score Note:
Name (print) Signature Student # Section Number CEM 351 3rd EXAM/Version A Friday, November 21, 2003 1:50 2:40 p.m. Room 138, Chemistry Key Grade? 1.(20 2.(20. 3.(20 4.(20 5.(20 6.(20 TTAL 100 Score Note:
1. Root of name depends on longest chain of C containing the double bond; ends in "ene"
 Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 2 ANSWER KEY July 10, 2002
 EMISTRY 314-81 MIDTERM # 2 ANSWER KEY July 10, 2002 Statistics: Average: 47 pts (67%); ighest: 69 pts (99%); Lowest: 26 pts (37%) Number of students performing at or above average: 12 (46%) 1. (7 pts)
EMISTRY 314-81 MIDTERM # 2 ANSWER KEY July 10, 2002 Statistics: Average: 47 pts (67%); ighest: 69 pts (99%); Lowest: 26 pts (37%) Number of students performing at or above average: 12 (46%) 1. (7 pts)
3 - CONJUGATION. More than one double bond can be in a given compound: n=0
 3 - JUGATIN 1. Terminology and Nomenclature (SF10 13.1 13.6) A compound containing a double bond is called an alkene, olefin or maybe simply "ene". There are often other names associated with double bonded
3 - JUGATIN 1. Terminology and Nomenclature (SF10 13.1 13.6) A compound containing a double bond is called an alkene, olefin or maybe simply "ene". There are often other names associated with double bonded
Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]
![Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms] Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]](/thumbs/89/100347388.jpg) Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Exam I Review Solution Set
 Exam I Review Solution Set Paul Bracher hem 30 Fall 2004 Exam I Problem 1 (refer to the Evans pk a table and Solvents and Solvent Effects in rganic hemistry by. Reichardt). Explain the trend in relative
Exam I Review Solution Set Paul Bracher hem 30 Fall 2004 Exam I Problem 1 (refer to the Evans pk a table and Solvents and Solvent Effects in rganic hemistry by. Reichardt). Explain the trend in relative
There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert:
 Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
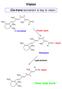 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
CYCLOADDITIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 CYCLOADDITIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 CYCLOADDITIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS Introduction Cycloaddition describes the union of two independent π-systems through a concerted process involving a cyclic movement
CYCLOADDITIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 CYCLOADDITIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS Introduction Cycloaddition describes the union of two independent π-systems through a concerted process involving a cyclic movement
17.3 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC ANIONS
 798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
More Tutorial at
 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
Pericyclic Reactions and Organic Photochemistry S. Sankararaman Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Pericyclic Reactions and Organic Photochemistry S. Sankararaman Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module No. #02 Lecture No. #09 Pericyclic Reactions Cycloaddition Reactions
Pericyclic Reactions and Organic Photochemistry S. Sankararaman Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module No. #02 Lecture No. #09 Pericyclic Reactions Cycloaddition Reactions
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
Atomic and Molecular Orbitals
 7 Atomic and Molecular Orbitals Chemists have developed a variety of methods for describing electrons in molecules. Lewis structures are the most familiar. These drawings assign pairs of electrons either
7 Atomic and Molecular Orbitals Chemists have developed a variety of methods for describing electrons in molecules. Lewis structures are the most familiar. These drawings assign pairs of electrons either
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16
 08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Chapter 14: Dienes and Conjugation. Topics Dienes: Naming and Properties. Conjugation. 1,2 vs 1,4 addition and the stability of the allyl cation
 rganic hemistry otes by Jim Maxka hapter 14: Dienes and onjugation Topics Dienes: aming and Properties onjugation 1,2 vs 1,4 addition and the stability of the allyl cation Diels Alder eaction Simple rbital
rganic hemistry otes by Jim Maxka hapter 14: Dienes and onjugation Topics Dienes: aming and Properties onjugation 1,2 vs 1,4 addition and the stability of the allyl cation Diels Alder eaction Simple rbital
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Pericyclic Reactions
 Pericyclic eactions Definition: 1. Concerted reaction that proceed via a cyclic transition state 2. No distinct intermediates in the reaction 3. Bond forming and bond breaking steps are simultaneous but
Pericyclic eactions Definition: 1. Concerted reaction that proceed via a cyclic transition state 2. No distinct intermediates in the reaction 3. Bond forming and bond breaking steps are simultaneous but
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring Instructor: Paul Bracher. Quiz # 2
 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Quiz # 2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Instructor: Paul Bracher Quiz # 2 Due: Monday, February 9 th, 2015 2:00 p.m. (in
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Quiz # 2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Instructor: Paul Bracher Quiz # 2 Due: Monday, February 9 th, 2015 2:00 p.m. (in
Molecular Orbital Theory. Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions between two bonded atoms
 Molecular Orbital Theory Valence Bond Theory: Electrons are located in discrete pairs between specific atoms Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions
Molecular Orbital Theory Valence Bond Theory: Electrons are located in discrete pairs between specific atoms Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions
Lecture 23. Amines. Chemistry 328N. April 12, 2016
 Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
11/26/ Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
 9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
