Chemosphere 74 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Chemosphere. journal homepage:
|
|
|
- Annabelle Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemosphere 74 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemosphere journal homepage: Validation of high-throughput measurement system with microwave-assisted extraction, fully automated sample preparation device, and gas chromatography-electron capture detector for determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in whale blubber Hiroyuki Fujita a, *, Katsuhisa Honda a, Noriaki Hamada b, Genta Yasunaga c, Yoshihiro Fujise c a Department of Environmental Science for Industry, Ehime University, Tarumi Matsuyama, Ehime , Japan b Miura Institute of Environmental Science, Miura Co. Ltd., Tsuji Hojyo Matsuyama, Ehime , Japan c The Institute of Cetacean Research, 4-5, Toyomi-cho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo , Japan article info abstract Article history: Received 14 July 2008 Received in revised form 28 October 2008 Accepted 28 October 2008 Available online 17 December 2008 Keywords: Polychlorinated biphenyls Microwave-assisted extraction Sample preparation device Gas chromatography-electron capture detector Whale blubber Validation of a high-throughput measurement system with microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), fully automated sample preparation device (SPD), and gas chromatography-electron capture detector (GC-ECD) for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in minke whale blubber was performed. PCB congeners accounting for >95% of the total PCBs burden in blubber were efficiently extracted with a small volume (20 ml) of n-hexane using MAE due to simultaneous saponification and extraction. Further, the crude extract obtained by MAE was rapidly purified and automatically substituted to a small volume (1 ml) of toluene using SPD without using concentrators. Furthermore, the concentration of PCBs in the purified and concentrated solution was accurately determined by GC-ECD. Moreover, the result of accuracy test using a certified material (SRM 1588b; Cod liver oil) showed good agreement with the NIST certified concentration values. In addition, the method quantification limit of total-pcb in whale blubbers was 41 ng g 1. This new measurement system for PCBs takes only four hours. Consequently, it indicated this method is the most suitable for the monitoring and screening of PCBs in the conservation of the marine ecosystem and safe distribution of foods. Ó 2008 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have been widely used in electrical equipments such as transformers and capacitors during (UNEP, 2001). In spite of the prohibition of their production and usage, PCBs are still present in the environment due to their lipophilic and highly persistent character. Particularly, top marine predators such as whales and seals tend to accumulate PCBs in their fatty tissues (Connell, 1988; Woodley et al.,1991; Gauthier et al., 1997). PCB residual levels in these animals have often exceeded the provisional limit of 0.5 lgg 1 (fresh weight) provided by the Japanese Ministry of Health in 1973 for seafood. Therefore, the continuous monitoring of PCBs in marine organisms and investigative whaling (JARPN) is essential for the conservation of the marine ecosystem and safe distribution of seafood. However, the conventional method of PCB analysis involves several complicated processes, takes a long time, and consumes a large volume of organic solvents. As a step toward the improvement of analytical techniques, the microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) * Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: fujita_hiroyuki@miuraz.co.jp (H. Fujita). method has been widely noted as a new extraction technique for PCBs in environmental solid samples and biological tissues (Vetter et al., 1998; Natalia et al., 2007). This extraction technique is used for reducing time and as a work-saving practice; the recovery of PCBs is highly efficient as compared to that obtained by conventional extraction methods, e.g., by using Soxhlet or liquid liquid separation. In the EPA method 3546, this extraction technique has been approved for the extraction of organochlorine compounds in environmental solid samples such as soil and sediments. In respect of the purification technique for environmental analytical chemistry, certain instruments of automation systems have been investigating and reported for the purification procedure of dioxin-like PCBs, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans (dioxins) and polybrominated diphenylethers (Focant and De Pauw, 2002; Focant et al., 2004). These automation systems are utilized by a few certification-testing laboratories for dioxins routine analysis. However, there are not utilized purification system with respect to PCBs routine monitoring and screening analysis and the handling is not still simple, and classical column chromatography have been using as the main purification method for PCB analysis. Therefore, further methods are essential for speedy PCB measurements in biological samples /$ - see front matter Ó 2008 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.chemosphere
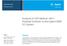
2 1070 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) In this report, we investigated the validation of a high-throughput measurement system for PCBs in whale blubber, examining followed by, (1) Detail of profile patterns of PCB congeners in whale blubber by high resolution gas chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry (HRGC-HRMS), (2) The extraction efficiency and precision of PCBs using MAE. Furthermore, (3) purification and recovery rates of PCBs using the fully automated sample preparation device (SPD), (4) the identification of PCB congeners on gas chromatography-electron capture detector (GC- ECD) chromatograms and (5) the validation of the new PCB measurement system combined with MAE, SPD, and GC-ECD using standard reference materials. 2. Experimental 2.1. Chemicals and reagents A mixture of 62 native congeners of PCBs (2.0 lgml 1 of each congener, BP-MS; Wellington Laboratories Inc., Canada) was used as the PCB standard solution for calibration by GC-ECD and HRGC-HRMS. 13 C 12 -labelled PCB standard solution (#3, #15, #28, #52, #118, #153, #180, #194, #208, and #209; EC-4189, 1.0 lgml 1 for individual PCB congeners; Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc., USA) was used as the surrogate standard solution for quantification by HRGC-HRMS. The determinations of 209 PCB congeners were performed by an extracted/purified fly ash solution. In order to examine the interference in PCB analyses by GC- ECD, a 10 ± 1 pg ll 1 standard solution of the organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) was prepared by mixing the compounds of HCB, a- HCH, b-hch, d-hch, cis-chlordane, trans-chlordane, p,p 0 -DDT, p,p 0 -DDD (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Japan), c-hch, o,p 0 -DDD (GL Sciences Inc., Japan), o,p 0 -DDT, o,p 0 -DDE, p,p 0 -DDE (Nisio Industries Ltd., Japan), oxychlordane, cis-nonachlor, and trans-nonachlor (AccuStandard Inc., USA). For PCBs and pesticides, analytical grade solvents of ethanol, n-hexane, dichloromethane, and toluene were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Japan, and the reagent for KOH was obtained from Kanto Chemical Co. Inc., Japan Samples Thirty-five samples of minke whale (Balaenoptera acutrostrata) blubber were obtained from the Western North Pacific in 2003 and 2004 under the Japanese Whale Research Program (JARPN II). These samples were provided by the Japan Institute of Cetacean Research and stored in polyethylene bags at 20 C until analysis. The standard reference material (SRM 1588b; Organics in Cod Liver Oil) for the accuracy test was obtained from USA National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The sub-reference material (whale blubber oil) was prepared from minke whale blubber for the validation of the new PCB measurement system in this study Liquid liquid extraction (LLE) and purification of the general method For liquid liquid extraction of PCBs, the epidermis was eliminated from the blubber and homogenized; then, approximately 10 g of the blubber was accurately weighed into a funnel. Then, 40 ml of ethanolic 1 M KOH and surrogate standard were added to the funnel and mixed for 1 h. The mixture was allowed to stand for 30 min, and then 40 ml of water and n-hexane each were added into the funnel and mixed. Thereafter, the saponified layer was extracted with 40 ml of n-hexane. This procedure was repeated two times. All of the n-hexane layers were combined and then washed with 100 ml of water. The extracts were filtered through 20 g of anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 and finally concentrated to 10 ml. Two milliliters of each of the extracts was purified using multilayer silica gel column chromatography composed of two components 4 g of silica gel impregnated with sulfuric acid (44% mass fraction: 44% H 2 SO 4 Si) and 3 g of silica gel impregnated with silver nitrate (10% mass fraction: 10% AgNO 3 Si). All of the PCB fractions were eluted with 90 ml of 2% dichloromethane in n-hexane. The eluate was concentrated and finally substituted with ll of decane MAE system MAE of PCBs in whale blubber was performed using a Model 7295 microwave sample preparation system (OI Analytical, USA). The poly-tetrafluoroethylene-co-perfluoropropylvinylether (PFA)- lined sample vessel is airtight, pressure-resistant (upto 200 psi), and with a volume of 60 ml; the inner pressure is monitored by an exclusive pressure sensor, and the microwave power is automatically controlled; the magnetron power output, being 950 W, is available to be set up to 100% of the power (2450 MHz). The operating conditions of this preparation system can be optimized by adjusting the three parameters of the magnetron power rate, the irradiating time, and the pressure value MAE method For performing MAE of PCBs in whale blubber, 2 5 g of the samples was accurately weighed into the sample vessels. Approximately 10 ml of the saponifying solution (ethanolic 1 M KOH: water = 1:1) and 20 ml of n-hexane were added as an extractant. MAE was carried out up to 20 psi with increments of 5 psi at 5 40% of magnetron power output for min. After cooling the vessels until room temperature, 5 10 ml of the n-hexane layer was pipetted and then cleaned up by multilayer silica gel column chromatography or SPD. The concentration of PCBs in one of the purified solutions was determined by GC-ECD or HRGC-HRMS after the addition of the surrogate standard solution to the extracts Principle and application of SPD for PCB analysis The purification for PCB analysis was performed using SPD (SPD-600GC; Miura Co. Ltd., Japan), which was originally developed for the purification method of dioxins analysis as high accuracy and rapidly. Fujita et al. investigated the purification effects by heating chemical impregnated silica gel columns, multilayer silica gel column. On this heating purification method, they reported that removal effects of various contaminants in crude extracts from environmental samples were highly efficient. For example, on 10% AgNO 3 Si at 60 C, effectiveness of chemical reaction with silver ions and sulfur compounds progressed, and while on 44% H 2 SO 4 Si at 60 C, their removal effects of mono- and poly-aromatic hydrocarbon compounds was excellent, and were so far better than those at room temperature. In the case of the combination of 10% AgNO 3 Si and 44% H 2 SO 4 Si, chemical impregnated multilayer silica gel column, the purification effects by heating at 60 C could be highly synergistic effect as compared to those at room temperature. It indicate that these results are useful for purification of sediment and biological samples enriched in sulfur compounds, and also for reduction of analytical time, amounts of solvents and contaminations in the capillary column and detector spot. (Kishino et al., 2004; Fujita et al., 2004; Miyawaki et al., 2007).
3 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) Column heater Sample collection vial Step 1; n-hexane 65mL Purification column Column joint Concentration column Step 2; Toluene 1.0mL Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the column flow channel of SPD-600GC. We applied the above-mentioned techniques and developed the device for PCBs analysis. Fig. 1 shows the schematic diagram of the column flow channel, which is as follows: The upper column is a multilayer silica gel column (Purification column; 200 mm 12.5 mm I.D.), and the lower one is a c-alumina column (Concentration column; 0.5 g, 30 mm 6 mm I.D.). These columns were obtained from the Miura Institute of Environmental Science, Miura Co. Ltd., Japan. The crude extract obtained by MAE or liquid liquid extraction was directly applied on top of the purification column, followed by setting the column parts and starting the program sequence. After heating the purification column to 60 C, the PCBs in the purification column were eluted with 65 ml of n-hexane maintained at 60 C, and then, the PCBs trapped in the concentration column were reversibly eluted with 1.0 ml of toluene maintained at approximately 60 C. A special feature of this device has nothing the valve, equipping a function of switching flow line by air pressure. When n-hexane on Step 1 flows, a solenoide air valve seals up a space of sample collection vial. While, at Step 2 flowing toluene for recovering PCBs, a solenoide air valve open a space of sample collection vial and shut the upper flow line of n-hexane at the same time. Therefore, there is little possibility of occurring carryover of PCBs; because of this device have nothing the valve contaminated by PCBs. To observe the recovery rates of PCBs by SPD, the recovery tests were examined in several crude extracts of the blubber obtained by liquid liquid extraction. The individual extracts were purified using SPD and the conventional clean-up technique (multilayer silica gel column chromatography), and the PCB concentrations in these purified solutions were measured by HRGC-HRMS. On the basis of the collected data, the recovery rates of PCBs by SPD were calculated. And, in order to confirm effects of purification in SPD, Full scan chromatograms of eluate from multilayer silica gel column and SPD were compared. The interferences in the eluate purified by SPD were also checked as follows: The OCPs standard solution (1.0 ml) was applied to the purification column and followed by starting the program sequence similar to the operation mentioned above; the OCP chromatograms in the purified solution were obtained by GC-ECD measurement. On the basis of the comparisons between the OCP chromatograms before/after the pretreatment by SPD, the influence of interferences for the PCB determination were evaluated Instrumental analysis The determination of PCBs were analyzed using GC-ECD (Agilent 6890N GC Micro-ECD; Agilent Technologies, DE, USA), equipped with a DB-5 ms capillary column (60 m, 0.25 mm I.D., 0.25 lm; J&W Scientific, USA) and the detector of the radioactive source 63 Ni at a constant flow rate of 0.7 ml N 2 min 1 as a carrier gas. The initial column temperature was maintained at 100 C for 1 min, and then increased to 190 C at the rate of 20 Cmin 1. Then, the temperature was increased to 250 C at the rate of 2 C min 1, raised to 280 C at the rate of 6 C min 1, and finally maintained at 280 C for 9.5 min. The injection port was operated in the splitless mode at 270 C, and the detector was maintained at 300 C. The quantification of PCBs was performed using external standard calibration, and the average response factor was generated from four point calibrations. Integration and calculations were accomplished using Agilent Chemstation software (Rev. B SR1 [260]). The linearity and detection limit (DL) were validated by Agilent Technologies: The linearity for quantification was in the range of ng g 1 ; the DLs of PCB congeners by GC-ECD were approximately 0.05 ng g 1 (Chanel and Chang, 2000). The DLs and quantification limits (QL) in this procedure were also calculated from the standard deviations of the repeated analyses using the sub-reference material, and the DL and QL in this case appeared as SD 3 and SD 10, respectively. The quantification and congener pattern for total PCBs of minke whales by HRGC-HRMS was performed using Agilent 6890N GC and JMS-700S (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). The gas chromatographic separations of PCB congeners were performed on HT8-PCB fused silica capillary column (60 m, 0.25 mm I.D., 0.2 lm film thickness; SGE, USA). Ultra-high-purity helium was used at a constant flow rate of 1.0 ml min 1 as a carrier gas. The oven temperature program for the measurements of tetra- to hepta-pcbs was maintained at 120 C for 1 min and then increased to 180 C at the rate of 20 C min 1. The temperature was raised to 280 C at the rate of 2 C min 1 and finally maintained at 280 C for 3 min. On the other hand, for mono-, di-, tri-, octa-, nona-, and deca-pcb, the temperature was initially set as 120 C, and after maintaining it for 1 min, the temperature was increased to 180 C at the rate of 20 Cmin 1. Finally, the temperature was raised to 280 C at the rate of 4 C min 1 and maintained for 9.5 min. For all of the PCB measurements, the injector temperature was maintained at 280 C, and 2 ll of sample was injected in the splitless injection mode. The HRMS was operated in the electron ionization mode, using selected ion monitoring at an electron energy of 38 ev and an ionizing current of 500 la. The resolution of the instrument was routinely more than 10,000 (10% valleys). Two isotope ions, M + and (M+2) + or (M+2) + and (M+4) +, which are known as a relative abundance, were monitored in each of the PCB congeners and 13 C-labelled surrogate standards. Concentrations of the identified PCB congeners were calculated using the mean relative response factors determined from standard calibration runs. The procedure QLs were in the range of 0.1 to 1.0 pg g 1 for mono- to deca-chlorinated congeners. The initial test of purification procedure was undertaken using gas chromatography low resolution mass spectrometry (GC- LRMS). GC-LRMS is Agilent 6890 N GC equipped with a JMS-K9 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). A capillary column and GC temperature programme were same GC-ECD procedure. PCBs fraction from silica gel column clean-up procedure and SPD was concentrated 50 ll
4 1072 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) Table 1 The concentrations of 173 PCB congeners in 35 minke whale blubber detected by HRGC-HRMS. Below all data were obtained by the conventional method. Congeners pg/g fresh weight % to total PCBs (b) (a) Average Maximum Minimum 1Cl # # # Cl # #8, # # # #13, # Cl # #18 * # # # # # # # # # # #28 * #20, # # # # Cl # # #53 * # # # #52, #69 * # #49 * #48, #47 * #44 * # # # #71 * # # # # #74 * # #66 * # # # # # # Cl # # # # # #102, #93, * #98, #95 # #91 * # #92 * #84 * # # #101 * # #99 * #112, # Table 1 (continued) Congeners pg/g fresh weight % to total PCBs (b) (a) Average Maximum Minimum # # #86, * #117, #97 #125, #116 #87, * #115 #85 * #120, * #110 # # #109, #107 # #118 * # #105 * # Cl # # # # #136 * # # #151 * #135 * #144, #147 * #149, #139 * # # # # # # #146 * #132 * #153 * # #137 * #130 * #164, #163 * #138 * #158 * # # #128 * #167 * #156 * # # Cl # # #179 * # #178 * # #182, #187 * #183 * # #174 * # #177 * #171 * # #180 * # # #170 * # #
5 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) Table 1 (continued) Congeners pg/g fresh weight % to total PCBs (b) toluene and analyzed by GC-LRMS full scan mode (mass range: ), respectively. 3. Results and discussion (a) Average Maximum Minimum 8Cl #202 * # # # # #198, #199 * # #203 * # #194 * # Cl # # # Cl # Total-PCBs (a) The congeners marked with an asterisk (*) in this table demonstrated a QL value > 200 pg/g in GC-ECD measurement. (b) Relative ratio (%) of each congeners to Total PCBs concentration Profile of PCB congeners in whale blubber In order to clarify the detailed profiles of PCB congeners in minke whale blubber, the concentration of total PCBs in 35 samples of whale blubber were prepared by LLE, multilayer silica gel column, and determined by HRGC-HRMS. The results presented in Table 1 show that the sum burden of 173 congeners among all the PCB congeners (209 congeners) could be actually represented as the total PCBs because the other PCB congeners (36 congeners) were either not detected or were less than the QL obtained by the HRGC-HRMS method. In the case of the PCB measurement by GC-ECD, considering the DL (0.05 ng g 1 ) and QL (0.2 ng g 1 ) of GC-ECD, PCBs with a higher concentration than the QL value included 65 congeners of tri- to octa-chlorinated PCBs, which are marked by asterisks in Table 1; their sum burden accounted for approximately 95% of the total PCB burden. On the other hand, the concentrations of the other congeners, i.e., mono-, di-, nona-, and deca-chlorinated congeners, was very low; moreover, their sum burden accounted for less than 1% of the total PCB burden. It is known that the relatively low residue levels of mono-, di-, nona-, and deca-chlorinated congeners in whale blubber are similar to those in environmental and biological samples, as mentioned in several reports (Ross et al., 2000; Andersen et al., 2001; Hobbs et al., 2001, 2003; Wurl and Obbard, 2005). Consequently, these results indicate that in the case of GC-ECD determination, the measurement of tri- to octa-chlorinated PCB congeners, i.e., 65 congeners, is essential for learning the residue levels of total PCBs in whale blubber Extraction efficiency with MAE In general, the method of LLE has been widely used for the extraction of PCBs in adipose tissues. Table 2 shows the extraction efficiency of PCBs using MAE as a percentage against the PCB concentrations obtained by LLE. Both cleanup were performed by Table 2 Extraction efficiencies from MAE and recoveries from SPD. Congeners Extraction efficiency (%) (a) Recoveries from SPD (%) (b) Average RSD Average RSD 3Cl # # Cl # #52, # # #48, # # # # # Cl #102, #93, #98, # # #92, # # # #86, #117, # #87, # # #120, # # # Cl # # # #144, # #149, # # # # # # #164, # # # # # # Cl # # # #182, # # # # # # # # Cl # #198, # # # # (a) 2 g, 3 g, 4 g and 5 g of blubbers were treated by MAE and LLE, respectively. And both purification were performed by silica gel column, determined by HRGC-HRMS. Relative efficiencies of MAE to LLE procedure were shown. (b) Individual five blubbers were analyzed by MAE and SPD, Simultaneously, those samples were analyzed by LLE and Silica gel column, determined by HRGC-HRMS. Relative recoveries of MAE/SPD procedure to conventional procedure were calculated. multilayer silica gel column. The averages of PCB extraction efficiencies obtained in individual samples, i.e. for 2 g, 3 g, 4 g, and 5 g, ranged from 78% to 103%, and their relative standard deviations (RSD, 1 13%) were relatively low. Even if the extracts were pipetted from no-accurately 20 ml n-hexane layer added the non-saponificated lipids of blubber, this result indicates that this MAE procedure can keep up the precision of efficiency and quantification, up to 5 g fresh
6 1074 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) weight. The sample weight for routine analysis are normally about 2 g, and sufficiently fulfill the quantification limit, below one-tenth of the provisional limit 0.5 lgg 1 (fresh weight). Therefore, after MAE, the operating is only pipetting without concentration processes, this extraction procedure is suitable into the routine monitoring and screening method for PCBs from whale blubbers. It is known that the degradation of highly chlorinated congeners may not occur during the process of saponification at room temperature (Booij and Berg, 1994; Greizerstein et al., 1997). In contrast, several researchers investigated the effects of saponification conditions on the determination of PCBs and reported that the decomposition of highly chlorinated congeners at high-temperature saponification was reduced by adding water to ethanolic KOH (Smedes and de Boer, 1997; Numata et al., 2005). In this study, the relatively high extraction efficiency of highly chlorinated congeners would also be considered due to using ethanolic KOH with the added water. Some previous studies have also shown that MAE is faster and a less time-consuming extraction method for the quantitative determination of PCBs in environmental samples. Vetter et al. examined the method of MAE for PCB analysis in seal blubber and cod livers (Vetter et al., 1998). They reported that good results were obtained using the microwave transformer Weflon due to the indirect rise of the temperature of the nonpolar solvent (n-hexane). Xiong et al. investigated the optimized conditions for MAE during the saponification process of biological tissues and the decomposition of OCPs with methanolic 1 M KOH (Xiong et al., 2000). However, further evaluation of the complex processes involved, such as the concentration of extracts, solvent substitution, and filtration after MAE, are required. In this study, the MAE method could be simultaneously carried out for both the saponification of adipose tissues and the extraction of PCBs Purification procedure of PCBs with SPD In order to evaluate the application of SPD in total PCB analysis, the PCB extracts obtained from five blubber samples using MAE were purified by SPD equipped with the purification and concentration columns mentioned above (Chapter 2.6), determined by HRGC-HRMS. The results were compared with those obtained by the multilayer silica gel column and HRGC-HRMS. Table 2 shows the PCB recoveries using SPD as a percentage against those obtained by the conventional method. In general, relatively high and stable recoveries of PCBs were observed in almost all the PCB congeners, indicating that SPD-600GC is an instrument delivering high performance. But no shown in Table 2, certain highly chlorinated PCB congeners (#188, #184, #202, #200, #197, #199, #208, #207, and #209) and lower chlorinated congeners showed relatively low recoveries, although their burdens were negligible with respect to the total PCB burden. It seems reasonable to con- Fig. 2. Chromatograms of individual purification procedures. (a) and (b) shows full scan total ion chromatograms by GC-LRMS treated a whale blubber by multilayer silica gel column and SPD, respectively. (c) Shows GC-ECD chromatogram prepared a whale blubber by SPD.
7 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) clude that these highly chlorinated congeners were elute from the concentration column packed with c-alumina. However, it have been known previously that an activated c-alumina column have been eliminated interferences from large amount of saturated cyclic and aliphatic hydrocarbons (Smedes and de Boer, 1997; Aries et al., 2004; Fujita et al., 2005). Therefore, we examined the comparison of two purification procedure, silica gel column and SPD. Fig. 2 shows three chromatograms, Fig. 2a and b are total ions chromatograms by GC-LRMS (these vertical axis maximum scale are same.) of PCBs fractions from silica gel column and SPD, respectively. Both the vertical axis of chromatograms shows same scale. Fig. 2c is GC-ECD chromatograms of PCBs fraction treated whale blubber extracts by SPD. Although co-elution of PCBs with saturated hydrocarbons goes on using n-hexane from silica gel column, it indicate no strong retention occurs on SPD with an activated c- alumina for non-polarity of saturated hydrocarbons. Consequently, purification procedure for PCBs analysis of whale blubbers requires the additional clean up step to free interferences. This SPD equipped highest activated c-alumina effectively eliminated the interferences as saturated and aliphatic hydrocarbons etc., furthermore, is expected by reducing overload of the detector of analytical instrument Interferences as OCPs The concentrations of PCBs in the blubber samples pretreated using MAE and SPD were determined by GC-ECD, and their chromatograms are shown in Fig. 3a. Each peak on the GC-ECD chromatograms was identified from the retention times of the PCB standard as results reported later (Rogers et al., 2004). The chromatograms presented in Fig. 3a demonstrate a good peak separation for almost all the PCB congeners, indicating that the Hz HCH HCB -HCH -HCH -HCH Oxy-Chlordane trans-chlordane o,p -DDE cis-chlordane trans-nonachlor p,p -DDE o,p -DDD cis-nonachlor, p,p -DDD o,p -DDT p,p -DDT min Hz 450 HCB p,p -DDE o,p -DDE trans-chlordane cis-chlordane trans-nonachlor min Hz #90,101,113 #99 #119,150 #116,148,85,p,p -DDE #92, min Fig. 3. GC-ECD chromatograms: (a) OCPs standard solution, (b) OCPs standard solution prepared by SPD, and (c) the extract of the blubber prepared by MAE and SPD.
8 1076 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) GC-ECD [ng/g] y = 1.10x R = HRGC-HRMS [ng/g] Fig. 4. Correlation between the total-pcb concentrations measured by GC-ECD and GC-HRMS. Table 3 Comparison in concentrations of PCBs in the SRM 1588b. GC-ECD determination of PCBs is certainly possible. However, peaks derived from coelutions with other PCB congeners or interferences were observed for several congeners (e.g., #92/84, #119/ 150 and 116/148/85). Generally, almost all the environmental samples were widely contaminated by the OCPs, which generally coexisted with PCBs in the extract solutions. As for the determination of PCBs by GC- ECD using DB-5 ms, some peaks of PCBs are known to overlap with OCP peaks (Vetter et al., 1994). Fig. 3 shows three chromatograms on same retention time: (a) the OCP standard solution consisting of the 16 congeners mentioned above; (b) the OCP standard solution treated by SPD; and (c) the blubber sample extract pretreated by MAE and SPD. The results imply that seven compounds, i.e., HCHs, trans-chlordane, o,p 0 -DDD, cis-nonachlor, p,p 0 -DDD, o,p 0 -DDT, and p,p 0 -DDT were completely removed from the OCP standard solution. In contrast, 10% of trans-chlordane, 6.5% of cis-chlordane, and 27% of trans-nonachlor remained in solution, and the compounds of o,p 0 -DDE and p,p 0 -DDE could not be removed almost at all. Nevertheless, the sum burden of the PCB congeners overlapping with these OCPs was only 1.2% of the total PCBs burden, indicat- Congeners (a) Certified or reference concentration (ng/g) MAE/SPD/GC-ECD (n = 5) Ave. (ng/g) SD (ng/g) RSD (%) PCB #18 (2,2 0,5-Trichlorobiphenyl) 7.96 ± 0.45(b) #12 (3,4-Dichlorobiphenyl) #13 (3,4 0 -Dichlorobiphenyl) PCB #28 (2,4,4 0 -Trichlorobiphenyl) 27.8 ± 1.4(b) #31 (2,4 0,5-Trichlorobiphenyl) 8.52 ± 0.50(b) PCB #52 (2,2 0,5,5 0 -Tetrachlorobiphenyl) 82.4 ± 1.7(b) #73 (2,3 0,5 0,6-Tetrachlorobiphenyl) PCB #49 (2,2 0,4,5 0 -Tetrachlorobiphenyl) 29.8 ± 0.6(b) PCB #44 (2,2 0,3,5 0 -Tetrachlorobiphenyl) 32.4 ± 2.7(b) i PCB #74 (2,4,4 0,5-Tetrachlorobiphenyl) 40 ± 11(c) PCB #66 (2,3 0,4,4 0 -Tetrachlorobiphenyl) 51.7 ± 7.5(b) i #95 (2,2 0,3,5 0,6-Pentachlorobiphenyl) 37.7 ± 8.2(b) PCB #101 (2,2 0,4,5,5 0 -Pentachlorobiphenyl) 127 ± 9(b) #90 (2,2 0,3,4 0,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl) PCB #99 (2,2 0,4,4 0,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl) 101 ± 12(b) PCB #87 (2,2 0,3,4,5 0 -Pentachlorobiphenyl) 54.6 ± 2.1(b) PCB #110 (2,3,3 0,4 0,6-Pentachlorobiphenyl) 69.3 ± 4.8(b) PCB #151 (2,2 0,3,5,5 0,6-Hexachlorobiphenyl) 48.1 ± 5.4(b) #82 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4-Pentachlorobiphenyl) 8.2 ± 1.6(c) PCB #149 (2,2 0,3,4 0,5 0,6-Hexachlorobiphenyl) 90 ± 11(b) #123 (2 0,3,4,4 0,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl) PCB #118 (2,3 0,4,4 0,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl) 172 ± 7(b) #140 (2,2 0,3,4,4 0,6 0 -Hexachlorobiphenyl) #139 (2,2 0,3,4,4 0,6-Hexachlorobiphenyl) PCB #153 (2,2 0,4,4 0,5,5 0 -Hexachlorobiphenyl) 275 ± 4(b) PCB #105 (2,3,3 0,4,4 0 -Pentachlorobiphenyl) 59.2 ± 1.2(b) PCB #138 (2,2 0,3,4,4 0,5 0 -Hexachlorobiphenyl) 212 ± 29(b) J # 163 (2,3,3 0,4 0,5,6-Hexachlorobiphenyl) 42.2 ± 3.2(c) #164 (2,3,3 0,4 0,5 0,6-Hexachlorobiphenyl) PCB #178 (2,2 0,3,3 0,5,5 0,6-Heptachlorobiphenyl) 28 ± 1(c) #129 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4,5-Hexachlorobiphenyl) PCB #187 (2,2 0,3,4 0,5,5 0,6-Heptachlorobiphenyl) 43.6 ± 7.2(b) #182 (2,2 0,3,4,4 0,5,6 0 -Heptachlorobiphenyl) PCB #183 (2,2 0,3,4,4 0,5 0,6-Heptachlorobiphenyl) 28.9 ± 1.8(b) #162 (2,3,3 0,4 0,5,5 0 -Hexachlorobiphenyl) PCB #128 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4,4 0 -Hexachlorobiphenyl) 39.9 ± 6.0(b) PCB #167 (2,3 0,4,4 0,5,5 0 -Hexachlorobiphenyl) 12.2 ± 0.8(c) PCB #177 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4 0,5,6-Heptachlorobiphenyl) 5.18 ± PCB #156 (2,3,3 0,4,4 0,5-Hexachlorobiphenyl) 18.0 ± 2.1(b) PCB #180 (2,2 0,3,4,4 0,5,5 0 -Heptachlorobiphenyl) 98.5 ± 6.3(b) PCB #170 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4,4 0,5-Heptachlorobiphenyl) 41.9 ± 3.8(b) J # 190 (2,3,3 0,4,4 0,5,6-Heptachlorobipheny l) PCB #194 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4,4 0,5,5 0 -Octachlorobiphenyl) 13.5 ± 1.2(b) PCB #206 (2,2 0,3,3 0,4,4 0,5,5 0,6-Nonachlorobiphenyl) 3.75 ± 0.07(b) (a) When two or more congeners are known to coelute using GC-ECD on DB-5 ms column, the PCB congener listed first is the major component, and the additional congeners may be present as minor components detected by GC-HRMS. (b) NIST-certified concentration values. (c) NIST-reference concentration values.
9 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) ing that these PCB congeners were possibly negligible in the total PCB quantifications. Xiong et al. investigated the microwave-assisted decomposition of OCPs, a-hch, b-hch, d-hch, c-hch, p,p 0 -DDE, p,p 0 -DDD, o,p 0 - DDT, p,p 0 -DDT, aldrin, and dieldrin in mussel samples (Xiong et al., 2000). According to their results, a-hch, b-hch, d-hch, c- HCH, p,p 0 -DDD, o,p 0 -DDT, and p,p 0 -DDT could be transformed, but decomposition for 30 45% of p,p 0 -DDE, aldrin, and dieldrin did not occur. In addition, their results demonstrated that dieldrin and its decomposing products were perfectly eliminated from the crude extracts by rinsing with concentrated H 2 SO 4 (Carro et al., 2002). The purification technique using SPD combined with MAE can be used for the removal of OCPs from crude extracts. However, since several PCB congeners could not be determined the detailed constitution of PCB congeners needs to be clarified further Comparison of GC-ECD and HRGC-HRMS In order to confirm the specificity of MAE/SPD/GC-ECD determination, nine samples of whale blubber were selected, and their PCB concentrations were analyzed according to the following procedure. The solutions prepared by MAE and SPD were equally divided into two vials, and then their PCB concentrations were quantified by GC-ECD and HRGC-HRMS, respectively. The correlation between the concentrations of total PCBs obtained by the two detectors is shown in Fig. 4. The concentrations of the total PCBs by GC-ECD was approximately 1.1 times higher than those obtained by HRGC-HRMS; further, they were significantly correlated (correlation coefficient = 0.998, P < 0.05). The slightly high values obtained by GC-ECD compared with those obtained with HRGC-HRMS might be due to the overlap of OCPs such as persistent organic pollutants, polychlorinated naphtalenes, PCDD/DFs, etc., as mentioned in previous reports (Ong and Hites, 1994; Hong et al., 2004). However, the total PCBs values using GC-ECD increases nearly linearly with an increase in PCB concentrations of blubbers using HRGC-HRMS Accuracy and precision In order to evaluate the accuracy and precision of the new method that combines MAE, SPD, and GC-ECD, a repeated analysis (n = 5) of PCBs was examined in SRM 1588(b). Table 3 shows the concentrations of PCB congeners obtained by the repeated analysis with certified concentration values. Almost all the congeners examined showed a good agreement with the certified values, and their RSDs except for those of three congeners, i.e., #18, #183, and #206 ranged from 1% to 7%. However, compared with the certified values, relatively low values were found in #183/162 and #206; this might be due to their relatively low recoveries on the concentration column of SPD. Coelutions of PCB congeners were observed in two pairs, #28/#31 and #66/#95. However the sum of #28 and #31was good agreement with the sum of their certified values, and the sum of #65 and #95, too. Furthermore, the value of congener #87 obtained in this study showed a good agreement with the certified value, which is most likely a result of the removal of dieldrin which generally coelutes with the #87 congener as reported later (Lefkovitz et al., 2001). Next, the repeated analysis (n = 5) of PCBs using MAE, SPD, and GC-ECD was also performed for the sub-reference material. The standard deviations (SD) were calculated as the repeatability and the DL/QL of this method. Almost all the RSDs for the PCB congeners showed lower values as compared with the maximum allowable RSD (15%) that was expected by a previous report (Shah et al., 1992). The QL of the total PCB calculated from that of the individual PCB congeners was 41 ng g 1, and this value was less than one-tenth of the provisional limit, i.e., 500 ng g Conclusions The validation of an analytical method for PCBs using MAE, SPD, and GC-ECD was performed for blubber samples of minke whales. The results indicated that PCBs in whale blubber could be efficiently extracted with a small volume (20 ml) of n-hexane using MAE because of the simultaneous effects of saponification and extraction; further, its crude extract could be rapidly purified and automatically substituted to a small volume (1 ml) of toluene using SPD without using concentrators. Furthermore, it was found that the PCB concentration in the purified and concentrated solution could be accurately and precisely determined by GC-ECD, indicating that the new method that combined MAE, SPD, and GC-ECD is appropriate and effective for the determination of PCBs in whale blubber. References Andersen, G., Kovacs, K.M., Lydersen, C., Skaare, J.U., Gjertz, I., Jenssen, B.M., Concentrations and patterns of organochlorine contaminants in white whales (Delphinapterus leucas) from Svalbard, Norway. Sci. Total Environ. 264, Aries, E., Anderson, D.R., Ordsmith, N., Hall, K., Fisher, R., Development and validation of a method for analysis of dioxin-like PCBs in environmental samples from the steel industry. Chemosphere 54, Booij, K., Berg, C., Comparison of techniques for the extraction of lipids and PCBs from benthic invertebrates. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 53, Carro, N., García, I., Ignacio, M.-C., Llompart, M., Yebra, M.-C., Mouteira, A., Microwave-assisted extraction and mild saponification for determination of organochlorine pesticides in oyster samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 374, Chanel, I., Chang, I., Analysis of organochlorine pesticides and PCP Congeners with the Agilent 6890 Micro-ECD, Publication Number: E. Connell, D.W., Bioaccumulation behavior of persistent organic chemicals with aquatic organisms. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 102, Focant, J.F., De Pauw, E., Fast automated extraction and clean-up of biological fluids for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 776, Focant, J.F., Pirard, C., De Pauw, E., Automated sample preparationfractionation for the measurement of dioxins and related compounds in biological matrices: a review. Talanta 63, Fujita, H., Hamada, N., Sawadaishi, K., Honda, K., Development of a sample preparation system for dioxins; application to immunoassay. Organohalogen Comp. 66, Fujita, H., Hamada, N., Sawadaishi, K., Honda, K., Investigation of the purification/concentration method for dioxins analysis by GC MS and bioassay. J. Environ. Chem. 15, (in Japanese with English abstract). Gauthier, J.M., Metcalfe, C.D., Sear, R., Validation of the blubber biopsy technique for monitoring of organochlorine contaminants in balaenopterid whales. Mar. Environ. Res. 43, Greizerstein, H.B., Gigliotti, P., Vena, J., Freudenheim, J., Kostyniak, P.J., Standardization of a method for the routine analysis of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and selected pesticides in human serum and milk. J. Anal. Toxicol. 21, Hobbs, K.E., Muir, D.C.G., Born, E.W., Dietz, R., Haug, T., Metcalfe, T., Metcalfe, C., Øien, N., Levels and patterns of persistent organochlorines in minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) stocks from the North Atlantic and European Arctic. Environ. Pollut. 121, Hobbs, K.E., Muir, D.C.G., Mitchell, E., Temporal and biogeographic comparisons of PCBs and persistent organochlorine pollutants in the blubber of fin whales from eastern Canada in Environ. Pollut. 114, Hong, J., Kim, Hye.-Y., Kim, Do-G., Seo, J., Kim, Kang-J., Rapid determination of chlorinated pesticides in fish by freezing-lipid filtration, solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1038, Kishino, J., Tokuda, Y., Takagi, Y., Kataoka, C., Fujita, H., Hamada, N., Sawadaishi, K., Honda, K., Evaluation of automated sample preparation system for immunoassay in dioxins analysis. Organohalogen Comp. 66, Lefkovitz, L.F., Neff, J.M., Lizotte, R., Hall, M., Comparison of two analytical methods for measurement of chlorinated pesticides and PCB congeners in biological tissue Trends in Boston Harbor lobster tissue. Boston: Massachusetts Water Resources Authority. Report ENQUAD p. plus appendices. Miyawaki, T., Fujita, H., Hamada, N., Yamamoto, K., Honda, K., Development of rapid analysis for dioxins by using sample pretreatment device and GC/MS measurement system. Organohalogen Comp. 69, Natalia, F.U., Elisa, B.G., Alfredo, S.M., Review Sample handling strategies for the determination of persistent trace organic contaminants from biota samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 590, Numata, M., Yarita, T., Aoyagi, Y., Yamazaki, M., Takatsu, A., Investigation of saponification for determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in marine sediments. Chemosphere 58,
10 1078 H. Fujita et al. / Chemosphere 74 (2009) Ong, V.S., Hites, R.A., Review electron capture mass spectrometry of organic environmental contaminants. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 13, Rogers, E., Petreas, M., Park, J.S., Zhao, G., Charles, M.J., Evaluation of four capillary columns for the analysis of organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human serum for epidemiologic studies. J. Chromatogr. B 813, Ross, P.S., Ellis, G.M., Ikonomou, M.G., Barrett-Lennard, L.G., Addison, R.F., High PCB concentrations in free-ranging pacific killer whales, orcinus orca: effects of age, sex and dietary preference. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 40, Shah, V.P., Midha, K.K., Dighe, S., McGilveray, I.J., Skelly, J.P., Yacobi, A., Layloff, T., Viswanathan, C.T., Cook, C.E., McDowall, R.D., Pittman, K.A., Spector, S., Analytical methods validation: bioavailability, bioequivalence and pharmacokinetic studies. Pharm. Res. 9, Smedes, F., de Boer, J., Determination of chlorobiphenyls in sediments analytical methods. Trends Anal. Chem. 16, UNEP (United Nations Environmental Program), Stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants, Stockholm, 22 May. Vetter, W., Luckas, B., Biermans, F., Mohnke, M., Rotzsche, H., Gas chromatographic separation of polychlorinated biphenyls on a new apolar capillary column. J. High Resolut. Chrom. 17, Vetter, W., Weichbrodt, M., Hummert, K., Glotz, D., Luckas, B., Combined microwave-assisted extraction and gel permeation chromatography for the determination of chlorinated hydrocarbons in seal blubber and cod livers. Chemosphere 37, Woodley, T.H., Brown, M.W., Kraus, S.D., Gaskin, D.E., Organochlorine concentrations in North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) blubber. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 21, Wurl, O., Obbard, J.P., Organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in Singapore s coastal marine sediments. Chemosphere 58, Xiong, G., He, X., Zhang, Z., Microwave-assisted extraction or saponification combined with microwave-assisted decomposition applied in pretreatment of soil or mussel samples for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls. Anal. Chim. Acta 413,
DEVELOPMENT OF A SAMPLE PREPARATION SYSTEM FOR DIOXINS: APPLICATION TO IMMUNOASSAY
 DEVELOPMENT OF A SAMPLE PREPARATION SYSTEM FOR DIOXINS: APPLICATION TO IMMUNOASSAY Hiroyuki Fujita 1, Noriaki Hamada 2, Kazuyuki Sawadaishi 3, Katsuhisa Honda 1 1 Environmental Science for Industry, Ehime
DEVELOPMENT OF A SAMPLE PREPARATION SYSTEM FOR DIOXINS: APPLICATION TO IMMUNOASSAY Hiroyuki Fujita 1, Noriaki Hamada 2, Kazuyuki Sawadaishi 3, Katsuhisa Honda 1 1 Environmental Science for Industry, Ehime
Yokogawa Analytical Systems Inc., Nakacho, Musashino-shi, Tokyo , Japan.
 Determination of organochlorine pesticides in river water by gas chromatography-negative-ion chemical-ionization mass spectrometry using large volume injection Sadao Nakamura,* Takashi Yamagami and Shigeki
Determination of organochlorine pesticides in river water by gas chromatography-negative-ion chemical-ionization mass spectrometry using large volume injection Sadao Nakamura,* Takashi Yamagami and Shigeki
METHOD 8082A. POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBs) BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
 METHOD 8082A POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBs) BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 8082 is used to determine the concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as s or as individual
METHOD 8082A POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBs) BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 8082 is used to determine the concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as s or as individual
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
 Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) 3 2 2 3 4 4 ()n 5 6 6 5 ()m Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have been the subject of a broad range of studies and investigations because of their environmental persistency
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) 3 2 2 3 4 4 ()n 5 6 6 5 ()m Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have been the subject of a broad range of studies and investigations because of their environmental persistency
METHOD 3600C CLEANUP
 METHOD 3600C CLEANUP 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3600 provides general guidance on selection of cleanup methods that are appropriate for the target analytes of interest. Cleanup methods are applied
METHOD 3600C CLEANUP 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3600 provides general guidance on selection of cleanup methods that are appropriate for the target analytes of interest. Cleanup methods are applied
METHOD 3600B CLEANUP
 METHOD 3600B CLEANUP 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3600 provides general guidance on selection of cleanup methods that are appropriate for the target analytes of interest. Cleanup methods are applied
METHOD 3600B CLEANUP 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3600 provides general guidance on selection of cleanup methods that are appropriate for the target analytes of interest. Cleanup methods are applied
Evaluation of Several Columns and Solvents for Post-Extraction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Clean-up of Fish Tissue Prior to PCB Analysis
 Evaluation of Several Columns and Solvents for Post-Extraction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Clean-up of Fish Tissue Prior to PCB Analysis Keywords: Automated GX-271 GPC Clean-up System, Contaminants,
Evaluation of Several Columns and Solvents for Post-Extraction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Clean-up of Fish Tissue Prior to PCB Analysis Keywords: Automated GX-271 GPC Clean-up System, Contaminants,
2015 Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit Jim Occhialini, Cindy McQueen Alpha Analytical
 Review of a Comprehensive, Alternate Approach for PCB Congener / Homolog Analysis 2015 Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit Jim Occhialini, Cindy McQueen Alpha Analytical What is TPH? PCB Chemistry
Review of a Comprehensive, Alternate Approach for PCB Congener / Homolog Analysis 2015 Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit Jim Occhialini, Cindy McQueen Alpha Analytical What is TPH? PCB Chemistry
Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls Using GC/MS/MS Operated in the MRM Mode
 PO-CON1610E Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls Using GC/MS/MS Operated in the MRM Mode Pittcon 2016 1110-2 Brahm Prakash, William Lipps, Di Wang, Shilpi Chopra, Nicole
PO-CON1610E Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls Using GC/MS/MS Operated in the MRM Mode Pittcon 2016 1110-2 Brahm Prakash, William Lipps, Di Wang, Shilpi Chopra, Nicole
Identification and Quantitation of PCB Aroclor Mixtures in a Single Run Using the Agilent 7000B Triple Quadrupole GC/MS
 Identification and Quantitation of PCB Aroclor Mixtures in a Single Run Using the Agilent 7B Triple Quadrupole GC/MS Application Note Authors Dale R. Walker and Fred Feyerherm Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Identification and Quantitation of PCB Aroclor Mixtures in a Single Run Using the Agilent 7B Triple Quadrupole GC/MS Application Note Authors Dale R. Walker and Fred Feyerherm Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Technical Report. Abstract: Pu Wang 1, Huizhong Sun 1, Qinghua Zhang 1, Feifei Tian 2, Lei Cao 2
 C46-E299 Technical Report Determination of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in Foodstuffs and Animal Feed Using a Triple Quadrupole GCMS-TQ8040 System with Smart MRM Transforms
C46-E299 Technical Report Determination of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in Foodstuffs and Animal Feed Using a Triple Quadrupole GCMS-TQ8040 System with Smart MRM Transforms
Organochlorine Pesticides by GCxGC-ECD
 Organochlorine Pesticides by GCxGC-ECD LECO Corporation; Saint Joseph, Michigan USA Key Words: GCxGC-ECD, Environmental, Quantification 1. Introduction United States Environmental Protection Agency Method
Organochlorine Pesticides by GCxGC-ECD LECO Corporation; Saint Joseph, Michigan USA Key Words: GCxGC-ECD, Environmental, Quantification 1. Introduction United States Environmental Protection Agency Method
ApplicationNOTE A STUDY OF THE ANALYSIS OF POLYBROMINATED DIPHENYL ETHER FLAME RETARDANTS BY GC/MS/MS. Introduction. Materials and Methods
 Abstract The development of a GC/MS/MS method for the analysis of brominated flame retardants will be presented. Standard methods require the use of high resolution magnetic sector instrumentation, which
Abstract The development of a GC/MS/MS method for the analysis of brominated flame retardants will be presented. Standard methods require the use of high resolution magnetic sector instrumentation, which
Aroclors, Homologs and Congeners An Evaluation of the Options for PCB Analysis and a Comparison of the Interpretive Value
 Aroclors, Homologs and Congeners An Evaluation of the Options for PCB Analysis and a Comparison of the Interpretive Value Chuck Neslund, Technical Director, Eurofins Lancaster Laboratories Environmental,
Aroclors, Homologs and Congeners An Evaluation of the Options for PCB Analysis and a Comparison of the Interpretive Value Chuck Neslund, Technical Director, Eurofins Lancaster Laboratories Environmental,
GC Analysis of Polybrominated Flame Retardants Application
 GC Analysis of Polybrominated Flame Retardants Application Environmental Authors Eberhardt Kuhn, Jason Ellis Agilent Technologies, Inc. 91 Blue Ravine Rd, Folsom, CA 9563 USA Steve Wilbur Agilent Technologies,
GC Analysis of Polybrominated Flame Retardants Application Environmental Authors Eberhardt Kuhn, Jason Ellis Agilent Technologies, Inc. 91 Blue Ravine Rd, Folsom, CA 9563 USA Steve Wilbur Agilent Technologies,
U.S. EPA Method 8270 for multicomponent analyte determination
 ENVIRONMENTAL application note U.S. EPA Method 8270 for multicomponent analyte determination Elaine A. LeMoine and Herman Hoberecht Introduction Multicomponent analytes are compounds that yield several
ENVIRONMENTAL application note U.S. EPA Method 8270 for multicomponent analyte determination Elaine A. LeMoine and Herman Hoberecht Introduction Multicomponent analytes are compounds that yield several
Quantification of Pesticides in Food without Calibration using GC/FID with the Polyarc Reactor
 Quantification of Pesticides in Food without Calibration using GC/FID with the Polyarc Reactor Application Note Pesticides Authors Charlie Spanjers and Paul Dauenhauer University of Minnesota, Twin Cities
Quantification of Pesticides in Food without Calibration using GC/FID with the Polyarc Reactor Application Note Pesticides Authors Charlie Spanjers and Paul Dauenhauer University of Minnesota, Twin Cities
HRMS PBDE Analysis on a Thermo DFS. Dave Hope, Pacific Rim Laboratories Inc
 HRMS PBDE Analysis on a Thermo DFS Dave Hope, Pacific Rim Laboratories Inc Outline PBDE what is it and why are we interested in it EPA 1614 HRMS analysis Considerations for Thermo DFS / Trace GC Food analysis
HRMS PBDE Analysis on a Thermo DFS Dave Hope, Pacific Rim Laboratories Inc Outline PBDE what is it and why are we interested in it EPA 1614 HRMS analysis Considerations for Thermo DFS / Trace GC Food analysis
Development of Environmental Analysis Methods Using Supercritical Fluid Extraction and Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
 Focusing Review Development of Environmental Analysis Methods Using Supercritical Fluid Extraction and Supercritical Fluid Chromatography National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ), National Institute
Focusing Review Development of Environmental Analysis Methods Using Supercritical Fluid Extraction and Supercritical Fluid Chromatography National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ), National Institute
Analysis of Total PCBs and PCB Congeners and Trans-nonachlor in Fish by Gas Chromatography/ Negative Chemical Ionization Single Ion Mass Spectrometry
 Analysis of Total PCBs and PCB Congeners and Trans-nonachlor in Fish by Gas Chromatography/ Negative Chemical Ionization Single Ion Mass Spectrometry Standard Operating Procedure SOP No. HC 519.D (Replaces:
Analysis of Total PCBs and PCB Congeners and Trans-nonachlor in Fish by Gas Chromatography/ Negative Chemical Ionization Single Ion Mass Spectrometry Standard Operating Procedure SOP No. HC 519.D (Replaces:
Worldwide Recognition for the Synthesis of All 209 PCB Congeners
 Worldwide Recognition for the Synthesis of All 209 PCB Congeners EPA Method 1668 Standards for the Analysis of All 209 Congeners AccuStandard, Inc. Here s why AccuStandard is the recognized market leader
Worldwide Recognition for the Synthesis of All 209 PCB Congeners EPA Method 1668 Standards for the Analysis of All 209 Congeners AccuStandard, Inc. Here s why AccuStandard is the recognized market leader
DETERMINATION OF OCs, PCBs AND SYNTHETIC PYRETHROIDS IN ANIMAL FAT
 DETERMINATION OF OCs, PCBs AND SYNTHETIC PYRETHROIDS IN ANIMAL FAT Peter Hancock 1, Mike Hetmanski 2 and Richard J. Fussell 2 1 Waters Corporation, Atlas Park, Simonsway, Manchester M22 5PP, UK 2 Central
DETERMINATION OF OCs, PCBs AND SYNTHETIC PYRETHROIDS IN ANIMAL FAT Peter Hancock 1, Mike Hetmanski 2 and Richard J. Fussell 2 1 Waters Corporation, Atlas Park, Simonsway, Manchester M22 5PP, UK 2 Central
Methods of Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Congeners Using an Application-Specific Capillary GC Column
 Methods of Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Congeners Using an Application-Specific Capillary GC Column Frank L. Dorman, Gary B. Stidsen, Chris M. English and Lydia Nolan Restek Corporation, Bellefonte,
Methods of Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Congeners Using an Application-Specific Capillary GC Column Frank L. Dorman, Gary B. Stidsen, Chris M. English and Lydia Nolan Restek Corporation, Bellefonte,
ONE STEP CLOSER TO A COOK BOOK METHOD FOR DIOXIN ANALYSIS PART 2: ANALYSIS OF FOOD SAMPLES
 ONE STEP CLOSER TO A COOK BOOK METHOD FOR DIOXIN ANALYSIS PART 2: ANALYSIS OF FOOD SAMPLES Patterson, Donald G. Jr 1, Shirkhan, Hamid 2, Sadeghi, Kambiz 2,Germansderfer, Phil-M 2, Focant, Jean-Francois
ONE STEP CLOSER TO A COOK BOOK METHOD FOR DIOXIN ANALYSIS PART 2: ANALYSIS OF FOOD SAMPLES Patterson, Donald G. Jr 1, Shirkhan, Hamid 2, Sadeghi, Kambiz 2,Germansderfer, Phil-M 2, Focant, Jean-Francois
Hiroyuki FUJITA 1 *, Takanori MAKINO1, Kenji INABA 1, Kazuki YAMAMOTO 2
 PAP2348_No14 Hiroyuki FUJITA 1 *, Takanori MAKINO1, Kenji INABA 1, Kazuki YAMAMOTO 2 1: MIURA CO., LTD., 864-1, Hojotsuji, Matsuyama, Ehime, 799-243, JAPAN; 2: Ehime University, 3-5-7, Tarumi, Matsuyama,
PAP2348_No14 Hiroyuki FUJITA 1 *, Takanori MAKINO1, Kenji INABA 1, Kazuki YAMAMOTO 2 1: MIURA CO., LTD., 864-1, Hojotsuji, Matsuyama, Ehime, 799-243, JAPAN; 2: Ehime University, 3-5-7, Tarumi, Matsuyama,
Multi-residue Analysis for PAHs, PCBs and OCPs on Agilent J&W FactorFour VF-Xms
 Multi-residue Analysis for PAHs, PCBs and OCPs on Agilent J&W FactorFour VF-Xms Application Note Author Laura Provoost Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction In multi-residue analysis different groups
Multi-residue Analysis for PAHs, PCBs and OCPs on Agilent J&W FactorFour VF-Xms Application Note Author Laura Provoost Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction In multi-residue analysis different groups
Spectra Library Electron Capture Negative Ion (ECNI) Mass Spectra of Selected Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs)
 Spectra Library Electron Capture Negative Ion (ECNI) Mass Spectra of Selected Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) The following 63 mass spectra were measured by gas chromatography (GC) (6890N, Agilent
Spectra Library Electron Capture Negative Ion (ECNI) Mass Spectra of Selected Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) The following 63 mass spectra were measured by gas chromatography (GC) (6890N, Agilent
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GCMS)
 Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GCMS) Organics Chlorinated pesticides DDT Chlordanes Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) DDT (Dichlorodiphenyl-trichloroethane) Used
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GCMS) Organics Chlorinated pesticides DDT Chlordanes Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) DDT (Dichlorodiphenyl-trichloroethane) Used
VALIDATION OF AN IMPROVED EUROPEAN STANDARD METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF PCBs IN OIL SAMPLES
 Nova Biotechnologica 9-3 (2009) 249 VALIDATION OF AN IMPROVED EUROPEAN STANDARD METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF PCBs IN OIL SAMPLES ZDENKA CENCIČ KODBA 1, DARINKA BRODNJAK VONČINA 2 1 Institute of Public
Nova Biotechnologica 9-3 (2009) 249 VALIDATION OF AN IMPROVED EUROPEAN STANDARD METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF PCBs IN OIL SAMPLES ZDENKA CENCIČ KODBA 1, DARINKA BRODNJAK VONČINA 2 1 Institute of Public
separation of the cleaned extract in subgroups of compounds (PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs) depending on their polarity and geometry. The fractions can then be a
 ONE STEP CLOSER TO A COOK BOOK METHOD FOR DIOXIN ANALYSIS PART 1: THE PROCEDURE Focant JF 1, Shirkhan H 2, Patterson Jr DG 3 1 CART, Organic and Biological Analytical Chemistry, Mass Spectrometry Laboratory,
ONE STEP CLOSER TO A COOK BOOK METHOD FOR DIOXIN ANALYSIS PART 1: THE PROCEDURE Focant JF 1, Shirkhan H 2, Patterson Jr DG 3 1 CART, Organic and Biological Analytical Chemistry, Mass Spectrometry Laboratory,
Accelerated Solvent Extraction GC-MS Analysis and Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil
 Accelerated Solvent Extraction GC-MS Analysis and Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil Che Jinshui, 1 Deng Guifeng, 1 Liang Lina, 1 and Aaron Kettle, 2 1 Thermo Fisher Scientific (China)
Accelerated Solvent Extraction GC-MS Analysis and Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil Che Jinshui, 1 Deng Guifeng, 1 Liang Lina, 1 and Aaron Kettle, 2 1 Thermo Fisher Scientific (China)
PosterReprint INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION 'Dioxins' refers to a group of chemical compounds that share certain similar chemical structures and biological characteristics. Several hundred of these toxic compounds exist and are members
INTRODUCTION 'Dioxins' refers to a group of chemical compounds that share certain similar chemical structures and biological characteristics. Several hundred of these toxic compounds exist and are members
environmental Rtx -CLPesticides and Rtx -CLPesticides2 Columns: The Ideal Confirmational Pair for Analyzing Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
 environmental #59120 Applications note Rtx -CLPesticides and Rtx -CLPesticides2 Columns: The Ideal Confirmational Pair for Analyzing Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are
environmental #59120 Applications note Rtx -CLPesticides and Rtx -CLPesticides2 Columns: The Ideal Confirmational Pair for Analyzing Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are
ApplicationNOTE THE ANALYSIS OF POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBS) BY GC-HIGH RESOLUTION MASS SPECTROMETRY USING THE MICROMASS AUTOSPEC ULTIMA NT
 Introduction PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) are a class of man-made chemicals first manufactured commercially in the late 1920's and were used primarily as a dielectric fluid in electrical equipment.
Introduction PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) are a class of man-made chemicals first manufactured commercially in the late 1920's and were used primarily as a dielectric fluid in electrical equipment.
Katherine K. Stenerson, Michael Ye, Michael Halpenny, Olga Shimelis, and Leonard M. Sidisky. Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Bellefonte, PA USA
 New Analytical Tools for the Determination of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Fatty Food and Beverage Matrices Using QuEChERS Extraction/Cleanup and Gas Chromatography (GC) Analysis Katherine K.
New Analytical Tools for the Determination of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Fatty Food and Beverage Matrices Using QuEChERS Extraction/Cleanup and Gas Chromatography (GC) Analysis Katherine K.
Dioxin, PCB analysis in fishmeal Comparison of two extraction techniques
 Dioxin, PCB analysis in fishmeal Comparison of two extraction techniques Abstract For the extraction of dioxins and PCBs from fish and derived products such as fish meal quite often classical soxhlet extraction
Dioxin, PCB analysis in fishmeal Comparison of two extraction techniques Abstract For the extraction of dioxins and PCBs from fish and derived products such as fish meal quite often classical soxhlet extraction
Data Glossary. Acceptance criteria - specific limits placed on characteristics of an item, process, or service defined in requirements documents.
 Data Glossary The purpose of this data glossary is to provide a reference for terms used in the analytical analysis of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congeners, utilizing high resolution gas chromatography/high
Data Glossary The purpose of this data glossary is to provide a reference for terms used in the analytical analysis of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congeners, utilizing high resolution gas chromatography/high
ApplicationNOTE ULTRA TRACE ANALYSIS OF DIOXINS AND FURANS IN HUMAN ADIPOSE TISSUE USING SFE-LC EXTRACTION/CLEANUP AND THE WATERS AUTOSPEC ULTIMA NT
 Introduction Legislative limits for dioxins and furans are ever decreasing 1, providing a greater challenge for the dioxin analyst. The extraction and clean-up processes used by the analyst can be imperative
Introduction Legislative limits for dioxins and furans are ever decreasing 1, providing a greater challenge for the dioxin analyst. The extraction and clean-up processes used by the analyst can be imperative
PCB Alternative Analysis Comparison of Aroclor to low and high-resolution GCMS. Laura Inouye (Ecology)
 PCB Alternative Analysis Comparison of Aroclor to low and high-resolution GCMS Laura Inouye (Ecology) Kelsey Van der Elst (USACE) Introduction Aroclor analysis is standard for sediments, but has its issues
PCB Alternative Analysis Comparison of Aroclor to low and high-resolution GCMS Laura Inouye (Ecology) Kelsey Van der Elst (USACE) Introduction Aroclor analysis is standard for sediments, but has its issues
PCB Congener Analysis of XAD-2 Resins and GFF Filters Using GC/ECD
 ` PCB Congener Analysis of XAD-2 Resins and GFF Filters Using GC/ECD Eric Crecelius and Lisa Lefkovitz Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Battelle Marine Sciences Laboratory 1529 West Sequim Bay Road
` PCB Congener Analysis of XAD-2 Resins and GFF Filters Using GC/ECD Eric Crecelius and Lisa Lefkovitz Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Battelle Marine Sciences Laboratory 1529 West Sequim Bay Road
Analysis of Trace (mg/kg) Thiophene in Benzene Using Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography and Flame Ionization Detection Application
 Analysis of Trace (mg/kg) Thiophene in Using Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography and Flame Ionization Detection Application Petrochemical Authors James D. McCurry and Bruce D. Quimby Agilent Technologies
Analysis of Trace (mg/kg) Thiophene in Using Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography and Flame Ionization Detection Application Petrochemical Authors James D. McCurry and Bruce D. Quimby Agilent Technologies
PCB Chemistry 101. Presented by Valerie Tillinghast O Reilly, Talbot & Okun Associates, Inc.
 PCB Chemistry 101 Presented by Valerie Tillinghast O Reilly, Talbot & Okun Associates, Inc. Short History of PCBs Reports indicate that PCBs were first synthesized by chemists in 1881 but significant commercial
PCB Chemistry 101 Presented by Valerie Tillinghast O Reilly, Talbot & Okun Associates, Inc. Short History of PCBs Reports indicate that PCBs were first synthesized by chemists in 1881 but significant commercial
SUPELCO. The Analysis of all 209 PCB Congeners on the SPB -Octyl and MDN -5S Capillary Columns. Katherine K. Stenerson and Leonard M.
 SUPELCO The Analysis of all 209 PCB Congeners on the SPB -Octyl and MDN -5S Capillary Columns Katherine K. Stenerson and Leonard M. Sidisky Supelco, Supelco Park, Bellefonte, PA USA 2000 Sigma-Aldrich
SUPELCO The Analysis of all 209 PCB Congeners on the SPB -Octyl and MDN -5S Capillary Columns Katherine K. Stenerson and Leonard M. Sidisky Supelco, Supelco Park, Bellefonte, PA USA 2000 Sigma-Aldrich
Determination Spectrometry. of Serum Glucose by Isotope Dilution Mass. National Chemical Laboratory for Industry, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305
 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES OCTOBER 1988, VOL. 4 487 Determination Spectrometry of Serum Glucose by Isotope Dilution Mass Akiko TAKATSU and Sueo NISHI National Chemical Laboratory for Industry, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
ANALYTICAL SCIENCES OCTOBER 1988, VOL. 4 487 Determination Spectrometry of Serum Glucose by Isotope Dilution Mass Akiko TAKATSU and Sueo NISHI National Chemical Laboratory for Industry, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Analysis of USP Method <467> Residual Solvents on the Agilent 8890 GC System
 Application Note Residual Solvent Analysis of USP Method Residual Solvents on the Agilent 889 GC System Author Lukas Wieder, Jie Pan, and Rebecca Veeneman Agilent Technologies, Inc. 8 Centerville Road
Application Note Residual Solvent Analysis of USP Method Residual Solvents on the Agilent 889 GC System Author Lukas Wieder, Jie Pan, and Rebecca Veeneman Agilent Technologies, Inc. 8 Centerville Road
CORUS R, D and T, Swinden Technology Centre, Rotherham, UK S60 3AR. HALL ANALYTICAL LABORATORIES, Manchester, UK M23 9YJ
 THE SUPELCO DIOXIN PREP SYSTEM - FLORISIL VERSION : A MULTI-LAYER SILICA GEL COLUMN CONNECTED IN SERIES TO AN ACTIVATED FLORISIL MICRO-COLUMN FOR RAPID DETERMINATIONS OF PCDD/Fs AND PCBs IN ENVIRONMENTAL
THE SUPELCO DIOXIN PREP SYSTEM - FLORISIL VERSION : A MULTI-LAYER SILICA GEL COLUMN CONNECTED IN SERIES TO AN ACTIVATED FLORISIL MICRO-COLUMN FOR RAPID DETERMINATIONS OF PCDD/Fs AND PCBs IN ENVIRONMENTAL
Analysis of Biomarkers in Crude Oil Using the Agilent 7200 GC/Q-TOF
 Analysis of Biomarkers in Crude Oil Using the Agilent 7 GC/Q-TOF Application Note Petrochemical and Environmental Authors Frank David Research Institute for Chromatography, Kennedypark 6, B-85 Kortrijk,
Analysis of Biomarkers in Crude Oil Using the Agilent 7 GC/Q-TOF Application Note Petrochemical and Environmental Authors Frank David Research Institute for Chromatography, Kennedypark 6, B-85 Kortrijk,
THE NEW QUANTITATIVE ANALYTICAL METHOD FOR ULTRATRACE SULFUR COMPOUNDS IN NATURAL GAS
 International Gas Union Research Conference 14 THE NEW QUANTITATIVE ANALYTICAL METHOD FOR ULTRATRACE SULFUR COMPOUNDS IN NATURAL GAS Main author Hironori IMANISHI Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. JAPAN himanishi@tokyo-.co.jp
International Gas Union Research Conference 14 THE NEW QUANTITATIVE ANALYTICAL METHOD FOR ULTRATRACE SULFUR COMPOUNDS IN NATURAL GAS Main author Hironori IMANISHI Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. JAPAN himanishi@tokyo-.co.jp
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
 PAGE: 1 of 12 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
PAGE: 1 of 12 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
A New Approach to the Analysis of Chlorinated Paraffins by Gas Chromatography Quadrupole Time of-flight Mass Spectrometry
 Application Note Environmental A New Approach to the Analysis of Chlorinated Paraffins by Gas Chromatography Quadrupole Time of-flight Mass Spectrometry Authors Wei Gao, Jing Wu, Yawei Wang, and Guibin
Application Note Environmental A New Approach to the Analysis of Chlorinated Paraffins by Gas Chromatography Quadrupole Time of-flight Mass Spectrometry Authors Wei Gao, Jing Wu, Yawei Wang, and Guibin
GUIDELINES FOR THE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING AND IMPACT ASSESSMENT ASSOCIATED WITH SUBSEA OIL RELEASES AND DISPERSANT USE IN UK WATERS.
 Technical Guideline No. 08 Processing and analysis of water, biota and sediment samples for the determination of hydrocarbon contamination using gas chromatography -mass spectrometry Robin Law 2014 To
Technical Guideline No. 08 Processing and analysis of water, biota and sediment samples for the determination of hydrocarbon contamination using gas chromatography -mass spectrometry Robin Law 2014 To
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs):
 Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Organic chemicals with a high vapour pressure at room temperature. High vapour pressure results from a low boiling point. The World Health Organization (WHO) defined
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Organic chemicals with a high vapour pressure at room temperature. High vapour pressure results from a low boiling point. The World Health Organization (WHO) defined
Food analysis. Solutions for Your Analytical Business Markets and Applications Programs
 Food analysis HIGH SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF TRACE ORGANIC POLLUTANTS IN MUSSEL TISSUE USING THE 7010 TRIPLE QUADRUPOLE MASS SPECTROMETER Solutions for Your Analytical Business Markets and Applications Programs
Food analysis HIGH SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF TRACE ORGANIC POLLUTANTS IN MUSSEL TISSUE USING THE 7010 TRIPLE QUADRUPOLE MASS SPECTROMETER Solutions for Your Analytical Business Markets and Applications Programs
T H E ANA LYSIS O F DIOX INS AND F U R A NS USING H RG C- H IG H R E SO LU T IO N MS W IT H T H E AU T OS P EC- ULTIMA NT
 [ application note ] T H E ANA LYSIS O F DIOX INS AND F U R A NS USING H RG C- H IG H R E SO LU T IO N MS W IT H T H E AU T OS P EC- ULTIMA NT Keith Worrall, Anthony Newton and Ramesh Rao, Waters Corporation,
[ application note ] T H E ANA LYSIS O F DIOX INS AND F U R A NS USING H RG C- H IG H R E SO LU T IO N MS W IT H T H E AU T OS P EC- ULTIMA NT Keith Worrall, Anthony Newton and Ramesh Rao, Waters Corporation,
Using Magnetic Sector GC-HRMS in a Commercial Dioxin Lab
 An Executive Summary Using Magnetic Sector GC-HRMS in a Commercial Dioxin Lab David Hope Chief Executive Officer Pacific Rim Laboratories Introduction Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are toxic chemicals
An Executive Summary Using Magnetic Sector GC-HRMS in a Commercial Dioxin Lab David Hope Chief Executive Officer Pacific Rim Laboratories Introduction Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are toxic chemicals
Research of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Vegetables by GC-MS/MS
 PO-CONE Research of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Pittcon 0 90-8 Xizhi Wang, Shiheng Luo, Feifei Tian, Jun Fan, Guixiang Yang, Taohong Huang, Shin-ichi Kawano, Yuki Hashi Shimadzu Global COE, Shimadzu
PO-CONE Research of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Pittcon 0 90-8 Xizhi Wang, Shiheng Luo, Feifei Tian, Jun Fan, Guixiang Yang, Taohong Huang, Shin-ichi Kawano, Yuki Hashi Shimadzu Global COE, Shimadzu
APPLICATION NOTE Authors Jane Cooper, 1 Jordi Parera, 2 Esteban Abad, 2 Richard Law,¹ and Cristian Cojocariu 1
 APPLICATION NOTE 10644 Overcoming analytical challenges for polybrominated diphenyl ethers (P) analysis in environmental samples using gas chromatography Orbitrap mass spectrometry Authors Jane Cooper,
APPLICATION NOTE 10644 Overcoming analytical challenges for polybrominated diphenyl ethers (P) analysis in environmental samples using gas chromatography Orbitrap mass spectrometry Authors Jane Cooper,
Determination of Elemental Sulfur in Explosives and. Explosive Residues by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Kimberly S.
 Determination of Elemental Sulfur in Explosives and Explosive Residues by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Kimberly S. Bradley Illinois State Police, Springfield Forensic Science Laboratory 24 Hill
Determination of Elemental Sulfur in Explosives and Explosive Residues by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Kimberly S. Bradley Illinois State Police, Springfield Forensic Science Laboratory 24 Hill
Putting the Pieces of the Puzzle Together. By Kim Kirkland, Methods Team Leader EPA s Office of Resource Conservation and Recovery
 Putting the Pieces of the Puzzle Together By Kim Kirkland, Methods Team Leader EPA s Office of Resource Conservation and Recovery Topics to Be Covered Item 1 Brief Review of Current Method Team Projects
Putting the Pieces of the Puzzle Together By Kim Kirkland, Methods Team Leader EPA s Office of Resource Conservation and Recovery Topics to Be Covered Item 1 Brief Review of Current Method Team Projects
Screening of Pesticide Residues in Water by Sequential Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction-Thermal Desorption with GC/MS
 Screening of Pesticide Residues in Water by Sequential Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction-Thermal Desorption with GC/MS Application Note Food Authors Nobuo Ochiai and Kikuo Sasamoto GERSTEL K.K. 2-13-18 Nakane
Screening of Pesticide Residues in Water by Sequential Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction-Thermal Desorption with GC/MS Application Note Food Authors Nobuo Ochiai and Kikuo Sasamoto GERSTEL K.K. 2-13-18 Nakane
Agilent G2350A Atomic Emission Detector (AED)
 Agilent G0A Atomic Emission Detector (AED) Specifications Elements Specifications Wavelength Minimum Detectable Selectivity Dynamic Measurement Group Element(s) (nm) Level (pg/sec) Over Carbon Range Compound
Agilent G0A Atomic Emission Detector (AED) Specifications Elements Specifications Wavelength Minimum Detectable Selectivity Dynamic Measurement Group Element(s) (nm) Level (pg/sec) Over Carbon Range Compound
Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene and Xylene in River Water by Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography
 2003 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 1365 Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene and Xylene in River Water by Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography Mohammad A. MOTTALEB,* Mohammad
2003 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 1365 Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene and Xylene in River Water by Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography Mohammad A. MOTTALEB,* Mohammad
Introduction to Gas Chromatography
 Introduction to Gas Chromatography 31-1 Objectives To know what is chromatography To understand the mechanism of compound separation To know the basic of gas chromatography system 31-2 Chromatography Definition
Introduction to Gas Chromatography 31-1 Objectives To know what is chromatography To understand the mechanism of compound separation To know the basic of gas chromatography system 31-2 Chromatography Definition
APPLICATION NOTE. A Capillary Approach to ASTM D3606: Test Method for Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor and Aviation Gasoline
 A Capillary Approach to ASTM D3606: Test Method for Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor and Aviation Gasoline Fast : Cycles in
A Capillary Approach to ASTM D3606: Test Method for Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor and Aviation Gasoline Fast : Cycles in
Validation of New VPH GC/MS Method using Multi-Matrix Purge and Trap Sample Prep System
 Validation of New VPH GC/MS Method using Multi-Matrix Purge and Trap Sample Prep System Application Note Abstract The Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) developed the Method
Validation of New VPH GC/MS Method using Multi-Matrix Purge and Trap Sample Prep System Application Note Abstract The Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) developed the Method
Table S1. Summary of target PCB congeners. Numbers are BZ numbers (Ballschmiter and Zell, 1980) listed in order of elution from an HT8-PCB column.
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 Table S1. Summary of target PCB congeners. Numbers are BZ numbers (Ballschmiter and Zell, 198) listed in order of elution from an HT8-PCB column. Homologue
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 Table S1. Summary of target PCB congeners. Numbers are BZ numbers (Ballschmiter and Zell, 198) listed in order of elution from an HT8-PCB column. Homologue
CALIBRATION OF GC/MS METHOD AND VALIDATION OF THE MODIFIED SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR DETERMINATION OF POLYCYCLIC AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
 Journal Ivan of Givechev, Chemical Dancho Technology Danalev, and Spaska Metallurgy, Yaneva, 53, Dimitar 4, 2018, Tanev 717-724 CALIBRATION OF GC/MS METHOD AND VALIDATION OF THE MODIFIED SAMPLE PREPARATION
Journal Ivan of Givechev, Chemical Dancho Technology Danalev, and Spaska Metallurgy, Yaneva, 53, Dimitar 4, 2018, Tanev 717-724 CALIBRATION OF GC/MS METHOD AND VALIDATION OF THE MODIFIED SAMPLE PREPARATION
The Truth About Dioxin Analysis: Using High Resolution GC-TOFMS and GCxGC-TOFMS to. Analytical Approaches
 The Truth About Dioxin Analysis: Using High Resolution GC-TOFMS and GCxGC-TOFMS to Uncover the Pollutants Ignored by Targeted Analytical Approaches Peter Gorst-Allman 1, Jack Cochran 2, Jayne de Vos 3
The Truth About Dioxin Analysis: Using High Resolution GC-TOFMS and GCxGC-TOFMS to Uncover the Pollutants Ignored by Targeted Analytical Approaches Peter Gorst-Allman 1, Jack Cochran 2, Jayne de Vos 3
Jennifer Bowman Dr. Natalie Kruse Dr. Glen Jackson Dr. Dina Lopez Mengliang Zhang
 Expedited Field Survey and Sampling Techniques for PCB Congeners and Dioxins: GIS Mapping of PCB Congeners and Dioxins in Sediments and Soils: Preliminary Assessment of Sediments on the PORTS site Jennifer
Expedited Field Survey and Sampling Techniques for PCB Congeners and Dioxins: GIS Mapping of PCB Congeners and Dioxins in Sediments and Soils: Preliminary Assessment of Sediments on the PORTS site Jennifer
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES SOP: 1828 PAGE: 1 of 14 REV: 0.0 DATE: 05/12/95 ANALYSIS OF METHYL PARATHION IN CARPET SAMPLES BY GC/MS
 PAGE: 1 of 14 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY CONTENTS 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
PAGE: 1 of 14 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY CONTENTS 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
Application Note. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry/Food Safety. Abstract. Authors
 Trace-Level Analysis of Melamine in Milk Products on Agilent 789A/5975C GC/MSD Using a ew Agilent J&W DB-5ms Ultra Inert Column and SampliQ SCX Cartridges Application ote Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry/Food
Trace-Level Analysis of Melamine in Milk Products on Agilent 789A/5975C GC/MSD Using a ew Agilent J&W DB-5ms Ultra Inert Column and SampliQ SCX Cartridges Application ote Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry/Food
Analyzing PCBs in Source Materials and Environmental Media: Soil, Water and Air. Jim Occhhialini Jim Okun Patricia McIsaac
 Analyzing PCBs in Source Materials and Environmental Media: Soil, Water and Air Jim Occhhialini Jim Okun Patricia McIsaac Agenda Background Information Analytical Methodology Options for Analytical Support
Analyzing PCBs in Source Materials and Environmental Media: Soil, Water and Air Jim Occhhialini Jim Okun Patricia McIsaac Agenda Background Information Analytical Methodology Options for Analytical Support
Validation of GC-MS/MS for Detection and Confirmation of Low-Level Dioxins
 Validation of GC-MS/MS for Detection and Confirmation of Low-Level Dioxins Cristian Cojocariu, 1 Paul Silcock, 1 and Alexander Kotz 2 1 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, U.K. 2 European Union Reference
Validation of GC-MS/MS for Detection and Confirmation of Low-Level Dioxins Cristian Cojocariu, 1 Paul Silcock, 1 and Alexander Kotz 2 1 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, U.K. 2 European Union Reference
Fast and Accurate Analysis of PBDEs in a Single Run, Including BDE-209
 Fast and Accurate Analysis of PBDEs in a Single Run, Including Kory Kelly, Xianrong (Jenny) Wei, and Matthew Trass Phenomenex, Inc., 411 Madrid Ave., Torrance, CA 90501 USA PO16570913_W_2 PO14400613_W_2
Fast and Accurate Analysis of PBDEs in a Single Run, Including Kory Kelly, Xianrong (Jenny) Wei, and Matthew Trass Phenomenex, Inc., 411 Madrid Ave., Torrance, CA 90501 USA PO16570913_W_2 PO14400613_W_2
Orbitrap GC-MS: An Opportunity to Help Address the Challenges of Chlorinated Paraffins Analysis
 An Executive Summary Orbitrap GC-MS: An Opportunity to Help Address the Challenges of Chlorinated Paraffins Analysis Kerstin Krätschmer European Union Reference Laboratory for Dioxins and PCBs in Feed
An Executive Summary Orbitrap GC-MS: An Opportunity to Help Address the Challenges of Chlorinated Paraffins Analysis Kerstin Krätschmer European Union Reference Laboratory for Dioxins and PCBs in Feed
Sulfotepp impurities in Chlorpyrifos EC formulations
 Page 1 of 16 Method DAS-AM-01-058 Sulfotepp impurities in Chlorpyrifos EC formulations A. ABSTRACT Method DAS-AM-01-058 has been validated for the analysis of the relevant impurity sulfotepp in chlorpyrifos
Page 1 of 16 Method DAS-AM-01-058 Sulfotepp impurities in Chlorpyrifos EC formulations A. ABSTRACT Method DAS-AM-01-058 has been validated for the analysis of the relevant impurity sulfotepp in chlorpyrifos
GC/MS/MS Dioxin and Dioxin-like PCBs in Feed and Food. Jessica Westland, LSAG Applications Chemist
 GC/MS/MS Dioxin and Dioxin-like PCBs in Feed and Food Jessica Westland, LSAG Applications Chemist What is a Dioxin? The term dioxins refers to a group of chemically and structurally related halogenated
GC/MS/MS Dioxin and Dioxin-like PCBs in Feed and Food Jessica Westland, LSAG Applications Chemist What is a Dioxin? The term dioxins refers to a group of chemically and structurally related halogenated
Fast and Accurate Analysis of PBDEs in a Single Run, Including
 Fast and Accurate Analysis of PBDEs in a Single Run, Including Kory Kelly, Adam Endeman, and Matthew Trass Phenomenex, Inc., 411 Madrid Ave., Torrance, CA 90501 USA PO14700713_2 PO14400613_W_2 Abstract
Fast and Accurate Analysis of PBDEs in a Single Run, Including Kory Kelly, Adam Endeman, and Matthew Trass Phenomenex, Inc., 411 Madrid Ave., Torrance, CA 90501 USA PO14700713_2 PO14400613_W_2 Abstract
Application Note. Abstract. Introduction. Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood by an Automated QuEChERS Solution
 Application Note Abstract Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood by an Automated QuEChERS Solution Page 1 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) are a large group of organic compounds
Application Note Abstract Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seafood by an Automated QuEChERS Solution Page 1 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) are a large group of organic compounds
Application. Gas Chromatography February Introduction
 Ambient Headspace Analysis with the Agilent 7683 Automatic Liquid Sampler Application Gas Chromatography February 1998 Authors Matthew S. Klee and Chin Kai Meng Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2850 Centerville
Ambient Headspace Analysis with the Agilent 7683 Automatic Liquid Sampler Application Gas Chromatography February 1998 Authors Matthew S. Klee and Chin Kai Meng Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2850 Centerville
METHOD 8111 HALOETHERS BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION METHOD 8111 HALOETHERS BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY 1.1 Method 8111 is a gas chromatographic (GC) method used to determine the concentration of haloethers. It describes wide-bore open-tubular,
1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION METHOD 8111 HALOETHERS BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY 1.1 Method 8111 is a gas chromatographic (GC) method used to determine the concentration of haloethers. It describes wide-bore open-tubular,
Monitoring of Contamination by Non-PBDE Brominated Flame Retardants in Asian Coastal Waters Using Mussels as a Bioindicator
 Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry Marine Environmental Modeling & Analysis, Eds., K. Omori, X. Guo, N. Yoshie, N. Fujii, I. C. Handoh, A. Isobe and S. Tanabe, pp. 205 211. by TERRAPUB,
Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry Marine Environmental Modeling & Analysis, Eds., K. Omori, X. Guo, N. Yoshie, N. Fujii, I. C. Handoh, A. Isobe and S. Tanabe, pp. 205 211. by TERRAPUB,
A novel high resolution accurate mass Orbitrap-based GC-MS platform for routine analysis of Short Chained Chlorinated Paraffins
 TECHNICAL NOTE 39 A novel high resolution accurate mass Orbitrap-based GC-MS platform for routine analysis of Short Chained Chlorinated Paraffins Author Cristian Cojocariu Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn,
TECHNICAL NOTE 39 A novel high resolution accurate mass Orbitrap-based GC-MS platform for routine analysis of Short Chained Chlorinated Paraffins Author Cristian Cojocariu Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn,
Immunoassay Screening Method for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Insulating Oil (PCB sensor)
 Immunoassay Screening Method for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Insulating Oil (PCB sensor) Sumika Chemical Analysis Service, Ltd. Ehime Laboratory Katsuya IMANISHI Low level quantities of PCBs were
Immunoassay Screening Method for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Insulating Oil (PCB sensor) Sumika Chemical Analysis Service, Ltd. Ehime Laboratory Katsuya IMANISHI Low level quantities of PCBs were
Determination of toxaphene congeners in fish samples from Danish waters
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 23, 2018 Determination of toxaphene congeners in fish samples from Danish waters Fromberg, Arvid; Cederberg, Tommy Licht; Hilbert, Gudrun Published in: Organohalogen
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 23, 2018 Determination of toxaphene congeners in fish samples from Danish waters Fromberg, Arvid; Cederberg, Tommy Licht; Hilbert, Gudrun Published in: Organohalogen
Enhancing the productivity of food sample analysis with the Agilent 7700x ICP-MS
 Enhancing the productivity of food sample analysis with the Agilent 77x ICP-MS Application note Foods testing Authors Sebastien Sannac, Jean Pierre Lener and Jerome Darrouzes Agilent Technologies Paris,
Enhancing the productivity of food sample analysis with the Agilent 77x ICP-MS Application note Foods testing Authors Sebastien Sannac, Jean Pierre Lener and Jerome Darrouzes Agilent Technologies Paris,
Fast Determination of Impurities in Propane- Propylene Streams Using a Pulsed Flame Photometric Detector (PFPD) and a New Capillary.
 Application Note 36720111 Fast Determination of Impurities in Propane- Propylene Streams Using a Pulsed Flame Photometric Detector (PFPD) and a New Capillary PLOT Column Keywords Pulsed Flame Photometric
Application Note 36720111 Fast Determination of Impurities in Propane- Propylene Streams Using a Pulsed Flame Photometric Detector (PFPD) and a New Capillary PLOT Column Keywords Pulsed Flame Photometric
Determination of Pesticides in Aqueous Samples by On-Line Coupling Solid-Phase Extraction to Gas Chromatography with At-Column Concentrating Interface
 Application Note No. 033 Determination of Pesticides in Aqueous Samples by On-Line Coupling Solid-Phase Extraction to Gas Chromatography with At-Column Concentrating Interface Ryoichi Sasano*, Takayuki
Application Note No. 033 Determination of Pesticides in Aqueous Samples by On-Line Coupling Solid-Phase Extraction to Gas Chromatography with At-Column Concentrating Interface Ryoichi Sasano*, Takayuki
Determination of Polybrominated Diphenylethers (PBDE) in Sediment and Sewage Sludge Application
 Deteration of Polybroated Diphenylethers (PBDE) in Sediment and Sewage Sludge Application Environmental Authors Sonia Wanner Centre d'analyse et de Recherche (CAR) 76 route du Rhin F-67441 Illkirch France
Deteration of Polybroated Diphenylethers (PBDE) in Sediment and Sewage Sludge Application Environmental Authors Sonia Wanner Centre d'analyse et de Recherche (CAR) 76 route du Rhin F-67441 Illkirch France
CLEEMANN ET AL.: JOURNAL OF AOAC INTERNATIONAL VOL. 82, NO. 5, 1999
 CLEEMANN ET AL.: JOURNAL OF AOAC INTERNATIONAL VOL. 82, NO. 5, 1999 1175 RESIDUES AND TRACE ELEMENTS Analyses of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Chlorinated Pesticides in Biota: Method and Quality Assurance
CLEEMANN ET AL.: JOURNAL OF AOAC INTERNATIONAL VOL. 82, NO. 5, 1999 1175 RESIDUES AND TRACE ELEMENTS Analyses of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Chlorinated Pesticides in Biota: Method and Quality Assurance
Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH Analysis Topic 5
 Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH 5730-6730 Analysis Topic 5 Chromatography! Group of separation techniques based on partitioning (mobile phase/stationary phase). Two immiscible
Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH 5730-6730 Analysis Topic 5 Chromatography! Group of separation techniques based on partitioning (mobile phase/stationary phase). Two immiscible
METHOD SUPERCRITICAL FLUID EXTRACTION OF POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBs) AND ORGANOCHLORINE PESTICIDES
 METHOD 3562 SUPERCRITICAL FLUID EXTRACTION OF POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBs) AND ORGANOCHLORINE PESTICIDES 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3562 describes the extraction with supercritical fluids
METHOD 3562 SUPERCRITICAL FLUID EXTRACTION OF POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCBs) AND ORGANOCHLORINE PESTICIDES 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3562 describes the extraction with supercritical fluids
This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products:
 A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
Quantitative Determination of Dioxins in Drinking Water by Isotope Dilution using Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS
 PO-CON1646E Quantitative Determination of Dioxins in Drinking Water by Isotope Dilution using Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS ASMS 2016 ThP 152 Jackie, Chiew Mei Chong, Hui Xian Crystal Yeong, Cynthia Melanie
PO-CON1646E Quantitative Determination of Dioxins in Drinking Water by Isotope Dilution using Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS ASMS 2016 ThP 152 Jackie, Chiew Mei Chong, Hui Xian Crystal Yeong, Cynthia Melanie
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES SOP: 1826 PAGE: 1 of 18 REV: 0.0 DATE: 03/30/95 ANALYSIS OF METHYL PARATHION IN WIPE SAMPLES BY GC/MS
 PAGE: 1 of 18 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
PAGE: 1 of 18 CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION, CONTAINERS, HANDLING AND STORAGE 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS
Mass Spectral Studies of Polypropylene Chromatographic Well Plates
 Mass Spectral Studies of Polypropylene Chromatographic Well Plates Brian King, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Detlev Lennartz, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Langerwehe, Germany White Paper
Mass Spectral Studies of Polypropylene Chromatographic Well Plates Brian King, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Detlev Lennartz, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Langerwehe, Germany White Paper
Highly Sensitive and Rugged GC/MS/MS Tool
 Highly Sensitive and Rugged GC/MS/MS Tool For Pesticide Multiresidue Analysis in Food Samples Agilent 7 Series Triple Quadrupole GC/MS. The world s first MS/MS designed specifically for GC Analysis Introduction
Highly Sensitive and Rugged GC/MS/MS Tool For Pesticide Multiresidue Analysis in Food Samples Agilent 7 Series Triple Quadrupole GC/MS. The world s first MS/MS designed specifically for GC Analysis Introduction
SPME EXTRACTION OF THE PCB S CONTAINING TRANSFORMER OILS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, Vol. 73, Iss. 2, 2011 ISSN 1454-2331 SPME EXTRACTION OF THE PCB S CONTAINING TRANSFORMER OILS Constantin TOADER 1, Nicoleta GRIGORIU 2, Aurelia MEGHEA 3 Lucrarea prezintă o
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, Vol. 73, Iss. 2, 2011 ISSN 1454-2331 SPME EXTRACTION OF THE PCB S CONTAINING TRANSFORMER OILS Constantin TOADER 1, Nicoleta GRIGORIU 2, Aurelia MEGHEA 3 Lucrarea prezintă o
Gas chromatography. Advantages of GC. Disadvantages of GC
 Advantages of GC Gas chromatography Fast analysis, typically minutes Effi cient, providing high resolution Sensitive, easily detecting ppm and often ppb Nondestructive, making possible on - line coupling;
Advantages of GC Gas chromatography Fast analysis, typically minutes Effi cient, providing high resolution Sensitive, easily detecting ppm and often ppb Nondestructive, making possible on - line coupling;
Polychlorinated Biphenyl Compounds (PCBs) Determination from Water by Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (GC MS)
 Polychlorinated Biphenyl Compounds (PCBs) Determination from Water by Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (GC MS) RALUCA SENIN 1,2 *, VIRGIL BADESCU 1, RUSANDICA STOICA 1 1 National Research
Polychlorinated Biphenyl Compounds (PCBs) Determination from Water by Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (GC MS) RALUCA SENIN 1,2 *, VIRGIL BADESCU 1, RUSANDICA STOICA 1 1 National Research
